

Music Business Plan Template

Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 5,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their music businesses. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a music business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What Is a Music Business Plan?
A music business plan provides a snapshot of your music business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Music Business Plan
If you’re looking to start a music business or grow your existing business you need a music business plan. A business plan will help you attract investors and raise money, if needed, and plan out the growth of your music business in order to improve your chances of success. Your music business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Source of Funding for Music Businesses
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a music business are bank loans and angel investors. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your music business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will want to see a professional music business plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a music business.
The second most common form of funding for a music business is angel investors. Angel investors are wealthy individuals who will write you a check. They will either take equity in return for their funding or, like a bank, they will give you a loan. Venture capitalists will not fund a music business.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How To Write a Music Business Plan
Your music business plan should include 10 sections as follows:
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your music business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your executive summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of music business you are operating and the status; for example, are you a startup, do you have a music business that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of music businesses?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the industry. Discuss the type of music business you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target audience. Provide a snapshot of your marketing plan. Identify the key members of your team, and offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of music business you are operating.
For example, you might operate one of the following types:
- Recorded Music – This type of music business sells music that has been recorded in a studio.
- Music Licensing – This type of music business licenses music for films, TV shows, video games, advertisements, online videos, etc.
- Live Music – This type of music business sells tickets to live concerts and tours. They might also operate a school that teaches people how to become successful musicians, or they might sell memorabilia such as T-shirts and posters.
- Music Publishing – This type of music business is in the rights business; they represent songwriters. If someone wants to use a song by a songwriter that is represented by the music publishing company, they need to get permission and then pay a royalty.
- Music Production – This type of music business provides a service for musicians and recording artists. They might produce and record an album and then provide marketing services such as radio promotion and public relations.
- Music Business Consulting – This type of business is in the business of providing advice to musicians on how to become successful. For example, they may offer consulting on how to promote your music and how to book gigs.
- Music Artist – This type of business operates as an individual musician or music group. For example, they might be solo artists, bands looking for a record deal, or groups of musicians hoping to become successful together.
- Music Education – This type of music business offers music lessons, either in-person or online.
- Retail Music Store – This type of music business sells instruments, sheet music, and other music-related items.
In addition to explaining the type of music business you operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to questions such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include sales goals you’ve reached, new store openings, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry analysis, you need to provide an overview of the music business.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy particularly if your research identifies market trends. For example, if there was a trend towards more people purchasing music online, you may want to focus your marketing efforts on digital platforms.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your music business plan:
- How big is the music business (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your music business. You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your music business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments for a retail music store:
- Adult beginning guitar players
- Teenage/college-aged students who want to learn how to play the electric guitar and will commit time and money to do so
- Middle-aged adults who want to learn how to play acoustic guitars for their own enjoyment
- Vintage guitar enthusiasts who are looking for specific instruments that are considered rare or valuable.
The following are examples of customer segments for a music education business:
- Parents who want their children to have a well-rounded education and believe that music is an important part of that
- Children who want to learn to play an instrument because they enjoy music
- Adults who want to improve their skills at playing an instrument they already know how to play
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will greatly depend on the type of music business you are operating. Clearly, baby boomers would want a different atmosphere, pricing, and product options, and would respond to different marketing promotions than millennials.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations, and income levels of the customers you seek to serve.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers or clients.
Finish Your Music Industry Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other music businesses within the same niche.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes physical stores, online stores, and even locally owned retail shops that sell instruments.
Here are some examples of indirect competitors within the music education niche:
- Local music store selling instruments
- Online retailer selling musical instruments
- The public school system offering a music program to students in grades K-12 or college offering a music ed program as a minor.
You need to mention such competition to show you understand that not everyone in the market is your direct competitor. Furthermore, including a SWOT analysis of your business in this section will demonstrate how you plan to compete against them.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What products/services do they offer?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to reach out to customers of your competitors and ask them what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide superior services?
- Will you provide amenities that your competitors don’t offer?
- Will you make it easier or faster for customers to book your own studio?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a music business plan, your marketing strategy and plan should include the following:
Product : in the product section, you should reiterate the type of music that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products you will be offering. For example, in addition to selling instruments, you may also offer music lessons, CD recordings of the lessons, and other merchandise related to your business.
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections, you are presenting the options you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location of your music business. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your music business located in a commercial district with a lot of foot traffic? If not, will you offer delivery or online sales?
Promotions : the final part of your marketing plan is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in local papers and magazines
- Reaching out to local bloggers and websites
- Partnerships with local organizations (e.g., partner with vendors to provide recording packages at a discount over a la carte services)
- Local radio stations advertising
- Banner ads at local music venues
- Social media advertising
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your music business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your music business such as serving customers, cleaning, ordering supplies, and so on. This section should list the specific tasks that will need to be completed each day and who will be responsible for them.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to serve your 25th customer, or when you hope to reach $X in sales. It could also be when you expect to hire your Xth employee or launch a new location.
Management Team
To demonstrate your music company’s ability to succeed as a business, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a music business.
Ideally, you and/or your team members have direct experience in the music business. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act as mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in music and/or successfully running small businesses.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statements.
Income Statement : an income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, how many customers will you serve? How much does it cost to provide your service/product? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets : While balance sheets include much information, to simplify them to the key items you need to know about, balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. For instance, if you spend $100,000 on building out your recording studio, that will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $100.000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement : Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your music business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a music business:
- Location build-out including design fees, construction, etc.
- Cost of equipment like studio gear, instruments, amps, inventory, etc.
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your studio design blueprint or location lease.
Music Business Plan Summary
Putting together a business plan for your music business is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will really understand the music business, your competition, and your potential customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful music business.
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Music Industry business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. See how a Growthink business plan consultant can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
Music Production Company
Back to All Business Ideas
How to Start an Independent Music Production Company
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on March 29, 2022

