Essay on Money for Students and Children
500+ words essay on money.
Money is an essential need to survive in the world. In today’s world, almost everything is possible with money. Moreover, you can fulfill any of your dreams by spending money. As a result, people work hard to earn it. Our parents work hard to fulfill our dreams .

Furthermore various businessmen , entrepreneurs have startup businesses to earn profits. They have made use of their skills and intelligence in getting an upper hand in earning. Also, the employee sector works day and night to complete their tasks given to them. But still, there are many people who take shortcuts to success and get involved in corruption.

Black Money
Black money is the money that people earn with corruption . For your information corruption involves the misuse of the power of high posts. For instance, it involves taking bribes, extra money for free services, etc. Corruption is the main cause of the lack of proper growth of the country .
Moreover, money that people having authority earns misusing their powers is black money. Furthermore, these earnings do not have proper documentation. As a result, the people who earn this do not pay income tax . Which is a great offense and the person who does this can be behind bars.
Money Laundering
In simple terms, money laundering is converting black money into white money. Also, this is another illegal offense. Furthermore, money laundering also encourages various crimes. Because it is the only way criminal can use their money from illegal sources. Money laundering is a crime, and the people who practice it are liable to go to jail.
Therefore the Government is taking various preventive measures to abolish money laundering. The government is linking bank accounts to AADHAR Card. To get all the transaction detail of each bank account. As a result, the government comes to know if any transaction is from an illegal source .
Also, every bank account has its own KYC (Know your Customer) this separates different categories of income of people. Businessmen are in the high-risk category. Then comes the people who are on a high post they are in the medium-risk category. Further, the last category is of the Employee sector they are at the lowest risk.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
White Money
White money is the money that people earn through legal sources. Moreover, it is the money on which the people have already paid the tax. The employee sector of any company always has white money income.
Because the tax is already levied on their income. Therefore the safest way to earn money is in the employment sector. But your income will be limited here. As a result, many people take a different path and choose entrepreneurship. This helps them in starting their own company and make profitable incomes .
Every person in this world works hard to earn money. People try different methods and set of skills to increase their incomes. But it is always not about earning money, it’s about saving and spending it. People should spend money wisely. Moreover, things should always be bought by judging their worth. Because money is not precious but the efforts you make for it are.
Q1. What is Black Money?
A1. Black money is the money that people earn through illegal ways. It is strictly prohibited in our country. And the people who have it can go to jail.
Q2. What is the difference between Black money and White money?
A2. The difference between black money and white money is, Black money comes from illegal earnings. But white money comes from legal sources with taxation levied on it.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Essays About Money: Top 5 Examples and 6 Prompts
With money comes great power; however, power must always come with responsibility. Discover thought-provoking essays about money in our guide.
Money is everywhere. We use it to eat, drink, clothe ourselves, and get shelter, among many other uses. Nowadays, it is an undisputed fact that “money makes the world go round.” The earliest known form of money dates back to around 5,000 years ago ; trade was previously carried out using a barter system. However, over the centuries, more and more nations began implementing a currency system, and money has become more critical.
In the contemporary world, it seems to be “all about money.” However, it is important not to lose sight of what is important; we must maintain good physical and mental health and healthy relationships with the people around us. Money is necessary; it is just not the only thing necessary. To start your essay, read these examples to write insightful essays about money.
| IMAGE | PRODUCT | |
|---|---|---|
| Grammarly | ||
| ProWritingAid |
5 Top Examples On Essay About Money
1. essay on money by prasanna, 2. how money changed human history by jacob wilkins, 3. capitalism: money that make money by ernestine montgomery, 4. is money the most important thing by seth higgins.
- 5. An Introduction to Saving Money by Jeremy Vohwinkle
Writing Prompts For Essays About Money
1. good uses for money, 2. the “dark side” of money, 3. money’s role in history, 4. morality vs. money, 5. can money buy happiness, 6. how to save money.
“Imagine the world without money. We will eventually come to a point where we will be asking questions like “what’s the point of life”. Hope and goals are some of the important things that will keep a man going in life. Without any sense of achievement or motivation, there wouldn’t be any inventions or progress in the world. People work to get money and then people work harder to get more money. This cycle of life that keeps a man motivated and hopeful is one of the biggest advantages of the system of money”
This essay gives readers a general outlook on money and its advantages and disadvantages. It gives people equal opportunity to work for their dreams and motivates them to be productive members of society, while it also raises the question of greed. Money, without a doubt, has its positive and negative aspects, but it exists and is only becoming more critical.
“But the barter economy was flawed. There was no universal measure for determining the value of an item. It was all based on the subjective opinion of the individuals involved. And to make matters worse, the barter economy relied on both sides wanting something the other had to offer. Trade, therefore, could be sluggish and frustrating. Human beings needed something different, and money was the answer.”
Wilkins writes about how money revolutionized the way trade was conducted. The barter system involved trading any objects if both parties agreed to a deal, such as trading animal skins for fish or medicine for timber. However, the only measure of an item’s value was how much one party wanted it- both sides needed to have something the other wanted. The introduction of money allowed people to put a solid value on commodities, making trade easier.
“So, if you were to closely observe the dirty, disordered canvas of economic progress during the 20th and 21 st century, you should conclude that, for all its warts, capitalism has been the winner. It has sometimes caused pain; suffered from serious cycles; and often needed the clout of the state- such as we have seen from September 2008. It has also been quite resistant to sensible regulation. Even so, the basic institutions of capitalism have worked, not just in the US and the OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and development) nations, but also many developing countries, of which India is one.”
Albeit lengthy, Montgomery’s essay discusses the debate between socialism and capitalism, a topic of which money is at the core. Montgomery describes Karl Marx’s criticism of capitalism: all the money goes to a few people, not the workers. She believes these are valid to an extent and criticizes certain forms of capitalism and socialism. Neither capitalism nor socialism is perfect, but according to Montgomery, capitalism creates a better economy.
“Being the richest man in the world does not mean you are the happiest man in the world, although money can buy you happiness sometimes, but not always. If we could all appreciate the way life is, the fun, and the beauty I think the world would be better. If people weren’t power hungry maybe we’d have a lesser demand for money. Those people who is money hungry and power hungry need to relax. Money can’t buy you happiness. These individuals need to understand that.”
Higgins implores readers to remember that money is not the only thing people need in the world. He stresses the necessity of money, as it is used to pay for various necessary goods and services; however, he believes it is not a prerequisite for happiness. Material things are temporary, and there are other things we should focus on, like family and friends.
5. An Introduction to Saving Money by Jeremy Vohwinkle
“A financial emergency may take the form of a job loss, significant medical or dental expense, unexpected home or auto repairs, a hurricane or major storm, or something unthinkable, such as a global pandemic. The last thing you want to do is to rely on credit cards with their hefty interest fees or to be forced to take out a loan. That’s where your emergency fund can come in handy. Historically, the formula for an emergency account is to have enough readily available cash to cover three to six months of living expenses.“
Vohwinkle’s essay gives readers some suggestions on how to save more money. Most importantly, he suggests setting up an emergency fund, as all other saving techniques stem from there. He also suggests creating an automatic savings plan and cutting down on “spending leaks,” like buying coffee. You might also be interested in these essays about celebration .
In this essay, write about why money is necessary and the ways to use it for the greater good, and include ways in which it can be used (investing, donating, etc.). For each point, you make, be sure to explain why. Of course, this is entirely subjective; feel free to write about what you consider “good uses” for money.
On the other hand, money also has a negative side —research on money-related issues, such as taxpayer-funded corruption and trading of illegal goods. In your essay, explore this side of money and perhaps give solutions on how to stop these problems.
Money has played a progressively more important role throughout human history. Discuss the development of currency and the economy, from the barter system to the digital world we live in today. You need not go too in-depth, as there is a lot of ground to cover and many eras to research. Be sure to cite reputable sources when discussing history.
Many people warn of “selling your soul” for financial gain. In your essay, you can write about the importance of having solid values in this day and age, where money reigns supreme. What principles do you need to keep in mind? Explain how you can still value money while staying grounded; mention the balance between material needs and others.
As stated in Higgins’ essay, more people have begun to prioritize money over all else. Do you believe that money is truly the most important thing? Can it alone make you happy? Discuss both sides of this question and choose your position accordingly. Be sure to provide precise supporting details for a stronger argument.

Enumerate tips on how you can save money. Anything works, from saving certain things for special occasions to buying more food in the grocery rather than eating out. This is your opinion; however, feel free to consult online sources and the people around you for extra advice.
For help with your essays, check out our round-up of the best essay checkers .If you’re still stuck, check out our general resource of essay writing topics .

Can Money Really Buy Happiness?
Money and happiness are related—but not in the way you think..
Updated November 10, 2023 | Reviewed by Chloe Williams
- More money is linked to increased happiness, some research shows.
- People who won the lottery have greater life satisfaction, even years later.
- Wealth is not associated with happiness globally; non-material things are more likely to predict wellbeing.
- Money, in and of itself, cannot buy happiness, but it can provide a means to the things we value in life.
Money is a big part of our lives, our identities, and perhaps our well-being. Sometimes, it can feel like your happiness hinges on how much cash is in your bank account. Have you ever thought to yourself, “If only I could increase my salary by 12 percent, I’d feel better”? How about, “I wish I had an inheritance. How easier life would be!” I don’t blame you — I’ve had the same thoughts many times.
But what does psychological research say about the age-old question: Can money really buy happiness? Let’s take a brutally honest exploration of how money and happiness are (and aren’t) related. (Spoiler alert: I’ve got bad news, good news, and lots of caveats.)
Higher earners are generally happier
Over 10 years ago, a study based on Gallup Poll data on 1,000 people made a big headline in the news. It found that people with higher incomes report being happier... but only up to an annual income of $75,000 (equivalent to about $90,000 today). After this point, a high emotional well-being wasn’t directly correlated to more money. This seemed to show that once a persons’ basic (and some “advanced”) needs are comfortably met, more money isn’t necessary for well-being.

But a new 2021 study of over one million participants found that there’s no such thing as an inflection point where more money doesn’t equal more happiness, at least not up to an annual salary of $500,000. In this study, participants’ well-being was measured in more detail. Instead of being asked to remember how well they felt in the past week, month, or year, they were asked how they felt right now in the moment. And based on this real-time assessment, very high earners were feeling great.
Similarly, a Swedish study on lottery winners found that even after years, people who won the lottery had greater life satisfaction, mental health, and were more prepared to face misfortune like divorce , illness, and being alone than regular folks who didn’t win the lottery. It’s almost as if having a pile of money made those things less difficult to cope with for the winners.
Evaluative vs. experienced well-being
At this point, it's important to suss out what researchers actually mean by "happiness." There are two major types of well-being psychologists measure: evaluative and experienced. Evaluative well-being refers to your answer to, “How do you think your life is going?” It’s what you think about your life. Experienced well-being, however, is your answer to, “What emotions are you feeling from day to day, and in what proportions?” It is your actual experience of positive and negative emotions.
In both of these studies — the one that found the happiness curve to flatten after $75,000 and the one that didn't — the researchers were focusing on experienced well-being. That means there's a disagreement in the research about whether day-to-day experiences of positive emotions really increase with higher and higher incomes, without limit. Which study is more accurate? Well, the 2021 study surveyed many more people, so it has the advantage of being more representative. However, there is a big caveat...
Material wealth is not associated with happiness everywhere in the world
If you’re not a very high earner, you may be feeling a bit irritated right now. How unfair that the rest of us can’t even comfort ourselves with the idea that millionaires must be sad in their giant mansions!
But not so fast.
Yes, in the large million-person study, experienced well-being (aka, happiness) did continually increase with higher income. But this study only included people in the United States. It wouldn't be a stretch to say that our culture is quite materialistic, more so than other countries, and income level plays a huge role in our lifestyle.
Another study of Mayan people in a poor, rural region of Yucatan, Mexico, did not find the level of wealth to be related to happiness, which the participants had high levels of overall. Separately, a Gallup World Poll study of people from many countries and cultures also found that, although higher income was associated with higher life evaluation, it was non-material things that predicted experienced well-being (e.g., learning, autonomy, respect, social support).
Earned wealth generates more happiness than inherited wealth
More good news: For those of us with really big dreams of “making it” and striking it rich through talent and hard work, know that the actual process of reaching your dream will not only bring you cash but also happiness. A study of ultra-rich millionaires (net worth of at least $8,000,000) found that those who earned their wealth through work and effort got more of a happiness boost from their money than those who inherited it. So keep dreaming big and reaching for your entrepreneurial goals … as long as you’re not sacrificing your actual well-being in the pursuit.

There are different types of happiness, and wealth is better for some than others
We’ve been talking about “happiness” as if it’s one big thing. But happiness actually has many different components and flavors. Think about all the positive emotions you’ve felt — can we break them down into more specifics? How about:
- Contentment
- Gratefulness
...and that's just a short list.
It turns out that wealth may be associated with some of these categories of “happiness,” specifically self-focused positive emotions such as pride and contentment, whereas less wealthy people have more other-focused positive emotions like love and compassion.
In fact, in the Swedish lottery winners study, people’s feelings about their social well-being (with friends, family, neighbors, and society) were no different between lottery winners and regular people.
Money is a means to the things we value, not happiness itself
One major difference between lottery winners and non-winners, it turns out, is that lottery winners have more spare time. This is the thing that really makes me envious , and I would hypothesize that this is the main reason why lottery winners are more satisfied with their life.
Consider this simply: If we had the financial security to spend time on things we enjoy and value, instead of feeling pressured to generate income all the time, why wouldn’t we be happier?
This is good news. It’s a reminder that money, in and of itself, cannot literally buy happiness. It can buy time and peace of mind. It can buy security and aesthetic experiences, and the ability to be generous to your family and friends. It makes room for other things that are important in life.
In fact, the researchers in that lottery winner study used statistical approaches to benchmark how much happiness winning $100,000 brings in the short-term (less than one year) and long-term (more than five years) compared to other major life events. For better or worse, getting married and having a baby each give a bigger short-term happiness boost than winning money, but in the long run, all three of these events have the same impact.
What does this mean? We make of our wealth and our life what we will. This is especially true for the vast majority of the world made up of people struggling to meet basic needs and to rise out of insecurity. We’ve learned that being rich can boost your life satisfaction and make it easier to have positive emotions, so it’s certainly worth your effort to set goals, work hard, and move towards financial health.
But getting rich is not the only way to be happy. You can still earn health, compassion, community, love, pride, connectedness, and so much more, even if you don’t have a lot of zeros in your bank account. After all, the original definition of “wealth” referred to a person’s holistic wellness in life, which means we all have the potential to be wealthy... in body, mind, and soul.
Kahneman, D., & Deaton, A.. High income improves evaluation of life but not emotional well-being. . Proceedings of the national academy of sciences. 2010.
Killingsworth, M. A. . Experienced well-being rises with income, even above $75,000 per year .. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2021.
Lindqvist, E., Östling, R., & Cesarini, D. . Long-run effects of lottery wealth on psychological well-being. . The Review of Economic Studies. 2020.
Guardiola, J., González‐Gómez, F., García‐Rubio, M. A., & Lendechy‐Grajales, Á.. Does higher income equal higher levels of happiness in every society? The case of the Mayan people. . International Journal of Social Welfare. 2013.
Diener, E., Ng, W., Harter, J., & Arora, R. . Wealth and happiness across the world: material prosperity predicts life evaluation, whereas psychosocial prosperity predicts positive feeling. . Journal of personality and social psychology. 2010.
Donnelly, G. E., Zheng, T., Haisley, E., & Norton, M. I.. The amount and source of millionaires’ wealth (moderately) predict their happiness . . Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin. 2018.
Piff, P. K., & Moskowitz, J. P. . Wealth, poverty, and happiness: Social class is differentially associated with positive emotions.. Emotion. 2018.

Jade Wu, Ph.D., is a clinical health psychologist and host of the Savvy Psychologist podcast. She specializes in helping those with sleep problems and anxiety disorders.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

Essay on Money

Introduction to The Power and Perils of Money
“Where Money Talks, Values Listen.”
Money is a fundamental aspect of modern society, serving as the lifeblood of economies and a cornerstone of daily life. Money holds immense significance in our lives, from facilitating transactions to influencing social dynamics. In this essay, we delve into the multifaceted nature of money, exploring its origins, functions, and profound impact on individuals and society.
As we navigate the complexities of money, we’ll unravel its historical roots, examine its various forms and functions, and delve into its role as a catalyst for economic growth and social change. Furthermore, we’ll explore the intricacies of personal finance, discussing the importance of financial literacy and responsible money management in achieving financial stability and well-being.
Watch our Demo Courses and Videos
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Mobile Apps, Web Development & many more.
Beyond its economic implications, we’ll also explore the broader societal effects of money, including its role in shaping social hierarchies, perpetuating economic inequality, and influencing political landscapes. Ultimately, this essay aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the significance of money in our lives, shedding light on its profound impact on both individual prosperity and societal dynamics.

