

How to Write an Essay Explaining a Concept

How to Write a Senior Project Paper
Writing an essay explaining a concept can be a challenging assignment. The first, and possibly most important step, is to choose a concept to explain that you are interested in and feel comfortable writing about. You could choose to write about a topic that you know something about. Alternatively, you could write about an unfamiliar topic that you have a desire to learn more about.
Research and Narrow the Topic
Once you know the concept you want to write about, take time to research your topic, noting important information and quotes from experts or well-documented facts to back up your idea. Many concepts, such as emotions like love or hate, make for broad topics that will prove difficult to work with, so you should narrow your essay idea as you research. You can focus your idea by looking at one aspect of the subject. For example, instead of writing about poverty, narrow your essay to discuss the effects of poverty on young students.
Introduce Your Topic
When you start writing, your first paragraph will introduce your topic, and you need to interest the reader in the concept you explicate in your essay. For example, if your essay involves an emotion, you might try to appeal to that emotion in your reader. On the other hand, you might give a personal anecdote or ask a question the reader should consider. Near the end of the introduction, you need to present your thesis, a sentence that states your argument or claim that you will prove in the body of your essay. In the sample topic of the effects of poverty on young students, your thesis might look like this: “Impoverished elementary students often have low self-esteem and decreased academic achievement in comparison with their peers.”
Form the Body
In most essay assignments, you will need to include at least three main points in the body of your essay. You can use research to back up your thesis, such as research and statistics on poverty. Also, if your teacher allows this approach, some concepts will benefit from your personal experience. This allows you to give true-to-life examples of your topic and will keep your reader involved. Begin each body paragraph with a general topic statement and grow more specific with each subsequent sentence. You will conclude each body paragraph by wrapping up the information. Throughout the paragraph, make sure the information you provide supports and is connected to your thesis.
Conclude Your Essay
In the last paragraph, you will conclude your essay by tying together the points you made in the body of your essay. Take this opportunity to solidify the connection between your reader and the concept by reiterating the impact of your topic. Also, show how your points prove or support your thesis. You can make suggestions to your reader in the conclusion, perhaps recommending a certain action the reader may want to take to create changes or improvements.
Related Articles

How to Write an Anecdotal Essay

What Are the Five Parts of an Argumentative Essay?

What Should a Thesis Statement on an Essay About a Short Story Look ...

How to Do an In-Depth Analysis Essay

How to Write an Introduction to a Reflective Essay

How to Write an Essay About Your Future Goals

How to Write a Controlling Idea Essay

How to Write Research Papers From Start to Finish
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: Essay Writing
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: Body Paragraphs
Kate Beck started writing for online publications in 2005. She worked as a certified ophthalmic technician for 10 years before returning to school to earn a Masters of Fine Arts degree in writing. Beck is currently putting the finishing touches on a novel.
- +44 (0) 207 391 9032
The OE Blog
Get an insight into the minds of our academics and team of educational creatives here at Oxbridge Essays. From expert guidance and practical advice on essay and dissertation writing, to commentary on current academic affairs, our blog covers all things student-related, with the goal of helping you do better during your time at university.

Writing to explain
Writing to explain may seem a simpler task to tackle than some of the other writing styles you may be asked to adopt, such as writing to argue , persuade and advise. However it is sometimes the essay writing styles which sound the simplest that require the most technique to get them just right and score maximum points, whether you are writing to explain GCSE or explaining a theory as part of an undergraduate dissertation. So read on below for our top tips on writing to explain!
Writing to explain: structure
To provide a clear explanation of a topic in your assignment writing, it is crucial that your essay is well structured , so that it flows logically from one point to the next, giving the reader a well laid out and coherent grasp of the topic. For example, if you are asked to write an essay explaining why you would like to live in a particular place, instead of launching straight in with a complex description as you might in an essay to persuade, it would be much more effective to focus the first paragraph on the weather, the second on the economy, the third on the local people and so on. This proves to the examiner that you are aware of the key aim of writing to explain – helping your reader to fully understand the whole picture.
Writing to explain: questions
If you were explaining something to somebody in person, key part of the process would be answering any questions they had about what you were saying. So show you awareness of this to the examiner in your essay writing to explain, by including common questions or likely queries and their answers.
For example:
“ You may wonder why I would want to live in such a cold, mountainous region, but the winter sports, from skiing and snowboarding to tobogganing and ice-skating, make it a paradise for winter fun!
Writing to explain: progressing your ideas
Remember, an important part of explaining something is to give the basic idea and then go into further detail about individual points. So make the style of your essay writing reflect this, with more simple sentences setting out clear points, followed by more complex , multi-clause sentences to thoroughly explain and expand on each idea.
Writing to explain: final top tip
Remember, the simplest way to check you are on the right track with assignment writing to explain is simply to read it back through to yourself, imagining you are new to the topic, and ask yourself whether you would fully understand it, or where there are any areas you might need explaining further – these are the parts you need to work on!
Recent Articles
- How to Write a Character Analysis Essay
- Best Colours for Your PowerPoint Presentation: How to Choose
- How to Write a Nursing Essay
- Top 5 Essential Skills You Should Build As An International Student
- How Professional Editing Services Can Take Your Writing to the Next Level
- How to Write an Effective Essay Outline
- How to Write a Law Essay: A Comprehensive Guide with Examples
- What Are the Limitations of ChatGPT?
- How to Properly Write an Essay Outline Using ChatGpt
- Why Presentation Skills Are Important for Students
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips
Writing Services
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- Journal Publication
- CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service
Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- [email protected]
- Contact Form
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.
What is an Essay?
10 May, 2020
11 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
Well, beyond a jumble of words usually around 2,000 words or so - what is an essay, exactly? Whether you’re taking English, sociology, history, biology, art, or a speech class, it’s likely you’ll have to write an essay or two. So how is an essay different than a research paper or a review? Let’s find out!
Defining the Term – What is an Essay?
The essay is a written piece that is designed to present an idea, propose an argument, express the emotion or initiate debate. It is a tool that is used to present writer’s ideas in a non-fictional way. Multiple applications of this type of writing go way beyond, providing political manifestos and art criticism as well as personal observations and reflections of the author.

An essay can be as short as 500 words, it can also be 5000 words or more. However, most essays fall somewhere around 1000 to 3000 words ; this word range provides the writer enough space to thoroughly develop an argument and work to convince the reader of the author’s perspective regarding a particular issue. The topics of essays are boundless: they can range from the best form of government to the benefits of eating peppermint leaves daily. As a professional provider of custom writing, our service has helped thousands of customers to turn in essays in various forms and disciplines.
Origins of the Essay
Over the course of more than six centuries essays were used to question assumptions, argue trivial opinions and to initiate global discussions. Let’s have a closer look into historical progress and various applications of this literary phenomenon to find out exactly what it is.
Today’s modern word “essay” can trace its roots back to the French “essayer” which translates closely to mean “to attempt” . This is an apt name for this writing form because the essay’s ultimate purpose is to attempt to convince the audience of something. An essay’s topic can range broadly and include everything from the best of Shakespeare’s plays to the joys of April.
The essay comes in many shapes and sizes; it can focus on a personal experience or a purely academic exploration of a topic. Essays are classified as a subjective writing form because while they include expository elements, they can rely on personal narratives to support the writer’s viewpoint. The essay genre includes a diverse array of academic writings ranging from literary criticism to meditations on the natural world. Most typically, the essay exists as a shorter writing form; essays are rarely the length of a novel. However, several historic examples, such as John Locke’s seminal work “An Essay Concerning Human Understanding” just shows that a well-organized essay can be as long as a novel.
The Essay in Literature
The essay enjoys a long and renowned history in literature. They first began gaining in popularity in the early 16 th century, and their popularity has continued today both with original writers and ghost writers. Many readers prefer this short form in which the writer seems to speak directly to the reader, presenting a particular claim and working to defend it through a variety of means. Not sure if you’ve ever read a great essay? You wouldn’t believe how many pieces of literature are actually nothing less than essays, or evolved into more complex structures from the essay. Check out this list of literary favorites:
- The Book of My Lives by Aleksandar Hemon
- Notes of a Native Son by James Baldwin
- Against Interpretation by Susan Sontag
- High-Tide in Tucson: Essays from Now and Never by Barbara Kingsolver
- Slouching Toward Bethlehem by Joan Didion
- Naked by David Sedaris
- Walden; or, Life in the Woods by Henry David Thoreau
Pretty much as long as writers have had something to say, they’ve created essays to communicate their viewpoint on pretty much any topic you can think of!