Investment range
$4,150 - $9,600
Revenue potential
$97,500 - $156,000 p.a.
Time to build
1 – 3 months
Profit potential
$78,000 - $124,800 p.a.
Industry trend
Important elements to think about when starting your music production company:
- Studio location — Choose a suitable location for your studio. Consider factors such as accessibility, noise levels, and space requirements. Invest in proper acoustic treatment to ensure high-quality sound recording and mixing. This includes soundproofing and installing acoustic panels.
- Equipment — Purchase essential studio equipment , such as microphones, audio interfaces, studio monitors, mixing consoles, and digital audio workstations (DAWs).
- Find talent — Hire skilled producers, engineers, and session musicians to work with your clients. Building a talented team is crucial for delivering high-quality productions .
- Register your business — A limited liability company (LLC) is the best legal structure for new businesses because it is fast and simple. Form your business immediately using ZenBusiness LLC formation service or hire one of the best LLC services on the market.
- Legal business aspects — Register for taxes, open a business bank account, and get an EIN .
- Music licensing — Get necessary music licenses to legally use and distribute copyrighted music. This includes performance rights, mechanical licenses, and synchronization licenses.
- Contracts — Draft clear and comprehensive contracts for all your projects that outline the terms of service, payment, and intellectual property rights.
Interactive Checklist at your fingertips—begin your music production company today!
You May Also Wonder:
How does a music production company make money?
A music production company can make money for recording time, mixing and mastering, and royalties. You can also expand your services and offer consulting on how to get music noticed or even connected with a record label.
How can I learn to be a music producer?
You can take courses on music production on sites like Udemy , generally for under $20. You can also get a music and recording certificate or degree from places like Full Sail University . If you go with the self-study route, you may have to study and practice for years to be good enough to make money.
Is music producer profitable business?
Music production can be a profitable business, but success and profitability depend on various factors, such as the producer’s skills, industry connections, reputation, demand for their services, and the ability to adapt to changing market trends.
What is a ghost producer?
A ghost producer is a music producer who creates and produces tracks for other artists or clients without receiving official credit for their work. They often work behind the scenes, allowing the artist or client to present the music as their own.
How much money does a producer make on a song?
The amount of money a producer makes on a song can vary widely and depends on factors such as the producer’s level of experience, reputation, the artist’s budget, and the terms of the agreement. Producers may receive a flat fee, a percentage of sales or royalties, or negotiate a custom payment arrangement.
How can I differentiate my music production company from competitors in the market?
Differentiate your music production company by creating a unique sound or style, offering exceptional production quality, building relationships with talented artists and songwriters, providing comprehensive services like mixing and mastering, maintaining strong communication and professionalism, delivering projects on time, and engaging with the music community through networking and collaborations.
How do I become a successful music producer?
To become a successful music producer, hone your production skills and musical knowledge, stay updated with industry trends and technology, build a strong network, develop your unique style, consistently produce high-quality work, seek collaboration opportunities, and continuously learn and evolve with new production techniques.

Step 1: Decide if the Business Is Right for You
Pros and cons.
Starting a music production company has pros and cons to consider before deciding if it’s right for you.
- Flexible – Start out with a home studio
- Fun! – Help make great music
- Good Money – Multiple revenue streams
- Education Required – Need to learn producing before you can start
- Expensive Equipment – Setting up your studio will be $$
Music production industry trends
Industry size and growth.

- Industry size and past growth – The global music production and distribution industry is worth $34 billion in 2022 after five years of 5% annual growth.(( https://www.ibisworld.com/global/market-size/global-music-production-distribution/ ))
- Growth forecast – The global music production and distribution industry is projected to grow 3.6% in 2022.
Trends and challenges

