

The History of Homework: Why Was it Invented and Who Was Behind It?
- By Emily Summers
- February 14, 2020
Homework is long-standing education staple, one that many students hate with a fiery passion. We can’t really blame them, especially if it’s a primary source of stress that can result in headaches, exhaustion, and lack of sleep.
It’s not uncommon for students, parents, and even some teachers to complain about bringing assignments home. Yet, for millions of children around the world, homework is still a huge part of their daily lives as students — even if it continues to be one of their biggest causes of stress and unrest.
It makes one wonder, who in their right mind would invent such a thing as homework?
Who Invented Homework?
Pliny the younger: when in ancient rome, horace mann: the father of modern homework, the history of homework in america, 1900s: anti-homework sentiment & homework bans, 1930: homework as child labor, early-to-mid 20th century: homework and the progressive era, the cold war: homework starts heating up, 1980s: homework in a nation at risk, early 21 st century, state of homework today: why is it being questioned, should students get homework pros of cons of bringing school work home.

Online, there are many articles that point to Roberto Nevilis as the first educator to give his students homework. He created it as a way to punish his lazy students and ensure that they fully learned their lessons. However, these pieces of information mostly come from obscure educational blogs or forum websites with questionable claims. No credible news source or website has ever mentioned the name Roberto Nevilis as the person who invented homework . In fact, it’s possible that Nevilis never even existed.
As we’re not entirely sure who to credit for creating the bane of students’ existence and the reasons why homework was invented, we can use a few historical trivia to help narrow down our search.
Mentions of the term “homework” date back to as early as ancient Rome. In I century AD, Pliny the Younger , an oratory teacher, supposedly invented homework by asking his followers to practice public speaking at home. It was to help them become more confident and fluent in their speeches. But some would argue that the assignment wasn’t exactly the type of written work that students have to do at home nowadays. Only introverted individuals with a fear of public speaking would find it difficult and stressful.
It’s also safe to argue that since homework is an integral part of education, it’s probable that it has existed since the dawn of learning, like a beacon of light to all those helpless and lost (or to cast darkness on those who despise it). This means that Romans, Enlightenment philosophers, and Middle Age monks all read, memorized, and sang pieces well before homework was given any definition. It’s harder to play the blame game this way unless you want to point your finger at Horace Mann.
In the 19 th century, Horace Mann , a politician and educational reformer had a strong interest in the compulsory public education system of Germany as a newly unified nation-state. Pupils attending the Volksschulen or “People’s Schools” were given mandatory assignments that they needed to complete at home during their own time. This requirement emphasized the state’s power over individuals at a time when nationalists such as Johann Gottlieb Fichte were rallying support for a unified German state. Basically, the state used homework as an element of power play.
Despite its political origins, the system of bringing school assignments home spread across Europe and eventually found their way to Horace Mann, who was in Prussia at that time. He brought the system home with him to America where homework became a daily activity in the lives of students.
Despite homework being a near-universal part of the American educational experience today, it hasn’t always been universally accepted. Take a look at its turbulent history in America.
In 1901, just a few decades after Horace Mann introduced the concept to Americans, homework was banned in the Pacific state of California . The ban affected students younger than 15 years old and stayed in effect until 1917.
Around the same time, prominent publications such as The New York Times and Ladies’ Home Journal published statements from medical professionals and parents who stated that homework was detrimental to children’s health.
In 1930, the American Child Health Association declared homework as a type of child labor . Since laws against child labor had been passed recently during that time, the proclamation painted homework as unacceptable educational practice, making everyone wonder why homework was invented in the first place.
However, it’s keen to note that one of the reasons why homework was so frowned upon was because children were needed to help out with household chores (a.k.a. a less intensive and more socially acceptable form of child labor).
During the progressive education reforms of the late 19 th and early 20 th centuries, educators started looking for ways to make homework assignments more personal and relevant to the interests of individual students. Maybe this was how immortal essay topics such as “What I Want to Be When I Grow Up” and “What I Did During My Summer Vacation” were born.
After World War II, the Cold War heated up rivalries between the U.S. and Russia. Sputnik 1’s launch in 1957 intensified the competition between Americans and Russians – including their youth.
Education authorities in the U.S. decided that implementing rigorous homework to American students of all ages was the best way to ensure that they were always one step ahead of their Russian counterparts, especially in the competitive fields of Math and Science.
In 1986, the U.S. Department of Education’s pamphlet, “What Works,” included homework as one of the effective strategies to boost the quality of education. This came three years after the National Commission on Excellence in Education published “ Nation at Risk: The Imperative for Educational Reform .” The landmark report lambasted the state of America’s schools, calling for reforms to right the alarming direction that public education was headed.
Today, many educators, students, parents, and other concerned citizens have once again started questioning why homework was invented and if it’s still valuable.
Homework now is facing major backlash around the world. With more than 60% of high school and college students seeking counselling for conditions such as clinical depression and anxiety, all of which are brought about by school, it’s safe to say that American students are more stressed out than they should be.
After sitting through hours at school, they leave only to start on a mountain pile of homework. Not only does it take up a large chunk of time that they can otherwise spend on their hobbies and interests, it also stops them from getting enough sleep. This can lead to students experiencing physical health problems, a lack of balance in their lives, and alienation from their peers and society in general.
Is homework important and necessary ? Or is it doing more harm than good? Here some key advantages and disadvantages to consider.
- It encourages the discipline of practice
Using the same formula or memorizing the same information over and over can be difficult and boring, but it reinforces the practice of discipline. To master a skill, repetition is often needed. By completing homework every night, specifically with difficult subjects, the concepts become easier to understand, helping students polish their skills and achieve their life goals.
- It teaches students to manage their time
Homework goes beyond just completing tasks. It encourages children to develop their skills in time management as schedules need to be organized to ensure that all tasks can be completed within the day.
- It provides more time for students to complete their learning process
The time allotted for each subject in school is often limited to 1 hour or less per day. That’s not enough time for students to grasp the material and core concepts of each subject. By creating specific homework assignments, it becomes possible for students to make up for the deficiencies in time.
- It discourages creative endeavors
If a student spends 3-5 hours a day on homework, those are 3-5 hours that they can’t use to pursue creative passions. Students might like to read leisurely or take up new hobbies but homework takes away their time from painting, learning an instrument, or developing new skills.
- Homework is typically geared toward benchmarks
Teachers often assign homework to improve students’ test scores. Although this can result in positive outcomes such as better study habits, the fact is that when students feel tired, they won’t likely absorb as much information. Their stress levels will go up and they’ll feel the curriculum burnout.
- No evidence that homework creates improvements
Research shows that homework doesn’t improve academic performance ; it can even make it worse. Homework creates a negative attitude towards schooling and education, making students dread going to their classes. If they don’t like attending their lessons, they will be unmotivated to listen to the discussions.
With all of the struggles that students face each day due to homework, it’s puzzling to understand why it was even invented. However, whether you think it’s helpful or not, just because the concept has survived for centuries doesn’t mean that it has to stay within the educational system.
Not all students care about the history of homework, but they all do care about the future of their educational pursuits. Maybe one day, homework will be fully removed from the curriculum of schools all over the world but until that day comes, students will have to burn the midnight oil to pass their requirements on time and hopefully achieve their own versions of success.
About the Author
Emily summers.

How Summer Camp Fosters Social Skills

6 reasons to read to your child regularly at home

Things to Know About Developmental Disability Services

Roofing 101 Essential Education for Future Industry Professionals

Debunking the Myth of Roberto Nevilis: Who Really Invented Homework?

Is the D Important in Pharmacy? Why Pharm.D or RPh Degrees Shouldn’t Matter

How to Email a Professor: Guide on How to Start and End an Email Conversation

Everything You Need to Know About Getting a Post-Secondary Education

Grammar Corner: What’s The Difference Between Analysis vs Analyses?

History Cooperative
The Homework Dilemma: Who Invented Homework?
The inventor of homework may be unknown, but its evolution reflects contributions from educators, philosophers, and students. Homework reinforces learning, fosters discipline, and prepares students for the future, spanning from ancient civilizations to modern education. Ongoing debates probe its balance, efficacy, equity, and accessibility, prompting innovative alternatives like project-based and personalized learning. As education evolves, the enigma of homework endures.
Table of Contents
Who Invented Homework?
While historical records don’t provide a definitive answer regarding the inventor of homework in the modern sense, two prominent figures, Roberto Nevelis of Venice and Horace Mann, are often linked to the concept’s early development.
Roberto Nevelis of Venice: A Mythical Innovator?
Roberto Nevelis, a Venetian educator from the 16th century, is frequently credited with the invention of homework. The story goes that Nevelis assigned tasks to his students outside regular classroom hours to reinforce their learning—a practice that aligns with the essence of homework. However, the historical evidence supporting Nevelis as the inventor of homework is rather elusive, leaving room for skepticism.
While Nevelis’s role remains somewhat mythical, his association with homework highlights the early recognition of the concept’s educational value.
Horace Mann: Shaping the American Educational Landscape
Horace Mann, often regarded as the “Father of American Education,” made significant contributions to the American public school system in the 19th century. Though he may not have single-handedly invented homework, his educational reforms played a crucial role in its widespread adoption.
Mann’s vision for education emphasized discipline and rigor, which included assigning tasks to be completed outside of the classroom. While he did not create homework in the traditional sense, his influence on the American education system paved the way for its integration.
The invention of homework was driven by several educational objectives. It aimed to reinforce classroom learning, ensuring knowledge retention and skill development. Homework also served as a means to promote self-discipline and responsibility among students, fostering valuable study habits and time management skills.
Why Was Homework Invented?
The invention of homework was not a random educational practice but rather a deliberate strategy with several essential objectives in mind.
Reinforcing Classroom Learning
Foremost among these objectives was the need to reinforce classroom learning. When students leave the classroom, the goal is for them to retain and apply the knowledge they have acquired during their lessons. Homework emerged as a powerful tool for achieving this goal. It provided students with a structured platform to revisit the day’s lessons, practice what they had learned, and solidify their understanding.
Homework assignments often mirrored classroom activities, allowing students to extend their learning beyond the confines of school hours. Through the repetition of exercises and tasks related to the curriculum, students could deepen their comprehension and mastery of various subjects.
Fostering Self-Discipline and Responsibility
Another significant objective behind the creation of homework was the promotion of self-discipline and responsibility among students. Education has always been about more than just the acquisition of knowledge; it also involves the development of life skills and habits that prepare individuals for future challenges.
By assigning tasks to be completed independently at home, educators aimed to instill valuable study habits and time management skills. Students were expected to take ownership of their learning, manage their time effectively, and meet deadlines—a set of skills that have enduring relevance in contemporary education and beyond.
Homework encouraged students to become proactive in their educational journey. It taught them the importance of accountability and the satisfaction of completing tasks on their own. These life skills would prove invaluable in their future endeavors, both academically and in the broader context of their lives.
When Was Homework Invented?
The roots of homework stretch deep into the annals of history, tracing its origins to ancient civilizations and early educational practices. While it has undergone significant evolution over the centuries, the concept of extending learning beyond the classroom has always been an integral part of education.
Earliest Origins of Homework and Early Educational Practices
The idea of homework, in its most rudimentary form, can be traced back to the earliest human civilizations. In ancient Egypt , for instance, students were tasked with hieroglyphic writing exercises. These exercises served as a precursor to modern homework, as they required students to practice and reinforce their understanding of written language—an essential skill for communication and record-keeping in that era.
In ancient Greece , luminaries like Plato and Aristotle advocated for the use of written exercises as a tool for intellectual development. They recognized the value of practice in enhancing one’s knowledge and skills, laying the foundation for a more systematic approach to homework.
The ancient Romans also played a pivotal role in the early development of homework. Young Roman students were expected to complete assignments at home, with a particular focus on subjects like mathematics and literature. These assignments were designed to consolidate their classroom learning, emphasizing the importance of practice in mastering various disciplines.
READ MORE: Who Invented Math? The History of Mathematics
The practice of assigning work to be done outside of regular school hours continued to evolve through various historical periods. As societies advanced, so did the complexity and diversity of homework tasks, reflecting the changing needs and priorities of education.
The Influence of Educational Philosophers
While the roots of homework extend to ancient times, the ideas of renowned educational philosophers in later centuries further contributed to its development. John Locke, an influential thinker of the Enlightenment era, believed in a gradual and cumulative approach to learning. He emphasized the importance of students revisiting topics through repetition and practice, a concept that aligns with the principles of homework.
Jean-Jacques Rousseau, another prominent philosopher, stressed the significance of self-directed learning. Rousseau’s ideas encouraged the development of independent study habits and a personalized approach to education—a philosophy that resonates with modern concepts of homework.
Homework in the American Public School System
The American public school system has played a pivotal role in the widespread adoption and popularization of homework. To understand the significance of homework in modern education, it’s essential to delve into its history and evolution within the United States.
History and Evolution of Homework in the United States
The late 19th century marked a significant turning point for homework in the United States. During this period, influenced by educational reforms and the growing need for standardized curricula, homework assignments began to gain prominence in American schools.
Educational reformers and policymakers recognized the value of homework as a tool for reinforcing classroom learning. They believed that assigning tasks for students to complete outside of regular school hours would help ensure that knowledge was retained and skills were honed. This approach aligned with the broader trends in education at the time, which aimed to provide a more structured and systematic approach to learning.
As the American public school system continued to evolve, homework assignments became a common practice in classrooms across the nation. The standardization of curricula and the formalization of education contributed to the integration of homework into the learning process. This marked a significant departure from earlier educational practices, reflecting a shift toward more structured and comprehensive learning experiences.
The incorporation of homework into the American education system not only reinforced classroom learning but also fostered self-discipline and responsibility among students. It encouraged them to take ownership of their educational journey and develop valuable study habits and time management skills—a legacy that continues to influence modern pedagogy.
Controversies Around Homework
Despite its longstanding presence in education, homework has not been immune to controversy and debate. While many view it as a valuable educational tool, others question its effectiveness and impact on students’ well-being.
The Homework Debate
One of the central controversies revolves around the amount of homework assigned to students. Critics argue that excessive homework loads can lead to stress, sleep deprivation, and a lack of free time for students. The debate often centers on striking the right balance between homework and other aspects of a student’s life, including extracurricular activities, family time, and rest.
Homework’s Efficacy
Another contentious issue pertains to the efficacy of homework in enhancing learning outcomes. Some studies suggest that moderate amounts of homework can reinforce classroom learning and improve academic performance. However, others question whether all homework assignments contribute equally to learning or whether some may be more beneficial than others. The effectiveness of homework can vary depending on factors such as the student’s grade level, the subject matter, and the quality of the assignment.
Equity and Accessibility
Homework can also raise concerns related to equity and accessibility. Students from disadvantaged backgrounds may have limited access to resources and support at home, potentially putting them at a disadvantage when it comes to completing homework assignments. This disparity has prompted discussions about the role of homework in perpetuating educational inequalities and how schools can address these disparities.
Alternative Approaches to Learning
In response to the controversies surrounding homework, educators and researchers have explored alternative approaches to learning. These approaches aim to strike a balance between reinforcing classroom learning and promoting holistic student well-being. Some alternatives include:
Project-Based Learning
Project-based learning emphasizes hands-on, collaborative projects that allow students to apply their knowledge to real-world problems. This approach shifts the focus from traditional homework assignments to engaging, practical learning experiences.
Flipped Classrooms
Flipped classrooms reverse the traditional teaching model. Students learn new material at home through video lectures or readings and then use class time for interactive discussions and activities. This approach reduces the need for traditional homework while promoting active learning.
Personalized Learning
Personalized learning tailors instruction to individual students’ needs, allowing them to progress at their own pace. This approach minimizes the need for one-size-fits-all homework assignments and instead focuses on targeted learning experiences.
The Ongoing Conversation
The controversies surrounding homework highlight the need for an ongoing conversation about its role in education. Striking the right balance between reinforcing learning and addressing students’ well-being remains a complex challenge. As educators, parents, and researchers continue to explore innovative approaches to learning, the role of homework in the modern educational landscape continues to evolve. Ultimately, the goal is to provide students with the most effective and equitable learning experiences possible.
Unpacking the Homework Enigma
Homework, without a single inventor, has evolved through educators, philosophers, and students. It reinforces learning, fosters discipline and prepares students. From ancient times to modern education, it upholds timeless values. Yet, controversies arise—debates on balance, efficacy, equity, and accessibility persist. Innovative alternatives like project-based and personalized learning emerge. Homework’s role evolves with education.
How to Cite this Article
There are three different ways you can cite this article.
1. To cite this article in an academic-style article or paper , use:
<a href=" https://historycooperative.org/who-invented-homework/ ">The Homework Dilemma: Who Invented Homework?</a>
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Who Invented Homework, and Why Was Homework Invented? Let’s Explore!
If you are or have ever been a student, you have probably asked this question multiple times, and it hardly was to thank the person who invented homework personally. We all know that feeling all too well—the deadline is looming, you’re staring at a blank page, and there isn’t a single viable idea in your head.
Sounds familiar? Then you’re likely curious to investigate the history of homework and the cruel, cruel people who stand behind this centuries-old tradition. It’s quite fascinating, actually, and you will most certainly be surprised at how long and turbulent the history of giving learners homework is.
When, How, Why, and Who Invented Homework
To answer the question of who the title of the inventor of homework belongs to, we will have to go all the way back to the first century, then jump to eighteenth-century Europe, and finally move domestically to explore the trials and errors of the homework tradition in the U.S.
Some of the names we will address here include:
- Pliny the Younger —The Roman lawyer and author credited with the “invention” of homework,
- Johann Gottlieb Fichte —The German philosopher who developed the ideological justification of homework,
- Horace Mann —The first known American educator who made homework the norm in the U.S., and more.
Let’s dive in.
Who Created Homework and Why—How Everything Started
So, who started homework? The simplistic answer would be the Roman lawyer Pliny the Younger, who we’ll discuss in more detail below. However, it’s not that simple. It never is when it comes to homework, a tradition that could have existed long before it was linked to any historical artifacts and, therefore, lost to history.
After all, as much as almost every student despises homework, its number one purpose (or, at least, what we perceive as its number one purpose today) is self-evident. Most teachers genuinely care about their learners’ progress and academic achievements, so it’s no wonder they give home assignments to help students improve their learning.
As a result, it’s no wonder students are looking for an EssayPro review or WritePapers review to find someone reputable who can help them cope with loads of homework.
However, as you will soon find out, making progress in learning is only one of the many homework goals. Historically, it hasn’t even always been the most important one. Societal events, dominant philosophical schools, and individual educational reformers have always affected the mainstream view of homework and its perceived functions.
We invite you to join us on a journey through centuries (and then back again), where we will try to understand the origins, evolution, and current state of the homework tradition. If nothing else, you might have a chance to impress your friends at a trivia night.
Pliny the Younger
Have you already thought of the Roman Empire this week? If not, now’s your chance. The first name historians come across when looking for the origins of homework is Pliny the Younger, a Roman magistrate, lawyer, and brilliant orator in the first century A.D.
Pliny the Younger had students like many other distinguished authors and public speakers in Rome. He taught rhetoric and public speaking and—you guessed it—tasked his students with practicing their speech composing and public speaking skills even outside his classes. Also, Pliny actively encouraged them to put their newly acquired skills to practice in appropriate settings.
Johann Gottlieb Fichte
Here comes a huge time jump—to eighteenth-century Germany. Sure, homework probably existed between the Roman times and the eighteenth century. However, nothing groundbreaking happened to it during all those centuries, so there’s no point in retelling every little step.
Johann Gottlieb Fichte was a German philosopher in post-Napoleon Europe who advocated for a uniform national education system, similar to other voices of German idealism. He emphasized that teaching the youth was as much about instilling a sense of national identity in them as teaching them traditional disciplines. For Fichte, homework was one of the strategies for achieving that.
Horace Mann
At this point, you might wonder, “What about the U.S.?” Well, the title of the pioneer of homework in the New World belongs to Horace Mann, otherwise known as “the father of the American public school system.” In the nineteenth century, education for children was still not compulsory, and Mann advocated for changing that.
Mann was the first educator to emphasize the role of parents in every child’s learning journey. He believed homework could reinforce the lessons taught in school, teach the youth self-discipline and improve their relationships with parents. He added a new layer to why homework was invented and made mainstream.
Roberto Nevilis: What Was His Role in the Origins of Homework?
The first thing you need to know about Roberto Nevilis is that he didn’t exist. A popular myth suggests that Nevilis invented homework at the beginning of the twentieth century as a form of punishment for students who didn’t work hard enough in class. That’s completely untrue.
Here are a few facts about Roberto Nevilis. According to the legend, Roberto Nevilis was an Italian teacher who lived at the end of the nineteenth and beginning of the twentieth century in Venice, Italy. He was supposedly the first educator to give homework to his students, which allegedly happened in 1905. If you look up his (more or less fictional) “story” online, you will find that he initially only gave home assignments to students who failed to understand the material in class or weren’t diligent enough.
Why did Roberto Nevilis create homework? As you can probably guess by now, the more accurate question would be, “Why would someone bother to invent the person named Roberto Nevilis and credit this semi-fictional character with inventing homework?” Sadly, though, there’s no clear answer. Whoever did this wanted students or the general public to believe that the number one purpose of homework was punishment for poor performance. That’s not the case.
Was the History of Homework in the United States Any Different?
Now, let’s move beyond Horace Mann’s name and explore homework history in the Americas or, more specifically, the U.S. One of the first questions people curious about the topic ask is, “What year was homework invented in the United States?” There’s no straightforward answer to this, either. All we know is that homework started becoming a standard practice somewhere on the cusp of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries—largely thanks to Mann’s effort.
The U.S. wasn’t any different from other countries in that the mainstream views on homework evolved with societal norms (which, in turn, shaped educational priorities). For example, by the beginning of the twentieth century, the idea became more or less universal: homework promoted students’ growth beyond learning the material taught in class. Educators believed it was also helpful for building character and applying the knowledge gained in practical contexts.
However, the beginning of the twentieth century was also when the progressive education movement grew increasingly popular. Among other things, its proponents advocated against homework because they believed that it contracted the fundamentals of child-centered learning. The opposing views on giving home assignments coexisted side by side; to an extent, they still do.
The Ban on Homework in the 1900s
The 1900s was the first time in American history since homework origin when it became very popular to reject the need for homework. The progressive movement grew more influential by the day, eventually culminating in the homework ban.
From being the underdogs of sorts, homework’s progressive critics turned into the loudest voice in the education system, and their demands were eventually met, albeit not everywhere.
Their arguments were straightforward and understandable, at least to an extent. They claimed that homework got in the way of students’ socializing after school hours, interfered with the family dynamics, and strained students’ physical and mental health.
The Need for Children’s Domestic Labor in the 1930s
The 1930s wasn’t a good time for the first homework advocates. This was when the Great Depression hit the U.S. severely and put the economic crisis at the forefront of basically everything happening in the country, including education.
More and more parents came forward demanding the end of homework because they needed their children to help at home—be it with domestic labor, farming, or anything else.
Parents’ demands were fruitful. The educational practices of the 1930s stemmed from the idea that outside of school hours, students should be able to focus on their lives at home without the additional burden of homework.
The Post-World War II Shift in the Views on Homework
The situation changed drastically after World War II. If you’re wondering how old is homework the way we know it today, that’s when it started.
First, the nation was thriving economically, which made it possible to focus on the importance of education. Also, as the Cold War started, the value of education became more apparent than ever. The U.S. needed well-educated citizens who could contribute to technological advancements and effectively protect the nation’s security.
For example, when the Soviets launched Sputnik in 1957, one of the main debates in the American media was about young people’s readiness to remain competitive on a global scale.
How Homework Looks for American Children in the 21st Century
.webp)
Today, we can still see some of the dilemmas surrounding the topic over a century ago. For example, there are two clear camps: educators who believe homework is necessary for academic achievement and their colleagues who don’t think that to become a well-rounded and successful individual, a child must spend hours daily completing home assignments.
Still, the most popular view is quite well-balanced. The main idea behind that is maximizing the educational benefits of homework while minimizing its potential drawbacks. This implies setting reasonable limits on the amount of homework, designing meaningful assignments, and prioritizing students’ holistic development.
Otherwise, being overloaded with homework often leads students to search for an EssayPro promo code to hire expert academic helpers without breaking the bank. Many view it as the only way to have proper rest.
What’s the Purpose of Homework?
Even a child knows the number one reason they must do their homework (even if they don’t necessarily agree). Obviously, the main purpose of homework is to help students better digest the material they learn in class.
But that’s not the only one. Other goals of homework include:
- To teach students how to work independently and think critically;
- To motivate students to prepare for upcoming lessons (thus making the teacher’s job a little easier);
- To encourage responsibility and organization;
- To cultivate collaboration skills (via group assignments);
- To strengthen the child-parent bond, and more.
What’s the Impact of Homework on the Quality of Education
So, how does homework improve the quality of education?
- Promotes understanding and reflection.
- Improves study habits and time management.
- Makes it possible for teachers to give anonymous and personalized feedback to each student.
- Prepares students for standardized assessments (such as SATs).
- Supports diverse learning needs.
The Pros of Homework
The complete list of the advantages of homework would be too long to include here, but here are some of the undeniable benefits of giving the students at least some work to do at home:
✅ Reinforces learning
✅ Promotes independent learning
✅ Develops positive study habits
✅ Increases retention
✅ Facilitates parental involvement
✅ Enables customized learning, and so on.
.webp)
The Cons of Homework
At the same time, even the most adamant proponents of homework recognize that the tradition does have its flaws. The drawbacks of homework include the following:
❌ Causes extra stress and anxiety
❌ Gets in the way of students’ relationships with family members and social lives
❌ Might get in the way of healthy extracurricular activities, such as sports
❌ Creates additional pressure on teachers.
Who made homework a thing?
Why was homework invented have the reasons changed since then, is homework really necessary for effective learning, when was homework first invented did it look the same, how does homework look today who writes the rules.
As you can see, homework history—both in the U.S. and worldwide—has been quite turbulent. Much to today’s students’ envy, there were times when it was illegal, at least in some places.
However, now is not one of those periods. While some non-mainstream educational systems and paradigms deny the need for homework, most educators believe that the benefits of homework outweigh its flaws. The key is to design genuinely stimulating and engaging assignments and avoid overdoing things. Students should be able to relax after school hours without the risk of falling behind.
If you ask an average teacher these days, they will probably tell you that the optimal amount of homework per week is roughly 7-10 hours. That’s enough to practice what was learned in class and engage with the material critically. At the same time, it’s not too much, so the risks of causing students extra stress and harming their social lives are very unlikely.
What matters the most is not how much homework a teacher gives but how creative and stimulating the assignments are. Ideally, students should be excited to complete them.
.webp)
You Might Also Be Interested In
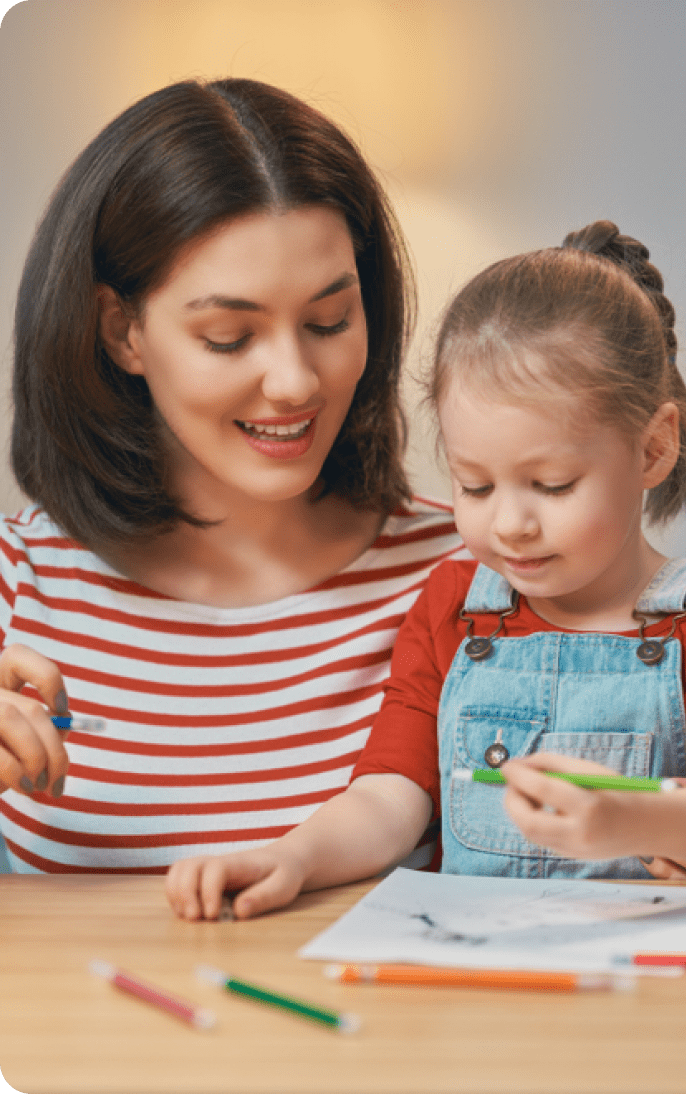