The Essay in Academics
Not only are students required to read a variety of essays during their academic education, but they will likely be required to write several different kinds of essays throughout their scholastic career. Don’t love to write? Then consider working with a ghost essay writer ! While all essays require an introduction, body paragraphs in support of the argumentative thesis statement, and a conclusion, academic essays can take several different formats in the way they approach a topic. Common essays required in high school, college, and post-graduate classes include:
Five paragraph essay
This is the most common type of a formal essay. The type of paper that students are usually exposed to when they first hear about the concept of the essay itself. It follows easy outline structure – an opening introduction paragraph; three body paragraphs to expand the thesis; and conclusion to sum it up.
Argumentative essay
These essays are commonly assigned to explore a controversial issue. The goal is to identify the major positions on either side and work to support the side the writer agrees with while refuting the opposing side’s potential arguments.
Compare and Contrast essay
This essay compares two items, such as two poems, and works to identify similarities and differences, discussing the strength and weaknesses of each. This essay can focus on more than just two items, however. The point of this essay is to reveal new connections the reader may not have considered previously.
Definition essay
This essay has a sole purpose – defining a term or a concept in as much detail as possible. Sounds pretty simple, right? Well, not quite. The most important part of the process is picking up the word. Before zooming it up under the microscope, make sure to choose something roomy so you can define it under multiple angles. The definition essay outline will reflect those angles and scopes.
Descriptive essay
Perhaps the most fun to write, this essay focuses on describing its subject using all five of the senses. The writer aims to fully describe the topic; for example, a descriptive essay could aim to describe the ocean to someone who’s never seen it or the job of a teacher. Descriptive essays rely heavily on detail and the paragraphs can be organized by sense.
Illustration essay
The purpose of this essay is to describe an idea, occasion or a concept with the help of clear and vocal examples. “Illustration” itself is handled in the body paragraphs section. Each of the statements, presented in the essay needs to be supported with several examples. Illustration essay helps the author to connect with his audience by breaking the barriers with real-life examples – clear and indisputable.
Informative Essay
Being one the basic essay types, the informative essay is as easy as it sounds from a technical standpoint. High school is where students usually encounter with informative essay first time. The purpose of this paper is to describe an idea, concept or any other abstract subject with the help of proper research and a generous amount of storytelling.
Narrative essay
This type of essay focuses on describing a certain event or experience, most often chronologically. It could be a historic event or an ordinary day or month in a regular person’s life. Narrative essay proclaims a free approach to writing it, therefore it does not always require conventional attributes, like the outline. The narrative itself typically unfolds through a personal lens, and is thus considered to be a subjective form of writing.
Persuasive essay
The purpose of the persuasive essay is to provide the audience with a 360-view on the concept idea or certain topic – to persuade the reader to adopt a certain viewpoint. The viewpoints can range widely from why visiting the dentist is important to why dogs make the best pets to why blue is the best color. Strong, persuasive language is a defining characteristic of this essay type.

The Essay in Art
Several other artistic mediums have adopted the essay as a means of communicating with their audience. In the visual arts, such as painting or sculpting, the rough sketches of the final product are sometimes deemed essays. Likewise, directors may opt to create a film essay which is similar to a documentary in that it offers a personal reflection on a relevant issue. Finally, photographers often create photographic essays in which they use a series of photographs to tell a story, similar to a narrative or a descriptive essay.
Drawing the line – question answered
“What is an Essay?” is quite a polarizing question. On one hand, it can easily be answered in a couple of words. On the other, it is surely the most profound and self-established type of content there ever was. Going back through the history of the last five-six centuries helps us understand where did it come from and how it is being applied ever since.
If you must write an essay, follow these five important steps to works towards earning the “A” you want:
- Understand and review the kind of essay you must write
- Brainstorm your argument
- Find research from reliable sources to support your perspective
- Cite all sources parenthetically within the paper and on the Works Cited page
- Follow all grammatical rules
Generally speaking, when you must write any type of essay, start sooner rather than later! Don’t procrastinate – give yourself time to develop your perspective and work on crafting a unique and original approach to the topic. Remember: it’s always a good idea to have another set of eyes (or three) look over your essay before handing in the final draft to your teacher or professor. Don’t trust your fellow classmates? Consider hiring an editor or a ghostwriter to help out!
If you are still unsure on whether you can cope with your task – you are in the right place to get help. HandMadeWriting is the perfect answer to the question “Who can write my essay?”

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
Essay Writing Tips: 10 Steps to Writing a Great Essay (And Have Fun Doing It!)
by Joe Bunting | 118 comments
Start Your Story TODAY! We’re teaching a new LIVE workshop this week to help you start your next book. Learn more and sign up here.
Do you dread essay writing? Are you looking for some essay tips that will help you write an amazing essay—and have fun doing it?