Trends in the music production industry include:
- Digital manipulation of audio is becoming more advanced, allowing music producers to alter and improve recordings.
- The explosion of TikTok is creating huge opportunities for music producers and artists to go viral and gain fans, boosting revenue.
Challenges in the music production industry include:
- Advancing technologies also present a challenge for music producers, as they have to update their equipment to keep up with technology.
- The widespread availability of digital audio production software has made it easier for artists to record themselves, rather than going to a music producer.
Demand hotspots
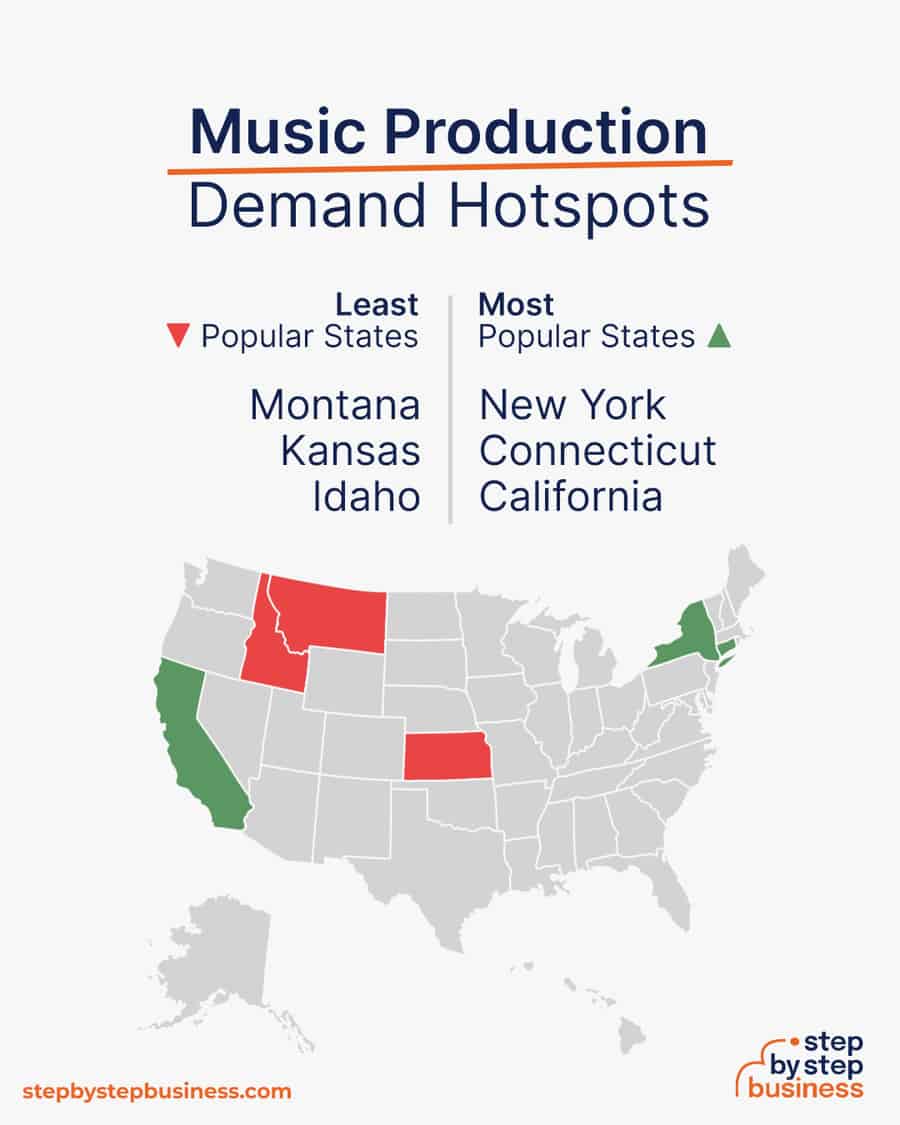
- Most popular states – The most popular states for music producers are New York, Connecticut, and California.(( https://www.zippia.com/music-producer-jobs/best-states/ ))
- Least popular states – The least popular states for music producers are Montana, Kansas, and Idaho.
What kind of people work in music production?

- Gender – 10.1% of music producers are female, while 81.8% are male.(( https://www.zippia.com/music-producer-jobs/demographics/ ))
- Average level of education – The average music producer has a bachelor’s degree.
- Average age – The average music producer in the US is 40.1 years old.
How much does it cost to start a music production business?
Startup costs for a music production company range from $4,000 to $9,500 for a home studio space. Costs include all the equipment, a computer and insulation pads for your walls.
You’ll need a handful of items to successfully launch your music production business, including:
- Digital audio workstation
- Audio interface
- DAW software
- Studio monitors and stands
- Microphones and stands
How much can you earn from a music production business?
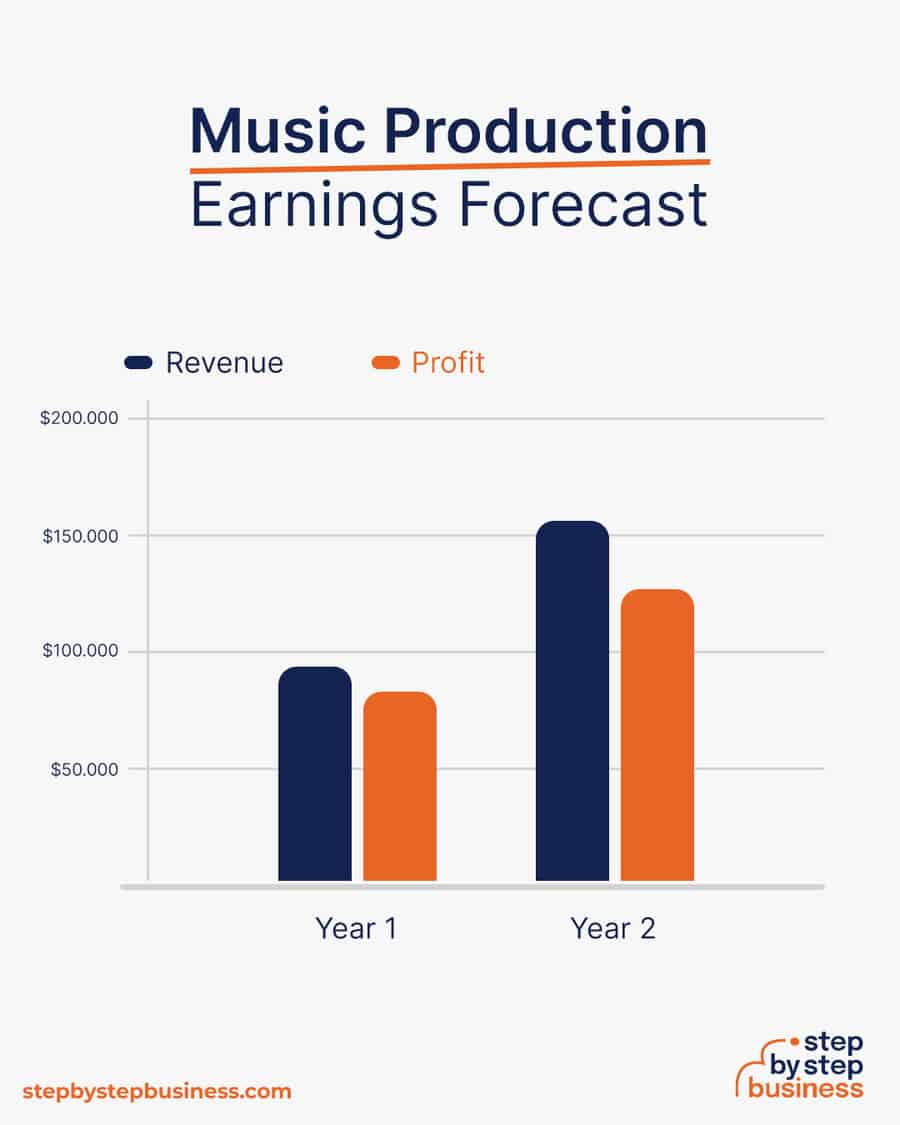
A home music production studio can bring in $50 to $100 per hour of recording, and the same for mixing and mastering. You can also make money from royalties. Your profit margin should be about 80%.
In your first year or two, you could average 25 hours of recording per week at $75 an hour, bringing in $97,500 in annual revenue. This would mean $78,000 in profit, assuming that 80% margin. As your brand gains recognition and you get referrals, you could work 40 hours a week. With annual revenue of $156,000, you’d make a tidy profit of $124,800. You may also be bringing in revenue from royalties at this point.
What barriers to entry are there?
There are a few barriers to entry for a music production company. Your biggest challenges will be:
- The skills required to make great music
- The startup costs of a home studio
Related Business Ideas