Who Invented Homework? A Big Question Answered with Facts

Crystal Bourque

Delving into the intriguing history of education, one of the most pondered questions arises: Who invented homework?
Love it or hate it, homework is part of student life.
But what’s the purpose of completing these tasks and assignments? And who would create an education system that makes students complete work outside the classroom?
This post contains everything you’ve ever wanted to know about homework. So keep reading! You’ll discover the answer to the big question: who invented homework?
Who Invented Homework?
The myth of roberto nevilis: who is he, the origins of homework, a history of homework in the united states, 5 facts about homework, types of homework.
- What’s the Purpose of Homework?
- Homework Pros
- Homework Cons
When, How, and Why was Homework Invented?

Daniel Jedzura/Shutterstock.com
To ensure we cover the basics (and more), let’s explore when, how, and why was homework invented.
As a bonus, we’ll also cover who invented homework. So get ready because the answer might surprise you!
It’s challenging to pinpoint the exact person responsible for the invention of homework.
For example, Medieval Monks would work on memorization and practice singing. Ancient philosophers would read and develop their teachings outside the classroom. While this might not sound like homework in the traditional form we know today, one could argue that these methods helped to form the basic structure and format.
So let’s turn to recorded history to try and identify who invented homework and when homework was invented.
Pliny the Younger

Credit: laphamsquarterly.org
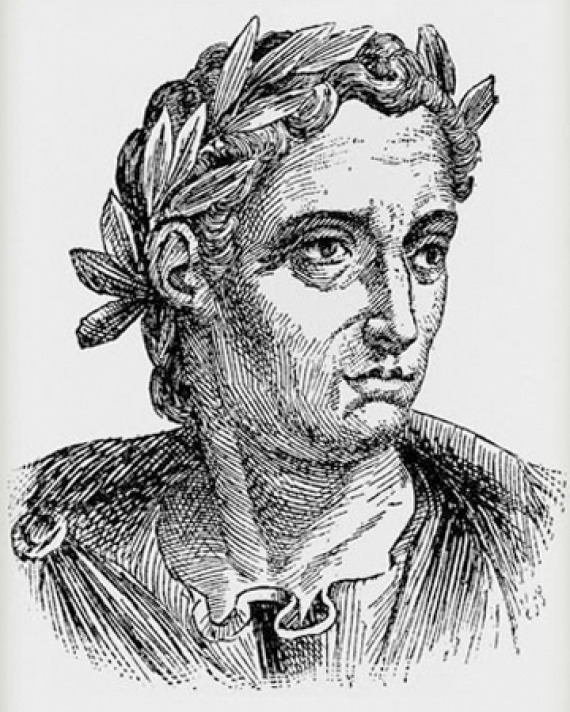
Mention of homework appears in the writings of Pliny the Younger, meaning we can trace the term ‘homework’ back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger (61—112 CE) was an oratory teacher, and often told his students to practice their public speaking outside class.
Pliny believed that the repetition and practice of speech would help students gain confidence in their speaking abilities.
Johann Gottlieb Fichte

Credit: inlibris.com
Before the idea of homework came to the United States, Germany’s newly formed nation-state had been giving students homework for years.
The roots of homework extend to ancient times, but it wasn’t until German Philosopher Johann Gottlieb Fichte (1762—1814) helped to develop the Volksschulen (People’s Schools) that homework became mandatory.
Fichte believed that the state needed to hold power over individuals to create a unified Germany. A way to assert control over people meant that students attending the Volksshulen were required to complete assignments at home on their own time.
As a result, some people credit Fichte for being the inventor of homework.
Horace Mann

Credit: commons.wikimedia.org
The idea of homework spread across Europe throughout the 19th century.
So who created homework in the United States?
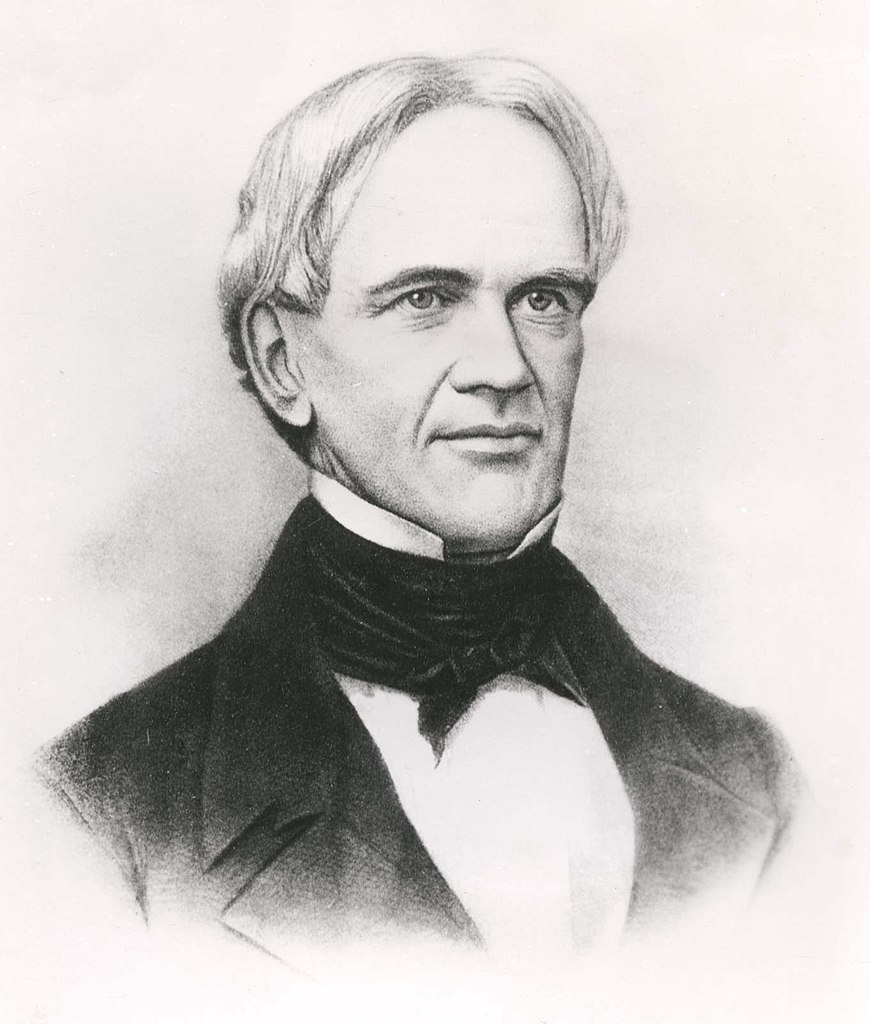
The history of education and homework now moves to Horace Mann (1796—1859), an American educational reformer, spent some time in Prussia. There, he learned more about Germany’s Volksshulen, forms of education , and homework practices.
Mann liked what he saw and brought this system back to America. As a result, homework rapidly became a common factor in students’ lives across the country.

Credit: medium.com
If you’ve ever felt curious about who invented homework, a quick online search might direct you to a man named Roberto Nevilis, a teacher in Venice, Italy.
As the story goes, Nevilis invented homework in 1905 (or 1095) to punish students who didn’t demonstrate a good understanding of the lessons taught during class.
This teaching technique supposedly spread to the rest of Europe before reaching North America.
Unfortunately, there’s little truth to this story. If you dig a little deeper, you’ll find that these online sources lack credible sources to back up this myth as fact.
In 1905, the Roman Empire turned its attention to the First Crusade. No one had time to spare on formalizing education, and classrooms didn’t even exist. So how could Nevilis spread the idea of homework when education remained so informal?
And when you jump to 1901, you’ll discover that the government of California passed a law banning homework for children under fifteen. Nevilis couldn’t have invented homework in 1905 if this law had already reached the United States in 1901.

Inside Creative House/Shutterstock.com
When it comes to the origins of homework, looking at the past shows us that there isn’t one person who created homework. Instead, examining the facts shows us that several people helped to bring the idea of homework into Europe and then the United States.
In addition, the idea of homework extends beyond what historians have discovered. After all, the concept of learning the necessary skills human beings need to survive has existed since the dawn of man.
More than 100 years have come and gone since Horace Mann introduced homework to the school system in the United States.
Therefore, it’s not strange to think that the concept of homework has changed, along with our people and culture.
In short, homework hasn’t always been considered acceptable. Let’s dive into the history or background of homework to learn why.
Homework is Banned! (The 1900s)
Important publications of the time, including the Ladies’ Home Journal and The New York Times, published articles on the negative impacts homework had on American children’s health and well-being.
As a result, California banned homework for children under fifteen in 1901. This law, however, changed again about a decade later (1917).
Children Needed at Home (The 1930s)
Formed in 1923, The American Child Health Association (ACHA) aimed to decrease the infant mortality rate and better support the health and development of the American child.
By the 1930s, ACHA deemed homework a form of child labor. Since the government recently passed laws against child labor , it became difficult to justify homework assignments. College students, however, could still receive homework tasks as part of their formal schooling.

Studio Romantic/Shutterstock.com
A Shift in Ideas (The 1940s—1950s)
During the early to mid-1900s, the United States entered the Progressive Era. As a result, the country reformed its public education system to help improve students’ learning.
Homework became a part of everyday life again. However, this time, the reformed curriculum required teachers to make the assignments more personal.
As a result, American students would write essays on summer vacations and winter breaks, participate in ‘show and tell,’ and more.
These types of assignments still exist today!
Homework Today (The 2000s)
The focus of American education shifted again when the US Department of Education was founded in 1979, aiming to uplevel education in the country by, among other things, prohibiting discrimination ensuring equal access, and highlighting important educational issues.
In 2022, the controversial nature of homework in public schools and formal education is once again a hot topic of discussion in many classrooms.
According to one study , more than 60% of college and high school students deal with mental health issues like depression and anxiety due to homework. In addition, the large number of assignments given to students takes away the time students spend on other interests and hobbies. Homework also negatively impacts sleep.
As a result, some schools have implemented a ban or limit on the amount of homework assigned to students.
Test your knowledge and check out these other facts about homework:
- Horace Mann is also known as the ‘father’ of the modern school system and the educational process that we know today (read more about Who Invented School ).
- With a bit of practice, homework can improve oratory and writing skills. Both are important in a student’s life at all stages.
- Homework can replace studying. Completing regular assignments reduces the time needed to prepare for tests.
- Homework is here to stay. It doesn’t look like teachers will stop assigning homework any time soon. However, the type and quantity of homework given seem to be shifting to accommodate the modern student’s needs.
- The optimal length of time students should spend on homework is one to two hours. Students who spent one to two hours on homework per day scored higher test results.
- So, while completing assignments outside of school hours may be beneficial, spending, for example, a day on homework is not ideal.
Explore how the Findmykids app can complement your child’s school routine. With features designed to ensure their safety and provide peace of mind, it’s a valuable tool for parents looking to stay connected with their children throughout the day. Download now and stay informed about your child’s whereabouts during their academic journey.

Ground Picture/Shutterstock.com
The U.S. Department of Education provides teachers with plenty of information and resources to help students with homework.
In general, teachers give students homework that requires them to employ four strategies. The four types of homework types include:
- Practice: To help students master a specific skill, teachers will assign homework that requires them to repeat the particular skill. For example, students must solve a series of math problems.
- Preparation: This type of homework introduces students to the material they will learn in the future. An example of preparatory homework is assigning students a chapter to read before discussing the contents in class the next day.
- Extension: When a teacher wants to get students to apply what they’ve learned but create a challenge, this type of homework is assigned. It helps to boost problem-solving skills. For example, using a textbook to find the answer to a question gets students to problem-solve differently.
- Integration: To solidify the student learning experience , teachers will create a task that requires the use of many different skills. An example of integration is a book report. Completing integration homework assignments helps students learn how to be organized, plan, strategize, and solve problems on their own. Encouraging effective study habits is a key idea behind homework, too.
Ultimately, the type of homework students receive should have a purpose, be focused and clear, and challenge students to problem solve while integrating lessons learned.
What’s the Purpose of Homework?