Origin and Evolution of Money
Money has been an essential part of human civilizations for thousands of years in all its manifestations. From basic barter systems to complex financial tools of the present day, money has always been important. Understanding the origin and evolution of money provides crucial insights into its significance and impact on society.
1. Barter Economy and the Emergence of Money:
- Barter System: In primitive societies, individuals engaged in barter, exchanging goods and services based on mutual needs, with each person trading one commodity for another. Limitations of the barter system, including the “double coincidence of wants,” led to inefficiencies and logistical challenges.
- Evolution to Commodity Money: Commodity money emerged as a solution to the shortcomings of barter, with certain items, such as cattle, grains, or precious metals, gaining widespread acceptance as mediums of exchange. Commodity money possessed intrinsic value and was universally recognized, facilitating trade and commerce across regions.
2. Development of Metal Coins:
- Introduction of Metal Coins: Metal coins, particularly gold and silver, emerged as standardized forms of currency in ancient civilizations, including Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Greece. Metal coins facilitated trade by providing a convenient and durable medium of exchange, standardized in terms of weight and purity.
- Coinage and State Authority: The minting of coins became centralized under the authority of states and rulers, leading to the establishment of monetary systems and the issuing of official currency. Coinage symbolized the sovereignty and power of states, with rulers often inscribing their images and symbols on coins as a means of propaganda and control.
3. Transition to Fiat Money:
- Rise of Paper Money: With the expansion of trade and commerce, the need for a more flexible and portable form of money led to the introduction of paper currency. Paper money initially represented claims to a specific quantity of precious metals, serving as promissory notes issued by banks and governments.
- Decoupling from Precious Metals: Over time, central banks and governments gradually abandoned the linkage between paper money and precious metals, transitioning currencies to fiat money and deriving their value from the trust and confidence of users rather than intrinsic value. Adopting fiat money allowed for greater flexibility in monetary policy and facilitated the expansion of credit and financial markets.
4. Evolution of Digital and Cryptocurrencies:
- Digital Currency: Digital currencies, electronic records with monetary value saved in digital form, result from the Internet’s and electronic banking’s development. Digital currencies, such as electronic bank transfers and payment systems, revolutionized how money is transferred and accessed, offering convenience and efficiency.
- Cryptocurrencies: Blockchain -based cryptocurrencies, like Ethereum and Bitcoin , are examples of decentralized digital money. Cryptocurrencies provide increased privacy, security, and decentralization but also present regulatory and stability concerns because they function independently of governments and central banks.
The Basic Need for Money
- Meeting Basic Needs: Money is essential for meeting basic human needs, such as food, shelter, clothes, and healthcare. Access to money enables individuals to purchase necessary goods and services for survival and well-being, ensuring a decent standard of living.
- Facilitating Economic Transactions: Money serves as a medium of exchange, enabling the exchange of goods and services in the marketplace. It enables individuals to engage in economic transactions, buy goods, pay for services, and participate in economic activities that contribute to economic growth and development.
- Access to Education and Skills Development: Money is necessary for education and skills development opportunities. Investing in education and training enhances individuals’ knowledge, skills, and employability, leading to better job prospects and higher earning potential.
- Healthcare and Medical Services: Money is vital for healthcare services and medical treatment. Individuals require financial resources to pay for medical expenses, health insurance, and access to quality healthcare facilities, ensuring their physical well-being and addressing health-related concerns.
- Housing and Shelter: Money is essential for securing housing and shelter providing individuals and families with a safe and stable living environment. Access to affordable housing options requires financial resources for rent, mortgage payments, or property ownership, ensuring adequate housing for individuals and communities.
- Transportation and Mobility: Money facilitates transportation and mobility, enabling individuals to travel for work, education, healthcare, and recreational purposes. Access to transportation choices, such as public transit, vehicles, or ride-sharing services, requires financial resources to cover transportation costs and maintain mobility.
- Emergency Preparedness and Resilience: Money is crucial for building emergency funds and financial resilience. Having savings and financial resources enables individuals to prepare for unexpected expenses, emergencies, and financial setbacks, providing a safety net during challenging times.
- Social and Recreational Activities: Money plays a role in accessing social and recreational activities that contribute to overall well-being and quality of life. Participating in leisure activities, entertainment, and social events often requires financial resources to cover expenses related to leisure pursuits and social engagements.
The Role of Money in Society
Money is a cornerstone of societal structures, influencing economic activities, social relationships, and individual well-being. Its multifaceted role extends beyond a mere medium of exchange, encompassing various functions integral to modern societies’ functioning.
1. Economic Significance of Money:
- Facilitating Trade and Commerce: Money acts as a universally accepted medium of exchange, facilitating the soft flow of goods and facilities in the market. Eliminating the need for direct barter enhances efficiency and encourages specialization in production.
- Measurement of Value: Money provides a common unit of account, allowing for the standardized measurement of the value of different goods and services. This function enables individuals to compare prices, make informed decisions, and confidently engage in economic transactions.
- Economic Growth and Development: A stable and reliable monetary system fosters economic growth and development . Governments and central banks use monetary policy tools to regulate money supply, interest rates, and inflation to maintain economic stability.
2. Social Significance of Money:
- Influence on Social Status and Power: The possession of wealth and financial resources often correlates with social status and power within a community. Economic disparities can create social hierarchies, impacting individuals’ access to opportunities and resources.
- Impact on Lifestyle and Standard of Living: The availability of financial resources influences an individual’s lifestyle and standard of living. Money provides access to education, healthcare, housing, and other essential services, shaping the quality of life for individuals and communities.
3. Money and Personal Finance:
- Importance of Financial Literacy: Financial education empowers people to make informed decisions about earning, spending, saving, and investing. Understanding the principles of personal finance is essential for achieving financial security and long-term well-being.
- Managing Personal Finances: Budgeting, saving, and investing are key to effective personal finance management. Individuals must make strategic financial decisions to meet their short-term and long-term goals.
- Psychological Aspects of Money: People often tie money to their emotions and psychological well-being. Developing a healthy money mindset involves understanding one’s relationship with money and addressing any emotional factors that may impact financial decisions.
4. Impact of Money on Society:
- Economic Inequality: The distribution of wealth and income in society can contribute to economic inequality. Addressing issues of inequality requires a nuanced understanding of the role of money and the implementation of policies that promote equitable wealth distribution.
- Consumerism and Materialism: Money influences consumer behavior , contributing to a culture of consumerism and materialism. Society’s emphasis on material possessions can impact individuals’ values and priorities.
- Influence on Politics and Governance: Money plays a significant role in political processes, affecting campaigns, lobbying, and policy decisions. The intersection of money and politics raises questions about transparency, accountability, and the democratic process.
- Environmental Implications: Economic activities driven by the pursuit of profit can have environmental consequences. Balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability requires careful consideration of the environmental impact of monetary and economic policies.
Functions of Money
- Medium of Exchange
- Money is a widely acknowledged medium of exchange for goods and services, facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers.
- It eliminates the inefficiencies of barter by providing a common unit of value that simplifies the exchange process.
- Unit of Account:
- Money provides a standardized unit of measurement for the value of goods and services, permitting easy comparison of prices and making economic calculations more efficient.
- It enables individuals and businesses to express the relative worth of different goods and services in terms of a common currency.
- Store of Value:
- Money serves as a store of value, permitting individuals to hold and accumulate wealth over time.
- Unlike perishable goods or assets with fluctuating value, money retains its purchasing power over extended periods, providing a reliable means of preserving wealth.
- Standard of Deferred Payment:
- Money facilitates transactions involving future obligations by serving as a medium for deferred payments.
- Contracts, loans, and other financial agreements often stipulate payments in a specific currency, with money as the standard for settling debts and fulfilling obligations.
- Money’s high liquidity enables it to be readily convertible into goods, services, or other assets without experiencing a significant loss of value.
- Its liquidity enables individuals to quickly access funds for urgent expenses or investment opportunities, contributing to economic flexibility and efficiency.
- Measure of Value:
- Money is a measure of value, providing a common denominator for expressing the worth of different goods and services.
- Its role as a measure of value facilitates economic decision-making, allowing individuals to assess the relative utility and worth of various goods and services.
- Facilitates Specialization and Efficiency:
- Money enables specialization and division of labor by allowing individuals and businesses to focus on producing goods and assistance in which they have a comparative advantage.
- Specialization leads to increased productivity and efficiency, driving economic growth and prosperity.
- Portability and Durability:
- Money is highly portable and durable, making it a convenient medium of interaction for transactions of varying sizes and distances.
- The physical forms of money (such as coins and banknotes) and their digital representation ensure ease of transportation and storage, contributing to its widespread use in modern economies.
The Ethics and Morality of Money
While essential for economic transactions and societal functioning, money raises ethical and moral considerations beyond its economic utility. From wealth distribution issues to the impact of financial decisions on individuals and society, exploring the ethical dimensions of money sheds light on complex moral dilemmas and societal values.
- Wealth Distribution and Economic Inequality: One of the most significant ethical concerns about money is the unequal distribution of wealth and income within societies. Critics argue that extreme wealth disparities contribute to social injustice and perpetuate systemic inequalities, raising questions about fairness and equity.
- Social Responsibility of Wealth: Accumulating wealth brings with it a moral obligation to contribute to society’s well-being. Concepts like philanthropy, corporate social responsibility, and impact investing highlight the ethical imperative for individuals and organizations to use their financial resources for the greater good.
- Ethical Consumption and Consumerism: Consumerism fueled by the pursuit of material wealth raises ethical questions about consumption patterns’ environmental and social impact. Ethical consumption movements advocate for mindful spending and sustainable lifestyles that consider the broader consequences of consumer choices.
- Ethics in Financial Services: The financial industry operates within a complex ethical landscape, with issues like transparency, conflicts of interest, and fair treatment of clients coming under scrutiny. Ethical codes of conduct and regulations aim to promote integrity and trust in financial services, ensuring that financial professionals prioritize the interests of their clients.
- Debt and Financial Vulnerability: Ethical considerations arise in lending practices, particularly regarding the responsible provision of credit and the treatment of borrowers, especially those in vulnerable financial situations. Predatory lending practices and exploitative debt arrangements raise ethical concerns about the consequences of financial transactions on individuals’ well-being.
- Corruption and Financial Crime: Money laundering, bribery, and other forms of financial crime undermine the integrity of financial systems and pose ethical challenges to businesses, governments, and individuals. Ethical frameworks and legal regulations aim to combat financial corruption and promote accountability and transparency in financial transactions.
- Psychological Impact of Money: Money’s influence on individuals’ attitudes, behaviors, and relationships raises ethical questions about the psychological effects of wealth and materialism. The pursuit of wealth can lead to ethical dilemmas related to greed, envy, and the prioritization of financial gain over other values.
- Cryptocurrency and Ethical Considerations: Emerging digital currencies, such as cryptocurrencies, introduce new ethical considerations related to privacy, security, and the potential for illegal activities like money laundering and fraud. Ethical discussions surrounding cryptocurrencies also touch on financial inclusivity, decentralization, and the democratization of finance.
Financial Education
Financial education is essential to enable people to make informed decisions concerning their money, investments, and overall economic well-being. It covers many topics, from basic budgeting and savings to more complex concepts like investing, debt relief, and retirement planning. The need for financial literacy is huge in today’s complex financial world, where individuals are more accountable for their financial future.
- Foundational Knowledge: Basic financial concepts like income, expenses, budgeting, and savings are the first things students learn about when they start their financial education. Comprehending these underlying concepts establishes the foundation for prudent financial judgment and accountable handling of finances.
- Budgeting and Saving: Effective budgeting and saving are essential for financial education. Individuals learn how to create and stick to a budget, allocate funds for essential expenses, savings, and discretionary spending, and build an emergency fund to weather unforeseen financial challenges.
- Debt Management: Financial education teaches individuals about managing debt responsibly, including understanding different types of debt, interest rates, and repayment strategies. It emphasizes the importance of avoiding excessive debt and using credit wisely to maintain financial health.
- Investing and Wealth Accumulation: Investing is a key aspect of financial education, enabling individuals to grow their wealth over the long term. Topics covered may include understanding investment options (stocks, bonds, mutual funds, etc.), risk tolerance, asset allocation, and strategies for assembling a diversified investment portfolio.
- Retirement Planning: Financial education helps individuals plan for their future financial security, including retirement. It covers retirement savings vehicles (e.g., employer-sponsored retirement plans, IRAs), estimating retirement expenses, and developing a strategy to achieve retirement goals.
- Risk Management and Insurance: Understanding risk management and insurance is integral to financial education. Individuals learn about different types of insurance (e.g., health, life, property) and how insurance can mitigate financial risks and protect against unexpected events.
- Financial Decision-making: Financial education supplies individuals with the knowledge and skills to make instructed financial decisions based on their goals, values, and circumstances. It encourages critical thinking and evaluating financial products and services, empowering individuals to navigate the financial marketplace effectively.
- Economic Empowerment: Financial education is a tool for economic empowerment, particularly for marginalized communities and underserved populations. Promoting financial literacy and capability helps individuals build financial resilience, reduce vulnerability to financial exploitation, and achieve greater economic independence.
- Lifelong Learning: Financial education is a lifelong journey with changing financial circumstances and economic conditions. It emphasizes the importance of ongoing learning, staying informed about financial trends and developments, and adapting financial strategies as needed throughout life.
- Social and Policy Implications: Financial education has broader social and policy implications, influencing financial inclusion, economic mobility, and societal well-being. Policies that promote financial education in schools, workplaces, and communities can contribute to building a financially literate society and reducing financial disparities.
Money in the Digital Age
- Digital Payments and Transactions: The addition of digital payment methods, including mobile wallets, online banking, and peer-to-peer payment platforms, has reshaped the conduct of transactions. Digital payments offer convenience, speed, and accessibility, allowing individuals to transfer funds, make purchases, and manage finances seamlessly across various digital channels.
- Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Technology: Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, represent a decentralized digital currency powered by blockchain technology. Blockchain technology enables secure, transparent, and tamper-proof transactions without intermediaries like banks or financial institutions.
- Financial Inclusion and Access: The digitalization of money can promote financial inclusion by delivering access to financial services for underserved populations. Digital payment platforms and mobile banking services empower individuals in small areas or underserved communities to participate in the formal financial system.
- Challenges and Risks: Despite the benefits, the digitalization of money presents challenges and risks, including cybersecurity threats, data privacy concerns, and regulatory challenges. Fraud, hacking, and data breaches highlight the importance of robust cybersecurity measures and regulatory frameworks to protect consumers and maintain trust in digital financial systems.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Central banks are exploring the vision of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) as a digital alternative to traditional fiat currencies. CBDCs combine the advantages of digital currencies with the stability and regulatory oversight provided by central banks, potentially reshaping the future of money and monetary policy.
- Smart Contracts and Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Smart contracts, facilitated by blockchain technology, automate and enforce the words of contracts without intermediaries. Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain and innovative contract technology to create decentralized financial services outside traditional banking systems, including lending, borrowing, and trading.
- Cross-Border Transactions and Remittances: Digital currency and blockchain technologies promise to stream international transfers and reduce expenses and inadequacies linked to conventional remittance systems. Cryptocurrencies and stablecoins offer an alternative means of transferring value globally, bypassing traditional banking channels and intermediaries.
- Regulatory Landscape and Policy Considerations: Governments and officials face regulatory hurdles due to the rapid evolution of digital currency. Regulatory frameworks must actively update to consider the changing landscape of digital finance to preserve consumer protection, financial stability, and compliance with know-your-customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering (AML) regulations.
Money is a cornerstone of modern society, serving as a medium of exchange, store of value, and facilitator of economic activities. Its significance extends beyond financial transactions, impacting individuals’ access to basic needs, economic opportunities, and overall well-being. Understanding the multifaceted role of money is crucial for promoting financial literacy, responsible money management, and equitable access to financial resources in today’s complex socioeconomic landscape.

*Please provide your correct email id. Login details for this Free course will be emailed to you
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Web Development & many more.
Forgot Password?
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the cookie policy. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to our Privacy Policy

Explore 1000+ varieties of Mock tests View more
Submit Next Question
🚀 Limited Time Offer! - 🎁 ENROLL NOW