13 Steps to Setting Up Your Own Record Label

13 Steps to Set Up a Music Recording Studio

Hit the Beat: Guide to Starting a Mobile DJ Business
Step 2: hone your idea.
Now that you know what’s involved in starting a music production company, it’s a good idea to hone your concept in preparation to enter a competitive market.
Market research will give you the upper hand, even if you’re already positive that you have a perfect product or service. Conducting market research is important, because it can help you understand your customers better, who your competitors are, and your business landscape.
Why? Identify an opportunity
Research music production companies in your area to examine their services, price points, and customer reviews. You’re looking for a market gap to fill. For instance, maybe the local market is missing a hip-hop music producer or a pop music producer.
You might consider targeting a niche market by specializing in a certain aspect of your industry, such as music production for new music artists, or for country artists.
This could jumpstart your word-of-mouth marketing and attract clients right away.
What? Determine your services
Your services will depend on your skills. You can do recording, sound manipulation, mixing and mastering, provide your own original beats, and even marketing and promotional services for your clients.
How much should you charge for music production?
You can charge different prices for various services, usually between $50 and $100 per hour. Your profit margin after things like software costs should be about 80%.
Once you know your costs, you can use this Step By Step profit margin calculator to determine your mark-up and final price points. Remember, the prices you use at launch should be subject to change if warranted by the market.
Who? Identify your target market
Your target market will probably be a younger demographic of artists, which you might find on TikTok or Instagram. It’s also a good idea to just get out and talk to people, at cafes, clubs, and bars, as many aspiring artists might be interested in your music production services. Once you start doing good work, you’re likely to get a lot of referrals because local music communities tend to be very connected.
Where? Choose your business premises
In the early stages, you may want to run your business from home to keep costs low. But as your business grows, you’ll likely need to hire workers for various roles and may need to rent out a studio space. You can find commercial space to rent in your area on sites such as Craigslist , Crexi , and Instant Offices .
When choosing a commercial space, you may want to follow these rules of thumb:
- Central location accessible via public transport
- Ventilated and spacious, with good natural light
- Flexible lease that can be extended as your business grows
- Ready-to-use space with no major renovations or repairs needed
Step 3: Brainstorm a Music Production Company Name
Here are some ideas for brainstorming your business name:
- Short, unique, and catchy names tend to stand out
- Names that are easy to say and spell tend to do better
- Name should be relevant to your product or service offerings
- Ask around — family, friends, colleagues, social media — for suggestions
- Including keywords, such as “music producer” or “music production”, boosts SEO
- Name should allow for expansion, for ex: “RhythmRoom” over “HipHop Hitmakers”
- A location-based name can help establish a strong connection with your local community and help with the SEO but might hinder future expansion
Once you’ve got a list of potential names, visit the website of the US Patent and Trademark Office to make sure they are available for registration and check the availability of related domain names using our Domain Name Search tool. Using “.com” or “.org” sharply increases credibility, so it’s best to focus on these.
Find a Domain
Powered by GoDaddy.com
Finally, make your choice among the names that pass this screening and go ahead with domain registration and social media account creation. Your business name is one of the key differentiators that sets your business apart. Once you pick your company name, and start with the branding, it is hard to change the business name. Therefore, it’s important to carefully consider your choice before you start a business entity.
Step 4: Create a Music Production Business Plan
Here are the key components of a business plan:
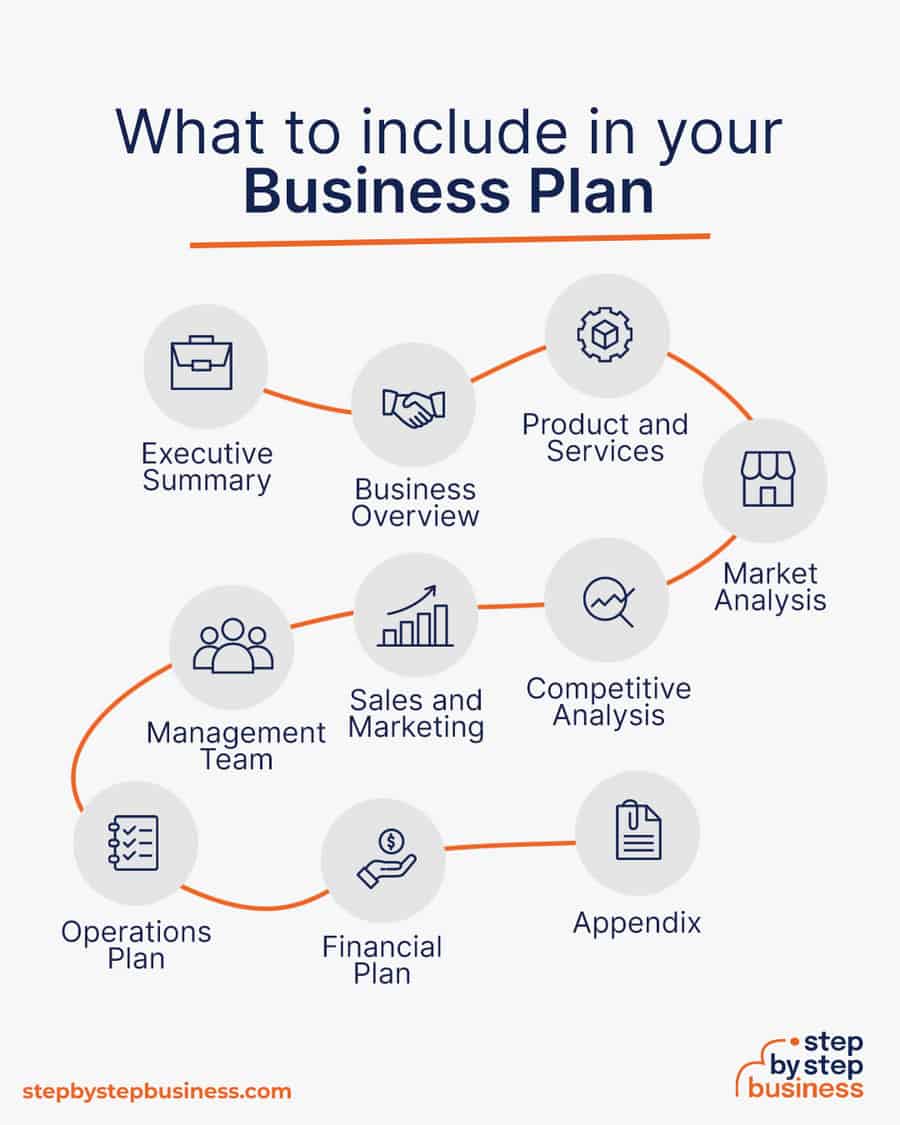