LightField Studios/Shutterstock.com
Homework aims to ensure individual students understand the information they learn in class. It also helps teachers to assess a student’s progress and identify strengths and weaknesses.
For example, school teachers use different types of homework like book reports, essays, math problems, and more to help students demonstrate their understanding of the lessons learned.
Does Homework Improve the Quality of Education?
Homework is a controversial topic today. Educators, parents, and even students often question whether homework is beneficial in improving the quality of education.
Let’s explore the pros and cons of homework to try and determine whether homework improves the quality of education in schools.
Homework Pros:
- Time Management Skills : Assigning homework with a due date helps students to develop a schedule to ensure they complete tasks on time. Personal responsibility amongst students is thereby promoted.
- More Time to Learn : Students encounter plenty of distractions at school. It’s also challenging for students to grasp the material in an hour or less. Assigning homework provides the student with the opportunity to understand the material.
- Improves Research Skills : Some homework assignments require students to seek out information. Through homework, students learn where to seek out good, reliable sources.
Homework Cons:
- Reduced Physical Activity : Homework requires students to sit at a desk for long periods. Lack of movement decreases the amount of physical activity, often because teachers assign students so much homework that they don’t have time for anything else. Time for students can get almost totally taken up with out-of-school assignments.
- Stuck on an Assignment: A student often gets stuck on an assignment. Whether they can’t find information or the correct solution, students often don’t have help from parents and require further support from a teacher. For underperforming students, especially, this can have a negative impact on their confidence and overall educational experience.
- Increases Stress : One of the results of getting stuck on an assignment is that it increases stress and anxiety. Too much homework hurts a child’s mental health, preventing them from learning and understanding the material.
Some research shows that homework doesn’t provide educational benefits or improve performance, and can lead to a decline in physical activities. These studies counter that the potential effectiveness of homework is undermined by its negative impact on students.
However, research also shows that homework benefits students—provided teachers don’t give them too much. Here’s a video from Duke Today that highlights a study on the very topic.
Homework Today
The question of “Who Invented Homework?” delves into the historical evolution of academic practices, shedding light on its significance in fostering responsibility among students and contributing to academic progress. While supported by education experts, homework’s role as a pivotal aspect of academic life remains a subject of debate, often criticized as a significant source of stress. Nonetheless, when balanced with extracurricular activities and integrated seamlessly into the learning process, homework continues to shape and refine students’ educational journeys.
Maybe one day, students won’t need to submit assignments or complete tasks at home. But until then, many students understand the benefits of completing homework as it helps them further their education and achieve future career goals.
Before you go, here’s one more question: how do you feel about homework? Do you think teachers assign too little or too much? Get involved and start a discussion in the comments!

Elena Kharichkina/Shutterstock.com
Who invented homework and why?
The creation of homework can be traced back to the Ancient Roman Pliny the Younger, a teacher of oratory—he is generally credited as being the father of homework! Pliny the Younger asked his students to practice outside of class to help them build confidence in their speaking skills.
Who invented homework as a punishment?
There’s a myth that the Italian educator Roberto Nevilis first used homework as a means of punishing his students in the early 20th century—although this has now been widely discredited, and the story of the Italian teacher is regarded as a myth.
Why did homework stop being a punishment?
There are several reasons that homework ceased being a form of punishment. For example, the introduction of child labor laws in the early twentieth century meant that the California education department banned giving homework to children under the age of fifteen for a time. Further, throughout the 1940s and 1950s, there was a growing emphasis on enhancing students’ learning, making homework assignments more personal, and nurturing growth, rather than being used as a form of punishment.
The picture on the front page: Evgeny Atamanenko/Shutterstock.com

The school year is now starting again and with that, the Internet is blowing up…

It’s impossible to overemphasize the importance of learning alphabet letters for kids. This primary milestone…

An aggressive child is not uncommon in the modern world. Unfortunately, for many parents this…
Subscribe now!
Glad you've joined us🎉🎉.

Who Invented Homework and Why

Who Invented Homework
Italian pedagog, Roberto Nevilis, was believed to have invented homework back in 1905 to help his students foster productive studying habits outside of school. However, we'll sound find out that the concept of homework has been around for much longer.
Homework, which most likely didn't have a specific term back then, already existed even in ancient civilizations. Think Greece, Rome, and even ancient Egypt. Over time, homework became standardized in our educational systems. This happened naturally over time, as the development of the formal education system continued.
In this article, we're going to attempt to find out who invented homework, and when was homework invented, and we're going to uncover if the creator of homework is a single person or a group of them. Read this article through to the end to find out.
Who Created Homework and When?
The concept of homework predates modern educational systems, with roots in ancient Rome. However, Roberto Nevilis is often, yet inaccurately, credited with inventing homework in 1905.Depending on various sources, this invention is dated either in the year 1095 or 1905.
The invention of homework is commonly attributed to Roberto Nevilis, an Italian pedagog who is said to have introduced it as a form of punishment for his students in 1905. However, the concept of homework predates Nevilis and has roots that go back much further in history.
The practice of assigning students work to be done outside of class time can be traced back to ancient civilizations, such as Rome, where Pliny the Younger (AD 61–113) encouraged his students to practice public speaking at home to improve their oratory skills.
It's important to note that the idea of formalized homework has evolved significantly over centuries, influenced by educational theories and pedagogical developments. The purpose and nature of homework have been subjects of debate among educators, with opinions varying on its effectiveness and impact on student learning and well-being.
It might be impossible to answer when was homework invented. A simpler question to ask is ‘what exactly is homework?’.
If you define it as work assigned to do outside of a formal educational setup, then homework might be as old as humanity itself. When most of what people studied were crafts and skills, practicing them outside of dedicated learning times may as well have been considered homework.
Let’s look at a few people who have been credited with formalizing homework over the past few thousand years.
Roberto Nevilis
Stories and speculations on the internet claim Roberto Nevilis is the one who invented school homework, or at least was the first person to assign homework back in 1905.
Who was he? He was an Italian educator who lived in Venice. He wanted to discipline and motivate his class of lackluster students. Unfortunately, claims online lack factual basis and strong proof that Roberto did invent homework.
Homework, as a concept, predates Roberto, and can't truly be assigned to a sole inventor. Moreover, it's hard to quantify where an idea truly emerges, because many ideas emerge from different parts of the world simultaneously or at similar times, therefore it's hard to truly pinpoint who invented this idea.
Pliny the Younger
Another culprit according to the internet lived a thousand years before Roberto Nevilis. Pliny the Younger was an oratory teacher in the first century AD in the Roman Empire.
He apparently asked his students to practice their oratory skills at home, which some people consider one of the first official versions of homework.
It is difficult to say with any certainty if this is the first time homework was assigned though because the idea of asking students to practice something outside classes probably existed in every human civilization for millennia.
Horace Mann
To answer the question of who invented homework and why, at least in the modern sense, we have to talk about Horace Mann. Horace Mann was an American educator and politician in the 19th century who was heavily influenced by movements in the newly-formed German state.
He is credited for bringing massive educational reform to America, and can definitely be considered the father of modern homework in the United States. However, his ideas were heavily influenced by the founding father of German nationalism Johann Gottlieb Fichte.
After the defeat of Napoleon and the liberation of Prussia in 1814, citizens went back to their own lives, there was no sense of national pride or German identity. Johann Gottlieb Fichte came up with the idea of Volkschule, a mandatory 9-year educational system provided by the government to combat this.
Homework already existed in Germany at this point in time but it became a requirement in Volkschule. Fichte wasn't motivated purely by educational reform, he wanted to demonstrate the positive impact and power of a centralized government, and assigning homework was a way of showing the state's power to influence personal and public life.
This effort to make citizens more patriotic worked and the system of education and homework slowly spread through Europe.
Horace Mann saw the system at work during a trip to Prussia in the 1840s and brought many of the concepts to America, including homework.
Who Invented Homework and Why?
Homework's history and objectives have evolved significantly over time, reflecting changing educational goals. Now, that we've gone through its history a bit, let's try to understand the "why". The people or people who made homework understood the advantages of it. Let's consider the following:
- Repetition, a key factor in long-term memory retention, is a primary goal of homework. It helps students solidify class-learned information. This is especially true in complex subjects like physics, where physics homework help can prove invaluable to learning effectively.
- Homework bridges classroom learning with real-world applications, enhancing memory and understanding.
- It identifies individual student weaknesses, allowing focused efforts to address them.
- Working independently at their own pace, students can overcome the distractions and constraints of a classroom setting through homework.
- By creating a continuous learning flow, homework shifts the perspective from viewing each school day as isolated to seeing education as an ongoing process.
- Homework is crucial for subjects like mathematics and sciences, where repetition is necessary to internalize complex processes.
- It's a tool for teachers to maximize classroom time, focusing on expanding understanding rather than just drilling fundamentals.
- Responsibility is a key lesson from homework. Students learn to manage time and prioritize tasks to meet deadlines.
- Research skills get honed through homework as students gather information from various sources.
- Students' creative potential is unleashed in homework, free from classroom constraints.
Struggling with your Homework?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease.
Who Invented Homework: Development in the 1900s
Thanks to Horace Mann, homework had become widespread in the American schooling system by 1900, but it wasn't universally popular amongst either students or parents.
The early 1900s homework bans
In 1901, California became the first state to ban homework. Since homework had made its way into the American educational system there had always been people who were against it for some surprising reasons.
Back then, children were expected to help on farms and family businesses, so homework was unpopular amongst parents who expected their children to help out at home. Many students also dropped out of school early because they found homework tedious and difficult.
Publications like Ladies' Home Journal and The New York Times printed statements and articles about the detrimental effects of homework on children's health.
The 1930 child labor laws
Homework became more common in the U.S. around the early 1900s. As to who made homework mandatory, the question remains open, but its emergence in the mainstream sure proved beneficial. Why is this?
Well, in 1930, child labor laws were created. It aimed to protect children from being exploited for labor and it made sure to enable children to have access to education and schooling. The timing was just right.
Speaking of homework, if you’re reading this article and have homework you need to attend to, send a “ do my homework ” request on Studyfy and instantly get the help of a professional right now.
Progressive reforms of the 1940s and 50s
With more research into education, psychology and memory, the importance of education became clear. Homework was understood as an important part of education and it evolved to become more useful and interesting to students.
Homework during the Cold War
Competition with the Soviet Union fueled many aspects of American life and politics. In a post-nuclear world, the importance of Science and Technology was evident.
The government believed that students had to be well-educated to compete with Soviet education systems. This is the time when homework became formalized, accepted, and a fundamental part of the American educational system.
1980s Nation at Risk
In 1983 the National Commission on Excellence in Education published Nation at Risk:
The Imperative for Educational Reform, a report about the poor condition of education in America. Still in the Cold War, this motivated the government in 1986 to talk about the benefits of homework in a pamphlet called “What Works” which highlighted the importance of homework.
Did you like our Homework Post?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay editing services!
Who Invented Homework: The Modern Homework Debate
Like it or not, homework has stuck through the times, remaining a central aspect in education since the end of the Cold War in 1991. So, who invented homework 😡 and when was homework invented?
We’ve tried to pinpoint different sources, and we’ve understood that many historical figures have contributed to its conception.
Horace Mann, in particular, was the man who apparently introduced homework in the U.S. But let’s reframe our perspective a bit. Instead of focusing on who invented homework, let’s ask ourselves why homework is beneficial in the first place. Let’s consider the pros and cons:
- Homework potentially enhances memory.
- Homework helps cultivate time management, self-learning, discipline, and cognitive skills.
- An excessive amount of work can cause mental health issues and burnout.
- Rigid homework tasks can take away time for productive and leisurely activities like arts and sports.
Meaningful homework tasks can challenge us and enrich our knowledge on certain topics, but too much homework can actually be detrimental. This is where Studyfy can be invaluable. Studyfy offers homework help.
All you need to do is click the “ do my assignment ” button and send us a request. Need instant professional help? You know where to go now.
Frequently asked questions
Who made homework.
As stated throughout the article, there was no sole "inventor of homework." We've established that homework has already existed in ancient civilizations, where people were assigned educational tasks to be done at home.
Let's look at ancient Greece; for example, students at the Academy of Athens were expected to recite and remember epic poems outside of their institutions. Similar practices were going on in ancient Egypt, China and Rome.
This is why we can't ascertain the sole inventor of homework. While history can give us hints that homework was practiced in different civilizations, it's not far-fetched to believe that there have been many undocumented events all across the globe that happened simultaneously where homework emerged.
Why was homework invented?
We've answered the question of "who invented homework 😡" and we've recognized that we cannot pinpoint it to one sole inventor. So, let's get back to the question of why homework was invented.
Homework arose from educational institutions, remained, and probably was invented because teachers and educators wanted to help students reinforce what they learned during class. They also believed that homework could improve memory and cognitive skills over time, as well as instill a sense of discipline.
In other words, homework's origins can be linked to academic performance and regular students practice. Academic life has replaced the anti-homework sentiment as homework bans proved to cause partial learning and a struggle to achieve conceptual clarity.
Speaking of, don't forget that Studyfy can help you with your homework, whether it's Python homework help or another topic. Don't wait too long to take advantage of expert help when you can do it now.
Is homework important for my learning journey?
Now that we've answered questions on who created homework and why it was invented, we can ask ourselves if homework is crucial in our learning journey.
At the end of the day, homework can be a crucial step to becoming more knowledgeable and disciplined over time.
Exercising our memory skills, learning independently without a teacher obliging us, and processing new information are all beneficial to our growth and evolution. However, whether a homework task is enriching or simply a filler depends on the quality of education you're getting.
The Surprising History of Homework Reform
Really, kids, there was a time when lots of grownups thought homework was bad for you.

Homework causes a lot of fights. Between parents and kids, sure. But also, as education scholar Brian Gill and historian Steven Schlossman write, among U.S. educators. For more than a century, they’ve been debating how, and whether, kids should do schoolwork at home .

At the dawn of the twentieth century, homework meant memorizing lists of facts which could then be recited to the teacher the next day. The rising progressive education movement despised that approach. These educators advocated classrooms free from recitation. Instead, they wanted students to learn by doing. To most, homework had no place in this sort of system.
Through the middle of the century, Gill and Schlossman write, this seemed like common sense to most progressives. And they got their way in many schools—at least at the elementary level. Many districts abolished homework for K–6 classes, and almost all of them eliminated it for students below fourth grade.
By the 1950s, many educators roundly condemned drills, like practicing spelling words and arithmetic problems. In 1963, Helen Heffernan, chief of California’s Bureau of Elementary Education, definitively stated that “No teacher aware of recent theories could advocate such meaningless homework assignments as pages of repetitive computation in arithmetic. Such an assignment not only kills time but kills the child’s creative urge to intellectual activity.”
But, the authors note, not all reformers wanted to eliminate homework entirely. Some educators reconfigured the concept, suggesting supplemental reading or having students do projects based in their own interests. One teacher proposed “homework” consisting of after-school “field trips to the woods, factories, museums, libraries, art galleries.” In 1937, Carleton Washburne, an influential educator who was the superintendent of the Winnetka, Illinois, schools, proposed a homework regimen of “cooking and sewing…meal planning…budgeting, home repairs, interior decorating, and family relationships.”
Another reformer explained that “at first homework had as its purpose one thing—to prepare the next day’s lessons. Its purpose now is to prepare the children for fuller living through a new type of creative and recreational homework.”
That idea didn’t necessarily appeal to all educators. But moderation in the use of traditional homework became the norm.
Weekly Newsletter
Get your fix of JSTOR Daily’s best stories in your inbox each Thursday.
Privacy Policy Contact Us You may unsubscribe at any time by clicking on the provided link on any marketing message.
“Virtually all commentators on homework in the postwar years would have agreed with the sentiment expressed in the NEA Journal in 1952 that ‘it would be absurd to demand homework in the first grade or to denounce it as useless in the eighth grade and in high school,’” Gill and Schlossman write.
That remained more or less true until 1983, when publication of the landmark government report A Nation at Risk helped jump-start a conservative “back to basics” agenda, including an emphasis on drill-style homework. In the decades since, continuing “reforms” like high-stakes testing, the No Child Left Behind Act, and the Common Core standards have kept pressure on schools. Which is why twenty-first-century first graders get spelling words and pages of arithmetic.
Support JSTOR Daily! Join our new membership program on Patreon today.

JSTOR is a digital library for scholars, researchers, and students. JSTOR Daily readers can access the original research behind our articles for free on JSTOR.
Get Our Newsletter
More stories.

Endangered: North American Cricket

Monastic Chant: Praising God Out Loud

The Complex History of American Dating

9 Ways to Create an “Intellectually Humble” Classroom
Recent posts.
- Painting Race
- The Governess, in Her Own Written Words
- Eisenhower and the Real-Life Nautilus
- How Renaissance Art Found Its Way to American Museums
- Lessons in Mannerism at the Palazzo del Te
Support JSTOR Daily
Sign up for our weekly newsletter.

- Homework Help
- Chat with AI
- Writing Assistant
- Browser Extension
- Discord Server
- Math Solver
- AI Answer Generator
- Code Generator
- Grammar Checker
- Plan & Pricing

Who Invented Homework? The Origins and Development
October 18th, 2023 — 5 min read
The origins of Homework dates back to ancient Greece and Rome. It is said that Roberto Nevelis, an Italian teacher, invented homework in 1905, but so far there is no credible historical evidence to support this, which makes it become an Internet myth. Pliny the Younger, Johann Gottlieb Fichte, and Hausmann are the most likely true inventors of homework.
I. Introduction
When it comes to homework, what is on your mind? Excited or struggling?Some people enjoy doing homework and challenging themselves with hard questions; Others dislike homework and struggle with it, considering that homework deprives them of their spare time. Whether you like it or not, homework is an essential part of our learning and growth.
For teachers, homework is a way to help students to consolidate knowledge, develop critical thinking skills, and improve problem-solving ability etc. As students, we might not view homework like our teachers, and maybe just complete homework to avoid punishment.
So we've all been doing homework since we were kids. Have you ever wondered who invented homework? This blog will elaborate on the origins and development of homework. Let's take a look at who started the journey of homework, and who made homework became a daily task for students.
II. Historical Background
Before tracing the origins of homework, let us ponder a question: was homework born at the same time as education? The answer is no. Education has a long history that can be traced back to ancient times. In the early stages, homework is not a part of educational system. Before writing was invented, people mainly passed on the values, traditions and life skills to the next generation through oral teaching. However, the advent of writing further developed the spread of civilization and diversified the ways of education.

There is no homework in early education, so how do students consolidate their learning? In the ancient Greek city-states, private education was prevalent. Students in Athens discussed, debated, and thought in study groups organized by philosophers or scholars to further reinforce knowledge. Students would participate in various public presentations to access their learning outcomes and broaden their horizons and thinking. In addition, by participating in all kinds of practical activities, such as museum visits, art exhibitions, and sports activities, students can apply what they have learned to real-life situations. Therefore, although there was no homework at that time, students could enhance their understanding and application of learning in a variety of ways.
With the continuous development of society, education gradually developed from social and family education to formal schooling, with professional people specialized in teaching subject knowledge and skills. So who invented homework? When did homework appear?
III. Inventors and Key Figures of Homework
1.roberto nevelis.

2.Pliny The Younger

3.Johann Gottlieb Fichte
So who invented homework? Johann Gottlieb Fichte,the German philosopher, was probably the true inventor of homework. He was not only the father of German nationalism, but also contributed and influenced the education of Germany. He helped develop people's schools, making mass schools and compulsory education an innovation at that period. The state provided education for students and also infiltrated patriotism into students' lives and encouraged them to contribute to the country.
Fichte's educational ideas had a profound influence on German education at that time. His ideas were widely adopted and implemented in the German education system, so that homework became an important part of students' learning.

4.Horace Mann
Horace Mann, a 19th-century American educator and politician, was often credited as a key figure in the development of homework. After graduating from Brown University, he actively supported education reform while serving as the state education secretary. He was regarded by many historians as the "father of American public education" and devoted himself to the educational system.
Mann not only engaged with teachers, but also participated in many public education presentations and visited other schools in and out of the state. While visiting schools in Europe, he was inspired by the Prussian education system and decided to reform education in Massachusetts, one of which was homework. He believes that homework can help students consolidate what they learn in class and develop the ability to learn independently and solve problems.