Essay on Importance of Money
Students are often asked to write an essay on Importance of Money in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Importance of Money
Introduction.
Money is a crucial part of our lives. It is the medium used for exchange of goods and services, and it helps us meet our basic needs.
Significance in Daily Life
Money allows us to acquire food, shelter, and clothing. Without money, survival would be difficult.
Role in Society
Money also plays a societal role. It helps us contribute to community development through taxes.
While money is important, it’s not everything. It’s a tool for survival and contribution, but happiness and fulfillment also require love, health, and peace.
250 Words Essay on Importance of Money
The significance of money.
Money, a medium of exchange, is a fundamental component of modern society. It is a tool that allows us to acquire goods, services, and experiences, thus playing a vital role in our lives.
Money as a Means of Exchange
Money simplifies trade, replacing the need for a direct barter system. It provides a standardized measure of value, enabling us to understand the worth of various commodities. This standardization facilitates smooth economic transactions and promotes economic efficiency.
Money and Freedom
Money also provides a certain level of freedom. It allows individuals to make choices about their lifestyle, from basic necessities to luxury items. It grants us the liberty to explore different opportunities, be it travel, education, or investment.
Money and Social Status
In many societies, money is often equated with power and status. While this perspective can lead to materialism and inequality, it also motivates individuals to strive for financial stability, fostering innovation and economic growth.
Money as a Tool, Not a Goal
However, it is crucial to remember that money is a means to an end, not an end in itself. The pursuit of money should not overshadow the importance of relationships, health, and personal fulfillment.
500 Words Essay on Importance of Money
Money, often seen as a simple medium of exchange, plays a pivotal role in modern society. Its importance transcends mere transactions, permeating every aspect of our lives – from the economy to social structures, personal relationships, and even our sense of self-worth.
The Economic Imperative
At its most basic level, money is the lifeblood of any economy. It facilitates trade, allowing for the efficient exchange of goods and services. Without money, barter would be the only alternative – a system fraught with inefficiencies and limitations. Money, therefore, enables economic growth by allowing for specialization and the division of labor.
Money as a Social Construct
The psychological dimension.
Money also has a profound psychological impact. It can influence our behavior, our motivations, and even our sense of self. Money can provide a sense of security and freedom, but it can also lead to stress and anxiety. The desire for money can motivate us to work harder and strive for success, but it can also lead to greed and materialism.
Money and Happiness
The relationship between money and happiness is a complex one. While money can provide for our basic needs and desires, research suggests that beyond a certain point, additional wealth does not lead to additional happiness. This suggests that while money is important, it is not the be-all and end-all of life.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades
Essay on Money | Money Essay for Students and Children in English
February 13, 2024 by Prasanna
Essay on Money: The concept of money was invented somewhere in 5000 B.C by a few traders in Western Europe. Ever since the invention, different countries have adopted it and started printing their own money with specific values, which was usually backed by gold. But before money was invented, trading used to happen with a system called a barter system, where you could buy one product or service with an exchange of another product. This is basically a brief history of money.
For centuries, money has been, gradually, incorporated into every corner of our lives. Not to sound cliché, but the entire world runs on one simple thing called money. Thanks to those traders hundreds of years back, our lives now entirely revolve around the man-made concept of money.
You can also find more Essay Writing articles on events, persons, sports, technology and many more.
Long and Short Essay on Money in English for Children & Students
In this article, we provide a 600-word long essay on money for school children for projects and assignments. We also provide a 200-word short essay on money for school and college assignments and project work.
Long Essay on Money
A very informative 400 to 600-word long essay on money for school and college projects and assignments can be found below.
While not everything is about money, we will have to come at a point of realization where we simply cannot live without money. It’s a hard truth. But isn’t the world being too negative about money? No essay on money will make sense if it is just about history and facts. So let us see how money has impacted our lives. Just like every attribute in our society, money has two sides. The evil and the good.
What’s the Good Side of Money?
When we say our lives revolve around money and everyone is just chasing it, it is usually considered with a negative connotation. Not everything about money should be taken in a bad light. The whole concept of money and capitalism has given people livelihood, better standards of living and most importantly an equal platform for everyone to work hard and fulfill their dreams.
Trust and Convenience of Money
Money is one of the biggest and most valuable and trustworthy forms of trade in which businesses can thrive and consumers can be saved from fraud and cheating. One of the biggest plus points of money is the trust factor it carries with it. Imagine having to carry out the barter system even today, where, to get a kilo of rice, you need to give a kilo of wheat. Sounds funny, isn’t it?
Equality of Money
This is, surprisingly, one thing that can bring people from different walks of life to agree upon. Money can buy you a good standard of living, it can buy you respect and value in society. Every person, irrespective gender, race, ethnicity or creed will be provided with an equal level playing field to earn money and lead a better life
Motivation and Direction of Money
Imagine the world without money. We will eventually come to a point where we will be asking questions like “what’s the point of life”. Hope and goals are some of the important things that will keep a man going in life. Without any sense of achievement or motivation, there wouldn’t be any inventions or progress in the world. People work to get money and then people work harder to get more money. This cycle of life that keeps a man motivated and hopeful is one of the biggest advantages of the system of money
What is the Evil Side of Money?
Well, not everything is hunky-dory about our financial systems. It would only be fair to talk about the disadvantages of money also to have a well-informed essay on money.
Whether it is capitalism or socialism, democracy, or communism or where its India or China, our system of money in the world has many cracks and fault lines within it.
- Broken system: If the concept of money in its pure form was used properly, there would have been equality on all scales and levels in the world. But, the reality is far from our imagination. The hierarchical system, in both capitalism or socialism, has created an immense amount of inequality and large gaps in income. It is true that more than 90% of the world’s wealth is in the hands of 2% of the population. If this is not a sign of a broken system, then we don’t know what is
- Greed: We need to understand the difference between desire and greed. When the fine line between the two is made more visible, then maybe our world will start healing itself. We are not necessarily talking about individual greed for money, but we are talking about issues on a much larger scale. Businesses are solely running to make profits, the government is more concerned about saving the economy than their own people or the environment we live in. The greed for money is destroying our nature, creating an imbalance in the natural cycle of the world and led us into wars, famine, poverty and pandemics.
Short Essay on Money
A short essay on money with a word limit of 150 to 200 can be found below for school assignment and projects
We can’t deny the fact that we cannot live without money. Money is undoubtedly the more important thing to live a happy and content life. Sure, the money will help us buy our dream car or impress and give a dignified life for our parents, but we also need to remember that there is more to life than just earning money.
Money can make or break many things, but like any other thing in the world, money also needs to have limits and should be used judiciously. The gap between rich and poor is because of poorly planned financial systems and an immense amount of greed which is a pet of human tendency
On a big picture level, governments need to fix the broken financial systems and modify our capitalist and socialist mindsets to create for ourselves a better world and leave an even better society to our next generation.
10 Lines on Money Essay
- Money is the only trustworthy and convenient way of trade
- The money we use is guaranteed and backed by our government
- Money, collected in the form of tax, helps us create a better environment for us
- Earning money will give people hope and direction to lead a happy life
- Money doest just buy tangible things like car or house, money also helps you earn respect and dignity in the society
- Hard work, responsibility and dedication is what reflects in a person’s character if they have a good amount of money
- Money is the core factor in all type of economies like a capitalist, socialist and communist economies
- Money has provided equal opportunities for everyone in the world
- Wrong use of money and greed has led to certain world issues like terrorism, pandemics and famine
- The difference between the amount of money rich and poor has, reflects loopholes and problems in our system
FAQ’s on Essay on Money
Question 1. What if the concept of money was not there?
Answer: We would be back to our age-old barter system. Globalization and industrialization would never be possible and each country and each village in the country would be self-sufficient and isolated
Question 2. Is money good or bad?
Answer: This is one of the most daunting questions that economists, leaders and other experts are pondering upon for years. There is no simple answer, but the present system, if modified well, can make money the best thing in the world.
Question 3. Why can’t governments just print money?
Answer: Every money, even a Rs. 1 is backed by government securities, usually in gold or dollars. If we print more than the security we have, our fiscal deficit will increase, which means that the value of money will get reduced as it will be available everywhere to everyone. It is a simple supply and demand theory.
Question 4. What are the different types of money?
Answer: In terms of value and currencies, we have dollar, rupees, pounds, yuan and many more for each country. In terms of physical existence, we have digital money (like bitcoins) and hard paper-based cash. In terms of tangibility, we have hard cash, commodities, fiduciary, representative and fiat money.
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education
Understanding Economics: Why Does Paper Money Have Value?
- U.S. Economy
- Supply & Demand
- Archaeology
- Ph.D., Business Administration, Richard Ivey School of Business
- M.A., Economics, University of Rochester
- B.A., Economics and Political Science, University of Western Ontario
While it may be true that money makes the world go around, it is not inherently valuable. Unless you enjoy looking at pictures of deceased national heroes, these colorfully imprinted pieces of paper have no more use than any other piece of paper. It is only when we agree as a country to assign a value to that paper—and other countries agree to recognize that value—that we can use it as currency.
Gold and Silver Standards
It didn't always work this way. In the past, money generally took the form of coins composed of precious metals such as gold and silver. The value of the coins was roughly based on the value of the metals they contained because you could always melt the coins down and use the metal for other purposes.
Until a few decades ago, the value of paper money in many countries, including the United States, was based on a gold or silver standard, or some combination of the two. The piece of paper money was simply a convenient way of "holding" that particular bit of gold or silver. Under the gold or silver standard, you could actually take your paper money to the bank and exchange it for an amount of gold or silver based on an exchange rate set by the government. Up until 1971, the United States operated under a gold standard , which since 1946 had been governed by the Bretton Woods system, which created fixed exchange rates that allowed governments to sell their gold to the United States treasury at the price of $35 per ounce. Believing that this system undermined the U.S. economy, President Richard M. Nixon took the country off the gold standard in 1971.
Since Nixon's ruling, the United States has operated on a system of fiat money, which means our currency is not tied to any other commodity. The word "fiat" originates in the Latin, the imperative of the verb facere, "to make or become." Fiat money is money whose value is not inherent but called into being by a human system. So these pieces of paper in your pocket are just that: pieces of paper.
Why We Believe Paper Money Has Value
So why does a five-dollar bill have value and some other pieces of paper do not? It’s simple: Money is a both a good and a method of exchange. As a good, it has a limited supply, and therefore there is a demand for it. There is a demand because people can use the money to purchase the goods and services they need and want. Goods and services are what ultimately matter in the economy, and money is a way that allows people to acquire the goods and services that they need or want. They earn this method of exchange by going to work, which is a contractual exchange of one set of goods—labor, intellect, etc.—for another. People work to acquire money in the present to purchase goods and services in the future.
Our system of money operates on a mutual set of beliefs; as long as enough of us believe in the value of money, for now, and in the future, the system will work. In the United States, that faith is engendered and supported by the federal government, which explains why the phrase "backed by the full faith and credit of the government" means what it says and no more: the money may have no intrinsic value, but you can trust using it because of its federal backing.
Furthermore, it is unlikely that money will be replaced in the near future because the inefficiencies of a purely barter system, in which goods and services are exchanged for other goods and services, are well known. If one currency is to be replaced by another, there will be a period in which you can switch your old currency for new currency. This is what happened in Europe when countries switched over to the Euro . So our currencies are not going to disappear entirely, although at some future time you may be trading in the money you have now for some form of money that supersedes it.
The Future Value of Money
Some economists don't trust our system of fiat currency and believe we cannot continue to declare that it has value. If the vast majority of us come to believe that our money won't be nearly as valuable in the future as it is today, then our currency becomes inflated . Inflation of the currency, if it becomes excessive, causes people to want to get rid of their money as quickly as possible. Inflation, and the rational way citizens react to it is bad for the economy. People will not sign profitable deals that involve future payments because they’ll be unsure what the value of money will be when they get paid. Business activity sharply declines because of this. Inflation causes all sorts of other inefficiencies, from a café changing its prices every few minutes to a homemaker taking a wheelbarrow full of money to the bakery in order to buy a loaf of bread. The belief in money and the steady value of the currency are not innocuous things.
If citizens lose faith in the money supply and believe that money will be worthless in the future, economic activity can grind to a halt. This is one of the main reasons the U.S. Federal Reserve acts diligently to keep inflation within bounds—a little is actually good, but too much can be disastrous.
Supply and Demand
Money is essentially a good, so as such is ruled by the axioms of supply and demand. The value of any good is determined by its supply and demand and the supply and demand for other goods in the economy. A price for any good is the amount of money it takes to get that good. Inflation occurs when the price of goods increases—in other words when money becomes less valuable relative to those other goods. This can occur when:
- The supply of money goes up.
- The supply of other goods goes down.
- Demand for money goes down.
- Demand for other goods goes up.
The key cause of inflation increases in the supply of money. Inflation can occur for other reasons. If a natural disaster destroyed stores but left banks intact, we’d expect to see an immediate rise in prices, as goods are now scarce relative to money. These kinds of situations are rare. For the most part, inflation is caused when the money supply rises faster than the supply of other goods and services.
To summarize, money has value because people believe that they will be able to exchange this money for goods and services in the future. This belief will persist so long as people do not fear future inflation or the failure of the issuing agency and its government.
- What Does "Money" Mean in an Economic Context?
- Interest - The Economics of Interest
- Economics for Beginners: Understanding the Basics
- Purchasing Power Parity
- What Is Capital Deepening?
- The Double Coincidence of Wants
- What Is Money?
- The Gold Standard
- What You Should Know About Econometrics
- Books to Study Before Going to Graduate School in Economics
- The Trade Deficit and Exchange Rates
- The Future of Money
- Expansionary vs. Contractionary Monetary Policy
- Properties and Functions of Money as Currency vs. Wealth
- Understanding The Stock Market
- What Is the Demand For Money?
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Life
Essay Samples on Money
The effects of money on human behavior.
Money, as a ubiquitous and powerful force in modern society, has a profound impact on human behavior. Whether consciously or unconsciously, individuals' attitudes, values, and actions are influenced by the presence and pursuit of money. In this essay, we will explore the multifaceted effects of...
Exploring Why Happiness Is More Important Than Money
Happiness is more important than money — a simple yet profound statement that encapsulates the essence of a fulfilling and meaningful life. While money is undoubtedly a vital resource, it pales in comparison to the profound impact that happiness has on overall well-being. This essay...
Exploring the Age-Old Question: Can Money Buy Happiness
The relationship between money and happiness has been a subject of contemplation for centuries. Can the accumulation of wealth truly lead to a fulfilled and contented life? Or simply: can money buy happiness? This essay delves into the complex interplay between money and happiness, examining...
Transitioning to a Cashless Economy: Challenges, Opportunities, and the Path Ahead
The world is now moving on from Paper Currency based economy to Cashless economy. By embracing Alternate Delivery Channels and other Cashless modes of payment which include old ones like NEFT,RTGS etc. to newer one’s like POS, e-wallets, debit and credit cards, UPI, BHIM etc....
Being Smart With Your Money: the Importance of Financial Literacy
Many people have discussed personal finance. Articles 'Should Financial Literacy Be Taught in More Schools' by Ramsey and 'Why is Learning Personal Finance Important' by Ryan discuss the reason why personal finance is beneficial to the educational system. Benefits of adding Personal finance to our...
- Personal Finance
Stressed out with your paper?
Consider using writing assistance:
- 100% unique papers
- 3 hrs deadline option
Unlocking Financial Literacy: Exploring the World of Finance and Money Management
Finance is a business term that is associated with banking, investments, capital, debt and credit. Managing money, such as balancing a checkbook, involves finance. At one point in every person's life, one must deal with finances. An important topic among finance is assets and liabilities....
The Value of Understanding Personal Finance Management for Students
As a student, learning this course about personal financial statement is important. It shows the individual's net worth 'their assets minus their liabilities' which reflects what that person has in cash if they sell all their assets and pay off all their debts. If their...
Why Personal Finance Should Be Taught in Modern Schools
About 59% of Americans have less than 1,000 dollars in savings. I think that Financial Literacy should be a requirement in schools all around the country. Financial planning should be taught in schools because finances affect everything, a lack of financial knowledge has consequences eventually,...
Evaluation of the Benefits and Risks of Cashless Economy
In a world where cybersecurity concerns are growing, the road to a cashless society is an inflection point. With countries across the world embracing digital forms of commerce and connectivity, the need for physical currency could soon become obsolete. But despite the increasing use of...
Can Money Buy Happiness: Sharing Persuasive Personal Viewpoint
Money is a defined as “any item or verifiable record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts, such as taxes, in a particular country or socio-economic context”. In what way does that relate to the emotional feeling of...
- Personal Beliefs
Budgeting and Types of Personal Budget
Budget can mean different things for different people, but in each case, it is used as an effective tool for achieving a wide range of short and long-term financial objectives. Contrary to popular belief, budgeting is not a cut-and-dry, one-size-fits-all process. Rather, it needs to...
Budgeting Technique to Build a Stable Financial Future
There’s nothing like the feeling of independence of when you’re in college, but since it’s the first time away from home for many, This is the time when most young people use their first debit/credit cards, take out their first loans, and write their first...
The Ascent of Money: Is Money the Root of All Evil
In Niall Ferguson’s The Ascent of Money, Ferguson analyzes the history of money, banking, and credit. He tracks the development of currency as a form of trade, explores its growth and effects on society, and looks forward to how it may continue to develop in...
Gold: One of the Most Expensive Metals on Earth
Being one of the first metals to be discovered, gold throughout history has always had a rich past from its use in ancient Egypt, Greece, Rome and Africa. It has been used within their culture for thousands of years, and has been essential to their...
The Impacts Of Physical Cash And Developing Into A Cashless Society
Imagine a future where everything is seamlessly paid for via your phone. It’s a beautiful vision of what a cashless society would look like, however, with some dangerous unintended consequences. A cashless society is one where purchases by physical cash are no longer available and,...
- Modern Society
The Advantages Of Credit Card Debt And Usage
Credit cards are a popular way to buy Things online and in Stores and Cover The cash back in installments afterwards . It's kind of debt centre employed by customer. It's beneficial for the client and a bank. No security security is necessary for credit...
- Credit Card
Getting Rid Of The Penny Because Of Its Negative Effects
Whether or not you believe picking up a penny will bring you luck, one thing it definitely won’t bring you is wealth. In fact, the penny is so worthless, many people want to do away with them for good. The penny is detrimental in many...
Ceos Being Paid Too Much Money Is A Bad Thing
Initially, the question as to whether or not CEOs are paid too much may seem to be a matter of subjective opinion. However, research indicates that pay disparity beyond a certain ratio can lead to adverse implications in society. According to one source, income inequality...
Minimum Wage Should Be Raised: The Pros And Cons Of Making More Money
Who wants to make more money? Kind of sounds like a funny question because who doesn't? Right. Well there has been a constant debate over what the minimum wage should be in the United States. Sure, more money sounds great, but what does that mean...
- Minimum Wage
Too Much Money Is A Bad Thing: Controlling The Money Demand
Recent advancements in information technology and technical innovations in general have revolutionized trade and commerce and contributed to existing literature in the modern world. High-speed and low-cost data transfer that was made possible by information technology, created an excellent platform for e-commerce to grow rapidly....
- Economic Development
the Emergence Of The Penny Press and Getting Rid Of It
In the streets of the United States in 1838, for the first time, the newspaper the New York Sun, which sold only one cent of the smallest unit of money. In contrast with the 15th century, printing technology has just appeared, and the prices of...
- Monetary Policy
Reasons Why Money Cannot Buy Happiness
If I asked a stranger to describe a wealthy individual, they would probably use the words “privileged,” “successful,” and “happy.” When, in reality, studies have proven that having a great deal of money does not always lead to happiness. In fact, despite popular belief, money...
Money Can Buy Happiness: The Speech On Achieving Happiness
“Money can buy happiness” is a common phenomenon, widely believed by people these days, I however beg to differ. Expectancy theory states that money will motivate employees as long as their personal goals are being satisfied and the perception that their pay is dependent upon...
The Issue Of Rich Still Out Weighing The Poor
Did you know that 1% of households in the US produced more than 25 times what a family in the 99% did (“US Income Inequality”)? Income inequality between the rich and the poor has been happening since before the Great Recession, a period of time...
- Poverty in America
Money Over Morality: Being Righteous For The Wrong Reasons
They say money is what makes the world go round but yet, in true fact, money is what tears the world apart. Many people have imagined a world without it but obviously our global system could not realistically run; however, the way money is treated...
Power Of The Rich And Weakness Of The Poor
Money equals power to some, but money can just cause trouble for others. People think that just because they got money that they can just do whatever they please. What people don't understand is that you can still ruin your life with or without money....
The Role Of Money And Finances On Happiness
Money is a fundamental aspect of human life throughout the world. People spend a large fraction of their time earning and spending money. In wealthy and poor societies around the globe, there is now an enormous concern about economic development, and in most nations, it...
Having Money Is More Important Than Having Knowledge
As children, our parents try to inculcate good habits such as honesty, hard work and dedication while also narrating the story about a monkey who stole butter from the cats in order to make both the cats' share equal. Being rich or being righteous doesn't...
Priorities in Money Management as a Student
Money is extremely important in each individual’s lifestyle as it makes them independent, have more control over decision-making skills, more freedom to do what they want and can fulfil and accomplish their long-term ambitions. An individual with great wealth is able to get a rich...
Gambling and Its Positive and Negative Effects on Society
In today’s society, Gambling is becoming more and more widespread, you must look at the positives and negative aspects of the casino establishments being built and how these establishments effect the community surrounding them. It is proven that casinos boost the economy by providing jobs...
- Gambling Addiction
The Importance of Being Careful With Money When it Comes to Lottery
I believe that winning the lottery is an exhilarating experience and can cause some issue to occur in one’s life. From the general perception of society, some individuals do not make good use of their winning, and this is the reason most people do not...
Character Of Mrs. Loisel In 'The Necklace'
Mrs. Loisel isn't the brightest person and can be seen as selfish, which signifies her only thinking for and about herself. The title of the short-story is 'The Necklace' and written by Guy De Maupassant. To give a brief overview, the Loisels aren't very wealthy,...
- The Necklace
Inclusion of Inflation Factor in the Calculation of Retirement Expenses
Inflation is the change in overall costs for merchandise and services. The most commonly used measure of inflation is the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which tracks the weighted average of prices of many consumer goods and services. Economists have found that if the rate of...
Major Presence of Financial Illiteracy in America
Research states that many Americans have not quite grasped the concept of saving. This is mostly due to a lack of education in finance and economy. Economists even go so far as to say that, if things don’t change, there could be chances of another...
Income Inequality: Why It Stands in a Way of US Economy
Income inequality has been a point of discussion since the time of ancient Greek philosophers and is an increasing concern today for many Americans. Income inequality means that the money people earn is unevenly distributed among the total population. Personal income can be categorized in...
- Income Inequality
Raising Minimum Wage in Ontario: Negative Impact
Is raising the minimum wage the right move? Ontario is the second province to move from $11.40 per hour towards a minimum wage of $15.00 per hour. According to News Ontario, “By October 2017, the general minimum wage will have increased by almost 70 per...
Crowdfunding, Its Aim And Objectives
Background Information Crowdfunding became quite popular recently but this fund raising platform has existed since 1700s. This can also be said to be a method which aids in financing a product or project. This implies in most cases that all individuals companies or people which...