- Executive Summary: A brief summary of the entire business plan, highlighting key points and objectives.
- Business Overview: An overview of the music production company’s mission, vision, and its place in the industry.
- Product and Services: Description of the music production services and products offered, such as recording, mixing, and mastering.
- Market Analysis: Examination of the music industry, target market, and trends, providing insights into the demand for your services.
- Competitive Analysis: Evaluation of competitors in the music production field, identifying strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities.
- Sales and Marketing: Strategies for promoting your music production services and reaching your target audience.
- Management Team: Introduction to the key team members and their roles within the company.
- Operations Plan: Details on the day-to-day operations of the music production business, from studio management to equipment maintenance.
- Financial Plan: Projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability, including startup costs and financial forecasts.
- Appendix: Supporting documents, such as resumes, contracts, and additional information that complements the business plan.
If you’ve never created a business plan, it can be an intimidating task. You might consider hiring a business plan specialist to create a top-notch business plan for you.
Step 5: Register Your Business
Registering your business is an absolutely crucial step — it’s the prerequisite to paying taxes, raising capital, opening a bank account, and other guideposts on the road to getting a business up and running.
Plus, registration is exciting because it makes the entire process official. Once it’s complete, you’ll have your own business!
Choose where to register your company
Your business location is important because it can affect taxes, legal requirements, and revenue. Most people will register their business in the state where they live, but if you’re planning to expand, you might consider looking elsewhere, as some states could offer real advantages when it comes to music production companies.
If you’re willing to move, you could really maximize your business! Keep in mind, it’s relatively easy to transfer your business to another state.
Choose your business structure
Business entities come in several varieties, each with its pros and cons. The legal structure you choose for your music production company will shape your taxes, personal liability, and business registration requirements, so choose wisely.
Here are the main options:
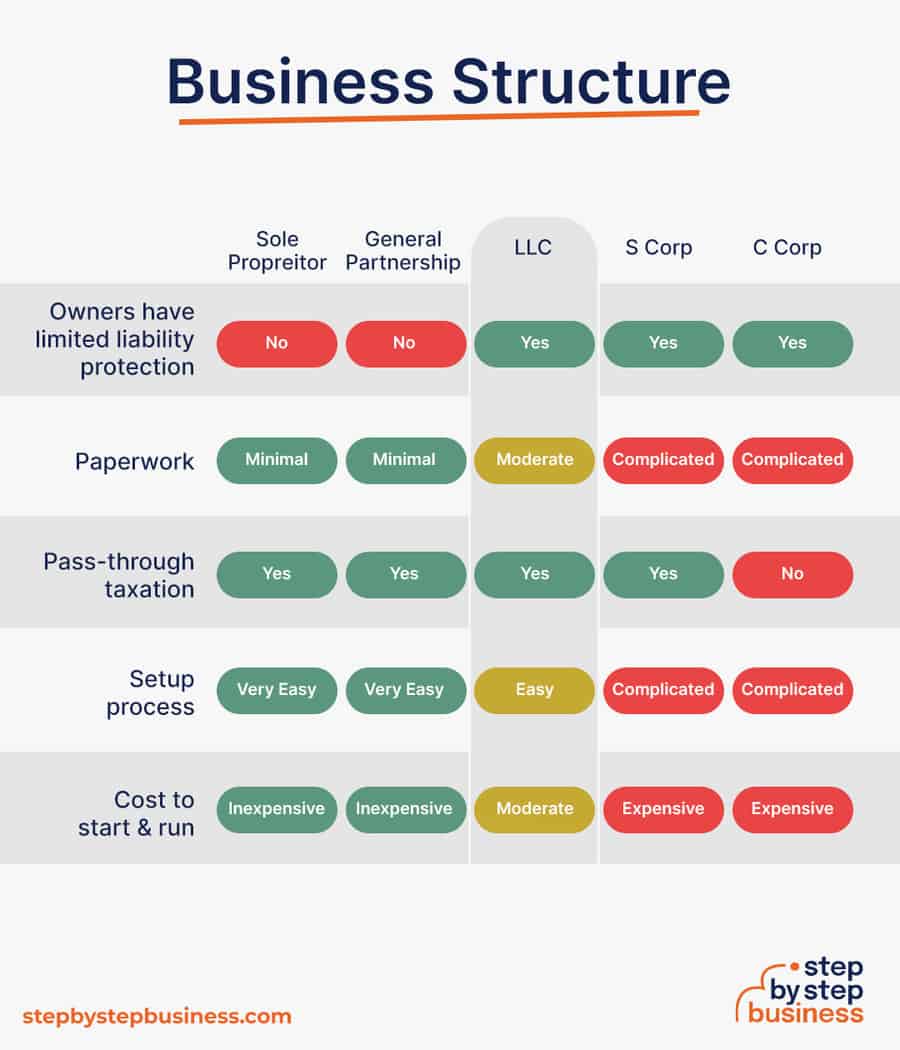
- Sole Proprietorship – The most common structure for small businesses makes no legal distinction between company and owner. All income goes to the owner, who’s also liable for any debts, losses, or liabilities incurred by the business. The owner pays taxes on business income on his or her personal tax return.
- General Partnership – Similar to a sole proprietorship, but for two or more people. Again, owners keep the profits and are liable for losses. The partners pay taxes on their share of business income on their personal tax returns.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC) – Combines the characteristics of corporations with those of sole proprietorships or partnerships. Again, the owners are not personally liable for debts.
- C Corp – Under this structure, the business is a distinct legal entity and the owner or owners are not personally liable for its debts. Owners take profits through shareholder dividends, rather than directly. The corporation pays taxes, and owners pay taxes on their dividends, which is sometimes referred to as double taxation.
- S Corp – An S-Corporation refers to the tax classification of the business but is not a business entity. An S-Corp can be either a corporation or an LLC , which just need to elect to be an S-Corp for tax status. In an S-Corp, income is passed through directly to shareholders, who pay taxes on their share of business income on their personal tax returns.
We recommend that new business owners choose LLC as it offers liability protection and pass-through taxation while being simpler to form than a corporation. You can form an LLC in as little as five minutes using an online LLC formation service. They will check that your business name is available before filing, submit your articles of organization , and answer any questions you might have.
Form Your LLC
Choose Your State
We recommend ZenBusiness as the Best LLC Service for 2024