Lots of students, young and old, dread essay writing. It's a daunting assignment, one that takes research, time, and concentration.
It's also an assignment that you can break up into simple steps that make writing an essay manageable and, yes, even enjoyable.
These ten essay tips completely changed my writing process—and I hope that they can do the same for you.
Essay Writing Can Be Fun
Honestly, throughout most of high school and college, I was a mediocre essay writer.
Every once in a while, I would write a really good essay, but mostly I skated by with B's and A-minuses.
I know personally how boring writing an essay can be, and also, how hard it can be to write a good one.
However, toward the end of my time as a student, I made a breakthrough. I figured out how to not only write a great essay, I learned how to have fun while doing it .
And since then, I've become a professional writer and have written more than a dozen books. I'm not saying that these essay writing tips are going to magically turn you into a writer, but at least they can help you enjoy the process more.
I'm excited to share these ten essay writing tips with you today! But first, we need to talk about why writing an essay is so hard.
Why Writing an Essay Is So Hard
When it comes to essay writing, a lot of students find a reason to put it off. And when they tackle it, they find it difficult to string sentences together that sound like a decent stance on the assigned subject.
Here are a few reasons why essay writing is hard:
- You'd rather be scrolling through Facebook
- You're trying to write something your teacher or professor will like
- You're trying to get an A instead of writing something that's actually good
- You want to do the least amount of work possible
The biggest reason writing an essay is so hard is because we mostly focus on those external rewards like getting a passing grade, winning our teacher's approval, or just avoiding accusations of plagiarism.
The problem is that when you focus on external approval it not only makes writing much less fun, it also makes it significantly harder.
Because when you focus on external approval, you shut down your subconscious, and the subconscious is the source of your creativity.
The subconscious is the source of your creativity.
What this means practically is that when you're trying to write that perfect, A-plus-worthy sentence, you're turning off most of your best resources and writing skills.
So stop. Stop trying to write a good essay (or even a “good-enough” essay). Instead, write an interesting essay, write an essay you think is fascinating. And when you're finished, go back and edit it until it's “good” according to your teacher's standards.
Yes, you need to follow the guidelines in your assignment. If your teacher tells you to write a five-paragraph essay, then write a five-paragraph essay! If your teacher asks for a specific type of essay, like an analysis, argument, or research essay, then make sure you write that type of essay!
However, within those guidelines, find room to express something that is uniquely you .
I can't guarantee you'll get a higher grade (although, you almost certainly will), but I can absolutely promise you'll have a lot more fun writing.
The Step-by-Step Process to Writing a Great Essay: Your 10 Essay Writing Tips
Ready to get writing? You can read my ten best tips for having fun while writing an essay that earns you the top grade, or check out this presentation designed by our friends at Canva Presentations .
1. Remember your essay is just a story.
Every story is about conflict and change, and the truth is that essays are about conflict and change, too! The difference is that in an essay, the conflict is between different ideas , and the change is in the way we should perceive those ideas.
That means that the best essays are about surprise: “You probably think it's one way, but in reality, you should think of it this other way.” See tip #3 for more on this.
How do you know what story you're telling? The prompt should tell you.
Any list of essay prompts includes various topics and tasks associated with them. Within those topics are characters (historical, fictional, or topical) faced with difficult choices. Your job is to work with those choices, usually by analyzing them, arguing about them, researching them, or describing them in detail.
2. Before you start writing, ask yourself, “How can I have the most fun writing this?”
It's normal to feel unmotivated when writing an academic essay. I'm a writer, and honestly, I feel unmotivated to write all the time. But I have a super-ninja, judo-mind trick I like to use to help motivate myself.
Here's the secret trick: One of the interesting things about your subconscious is that it will answer any question you ask yourself. So whenever you feel unmotivated to write your essay, ask yourself the following question:
“How much fun can I have writing this?”
Your subconscious will immediately start thinking of strategies to make the writing process more fun.
The best time to have your fun is the first draft. Since you're just brainstorming within the topic, and exploring the possible ways of approaching it, the first draft is the perfect place to get creative and even a little scandalous. Here are some wild suggestions to make your next essay a load of fun:
- Research the most surprising or outrageous fact about the topic and use it as your hook.
- Use a thesaurus to research the topic's key words. Get crazy with your vocabulary as you write, working in each key word synonym as much as possible.
- Play devil's advocate and take the opposing or immoral side of the issue. See where the discussion takes you as you write.
3. As you research, ask yourself, “What surprises me about this subject?”
The temptation, when you're writing an essay, is to write what you think your teacher or professor wants to read.
Don't do this .
Instead, ask yourself, “What do I find interesting about this subject? What surprises me?”
If you can't think of anything that surprises you, anything you find interesting, then you're not searching well enough, because history, science, and literature are all brimming over with surprises. When you look at how great ideas actually happen, the story is always, “We used to think the world was this way. We found out we were completely wrong, and that the world is actually quite different from what we thought.”
These pieces of surprising information often make for the best topic sentences as well. Use them to outline your essay and build your body paragraphs off of each unique fact or idea. These will function as excellent hooks for your reader as you transition from one topic to the next.
(By the way, what sources should you use for research? Check out tip #10 below.)
4. Overwhelmed? Write five original sentences.
The standard three-point essay is really made up of just five original sentences surrounded by supporting paragraphs that back up those five sentences. If you're feeling overwhelmed, just write five sentences covering your most basic main points.
Here's what they might look like for this article:
- Introductory Paragraph: While most students consider writing an essay a boring task, with the right mindset, it can actually be an enjoyable experience.
- Body #1: Most students think writing an essay is tedious because they focus on external rewards.
- Body #2: Students should instead focus on internal fulfillment when writing an essay.
- Body #3: Not only will focusing on internal fulfillment allow students to have more fun, it will also result in better essays.
- Conclusion: Writing an essay doesn't have to be simply a way to earn a good grade. Instead, it can be a means of finding fulfillment.
After you write your five sentences, it's easy to fill in the paragraphs for each one.
Now, you give it a shot!
5. Be “source heavy.”
In college, I discovered a trick that helped me go from a B-average student to an A-student, but before I explain how it works, let me warn you. This technique is powerful , but it might not work for all teachers or professors. Use with caution.
As I was writing a paper for a literature class, I realized that the articles and books I was reading said what I was trying to say much better than I ever could. So what did I do? I quoted them liberally throughout my paper. When I wasn't quoting, I re-phrased what they said in my own words, giving proper credit, of course. I found that not only did this formula create a well-written essay, it took about half the time to write.
It's good to keep in mind that using anyone else's words, even when morphed into your own phrasing, requires citation. While the definition of plagiarism is shifting with the rise of online collaboration and cooperative learning environments, always err on the side of excessive citation to be safe.
When I used this technique, my professors sometimes mentioned that my papers were very “source” heavy. However, at the same time, they always gave me A's.
To keep yourself safe, I recommend using a 60/40 approach with your body paragraphs: Make sure 60% of the words are your own analysis and argumentation, while 40% can be quoted (or text you paraphrase) from your sources.
Like the five sentence trick, this technique makes the writing process simpler. Instead of putting the main focus on writing well, it instead forces you to research well, which some students find easier.
6. Write the body first, the introduction second, and the conclusion last.
Introductions are often the hardest part to write because you're trying to summarize your entire essay before you've even written it yet. Instead, try writing your introduction last, giving yourself the body of the paper to figure out the main point of your essay.
This is especially important with an essay topic you are not personally interested in. I definitely recommend this in classes you either don't excel in or care much for. Take plenty of time to draft and revise your body paragraphs before attempting to craft a meaningful introductory paragraph.
Otherwise your opening may sound awkward, wooden, and bland.
7. Most essays answer the question, “What?” Good essays answer the “Why?” The best essays answer the “How?”
If you get stuck trying to make your argument, or you're struggling to reach the required word count, try focusing on the question, “How?”
For example:
- How did J.D. Salinger convey the theme of inauthenticity in The Catcher In the Rye ?
- How did Napoleon restore stability in France after the French Revolution?
- How does the research prove girls really do rule and boys really do drool?
If you focus on how, you'll always have enough to write about.
8. Don't be afraid to jump around.
Essay writing can be a dance. You don't have to stay in one place and write from beginning to end.
For the same reasons listed in point #6, give yourself the freedom to write as if you're circling around your topic rather than making a single, straightforward argument. Then, when you edit and proofread, you can make sure everything lines up correctly.
In fact, now is the perfect time to mention that proofreading your essay isn't just about spelling and commas.
It's about making sure your analysis or argument flows smoothly from one idea to another. (Okay, technically this comprises editing, but most students writing a high school or college essay don't take the time to complete every step of the writing process. Let's be honest.)
So as you clean up your mechanics and sentence structure, make sure your ideas flow smoothly, logically, and naturally from one to the next as you finish proofreading.
9. Here are some words and phrases you don't want to use.
- You (You'll notice I use a lot of you's, which is great for a blog post. However, in an academic essay, it's better to omit the second-person.)
- To Be verbs (is, are, was, were, am)
Don't have time to edit? Here's a lightning-quick editing technique .
A note about “I”: Some teachers say you shouldn't use “I” statements in your writing, but the truth is that professional, academic papers often use phrases like “I believe” and “in my opinion,” especially in their introductions.
10. It's okay to use Wikipedia, if…
Wikipedia is one of the top five websites in the world for a reason: it can be a great tool for research. However, most teachers and professors don't consider Wikipedia a valid source for use in essays.
Don't totally discount it, though! Here are two ways you can use Wikipedia in your essay writing:
- Background research. If you don't know enough about your topic, Wikipedia can be a great resource to quickly learn everything you need to know to get started.
- Find sources . Check the reference section of Wikipedia's articles on your topic. While you may not be able to cite Wikipedia itself, you can often find those original sources and cite them . You can locate the links to primary and secondary sources at the bottom of any Wikipedia page under the headings “Further Reading” and “References.”
You Can Enjoy Essay Writing
The thing I regret most about high school and college is that I treated it like something I had to do rather than something I wanted to do.
The truth is, education is an opportunity many people in the world don't have access to.
It's a gift, not just something that makes your life more difficult. I don't want you to make the mistake of just “getting by” through school, waiting desperately for summer breaks and, eventually, graduation.
How would your life be better if you actively enjoyed writing an essay? What would school look like if you wanted to suck it dry of all the gifts it has to give you?
All I'm saying is, don't miss out!
Looking for More Essay Writing Tips?
Looking for more essay tips to strengthen your essay writing? Try some of these resources:
- 7 Tips on Writing an Effective Essay
- Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
How about you? Do you have any tips for writing an essay? Let us know in the comments .
Need more grammar help? My favorite tool that helps find grammar problems and even generates reports to help improve my writing is ProWritingAid . Works with Word, Scrivener, Google Docs, and web browsers. Also, be sure to use my coupon code to get 20 percent off: WritePractice20
Coupon Code:WritePractice20 »
Ready to try out these ten essay tips to make your essay assignment fun? Spend fifteen minutes using tip #4 and write five original sentences that could be turned into an essay.
When you're finished, share your five sentences in the comments section. And don't forget to give feedback to your fellow writers!
[wp_ad_camp_2]
Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Best Resources for Writers Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.
Home ➔ What's an Essay?
What Is an Essay and Its Features?
The are various definitions for “essay.” But here, we will focus on the meaning of this word, which has become a significant element of education in countries such as the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, and Australia.
If summarized in simple terms within the academic context, the essay’s definition would be the following:
An essay is a short, nonfictional piece of formal writing assigned to students to improve their writing skills or assess their knowledge of a given subject.

Alternative Essay Definitions
Here are some of the many definitions of an essay:
- According to Frederick Crews, professor of English at the University of California at Berkeley, an essay is “a fairly brief piece of nonfiction that tries to make a point in an interesting way.”
- A famous essayist, Aldous Huxley, notes that “the essay is a literary device for saying almost everything about almost anything” and divides essays into personal-biographical, objectively-factual, and abstract-universal.
- The Oxford Dictionary defines it as “a short piece of writing on a particular subject.”
Essays can be broadly categorized into formal essays and informal essays. Formal essays are characterized by their structured nature, employing a more formal language, and having a clearly defined purpose, contrasting with the more free-form and personal tone of informal essays.
Note: Apart from the secondary and tertiary education purpose, essays (also called papers reports) are often required when applying to colleges and universities to help them select the best applicants during the admissions.
If you study the word’s origin and history, you might better understand its purpose. The word “essay” comes from the Middle French word essayer, which in turn comes from Latin exigere, meaning “to test,” “examine,” and “drive out.”
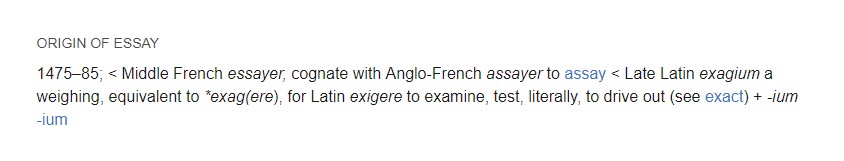
This “archaeological” linguistic journey reveals the idea behind essays, encouraging learners to examine their ideas concerning a particular topic in-depth and test them. By nature, essays are short and require a clearly defined purpose of writing that you must adhere to in your paper.
There’s a lot to be learned from essay writing: critical analysis, observation, interpretation, narration, persuasion, close reading, preparation, and time management. All these skills can be valuable even beyond the school walls.
Lastly, in the visual arts, creative works can also be called essays if they present a personal reflection on a particular matter. So, film essays or photo essays fall into the general category of essays.
What is an essay structure like?
An essay is generally composed of three parts and has the following structure :
- Introduction (hook, background information, and your thesis statement) – provides context for the reader and gives an argument in the form of a thesis statement.
- Body section (usually, one paragraph for each main idea) – the main section where evidence is presented to persuade the reader to adopt the writer’s point of view or prove something.
- Conclusion – the last section that summarizes everything you have discussed in your essay and provides the final perspective on the subject.
Generally, an essay must focus on the author’s argument and supporting evidence. However, the variety of essay types involves many other forms and styles. Argumentative and expository essays are particularly common in university-level education, known for their structured approach to presenting information and making clear points.
Common Essay Types
Understanding the different types of essays is pretty important for your academic success. Each essay type serves its own purpose and requires a different approach, so here’s a brief look at some of the most common essay types you might encounter during your school times.
Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay demands you to present a viewpoint on a (usually) controversial issue. Your task would generally be to persuade the reader through some solid logical reasoning and credible evidence with relevant examples. All that will involve creating a very clear thesis statement, presenting well-researched evidence, and addressing opposing views and ideas, if there are such. Getting an argumentative essay as an assignment is common in subjects like politics, ethics, and social sciences, where there’s a lot of debate on different topics. An example of a common topic for this essay would be something like “Should the death penalty be abolished?”