An Incentive-Pricing Analysis Of Price-Cap Regulatory Regimes
Regulation is of paramount importance when there are natural monopolies in the society, since the existence of monopolies alone is costly to the society due to deadweight losses from mark-up pricing. Laffont (1994) describes regulation as two-fold using the incentive-pricing dichotomy and divided the regulation...
- Pricing Strategy
Analysis Of High-Quality Stocks In Hong Kong
In Hong Kong, there are many high-quality stocks with the characteristics of durable competitive advantage (DCA), which means the company can generate profits sustainably in the long time. In the following, I would like to recommend three stocks, which are HK & CHINA GAS (00003),...
Analysis Of Monetary Policy Frameworks
There are four main types of monetary policy frameworks identified from review: exchange rate targeting, inflation targeting, monetary quantity targeting and dollarization. Developing countries can chose from inflation, exchange rate and money supply as nominal targets. Most countries are moving towards inflation targeting due to...
Budgeting as the First Step to Financial Freedom
Creating a budget sheet is the first step to gaining financial success. I’ve found that a budget sheet can be a wonderful tool through personal experience. I created my first budget sheet about a year ago and found it to be very beneficial compared to...
Diversity Of Global Agent Banking Models And Its Applicability
According to McKay (2010) there is global concern to entrench financial access to previously ignored hence the emergency of agency banking. This has been adopted in several countries around the world Brazil being the first in 1999 Colombia and Pare have been declared to be...
Effect Of Budgetary Issues On Psychological Wellness
Budgetary issues or monetary weight is where cash stresses are causing pressure. There are as yet numerous families confronting hard money related circumstances and the effect on psychological wellness can be huge. These issues can appear to be difficult to defeat can appear to be...
- Cognitive Psychology
For The Love Of Money
“A wise person should have money in their head, but not in their heart” (Jonathan Swift) Money is any clearly identifiable object of value according to the Webster Dictionary. The history of money concerns the development of how it is exchanged and used. Money is...
- Business Success
General Purpose Financial Report
General Purpose Financial Report basically provides the information and analysis about the scarce resources of a public sector or a private sector company. It normally focuses the general and overall financial information and produces the result for shareholders and board of directors to analyze the...
Great Money Saving Tips For Buying Your First Home
Saving up for a home is never easy, no matter how much you earn. It's even more difficult when you are trying to buy your first home, after all, you have no capital (or not much at all), and when you are spending a large...
History Of Systems Determining Relative Value Of Two Currencies
The smooth functioning of international trade required a universally accepted foreign currency to settle the internal trade and a way to balance the trade imbalances amongst countries. This led to the question of determining relative value of two currencies? Different systems were tried in past...
How Mutual Funds Can Be A Good Investment
Shared assets are an extremely well known kind of venture - yet would they say they are great speculations? The appropriate response relies upon the specific common store you are discussing, and on how much work you did to decide whether the reserve fits with...
How People Of Different Age Groups Spend Their Money
People in the age group of 18-25 mostly prefer savings a/c and take education loan whereas people in the age group of 25-35 mostly prefer savings a/c, personal loan and two wheeler or car loan, insurance such as motor insurance, current a/c, and credit card....
Macroeconomic Equilibrium: Definition And Overview
In financial aspects, monetary balance is where monetary powers, for example, free market activity are adjusted and without outside impacts the (harmony) estimations of monetary factors won't change. For instance, in the standard course book model of immaculate rivalry, harmony happens at the time when...
Monetary Policy And Asset Prices Linkages
A number of theories exist that explain the link between monetary policy and asset prices. In general, there is no theoretical consensus, in terms of direction of causality between monetary policy and asset prices; regarding reactions of monetary policy to asset price volatility or approaches...
Overview Of The Financial Consolidation
Financial consolidation (FC) relates to a large fall in the deficit by more than 1.5% of GDP. The assumption is that a sharp reduction in the cyclically adjusted deficit would have to be a result of some policy action such as an increase in tax...
Overview Of Theory Of Financial Intermediation
Theory of financial intermediation has been successful because of reduction on information and transactions cost. The intermediaries provide liquidity especially liquid assets by reducing cost of exchange between lender and borrowers. Financial intermediaries can obtain information at lower cost than individual investors because the former...
Overview Of Tobin's Theory Of Investment
Tobin’s Theory, named after the economist who developed it, is centered around a variable named q, which is equal to the ratio between the market value of a given company and its replacement cost of capital. A q value greater than 1 signals the fact...
Intensive Motherhood And The Ideal Mother
Philanthrocapitalism is a novel type of philanthropy and involves donors who merge business goals with humanitarian acts (McGoey 2012). An example would be the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, a Global Health Program funding various types of activity such as research projects for malaria (McCoy,...
Rules And Restrictions To Invest In Cfds
In spread betting, the speculator should be able to estimate when the price increases or falls. The investment can be made in global markets, indices, commodities, currencies and shares. One can buy the needed units to trade. Its trade is similar to shares with only...
Secrets Behind Zcash (Zec) And Gemini Deal
A lot of crypto interest has shifted to privacy coins and some of them have been found not to be what they promise on paper. ZCash has however remained focused on provision of the best privacy in the market. Earlier in the year, the coin...
Importance Of Investing And How We Save Our Money
July 27-28 2018 Laguna College held its first celebration of Accounting week. The seminar started early in the morning, in the seminar, the guest speaker Mr. John Richard Valdeavilla, listed and explained the about importance of investing and how we save our money. This topic...
Foundational Principles of School Financial Management
Starting, running and improving an ESL school cannot take place without proper financial and operations management. Clear policies and procedures in the areas of finance, operations and risk are critical for a financially-sustainable school. By consistently implementing these policies and procedures, schools ensure their ability...
- Public School
The 5G Economy: How 5G Will Impact Global Industries
We humans are an increasing number of interacting with every other and with our surroundings via statistics and communications technologies, both on a non-public and on a expert level. this marked socio cultural fashion can also be pondered within the call for tourist hobby. the...
- Business Analysis
The Influence Of Financial Literacy On Financial Behavior Of Working Millennials
Millennials, also known as generation Y, are individuals born in the early 80s to mid-90s particularly from 1981 to 1996 (Pew Research Center, 2018). According to an article in Live Science (Main, 2017), millennials are regarded as more open-minded, self-expressive, and receptive to new ideas;...
- Millennial Generation
Top Personal Finance Advice All South Africans Should Read About
Advice on how to manage multiple sources of income as a “slasher”. In the fast-paced world of today, most people can no longer afford to rely on just one source of income. Beyond just financial reasons, a lot more people are choosing to pursue their...
- South Africa
Best topics on Money
1. The Effects of Money on Human Behavior
2. Exploring Why Happiness Is More Important Than Money
3. Exploring the Age-Old Question: Can Money Buy Happiness
4. Transitioning to a Cashless Economy: Challenges, Opportunities, and the Path Ahead
5. Being Smart With Your Money: the Importance of Financial Literacy
6. Unlocking Financial Literacy: Exploring the World of Finance and Money Management
7. The Value of Understanding Personal Finance Management for Students
8. Why Personal Finance Should Be Taught in Modern Schools
9. Evaluation of the Benefits and Risks of Cashless Economy
10. Can Money Buy Happiness: Sharing Persuasive Personal Viewpoint
11. Budgeting and Types of Personal Budget
12. Budgeting Technique to Build a Stable Financial Future
13. The Ascent of Money: Is Money the Root of All Evil
14. Gold: One of the Most Expensive Metals on Earth
15. The Impacts Of Physical Cash And Developing Into A Cashless Society
- Personality
- Personal Experience
- Perseverance
- Career Goals
- Being Different
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
- Share full article

From the Heart to Higher Education: The 2021 College Essays on Money
Each year, we ask high school seniors to send us college application essays that touch on money, work or social class. Here are five from this year’s incoming college freshmen.
Credit... Robert Neubecker
Supported by

By Ron Lieber
- June 18, 2021
When the most selective — or, even better, rejective — schools in the United States are accepting under 10 percent of the people pleading for a spot in the next freshman class, it eventually becomes impossible to know why any one person receives an offer, or why a student chooses a particular school.
So in this particularly unpredictable season — as we publish a selection of application essays about money, work or social class for the ninth time — we’ve made one small but permanent change: We (and they) are going to tell you where the writers come from, but not where they are headed.
Our overarching point in publishing their essays isn’t to crack the code on writing one’s way into Yale or Michigan, as if that were even possible. Instead, it’s to celebrate how meaningful it can be to talk openly about money and write about it in a way that makes a reader stop and wonder about someone else’s life and, just maybe, offers a momentary bit of enlightenment and delight.
One writer this year helps her mother find a new way of bringing joy into the world, while another discovers the cost of merely showing up if you’re a female employee. A young man reflects on his own thrift, while a young woman accepts a gift of ice cream and pays a price for it. Finally, caregiving becomes a source of pride for someone young enough to need supervision herself.
Each of the writers will make you smile, eventually. And this year in particular, we — and they — deserve to.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Advertisement
Essay on Money
Money is a significant part of human civilisation. It is difficult to think about the world without money. Everybody needs money for various purposes, starting from day-to-day transactions to savings for the future. But if we go back to history, we will find that before money came into existence, there was a barter system to facilitate transactions among individuals in society. With the development of civilisation over time, the barter system lost its ground and was replaced by money. This essay on money will provide ideas to students so they can effectively write essays on this topic. They can also check out the list of CBSE Essays to practise more essays on different topics and boost their writing skills.
500+ Words Essay on Money
Money is any object or record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts which also acts as a standard of deferred payments. The main functions of money are distinguished as: a medium of exchange, a unit of account and a store of value. The money supply of a country consists of currency (banknotes and coins) and bank money. Bank money usually forms the largest part of the money supply.
With the help of money, we can fulfil our dream. We can go on trips to various places, eat tasty food, buy a beautiful house and can buy any luxury items. Many businessmen earn a lot of money by making profits from their businesses. They provide services or make products that people need and make money from them. Now, there are many industries and startups which have set up their business and gained success. But still, there are many people who use illegal modes to earn money and become a part of corruption.
Significance of Money in Economy
Money plays an important role in shaping the economy of any country. Money can stimulate or even hamper economic progress. Money affects the income, output, employment, consumption and economic welfare of the community at large. Money through its purchasing power increases consumption and, as a store of value, increases investment, and employment and leads to economic development.
Demonetisation in India
The Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi, announced demonetisation on 8th November 2016, where Rs 500 and Rs 1000 notes were withdrawn from circulation. It was a major event of the year 2016. The demonetisation decision was taken by the Government in consultation with the RBI. The action was taken to tackle Black Money which is available in various forms like cash, investment in property and real estate, luxury goods like jewellery or with foreign currency dealers and private financiers. The target was to curb the use of black money.
The other motto of demonetisation was to reduce corruption. With demonetisation, the cash in the hands of corrupt people becomes useless, and if the same is deposited in the banks, it loses anonymity, and the person has to pay taxes on the said amount.
The demonetisation also helped in promoting digitalisation through online transactions. A large section of the Indian economy was being run on the cash system, which does not get captured by the tax department as it does not leave any trail. So, the Government thought about promoting digitisation and formalisation of the economy through online transactions, e-wallets, and various payment instruments like Paytm, Rupay cards, the BHIM app etc. The beauty of these instruments is that the entire economic activity gets captured. It reduces tax evasion and improves tax collection.
Students must have found this essay on money useful for improving their essay-writing skills. They can get the study material and the latest updates on CBSE/ICSE/State Board/Competitive Exams, at BYJU’S.
| CBSE Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Essay on Money: Meaning, Functions and Role
Read this essay to learn about the meaning, functions and role of money.
Meaning of Money:
Money has been defined differently by different economists. Some, like F.A. Walker, define it in terms of its functions, while others like G.D.H. Cole, J.M. Keynes, Seligman and D.H. Robertson lay stress on the ‘general acceptability’ aspect of money.
According to Prof. D.H. Robertson, “anything which is widely accepted in payment for goods or in discharge of other kinds of business obligation, is called money.” Seligman defines money as “one thing that possesses general acceptability.” Prof. Ely says: “Money is anything that passes freely from hand to hand as a medium of exchange and is generally received in final discharge of debts.”
Prof. A. Walker says “Money is that money does.” But these definitions are defective because they do not lay proper emphasis on all the essential functions of money. Prof. Crowther’s definition of money is considered better as it takes into account all the important functions of money. He defines money as “anything that is generally acceptable as a means of exchange (i.e., as a means of setting debts) and at the same lime, acts as a measure and a store of value.”
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is a fact that although money was the first economic object to attract men’s thoughtful attention…there is at the present day not even an approximate agreement as to what ought to be designated by the world…the business world makes use of the term in several senses; while amongst economists there are almost as many different conceptions as there are writers on the subject.’
Functions of Money :
Money is a matter of functions four, a medium, a measure, a standard, a store.
Money in a modern economy performs important functions which have been classified by Kinley as follows:
(a) Primary functions also called fundamental and original functions like the medium of exchange and measure of value.
(b) Secondary functions like standard of deferred payments, store of value and transfer of value.
(c) Contingent functions like distribution of income, measurement and maximisation of utility etc.
Medium of exchange:
Money serves as a medium of exchange and facilitates the buying and selling of goods, thereby eliminating the need for double coincidence of wants as under barter. A man who wants to sell wheat in exchange for rice can sell it for money and purchase rice.
Measure of value:
Money has also removed the difficulty of barter system by serving as a common measure of value. The values of various commodities are expressed in terms of money. Money as a measure of value has made transactions simple and easy. It may be understood that this function of money follows from the first basic function (medium of exchange). It is because money is used as a medium to exchange goods, that each good gets a value in terms of money (called price). As such, money also serves as a unit of account. In India, the unit of account is the Rupee, in USA, the Dollar; in USSR, the Rouble and the Yen in Japan.
Store of Value:
Classical economists did not recognize the store of value function of money. Keynes laid stress on this function of money. People store money to provide again the rainy day and to meet unforeseen contingencies. According to Keynes, people also store money to take advantage of the changes in the rate of interest. Money as a store preserves value through time and space. Money as a store of value through time means the shifting of purchasing power from the present to the future and as such it serves as an important link between the present and the future.
Money in this case is stored as a form of ‘asset’. Money is an asset or a form of wealth because it is a claim. It is the most convenient way of laying claim to such goods and services as one wishes to buy. Thus, rather than keeping their wealth in the form of non-liquid assets like houses, shares, etc., people prefer to keep their wealth in the form of money.
Money is the most liquid of all assets i.e., money can be readily exchanged for goods and services without any difficulty and the price of money or its value is stable at least over a short period. In fact, all assets like bonds, saving accounts, treasury bills, government securities, inventories and real estate do serve as stores of value, but they differ in the degree of liquidity; money amongst these possesses highest degree of liquidity and that is why people prefer it most as a store of value.
However, we should not give it undue importance because the value of money does not remain stable through time. As prices rise, people try to get rid of money as its value falls. Moreover, in modern economies storing wealth in the form of money is unimportant as it is done in the form of interest-bearing securities.
Money as a store of value through space continues to be important; for instance, an Indian businessman who sells his business and property and goes to USA and settles down there is a case of exporting value through space. In ancient times, gold and silver coins were used as a store of value followed by currency notes. In advanced countries today money is stored in the form of bank deposits.
Standard of Deferred Payments:
Money has always been used as a standard of deferred payment. This function of money has attained more importance in modern times with the extension of trade based on credit. As a result of this function, it has become possible to express future payments in terms of money. A borrower who borrows a certain sum in the present undertakes to pay the same in future. Similarly, a person who purchases on credit agrees to pay in future when his bills become due. Money as a standard of deferred payments is performing useful function enabling the current and present transactions to be discharged in future.
Contingent Functions:
Besides, the primary and secondary functions of money, Prof. Kinley lays stress on the contingent functions of money. Money facilitates the distribution of national income among the various factors of production. Land, labour, capital and organization all co-operate in an act of production and the product is the result of their joint efforts, which belongs to all of them.
Money makes the distribution of joint production, amongst various factors easy and paves the way for economic progress. Further, a concept like utility is measured in terms of money. A consumer as well as a producer measures the utilities of different goods and factors of production with the help of money and try to get maximum satisfaction or maximum returns.
Again, credit is the basis of modern economic progress. Money constitutes the basis of credit. Banks create credit not out of thin air but with the help of money. Moreover, money gives liquidity to various forms of wealth. A person by keeping his wealth in the form of money renders it most liquid.
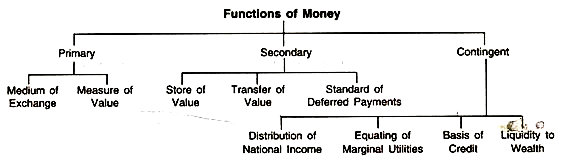
Role of Money:
Money plays a vital role in the determination of income and employment. The basic problems of macroeconomics are the determination of income, output, employment and the general price levels, including the determination of the long-run rate of growth of income. As far as the growth theory is concerned, the supply and demand for money have been largely ignored until recently, yet all but the very simplest short-run income and price level determination models have a money market included in them.
As such, money becomes an economic force in its own right, which under certain circumstances, powerfully affects economic activities. This is the main subject matter of monetary economics. Monetary theory is that branch of economics which aims at discovering and explaining how the use of money in its various forms affects production, consumption and distribution of goods. As a matter of fact, the advocates of monetary theory plead that a large number of factors affect the volume of production, consumption and distribution. To them, money is no more a veil, a medium to facilitate exchange of goods: but something more vital, more crucial and more important, which affects the general level of economic activity.
Monetary theorists hold that the use of money as a medium of exchange, as a store of value, as a measure of value, as a standard of deferred payments along with its contingent functions has the capacity of influencing the volume and direction of economic activity that would not occur in a barter economy. In a monetary economy, according to Keynes, “money plays a part of its own and affects motives and decisions and is, in short, one of the operative factors in the situation, so that the course of events cannot be predicted, either in the long period or in the short, without a knowledge of the behaviour of money between the first state and the last.” In such a world, money is not a neutral phenomenon rather a phenomenon governed by principles very different from those that hold sway over the process of production and exchange.
In modern income and employment analysis, these are two spheres of economic activity. There is, on the one hand, the real or goods sector, which has to do with forces of aggregate demand and supply and the conditions under which an equilibrium of output and employment is achieved. On the other hand, there is the monetary sphere in which the economic forces at work are those centering around the demand for money.
According to the modern view, the existence of a separate monetary sphere of activity is a fact of profound significance; what takes place in the monetary sphere may suddenly and dramatically influence the level of both output and employment. The method by which Keynes brings money into the picture is through the development of a theory of interest in which the demand for money is dominant. The rate of interest is the link between the real sphere and the monetary sphere. It is a factor around which the theory of investment is constructed and investment expenditure is one of the key determinants of income and employment.
Related Articles:
- Essay on Money: Meaning and Main Functions of Money
- Money: Meaning and Functions of Money – Discussed!
- Top 4 Functions of Money – Discussed!
- Top 2 Functions of Money | Economy
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