Step 6: Register for Taxes
The final step before you’re able to pay taxes is getting an Employer Identification Number , or EIN. You can file for your EIN online or by mail or fax: visit the IRS website to learn more. Keep in mind, if you’ve chosen to be a sole proprietorship you can simply use your social security number as your EIN.
Once you have your EIN, you’ll need to choose your tax year. Financially speaking, your business will operate in a calendar year (January–December) or a fiscal year, a 12-month period that can start in any month. This will determine your tax cycle, while your business structure will determine which taxes you’ll pay.
The IRS website also offers a tax-payers checklist , and taxes can be filed online.
It is important to consult an accountant or other professional to help you with your taxes to ensure you’re completing them correctly.
Step 7: Fund your Business
Securing financing is your next step and there are plenty of ways to raise capital:
- Bank loans : This is the most common method but getting approved requires a rock-solid business plan and strong credit history.
- SBA-guaranteed loans : The Small Business Administration can act as guarantor, helping gain that elusive bank approval via an SBA-guaranteed loan .
- Government grants : A handful of financial assistance programs help fund entrepreneurs. Visit Grants.gov to learn which might work for you.
- Venture capital : Venture capital investors take an ownership stake in exchange for funds, so keep in mind that you’d be sacrificing some control over your business. This is generally only available for businesses with high growth potential.
- Angel investors : Reach out to your entire network in search of people interested in investing in early-stage startups in exchange for a stake. Established angel investors are always looking for good opportunities.
- Friends and Family : Reach out to friends and family to provide a business loan or investment in your concept. It’s a good idea to have legal advice when doing so because SEC regulations apply.
- Crowdfunding : Websites like Kickstarter and Indiegogo offer an increasingly popular low-risk option, in which donors fund your vision. Entrepreneurial crowdfunding sites like Fundable and WeFunder enable multiple investors to fund your business.
- Personal : Self-fund your business via your savings or the sale of property or other assets.
Bank and SBA loans are probably the best option, other than friends and family, for funding a music production business. You might also try crowdfunding if you have an innovative concept. If you get to a point where your company is poised for high growth, you might be able to attract angel investors or venture capital.
Step 8: Apply for Licenses and Permits
Starting a music production business requires obtaining a number of licenses and permits from local, state, and federal governments.
Federal regulations, licenses, and permits associated with starting your business include doing business as (DBA), health licenses and permits from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration ( OSHA ), trademarks, copyrights, patents, and other intellectual properties, as well as industry-specific licenses and permits.
You may also need state-level and local county or city-based licenses and permits. The license requirements and how to obtain them vary, so check the websites of your state, city, and county governments or contact the appropriate person to learn more.
You could also check this SBA guide for your state’s requirements, but we recommend using MyCorporation’s Business License Compliance Package . They will research the exact forms you need for your business and state and provide them to ensure you’re fully compliant.
This is not a step to be taken lightly, as failing to comply with legal requirements can result in hefty penalties.
If you feel overwhelmed by this step or don’t know how to begin, it might be a good idea to hire a professional to help you check all the legal boxes.
Step 9: Open a Business Bank Account
Before you start making money, you’ll need a place to keep it, and that requires opening a bank account .
Keeping your business finances separate from your personal account makes it easy to file taxes and track your company’s income, so it’s worth doing even if you’re running your music production business as a sole proprietorship. Opening a business bank account is quite simple, and similar to opening a personal one. Most major banks offer accounts tailored for businesses — just inquire at your preferred bank to learn about their rates and features.
Banks vary in terms of offerings, so it’s a good idea to examine your options and select the best plan for you. Once you choose your bank, bring in your EIN (or Social Security Number if you decide on a sole proprietorship), articles of incorporation, and other legal documents and open your new account.
Step 10: Get Business Insurance
Business insurance is an area that often gets overlooked yet it can be vital to your success as an entrepreneur. Insurance protects you from unexpected events that can have a devastating impact on your business.
Here are some types of insurance to consider:
- General liability : The most comprehensive type of insurance, acting as a catch-all for many business elements that require coverage. If you get just one kind of insurance, this is it. It even protects against bodily injury and property damage.
- Business Property : Provides coverage for your equipment and supplies.
- Equipment Breakdown Insurance : Covers the cost of replacing or repairing equipment that has broken due to mechanical issues.
- Worker’s compensation : Provides compensation to employees injured on the job.
- Property : Covers your physical space, whether it is a cart, storefront, or office.
- Commercial auto : Protection for your company-owned vehicle.
- Professional liability : Protects against claims from a client who says they suffered a loss due to an error or omission in your work.
- Business owner’s policy (BOP) : This is an insurance plan that acts as an all-in-one insurance policy, a combination of the above insurance types.
Step 11: Prepare to Launch
As opening day nears, prepare for launch by reviewing and improving some key elements of your business.
Essential software and tools
Being an entrepreneur often means wearing many hats, from marketing to sales to accounting, which can be overwhelming. Fortunately, many websites and digital tools are available to help simplify many business tasks.
You may want to use industry-specific software, such as Studio Director , Sonido , or Skedda , to manage your bookings, schedule, invoicing, and payments.
- Popular web-based accounting programs for smaller businesses include Quickbooks , Freshbooks , and Xero .
- If you’re unfamiliar with basic accounting, you may want to hire a professional, especially as you begin. The consequences for filing incorrect tax documents can be harsh, so accuracy is crucial.
Develop your website
Website development is crucial because your site is your online presence and needs to convince prospective clients of your expertise and professionalism.
You can create your own website using services like WordPress, Wix, or Squarespace . This route is very affordable, but figuring out how to build a website can be time-consuming. If you lack tech-savvy, you can hire a web designer or developer to create a custom website for your business.
They are unlikely to find your website, however, unless you follow Search Engine Optimization ( SEO ) practices. These are steps that help pages rank higher in the results of top search engines like Google.
Here are some powerful marketing strategies for your future business:
- Collaborate with Local Artists and Events: Partner with local musicians, bands, and event organizers to offer your services, showcasing your expertise in live productions and studio work, while tapping into existing fan bases.
- Social Media Challenges and Campaigns: Engage your audience on platforms like Instagram and TikTok by creating music-related challenges or campaigns that encourage user-generated content, fostering a sense of community around your brand.
- Exclusive Content and Behind-the-Scenes Access: Share behind-the-scenes glimpses of your studio sessions, equipment, and collaborations, providing followers with exclusive content that builds intrigue and positions your company as an industry insider.
- Online Tutorials and Educational Content: Establish your authority in the industry by creating and sharing online tutorials, tips, and educational content about music production on platforms like YouTube. This not only attracts aspiring musicians but also showcases your expertise.
- Strategic Sponsorships and Partnerships: Sponsor local music events, festivals, or even collaborate with music schools to gain exposure and build relationships within the music community, enhancing the credibility of your production company.
- Client Testimonials and Success Stories: Highlight client success stories through case studies and testimonials on your social media channels and website, demonstrating the value and quality of your music production services.
- Email Marketing with Personalized Offers: Build an email list and regularly communicate with your audience through newsletters. Include personalized offers, discounts, or exclusive deals to incentivize repeat business and referrals.
- Podcast Hosting and Guest Appearances: Host a podcast related to music production or become a guest on existing podcasts, showcasing your knowledge and simultaneously reaching a wider audience interested in the music industry.
- Interactive Virtual Events and Webinars: Host virtual events, webinars, or Q&A sessions that allow your audience to interact with you directly, fostering a sense of connection and providing value beyond your core services.
- Consistent Branding Across Platforms: Ensure consistent branding across all your online and offline platforms to create a strong, recognizable identity, helping to establish trust and credibility in the competitive music production landscape.
Focus on USPs