So, what about the future of homework in the United States?
IV.Brief History of Homework in the US
Early 20th century: the rise of the homework ban.
In the 19th century, while economic development was limited, most children in the United States dropped out of elementary school to ease the burden on their families. With the increasing development of society, more and more children can receive basic secondary education, but some problems about homework appear at the same time. Many parents are tired of helping their children with homework and even think that school work has no meaning.

1920s and 1930s: The Ban was Intensified
Under the influence of the homework ban, primary and secondary schools in big cities in the United States have made a series of reform measures to protect the physical and mental health of preschool children. Public schools in New York are prohibited from assigning homework to students in grades one through three. San Diego, California, bans homework for elementary and middle school students in grades 1 through 8. Chicago bans all public elementary and secondary schools from assigning homework to students at any grade level.
1950s: In response to the Cold War, Homework Returned
In 1957, the launch of the Soviet Union's Sputnik satellite brought a huge shock to the United States, and also changed the American concept of education. For 50 years, the United States had little homework, putting it at a competitive disadvantage against the Soviet Union. However, the incident galvanized the urgent need for educational reform in the U.S. government and educational institutions, including a reevaluation and reform of homework. Teachers began to provide students with targeted assignments to meet each student's learning needs. Assignments have also become more challenging and practical to help students consolidate what they have learned and expand their thinking and application skills.
Early 2000s: Homework Attracted Great Attention
In the early 1980s, the United States government organized a special committee to investigate the learning level of American students, and the survey results were very painful for Americans. That is, the basic education in the United States is poor, 23 million adults do not have enough literacy. The results of the survey triggered wide attention and discussion, and the US government and educational institutions took a series of measures to improve basic education, including improving the salary and training level of teachers, requiring teachers to assign more personalized tasks, and ensuring the improvement of teaching quality and student learning outcomes.
Looking at the history of homework in the United States, we can see from the introduction of homework to the promulgation of homework bans, to the re-strengthening of homework. The homework not only had a positive impact, but also triggered negative voices. Around the world, homework has been a controversial topic. Does it do more good than harm? Or does it do more harm than good? Let's look at the advantages and disadvantages of homework.
V. Homework: Pros and Cons
When we talk about the pros and cons of homework, we should focus on the amount of homework assigned.
Proper Amount of Homework
1.Improve the quality of school education By assigning homework, students can consolidate the knowledge learned in class, deepen the understanding and application of knowledge, enhance the learning effect, and the quality of school education will also be improved.
2.Expand students' knowledge and improve students' learning skills Through homework, students can further expand their learning, accumulate more knowledge, and improve learning skills such as reading, writing, problem solving etc. 3.Promote students' independence and sense of responsibility By completing homework independently, students can improve their self-management skills and independent thinking. At the same time, the completion of homework also requires students to have a sense of responsibility and complete the task on time, which is very important for the growth and development of students.

Excessive Homework
1.Lead to lack of sleep and affect students' health Long hours of assignment writing will leave students without enough time for rest, which is bad for students' physical and mental health.
2.Putting too much pressure on students Students need to bare academic pressure under heavy homework tasks, which may lead to anxiety and boredom of students.
3.Deprive students of their spare time Students need enough time for rest, recreation and other interests, which are very important for their well-rounded development. Too much homework may leave students no time to participate in other activities and limit their room for development.
4.Lead to cheating Too much homework may lead to cheating. When students are faced with too much homework pressure, they may look for other ways to complete the homework, such as copying or having someone write it for them. Such behavior not only violates academic ethics, but also weakens students' learning effect and ability
VI.Conclusion
You may not have thought and explored who invented homework, but I believe you have been crazy about homework. From birth to development, homework has experienced the baptism of the long river of history, and also continues to develop from time to time. Although homework once aroused the resistance of parents and students, it has to be admitted that homework plays a key role in consolidating knowledge and improving ability in our learning process. What do you think of homework? Do you think homework should be born?
With the rapid progress and development of science and technology, many countries continue to combine science and technology with education, and launch a variety of educational products to meet the learning needs of students in the new era. When it comes to homework, the use of technology has also opened up many new possibilities. While you may still be used to writing your homework with a pen and paper, or typing your answers on a computer, now is the time to try StudyX , a tool dedicated to providing a whole new way of doing homework. What is the innovation in it? Try it and you'll see!
Related Posts
Assignment Writing
Unlocking Efficiency: Mastering Assignment Writing on StudyX with Insider Tips
In the fast-paced world of academia, as a college student, are you always find yourself juggling multiple courses, extracurricular activities, and personal commitments? Among the many challenges you face, one critical aspect must be the art of assignment writing. Normally, you could dive into libraries, scouring through countless books and journals, or turning to online resources and tutorials, all in the hope of extracting the information needed for the essays, reports, or other kinds of assignments.

Homework-Efficiency
Empowering College Students to Enhance Homework Efficiency
StudyX, which stands for Study Infinity. We are committed to enhancing the efficiency of college students' homework. We are about equipping you with the tools you need to supercharge your homework efficiency and overcome the challenges you encounter with inefficient homework completion. In this article, you'll delve into how StudyX

Who Invented Homework And Why? The Facts Everyone Should Know

- Post author By admin
- September 17, 2022
Homework is now an essential part of the educational process; it facilitates and improves learning.
We’ve been completing tasks since we were in elementary school. And few of us were considering who invented homework. Why was homework invented?
Who was Robert Novelis? Who was Horace Mann? Was homework invented as a punishment?
In this blog, we’ll learn who invented homework and why, and the brief history of homework.
Table of Contents
Who invented homework?
We have no clear idea who invented homework although many people do homework most days of the week.
Many names are included with the invention of homework.
In reality, anyone who has attempted to learn something has most probably practiced it in their own place and time, so homework is simply a part of the learning process.
Homework was first mentioned in ancient Rome, in the writings of Piny the Younger, in 1AD.
Pliny, an oratory teacher, is said to have asked his students to practice public speaking at home to boost their confidence.
At the end of the 19th century, homework became universal as school/colleges became compulsory worldwide.
Why Was Homework Invented?
Over the years, supporters of homework have given a variety of reasons for its creation.
These are some of them:
- Students can consolidate their learning by practising what they’ve learned in school;
- Teachers and students can uncover learning gaps when students hand in assignments that they’ve completed independently;
- It provides students extra time to study something;
- It helps students manage their time.
On the other hand, homework has not always been popular, and in the early 1900s, it was even banned in the state of California for 15 years.
Who Was Roberto Novelis?

Roberto Novelis might well not be anyone.
It is frequently said that this name is responsible for the invention of homework.
But he might not even be real, because no one appears to know whether he developed homework in 1095 or 1905.
He is supposed to have devised the concept of homework to punish what he saw to be lazy students.
However, there is no formal confirmation of this story or even his existence.
Who Was Horace Mann?

Horace Mann was a nineteenth-century politician and educational reformer.
He believed strongly in compulsory education and was essential in the establishment of state-funded education in the United States.
After seeing it in the German Volksschulen, or “People’s Schools,” when he visited in 1843, he brought the idea of mandatory assignments to be done at home – homework – to the United States.
Brief History of Homework

- 1901-1917 : All students under the age of 15 in the state of California were prohibited from doing homework. A number of letters and statements opposing homework were published in the Ladies Home Journal and the New York Times.
- 1930: The American Child Health Association proclaimed homework to be a kind of child labour, which was a novel legal idea in the United States at the time.
- 1950: During the Cold War, the United States went on a large homework push in order for American children to thrive, particularly in math and science.
- 2000 onwards: The idea that homework was harmful to a child’s or family’s health resurfaced with the publication of homework books.
Meanwhile, students in the United Kingdom often have more homework than kids in many other European countries. I hope you have known about who invented homework.
- 16 Powerful Tips on How to Finish your Homework Faster
Was Homework Invented As a Punishment?
Yes, at first, Roberto used homework as a form of punishment. however, He also used it to guarantee that students fully absorbed and comprehended what they had studied. But because homework was created at a time when the globe was creating a formal education system, it became a vital part of that system.
People in countries like the United States, on the other hand, did not take education seriously until the twentieth century. Parents considered schooling as a hindrance in such places because they wanted their children to help them with household tasks. However, During World War II things changed when such countries realized they required educated personnel, such as scientists.
Homework in the public school system in the United States
Homework is given in schools for several different reasons. One reason is to give students a chance to put what they’ve learned in class into practice. Homework can also help kids learn how to study and handle their time. Students can also learn how to work independently by doing their schoolwork.
But there are different opinions on how much study is too much. Some experts say that giving kids too much schoolwork can harm them. They say it can cause stress, worry, and burnout. They also say that it can cut into students’ free time, which is important for their social and mental growth.
The amount of homework given changes from school to school and teacher to teacher. But some broad rules can be used as a guide. The National Education Association (NEA) says that elementary school students shouldn’t have more than an hour of schoolwork per night, middle school students shouldn’t have more than two hours of homework per night, and high school students shouldn’t have more than three hours of homework per night.
These are, of course, just suggestions. The right amount of homework for each student will depend on their needs and how well they can do it. Parents and teachers must work together to find the right balance for each kid.
Here are some ways to get your homework done:
- Set aside a certain amount of time every day to do homework.
- Find a place to work where it’s quiet and no one will bother you.
- Break up big chores into smaller ones that are easier to handle.
- When you need a break, take one.
- Ask for help if you are suffering.
Benefits Of Homework
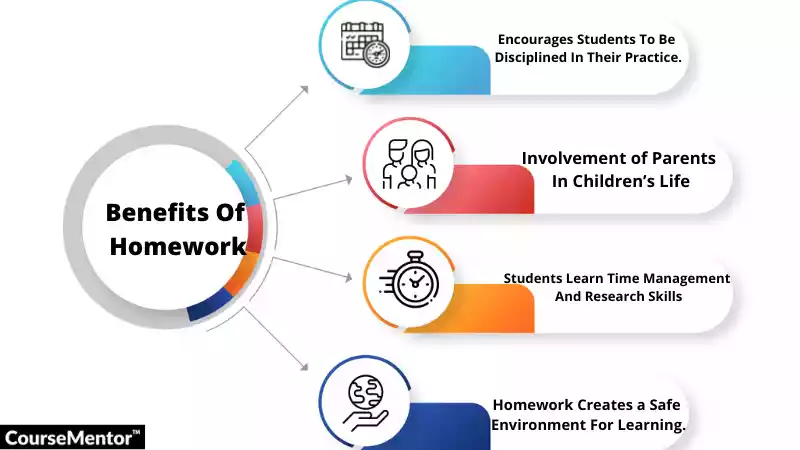
Is homework actually beneficial? Of course, there are numerous advantages for students. Let’s take a look at all of the advantages that homework can give to students in various ways.
Encourages Students To Be Disciplined In Their Practice.
Homework assists in the installation of discipline in students. Frequently, you will receive the same type of work for homework as you did in class. Practicing the same task over and over will improve your abilities in that area. You will gain a clearer and more informed understanding of the subject. If you are studying mathematics and solving a hundred numerical problems, you will gain knowledge in that subject. Reading the same material twice or three times at home will also help you gain a good grasp of the subject. Discipline like this will benefit you in other aspects of your life as well.
Involvement of Parents In Children’s Life
Parents are perplexed when they see their children’s homework. That’s quite normal. However, homework has helped in the development of a close bond between parents and children. Parents that assist their children with schoolwork learn about their child’s weak areas. Furthermore, parents want to see the homework since it will help them understand what their children are learning in school. This particular benefit is primarily for school students.
Students Learn Time Management And Research Skills
Students frequently struggle with time management. Homework helps with time management. Students will recognise the importance of time and abandon their procrastinating habits. Make a schedule and stick to it when you get your homework. A well-planned timetable will keep you motivated and on track. While doing your assignment, you will also gain research skills. You must conduct extensive research on a certain work in order to prepare for research papers and dissertations.
Homework Creates a Safe Environment For Learning.
Despite the fact that school and college are places where students should be studying, they are frequently distracted. Distractions from friends and other activities cause them to lose attention. A home is a place where one can be completely comfortable while also being able to concentrate. It is possible to learn effectively at home as well. Home is the ideal place to study because it is free of interruptions and has a quiet environment.
Demerits of homework
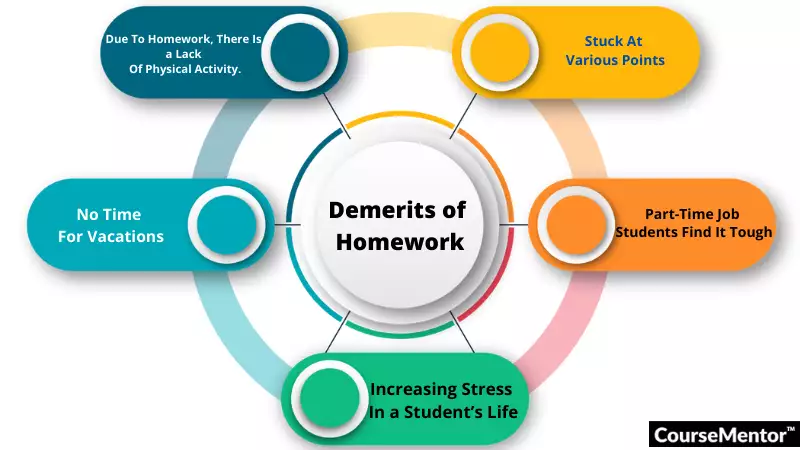
Due To Homework, There Is a Lack Of Physical Activity.
Being studious is a great thing, but physical activity is also required for a healthy lifestyle. You may have noticed that universities and institutions have begun to overburden students with homework. They don’t have any spare time at home to do other things. Due to a lack of time for outdoor activities, homework has become a barrier to students’ growth and physical development. Furthermore, a lack of physical activities causes tension among students. This has a direct impact on academic performance. As a result, many students have begun to seek online homework assistance. They prefer to hire professional writers to help them manage their academic and personal lives.
Stuck At Various Points
Students get stuck at various stages when working on their assignments. They don’t understand the concept of clarity, and they never get the right solution to a math issue. They may require assistance from some teachers or professors in such situations. Most of the time, it is not available at home.
No Time For Vacations
Students who study abroad spend little time with their families. They have so much homework and assignments that they don’t have time to spend with family or friends even on vacation. That is why most students perceive homework to be a difficult academic activity to complete and want to know “who invented homework.”
Part-Time Job Students Find It Tough
Many students work part-time jobs while pursuing their studies at the university level. Homework is difficult for such students. They have to sit with schoolwork after working for nearly half a day for their bellies. In a nutshell, homework is destroying their physical and social life. Thanks to online assignment help services, students may get support when they need it.
Increasing Stress In a Student’s Life
As you can see, there are a variety of factors that make homework a nightmare for students. As a result, students frequently ask, “Who invented homework?” They are so frustrated that they want to track down the culprit and punish him for his crime. In fact, however, this is not achievable. However, it is true that homework has contributed to a variety of mental health issues among kids. They are constantly under pressure to perform effectively and complete the assignment on schedule. Their health is unquestionably deteriorating, and homework is the primary cause.
- 10 Best Homework Help Websites- Here Are the Ones You Should Go For!
How Homework Improves the Quality of Education
You must realize that the main goal of homework is not to manage people or to punish children! This is just a fantastic approach to organizing and memorizing all of the material that has been studied. Many critical talents cannot be developed without homework. Of course, professors provide them with a wealth of material during class, but the purpose of homework is to integrate that knowledge with practical assignments in order to demonstrate how effectively the student has studied and comprehended the subject.
Many experienced psychologists believe that assimilation of both knowledge and activity approaches is critical. It encourages students to think outside the box, discover the information they need to complete a task, learn new abilities, manage their time, and apply their new skills and knowledge in the future. Every student receives their homework grades, which motivates students to spend more time studying at home, absorb the content thoroughly in class, achieve good grades, and be noticed and encouraged by their teachers.
Why Should Homework Be Banned?
Even with all the potential benefits of homework, some people say it should be prohibited because spending more time on it costs children too much time, produces a stressful environment at home and at school, and fosters unequal access to resources between rich and poor families.
In addition to these concerns, some opponents of homework argue that helping their children with homework is unfair to parents who work long hours or have numerous jobs outside the home.
The other side of the argument for making homework illegal is that if it were made illegal, students would spend more time doing other constructive things like sports or spending time with their families. The concept is based on the premise that children will be better prepared to engage in these activities if they had a day off from school.
The final point is that homework does not always boost learning or grades; in fact, some research suggest that the amount of time spent on homework and standardised test scores may be negatively correlated.
Students’ work quality deteriorates when they become tired or bored while completing it, and they don’t learn from homework if all they care about is finishing it.
Those who oppose banning it propose giving children smaller amounts of work to do each night instead of an entire night’s worth of homework.
Quick Facts About Homework
- Roberto Nevilis isn’t the person who invented homework.
- Johann Gottlieb Fichte invented homework.
- Horace Mann, who is wrongly credited with inventing homework, brought it to the United States in the nineteenth century.
Conclusion (Who Invented Homework)
In this blog, we have discussed who invented homework in detail. Regardless of who invented homework, it is here to stay.
While homework has many advantages, educators must know when and how to use it as a tool to classroom learning rather than as a replacement.
anxiety, depression and anger are common symptoms of overworked children.
Homework is not always useful for students because it might take time away from studying or playing outside, both of which are essential for a child’s holistic development.
If you have other ideas and questions about who invented homework and why feel free to share your comments in the below section.

FAQs Related To Who Invented Homework
Is it normal to cry over homework.
Sometimes, homework upsets our children. Executive function deficits, learning disabilities, or difficult subjects can make children cry or lash out during homework time.
How is homework harmful?
“The findings were troubling: Research showed that excessive homework is associated with high-stress levels, physical health problems and lack of balance in children’s lives; 56% of the students in the study cited homework as a primary stressor in their lives,” according to the CNN story.
- australia (2)
- duolingo (13)
- Education (284)
- General (78)
- How To (18)
- IELTS (127)
- Latest Updates (162)
- Malta Visa (6)
- Permanent residency (1)
- Programming (31)
- Scholarship (1)
- Sponsored (4)
- Study Abroad (187)
- Technology (12)
- work permit (8)
Recent Posts


The Unknown History of Homework: Find Out Its True Origins!

I. Introduction
For countless generations, homework has been a staple in educational systems worldwide, but have you ever stopped to wonder why homework was invented in the first place? This article takes a deep dive into the history of homework, its evolution, and its purpose in education.
II. Defining Homework
A. what is homework .
Before we delve into the history of homework, it is crucial that we first understand what exactly it entails. Homework is traditionally defined as tasks assigned to students by their teachers to be completed outside of class hours. These tasks include individual assignments, collaborative projects, reading, or preparation for future lessons.
B. Different Types of Homework
While most of us think homework is completing worksheets or reading textbook chapters, homework can take many forms. From solving math problems to conducting scientific experiments and writing essays, the variety of homework is vast and multifaceted.
III. Historical Overview of Homework
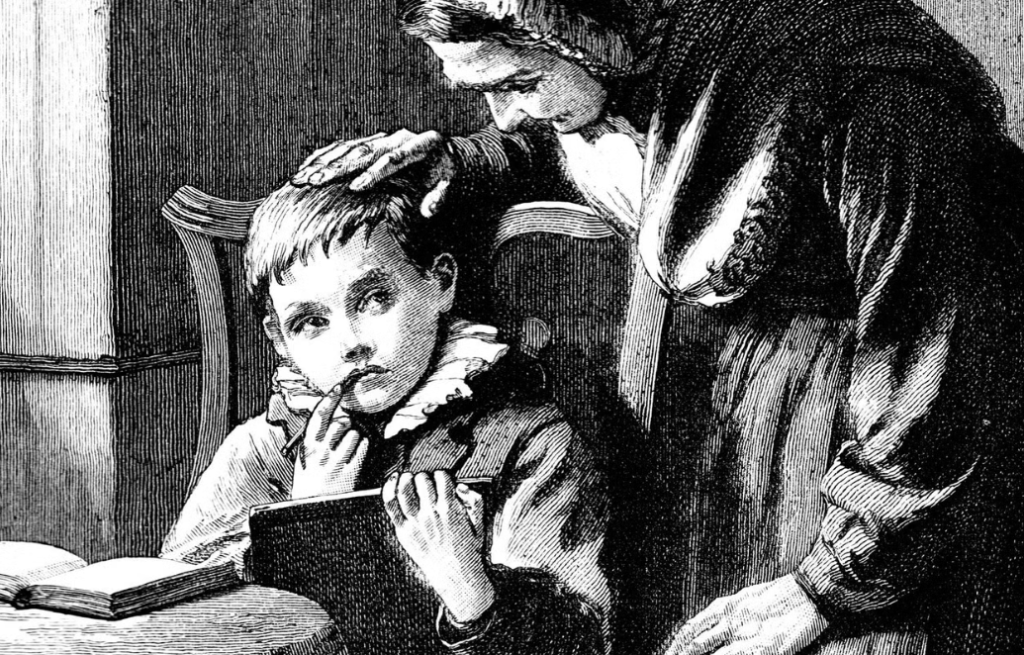

A. History of Homework
The origins of homework can be traced back to ancient times , much earlier than many of us might guess. In fact, the seeds of homework were sown in the education systems of some of the world’s earliest civilizations.
One of the first recorded instances of homework was seen in ancient Rome. A teacher named Pliny the Younger, who lived in the 1st century CE, instructed his followers to practice public speaking at home. The aim was to strengthen their oratory skills, a highly prized quality in Roman society, where eloquent and persuasive speech held the key to political power and social prestige.
This simple practice of extending learning beyond the confines of the classroom set the stage for what we now recognize as homework. From these humble beginnings in ancient Rome, the concept spread through the ages and across different cultures, evolving in response to various educational philosophies and societal needs.