Expository Essay
An expository essay focuses more on explaining a topic in a straightforward and logical manner. In such an essay, you will be presenting facts, statistics, and examples without any kind of your personal opinion. It’s usually built around a clear thesis statement and uses logical transitions to connect ideas from one paragraph to another. In general, expository essays are often used in academic settings to test students’ understanding of a subject or to explain complex ideas in a simple way. A common topic would be “The process of photosynthesis in plants.”, for example.
Narrative Essay
Narrative essays tell a story. These are often personal and can be both factual (based on a true story) and fictional. The key elements of this essay include a plot, characters, setting, and a climax. Unlike other essays, a narrative essay is much more creative and allows you to express your experiences or a story imaginatively and without some kind of rigid structure to follow. It’s often used in high school and college writing courses to develop storytelling skills. You would write about something like “A memorable trip to the mountains.”
Descriptive Essay
A descriptive essay aims to paint a picture but with words. This essay uses vivid descriptions and sensory details to engage the reader’s senses and emotions and is more focused on the details and nuances of the subject, whether it’s a person, place, object, or event. Descriptive essays are great for creative writing classes and help develop one’s ability to describe something in great detail. One of the possible topics here might be “The bustling atmosphere of a city market.”
Critical Essay
A critical essay evaluates a text, piece of art, or performance. It involves a thorough analysis and interpretation of the work, supported by credible evidence. The goal when writing this one is to provide a critical perspective, assessing the subject’s strengths and weaknesses. This type of essay is a common assignment in literature, film studies, and art history courses, where critical thinking and analytical skills are essential for the subject. A common topic here would be ‘An analysis of the themes in “To Kill a Mockingbird.”‘
History Essay
A history essay examines historical events and their impact. This type requires extensive research and a deep understanding of historical context. When writing it, you will be analyzing various historical sources, presenting a clear argument on the topic, and supporting it with historical evidence. History essays are obviously assigned in history courses and help develop research and analytical skills, as well as the ability to construct coherent historical narratives. Something like “The causes and effects of the French Revolution.” would be a common topic here.
10 Characteristics of a Good Essay
The structure and characteristics vary, but there are criteria you can apply to almost any academic essay. Below are ten characteristics that make a good essay.
You can find many works like Victor Segalen’s “Essay on Exoticism: An Aesthetics of Diversity” spanning many pages. But, as an academic assignment, essays are usually concise and range from 200 to 500 words.
Note: To learn more about essay length, check this article — How Long Should My Paper Be?
A narrowed-down topic
Because of the word count limit, your topic cannot be extensive and should focus on one aspect of the subject.
A subject is a broad concept: gun control, US history, WWII, Napoleonic Wars, business ethics, academic dishonesty, school dress code, etc. Those are not topics because you can write books on them.
Choose a more specific topic to cover. Ask yourself “Who? What? Where? When? Why? and How?” questions about the subject matter. That strategy will allow you to limit the number of choices and pick something you like.
For instance, let’s narrow down the gun control subject . Something like “Video games are not the problem, but poor gun control policies are” can be your topic.
Well-structured body paragraphs
In a nutshell, an essay’s body can be described as a series of paragraphs. But they all have a uniform structure you must maintain in the paper. It goes as follows:
1. Topic sentence
This is the first sentence, and it expresses the paragraph’s main idea. It acts like a mini-hook that attracts the reader’s attention.
Let’s say you’re working on a descriptive essay about your brother’s room.
Bad topic sentence:
My brother’s room is a mess.
Good topic sentence:
If they gave me one dollar every time I walked into my brother’s room and thought it was clean, I would be dead broke.
2. The main part
Here, you develop your topic sentence further, and there are many ways to do that:
- Provide facts or statistics
- Give reasons
- Illustrate with examples
- Use relevant quotes
- Present your opinion
- Share experiences
- Leverage human senses
Note: Make sure to cite your sources properly. Learn more here: How to Cite Sources (MLA and APA styles) .
3. Conclusion with a transition
If you had to write only one paragraph, this is where you would end the narrative. But, in academic essays, this last sentence transitions to the next idea — the next paragraph.
Clear thesis statement
A thesis is the main idea of your paper. It’s usually one sentence that shows the reader what your essay is about. The challenging part is to squeeze the purpose of your writing into one sentence and in such a way that would make the reader want to debate it.
To check if your thesis statement is correct, make sure:
- It’s not just an announcement of purpose that starts with “In this paper.”
- It’s not a question because thesis statements answer, not ask.
- It’s not a mere fact.
- It’s not a broad topic without a challenging opinion.
- It’s not a vague thought — make it more focused.
- It’s not disconnected from the main paragraphs.
Personal motivation
This one seems quite simple, but you won’t always find the answer to the “Why do I want to write about this topic” question easily. Even if the subject feels like the last thing you’d be interested in, there’s always something that can motivate you to write.
The reader would notice if you had zero motivation while writing the essay.
There’s no trick — just start writing . Once you are working on it, brainstorm all the ideas related to the subject. If you find it challenging to organize your thoughts right away, try freewriting — start writing everything that comes to your mind. Yes, there will be a lot of ideas not connected with one another, but you can choose the ones making sense and work with them further.
Evidence and examples support claims
Each of your topic sentences in the main paragraphs should be supported. You can:
- Explain what you meant by defining the main terms or phenomena.
- Provide more details about the topic sentence.
- Illustrate with examples, facts, or statistics.
- Cite field experts who support your opinion.
- Share your relevant experience, if any.
Use the method you believe is the most appropriate in your case.
Evidence is analyzed
Just facts, statistics, or quotations are not enough. You must analyze the proof and show how you can compare data and establish causal links.
Note: Use cohesive devices like transition words and conjunctions to hold your essay together as one unit.
No grammar mistakes
The last period is placed, and you think, “Finally, it’s done! Now, back to the fun stuff.” By doing so, you will hand in an essay riddled with mistakes.
Proofreading matters. After the first draft, double-check it for all possible mistakes: grammar, punctuation, word usage, logic flow, etc.
- Read it out loud.
- Ask your friend or family member to give their opinion.
- Put it away for some time to proofread it later.
The structure is consistent
Ensure your paper follows the structure described before. Check if your conclusion and introduction are about the same — the same applies to the body paragraphs.
Note: This article will give you valuable insights into the structure — How to Write an Essay .
It is coherent
Another criterion they use to grade your essay is its coherence (unity). To check this point, ask yourself:
- Are all ideas related to the essay’s topic and thesis statement?
- Are all my evidence, arguments, and conclusions connected to my thesis statement?
- Are all ideas arranged in a logical order?
- Are there enough linking words? Or is it too many of them?
- Are there enough pronouns and synonyms so that the essay isn’t repetitive?
The last tip on essay writing: always check your assignment sheet and clarify anything you don’t understand with your tutor or professor. Your college might have some special requirements regarding the content or style. So, make sure you studied all the instructions for the task thoroughly.
Why do we have to write essays in school?
Writing essays in school is a crucial component of academic writing, serving as a foundational practice for developing skills in various types of essays, such as argumentative, descriptive, narrative, expository, and more. Through the process of essay writing, students learn to articulate their ideas and thoughts more coherently, practice forming main and alternative arguments backed up by evidence, and enhance their ability to present clear explanations, craft creative descriptions, and structure narratives effectively. This practice not only helps build strong academic writing skills but also prepares students for writing research papers, submission essays, and contributing to academic journals, thereby playing a significant role in their academic and professional growth.
How are essays evaluated?
In schools, essays are typically evaluated based on a combination of criteria such as quality of your argument, evidence you presented, structure and organization, grammar and vocabulary accuracy, adherence to formatting requirements (if any), creativity, originality, critical thinking skills displayed, etc. The evaluator (usually your teacher or professor) will look at all these aspects to assess the essay’s overall quality.
How many paragraphs should there be in an essay?
The number of paragraphs in an essay will vary depending on its length and purpose. In general, a standard essay should have at least 3-4 paragraphs: an introduction paragraph to provide background information and set out your main argument; 2-3 body paragraphs where you flesh out your argument with evidence; and a conclusion paragraph summarizing your key points or drawing conclusions from your evidence.

The list of references
- What is an essay? — Bow Valley College
- Overview of the Academic Essay — Harvard University
- Essay Writing — Purdue University
- Basic Essay and Paragraph Format — Utah Valley University
Was this article helpful?
Did you know the word ‘essay’ is derived from a Latin word ‘exagium’, which roughly translates to presenting one’s case? So essays are a short piece of writing representing one’s side of the argument or one’s experiences, stories, etc. Essays are very personalized. So let us learn about types of essays, format, and tips for essay-writing.
Suggested Videos

An essay is generally a short piece of writing outlining the writer’s perspective or story . It is often considered synonymous with a story or a paper or an article. Essays can be formal as well as informal. Formal essays are generally academic in nature and tackle serious topics. We will be focusing on informal essays which are more personal and often have humorous elements.
Browse more Topics under Writing
- Descriptive Essay
- Diary Entry
- Formal Letters
- Informal Letters
- Letter Writing
- Non-Classified/Display Advertisements
- Story: Characters
- Story: Setting
Get 500+ Essay Topics and Ideas for College and School Students here .