Unique selling propositions, or USPs, are the characteristics of a product or service that sets it apart from the competition. Customers today are inundated with buying options, so you’ll have a real advantage if they are able to quickly grasp how your music production company meets their needs or wishes. It’s wise to do all you can to ensure your USPs stand out on your website and in your marketing and promotional materials, stimulating buyer desire.
Global pizza chain Domino’s is renowned for its USP: “Hot pizza in 30 minutes or less, guaranteed.” Signature USPs for your music production business could be:
- Our full-service music production will make you a star
- You bring the beats; we’ll make your hip hop great
- Wanna hit the charts? We’ll take your music to the next level
You may not like to network or use personal connections for business gain. But your personal and professional networks likely offer considerable untapped business potential. Maybe that Facebook friend you met in college is now running a music production business, or a LinkedIn contact of yours is connected to dozens of potential clients. Maybe your cousin or neighbor has been working in music for years and can offer invaluable insight and industry connections.
The possibilities are endless, so it’s a good idea to review your personal and professional networks and reach out to those with possible links to or interest in music production. You’ll probably generate new customers or find companies with which you could establish a partnership.
Step 12: Build Your Team
If you’re starting out small from a home office, you may not need any employees. But as your business grows, you will likely need workers to fill various roles. Potential positions for a music production business include:
- Sound Engineers – assist with music production
- General Manager – scheduling, accounting
- Marketing Lead – SEO strategies, social media
At some point, you may need to hire all of these positions or simply a few, depending on the size and needs of your business. You might also hire multiple workers for a single role or a single worker for multiple roles, again depending on need.
Free-of-charge methods to recruit employees include posting ads on popular platforms such as LinkedIn, Facebook, or Jobs.com. You might also consider a premium recruitment option, such as advertising on Indeed , Glassdoor , or ZipRecruiter . Further, if you have the resources, you could consider hiring a recruitment agency to help you find talent.
Step 13: Run a Music Production Business – Start Making Money!
Imagine helping up-and-coming artists bring their music to life, then seeing that music embraced by legions of fans — how rewarding! And this is in addition to the financial rewards you’ll reap from a large and growing industry. Starting a music production business is fairly easy, and you can set up your studio in your home for a small investment. If you just get a few clients and do excellent work, you’re bound to get referrals and start building your music empire.
Now that you understand the business, get that studio set up and running and live out your entrepreneurial dream of being the next major music mogul.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Decide if the Business Is Right for You
- Hone Your Idea
- Brainstorm a Music Production Company Name
- Create a Music Production Business Plan
- Register Your Business
- Register for Taxes
- Fund your Business
- Apply for Licenses and Permits
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Get Business Insurance
- Prepare to Launch
- Build Your Team
- Run a Music Production Business - Start Making Money!
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.