Money Essay | Importance and Benefits of Money Essay in English
Money Essay: Money is a vital wellspring of everyday routine to experience a solid and satisfying life, despite the fact that it can not measure up to adore and mind. Both have their own significance and benefit. We are giving articles on Money to partake in a paper composing contest in basic and basic words here.
Money is the medium utilized by individuals to purchase required labor and products. It is utilized as the source to satisfy fundamental requirements and is additionally a wellspring of solace throughout everyday life. Money is the main source to carry on with a sound and prosperous life; nonetheless, it couldn’t measure up to the meaning of affection and care. Both have their own significance and advantages. By the way, Money is a helpful and important product to live cheerily arranging all your standard liabilities towards your family and friends and family.
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more.
Short Essay on Money 300 Words in English
Money is the fundamental need of life, without which nobody can envision a sound and tranquil life. We need money to satisfy our littlest needs. In present-day times, when progress is growing quickly and everybody is following western culture, in such a period, we need more money because of expanding merchandise. On prior occasions, there was training called trade framework, in which anybody would get another thing in return for a certain something. In any case, presently in this advanced world, just Money is expected to purchase everything or thing. it happens.
These days you need Money for each work, for garments, for food, for a safe house and surprisingly in numerous spots you need to pay for water. Despite the fact that it can likewise be said that ‘Money can’t give joy’s yet would you be able to be content with no Money? Since Money is a major piece of our life, at any rate you need Money to be content.
The significance of Money is expanding step by step, in light of the fact that our living has gotten over the top expensive. The significance of Money has expanded for a huge scope in the fields of creation, utilization, trade, circulation, public income and so on It assumes a vital part in deciding pay, work, continues partnership, general value level and so on On the off chance that we take a gander at the present-day situation, there is no uncertainty that he, who has a lot of riches, is viewed as more cultivated on the planet. Consequently, we can say that Money is vital in each part of life.
Importance of Money
Money is a fundamental thing throughout everyday life. In any case, it can’t accept things like time, love and genuine consideration. It can just satisfy the outer requirements of an individual and not the interior necessities like love. These days, everything has gotten costly yet getting them is vital to carry on with basic life. In the event that we don’t have money, nobody can envision the reality of how our circumstances will be.
The demise of an individual is sure because of the absence of Money and on the off chance that he endures, he experiences to confront numerous difficulties. Abundance empowers us to purchase every one of the essential things and helps us for the duration of our life. In the event that we comprehend the significance of Money throughout everyday life, we won’t ever go through Money with no reason or abuse. We can’t look at Money and love, in light of the fact that to carry on with a fruitful life we need both Money and love.
In this cutthroat world, to bring in Money by finding a decent line of work, everybody needs to concentrate well with advanced education from a notable school or college. An individual needs to bring in more money to satisfy the prerequisite of the relative multitude of individuals in the family, particularly for the individual who is the lone worker in the family.
An individual necessities Money to address the issues of all his relatives to eat, wear, and live. The rich have an uncommon personality and notoriety in the general public, be that as it may, the needy individuals spend their lives just getting two suppers per day. Every one of these progressions and contrasts are because of Money as it were.
In any place where there is a shortage of money in the house, there are a lot of struggles. There are squabbles among a couple. Neither does anybody regard each other in the case of bringing in Money. Neighbors and family members likewise peer downward on the destitute individual. He begins cutting her reasoning that the individual never requests Money from her. With this, nobody needs to get to know a destitute individual in the present time.
Money can neither purchase nor stop time nor purchase genuine romance and care together. Yet at the same time it is needed by all, so life can be taken in the correct way. Despite the fact that Money can’t give time and love, it certainly gives us bliss, certainty, fulfillment, physical and mental harmony. Because of which we can carry on with life effectively and each troublesome issue can be settled.

Advantage from Money
You can carry on with a conscious life: An individual is regarded just when he is monetarily prosperous. Something else, in the present society, the bankrupt individual has no regard.
Unadulterated and nutritious food can be eaten: The individuals who have abundance can appreciate an assortment of heavenly and nutritious dinners. What’s more, they can shield themselves from sicknesses.
Your assurance should be possible: In the present society, burglary, theft have expanded a great deal and rich individuals can give security to themselves because of Money.
The credit is repayable: Obligation taken from an individual rich individual can reimburse the credit without any problem.
The happiness regarding material delights can be achieved: With an adequate measure of riches, all material solaces can be appreciated like taking a decent house, great garments, vehicles and different things.
FAQ’s on Money Essay
Question 1. What is the requirement for money?
Answer: The main capacity of cash is to fill in as a mechanism of trade. As a mechanism of trade, cash addresses every one of the troubles of the deal. There is no need for a twofold fortuitous event of needs in a cash economy.
Question 2. What are the benefits of money?
Answer: Having money with you gives you a respectful life, you can have a healthy and nutritious life, you can pay your loans, have a luxurious life, etc.
Question 3. How can we earn money?
Answer: There are a number of ways to earn money such as;
- You can be an employee in a company
- You can start your own business
- You can be an entrepreneur
- You can use social media channels to provide your service
About Stanford GSB
- The Leadership
- Dean’s Updates
- School News & History
- Commencement
- Business, Government & Society
- Centers & Institutes
- Center for Entrepreneurial Studies
- Center for Social Innovation
- Stanford Seed
About the Experience
- Learning at Stanford GSB
- Experiential Learning
- Guest Speakers
- Entrepreneurship
- Social Innovation
- Communication
- Life at Stanford GSB
- Collaborative Environment
- Activities & Organizations
- Student Services
- Housing Options
- International Students
Full-Time Degree Programs
- Why Stanford MBA
- Academic Experience
- Financial Aid
- Why Stanford MSx
- Research Fellows Program
- See All Programs
Non-Degree & Certificate Programs
- Executive Education
- Stanford Executive Program
- Programs for Organizations
- The Difference
- Online Programs
- Stanford LEAD
- Seed Transformation Program
- Aspire Program
- Seed Spark Program
- Faculty Profiles
- Academic Areas
- Awards & Honors
- Conferences
Faculty Research
- Publications
- Working Papers
- Case Studies
Research Hub
- Research Labs & Initiatives
- Business Library
- Data, Analytics & Research Computing
- Behavioral Lab
Research Labs
- Cities, Housing & Society Lab
- Golub Capital Social Impact Lab
Research Initiatives
- Corporate Governance Research Initiative
- Corporations and Society Initiative
- Policy and Innovation Initiative
- Rapid Decarbonization Initiative
- Stanford Latino Entrepreneurship Initiative
- Value Chain Innovation Initiative
- Venture Capital Initiative
- Career & Success
- Climate & Sustainability
- Corporate Governance
- Culture & Society
- Finance & Investing
- Government & Politics
- Leadership & Management
- Markets and Trade
- Operations & Logistics
- Opportunity & Access
- Technology & AI
- Opinion & Analysis
- Email Newsletter
Welcome, Alumni
- Communities
- Digital Communities & Tools
- Regional Chapters
- Women’s Programs
- Identity Chapters
- Find Your Reunion
- Career Resources
- Job Search Resources
- Career & Life Transitions
- Programs & Webinars
- Career Video Library
- Alumni Education
- Research Resources
- Volunteering
- Alumni News
- Class Notes
- Alumni Voices
- Contact Alumni Relations
- Upcoming Events
Admission Events & Information Sessions
- MBA Program
- MSx Program
- PhD Program
- Alumni Events
- All Other Events
Is Money Really the Best Measure of Value?
If we want a more equitable world, then we need to consider the different ways people value money.
April 03, 2024

While some economic theories might assert that one dollar is in fact worth one dollar, Mohammad Akbarpour says this overlooks an important fact: Different people value money differently.
“How to allocate scarce resources and who should get what and why is the fundamental question of economic sciences,” says Akbarpour , who is an associate professor of economics at Stanford Graduate School of Business. In a free market, money plays a central role in answering that question, but as Akbarpour discusses in this episode of If/Then: Business, Leadership, Society , if we want a more equitable world, then we need to consider the different ways people value money.
Much of Akbarpour’s research has explored economic scenarios where wealth inequality presents an impediment to market maximization. One example is ride-sharing in Chicago, where Akbarpour identified systematic income disparities at play between an app’s riders and drivers, as well as among the riders themselves. Because riders in the city’s south side tend to be less affluent than those in the north, market-based pricing incentivizes drivers to concentrate in wealthy areas where riders can afford surge prices, leaving less affluent riders with less access to transportation.
Instead of allowing market forces to determine the cost of fares at a one-size-fits-all rate, Akbarpour argues for tailoring pricing based on income levels and people’s marginal value for money. “Once we believe in this one assumption and add it to the classic models, then we can ask the question of how to allocate scarce resources,” Akbarpour says. “If you care about the utility of these people too, then a policy that increases prices here and decreases prices there can start making sense.”
As Akbarpour explores in this episode of If/Then , creating a more equitable world requires that we challenge our prevailing assumptions about money and the value that people place on it.
Senior Editor, Stanford GSB
Listen & Subscribe
If/Then is a podcast from Stanford Graduate School of Business that examines research findings that can help us navigate the complex issues we face in business, leadership, and society. Each episode features an interview with a Stanford GSB faculty member.
Full Transcript
Note: Transcripts are generated by machine and lightly edited by humans. They may contain errors.
Kevin Cool: If we want a more equitable world then we need to consider the different ways people value money.
Aziz: I like it because I can work whenever I like. I’m not a morning person. I used to be a cab driver for five years, and the car was sitting in the garage so I decided just to do Uber with my car. It’s just sitting there.
Kevin Cool: Meet Aziz. He’s an Uber driver in Chicago. Driving his red Toyota Yaris around the city most afternoons and evenings, and he’s been doing it a long time.
Aziz: I start 2013 so it’s almost 10 years.
Kevin Cool: Aziz has driven more than 20,000 Uber trips in those 10 years.
Aziz : So with Uber you just drive and more relaxing of driving. Not like that stress. Yeah, a lot of cab drivers, they were killed just for 50 bucks, but now, with Uber I don’t carry cash with me. It’s good. Yeah, it’s more safe, and you can drive whenever you are. If it’s busy in the summer I can stay in the summer. With Uber it’s more safe for me.
Kevin Cool: For Aziz, one of the biggest benefits of working for Uber is the control and choice he has. When he works, where he drives and which rides he accepts.
Aziz: So sometimes, I drive to Indiana or Michigan. I have no problems driving around. I drive south, north, west, northeast … the lake.
Kevin Cool: Aziz, like a number of the Uber drivers we met in Chicago, just wants to stay busy keeping the back seat of his car full of passengers for as much time as possible. The more rides with less down time affects what he takes home at the end of the day. Yet all the drivers we spoke to are very aware of the incentive prices for both drivers and passengers like surge pricing for different parts of the city.
Aziz: Now, I said it depends — what do you call it? When it’s busy, full charge, and if it’s not busy, they will get a price. You can make like between 20 bucks per hour until if it’s busy you can reach 30 or 35 per hour. So holidays like Thanksgiving we can do when it’s — only when the weather is bad like snowing it’s like people gave us work so you can make some extra money. It shows here like you are in the summer, and if it’s busy I stay there. Why I have to come to downtown because it’s busy in downtown or the surcharges? Sometimes, it’s like surcharge is very high in the south.
Kevin Cool: Price incentives determine where drivers like Aziz pick up rides, but if the only people who can afford those surge prices are in the wealthier parts of Chicago, is that fair for the people who need cars just as much in poorer neighborhoods on the South Side?
Higher prices are easier to stomach for people with lots of money, but what if these incentives could also help people who value money differently? It may sound simple, but it’s not something that conventional economics usually takes into account.
I’m Kevin Cool, Senior Editor at the GSB. Today, we explore the differences in how people value money and how those differences affect market dynamics with Mohammad Akbarpour, associate professor of Economics.
Mohammad Akbarpour: Really, one of the most fundamental questions of economics I try to answer in the project of economics is how to allocate scarce resources. If you read the classics like, “The Wealth of Nations,” the Karl Marx books from left and right this question of how to allocate the scarce resources, and who should get what, and why is a fundamental question of economic sciences.
And the most accepted, widely-recognized answer to this question is the market mechanism. It’s the free market. So if someone is willing to pay more than me for the good they have to get it. So let’s find the market-clearing price, the price at which the supply of something is equal to the demand and let the market work.
What we did in this paper was really to ask the very same question with one extra assumption. And the extra assumption was: different people have different marginal value for money. The whole idea of Econ 101 when you have supply curve, and demand curve, and the intersection of supply and demand curve will give you the market equilibrium, and that’s the point that the total value is maximized. That’s a picture that pretty much everyone who has taken one class in Economics has seen.
That idea that market equilibrium maximizes the total value, total surplus, or even total welfare comes from the belief that getting one dollar from me, and giving it to Elon Musk, is welfare-neutral. That one dollar has the same value for Elon Musk or Mohammad.
If we do not believe in this, which I do find an uncontroversial assumption, although we can talk about that like there is a fundamental philosophical critique to this assumption, if we believe that different people have different marginal values for cash then we should immediately believe that if you’re willing to pay more for something, that does not mean that the social welfare is maximized for giving a good to you. Because it could be that you are rich.
Once we believe in this one assumption and add it to the classic models, then we can ask the question of how to allocate the scarce resources in this way. And it turns out that with that one assumption, we can identify conditions under which free market remains efficient, and optimal, and fair, but that’s not always the case.
There would be many, many cases in which you want to start using non-market allocation mechanisms. And by non-market allocation mechanisms I mean things such as rationing, running a lottery, people waiting in the queue, and allocating the good for free like the allocation of vaccines.
Kevin Cool: So I want to ask you about a few examples in which this plays out, but the one I want to start with is Taylor Swift. I understand you just recently went to a Taylor Swift concert. Is that right?
Mohammad Akbarpour: Yeah, that’s right. I did not plan to, but I had a free ticket.
Kevin Cool: So you didn’t have to make the decision about how much it was, quote, unquote, worth, right? Yeah, but this does seem like a place where the free market failed or at least was flawed. There were some people who paid 70 times the face value. Seven-zero times the face value for a ticket. And, of course, legions of fans who were priced out and were angry about that. I know it’s just concert tickets, but what can we learn from these exorbitant prices and the calls for change that resulted?
Mohammad Akbarpour: Well, I should start by saying that this is really difficult problem. As we are sitting here multiple economists are thinking about the problem of ticket allocation because it’s a really difficult problem. So everything starts by this observation that if Taylor Swift concert tickets are allocated completely by some competitive equilibrium or free markets, then people who are going to be able to go to this concert are not necessarily people who love Taylor Swift the most.
This is again, should be uncontroversial. In fact, that’s the reason that Taylor Swift has started Very Fine Fans. And saying that if you are a Very Fine Fan now you can get the ticket before other people at lower prices. This is also the case for say, WorkUP. Whoever is happy to wake up at 5:00 a.m. and be the first person who signs in, in that website can get it.
FIFA for the World Cup decided that, “We are going to allocate tickets by lottery.” So everyone puts their name down for a hundred-dollar ticket, and then, “We are going to allocate it with lottery and 10 percent of people are going to get it.” These are all allocation mechanisms that Econ 101, the supply and demand curve, would tell you they are wrong. There is someone who was willing to pay more for this ticket, and you did not give the ticket to them.
And yet, policymakers do that, and in this paper, if you like, in this sequence of papers and research agenda that I started with my fantastic co-authors, Piotr Dworczak and Scott Kominers basically, our idea was people are doing it out there in the world. Some economists think that that is wrong. Could we actually make sense of this policy decision based on economic principles? Based on first principles.
And we could do that by just adding one feature to the model which is different people have different marginal value for money. So if someone is willing to pay $1,000 for a Taylor Swift concert they do not necessarily get more value from going to Taylor Swift concert than someone who is willing to pay $500.
Kevin Cool: Another example. A lot of the people who went to these concerts probably arrived in a Lyft or an Uber. And you’ve done some work looking at ride-sharing companies and how those mechanisms or how the market works in that. First of all, what is wrong with that market that needs to be fixed, and what would you propose as a remedy?
Mohammad Akbarpour: One thing that we discovered in the mathematics of the model was that there are two different types of inequality that can change the way you regulate a market. One type of inequality is the inequality across two sides of the market. In the Uber example that you just said or Lyft example, drivers are systematically poorer than riders.
That’s a fact that you can look at their tax returns. It’s clear that the typical Uber passenger is, on average, more well-off than a typical Uber driver. So that’s what we call the cross-saving equality. The other type of inequality is with inside inequality. Within riders. Some riders are rich, some riders are poor.
And these two different types of inequality give rise to two different policies or different types of policy outcomes. Within the framework of your question, drivers are systematically poorer than riders. And then, if you go to Chicago, riders of South Side Chicago are actually much poorer than riders of Lincoln Park, which is a much more well-off neighborhood.
And then when we take that observation that’s like basically, distribution of marginal values for cash which comes from the distribution of inequality into the model we will see that policies such as increased prices under Lincoln Park, because passengers are much less price-sensitive, and decreased prices on the South Side because passengers are very price-sensitive. And, in fact, you might even start getting negative revenue on the South Side. It doesn’t make sense for you to have business there. But if you have some redistributive goal, if you care about the utility of these people, too, then a policy that increases prices here and decreases prices here can start making sense.
Another policy that can start making sense is to detach the price of drivers and passengers. Instead of saying that the price is $100, and I’m going to get 40 percent of it as Uber as the platform you can set a higher price for riders, a lower price for drivers you will generate some revenue that is more than what you could do otherwise because now, you can charge riders much more. And then, you can use that revenue to give drivers benefits like such as health insurance and stuff like that as part of their compensation.
And I should emphasize, these are policies that are optimal if you are a social planner thinking about welfare, or a regulator who wants to actually maximize welfare. From an Uber perspective, if their only objective is revenue then it’s unclear that this is a good policy.
But I believe and working with different companies, I believe that even companies, even if it’s only about their own long term stock value, they do care about consumer welfare. They do care about actually creating a great PR, making sure that they are a company known as a good company. And in that case, if they want to help drivers this is the way they can do that.
Kevin Cool: You’re listening to “ If/Then ,” a podcast from Stanford Graduate School of Business. We’ll continue our conversation after the break.
[Music plays]
Kevin Cool: So you’re making an economic argument here, but it seems to me that it’s possible that someone would interpret this as a political argument. It’s redistributing money in a way from the rich to the poor. Have you had any pushback on that in that regard?
Mohammad Akbarpour: A lot of pushback. The very first few economists whom I really appreciate we talked about this idea, they were like very much against it because of several reasons. And let me actually get into some of the detail.
The first reason is what we are doing here is what a classic economist would call an interpersonal utility comparison, which means I’m saying that if I give one dollar to you versus one dollar to me this will generate more utility in your brain. This is going to give you more happiness than if I give it to Elon Musk.
I’m basically making a comparison of what happens in your brain. There is no reason to believe that actually, maybe Elon Musk is still as happier with getting one dollar than you. How do I know that? This is a really subtle philosophical critique. That’s why economists historically were really against interpersonal utility comparison. They were like, “The only thing we can observe is willingness to pay. How much you’re willing to pay for this tea. And if you are willing to pay more you probably enjoy it more.”
Kevin Cool: So the market is determining what happens?
Mohammad Akbarpour: Exactly.
Kevin Cool: Yeah, right.
Mohammad Akbarpour: So we are here in this paper, we are making these sequence of papers. We are making interpersonal utility comparisons. We are saying, “No, one dollar for an average American is more valuable than one dollar for Elon Musk,” and we are happy to take that stand.
The second critique, which is much more fundamental, is economists are actually not against redistribution. They believe — or at least some economists, I would call them market fundamentalists — they believe that the right way to do a distribution is through the tax system. It’s not through redistribution through markets that we do. It’s not distorting markets or that we suggest that it is sometimes optimal.
They say, “Let the markets work. If you want to actually have the poor tax the rich, and then redistribute using all kinds of redistributive policies from lump sum transfer, to free insurance, to free school.” All the social and welfare systems that we have in the United States and everywhere in the world.
What we’re doing in the very first part of our very first paper in this agenda is to actually debunk this by showing that if people have private information about how much they value something, if I know that the value of this concert ticket or value of this cancer treatment for me is a million dollars, but you don’t know that as the market-maker or as the regulator, then we show that actually, this result that the optimal path is to let the market work and redistribute. And we argue that this is a private information in pretty much any market. You really don’t know how much someone values a piece of vaccine, a dose of vaccine, or a cancer treatment, or a Taylor Swift concert.
Second argument is yes, it’s amazing if we could have an optimal tax system, but that’s really a political outcome. Can we really control the whole tax system? Like Democrats have an ideal tax point. Republicans have a different ideal tax point, and we can never be at the optimal tax system which makes distorting markets irrelevant.
So what we do here is to say, “Hey, we cannot change the tax system in short term or medium term, so let’s take that as given. And then given the tax system, how should we design a market? How should we allocate public housing? How should we allocate healthcare? How should we allocate even concert tickets?” And then, we can identify conditions under which market distortion makes sense.
Kevin Cool: Is one of the goals of your research to help solve inequality? And do you think more economists should be pursuing research with that goal in mind?
Mohammad Akbarpour: They say academia is the opposite of the military. Military people do what you tell them and academia people do not listen to anyone. So I cannot really tell what economists should work on. I think what we are doing is alleviating the problem of inequality. Solving the problem of inequality really comes at a macro level. That’s my view that you have to have the government and society who believes, “I don’t want to live in a society that’s extremely unequal.”
And then, the tax system, the welfare system is going to take care of that. So the reason that Scandinavia is a much more equal country than United States is not because of market distortions. It’s because the society as a whole and the government has decided, “We want to have a really, really progressive tax system.”
That doesn’t mean that Scandinavia is in a better situation than United States. That’s really a choice. A social choice of a society. Maybe in America we love to have a country that accepts some high-level of inequality in the name of innovation and growth. That’s a separate question.
So I think solving inequality comes at that level so what we’re doing in this paper is to take inequality as given, and then think about the question of, “How can you alleviate this problem that inequality exists through tools that you have in the market?” And it turns out that what we find is that for most of the day-to-day goods, for yogurt, for oat milk, for a car you actually don’t want to have market distortions.
The paper and this agenda mathematically we prove, and then we can look at data as well, that you want to start having market distortions for goods in which people do not have a huge valuation in their taste. So the social planner kind of knows, the regulator knows that the value of one dose of vaccine for different people with the same observables cannot be that massively different.
A better example is cancer treatment. If you and I both have some kind of cancer, probably both of us would like to get the best treatment equally. There is no reason for me to love my life significantly more than you. So if someone is willing to pay a million dollars for a cancer treatment and someone is willing to pay $10,000 for the cancer treatment I would argue most of the difference comes from the fact that the first one is much richer. It’s a budget constraint more than an actual value.
And the paper says for these types of goods, goods in which variation and willingness to pay can be mostly explained by variation in wealth. You want to have non-market mechanisms. So we are not solving the problem of inequality, but we are alleviating this problem for these types of goods that we refer to as essential goods.
Kevin Cool: Are you optimistic that policymakers, regulators could be persuaded that we have tools to make markets more fair or that that should happen?
Mohammad Akbarpour: I think it’s to some extent already happening in a lot of places. So one in every 10 almost houses in New York City are public houses. This is a redistributive program. Fifty percent of Amsterdam housing is public so we are already seeing this happening in practice.
What I’m optimistic we are going to do more and more with more data and more analysis is that policymakers and regulators start thinking about this problem more rigorously and identify the best policies instead of just some policy that we think might work.
Kevin Cool: What drew you to first of all, become an economist and to this research in particular?
Mohammad Akbarpour: The economics really came from the fact that I always loved mathematics, and I also loved looking at humans. Reading novels. Thinking about psychology. “Brothers Karamazov” was my favorite novel, and I realized that economics is somehow a great mix of thinking about humans and mathematics.
I came to Stanford University as a PhD student in the School of Engineering. And then, I got a few economics classes, and I fell in love with economics, and then I switched to economics. So that’s how it really all started for me thinking about economics.
This particular research I was uncomfortable by this assumption. From day one I saw it. This fact that the whole economics builds on the fact that moving one dollar from A to B or at least the whole Econ 101 is welfare-neutral. And coming from Iran I was kind of in the middle class myself, but I had a lot of family members in a really small city five hours away from the capital who are really, really poor.
And it was so clear that one dollar to them is significantly different than one dollar to people that I was surrounded with in Tehran in my university. So all of those really existed in my brain and I was uncomfortable with this question. And then, with my two fantastic co-authors they had different personal experiences and we were talking about these topics.
And we were like, “Do we want to commit the crime and do interpersonal utility comparison?” And we wrote the papers. I do remember that when I told this to one of my friends who is also an economist he was like, “I think with probability five percent this paper is going to start a whole new way of thinking. And with probability 95 percent people are going to laugh at you.” And I was like, “I will take that bet.”
Kevin Cool: You’ll take the five percent?
Mohammad Akbarpour: Yeah.
Kevin Cool: Yeah.
Mohammad Akbarpour: I will take the five percent. Life is too short to get the risk-less papers.
Kevin Cool: “ If/Then ” is produced by Jesse Baker and Eric Nuzum of Magnificent Noise for Stanford Graduate School of Business. Our show is produced by Jim Colgan and Julia Natt. Mixing and sound design by Kristin Mueller. From Stanford GSB, Jenny Luna, Sorel Husbands Denholtz, and Elizabeth Wyleczuk-Stern.
If you enjoyed this conversation we’d appreciate you sharing this with others who might be interested and hope you’ll try some of the other episodes in this series. For more on our professors and their research or to discover more podcasts coming out of Stanford GSB visit our website at gsb.stanford.edu. Find more on our YouTube channel. You can follow us on social media at StanfordGSB. I’m Kevin Cool.
For media inquiries, visit the Newsroom .
Explore More
Africa’s economic horizon: a conversation with acha leke, chairman, mckinsey africa, studying social networks in developing worlds: five key insights, editor’s picks.