(Source: thewritelife)
Types of Essays
The type of essay will depend on what the writer wants to convey to his reader. There are broadly four types of essays. Let us see.
- Narrative Essays: This is when the writer is narrating an incident or story through the essay. So these are in the first person. The aim when writing narrative essays is to involve the reader in them as if they were right there when it was happening. So make them as vivid and real as possible. One way to make this possible is to follow the principle of ‘show, don’t tell’. So you must involve the reader in the story.
- Descriptive Essays : Here the writer will describe a place, an object, an event or maybe even a memory. But it is not just plainly describing things. The writer must paint a picture through his words. One clever way to do that is to evoke the senses of the reader. Do not only rely on sight but also involve the other senses of smell, touch, sound etc. A descriptive essay when done well will make the reader feel the emotions the writer was feeling at the moment.
- Expository Essays: In such an essay a writer presents a balanced study of a topic. To write such an essay, the writer must have real and extensive knowledge about the subject. There is no scope for the writer’s feelings or emotions in an expository essay. It is completely based on facts, statistics, examples etc. There are sub-types here like contrast essays, cause and effect essays etc.
- Persuasive Essays : Here the purpose of the essay is to get the reader to your side of the argument. A persuasive essay is not just a presentation of facts but an attempt to convince the reader of the writer’s point of view. Both sides of the argument have to presented in these essays. But the ultimate aim is to persuade the readers that the writer’s argument carries more weight.
Learn more about Letter Writing here in detail .
Format of an Essay
Now there is no rigid format of an essay. It is a creative process so it should not be confined within boundaries. However, there is a basic structure that is generally followed while writing essays. So let us take a look at the general structure of an essay.
Introduction
This is the first paragraph of your essay. This is where the writer introduces his topic for the very first time. You can give a very brief synopsis of your essay in the introductory paragraph. Some paragraph writing skills can be a help here. Generally, it is not very long, about 4-6 lines.

There is plenty of scopes to get creative in the introduction of essays. This will ensure that you hook the reader, i.e. draw and keep his attention. So to do so you can start with a quote or a proverb . Sometimes you can even start with a definition. Another interesting strategy to engage with your reader is to start with a question.
This is the main crux of your essays. The body is the meat of your essay sandwiched between the introduction and the conclusion. So the most vital and important content of the essay will be here. This need not be confined to one paragraph. It can extend to two or more paragraphs according to the content.
Usually, we have a lot of information to provide in the body. And the mistakes writers generally make is to go about it in a haphazard manner which leaves the reader confused. So it is important to organize your thoughts and content. Write the information in a systematic flow so that the reader can comprehend. So, for example, you were narrating an incident . The best manner to do this would be to go in a chronological order.
Learn more about Story Writing here in detail .
This is the last paragraph of the essay. Sometimes a conclusion will just mirror the introductory paragraph but make sure the words and syntax are different. A conclusion is also a great place to sum up a story or an argument. You can round up your essay by providing some moral or wrapping up a story. Make sure you complete your essays with the conclusion, leave no hanging threads.
Tips for Essay Writing
- Give your essays an interesting and appropriate title. It will help draw the attention of the reader and pique their curiosity
- Keep it between 300-500 words. This is the ideal length, you can take creative license to increase or decrease it
- Keep your language simple and crisp. Unnecessary complicated and difficult words break the flow of the sentence.
- Do not make grammar mistakes , use correct punctuation and spellings . If this is not done it will distract the reader from the content
- Before beginning the essay organize your thought and plot a rough draft . This way you can ensure the story will flow and not be an unorganized mess.
Solved Question for You
Q: What is a thesis statement of essays?
Ans: The thesis statement is a clear, one-sentence explanation of your position that leaves no doubt in the readers’ mind about which side you are on from the beginning of your essay.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Non-Classified or Display Advertisements
5 responses to “Story: Characters”
great article
very clean post.
awesome work
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Skip to Content
Other ways to search:
- Events Calendar
Want to write a college essay that sets you apart? Three tips to give you a head start

1. Keep it real. It’s normal to want to make a good impression on the school of your choice, but it’s also important to show who you really are. So just be yourself! Compelling stories might not be perfectly linear or have a happy ending, and that’s OK. It’s best to be authentic instead of telling schools what you think they want to hear.
2. Be reflective . Think about how you’ve changed during high school. How have you grown and improved? What makes you feel ready for college, and how do you hope to contribute to the campus community and society at large?
3. Look to the future. Consider your reasons for attending college. What do you hope to gain from your education? What about college excites you the most, and what would you like to do after you graduate? Answering these questions will not only give colleges insight into the kind of student you’ll be, but it will also give you the personal insight you’ll need to choose the school that’s right for you.
Have questions about college prep? We're here to help.
Written by CU Boulder Office of Admissions
- College-Prep
The University of Colorado does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, age, pregnancy, disability, creed, religion, sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression, veteran status, political affiliation, or political philosophy. All qualified individuals are encouraged to apply. You may view the list of ADA and Title IX coordinators and review the Regent policy .
As a student or prospective student at CU Boulder, you have a right to certain information pertaining to financial aid programs, the Clery Act, crime and safety, graduation rates, athletics and other general information such as the costs associated with attending CU Boulder. To view this information visit colorado.edu/your-right-know .
Apply for Admission
Visit Campus
Support CU Boulder
- Safety & Health Services
- COVID-19 Information
- Campus Communications
- Emergency Alert System
- New Student & Family Programs
Getting Around
- Campus Events
- Parking & Transportation
- Visit Information
Information for
- Faculty & Staff
- Journalists
Initiatives
- Business & Industry Collaborations
- Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
- Free Speech
- Innovation & Entrepreneurship
- Public & Outreach Programs
- Sustainability
- Understanding Your Cost of Attendance
Home > Blog > How To Write an Outline for Essays

How To Write an Outline for Essays
- Smodin Editorial Team
- Updated: August 13, 2024
- Step-by-Step Instructions for Writing
Think of an outline for an essay as a guide that will shape your writing. Persuasive essays need to be thought out carefully, with body paragraphs planned out in detail. It isn’t advisable to go into an essay blind – it won’t have a logical order, and your draft won’t make much sense.
If you’ve never written an outline before, read on. We’re covering how to incorporate it into your writing process and list some essay outline examples to help you get started.

What Is an Outline for an Essay?
An essay outline is like a roadmap for your writing journey. It guides you from the introduction section to the conclusion in a clear and organized way. It’s the bare bones of what you’re going to write about, allowing you to set out your key points and showing you how you’re going to structure them in the body paragraphs.
Laying out the main points and subpoints in an argumentative essay outline or other types of essays you’ll cover will help you ensure there is logical flow and all the necessary aspects of your topic are covered.
Creating an outline might seem like an extra step, but it can save you a lot of time and frustration in the long run. It allows you to see the big picture before you dive into writing, making it easier to stay on track and avoid wandering off-topic.
Plus, with a solid outline, you can spot any gaps in your argument or areas that need more research before you start the essay writing process.
So, whether you’re tackling a high school assignment, crafting a complex research paper , or diving into expository essays, starting with an outline is a smart move. It helps you stay focused on the topic and confident in where you’re going with your paper.
So now that you know what is an outline for an essay, let’s discuss how it can help you during the writing process in more detail.

How Can an Essay Outline Help You During the Writing Process?
Good essays are a measure of academic success, according to the Honor Society . Hence, you need to ensure that your essays are well-researched and well-written. Effective essay outlines are an easy way to make your writing process much easier when writing a paper.
Here’s why an essay outline is helpful.
1. Organizes Your Thoughts
An outline acts as a map for your essay. It helps you organize your thoughts and ideas so everything flows logically. By planning out your main points and supporting all your details in advance, you can make sure your essays or research papers make sense from start to finish.
2. Saves Time
Taking a little time to create an outline, including your body paragraphs, intro, and conclusion, can save you a ton of time later. With a clear plan in place, you can write faster and avoid getting stuck or going off on tangents.
3. Ensures Coherence and Clarity in Your Writing
A good essay outline makes sure your essay stays clear and easy to follow. It helps you move from one idea to the next in a logical way so your readers can understand your argument or story without getting lost.
4. Helps Identify Gaps and Weaknesses
When you outline your essay, you can spot any gaps in your research or weak points in an argumentative essay, for example. This lets you fix these issues early on, making your overall essay stronger. This is particularly important for an expository essay outline, where you need to weave arguments throughout.
5. Creates a Balanced Structure
An outline helps you balance your essay. You can make sure each section gets enough attention and that no part is too long or too short.
6. Reduces Your Stress Levels
Having a clear plan can reduce the stress of writing. Knowing what you need to write next keeps you focused and helps prevent writer’s block.
7. Improves Overall Quality
In the end, a well-made outline leads to a better essay. It helps you present your ideas in a structured, persuasive, and polished way, making a strong impression on your readers. It’s the foundation that helps you build a compelling and well-organized essay.