- FAST HOMEWORK HELP
- HELP FROM TOP TUTORS
- ZERO PLAGIARISM
- SECURE PAYMENT SYSTEM
- PRIVACY GUARANTEED
B. Evolution of Homework Over the Ages
Contrary to what many might assume, homework is not static; it has transformed significantly over the centuries, mirroring the shifts in educational paradigms and societal changes.
A crucial period in the evolution of homework was during the industrial revolution. In this era, schools were modeled after factories, with their bell schedules, standardization, and age-based cohorts. Homework, in this context, was seen as a means to instill discipline and punctuality in students, echoing the rigors of factory work.
The industrial revolution marked a shift from an agrarian society to an industrial one, and homework was seen as a tool to prepare students for this new world. It was used to reinforce rote memorization and obedience, skills that were deemed essential for thriving in an industrialized society.
As the years passed, the purpose of homework underwent further changes. In the 20th century, the advent of progressive education movements led to a rethinking of homework. Emphasis shifted from rote learning to understanding and from individual tasks to collaborative projects. This period saw an increase in homework that encouraged critical thinking and creativity.
Today, homework is used to reinforce classroom teaching and promote independent learning, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. The nature of assignments has also changed; they’re often more engaging and interactive, incorporating modern technology and multimedia resources.
Thus, the homework journey from ancient Rome to the present day is a testament to its adaptability and enduring role in education.
IV. The Original Purpose of Homework

A. Enforcing Discipline and Routine
One of the homework’s earliest and most enduring purposes was to enforce discipline and routine among students. In a time when formal education was still finding its footing, homework served as a tool to teach students key skills that extended beyond academics.
Assigning tasks to be completed outside of the classroom instilled a sense of responsibility in students. They learned to manage their time effectively, allocate resources, and meet deadlines, skills that are crucial in both academic and real-world scenarios. Moreover, a structured routine helped students to cultivate good work habits, improved focus, and fostered a consistent work ethic.
B. Reinforcing Class Learning
Beyond instilling discipline and routine, homework was conceived as a crucial tool for reinforcing the learning that took place within the classroom walls. While an integral site for learning, the classroom had its limitations – fixed timings, varying student understanding, and limited opportunities for individual attention.
Homework offered a solution to these constraints. By revisiting lessons at home, students could cement their understanding and explore topics at their own pace. It served to supplement in-class learning, giving students the chance to review, practice, and integrate what they had learned. It allowed the learning process to continue beyond the school, bridging the gap between the classroom and the home.
V. Noteworthy Proponents and Critics of Homework Through the Ages

A. Early Supporters of Homework
From ancient philosophers to modern educators, numerous notable figures have supported the practice of homework. One of the earliest proponents was Pliny the Younger in ancient Rome who saw homework as a way to refine public speaking skills.
Fast forward to more recent times, educational theorists like John Dewey and E.L. Thorndike have also advocated for homework. They saw it as a means to extend learning time, encourage independent thought, and foster a passion for lifelong learning. By promoting homework, these figures aimed to nurture self-directed learners who could take ownership of their educational journey.

NEED HOMEWORK HELP? CLICK THIS BUTTON TO GET A TUTOR
B. Famous Criticisms and Critics
Despite the widespread implementation of homework, it has not been without its fair share of critics throughout history. Critics argue that while homework in moderation can be beneficial, excessive amounts can lead to detrimental effects.
Among the critics, Alfie Kohn, an influential American author and lecturer in the areas of education and human behavior, argues that homework might not be as beneficial as we believe it to be. He asserts that excessive homework can lead to stress, reduced leisure and family time, and even a counterproductive attitude towards learning. He believes learning should be an engaging and enjoyable process, not a chore.
This highlights the need for a balanced and thoughtful approach to homework. It reminds us that while homework can serve as a powerful learning tool, like all tools, its effectiveness depends largely on how it’s used.
VI. Impact of Homework on Education Systems Globally
A. comparison across different cultures .
The role, importance, and amount of homework can vary dramatically from one culture to another, painting a fascinating global picture. Consider the case of Finland and Japan – two countries with starkly different approaches to homework.
In Finland, ranked consistently among the world’s highest in terms of academic achievement, the education system takes a somewhat unconventional approach to homework. Finnish schools believe that students should have more time for leisure and activities outside of school. They place a greater emphasis on in-class work and interactive learning rather than after-school assignments. The homework given is minimal and often open-ended, aimed to promote critical thinking and creativity. The Finnish philosophy is predicated on the belief that there should be a balance between work and play, and that less can be more when it comes to homework.
On the other hand, countries like Japan are known for their rigorous academic demands. In this educational system, after-school self-study is deeply ingrained in the culture, and homework is seen as an integral part of learning. Japanese students often spend hours on homework after school, which is seen as a means of reinforcing lessons, building perseverance, and instilling a strong work ethic. The goal is often to prepare students for competitive entrance exams and the demanding work culture.
These contrasting approaches illustrate how different societies value and utilize homework in their education systems. They show that there is more than one way to achieve academic excellence, and the ‘right’ amount of homework can depend greatly on cultural context and educational philosophy

B. Studies on the Effectiveness of Homework
Numerous studies have been conducted on the effectiveness of homework, and their conclusions may surprise you. On the one hand, research unequivocally indicate s that homework, when used appropriately, can boost academic achievement. It reinforces what students learn in the classroom, allows them to practice and apply their understanding, and enhances their study skills and work habits.
A seminal study by Harris Cooper, known as the ‘Homework Guru,’ found that there is a correlation between homework and academic achievement. This correlation is stronger in older students (those in high school) compared to younger ones (those in elementary school). This suggests that homework can be a powerful tool in enhancing learning outcomes.
However, it’s not as simple as ‘more homework equals better grades.’ In fact, there seems to be a ‘sweet spot’ for the amount of homework students should do. Cooper’s research indicates that the benefits of homework are robust up to about an hour to two hours per night for high school students, and less for younger students. Beyond this point, the positive effects start to diminish, and could even turn negative due to fatigue and stress. This means that quality, not quantity, of homework is crucial.
A notable study from Stanford University found that excessive homework can lead to high stress levels, physical health problems, and less time for leisure, socializing, and extracurricular activities. Students in the study who were given more than two hours of homework a night reported higher levels of stress, sleep disruption, and other health issues.
These studies underline the importance of finding the right balance in assigning homework. While it can be a useful learning tool, it’s crucial to ensure that it does not become a source of undue stress for students, and that it is tailored to their age, individual capabilities, and the course’s learning objectives.”

VII. The Modern Purpose and Future of Homework
A. current views on homework.
In the 21st century, the purpose of homework has adapted and evolved in response to modern educational theories and research. Today, homework is seen as a tool for rote learning and developing critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills.”
B. The Future of Homework
As we look to the future, the concept of homework is likely to continue evolving to meet the needs of a rapidly changing educational landscape. With the rise of technology, digital homework and ‘flipped classrooms’ are becoming more common, transforming the way we think about homework.
VIII. Reflections on Homework’s Role in Education
As we look back on the journey of how homework was conceived and how it has morphed over time, we can gain a deeper understanding of its role and significance in our education systems. This understanding can help us form a more balanced and nuanced perspective of homework, rather than viewing it as either entirely beneficial or entirely detrimental.
In its inception, homework was seen as a tool to instill discipline and routine. As time went on, it evolved into an instrument for reinforcing lessons taught in the classroom and promoting independent study. Today, the role of homework has expanded further to encourage critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and even digital proficiency. It serves multiple purposes, from enabling teachers to assess a student’s understanding and progress, to providing students with an opportunity to apply and extend their learning.
However, as much as we recognize the benefits of homework, we also need to consider the criticisms. The potential for stress and burnout, the encroachment on free time, and the potential for exacerbating socio-economic disparities are all significant concerns that can’t be overlooked. Therefore, educators must strive for a balance – assigning meaningful and manageable homework that can enhance learning without causing undue pressure.
Whether you’re an advocate or a critic of homework, there’s no denying that it plays a significant role in education. Homework influences academic outcomes and shapes a student’s work ethic, time management skills, and attitudes towards learning. As such, the dialogue about homework and how it can be optimally utilized is important for all stakeholders in education – from policymakers and educators to parents and students.
In the end, our collective aim should be to leverage homework as a constructive tool that aids and enriches a student’s educational journey rather than as a stress-inducing burden. This requires an ongoing review, reflection, and adjustment process to ensure that homework enhances student learning and development.

XI. What to Do If Unable to Complete Homework
Feeling overwhelmed by homework is something almost every student experiences at some point in their academic journey. If you find yourself unable to complete your homework, don’t despair. Several strategies can help:
A. Break it Down Into Manageable Parts
Instead of viewing your homework as one monumental task, try breaking it down into smaller, manageable tasks. This will make it less overwhelming and easier to start.
B. Set a Schedule .
Allocate specific time slots for your homework. Having a structured schedule can help increase your productivity and prevent procrastination.
C. Seek Help from Teachers or Peers
If you’re struggling with a particular task, don’t hesitate to reach out to your teachers or classmates for clarification or help. Sometimes, a different perspective can make all the difference.
D. Use Online Resources
The internet is a treasure trove of information and resources. Websites like Khan Academy, Coursera, and others offer free lessons and exercises on a variety of subjects.
E. Hire a Tutor
If you consistently struggle with your homework, it might be worthwhile to consider hiring a tutor. A tutor can provide personalized guidance and help you grasp difficult concepts. Websites like ProofTutors provide online tutoring services that can assist you in a wide range of subjects at any time that is convenient for you.

IX. FAQs
Who invented homework?
Homework, as we know it today, is attributed to Roberto Nevilis, an Italian pedagog who reportedly invented homework in 1905 as a punishment for his students—however, the concept of studying at home dates back to ancient civilizations.
Why is homework important? Homework serves several purposes. It reinforces what has been taught in class, prepares students for upcoming lessons, promotes responsibility and discipline, and encourages independent work. Homework also allows parents to be involved in their child’s education.
What are the pros and cons of homework?
The pros of homework include reinforcing classroom learning, teaching responsibility, and time management, and allowing parents to track their child’s progress. On the downside, excessive homework can cause stress and burnout, limit students’ time for other activities, and exacerbate socio-economic disparities if not all students have equal access to resources for completing homework.
How much homework is too much?
This can vary significantly depending on the age and level of the students, the subject, and the school’s homework policy. However, the National PTA and the National Education Association recommend the “10-minute rule,” which suggests 10 minutes of homework per grade level per night, starting from first grade.
How has the purpose of homework changed over time?
Originally, homework served primarily to instil discipline and punctuality, but over time, it has evolved to reinforce class learning, promote independent study, and foster critical thinking skills. Nowadays, homework also incorporates digital skills and is sometimes part of a ‘flipped classroom’ approach to teaching.
How does homework vary across different cultures?
Homework policies and practices vary widely across different cultures. For example, in Finland, there’s less emphasis on homework, and education focuses more on student well-being and holistic learning. In contrast, Asian countries like Japan and China tend to emphasize homework and academic rigor more.

What’s the point of homework?
Deputy Dean, School of Education, Western Sydney University
Disclosure statement
Katina Zammit does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Western Sydney University provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
Homework hasn’t changed much in the past few decades. Most children are still sent home with about an hour’s worth of homework each day, mostly practising what they were taught in class.
If we look internationally, homework is assigned in every country that participated in the OECD’s Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) in 2012.
Across the participating countries, 15-year-old students reported spending almost five hours per week doing homework in 2012. Australian students spent six hours per week on average on homework. Students in Singapore spent seven hours on homework, and in Shanghai, China they did homework for about 14 hours per week on average.
Read more: Aussie students are a year behind students 10 years ago in science, maths and reading
Shanghai and Singapore routinely score higher than Australia in the PISA maths, science and reading tests. But homework could just be one of the factors leading to higher results. In Finland, which also scores higher than Australia, students spent less than three hours on homework per week.
So, what’s the purpose of homework and what does the evidence say about whether it fulfils its purpose?
Why do teachers set homework?
Each school in Australia has its own homework policy developed in consultation with teachers and parents or caregivers, under the guiding principles of state or regional education departments.
For instance, according to the New South Wales homework policy “… tasks should be assigned by teachers with a specific, explicit learning purpose”.
Homework in NSW should also be “purposeful and designed to meet specific learning goals”, and “built on knowledge, skills and understanding developed in class”. But there is limited, if any, guidance on how often homework should be set.
Research based on teacher interviews shows they set homework for a range of reasons. These include to:
establish and improve communication between parents and children about learning
help children be more responsible, confident and disciplined
practise or review material from class
determine children’s understanding of the lesson and/or skills
introduce new material to be presented in class
provide students with opportunities to apply and integrate skills to new situations or interest areas
get students to use their own skills to create work.
So, does homework achieve what teachers intend it to?
Do we know if it ‘works’?
Studies on homework are frequently quite general, and don’t consider specific types of homework tasks. So it isn’t easy to measure how effective homework could be, or to compare studies.
But there are several things we can say.
First, it’s better if every student gets the kind of homework task that benefits them personally, such as one that helps them answer questions they had, or understand a problem they couldn’t quite grasp in class. This promotes students’ confidence and control of their own learning.
Read more: Learning from home is testing students' online search skills. Here are 3 ways to improve them
Giving students repetitive tasks may not have much value . For instance, calculating the answer to 120 similar algorithms, such as adding two different numbers 120 times may make the student think maths is irrelevant and boring. In this case, children are not being encouraged to find solutions but simply applying a formula they learnt in school.
In primary schools, homework that aims to improve children’s confidence and learning discipline can be beneficial. For example, children can be asked to practise giving a presentation on a topic of their interest. This could help build their competence in speaking in front of a class.

Homework can also highlight equity issues. It can be particularly burdensome for socioeconomically disadvantaged students who may not have a space, the resources or as much time due to family and work commitments. Their parents may also not feel capable of supporting them or have their own work commitments.
According to the PISA studies mentioned earlier, socioeconomically disadvantaged 15 year olds spend nearly three hours less on homework each week than their advantaged peers.
Read more: 'I was astonished at how quickly they made gains': online tutoring helps struggling students catch up
What kind of homework is best?
Homework can be engaging and contribute to learning if it is more than just a sheet of maths or list of spelling words not linked to class learning. From summarising various studies’ findings, “good” homework should be:
personalised to each child rather than the same for all students in the class. This is more likely to make a difference to a child’s learning and performance
achievable, so the child can complete it independently, building skills in managing their time and behaviour
aligned to the learning in the classroom.
If you aren’t happy with the homework your child is given then approach the school. If your child is having difficulty with doing the homework, the teacher needs to know. It shouldn’t be burdensome for you or your children.
- Disadvantaged students

Casual Facilitator: GERRIC Student Programs - Arts, Design and Architecture

Senior Lecturer, Digital Advertising

Associate Professor, Psychology

Service Delivery Fleet Coordinator

Manager, Centre Policy and Translation
Who Invented Homework?
Have you ever asked yourself who invented homework? Have you ever thought of how it became a school requirement? The concept of homework has created a lot of debate among instructors and learners. Students frequently despise it, seeing it as an unnecessary laborious task. Instructors on the other hand, usually believe it is essential for academic progress.
Homework is a collection of instructional duties assigned to learners by teachers. It often applies in regular free time. It promotes classroom learning and enables students to practice what they've learned. Homework promotes individual study habits, self-discipline, and time management abilities.
Homework became more prevalent as formal scholars, and educators sought ways to reinforce classroom learning, foster independent study habits, and prepare students for academic challenges.
When was Homework Invented?
The Invention of homework has vague timelines with its origins not pinpointed to a specific time or individual. Although it has ancient roots, modern assignment began in the 19th and early 20th centuries.
The early 20th century is often associated with the popularization of homework. Roberto Nevilis, an Italian teacher, is sometimes credited with inventing homework. However, historical documentation regarding Nevilis and his role in developing assignments is limited. His educational career evolved through the contributions of other educators.
How was homework invented?
Homework has been evolving in response to changes in educational philosophies and practices. It has undergone different transitions based on historical trends and other external factors like culture.
Homework evolved organically over centuries as a response to changing educational needs and philosophies. It was shaped by influential educators, cultural practices, and the evolving understanding of how learning occurs.
The invention of homework is more accurately described as a gradual development rather than an event initiated by a single person.
Who invented homework?
Though the idea of homework has a long history and cannot be credited to a single creator, there is a suggestion that in the early twentieth century, Roberto Nevilis, an Italian educator, had a part in popularizing the present practice of homework.
However, assigning homework to be accomplished outside of regular class hours evolved and was inspired by various educational concepts and systems.
How Roberto Nevilis Invented Homework
Roberto Nevilis is credited with being the inventor of homework. Nevilis felt that students should have done extra learning or exploration after leaving their class. Most of them failed in their exams. He was disappointed and had to take a different measure.
Contributions of Roberto Nevilis to education
Roberto Nevilis is often credited as the inventor of homework. However, there needs to be more historical evidence of how he came up with the idea of issuing homework. Little is known about his life. He introduced the practice of assigning students academic tasks to be completed outside of regular class hours.
Nevilis was an Italian educator who implemented homework in the early 20th century. He invented homework to extend the learning process beyond the classroom. Roberto Nevilis aimed to reinforce lessons through additional practice and study.
The Homework Myth of Roberto Nevilis
The association of Roberto Nevilis with inventing homework appears to be more of a myth than a verifiable historical fact. Although Nevilis is often credited with having invented homework in the early 20th century, the evidence supporting this claim is sparse and lacks definitive historical documentation.
Attributing homework to Nevilis will likely simplify a more complex historical evolution. Homework, as a concept, has ancient roots, and its development has been influenced by various educational philosophies, cultural practices, and reform movements over centuries.
In critical historical analysis, Roberto Nevilis invented homework. However, it's essential to approach his role in the invention of homework with skepticism, acknowledging that the history of education is a nuanced and multifaceted narrative shaped by the contributions of many individuals and evolving educational systems.
What if Roberto Nevillis did not exist?
If Roberto Nevilis did not exist, it would not have changed the historical evolution of homework. Assigning homework to be completed outside of regular class hours has deep historical roots, going back to ancient civilizations. Various cultures and educational systems have contributed to homework development over time.
While the association of Nevilis with the invention of homework is often cited, it is more of a myth or anecdote than a well-documented historical fact. The practice of assigning homework outside of the classroom evolved organically, influenced by changing educational philosophies, societal needs, and pedagogical innovations.
If Roberto Nevilis was removed from the narrative, the discussion on who invented homework would persist. Other educators, philosophers, and educational reformers throughout history would have gained that recognition. The key factors influencing homework practice extend beyond any individual, making it a complex and multifaceted aspect of the educational landscape.
Why was homework invented?
Nevilis invented homework to reinforce classroom learning and extend educational opportunities beyond regular school hours. Its invention is linked to the belief that repetitive practice and individual study enhance comprehension and retention of knowledge.
Homework serves to solidify concepts, offering students a chance to apply what they've learned independently. Additionally, it promotes time management skills, responsibility, and autonomy in learning.
Other Key Players in Homework
Homework has evolved dynamically due to historical, cultural, and educational forces. Different philosophers and academic enthusiasts have played an extensive role in ensuring homework in their respective countries.
Horace Mann
Horace Mann significantly contributed to education in the United States during the 19th century. He is well referred to as the father of modern homework. Horace created homework from the ideas he gained from the German’s private institutions. He is often referred to as the Father of the Common School Movement. Mann was pivotal in shaping the American public education system as the Massachusetts Board of Education Secretary.
One of his key contributions was the advocacy for the common school model, which aimed to provide free, non-sectarian education to all children. Mann believed that education was essential for preserving democracy and social equality, and he worked tirelessly to establish a system that would serve the needs of a diverse and growing society.
Mann's influence extended beyond the structural aspects of public education. He emphasized the moral and civic dimensions of learning, arguing that any school should instill values such as responsibility, discipline, and civic virtues. He also recommended a tax-funded public education for all American students.
Mann also noted that homework enhanced good discipline and character development. His vision helped shape the broader goals of American private and public education, emphasizing its role in creating informed and responsible citizens capable of contributing to the democratic fabric of the nation.
Johann Heinrich
Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi was a Swiss educational reformer who lived between 1746 and 1827. He contributed substantially to education, particularly during the late 18th and early 19th centuries. His ideas and practices revolutionized pedagogy, emphasizing a holistic approach to education.
- May 23 Classical Academy says goodbye to first-ever Saudi Arabian foreign exchange student
- May 23 Senior Brady Goe receives lucrative baseball scholarship
- May 10 Chess World Championship Tournament Ends in a Victory for Chinese Grandmaster
- January 31 Did Knives Out Age Like Milk?
- January 25 See How They Run: An Wall-Breaking Whodunnit