Redistribution Through Markets Piotr Dworczak Scott Duke Kominers Mohammad Akbarpour
November 22, 2021 What If Markets Maximized Both Efficiency and Fairness? A Stanford GSB economist argues that well-designed markets can address inequality while remaining competitive.
August 21, 2018 Rigged Auctions? Why Top Bidders Don’t Always Feel Like Winners New research casts suspicion about auctions in the online advertising market.
October 15, 2021 A Beautiful Application: Using Economics to Make Kidney Exchanges More Efficient and Fair Even modest improvements to organ exchange markets can save many lives. That’s where economists and operations experts come in.
March 13, 2017 Is It Ever OK to Sell (or Buy) a Kidney? Research seeks ways to reduce wait times and increase matches for kidney transplants.
- See the Current DEI Report
- Supporting Data
- Research & Insights
- Share Your Thoughts
- Search Fund Primer
- Teaching & Curriculum
- Affiliated Faculty
- Faculty Advisors
- Louis W. Foster Resource Center
- Defining Social Innovation
- Impact Compass
- Global Health Innovation Insights
- Faculty Affiliates
- Student Awards & Certificates
- Changemakers
- Dean Jonathan Levin
- Dean Garth Saloner
- Dean Robert Joss
- Dean Michael Spence
- Dean Robert Jaedicke
- Dean Rene McPherson
- Dean Arjay Miller
- Dean Ernest Arbuckle
- Dean Jacob Hugh Jackson
- Dean Willard Hotchkiss
- Faculty in Memoriam
- Stanford GSB Firsts
- Class of 2024 Candidates
- Certificate & Award Recipients
- Dean’s Remarks
- Keynote Address
- Teaching Approach
- Analysis and Measurement of Impact
- The Corporate Entrepreneur: Startup in a Grown-Up Enterprise
- Data-Driven Impact
- Designing Experiments for Impact
- Digital Marketing
- The Founder’s Right Hand
- Marketing for Measurable Change
- Product Management
- Public Policy Lab: Financial Challenges Facing US Cities
- Public Policy Lab: Homelessness in California
- Lab Features
- Curricular Integration
- View From The Top
- Formation of New Ventures
- Managing Growing Enterprises
- Startup Garage
- Explore Beyond the Classroom
- Stanford Venture Studio
- Summer Program
- Workshops & Events
- The Five Lenses of Entrepreneurship
- Leadership Labs
- Executive Challenge
- Arbuckle Leadership Fellows Program
- Selection Process
- Training Schedule
- Time Commitment
- Learning Expectations
- Post-Training Opportunities
- Who Should Apply
- Introductory T-Groups
- Leadership for Society Program
- Certificate
- 2024 Awardees
- 2023 Awardees
- 2022 Awardees
- 2021 Awardees
- 2020 Awardees
- 2019 Awardees
- 2018 Awardees
- Social Management Immersion Fund
- Stanford Impact Founder Fellowships
- Stanford Impact Leader Prizes
- Social Entrepreneurship
- Stanford GSB Impact Fund
- Economic Development
- Energy & Environment
- Stanford GSB Residences
- Environmental Leadership
- Stanford GSB Artwork
- A Closer Look
- California & the Bay Area
- Voices of Stanford GSB
- Business & Beneficial Technology
- Business & Sustainability
- Business & Free Markets
- Business, Government, and Society Forum
- Get Involved
- Second Year
- Global Experiences
- JD/MBA Joint Degree
- MA Education/MBA Joint Degree
- MD/MBA Dual Degree
- MPP/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Computer Science/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Electrical Engineering/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Environment and Resources (E-IPER)/MBA Joint Degree
- Academic Calendar
- Clubs & Activities
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Military Veterans
- Minorities & People of Color
- Partners & Families
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Support
- Residential Life
- Student Voices
- MBA Alumni Voices
- A Week in the Life
- Career Support
- Employment Outcomes
- Cost of Attendance
- Knight-Hennessy Scholars Program
- Yellow Ribbon Program
- BOLD Fellows Fund
- Application Process
- Loan Forgiveness
- Contact the Financial Aid Office
- Evaluation Criteria
- GMAT & GRE
- English Language Proficiency
- Personal Information, Activities & Awards
- Professional Experience
- Letters of Recommendation
- Optional Short Answer Questions
- Application Fee
- Reapplication
- Deferred Enrollment
- Joint & Dual Degrees
- Entering Class Profile
- Event Schedule
- Ambassadors
- New & Noteworthy
- Ask a Question
- See Why Stanford MSx
- Is MSx Right for You?
- MSx Stories
- Leadership Development
- How You Will Learn
- Admission Events
- Personal Information
- GMAT, GRE & EA
- English Proficiency Tests
- Career Change
- Career Advancement
- Daycare, Schools & Camps
- U.S. Citizens and Permanent Residents
- Requirements
- Requirements: Behavioral
- Requirements: Quantitative
- Requirements: Macro
- Requirements: Micro
- Annual Evaluations
- Field Examination
- Research Activities
- Research Papers
- Dissertation
- Oral Examination
- Current Students
- Education & CV
- International Applicants
- Statement of Purpose
- Reapplicants
- Application Fee Waiver
- Deadline & Decisions
- Job Market Candidates
- Academic Placements
- Stay in Touch
- Faculty Mentors
- Current Fellows
- Standard Track
- Fellowship & Benefits
- Group Enrollment
- Program Formats
- Developing a Program
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Strategic Transformation
- Program Experience
- Contact Client Services
- Campus Experience
- Live Online Experience
- Silicon Valley & Bay Area
- Digital Credentials
- Faculty Spotlights
- Participant Spotlights
- Eligibility
- International Participants
- Stanford Ignite
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Operations, Information & Technology
- Organizational Behavior
- Political Economy
- Classical Liberalism
- The Eddie Lunch
- Accounting Summer Camp
- California Econometrics Conference
- California Quantitative Marketing PhD Conference
- California School Conference
- China India Insights Conference
- Homo economicus, Evolving
- Political Economics (2023–24)
- Scaling Geologic Storage of CO2 (2023–24)
- A Resilient Pacific: Building Connections, Envisioning Solutions
- Adaptation and Innovation
- Changing Climate
- Civil Society
- Climate Impact Summit
- Climate Science
- Corporate Carbon Disclosures
- Earth’s Seafloor
- Environmental Justice
- Operations and Information Technology
- Organizations
- Sustainability Reporting and Control
- Taking the Pulse of the Planet
- Urban Infrastructure
- Watershed Restoration
- Junior Faculty Workshop on Financial Regulation and Banking
- Ken Singleton Celebration
- Marketing Camp
- Quantitative Marketing PhD Alumni Conference
- Presentations
- Theory and Inference in Accounting Research
- Stanford Closer Look Series
- Quick Guides
- Core Concepts
- Journal Articles
- Glossary of Terms
- Faculty & Staff
- Researchers & Students
- Research Approach
- Charitable Giving
- Financial Health
- Government Services
- Workers & Careers
- Short Course
- Adaptive & Iterative Experimentation
- Incentive Design
- Social Sciences & Behavioral Nudges
- Bandit Experiment Application
- Conferences & Events
- Reading Materials
- Energy Entrepreneurship
- Faculty & Affiliates
- SOLE Report
- Responsible Supply Chains
- Current Study Usage
- Pre-Registration Information
- Participate in a Study
- Founding Donors
- Location Information
- Participant Profile
- Network Membership
- Program Impact
- Collaborators
- Entrepreneur Profiles
- Company Spotlights
- Seed Transformation Network
- Responsibilities
- Current Coaches
- How to Apply
- Meet the Consultants
- Meet the Interns
- Intern Profiles
- Collaborate
- Research Library
- News & Insights
- Program Contacts
- Databases & Datasets
- Research Guides
- Consultations
- Research Workshops
- Career Research
- Research Data Services
- Course Reserves
- Course Research Guides
- Material Loan Periods
- Fines & Other Charges
- Document Delivery
- Interlibrary Loan
- Equipment Checkout
- Print & Scan
- MBA & MSx Students
- PhD Students
- Other Stanford Students
- Faculty Assistants
- Research Assistants
- Stanford GSB Alumni
- Telling Our Story
- Staff Directory
- Site Registration
- Alumni Directory
- Alumni Email
- Privacy Settings & My Profile
- Success Stories
- The Story of Circles
- Support Women’s Circles
- Stanford Women on Boards Initiative
- Alumnae Spotlights
- Insights & Research
- Industry & Professional
- Entrepreneurial Commitment Group
- Recent Alumni
- Half-Century Club
- Fall Reunions
- Spring Reunions
- MBA 25th Reunion
- Half-Century Club Reunion
- Faculty Lectures
- Ernest C. Arbuckle Award
- Alison Elliott Exceptional Achievement Award
- ENCORE Award
- Excellence in Leadership Award
- John W. Gardner Volunteer Leadership Award
- Robert K. Jaedicke Faculty Award
- Jack McDonald Military Service Appreciation Award
- Jerry I. Porras Latino Leadership Award
- Tapestry Award
- Student & Alumni Events
- Executive Recruiters
- Interviewing
- Land the Perfect Job with LinkedIn
- Negotiating
- Elevator Pitch
- Email Best Practices
- Resumes & Cover Letters
- Self-Assessment
- Whitney Birdwell Ball
- Margaret Brooks
- Bryn Panee Burkhart
- Margaret Chan
- Ricki Frankel
- Peter Gandolfo
- Cindy W. Greig
- Natalie Guillen
- Carly Janson
- Sloan Klein
- Sherri Appel Lassila
- Stuart Meyer
- Tanisha Parrish
- Virginia Roberson
- Philippe Taieb
- Michael Takagawa
- Terra Winston
- Johanna Wise
- Debbie Wolter
- Rebecca Zucker
- Complimentary Coaching
- Changing Careers
- Work-Life Integration
- Career Breaks
- Flexible Work
- Encore Careers
- Join a Board
- D&B Hoovers
- Data Axle (ReferenceUSA)
- EBSCO Business Source
- Global Newsstream
- Market Share Reporter
- ProQuest One Business
- RKMA Market Research Handbook Series
- Student Clubs
- Entrepreneurial Students
- Stanford GSB Trust
- Alumni Community
- How to Volunteer
- Springboard Sessions
- Consulting Projects
- 2020 – 2029
- 2010 – 2019
- 2000 – 2009
- 1990 – 1999
- 1980 – 1989
- 1970 – 1979
- 1960 – 1969
- 1950 – 1959
- 1940 – 1949
- Service Areas
- ACT History
- ACT Awards Celebration
- ACT Governance Structure
- Building Leadership for ACT
- Individual Leadership Positions
- Leadership Role Overview
- Purpose of the ACT Management Board
- Contact ACT
- Business & Nonprofit Communities
- Reunion Volunteers
- Ways to Give
- Fiscal Year Report
- Business School Fund Leadership Council
- Planned Giving Options
- Planned Giving Benefits
- Planned Gifts and Reunions
- Legacy Partners
- Giving News & Stories
- Giving Deadlines
- Development Staff
- Submit Class Notes
- Class Secretaries
- Board of Directors
- Health Care
- Sustainability
- Class Takeaways
- All Else Equal: Making Better Decisions
- If/Then: Business, Leadership, Society
- Grit & Growth
- Think Fast, Talk Smart
- Spring 2022
- Spring 2021
- Autumn 2020
- Summer 2020
- Winter 2020
- In the Media
- For Journalists
- DCI Fellows
- Other Auditors
- Academic Calendar & Deadlines
- Course Materials
- Entrepreneurial Resources
- Campus Drive Grove
- Campus Drive Lawn
- CEMEX Auditorium
- King Community Court
- Seawell Family Boardroom
- Stanford GSB Bowl
- Stanford Investors Common
- Town Square
- Vidalakis Courtyard
- Vidalakis Dining Hall
- Catering Services
- Policies & Guidelines
- Reservations
- Contact Faculty Recruiting
- Lecturer Positions
- Postdoctoral Positions
- Accommodations
- CMC-Managed Interviews
- Recruiter-Managed Interviews
- Virtual Interviews
- Campus & Virtual
- Search for Candidates
- Think Globally
- Recruiting Calendar
- Recruiting Policies
- Full-Time Employment
- Summer Employment
- Entrepreneurial Summer Program
- Global Management Immersion Experience
- Social-Purpose Summer Internships
- Process Overview
- Project Types
- Client Eligibility Criteria
- Client Screening
- ACT Leadership
- Social Innovation & Nonprofit Management Resources
- Develop Your Organization’s Talent
- Centers & Initiatives
- Student Fellowships
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is the Time Value of Money?
Future value basics, calculating future value, present value basics, calculating present value, present value of a future payment, the bottom line.
- Fundamental Analysis
Understanding the Time Value of Money
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ShaunaCroome-4dc1a2fd51ac4cb39c1cd82ba1fe2d28.jpeg)
Pete Rathburn is a copy editor and fact-checker with expertise in economics and personal finance and over twenty years of experience in the classroom.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/E7F37E3D-4C78-4BDA-9393-6F3C581602EB-2c2c94499d514e079e915307db536454.jpeg)
The time value of money is a financial concept that holds that the value of a dollar today is worth more than the value of a dollar in the future. This is true because money you have now can be invested for a financial return, also the impact of inflation will reduce the future value of the same amount of money.
Key Takeaways
- The time value of money is a financial principle that states the value of a dollar today is worth more than the value of a dollar in the future.
- This philosophy holds true because money today can be invested and potentially grow into a larger amount in the future.
- The present value of a future cash flow is calculated by dividing the future cash flow by a discount factor that incorporates the amount of time that will pass and expected interest rates.
- The future value of a sum of money today is calculated by multiplying the amount of cash by a function of the expected rate of return over the expected time period.
- The time value of money is used to make strategic, long-term financial decisions such as whether to invest in a project or which cash flow sequence is most favorable.
You have won a cash prize. You have two options available to you. A) receive $10,000 now, or B) Receive $10,000 in 3 years. Which do you choose?
If you're like most people, you would choose to receive the $10,000 now. After all, three years is a long time to wait. Why would any rational person defer payment into the future when they could have the same amount of money now? For most of us, taking the money in the present is just plain instinctive. So at the most basic level, the time value of money demonstrates that all things being equal, it seems better to have money now rather than later.
But why is this? A $100 bill has the same value as a $100 bill one year from now, doesn't it? Actually, although the bill is the same, you can do much more with the money if you have it now because over time you can earn more interest on your money.
Back to our example: By receiving $10,000 today, you are poised to increase the future value of your money by investing and gaining interest over a period of time. For Option B, you don't have time on your side, and the payment received in three years would be your future value. To illustrate, we have provided a timeline:
If you are choosing Option A, your future value will be $10,000 plus any interest acquired over the three years. The future value for Option B, on the other hand, would only be $10,000. So how can you calculate exactly how much more Option A is worth, compared to Option B? Let's take a look.
Time value of money often ignores detrimental impacts to finance such as negative interest rates or capital losses. In situations where losses are known and unavoidable, negative growth rates can be used.
If you choose Option A and invest the total amount at a simple annual rate of 4.5%, the future value of your investment at the end of the first year is $10,450. We arrive at this sum by multiplying the principal amount of $10,000 by the interest rate of 4.5% and then adding the interest gained to the principal amount:
$ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × 0 . 0 4 5 = $ 4 5 0 \begin{aligned} &\$10,000 \times 0.045 = \$450 \\ \end{aligned} $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × 0 . 0 4 5 = $ 4 5 0
$ 4 5 0 + $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 = $ 1 0 , 4 5 0 \begin{aligned} &\$450 + \$10,000 = \$10,450 \\ \end{aligned} $ 4 5 0 + $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 = $ 1 0 , 4 5 0
You can also calculate the total amount of a one-year investment with a simple manipulation of the above equation:
OE = ( $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × 0 . 0 4 5 ) + $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 = $ 1 0 , 4 5 0 where: OE = Original equation \begin{aligned} &\text{OE} = ( \$10,000 \times 0.045 ) + \$10,000 = \$10,450 \\ &\textbf{where:} \\ &\text{OE} = \text{Original equation} \\ \end{aligned} OE = ( $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × 0 . 0 4 5 ) + $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 = $ 1 0 , 4 5 0 where: OE = Original equation
Manipulation = $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × [ ( 1 × 0 . 0 4 5 ) + 1 ] = $ 1 0 , 4 5 0 \begin{aligned} &\text{Manipulation} = \$10,000 \times [ ( 1 \times 0.045 ) + 1 ] = \$10,450 \\ \end{aligned} Manipulation = $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × [ ( 1 × 0 . 0 4 5 ) + 1 ] = $ 1 0 , 4 5 0
Final Equation = $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × ( 0 . 0 4 5 + 1 ) = $ 1 0 , 4 5 0 \begin{aligned} &\text{Final Equation} = \$10,000 \times ( 0.045 + 1 ) = \$10,450 \\ \end{aligned} Final Equation = $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × ( 0 . 0 4 5 + 1 ) = $ 1 0 , 4 5 0
The manipulated equation above is simply a removal of the like-variable $10,000 (the principal amount) by dividing the entire original equation by $10,000.
If the $10,450 left in your investment account at the end of the first year is left untouched and you invested it at 4.5% for another year, how much would you have? To calculate this, you would take the $10,450 and multiply it again by 1.045 (0.045 +1). At the end of two years, you would have $10,920.25.
The above calculation, then, is equivalent to the following equation:
Future Value = $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × ( 1 + 0 . 0 4 5 ) × ( 1 + 0 . 0 4 5 ) \begin{aligned} &\text{Future Value} = \$10,000 \times ( 1 + 0.045 ) \times ( 1 + 0.045 ) \\ \end{aligned} Future Value = $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × ( 1 + 0 . 0 4 5 ) × ( 1 + 0 . 0 4 5 )
Think back to math class and the rule of exponents, which states that the multiplication of like terms is equivalent to adding their exponents. In the above equation, the two like terms are (1+ 0.045), and the exponent on each is equal to 1. Therefore, the equation can be represented as the following:
Future Value = $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × ( 1 + 0 . 0 4 5 ) 2 \begin{aligned} &\text{Future Value} = \$10,000 \times ( 1 + 0.045 )^2 \\ \end{aligned} Future Value = $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × ( 1 + 0 . 0 4 5 ) 2
We can see that the exponent is equal to the number of years for which the money is earning interest in an investment. So, the equation for calculating the three-year future value of the investment would look like this:
Future Value = $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × ( 1 + 0 . 0 4 5 ) 3 \begin{aligned} &\text{Future Value} = \$10,000 \times ( 1 + 0.045 )^3 \\ \end{aligned} Future Value = $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × ( 1 + 0 . 0 4 5 ) 3
However, we don't need to keep on calculating the future value after the first year, then the second year, then the third year, and so on. You can figure it all at once, so to speak. If you know the present amount of money you have in an investment, its rate of return, and how many years you would like to hold that investment, you can calculate the future value (FV) of that amount. It's done with the equation:
FV = PV × ( 1 + i ) n where: FV = Future value PV = Present value (original amount of money) i = Interest rate per period n = Number of periods \begin{aligned} &\text{FV} = \text{PV} \times ( 1 + i )^ n \\ &\textbf{where:} \\ &\text{FV} = \text{Future value} \\ &\text{PV} = \text{Present value (original amount of money)} \\ &i = \text{Interest rate per period} \\ &n = \text{Number of periods} \\ \end{aligned} FV = PV × ( 1 + i ) n where: FV = Future value PV = Present value (original amount of money) i = Interest rate per period n = Number of periods
If you received $10,000 today, its present value would, of course, be $10,000 because the present value is what your investment gives you now if you were to spend it today. If you were to receive $10,000 in one year, the present value of the amount would not be $10,000 because you do not have it in your hand now, in the present.
To find the present value of the $10,000 you will receive in the future; you need to pretend that the $10,000 is the total future value of an amount you invested today . In other words, to find the present value of the future, $10,000, we need to find out how much we would have to invest today in order to receive that $10,000 in one year.
To calculate the present value or the amount that we would have to invest today, you must subtract the (hypothetical) accumulated interest from the $10,000. To achieve this, we can discount the future payment amount ($10,000) by the interest rate for the period. In essence, all you are doing is rearranging the future value equation above so that you may solve for present value (PV) . The above future value equation can be rewritten as follows:
PV = FV ( 1 + i ) n \begin{aligned} &\text{PV} = \frac{ \text{FV} }{ ( 1 + i )^ n } \\ \end{aligned} PV = ( 1 + i ) n FV
An alternate equation would be:
PV = FV × ( 1 + i ) − n where: PV = Present value (original amount of money) FV = Future value i = Interest rate per period n = Number of periods \begin{aligned} &\text{PV} = \text{FV} \times ( 1 + i )^{-n} \\ &\textbf{where:} \\ &\text{PV} = \text{Present value (original amount of money)} \\ &\text{FV} = \text{Future value} \\ &i = \text{Interest rate per period} \\ &n = \text{Number of periods} \\ \end{aligned} PV = FV × ( 1 + i ) − n where: PV = Present value (original amount of money) FV = Future value i = Interest rate per period n = Number of periods
Let's walk backward from the $10,000 offered in Option B. Remember, the $10,000 to be received in three years is really the same as the future value of an investment. If we had one year to go before getting the money, we would discount the payment back one year. Using our present value formula (version 2), at the current two-year mark, the present value of the $10,000 to be received in one year would be $10,000 x (1 + .045) -1 = $9569.38.
Note that if today we were at the one-year mark, the above $9,569.38 would be considered the future value of our investment one year from now.
Continuing on, at the end of the first year we would be expecting to receive the payment of $10,000 in two years. At an interest rate of 4.5%, the calculation for the present value of a $10,000 payment expected in two years would be $10,000 x (1 + .045) -2 = $9,157.30.
Of course, because of the rule of exponents, we don't have to calculate the future value of the investment every year counting back from the $10,000 investment in the third year. We could put the equation more concisely and use the $10,000 as FV. So, here is how you can calculate today's present value of the $10,000 expected from a three-year investment earning 4.5%:
$ 8 , 762.97 = $ 10 , 000 × ( 1 + . 045 ) − 3 \begin{aligned} &\$8,762.97 = \$10,000 \times ( 1 + .045 )^{-3} \\ \end{aligned} $ 8 , 7 6 2 . 9 7 = $ 1 0 , 0 0 0 × ( 1 + . 0 4 5 ) − 3
So the present value of a future payment of $10,000 is worth $8,762.97 today if interest rates are 4.5% per year. In other words, choosing Option B is like taking $8,762.97 now and then investing it for three years. The equations above illustrate that Option A is better not only because it offers you money right now but because it offers you $1,237.03 ($10,000 - $8,762.97) more in cash! Furthermore, if you invest the $10,000 that you receive from Option A, your choice gives you a future value that is $1,411.66 ($11,411.66 - $10,000) greater than the future value of Option B.
If your compounding period is less than a year, remember to divide the expected rate by the appropriate number of periods. For example, imagine a situation that uses 6% annual interest with $100 cash flow every month for one year. For this situation, you would divide the rate by 12 and use 0.50% as the discount rate. This is because the number of periods would be 12, the number of cash flow periods.
Let's up the ante on our offer. What if the future payment is more than the amount you'd receive right away? Say you could receive either $15,000 today or $18,000 in four years. The decision is now more difficult. If you choose to receive $15,000 today and invest the entire amount, you may actually end up with an amount of cash in four years that is less than $18,000.
How to decide? You could find the future value of $15,000, but since we are always living in the present, let's find the present value of $18,000. This time, we'll assume interest rates are currently 4%. Remember that the equation for present value is the following:
PV = FV × ( 1 + i ) − n \begin{aligned} &\text{PV} = \text{FV} \times ( 1 + i )^{-n} \\ \end{aligned} PV = FV × ( 1 + i ) − n
In the equation above, all we are doing is discounting the future value of an investment. Using the numbers above, the present value of an $18,000 payment in four years would be calculated as $18,000 x (1 + 0.04) -4 = $15,386.48.
From the above calculation, we now know our choice today is between opting for $15,000 or $15,386.48. Of course, we should choose to postpone payment for four years!
What Is Time Value of Money?
Time value of money is the concept that money today is worth more than money tomorrow. That is because money today can be used, invested, or grown. Therefore, $1 earned today is not the same as $1 earned one year from now because the money earned today can generate interest, unrealized gains, or unrealized losses.
How Do I Calculate Time Value of Money?
The time value of money has several different calculations depending on when the cash flow is being received and in which direction you want to value money. The direction depends on whether you want to know the present value (the value today) or the future value (the value at a date in the future).
In addition, there are different formulas depending on the cash flow. You can either calculate the present value or future value of a single lump sum or a series of payments (i.e., $5,000 received every year for the next 5 years).
In general, you calculate the time value of money by assessing a discount factor of future value factor to a set of cash flows. The factor is determined by the number of periods the cash flow will impacted as well as the expected rate of interest for the period.
What Is the Difference Between Present Value and Future Value?
Present value is the time value of money for a series of cash flow that calculates the value of the money today. For example, if you want to find the value of $1,000 to be received one year from now or the value of $2,500 to be received each month for the next two years, you are trying to find the present value.
Alternatively, future value is time value of money concept of finding the value of a series of cash flows at a point in time in the future. You'd be calculating the future value if you want to know what your $500 may be worth in 10 years. You'd also be finding the future value if you want to find out what your retirement balance will be if you contribute $250 every month for 10 years.
Why Does Time Value of Money Matter?
The time value of money helps decision-makers select the best option. Time value of money equalizes options based on timing, as absolute dollar amounts spanning different time spans should not be valued equally.
Businesses often use time value of money to compare projects with varying cashflows. Businesses also use time value of money to determine whether a project with an initial cash outflow and subsequent cash inflows will be profitable. Companies may also be required to use time value of money principles for external reporting requirements.
Individual investors use time value of money to better understand the true value of their investments and obligations over time. The time value of money is used to calculate what an investor's retirement balance will be in the future.
These calculations demonstrate that time literally is money—the value of the money you have now is not the same as it will be in the future and vice versa. So, it is important to know how to calculate the time value of money so that you can distinguish between the worth of money related options offered to you now and in the future. These options could be investment opportunities, loan transactions, mortgage payment options, or even charity related donations. Whenever, money coming or going, at some point in time, is involved, time value of money should be considered.
Financial Accounting Standards Board. " Leases (Topic 842). "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/investing19-5bfc2b8f4cedfd0026c1194c.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Time Value of Money Exemplification Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Decisions that utilized the concept of time value of money, reference list.
According to Kuhlemeyer (2004), time value of money means that money at hand today is worth more than the same amount at a future date. It is the amount by which money will grow to in the future. In simpler terms, it is the net increase or decrease in the amount of money. He affirms that the concept helps to determine the amount that one will earn in the future.
This concept results from the existence of charges due to the use of other people money. There are different sections under time value of money. According to Kuhlemeyer (2004), the concept of simple interest, compound interest, compounding and discounting are used to assess the time value of money.
The process of growing money from its present value to its future value at a given duration and interest rate is known as compounding. Discounting is the process of calculating how much future value of money equal to at present.
The instance was when one of my business partners owed me money which I had lent to him as a loan. The person was reluctant to repay the money, and I took him to a law court. After the careful analysis of the evidence that I presented, the case was ruled in my favor and the judgment specified that the loan should be repaid to me.
I further made a request that the borrower should not repay the exact amount that I lent. In that instance, I was claiming that the amount I lent should be repaid with an interest. An agreement had to be entered to determine the amount of interest that was payable to me. The rate of interest was determined by considering the prevailing economic conditions, and it was determined as the prevailing market interest rate at that time.
Compounding was done on the amount that I had lent out using the market rate over the duration of time the person held my money. As a result, the amount of money that I received increased tremendously.
Computation was done using the future value annuity factor, considering that variables like principal, interest rate and duration were known. Having applied the concept of time value money, I was able to obtain extra income from that transaction. If I had claimed the original amount I had lent out, I would have obtained relatively less.
Another instance where the concept of time value of money was applied was during a rotary competition in my home country. The winners were to be awarded a total of half a million shillings. It happened that I was declared a winner among other people. As the winner claimed their money, I was reluctant since I had a decision to grow the money so that it could increase.
An agreement was entered between the rotary committee and me so that they could be paying me as an annuity at the end of every month. This was advantageous move as the money was earning me interest at the prevailing interest rate. The compounding formula was applied to determine the amount at the end of every month. If I had claimed the money as a lump sum, then I could have obtained a lesser amount than what I finally got.
Kuhlemeyer, A. (2004). Fundamentals of financial management . USA, Pearson Carroll College: Waukesha Pearson Education Limited.
- Financial Performance of Covidien PLC
- Option Theory in Finance
- Financial Compounding and Net Present Value
- Adaptive Reuse: Compounding Pharmacy in Las Vegas City
- DC Stepper Motors: Power Element for Control
- Planning Financial Strategies
- Financial Management: Johns Hopkins Hospital
- Corporate Financing: Long Term and Short Term
- Life-Cycle Costing in the UAE Private and Public Sectors
- Financial Markets After Terrorist Assault and The Enron Financial Outrage
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, June 26). Time Value of Money. https://ivypanda.com/essays/time-value-of-money/
"Time Value of Money." IvyPanda , 26 June 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/time-value-of-money/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Time Value of Money'. 26 June.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Time Value of Money." June 26, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/time-value-of-money/.
1. IvyPanda . "Time Value of Money." June 26, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/time-value-of-money/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Time Value of Money." June 26, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/time-value-of-money/.
Home — Essay Samples — The time value of money
The Time Value of Money
About this sample