How To Do an Outline for an Essay That’s a Thesis Statement
Wondering how to do an outline for an essay that’s a thesis statement? We’ve got you covered! When you write an essay outline, you’re forced to think about the main points you want to cover. This process helps you narrow down your focus and get a clearer idea of your main argument.
As you organize your ideas and see how they fit together, you can start to see the big picture of your essay. This big picture is what your thesis statement is all about.
Your thesis statement is the heart of your essay—it tells your reader what your main point is and sets the direction for your whole paper. By outlining first, you make sure that your thesis statement is strong and clearly reflects the main ideas you’ll be discussing.
Plus, if you find that your ideas aren’t quite lining up as you outline, you can tweak your thesis statement to match your essay’s direction better. It’s much easier to make these adjustments early on rather than having to rewrite large parts of your essay later.
Creating an outline not only helps you organize your essay but also ensures your thesis statement is clear, focused, and on point.
Outline Examples for Essays: 3 Most Common Essay Types
To help you start writing your essay outline, here are three outline examples for essays of different types.
1. A Descriptive Essay Outline Example
Creating a clear outline for a descriptive essay helps ensure your writing is organized and engaging. Here’s an example of a descriptive essay you might write at college.
Example Outline: The Library at My University
I. Introduction
- Hook: “Stepping into the university library is like entering a sanctuary of knowledge.”
- Background info: Brief introduction to the library’s significance
- Thesis statement: “The university library is my favorite place due to its peaceful atmosphere, extensive resources, and inspiring architecture.”
II. Body Paragraphs
A. Atmosphere
- Topic sentence: “The library offers a serene atmosphere for studying.”
- Details: Quiet study areas, comfortable seating, natural light
- Sensory descriptions: The silence, the soft rustling of pages
B. Resources
- Topic sentence: “The library provides a wealth of resources.”
- Details: Vast book collections, digital databases, research assistance
- Sensory descriptions: The smell of old books, the glow of computer screens
C. The Architecture
- Topic sentence: “The architecture of the library is inspiring.”
- Details: High ceilings, large windows, modern design
- Sensory descriptions: The grandeur of the building, the brightness of the space
III. Conclusion
- Restate thesis: “The library’s atmosphere, resources, and design make it an ideal study spot.”
- Closing thought: “It’s a place where learning comes alive.”
2. A Narrative Essay Outline Example
Creating a clear outline for a narrative essay helps ensure your story is well-organized and engaging. Here’s an example focused on a more academic topic.
Example Outline: My First Science Fair
- Hook: “I’ll never forget the excitement of my first science fair.”
- Background info: Brief introduction to the event and its significance
- Thesis statement: “Participating in my first science fair taught me valuable lessons about perseverance, creativity, and teamwork.”
A. Preparing for the Fair
- Topic sentence: “Preparation was a journey of discovery.”
- Details: Choosing the project, researching, and building the model
- Sensory descriptions: The smell of glue, the feel of experiment materials
B. The Day of the Fair
- Topic sentence: “The day of the fair was filled with excitement and nerves.”
- Details: Setting up the display, presenting to judges, and interacting with other participants
- Sensory descriptions: The buzz of conversations, the bright fair lights
C. The Results and Reflection
- Topic sentence: “The results taught me valuable lessons.”
- Details: Waiting for the results, receiving feedback, winning an award
- Sensory descriptions: The anxiety of waiting, the joy of recognition
- Restate thesis: “The science fair experience was unforgettable and educational.”
- Closing thought: “It sparked a lifelong interest in science and learning.”
3. An Expository Essay Outline Example
Creating a clear outline for an expository essay helps ensure your content is well-organized and informative. Here’s an example focused on an academic topic.
Example Outline: The Impact of Social Media on Teenagers
- Hook: “In today’s digital age, social media has become a significant part of teenagers’ lives.”
- Background info: Brief introduction to the topic and its relevance
- Thesis statement: “Social media influences teenagers’ social interactions, self-esteem, and academic performance in both positive and negative ways.”
A. Social Interactions
- Topic sentence: “Social media affects how teenagers interact with their peers.”
- Details: Communication methods, peer pressure, forming relationships
- Examples: Messaging apps, online communities, influence of trends
B. Self-Esteem
- Topic sentence: “Social media impacts teenagers’ perceptions of themselves.”
- Details: Comparisons, feedback loops, self-expression
- Examples: Likes, comments, body image issues
C. Academic Performance
- Topic sentence: “Social media usage can affect teenagers’ academic achievements.”
- Details: Distractions, study habits, access to information
- Examples: Procrastination, online research, and educational resources
- Restate thesis: “Social media’s influence on teenagers is complex, impacting their social interactions, self-esteem, and academic performance.”
- Closing thought: “Understanding these influences is crucial for navigating the digital world responsibly.”

Frequently Asked Questions
Why do i need to create an outline for my essay.
Think of an essay outline as your roadmap. It helps you organize your thoughts and ensure your essay flows logically from start to finish. Without an outline, your essay may lack a clear structure, making it difficult for readers to follow your arguments or narrative.
By planning your main points and supporting details ahead of time, you can save time, maintain focus, and create a cohesive and well-structured essay.
What should be included in an essay outline?
An effective essay outline typically includes:
- Introduction: Include a hook, background information, and thesis statement.
- Body paragraphs: Each paragraph should start with a topic sentence, followed by details, examples, and sensory descriptions where applicable.
- Conclusion: Restate the thesis and provide a closing thought that leaves a lasting impression.
This structure ensures that your essay is well-organized and covers all necessary aspects of your topic, whether you’re writing a persuasive essay, narrative, or expository piece.
Can an outline help me refine my thesis statement?
Absolutely! When you create an outline, you’re forced to clarify your main points and how they support your thesis. This process helps you identify any weak arguments or gaps in your research early on. By outlining first, you can ensure that your thesis statement is strong, focused, and reflective of the ideas you’ll develop throughout your essay.
This approach not only enhances the coherence of your writing but also sets a clear direction for your entire paper.

Get Help With Smodin AI: Your Outline Generator
Ready to streamline your essay writing process? Smodin AI is your ultimate research assistant, writing companion, and outline generator. Whether you’re crafting an essay, research paper, or any other written piece, Smodin AI offers powerful tools to enhance your writing experience.
With Smodin AI, you can conduct AI-powered research to access comprehensive and accurate information instantly, aiding your research process. Create elegantly structured content with in-text citations and references formatted in MLA or APA styles, ensuring your work meets academic standards.
Experience how Smodin AI can elevate your writing to new heights. Empower your writing process with smart tools and expert guidance. Get started with Smodin AI today and discover the difference in your writing quality.