Entertainment
Homework: The True Reality Behind It
Sophia Wecker , Editor | March 16, 2021

Photo provided by Sigmund
Homework. Something almost everyone in school— no matter what age, grade or where they live— all dread. But, why do we have homework?
In 1905, an Italian teacher named Roberto Nevilis invented the concept of “homework.” Originally, its purpose was to be used as a punishment for students who were lazy in class or for those who were disobedient or rude to their teacher. This practice became popular and became more frequently used around the world. A few years after it was invented, it became a standard thing that almost all teachers worldwide began regularly giving out to students after school every day or most days.
Students are usually mentally and physically drained when they come home from school, sports, or after they go somewhere after school and having homework assigned to them puts more even stress onto their plates. Whereas other students might like homework or enjoy doing it because it can benefit them academically or might help with avoiding boredom. Either way, there are both positive and negative sides to homework.
Nowadays, teachers assign homework for either what was left over from class or for extra work to help expand upon the topics taught while in school. But, is that really a smart and good reason to assign homework? Like what was mentioned earlier, students like to come home after a long day of school and relax and have some downtime or possibly hang out with their friends and/or family. But if they have assignments that could take them multiple hours to do that are all due by midnight, this erases this precious free time for students.
Though we may hate to admit it, there are some upsides to homework. Students who need extra help or practice on a topic or subject may benefit from additional work through their homework. Others might like some extra practice to better their understanding or to possibly get ahead in a subject to get higher test and quiz scores.
Despite the extra help homework gives, it’s not always necessary. Like mentioned earlier, some students may have a hard time completing homework because of time, their own individual lives and it just might not be needed for some students so it shouldn’t be necessary for them.
Although homework is annoying and isn’t always necessary, we need to continue to do our best and complete this task because it will benefit us later in life. But I do ask teachers to give students a break or to give them time to rest up after long and hard days. On a personal note, homework has always been a struggle for me to get done because of my busy schedule, but as mentioned before, I do ask teachers to give less or no homework, out of the courtesy of students’ time. Although we might need homework for extra help, those who do excel and are carrying good grades in a class do not need extra work. Teachers, please take from this article and help the students in your classrooms to do their best, not by giving them homework, but by understanding their circumstances and their own individual lives.

Red Velvet – Your Sweet New Obsession

Spotify’s Newest Non-Genre

Rating Halloween Candy as Someone Who Hates Food

Mental, Physical, and Emotional: Keep Yourself Healthy

Dear Discouraged Student

Chess World Championship Tournament Ends in a Victory for Chinese Grandmaster

Did Knives Out Age Like Milk?

See How They Run: An Wall-Breaking Whodunnit

Decision To Leave – An Impressive Waste Of Time?

From an Irate Senior to CAHS Administration: A Letter Concerning the 2022-2023 Phone Policy
Comments (10).
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Logan • Oct 20, 2022 at 11:28 am
if you are doing an essay on homework here are some more websites for 6-8th grade: Johnson, Geoff. “Piling Homework on Kids Is a Mistake That Undermines Work/Life Balance.” Times-Colonist, 09/05 2021. ProQuest; SIRS Issues Researcher, https://explore.proquest.com/sirsissuesresearcher/document/2578243016?accountid=65482 .
Moniuszko, S. M. (2021, 08/23). Heavy Homework Load May Be Detrimental to Health. USA TODAY https://explore.proquest.com/sirsissuesresearcher/document/2564234859?accountid=65482
Patterson, K. (2021, 11/09). Homework Isn’t Helpful in First Grade Or in College. University Wire https://explore.proquest.com/sirsissuesresearcher/document/2617064023?accountid=65482
Logan • Oct 20, 2022 at 11:31 am
also the cites are in APA 7
ethan • Oct 17, 2022 at 7:07 am
you helped my essay
FreezingZozi • Oct 4, 2022 at 8:59 am
why don’t they give homework to students that want or need homework not everyone in a class
Ece • Oct 1, 2022 at 1:43 pm
tysm good story
Ali Syed Karim • Sep 25, 2022 at 6:43 pm
The fact that homework is for all students is annoying, and its original use was just for students who were lazy or who were being disrespectful and disobedient in class. I hate homework.
James • Jun 7, 2022 at 6:02 am
this is relay helpful
Matthew • Apr 7, 2022 at 12:27 pm
James • Jun 7, 2022 at 6:17 am
Karen • Aug 3, 2022 at 6:42 pm
Great story
History of Homework
The institution of homework is deeply embedded in the American culture. How many times as a child have you heard your parents say that you can’t go outside, play games, or get dessert until you have finished your homework? Or how many times have you uttered that phrase to your own children? Although the concept of a homework assignment has been questioned throughout history, and probably will be, time and time again, it is still viewed as something normal, and as a part of every student’s life. Even outside the school, phrases like “you haven’t done your homework on that pitch/project” are used to suggest that a person hasn’t done all they could have done to prepare for a certain challenge.
Now, over time, the public’s attitude toward homework has changed numerous times, keeping in line with then active social trends and philosophies, and that battle is still raging on today. But before we take a look at what the future holds for the concept of homework, let’s take a trip down memory lane first. You will find that the arguments in favor or against homework were almost exactly the same as they are today.
Homework through History
Seeing as primary education at the end of 19th century was not mandatory, student attendance couldn’t be described as regular. The classrooms were a lot different, as well, with students of different ages sitting together in the same class. Moreover, a very small percentage of children would choose to pursue education past the 4th grade. Once they have learned to read, write, and do some basic arithmetic, they would leave school in order to find work or to help around the house. Homework was rare occurrence, because setting aside a few hours for learning each night interfered with their chores and daily obligations.
As education became more available and more progressive at the turn of the 20th century, there was a strong rebellion against homework taking place in academic circles. Even pediatricians got in on the debate, stating that children should not be made to do homework, as it robs them of all the benefits provided by physical activities and time spent outside the house. Seeing as conditions such as the attention deficit disorder were not diagnosed back then, homework was to blame.
This anti-homework movement reached its peak in the 1930s, with a Society for the Abolition of Homework being formed in order to prevent schools from giving students homework, with numerous school districts following their lead. Even in those schools where homework was not abolished, very few homework assignments were given. This continued all the way until the end of the 1950s, which marked a sharp turn in country’s attitude towards homework.
The reason for this was the launch of the Sputnik I satellite by the Soviet Union in 1957. Seeing as the entire Cold War era was marked by the constant competition between USA and the Soviet Union, U.S. educators, teachers, and even parents were afraid that their children, and the entire nation, would be left behind by their Soviet counterparts, who would lead the way into the future, which meant that homework was once again back on the map, and more important than ever.
Things changed again in the late 60s and early 70s. Vietnam War was still raging on, giving birth to civil rights movement and counterculture, which were looking to shake up all of the previously established norms. Homework was yet again under the microscope. It was argued that homework got in the way of kids socializing, and even their sleep, which meant that homework had yet again fallen from grace, just like it had at the beginning of the century.
In the 1980s, the climate changed again, spurred on by the study called A Nation at Risk which blamed the shaky U.S. economy on schools which weren’t challenging their students enough. As a result, the entire school system was labeled as mediocre in an age where the entire country was striving toward excellence, as saw the bright young minds of tomorrow as its way out. There was more of everything: classes, grades, tests, and more homework. This trend spilled over into the 90s, as well.
At the end of the 90s, homework was yet again under the attack. It was cited that children are overworked and stressed out. The increasing demand for tutors was the key argument. If students needed homework assignment help, there was too much of it. But, besides homework help, homework was also viewed as an obstacle for families with two working parents. The only time parents would get to spend time with their children was being usurped, as kids were forced to work on their homework for hours.
Present Day
While few will argue the role homework plays in reinforcing the information taught in class, there is still talk about how much homework is too much. According to certain studies, the effectiveness of homework starts to decline if the students are given more than 90 minutes of homework every day, which is evident by their test results. Current trends are not concerned with whether or not homework has its merits. It does, there is no question about it, but the main goal right now find the right balance between quantity and quality.
Also, homework in a traditional sense might be susceptible to change, because of the increasingly important role modern technology plays in our lives, and it affects the students, as well. We don’t know what the future holds, but one thing is for sure: we should always do our homework and be prepared.

What’s the Purpose of Homework?
Finding the right balance between school and home..
Posted November 4, 2014 | Reviewed by Jessica Schrader
- What Is Stress?
- Take our Burnout Test
- Find a therapist to overcome stress

Remember the days of sitting in class waiting eagerly for the bell to ring before the teacher said that dreaded word, “homework”? Sighs, rolling eyes, and grunts quickly filled the quiet classroom at the mention of that word. Well, not much has changed today except for the fact that many teachers post assignments electronically. I have yet to see a student jump for joy when the word homework is mentioned, nor have I seen students eager to get home to do their homework (maybe finish it, but not to do it). This brings up the question, “What’s the purpose of homework?”
Research shows mixed results when it comes to homework. Some research has shown that students aren’t doing any more homework than their parents did at their age. In a study, school-aged children and parents completed surveys about how much homework youth have. The results showed that the typical elementary student has 30-45 minutes of homework each night. The average high-school student has about 60 minutes per night. Interestingly, these numbers have remained consistent since 1984!
As an educator, I would like to see a replication of this study. Today's teens are taking college-level courses as early as the ninth and tenth grade. With the push of programs such as Advanced Placement, International Baccalaureate, and Dual Enrollment, it is amazing that teens are not completely burnt out. No wonder 8% of teen's age 13-18 years meet the criteria for an anxiety disorder. Too many teens are spending a lot of time on schoolwork outside of the classroom. Ask today's teen what has him/her so stressed and you'll find that about 80% of them will say school.

There are those who argue that homework does serve a purpose . For example, it helps to prepare students for national and statewide exams and tests. It helps to reinforce what’s being taught in the classroom. It enables parents to actively engage in their child’s education . Plus, it helps teach fundamental skills such as time management , organization, task completion, as well as responsibility. What’s more important is students get to demonstrate mastery of material without the assistance of a teacher.
How much homework should your child do each night? Organizations such as the National Parent Teacher Association support giving students about 10 minutes of homework each night, per grade level, starting in first grade. So a middle school student would have a full day in school and then an additional 60 minutes of homework after school. Is that too much? Are these guidelines being followed? I would recommend speaking with high-achieving teens and let them share how much of their time is consumed with homework. Many will tell you that they spend hours upon hours each night studying for tests, and preparing for papers and projects, etc.
According to Stanford University , more than a couple of hours of homework a night may be counterproductive. Researchers looked at students in high achieving communities, defined as a median household income exceeding $90,000, and 93% of the students attended post-secondary institutions. Students in these areas spent an average of three-plus hours on homework every night. So imagine a teen spending an entire day at school, going to work or extracurricular activities, then going home to do three or more hours of homework each night; only to get up the next day to do it all again.
Researchers have found that students who spend too much time on homework experience more levels of stress and physical health problems. Too much homework has also been shown to have a negative impact on students’ social lives. This is no surprise to the parents who rarely see their child because he/she is too busy working on homework, or to the parent who gets up at 12:30 A.M. to check to see if their child has made it to bed yet. Overall, high school students shouldn’t be spending over two hours on homework each night.

According to the Stanford study , too much homework leads to:
•Stress: 56% of the students surveyed considered homework a primary source of stress. Less than 1% of the students said homework was not a stressor.
•Poor health: Many students reported sleep deprivation, headaches, stomach problems, weight loss, and exhaustion.
•Less time for a social life : Students reported that spending too much time on homework led to pulling out of enjoyable activities, quitting extracurricular activities, and not spending much time with family and friends.
OK, I know not all students spend a lot of time doing homework. According to a survey by the U.S. Dept. of Education’s National Center for Education Statistics , the majority of youth spend an average of seven hours of homework outside of school each week. So while that doesn't seem like an unreasonable amount, what about the student who spends three-plus hours per night? Where is the happy medium?

There are definitely pros and cons to doing homework. I think the bigger question that educators need to address is “what’s the purpose of the assignment?” Is it merely a way to show parents and administration what's going on in the class? Is it a means to help keep the grades up? Is the homework being graded for accuracy or completion? If so, then what if the assignment is wrong? Have the necessary skills been taught so the student can master the material on his or her own? I read an article once that stated teachers underestimate the amount of homework they assign by 50%. If that's accurate then there is definitely cause for concern.
In summary, there seems to be no clear answer on the homework debate. I started the blog with a question “What’s the purpose of homework?” I’ll end with the same question. If a teacher who is assigning the homework can’t provide a clear rationale behind this question, then maybe the homework shouldn’t be assigned.
I welcome you to weigh in with your thoughts. Do you think students have too much homework? If you are a teen reading this, how much homework do you have on an average night?

Raychelle Cassada Lohman n , M.S., LPC, is the author of The Anger Workbook for Teens .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
share this!
September 1, 2021
What's the point of homework?
by Katina Zammit, Western Sydney University

Homework hasn't changed much in the past few decades. Most children are still sent home with about an hour's worth of homework each day, mostly practicing what they were taught in class.
If we look internationally, homework is assigned in every country that participated in the OECD's Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) in 2012.
Across the participating countries, 15-year-old students reported spending almost five hours per week doing homework in 2012. Australian students spent six hours per week on average on homework. Students in Singapore spent seven hours on homework, and in Shanghai, China they did homework for about 14 hours per week on average.
Shanghai and Singapore routinely score higher than Australia in the PISA maths, science and reading tests. But homework could just be one of the factors leading to higher results. In Finland, which also scores higher than Australia, students spent less than three hours on homework per week.
So, what's the purpose of homework and what does the evidence say about whether it fulfills its purpose?
Why do teachers set homework?
Each school in Australia has its own homework policy developed in consultation with teachers and parents or caregivers, under the guiding principles of state or regional education departments.
For instance, according to the New South Wales homework policy "… tasks should be assigned by teachers with a specific, explicit learning purpose."
Homework in NSW should also be "purposeful and designed to meet specific learning goals," and "built on knowledge, skills and understanding developed in class." But there is limited, if any, guidance on how often homework should be set.
Research based on teacher interviews shows they set homework for a range of reasons. These include to:
- establish and improve communication between parents and children about learning
- help children be more responsible, confident and disciplined
- practice or review material from class
- determine children's understanding of the lesson and/or skills
- introduce new material to be presented in class
- provide students with opportunities to apply and integrate skills to new situations or interest areas
- get students to use their own skills to create work.
So, does homework achieve what teachers intend it to?
Do we know if it 'works'?
Studies on homework are frequently quite general, and don't consider specific types of homework tasks. So it isn't easy to measure how effective homework could be, or to compare studies.
But there are several things we can say.
First, it's better if every student gets the kind of homework task that benefits them personally, such as one that helps them answer questions they had, or understand a problem they couldn't quite grasp in class. This promotes students' confidence and control of their own learning.
Giving students repetitive tasks may not have much value . For instance, calculating the answer to 120 similar algorithms, such as adding two different numbers 120 times may make the student think maths is irrelevant and boring. In this case, children are not being encouraged to find solutions but simply applying a formula they learnt in school.
In primary schools , homework that aims to improve children's confidence and learning discipline can be beneficial. For example, children can be asked to practice giving a presentation on a topic of their interest. This could help build their competence in speaking in front of a class.
Homework can also highlight equity issues. It can be particularly burdensome for socioeconomically disadvantaged students who may not have a space, the resources or as much time due to family and work commitments. Their parents may also not feel capable of supporting them or have their own work commitments.
According to the PISA studies mentioned earlier, socioeconomically disadvantaged 15 year olds spend nearly three hours less on homework each week than their advantaged peers.
What kind of homework is best?
Homework can be engaging and contribute to learning if it is more than just a sheet of maths or list of spelling words not linked to class learning. From summarizing various studies' findings, "good" homework should be:
- personalized to each child rather than the same for all students in the class. This is more likely to make a difference to a child's learning and performance
- achievable, so the child can complete it independently, building skills in managing their time and behavior
- aligned to the learning in the classroom.
If you aren't happy with the homework your child is given then approach the school. If your child is having difficulty with doing the homework, the teacher needs to know. It shouldn't be burdensome for you or your children .
Provided by Western Sydney University
Explore further
Feedback to editors

The banana apocalypse is near, but biologists might have found a key to their survival

Scientists pinpoint dino-killing asteroid's origin: past Jupiter
Soundscape study shows how underground acoustics can amplify soil health
6 hours ago

Scottish and Irish rocks confirmed as rare record of 'snowball Earth'
11 hours ago

Blind cavefish have extraordinary taste buds that increase with age, research reveals
13 hours ago

'Mercury bomb' threatens millions as Arctic temperatures rise, study warns

Team develops method for control over single-molecule photoswitching
14 hours ago

X-ray irradiation technique helps to control cancer-causing poison in corn
15 hours ago
Physicists uncover new phenomena in fractional quantum Hall effects

Researchers observe 'locked' electron pairs in a superconductor cuprate
Relevant physicsforums posts, incandescent bulbs in teaching.
16 hours ago
Free Abstract Algebra curriculum in Urdu and Hindi
Aug 14, 2024
Sources to study basic logic for precocious 10-year old?
Jul 21, 2024
Kumon Math and Similar Programs
Jul 19, 2024
AAPT 2024 Summer Meeting Boston, MA (July 2024) - are you going?
Jul 4, 2024
How is Physics taught without Calculus?
Jun 25, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in
Aug 16, 2021

How to help your kids with homework—without doing it for them
Jan 24, 2020

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

Homing in on homework help
Oct 10, 2017

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Type of maternal homework assistance affects child's persistence
May 9, 2018
Recommended for you

Statistical analysis can detect when ChatGPT is used to cheat on multiple-choice chemistry exams

Larger teams in academic research worsen career prospects, study finds

The 'knowledge curse': More isn't necessarily better
Aug 7, 2024

Visiting an art exhibition can make you think more socially and openly—but for how long?
Aug 6, 2024

Autonomy boosts college student attendance and performance
Jul 31, 2024

Study reveals young scientists face career hurdles in interdisciplinary research
Jul 29, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Why homework matters

Homework is the perennial bogeyman of K–12 education. Any given year, you’ll find people arguing that students, especially those in elementary school, should have far less homework—or none at all . I have the opposite opinion. The longer I run schools—and it has now been more than sixteen years—the more convinced I am that homework is not only necessary, but a linchpin to effective K–12 education.
It is important to remember that kids only spend a fraction of their time in school. The learning that does or does not take place in the many hours outside of school has a monumental effect on children’s academic success and is a root cause of educational inequity.
The pandemic gave us a stark demonstration of this reality. Achievement gaps widened between affluent and low-income children not only because low-income students received less in-person or high-quality online instruction during the years of disrupted school, but also because children of college-educated and affluent parents were already less dependent on schools for learning. Affluent children are far more likely to have the privilege of tutors or other types of supplementary instruction, as well as a family culture of reading, and opportunities to travel, visit museums, and more. Homework is a powerful tool to help narrow these inequities, giving children from all backgrounds the opportunity to keep learning when they are not in school.
At Success Academy, the charter school network I founded and lead, we seek to develop students as lifelong learners who have the confidence and curiosity to pursue and build knowledge in all facets of their lives. Homework cultivates these mindsets and habits. Indeed, when teachers don’t assign homework, it reflects an unconscious conviction that kids can’t learn without adults. Kids internalize this message and come to believe they need their teacher to gain knowledge. In reality, they are more than capable of learning all sorts of things on their own. Discovering this fact can be both incredibly exciting and deeply empowering for them.
We also know that none of these benefits accrue when homework is mere busywork. Low-quality homework is likely what drives the mixed research evidence on the impact of homework on student achievement. It also sends the message to kids that doing it is simply an exercise in compliance and not worth their time. Homework must be challenging and purposeful for kids to recognize its value.
For this reason, at Success, we take great care with the design of our homework assignments, ensuring they are engaging and relevant to what takes place in class the next day. When done well, homework can be a form of the “flipped classroom”—a model developed by ed tech innovators to make large college lecture classes more engaging. In flipped classrooms, students learn everything they can on their own at home (in the original conception, via recorded lectures); class time builds on what they learned to address confusion and elevate their thinking to a more sophisticated level. It’s an approach that both respects kids’ capacity to learn independently, and assumes that out-of-class learning will drive the content and pace of the in-person lesson.
Students always need a “why” for the things we ask them to do, and designing homework this way is motivating for them because it gives them that clear why. Class is engaging and interesting when they are prepared; when they aren’t, they won’t have the satisfaction of participating.
At this point, some teachers may be saying, “I can’t get my kids to hand in a worksheet, let alone rely on them to learn on their own.” And of course, effective use of homework in class relies on creating a strong system of accountability for getting kids to do it. This can be hard for teachers. It’s uncomfortable to lean into students’ lives outside of school, and many educators feel they don’t have that right. But getting over that discomfort is best for kids.
Educators should embrace setting an exacting norm for completing homework. This should include a schoolwide grading policy—at Success schools, missing and incomplete homework assignments receive a zero; students can get partial credit for work handed in late; and middle and high schoolers can revise their homework for a better grade—as well as consistently and explicitly noticing when kids are or are not prepared and offering praise and consequences. Enlisting parents’ help in this area is also highly effective. I guarantee they will be grateful to be kept informed of how well their children are meeting their responsibilities!
Ultimately, minimizing homework or getting rid of it entirely denies children autonomy and prevents them from discovering what they are capable of. As we work to repair the academic damage from the last two-plus years, I encourage educators to focus not on the quantity of homework, but instead on its quality—and on using it effectively in class. By doing so, they will accelerate kids’ engagement with school, and propel them as assured, autonomous learners and thinkers who can thrive in college and beyond.