Words: 1248 |
Published: Jul 10, 2019
Words: 1248 | Pages: 3 | 7 min read
Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Money: Short Essay on Value of Money
Value of Money
The Value of Money has always played a key role in the human world. Money has changed it faces, changed its shape and size, changed its colour and usage, but the Value and Central Role of Money has always stayed the same.
Money is the means or the currency used for exchange of goods, or for the purpose of business or for the purpose of trade and commerce or for the purpose of valuing a particular goods or service. All these exchanges and valuations are central to our everyday existence and hence the Value of Money is also central to our everyday existence.
Applications of the Value of Money in daily life: We receive Money or earn Money by engaging in a particular profession, career or business. We get paid for the work that we do. This can be physical or intellectual work. The Value of our Work is evaluated by the Value of the Money that we receive for it. We spend this money to buy Services and Goods that we need for our daily life. These include a house, a car, clothes, food, drinks, water, electricity, household goods, household electronics like TV, Refrigerator, etc. These also include services like food delivery, barber shop, legal services, medical consultation, etc. All of these we buy with the Value of the Money we have. All of these have a Value tag attached to them, and if we have that Money we can buy them, otherwise not. So what we can afford and how we live our daily life directly depends on the Value of the Money we have. To increase the level of our lifestyle we need to increase the Value of the Money we possess. The entire human race spends most of its lifespan on increasing and accumulating more Money so that the Value it can add to one’s life increases.
Dimensions of the Value of Money: There are Material, Emotional and Spiritual dimensions to the real Value of Money in our lives. The material dimension determines how many material possessions we can have. The emotional dimension determines the dreams we associate with our Money. The Spiritual dimension determines the satisfaction we derive from our Money.
Conclusion: Follow the material Value of Money so that you can earn a successful life, but also realise its deeper Value so that it can give you inner satisfaction.
Newspaper: Short Essay on Importance of Newspaper in Our Daily Life
Newspaper: Short Essay on Value of Newspaper
Abraham Lincoln: From Humble Beginnings to Legendary Leadership
Vikram Sarabhai: The Visionary Behind India’s Space Program
Essay on Mahavir Jayanti for all Class in 100 to 500 Words in English
Essay on Indian Heritage for Students and Children
Essay on Gender Equality
Eassy on Good Habits
Eassy on saving for future
Essay – My Dream
Pencil: An Essay on Pencil
Short Essay on Pencil
Comments are closed.
Welcome, Login to your account.
Recover your password.
A password will be e-mailed to you.
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
Prize-winning essays on the future of money
To read this article for free, register now.
Once registered, you can: • Read free articles • Get our Editor's Digest and other newsletters • Follow topics and set up personalised events • Access Alphaville: our popular markets and finance blog
Explore more offers.
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism. Cancel anytime during your trial.
FT Digital Edition
Today's FT newspaper for easy reading on any device. This does not include ft.com or FT App access.
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
Standard Digital
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- FT App on Android & iOS
- FT Edit app
- FirstFT: the day's biggest stories
- 20+ curated newsletters
- Follow topics & set alerts with myFT
- FT Videos & Podcasts
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.