Title Page Setup
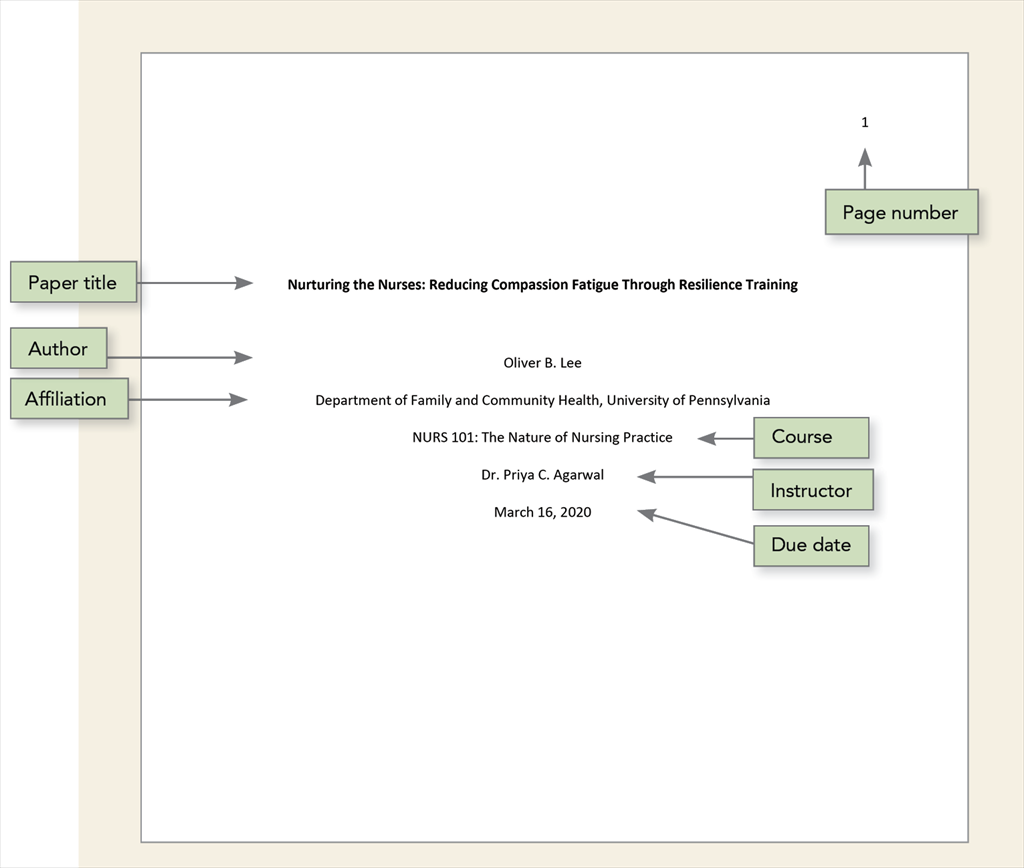
A title page is required for all APA Style papers. There are both student and professional versions of the title page. Students should use the student version of the title page unless their instructor or institution has requested they use the professional version. APA provides a student title page guide (PDF, 199KB) to assist students in creating their title pages.
Student title page
The student title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation, course number and name for which the paper is being submitted, instructor name, assignment due date, and page number, as shown in this example.
Title page setup is covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 2.3 and the Concise Guide Section 1.6
Related handouts
- Student Title Page Guide (PDF, 263KB)
- Student Paper Setup Guide (PDF, 3MB)
Student papers do not include a running head unless requested by the instructor or institution.
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the student title page.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Paper title | Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired. There is no maximum length for titles; however, keep titles focused and include key terms. |
|
| Author names | Place one double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author names. Center author names on their own line. If there are two authors, use the word “and” between authors; if there are three or more authors, place a comma between author names and use the word “and” before the final author name. | Cecily J. Sinclair and Adam Gonzaga |
| Author affiliation | For a student paper, the affiliation is the institution where the student attends school. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated by a comma. Center the affiliation on the next double-spaced line after the author name(s). | Department of Psychology, University of Georgia |
| Course number and name | Provide the course number as shown on instructional materials, followed by a colon and the course name. Center the course number and name on the next double-spaced line after the author affiliation. | PSY 201: Introduction to Psychology |
| Instructor name | Provide the name of the instructor for the course using the format shown on instructional materials. Center the instructor name on the next double-spaced line after the course number and name. | Dr. Rowan J. Estes |
| Assignment due date | Provide the due date for the assignment. Center the due date on the next double-spaced line after the instructor name. Use the date format commonly used in your country. | October 18, 2020 |
|
| Use the page number 1 on the title page. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word processing program to insert page numbers in the top right corner of the page header. | 1 |
Professional title page
The professional title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation(s), author note, running head, and page number, as shown in the following example.
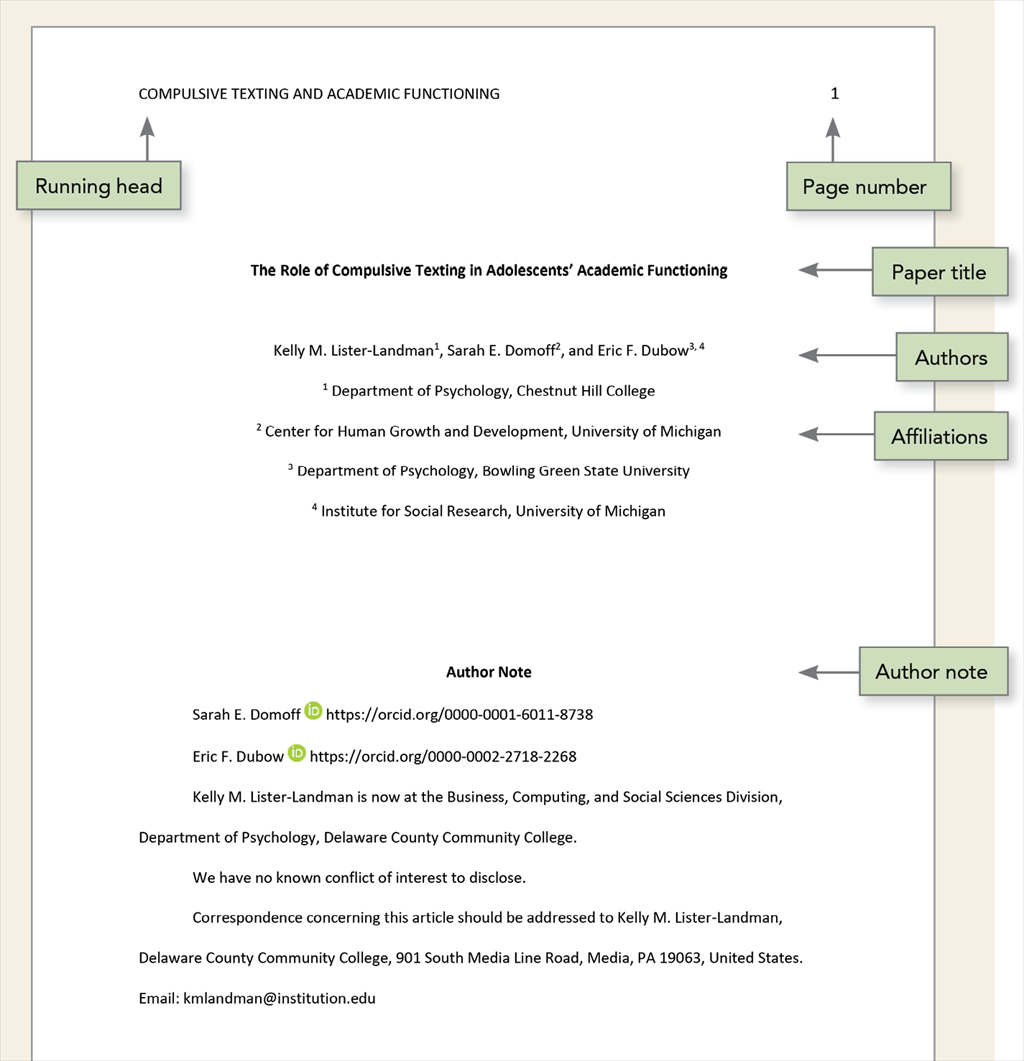
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the professional title page.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Paper title | Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired. There is no maximum length for titles; however, keep titles focused and include key terms. |
|
| Author names
| Place one double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author names. Center author names on their own line. If there are two authors, use the word “and” between authors; if there are three or more authors, place a comma between author names and use the word “and” before the final author name. | Francesca Humboldt |
| When different authors have different affiliations, use superscript numerals after author names to connect the names to the appropriate affiliation(s). If all authors have the same affiliation, superscript numerals are not used (see Section 2.3 of the for more on how to set up bylines and affiliations). | Tracy Reuter , Arielle Borovsky , and Casey Lew-Williams | |
| Author affiliation
| For a professional paper, the affiliation is the institution at which the research was conducted. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated by a comma. Center the affiliation on the next double-spaced line after the author names; when there are multiple affiliations, center each affiliation on its own line.
| Department of Nursing, Morrigan University |
| When different authors have different affiliations, use superscript numerals before affiliations to connect the affiliations to the appropriate author(s). Do not use superscript numerals if all authors share the same affiliations (see Section 2.3 of the for more). | Department of Psychology, Princeton University | |
| Author note | Place the author note in the bottom half of the title page. Center and bold the label “Author Note.” Align the paragraphs of the author note to the left. For further information on the contents of the author note, see Section 2.7 of the . | n/a |
|
| The running head appears in all-capital letters in the page header of all pages, including the title page. Align the running head to the left margin. Do not use the label “Running head:” before the running head. | Prediction errors support children’s word learning |
|
| Use the page number 1 on the title page. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word processing program to insert page numbers in the top right corner of the page header. | 1 |
- Share full article

Artists and Activists Both Have a Role. But Not the Same One.
As the literary world is roiled by fights over politics and war, are we losing sight of the writer’s purpose?
Credit... Photo illustration by Derek Brahney
Supported by
By Phil Klay
Phil Klay is a novelist and an essayist and a Marine Corps veteran of the Iraq war.
- Aug. 5, 2024
Two decades ago, I was a public-affairs officer in the Marine Corps, a public-relations guy for the military, tasked with “telling the Marine Corps story” and providing accurate information about military operations to maintain the trust of the American people. We weren’t propagandists — we told the truth, and in Iraq we welcomed plenty of embedded reporters who we knew would write extremely skeptical articles on the progress of the war — but there were fairly tight borders around what the military thought the American people needed to know.
Listen to this article, read by Robert Petkoff
Coming back from Iraq in 2008, though, I had a set of stories that didn’t fit perfectly with the official one I had a license to tell. Some were things I’d seen, things I could report on in a journalistic way, sure of the facts, but others were things I’d heard, stories that I couldn’t vouch for personally but that, passed to me by word of mouth and preserved in my memory, that unstable medium, nevertheless seemed to express something true and unsettling.
One was told to me by a young combat correspondent, a Marine whose job in the corps was writing articles and making videos about the work we were doing. He had been in Ramadi when a suicide bomber detonated among a crowd of civilians, killing and grievously wounding dozens. The local unit took the injured to the Ramadi combat hospital, where Navy doctors, nurses and corpsmen got to work as Marines lined up to donate blood.
Horrible slaughter in a region of Iraq where violence has spiraled out of control does not make for a good news story, but there were messages the Marine Corps was happy to put out: that unlike our barbaric enemy, who brutally murdered men, women and children, we cared about Iraqi civilians and would work tirelessly to save lives. And so this young combat correspondent asked one of the Navy surgeons, who for long hours had been feverishly working among the mangled and bloody innocents, to give an interview. And because the only quiet place was the room where they had placed and bagged the dead, the cameraman set up near the bodies of all the people they had failed to save.
Undoubtedly, the doctor knew what messages he was supposed to deliver to the camera, and undoubtedly, he believed in them, too — that he had a noble mission to carry out, and that his noble colleagues were dedicated and skilled and humane. Nor was he new to death. He was a surgeon in a shock-trauma platoon in the most violent city in Iraq, all too familiar with amputating limbs, with stitching intestines back together, with treating burns that devoured faces, ears and fingers. That day could not have been the first time he bowed his head as the chaplain whispered prayers over those who died on the table. But before the interview started and the red light of the camera turned on, he took a moment, sat down among the dead and quietly wept. The young Marine cameraman stood there, silent, patient, and waited for the doctor to collect himself so he could tell his story about the good will of the American military, whose invasion had unleashed this chaos.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Advertisement
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on February 4, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A good introduction paragraph is an essential part of any academic essay . It sets up your argument and tells the reader what to expect.
The main goals of an introduction are to:
- Catch your reader’s attention.
- Give background on your topic.
- Present your thesis statement —the central point of your essay.
This introduction example is taken from our interactive essay example on the history of Braille.
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: hook your reader, step 2: give background information, step 3: present your thesis statement, step 4: map your essay’s structure, step 5: check and revise, more examples of essay introductions, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Your first sentence sets the tone for the whole essay, so spend some time on writing an effective hook.
Avoid long, dense sentences—start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
The hook should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of the topic you’re writing about and why it’s interesting. Avoid overly broad claims or plain statements of fact.
Examples: Writing a good hook
Take a look at these examples of weak hooks and learn how to improve them.
- Braille was an extremely important invention.
- The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
The first sentence is a dry fact; the second sentence is more interesting, making a bold claim about exactly why the topic is important.
- The internet is defined as “a global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities.”
- The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education.
Avoid using a dictionary definition as your hook, especially if it’s an obvious term that everyone knows. The improved example here is still broad, but it gives us a much clearer sense of what the essay will be about.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is a famous book from the nineteenth century.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement.
Instead of just stating a fact that the reader already knows, the improved hook here tells us about the mainstream interpretation of the book, implying that this essay will offer a different interpretation.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Next, give your reader the context they need to understand your topic and argument. Depending on the subject of your essay, this might include:
- Historical, geographical, or social context
- An outline of the debate you’re addressing
- A summary of relevant theories or research about the topic
- Definitions of key terms
The information here should be broad but clearly focused and relevant to your argument. Don’t give too much detail—you can mention points that you will return to later, but save your evidence and interpretation for the main body of the essay.
How much space you need for background depends on your topic and the scope of your essay. In our Braille example, we take a few sentences to introduce the topic and sketch the social context that the essay will address:
Now it’s time to narrow your focus and show exactly what you want to say about the topic. This is your thesis statement —a sentence or two that sums up your overall argument.
This is the most important part of your introduction. A good thesis isn’t just a statement of fact, but a claim that requires evidence and explanation.
The goal is to clearly convey your own position in a debate or your central point about a topic.
Particularly in longer essays, it’s helpful to end the introduction by signposting what will be covered in each part. Keep it concise and give your reader a clear sense of the direction your argument will take.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