Eva Moskowitz is the CEO of Success Academy Charter Schools .
Related Content

Dear Admissions Committee: Please reject my college application

They’re still not book bans

Threading the needle on selective enrollment public schools

What’s the Purpose of Homework?

- Homework teaches students responsibility.
- Homework gives students an opportunity to practice and refine their skills.
- We give homework because our parents demand it.
- Our community equates homework with rigor.
- Homework is a rite of passage.
- design quality homework tasks;
- differentiate homework tasks;
- move from grading to checking;
- decriminalize the grading of homework;
- use completion strategies; and
- establish homework support programs.
- Always ask, “What learning will result from this homework assignment?” The goal of your instruction should be to design homework that results in meaningful learning.
- Assign homework to help students deepen their understanding of content, practice skills in order to become faster or more proficient, or learn new content on a surface level.
- Check that students are able to perform required skills and tasks independently before asking them to complete homework assignments.
- When students return home, is there a safe and quite place for them to do their homework? I have talked to teachers who tell me they know for certain the home environments of their students are chaotic at best. Is it likely a student will be able to complete homework in such an environment? Is it possible for students to go to an after school program, possibly at the YMCA or a Boys and Girls Club. Assigning homework to students when you know the likelihood of them being able to complete the assignment through little fault of their own doesn’t seem fair to the learner.
- Consider parents and guardians to be your allies when it comes to homework. Understand their constraints, and, when home circumstances present challenges, consider alternative approaches to support students as they complete homework assignments (e.g., before-or after-school programs, additional parent outreach).

Howard Pitler is a dynamic facilitator, speaker, and instructional coach with a proven record of success spanning four decades. With an extensive background in professional development, he works with schools and districts internationally and is a regular speaker at national, state, and district conferences and workshops.
Pitler is currently Associate Professor at Emporia State University in Kansas. Prior to that, he served for 19 years as an elementary and middle school principal in an urban setting. During his tenure, his elementary school was selected as an Apple Distinguished Program and named "One of the Top 100 Schools in America" by Redbook Magazine. His middle school was selected as "One of the Top 100 Wired Schools in America" by PC Magazine. He also served for 12 years as a senior director and chief program officer for McREL International, and he is currently serving on the Board of Colorado ASCD. He is an Apple Distinguished Educator, Apple Teacher, National Distinguished Principal, and Smithsonian Laureate.
He is a published book author and has written numerous magazine articles for Educational Leadership ® magazine, EdCircuit , and Connected Educator , among others.
ASCD is dedicated to professional growth and well-being.
Let's put your vision into action., related blogs.

Want Students to Love Science? Let Them Compete!

Rethinking Our Definition of STEM

How to Grow Strong and Passionate Writers

A Common Math Curriculum Adds Up to Better Learning

“Diverse” Curriculum Still Isn’t Getting It Right, Study Finds
Watch CBS News
In Matthew Perry's death, 5 charged including 2 doctors, assistant and woman known as Hollywood "Ketamine Queen"
By Marissa Wenzke
Updated on: August 15, 2024 / 5:53 PM PDT / KCAL News
Federal prosecutors announced criminal charges against five defendants, including two doctors, in the death of "Friends" actor Matthew Perry, nearly a year after he was found unresponsive at his home.

U.S. Attorney for the Central District of California Martin Estrada said at a news conference Thursday that the defendants distributed "large quantities" of ketamine to Perry and others as part of a "broad underground criminal network." In addition to the two doctors, the defendants include Perry's live-in assistant and a "major source of drug supply known as the 'Ketamine Queen,'" Estrada said.
"These defendants took advantage of Mr. Perry's addiction issues to enrich themselves," Estrada told reporters.
"They knew what they were doing was wrong," he said. "They knew what they were doing was risking great danger to Mr. Perry, but they did it anyways. In the end, these defendants were more interested in profiting off Mr. Perry than caring for his well-being."
The arrests come almost a year after the 54-year-old actor was found in the jacuzzi of his home in the Pacific Palisades area of Los Angeles on Oct. 28, 2023. The toxicology report released by the Los Angeles County medical examiner attributed Perry's cause of death to the "acute effects of ketamine," with contributing factors including "drowning, coronary artery disease and buprenorphine effects." Buprenorphine is a medication used to treat opioid use disorder.
Criminal charges against assistant, doctors, "Ketamine Queen"
Five people in Southern California are facing federal criminal charges in connection with Perry's death.
An alleged drug dealer prosecutors say is known as the "Ketamine Queen" was identified in the federal indictment as Jasveen Sangha, 41, of North Hollywood. She faces up to life in prison if convicted of all charges, according to prosecutors.
The doctors listed as defendants are Dr. Salvador Plasencia, 42, a.k.a. "Dr. P," of Santa Monica, and Dr. Mark Chavez, 54, of San Diego. The remaining two defendants are Erik Fleming, 54, of Hawthorne, and Perry's live-in assistant, Kenneth Iwamasa, 59, of Toluca Lake. Fleming was described by federal authorities as a street dealer who acted as a middleman.
Plasencia faces up to 120 years in federal prison, prosecutors say.
Sangha's North Hollywood home was described by Estrada as a "drug-selling emporium" and has been tied to the 2019 ketamine-related death of a 33-year-old man, according to federal prosecutors. Sangha has been described by prosecutors as a large-scale dealer of meth and ketamine throughout L.A. County.
According to a newly unsealed 18-count superseding indictment , Sangha's distribution of the drug on Oct. 24, 2023, caused Perry's death four days later. Just weeks before the actor was found unresponsive on Oct. 28, 2023, the defendants allegedly conspired to distribute an illegal, unethical, and fatal amount of ketamine to him, according to federal prosecutors.

Sangha and Plasencia both pleaded not guilty at their arraignments in downtown Los Angeles on Thursday afternoon.
U.S. Magistrate Judge Alka Sagar ordered Sangha to be held without bond and set Plasencia's bond at $100,000.
Plasencia was released after posting bail. He is allowed to continue his medical practice but with restrictions outlined by the judge.
Plasencia's trial date was set for October 8, while Sangha's was scheduled for October 15.
Fleming and Iwamasa have both pleaded guilty to charges, while Chavez has agreed to a plea agreement.
"I wonder how much this moron will pay"
The ketamine distributed to Perry between September and October 2023 was paid for with at least $55,000 in cash, prosecutors said.
Federal prosecutors say the doctors charged $2,000 for a vial of ketamine that cost Chavez just $12.
DEA Administrator Anne Milgram said Thursday that Perry had become addicted to the drug after receiving ketamine treatments for depression and anxiety at a local clinic. The indictment details escalating purchases and injections of the drug over just a few weeks that ended with Perry's death in October 2023.
"He turned to unscrupulous doctors who saw Perry as a way to make quick money," Milgram said.
On Sept. 30, 2023, less than a month before Perry died, Plasencia allegedly texted fellow physician Chavez after learning that the actor was looking to obtain ketamine.
"I wonder how much this moron will pay," Plasencia allegedly wrote to Chavez. "Let's find out."
Chavez allegedly sent Plasencia a photo of ketamine lozenges and agreed to sell the drug to him. According to prosecutors, the San Diego doctor had obtained them by writing a fraudulent prescription for another patient — without that patient's knowledge.
Plasencia bought at least four vials of liquid ketamine from Chavez, as well as gloves, syringes, ketamine lozenges and the fraudulent prescription. Prosecutors said Plasencia also texted Perry on Sept. 30, 2023, saying he planned to provide him with vials of ketamine that the actor could administer himself.
"I will give you first dose if you would like and leave supplies with you," Plasencia allegedly texted the actor.
"Too far gone and spiraling in his addiction"
The Santa Monica doctor allegedly instructed Perry's live-in assistant Iwamasa — who prosecutors said has no medical training — on how to inject ketamine, leaving him with vials and syringes. Iwamasa handed over $4,500 in cash to Plasencia in exchange for the vials of ketamine, prosecutors said.
On Oct. 4, 2023, Iwamasa texted Plasencia using coded language to discuss buying more ketamine, telling him that he needed "to get more cans of dr pepper from you today, I can come to you to make it convenient."
According to the indictment, Iwamasa texted Plasencia the same day to tell him that he had successfully injected Perry, writing that he "[f]ound the sweet spot but trying different places led to running out" of ketamine.
Plasencia allegedly went to Irvine to purchase more ketamine from Chavez. He then met Perry to inject him again and sold more vials of the drug to Iwamasa.
Over the following days, according to the indictment, Plasencia worked with Chavez and Iwamasa to keep providing the drug to Perry. Plasencia met Perry and Iwamasa in a public parking lot in Long Beach on Oct. 10, 2023, where the doctor injected the actor with ketamine inside a car.
Two days later, on Oct. 12, 2023, Plasencia allegedly visited Perry's home to sell Iwamasa ketamine that prosecutors said was paid for with $21,500 in cash. That same day, prosecutors said, Perry froze up and his blood pressure spiked when Plasencia injected him again before leaving more vials of the drug at the actor's home.
Another order was placed by Plasencia on Oct. 24, 2023, for 10 vials of ketamine to provide to Perry. Less than a week before Plasencia made the order, he told a patient at his clinic that Perry was "too far gone and spiraling in his addiction," the indictment states.
Prosecutors said Plasencia texted Iwamasa again on Oct. 27, 2023, the day before Perry was found dead, and said: "I know you mentioned taking a break."
"I have been stocking up on the meanwhile," Plasencia allegedly wrote to Iwamasa. "I am not sure when you guys plan to resume but in case its when im out of town this weekend I have left supplies with a nurse of mine."
"Delete all our messages"
In the weeks before Perry's death, Iwamasa was also in communication with Fleming, who prosecutors say helped broker ketamine deals with Sangha over the encrypted messaging app, Signal.
According to the indictment, Sangha offered to provide Fleming with a sample for Perry to try, saying of the drug in an Oct. 11, 2023, message that "it's unmarked but it's amazing – he take one and try it and I have more if he likes."
Fleming allegedly sent a screenshot of the message to Iwamasa, telling him that Sangha "only deal[s] with high end and celebs. If it were not great stuff she'd lose her business."
Two days later, on Oct. 13, 2023, Fleming allegedly drove to Sangha's North Hollywood "stash house" to pick up a sample vial of ketamine and then drove to Perry's home to deliver it to Iwamasa. Later that day, Iwamasa and Fleming communicated again, with Perry's assistant telling the broker that he would purchase "25 vials $5500 @220 +500 for you for logistics." Fleming picked up the ketamine and sold it to Iwamasa the next day.
Iwamasa continued to buy dozens of vials from Fleming in the days that followed, prosecutors said, allegedly spending thousands of dollars on drugs from Sangha's supply. According to the indictment, Sangha included ketamine lollipops as an "add-on" for the large order.
Prosecutors said Fleming distributed the ketamine that killed Perry. According to the indictment, Iwamasa allegedly injected the actor with drugs from Sangha's supply using a syringe he obtained from Plasencia.
When news of the actor's death broke, Sangha allegedly wrote to Fleming over Signal, instructing him to "Delete our messages."
The criminal charges
Iwamasa confessed to injecting the actor repeatedly, giving him multiple injections on the day he died, according to federal prosecutors.
Chavez, the San Diego doctor, admitted in his plea agreement that he sold the drug to Plasencia. Prosecutors said that includes some of the substance he diverted from his former ketamine clinic. Prosecutors said Chavez also made false representations to a wholesale distributor of the drug so he could then transfer more of it to Plasencia.
In the plea agreement, Chavez also confessed to procuring more ketamine illegally by submitting a fraudulent prescription, using the name of a former patient without getting that patient's consent and without their knowledge.
The criminal charges detailed in the indictment include:
- Sangha has been charged with one count of conspiracy to distribute ketamine; one count of maintaining a drug-involved premises; one count of possession with intent to distribute methamphetamine; one count of possession with intent to distribute ketamine and five counts of distribution of ketamine
- Plasencia has been charged with one count of conspiracy to distribute ketamine, seven counts of distribution of ketamine, and two counts of altering and falsifying documents or records related to the federal investigation.
- Fleming pleaded guilty on Aug. 8 to one count of conspiracy to distribute ketamine and one count of distribution of ketamine resulting in death.
- Iwamasa pleaded guilty on Aug. 7 to one count of conspiracy to distribute ketamine causing death
- Chavez agreed to a plea deal with prosecutors in which he pleaded guilty to one count of conspiracy to distribute ketamine.

Perry's cause of death
In 2023, the Los Angeles County coroner said Perry's death was accidental and that there were no signs of foul play. But months later, the Los Angeles Police Department announced there was an open criminal investigation into the actor's death , which was being assisted by the U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency.
Trace amounts of ketamine were found in Perry's stomach, according to the autopsy report, but the amount discovered in his bloodstream was the same as what would be used in general anesthesia.
At the time of his death, Perry had been undergoing medically supervised ketamine treatments for depression and anxiety. According to the autopsy report, his last prescribed ketamine treatment was a week and a half before his death.
The report also noted that Perry's cause of death was not connected to his prior sessions of ketamine infusion therapy, as the drug's half-life is just three to four hours. So, the ketamine was taken in another manner, according to the report.
What is ketamine?
Ketamine, a dissociative anesthetic with hallucinogenic properties that is listed by the DEA as a Schedule III drug , has become known for its use in therapy in recent years.
"There are now uses of ketamine for depression given in clinics," said Angelique Campen, an emergency room doctor at Providence St. Joseph Medical Center in Burbank.
"Typically, it doesn't stop your breathing like opioids and other anesthetics would. ... It has an excellent safety profile," she said. "Of course, with any drug, it needs to be given under medical supervision, especially an anesthetic."
She also said ketamine can be "very dangerous" when it's used recreationally.
"Friends" actor known for his "brilliant talent"
The sudden death of Perry, best known for his role as Chandler Bing on "Friends," sent shockwaves through Hollywood.
His character quickly became a fan favorite on the hit sitcom, known for his lovable, quirky personality as he went from the single-guy roommate to Joey Tribbiani to the husband of Monica Geller.
In the wake of Perry's death, the show's co-creators and executive producer — Marta Kauffman, David Crane and Kevin Bright — released a statement saying they were "shocked and deeply, deeply saddened," and described Perry as "the sweetest, with a giving and selfless heart."
"He was a brilliant talent," the statement read. "It's a cliché to say that an actor makes a role their own, but in Matthew's case, there are no truer words. From the day we first heard him embody the role of Chandler Bing, there was no one else for us."
The co-stars with whom Perry rose to fame over the show's 10 seasons, from 1994 to 2004, released a joint statement soon after he died.
"We are all so utterly devastated by the loss of Matthew. We were more than just cast mates. We are a family," their statement read. "There is so much to say, but right now we're going to take a moment to grieve and process this unfathomable loss."
In the years after the show ended, Perry spoke fondly about his time as Chandler Bing.
"It's great, it's a wonderful time in my life," he told CBS News in a 2015 interview . "People come up to me that I know were not born when we shot the show, for sure. And they're just surprised at how elderly I look."
Months after his death, Jennifer Aniston, who starred alongside Perry as Rachel Green, spoke about the outpouring of love from fans and colleagues in an interview with Variety .
"It's so beautiful," Aniston said. "I hope he can know that he was loved in a way he never thought he was."
She told the news outlet that she had texted Perry the day he died and he seemed to be in good spirits.
"He was happy. He was healthy," she said. "He had quit smoking. He was getting in shape. He was happy — that's all I know."
Perry also starred in films and TV shows such as "Growing Pains," "Ally McBeal," "17 Again" and "The Whole Nine Yards."
In recent years, he had been vocal about his struggles with addiction, addressing them in his best-selling memoir "Friends, Lovers and the Big Terrible Thing." The book was released two years before he died.
Marissa Wenzke is a journalist based in Los Angeles. She has a bachelor's degree in political science from UC Santa Barbara and is a graduate of Columbia Journalism School.
Featured Local Savings
More from cbs news.

Three school buses catch on fire in Riverside County, prompting investigation

First suspect in brutal killing of Karla Terron arrested in San Fernando

3 people die after motorcycle and bicycle collide in Victorville

Discovery of 1 million fentanyl pills in LA County leads to prison time for dealers
Resurfaced Podcast With JD Vance Has Weird Audio About The ‘Postmenopausal Female'

Senior Reporter, HuffPost

Vice presidential candidate JD Vance agreed with a podcast host in 2020 that the “whole purpose of the postmenopausal female” is to help raise grandchildren.
The remark came during an appearance on a podcast called “The Portal,” hosted by Eric Weinstein, who at the time was the managing director of an investment firm founded by billionaire Vance backer Peter Thiel. Vance was speaking about how the mother of his wife, Usha Vance, took a sabbatical for a year to help take care of their newborn son.
The podcast was resurfaced by Heartland Signal .
“You can sort of see the effect it has on him to be around them, they spoil him, all the classic stuff that grandparents do to grandchildren,” Vance said. “But it makes him a much better human being to have exposure to his grandparents.”
“That’s the whole purpose of the postmenopausal female in theory,” Weinstein replied.
Vance agreed with the remarks in the middle of the statement. Later, Weinstein said that having grandparents on hand to help with a newborn was a “weird, unadvertised feature of marrying an Indian woman.” Vance, whose in-laws immigrated from India, didn’t push back on that remark.
NEW VANCE AUDIO: In an interview from 2020, JD Vance agrees with a podcast host who says having grandmothers help raise children is “the whole purpose of the postmenopausal female.” He also agrees when the host says grandparents helping raise children is a "weird, unadvertised… pic.twitter.com/W4KwHfZyw2 — Heartland Signal (@HeartlandSignal) August 14, 2024
A spokesperson for the Ohio senator, who officially became Donald Trump ’s running mate at last month’s Republican National Convention, rejected claims that Vance had agreed with the statements.
“The media is dishonestly putting words in JD’s mouth — of course he does not agree with what the host said,” the spokesperson told the Daily Beast . “JD reacted to the first part of the host’s sentence, assuming he was going to say: ‘that’s the whole purpose of spending time with grandparents.’”
“It’s a disgrace that the media is lying about JD instead of holding Kamala Harris accountable for her policies that caused sky high prices for groceries and everyday necessities, a disaster at the southern border, and a historic drug overdose epidemic.”
The remarks add another hitch to Vance’s efforts to shore up support for the Trump ticket before the November election. Last month, past comments he’d made lumping Harris into his description of the left wing’s “childless cat ladies” who are “miserable” with their lives caused an uproar on the campaign trail.
Democratic organizers, however, embraced the designation and have used it to draw more support for her campaign.
From Our Partner
More in politics.