Essay on Money in English for Children and Students

Table of Contents
Essay on Money: Money is the medium used by people to buy required goods and services. It is used as the source to fulfill basic needs and is also a source of comfort in life. Money is the most important source to live a healthy and prosperous life; however, it cannot be compared with the significance of love and care. Both have their own importance and benefits. Nevertheless, money is a useful and necessary commodity to live contentedly disposing all your usual liabilities towards your family and loved ones.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
Long and Short Essay on Money in English
We have provided some simply written essay on money to help your kids to do better in their essay writing competition.
These Money Essay are written in easy English so that student of any class can easily understand it and also reiterate it or write it down, whenever required.
We have divided following essays under long and short essay on money in English according to the need, to help your kids to do better in their school competitions.
These essay on money will prove useful in your school assignments or general discussion with your family and friends.
Money Essay 1 (100 words)
Money is the most basic requirement of the life without which one cannot fulfill his basic needs and requirements of the daily routine. We can never compare the importance of the money with the importance of love or care. When one need money, love cannot fulfill this requirement and if one need love, money cannot fulfill this requirement.
Both are highly required for the healthy life but they have their significance and importance separately. Both are required by us on urgent basis so we cannot rank both on the same scale. We need money everywhere such as to eat food, to drink water or milk, to see TV, news, subscribe newspaper, wear clothe, get admission and many more requirements.

Money Essay 2 (150 words)
Money is the basic requirement of the life without which one cannot imagine a healthy and peaceful life. We need money even buying a little needle. In the modern time, where growth of civilization is going very fast and following western culture, we need more money because of the increasing prices of everything. Earlier there was a system called barter system in which one was allowed to exchange things to get goods however, in the modern one need only money to buy everything.
The importance of money is increasing day by day as the living has become so costly. The significance of money has increased to a great extent in the field of production, consumption, exchange, distribution, public finance and etc. It plays a very crucial role in determining the input, income, employment, output, general price level of anything, etc.
Money Essay 3 (200 words)
In such a costly and competitive society and world, no one of us can live without money. We need money to fulfil our basic needs of the life such as buying food, and other many basic necessities of life which are almost impossible to buy without money. People in the society who are rich and have property are looked as honourable and respectful person of the society however a poor person is seen as hatred without any good impression.
Money increases the position of the person in the society and gives good impression to him. All of us want to be rich by earning more money through good job or business in order to fulfil all the increasing demands of the modern age. However, only few people get this chance of completing their dreams of being a millionaire.
So, money is the thing of great importance all through the life. Money is required by everyone whether he/she is rich or poor ad living in urban areas or rural areas. People in the urban areas are earning more money than the people living in backward or rural areas as the people of the urban areas have more access to the technologies and get more opportunity because of the easy sources.
Essay on Jan Dhan Yojana
Money Essay 4 (250 words)
Money is very much required thing in the life however; it cannot buy things like time, love and true care. It can only fulfil the outer needs of the person and not the inner needs like true love. Now-a-days, everything has become so costly but necessary to buy for living a simple life. And what if we have no money, either we would die or suffer more if saved.
Money has capability to buy anything virtually and helps us a lot throughout the life. By taking the importance of the money in our life we should never destroy or waste the money without any purpose. We should not compare the money and love because both are required separately to run a successful life.
In this competitive world, everyone wants to get good study with higher education from the popular college and university to get good job in order to earn more money. A person needs more money to fulfil the requirement of the all members of the family especially one who is only working person of the family.
He or she needs to fulfil the eating, clothing and living requirements of the family members and for that money is required. Rich people of the society are given particular recognition and popularity however poor people live their life by arranging just food for two times a day. All the changes and differences are just because of the money.

Money Essay 5 (300 words)
Money is really a very important thing for the human beings to lead their life in the satisfactory way. Unlike animals and plants, we need more money everywhere. In order to live in the society, we need to maintain our status and position in the society for which we need money. In order to eat food or drink water, wear cloth, get admission to the school, take medicine or go to the hospital and other many activities we need lots of money. Now the topic arise is, where we got such required money. We need to get higher level study and do hard works to get good job or open our own business which requires more skill and confidence.
Earlier the condition of poor people was very poor because of the pressure of the rich people. They were not helping the poor people and use them only as a servant on the very low salary. However the condition of the poor people has become good as the rule and regulations of the government as been change in order to equalize the condition of both. Now everyone has equal rights to study higher and get good job. Many people understand that money is the origin of the evil in the mind however I do not think so because thinking is the process of human mind and not the creation of money.
I understand and believe that money is the most important key of happiness gifted by the God. It is the human mind to take anything in different ways. Some people take it only to fulfil their physical needs and they never take it heartily however some people understand everything to the money and they can do anything for getting the money such murder, corruption, underworld work, smuggling, promoting bribe, etc.
Money Essay 6 (400 words)
There is no any doubt that money is so essential for our healthy living. Money is almost everything for us to live a life and maintain the good stats in the society. It is the money which fulfils the need of bringing necessary comforts and amenities of the life. If one has money, he/she can get anything in his/her life. It is the money which helps us in developing good personality, improving confidence, makes us able to creditworthiness, improving capacity, increasing capabilities and enhancing our courage to a great level. Without money we feel helpless and alone in this world where no one is ready to help and assist. In the current materialistic world, money is very important and powerful thing without which one cannot live and survive.
Now-a-days, in order to earn more money in wrong ways, bad people are taking help of corruption, bribe, smuggling, murder rich people of the society, and other callous activities by degrading the moral and ethical values of the humanity. Lazy people follow wrong ways to earn money as they understand that these ways are simple and easy however it is not true. One can earn more money in less time and effort but not for long; surely he would be lost in the near future as he is following wrong and weak way. The people who are earning money by following all the rules of humanity earn less money but for long time and they become the high status personality of the society.
People doing corruption save their money as a black money in other countries to keep hidden from the common public and use that money for bad works or increasing their physical luxury. However, common people of the society respects a lot to the people earning money using wrong techniques as they have fear of them and little bit greediness that they can get some money in return whenever required by giving them respect. They are generally called as the bhai or dada or don. Money cannot buy or stay the time as well as cannot give true love and care however highly required by all of us to run the life on the right path. It cannot give time and love however gives happiness, confidence, satisfaction, feeling of well being mentally and physically, makes life easy by solving all the difficulties, and many more.
All the essays on money given above are written by the professional content writer to help students in getting fulfilled their needs and requirements. Essay on money is generally assigned to the students to write something in their own way. Money essay is given under the category of general essay.
Frequently Asked Questions on Money
Who found money.
Money, in various forms like barter or trade, has existed since ancient times. The first coined money is believed to have been created by the Lydians, in what is now Turkey, around 600 BC.
Who said money is life?
This specific quote isn't attributed to a singular famous person. Various interpretations and contexts might exist, but the idea that money plays a significant role in many aspects of life is widely acknowledged.
What is money quotes?
A popular quote about money is, Money can't buy happiness, but it certainly helps.
What is the nature of money?
The nature of money is abstract. It has no intrinsic value but is accepted as a medium of exchange. Its value is determined by trust and the backing of an authority, like a government.
What is the value of money in life?
The value of money in life goes beyond purchasing power. It provides security, freedom, and opportunities, but isn't the sole determinant of happiness or success.
What is the importance of money?
Money is essential as it enables trade, provides financial security, meets daily needs, and offers the potential for a better life. It's a measure of one's ability to afford services and products.
What is money in own words?
Money is a tool that facilitates trade, allowing us to purchase what we need or desire. It represents value and can be saved, spent, or invested.
What is the few lines on money?
Money is a medium of exchange, used to buy goods and services. It acts as a unit of account, a store of value, and is universally accepted in transactions.
Related content

Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
Select your Course
Please select class.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The Value Of Money In Our Life Essay. 761 Words4 Pages. Money is the most important thing of material value in our lives, and as such, it became an integral part of our lives as well. It is a proven fact that money can buy you happiness, according the recent scientific studies. As a matter of fact, the more the person earns, the more satisfied ...
10 Lines on Value of Money; 250 Words Essay on Value of Money The Concept of Value. Money, a medium of exchange, has transformed from barter to digital currencies. It holds a value that is universally acknowledged, enabling people to acquire goods and services. However, the value of money isn't merely its purchasing power.
100 Words Essay On Importance Of Money. Money is a critical factor in our lives as it helps us to meet our basic needs and desires. It provides us with a sense of security and helps us to plan for the future. Money enables us to buy food, shelter, and clothing, and to access healthcare and education. Additionally, it provides us with the means ...
500+ Words Essay on Money. Money is an essential need to survive in the world. In today's world, almost everything is possible with money. Moreover, you can fulfill any of your dreams by spending money. As a result, people work hard to earn it.
5 Top Examples On Essay About Money. 1. Essay on Money by Prasanna. "Imagine the world without money. We will eventually come to a point where we will be asking questions like "what's the point of life". Hope and goals are some of the important things that will keep a man going in life.
Money, in and of itself, cannot buy happiness, but it can provide a means to the things we value in life. Money is a big part of our lives, our identities, and perhaps our well-being.
In this essay, we delve into the multifaceted nature of money, exploring its origins, functions, and profound impact on individuals and society. ... Measurement of Value: Money provides a common unit of account, allowing for the standardized measurement of the value of different goods and services. This function enables individuals to compare ...
However, its value lies in its ability to enable us to achieve our goals, not in its mere accumulation. 500 Words Essay on Importance of Money Introduction. Money, often seen as a simple medium of exchange, plays a pivotal role in modern society. Its importance transcends mere transactions, permeating every aspect of our lives - from the ...
February 13, 2024 by Prasanna. Essay on Money: The concept of money was invented somewhere in 5000 B.C by a few traders in Western Europe. Ever since the invention, different countries have adopted it and started printing their own money with specific values, which was usually backed by gold. But before money was invented, trading used to ...
Money is essentially a good, so as such is ruled by the axioms of supply and demand. The value of any good is determined by its supply and demand and the supply and demand for other goods in the economy. A price for any good is the amount of money it takes to get that good. Inflation occurs when the price of goods increases—in other words ...
Can Money Buy Happiness: Sharing Persuasive Personal Viewpoint. 11. Budgeting and Types of Personal Budget. 12. Budgeting Technique to Build a Stable Financial Future. 13. The Ascent of Money: Is Money the Root of All Evil. 14. Gold: One of the Most Expensive Metals on Earth. 15. The Impacts Of Physical Cash And Developing Into A Cashless ...
A young man reflects on his own thrift, while a young woman accepts a gift of ice cream and pays a price for it. Finally, caregiving becomes a source of pride for someone young enough to need ...
500+ Words Essay on Money. Money is any object or record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts which also acts as a standard of deferred payments. The main functions of money are distinguished as: a medium of exchange, a unit of account and a store of value. The money supply of a country consists of ...
This essay will delve into the complex relationship between money and happiness, examining various perspectives and evidence to ultimately determine whether money truly brings happiness or if there are other factors that contribute to our overall well-being.
The Complete History of Money and Its Origins. 3 pages / 1372 words. There is much debate between the complete history of money and its origins. For the relevance of this essay, we will disregard the debate and discuss the history of money and barter only in regards to money economic value and use.
Read this essay to learn about the meaning, functions and role of money. Meaning of Money: Money has been defined differently by different economists. Some, like F.A. Walker, define it in terms of its functions, while others like G.D.H. Cole, J.M. Keynes, Seligman and D.H. Robertson lay stress on the 'general acceptability' aspect of money. According to Prof. D.H. Robertson, "anything which is ...
Firstly, money is generally accepted amongst numerous individuals. This makes it to be used as a medium of exchange. Additionally, by acting as a medium of exchange, money plays a very important role in facilitating transactions. This is made possible by the fact that individuals can use money to measure the value of a particular commodity.
June 1, 2023 by Laxmi. Money Essay: Money is a vital wellspring of everyday routine to experience a solid and satisfying life, despite the fact that it can not measure up to adore and mind. Both have their own significance and benefit. We are giving articles on Money to partake in a paper composing contest in basic and basic words here.
If we want a more equitable world, then we need to consider the different ways people value money. April 03, 2024. ... and in this paper, if you like, in this sequence of papers and research agenda that I started with my fantastic co-authors, Piotr Dworczak and Scott Kominers basically, our idea was people are doing it out there in the world ...
The time value of money is a financial principle that states the value of a dollar today is worth more than the value of a dollar in the future. This philosophy holds true because money today can ...
The Value Of Money English Literature Essay. Probably, most people have lived situations which money played a fundamental role. Maybe an illness like cancer is an evident reason to need money. Also, there are basic needs of daily life, such as food, house, studies, locomotion, clothes, etc. Those needs require spending money to cover them to ...
Introduction. According to Kuhlemeyer (2004), time value of money means that money at hand today is worth more than the same amount at a future date. It is the amount by which money will grow to in the future. In simpler terms, it is the net increase or decrease in the amount of money. He affirms that the concept helps to determine the amount ...
The TVM theory primarily posits that the value of money in hand today is worth much more than the value of the similar amount in the future (Scott & Moore, 2015). This is because money received today can be invested to generate earning, i.e., interest, as opposed to delaying such amount into the future (Scott & Moore, 2015).
Value of Money The Value of Money has always played a key role in the human world. Money has changed it faces, changed its shape and size, changed its colour and usage, but the Value and Central Role of Money has always stayed the same. Money is the means or the currency used for exchange […]
Artistic pieces are not only creatively enriching society, but giving money a new ability to store value, regardless of a currency's worth. The future may not necessarily be free of cash payments.
Money Essay 4 (250 words) Money is very much required thing in the life however; it cannot buy things like time, love and true care. It can only fulfil the outer needs of the person and not the inner needs like true love. Now-a-days, everything has become so costly but necessary to buy for living a simple life.