As you research and write, your argument might change focus or direction as you learn more.
For this reason, it’s often a good idea to wait until later in the writing process before you write the introduction paragraph—it can even be the very last thing you write.
When you’ve finished writing the essay body and conclusion , you should return to the introduction and check that it matches the content of the essay.
It’s especially important to make sure your thesis statement accurately represents what you do in the essay. If your argument has gone in a different direction than planned, tweak your thesis statement to match what you actually say.
To polish your writing, you can use something like a paraphrasing tool .
You can use the checklist below to make sure your introduction does everything it’s supposed to.
Checklist: Essay introduction
My first sentence is engaging and relevant.
I have introduced the topic with necessary background information.
I have defined any important terms.
My thesis statement clearly presents my main point or argument.
Everything in the introduction is relevant to the main body of the essay.
You have a strong introduction - now make sure the rest of your essay is just as good.
- Argumentative
- Literary analysis
This introduction to an argumentative essay sets up the debate about the internet and education, and then clearly states the position the essay will argue for.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
This introduction to a short expository essay leads into the topic (the invention of the printing press) and states the main point the essay will explain (the effect of this invention on European society).
In many ways, the invention of the printing press marked the end of the Middle Ages. The medieval period in Europe is often remembered as a time of intellectual and political stagnation. Prior to the Renaissance, the average person had very limited access to books and was unlikely to be literate. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century allowed for much less restricted circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
This introduction to a literary analysis essay , about Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein , starts by describing a simplistic popular view of the story, and then states how the author will give a more complex analysis of the text’s literary devices.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale. Arguably the first science fiction novel, its plot can be read as a warning about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, and in popular culture representations of the character as a “mad scientist”, Victor Frankenstein represents the callous, arrogant ambition of modern science. However, far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to gradually transform our impression of Frankenstein, portraying him in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
The “hook” is the first sentence of your essay introduction . It should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of why it’s interesting.
To write a good hook, avoid overly broad statements or long, dense sentences. Try to start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/introduction/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to conclude an essay | interactive example, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

COMMENTS
Set a timer for 10 minutes. Write a list of anything you know a lot about. Think about your hobbies, things you've studied, sports you've been in, personal lessons you have learned, jobs you've had, and advice you like to give to others. Take a look at that list and choose the top three that interest you. Pick one and then set the timer again ...
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
Basic essay structure: the 3 main parts of an essay. Almost every single essay that's ever been written follows the same basic structure: Introduction. Body paragraphs. Conclusion. This structure has stood the test of time for one simple reason: It works. It clearly presents the writer's position, supports that position with relevant ...
Reading the relevant texts closely (e.g. for literary analysis ). Collecting data using relevant research methods (e.g. experiments, interviews or surveys) From a writing perspective, the important thing is to take plenty of notes while you do the research. Keep track of the titles, authors, publication dates, and relevant quotations from your ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates. In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills. Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence ...
The basic steps for how to write an essay are: Generate ideas and pick a type of essay to write. Outline your essay paragraph by paragraph. Write a rough first draft without worrying about details like word choice or grammar. Edit your rough draft, and revise and fix the details. Review your essay for typos, mistakes, and any other problems.
An essay is a written composition that presents and supports a particular idea, argument, or point of view. It's a way to express your thoughts, share information, and persuade others to see things from your perspective. Essays come in various forms, such as argumentative, persuasive, expository, and descriptive, each serving a unique purpose.
Step 2: Brainstorm Ideas and Topics. Okay, so now you know how to write for a particular essay type, and now you need to figure out what to write to fit the assignment. It seems like a daunting task. It is not a daunting task. The best way to brainstorm is to make a list. Good ideas, bad ideas—you'll want them all.
When you start writing, your first paragraph will introduce your topic, and you need to interest the reader in the concept you explicate in your essay. For example, if your essay involves an emotion, you might try to appeal to that emotion in your reader. On the other hand, you might give a personal anecdote or ask a question the reader should ...
Writing to explain: progressing your ideas. Remember, an important part of explaining something is to give the basic idea and then go into further detail about individual points. So make the style of your essay writing reflect this, with more simple sentences setting out clear points, followed by more complex, multi-clause sentences to ...
The essay is a written piece that is designed to present an idea, propose an argument, express the emotion or initiate debate. It is a tool that is used to present writer's ideas in a non-fictional way. Multiple applications of this type of writing go way beyond, providing political manifestos and art criticism as well as personal ...
What are the 5 parts of an essay? Explore how the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion parts of an essay work together.
Body #1: Most students think writing an essay is tedious because they focus on external rewards. Body #2: Students should instead focus on internal fulfillment when writing an essay. Body #3: Not only will focusing on internal fulfillment allow students to have more fun, it will also result in better essays.
The structure of your expository essay will vary according to the scope of your assignment and the demands of your topic. It's worthwhile to plan out your structure before you start, using an essay outline. A common structure for a short expository essay consists of five paragraphs: An introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
3 Identify the points you'll make in each paragraph. Using the list of points you wrote down, identify the key arguments you'll make in your essay. These will be your body sections. For example, in an argumentative essay about why your campus needs to install more water fountains, you might make points like:
An expository essay is a genre of writing that explores and explains a specific topic in a logical and straightforward manner. The main goals of expository writing are to inform the reader, explain a subject, or describe a topic in a way that is accessible and comprehensible. You're not trying to confuse or overwhelm a reader with all of your ...
A famous essayist, Aldous Huxley, notes that "the essay is a literary device for saying almost everything about almost anything" and divides essays into personal-biographical, objectively-factual, and abstract-universal. The Oxford Dictionary defines it as "a short piece of writing on a particular subject.".
Tips for Essay Writing. Give your essays an interesting and appropriate title. It will help draw the attention of the reader and pique their curiosity. Keep it between 300-500 words. This is the ideal length, you can take creative license to increase or decrease it. Keep your language simple and crisp.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Writing an essay is an essential part of school at any level. Become an essay expert with these essay examples to prepare you on your academic journey. ... It's always to explain some integral concept to the reader. As such, they inform, describe, and explain. When writing an expository essay, the text needs to: be concise and easy to ...
Writing the personal essay for your college application can be tough, but we're here to help. Sometimes the hardest part is just getting started, but the sooner you begin, the more time and thought you can put into an essay that stands out. Check out some tips: 1. Keep it real.
Outline Examples for Essays: 3 Most Common Essay Types. To help you start writing your essay outline, here are three outline examples for essays of different types. 1. A Descriptive Essay Outline Example. Creating a clear outline for a descriptive essay helps ensure your writing is organized and engaging. Here's an example of a descriptive ...
The student title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation, course number and name for which the paper is being submitted, instructor name, assignment due date, and page number, as shown in this example.
An essay outline is a way of planning the structure of your essay before you start writing. It involves writing quick summary sentences or phrases for every point you will cover in each paragraph, giving you a picture of how your argument will unfold. You'll sometimes be asked to submit an essay outline as a separate assignment before you ...
In an essay for the journal Liberties on a recent slate of novels, from those by Sally Rooney and Emma Cline to Ben Lerner's "The Topeka School," the critic Becca Rothfeld labels this sort ...
Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.