- Shop to Support Independent Journalism
- We Have Issues
- Investigations
- Ethics Policy
- Ad-Free Login
New audio reveals J.D. Vance's views on the 'whole purpose of the postmenopausal female'

Kathleen Culliton
Kathleen culliton is raw story's assistant managing editor. she's been covering local and national news for more than a decade for outlets that include the new york post, al jazeera, dnainfo new york, bustle, the new york daily news, wnyc, ny1, city limits and the new york city patch. kathleen is a proud alumna of the cuny graduate school of journalism. here's a shocker; she is from new york city. .

New audio reveals what Donald Trump's running mate Sen. J.D. Vance (R-OH) said he believes is the lone purpose of women who no longer ovulate.
The political news station Heartland Signal took to X Wednesday to share a podcast interview from April 2020 in which Vance discussed the role his mother-in-law played in raising his son.
"It makes him a much better human being to have exposure to his grandparents," Vance said.
"That's the whole purpose of the post-menopausal female," Eric Weinstein, host of “ The Portal ,” said.
Vance replied, "Yes."
ALSO READ: Trump’s smear job climaxed prematurely — and now he’s stuck
The pair continue to discuss what the podcaster described as the "weird, unadvertised feature of marrying an Indian woman."
Vance explains how Lakshmi Chilukuri, mother of his wife, Usha, and a professor of molecular biology, took a yearlong sabbatical from teaching to help her daughter take care of their baby.
"This is what you do," Vance said.
Weinstein clarified, "A biology professor, PhD, drops what they're doing to immediately tend to the needs of a new mother with her infant?"
Vance confirmed that characterization was correct and described the decision as not fiscally efficient — arguing a college professor would have the disposable income to send her daughter money for childcare — but worth it.
"That is the thing that the hyper-liberalized economics wants you to do," Vance said. "The economic logic of always prioritizing paid wage labor over other ways of contributing to society...it's actually a consequence of a sort of fundamental liberalism that is ultimately going to unwind and collapse upon itself."
This adds a new category to the growing list of voter blocs upon which Vance has expressed controversial decisions.
Vance has repeatedly dubbed childless Americans "sociopaths ," mocked single women as " cat ladies " and managed to outrage the Pokemon fan community by admitting he told his son to " shut the hell up " about one of its characters.
Responded former prosecutor and political commentator Andrew Weissmann on Wednesday, "It just gets worse."
UPDATE: Vance spokesperson Taylor Van Kirk provided Raw Story a comment denying Vance agreed with the comment.
"The media is dishonestly putting words in JD's mouth - of course he does not agree with what the host said. JD reacted to the first part of the host's sentence, assuming he was going to say: 'that's the whole purpose of spending time with grandparents.' It's a disgrace that the media is lying about JD instead of holding Kamala Harris accountable for her policies that caused sky high prices for groceries and everyday necessities, a disaster at the southern border, and a historic drug overdose epidemic.”
Listen to the audio below or click here .
Stories Chosen For You
Do you think vice president kamala harris should be the next president, cnn commentator van jones says trump's 'worst 3 weeks' showcase his 'pure narcissism'.
Donald Trump was indicted, convicted and shot at this year — and all of those events weren't as important to him as Vice President Kamala Harris outshining him, remarked CNN political commentator Van Jones, which he said highlights the former president's "pure narcissism."
Jones' comment came in response to a question on CNN's "The Source" in which he was asked whether Democrats ought to push back against Trump's repeating of false claims that he won the 2020 election .
"Here's something to observe about the psychology of this guy," said Jones. "The past three weeks have apparently been the worst three weeks of his campaign. 'The worst three weeks, the worst three weeks.' This year he was convicted — he was a convicted crook — he was indicted, to your point, shot at and actually hit by a bullet. All of those things are not as important as the past few weeks where somebody is getting more attention than him."
ALSO READ: Donald Trump deep in debt while foreign money keeps coming: disclosure
Trump has grown more off-message and become more upset than any of those events solely because he's not the focus of attention, argued Jones.
"That gives you a sense — you're dealing with a level of just pure narcissism that I think people need to take serious account of," he said.
Jones noted with a laugh that Trump said Democrats cheated even when he won in 2016.
"Democrats can't get distracted with that. We know what he's going to do. We know how he's going to act," he said.
What they ought to do: double down on optimism — and change. Highlight that Harris is not President Joe Biden , in that she's younger and from the opposite side of the country.
"As long as [Trump] keeps throwing fits, he's going to keep falling," said Jones.
Watch the clip below or at this link .
Expert debunks Trump's claim Harris ticket is unconstitutional: 'completely open-and-shut'
Former President Donald Trump and his supporters, faced with a tougher election now that Vice President Kamala Harris has stepped in as the nominee , have taken to claiming that the replacement of President Joe Biden from the ticket is a "coup," or even that it could be "unconstitutional" and invalid on state ballots.
But this is nonsense, former federal prosecutor and CNN legal commentator Jeffrey Toobin told Anderson Cooper on Thursday.
"So is there any legal footing for this argument that it was unconstitutional for Harris to become the nominee?" asked Cooper.
"Anderson, I try to give balanced answers whenever it's possible, but it's really not possible in a circumstance like this, you know, this is a completely open-and-shut situation," said Toobin,
"Yes, it's true that the voters voted in the Democratic primaries for Joe Biden," he continued. However, "Joe Biden has withdrawn as a candidate, so the delegates who were elected in those primaries now get to pick a different candidate. They have picked Kamala Harris, that's how the Democratic Party rules work. It makes sense. There is no impediment in the Democratic Party to this. And that's the end of the story. There is no legal impediment to Kamala Harris being the party, the nominee in all 50 states."
"And just to be clear, I mean, the Constitution, which is what the former president is referring to — he's suddenly very interested in what's unconstitutional — the Constitution does not address the party nomination process, correct?" asked Cooper.
"No," confirmed Toobin. "I mean, there is a general provision in the 5th and 14th Amendments that says the government has to act with due process of law, but that applies to the government's behavior. The Democratic Party is a private entity and in any case ... there's no argument that there was an absence of due process here. They had a candidate who won primaries, who's not a candidate anymore. They have to pick someone else. They have picked someone else. That is not — there is no constitutional provision that would bar that under any circumstance."
Watch the video below or at the link here .
Vance's favorability numbers plummet below Sarah Palin's: analyses
Donald Trump's running mate is less popular with American voters than Sarah Palin was as she ran alongside Sen. John McCain, polls and analyses show.
FiveThirtyEight , an aggregator of national polls, found this week that Vance's net favorability has plummeted six points from -3.3 percent on July 18 to -9.3 on Wednesday, Aug. 14.
A New Republic analysis declared Thursday, "Vance is possibly the least popular vice presidential candidate of the 21st century."
Vance's unfavorably numbers jumped more than 13 points in less than a month, with 28.9 percent of voters viewing him poorly in a July poll but 42.4 percent feeling the same way in August, according to the analysis.
The number of voters who view Vance favorably increased only 7 points from 25.6 in July to 33.1 percent in August, FiveThirtyEight reports.
ALSO READ: Trump's insatiable ego is destroying the former president
The increase in both numbers reflects Vance's growing exposure as the Republican nominee running alongside Trump , the New Republic argues.
The outlet blamed gaffes and questionable claims about cat ladies and childless Americans for the increase in unfavorable polling.
"As a result of his botched rollout, which included widespread backlash for his egregiously sexist comments and low-energy speaking events marred by gaffes, Vance’s net favorability dropped even lower," the analysis states.
"Vance is officially less liked than Sarah Palin, who is widely regarded as one of the least popular vice-presidential candidates in recent history," according to ABC News .
Vice President Kamala Harris ' running mate Gov. Tim Walz (D-MN) has also seen his favorability drop , the data showed. As of Wednesday, he had a net favorability of 4.7 percent, 14 points above Vance's.

This Project 2025 goal is on a fast track despite Trump and Vance distancing themselves
Pleasure vs. pain: how kamala harris is flipping the script on the gop, sen. john fetterman violates financial law with botched corporate bond disclosures.
Copyright © 2024 Raw Story Media, Inc. PO Box 21050, Washington, D.C. 20009 | Masthead | Privacy Policy | Manage Preferences | Debug Logs For corrections contact [email protected] , for support contact [email protected] .
‘Youth (Hard Times)’ Review: Wang Bing’s Labor Documentary Sequel Disorients With a Purpose
The Chinese docmaker's follow-up to last year's sprawling textile worker study "Youth (Spring)" is even longer at 227 minutes, but more refined.
By Siddhant Adlakha
Siddhant Adlakha
- ‘Youth (Hard Times)’ Review: Wang Bing’s Labor Documentary Sequel Disorients With a Purpose 19 hours ago
- ‘The Fabulous Four’ Review: An Incoherent Girls-Trip Comedy in the Vein of ’80 for Brady’ 3 weeks ago
- ‘Altered Perceptions’ Review: DIY Sci-Fi Gets Lost in Its Repetitive Message 1 month ago

Just when it seems like Wang Bing ‘s textile documentaries might run out of observations, the Chinese filmmaker’s “ Youth (Hard Times) ” — the second in his planned trilogy — presents the passage of time in unforeseen ways. His narrative, about young workers’ growing frustrations in Zhili (a district of Huzhou City), is built obliquely but precisely, covering a variety of human subjects whose lives don’t often overlap, but who are bound by common circumstances. At nearly four hours in length, it surpasses even its gargantuan predecessor “ Youth (Spring) ,” but it also uses that film as a platform for deeper exploration.
Related Stories
Some olympics tv is in 4k, but viewers care little for the format: survey, 'star wars' starfighter miniature sells for $1.55 million, princess leia bikini goes for $175k at auction, popular on variety.
Most of the workers Wang introduces (through on-screen text) are in their early twenties and hail from Anhui province, a name whose repetition across such a lengthy runtime stokes curiosity. This subtle flourish ends up an intriguing bullet loaded in the movie’s chamber; it’s aimed squarely at a late payoff that, by necessity, must be meticulously earned. Along the way, Wang captures the kind of camaraderie and interpersonal drama that makes it worth the wait.
Wang’s focus, once again, never remains on any one character for too long, but he builds his overarching narrative through symbolic ironies. He captures shirtless men in the sweltering summer slaving over winter jackets they’ll never afford, or prospective couples denied the chance to explore romantic and sexual tensions — given the lack of time and space — working on crotchless lingerie.
A small handful of older workers broaden the story at hand. One woman brings her young daughter to help out. Another brings her mother. A stray shot of a visiting middle-aged relative with cotton balls stuffed in her nose (for reasons unexplained; perhaps the stench of sweat or clutter) calls to mind the process of embalming corpses in many countries, including China. Collectively, these images hold immense dramatic weight. They ask: Is this all there is for China’s poor, from the cradle to the grave — and beyond?
Before long, pay disagreements arise between the workers and their bosses, and for the first time in Wang’s trilogy, the sewing machines come to a stop. The ensuing silence, however, is eerie, as though a piece of the movie were missing. It’s almost depressing to consider, but perhaps toil under capitalist exploitation has become such a normal part of these people’s lives that the very act of grinding away now defines their identities, and consumes their sense of self. “Youth (Hard Times)” confronts this dilemma by pivoting towards tales of internal disagreements, of collective bargaining, and of the stark consequences therein. It becomes about China’s migrant youth attempting to break free of their bewildering confines within these factories, in which forced overtime and pittance-pay go hand-in-hand with losing one’s sense of the world outside, and the very experiences that make one human.
Reviewed online, Aug. 14, 2024. In Locarno Film Festival (Competition). Running Time: 227 MIN. (Original title: "Qing chun (Ku)")
- Production: (Documentary — France-Luxembourg-Netherlands) A House on Fire, Gladys Glover, CS Production production in co-production with Arte France Cinéma, Les Films Fauves, Volya Films, Eastern-Lion, Culture Media Co., Beijing Contemporary Art Foundation, Le Fresnoy – Studio national des arts contemporains. (World sales: Pyramide International, Paris.) Producers: Sonia Buchman, Mao Hui, Nicolas R. De La Mothe, Vincent Wang. Executive producer: Wang Yang. Co-producers: Gilles Chanial, Denis Vaslin, Fleur Knopperts, Wang Jia, Qiao Cui.
- Crew: Director: Wang Bing. Camera: Shan Xiaohui, Song Yang, Sing Bihan, Liu Xianhui, Maeda Yoshitaka, Wang Bing. Editors: Dominique Auvray, Xu Bingyuan.
- With: (Mandarin dialogue)
More from Variety
Margot robbie, colin farrell romantic fantasy ‘a big bold beautiful journey’ sets mother’s day 2025 release, bungie layoffs highlight post-m&a issues for gaming industry as its unions react, barbie grows up in new ‘dream besties’ collection, ‘the masked singer’ plans miley cyrus, barbie and ‘footloose’ tributes for season 12, ‘deadpool & wolverine’ underscores mcu’s much-needed evolution, more from our brands, trump says medal he gave billionaire donor ‘much better’ than military medal of honor, thieves who allegedly stole a $1 million patek philippe from a man in beverly hills just got nabbed, notre dame suspends men’s swim team after gambling probe, the best loofahs and body scrubbers, according to dermatologists, evil recap: last rites — are you ready for next week’s series finale.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Mentions of the term "homework" date back to as early as ancient Rome. In I century AD, Pliny the Younger, an oratory teacher, supposedly invented homework by asking his followers to practice public speaking at home. It was to help them become more confident and fluent in their speeches.
Horace Mann, often regarded as the "Father of American Education," made significant contributions to the American public school system in the 19th century. Though he may not have single-handedly invented homework, his educational reforms played a crucial role in its widespread adoption. Mann's vision for education emphasized discipline ...
Pliny the Younger —The Roman lawyer and author credited with the "invention" of homework, Johann Gottlieb Fichte —The German philosopher who developed the ideological justification of homework, Horace Mann —The first known American educator who made homework the norm in the U.S., and more. Let's dive in.
If you've ever felt curious about who invented homework, a quick online search might direct you to a man named Roberto Nevilis, a teacher in Venice, Italy. As the story goes, Nevilis invented homework in 1905 (or 1095) to punish students who didn't demonstrate a good understanding of the lessons taught during class.
A person doing geometry homework Children doing homework on the street, Tel Aviv, 1954. Homework is a set of tasks assigned to students by their teachers to be completed at home.Common homework assignments may include required reading, a writing or typing project, mathematical exercises to be completed, information to be reviewed before a test, or other skills to be practiced.
Who Invented Homework. Italian pedagog, Roberto Nevilis, was believed to have invented homework back in 1905 to help his students foster productive studying habits outside of school. However, we'll sound find out that the concept of homework has been around for much longer. Homework, which most likely didn't have a specific term back then ...
One teacher proposed "homework" consisting of after-school "field trips to the woods, factories, museums, libraries, art galleries.". In 1937, Carleton Washburne, an influential educator who was the superintendent of the Winnetka, Illinois, schools, proposed a homework regimen of "cooking and sewing…meal planning…budgeting, home ...
The origins of Homework dates back to ancient Greece and Rome. It is said that Roberto Nevelis, an Italian teacher, invented homework in 1905, but so far there is no credible historical evidence to support this, which makes it become an Internet myth. Pliny the Younger, Johann Gottlieb Fichte, and Hausmann are the most likely true inventors of homework.
The 19th-century politician and educational reformer Horace Mann played a large role in the history of homework. Mann, like his contemporaries Henry Barnard and Calvin Ellis Stowe, had a strong ...
Horace Mann. The practice of homework entered American life through Horace Mann (1796-1859). The reformer traveled for more than 5 months to the countries of Europe. He was inspired by the "folk schools" and brought the concept of homework to the US.
Purpose. The most common purpose of homework is to have students practice material already presented in class so as to reinforce learning and facilitate mastery of specific skills. Preparation assignments introduce the material that will be presented in future lessons. These assignments aim to help students obtain the maximum benefit when the ...
1930: The American Child Health Association proclaimed homework to be a kind of child labour, which was a novel legal idea in the United States at the time. 1950: During the Cold War, the United States went on a large homework push in order for American children to thrive, particularly in math and science.
When the twentieth century began, the mind was viewed as a muscle that strengthened through mental exer-cise, so homework that involved practice was viewed favor-ably. During the 1940s, as the emphasis in education shifted from drill to problem solving, homework fell out of favor. The launch of Sputnik by the Russians in the mid-1950s led to ...
This article takes a deep dive into the history of homework, its evolution, and its purpose in education. II. Defining Homework A. What is Homework? Before we delve into the history of homework, it is crucial that we first understand what exactly it entails. Homework is traditionally defined as tasks assigned to students by their teachers to be ...
These include to: establish and improve communication between parents and children about learning. help children be more responsible, confident and disciplined. practise or review material from ...
Roberto Nevilis is often credited as the inventor of homework. However, there needs to be more historical evidence of how he came up with the idea of issuing homework. Little is known about his life. He introduced the practice of assigning students academic tasks to be completed outside of regular class hours.
Homework. Something almost everyone in school— no matter what age, grade or where they live— all dread. But, why do we have homework? In 1905, an Italian teacher named Roberto Nevilis invented the concept of "homework." Originally, its purpose was to be used as a punishment for students who were lazy in class or for those who were disobedient or rude to their teacher.
Things changed again in the late 60s and early 70s. Vietnam War was still raging on, giving birth to civil rights movement and counterculture, which were looking to shake up all of the previously established norms. Homework was yet again under the microscope. It was argued that homework got in the way of kids socializing, and even their sleep ...
Source: Maarten/Flickr Commons. There are those who argue that homework does serve a purpose. For example, it helps to prepare students for national and statewide exams and tests. It helps to ...
Research based on teacher interviews shows they set homework for a range of reasons. These include to: establish and improve communication between parents and children about learning. help ...
Homework is the perennial bogeyman of K-12 education. In any given year, you'll find people arguing that students, especially in elementary school, should have far less homework—or none at all. Eva Moskowitz, the founder and CEO of Success Academy charter schools, has the opposite opinion. She's been running schools for sixteen years, and she's only become more convinced that ...
Others have found that homework can help students strengthen their self-regulation skills such as managing time, setting goals, self-reflecting on their performance, and delaying gratification (Ramdass & Zimmerman, 2011). On the flip side, there's some research highlighting negative aspects of homework, including disruption of family time ...
Sangha's North Hollywood home was described by Estrada as a "drug-selling emporium" and has been tied to the 2019 ketamine-related death of a 33-year-old man, according to federal prosecutors.
Vice presidential candidate JD Vance agreed with a podcast host in 2020 that the "whole purpose of the postmenopausal female" is to help raise grandchildren. The remark came during an appearance on a podcast called "The Portal," hosted by Eric Weinstein, who at the time was the managing director of an investment firm founded by ...
New audio reveals what Donald Trump's running mate Sen. J.D. Vance (R-OH) said he believes is the lone purpose of women who no longer ovulate. The political news station Heartland Signal took to X ...
Discuss the purpose of a Safety Data Sheet (SDS), and summarize safety techniques to minimize physical, chemical, and biological hazards in the clinical laboratory. Your solution's ready to go! Enhanced with AI, our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy-to-learn solution you can count on.
'Youth (Hard Times), the second entry in Wang Bing's documentary trilogy of textile worker studies, is a long haul but a refined one.
Rachael Gunn failed to score a single point with the judges as she lost all three of her breaking round-robin battles.
Mr Plasencia, 42, provided Perry ketamine "outside the usual course of professional practice and without a legitimate medical purpose", according to the indictment.