10 Best Business Ideas for Musicians and Music Lovers
Esther Strauss
Published on November 4, 2022
Music is big business and could provide you with a steady stream of big profits if you make the right connections and know what your audienceneeds.& ...

44 Exciting Entertainment Business Ideas to Start Today
Natalie Fell
Published on July 13, 2022
Let the good times roll! With entertainment outlets now open and people coming together for all kinds of celebrations, the entertainment industry is ...

15 Best Software Business Ideas for Startups & SMEs
Carolyn Young
Published on June 16, 2022
The global software industry is worth a massive $600 billion and projected to expand nearly a third by 2027. For software developers and engineers,t ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.
How to Start a Profitable Music Production Business [11 Steps]
By Nick Cotter Updated Feb 02, 2024

Business Steps:
1. perform market analysis., 2. draft a music production business plan., 3. develop a music production brand., 4. formalize your business registration., 5. acquire necessary licenses and permits for music production., 6. open a business bank account and secure funding as needed., 7. set pricing for music production services., 8. acquire music production equipment and supplies., 9. obtain business insurance for music production, if required., 10. begin marketing your music production services., 11. expand your music production business..
Starting a music production business requires a keen understanding of the current market dynamics. An in-depth market analysis can help you identify trends, understand your competition, and pinpoint your target audience. Here's how to go about it:
- Analyze the music genres that are trending and determine which you are best suited to produce. Look into sales charts, streaming services, and social media for popular music trends.
- Research potential competitors, including their services, pricing, and market share. Understand their strengths and weaknesses to find gaps in the market you can fill.
- Identify your target audience's demographics, preferences, and habits. Use surveys, focus groups, and online analytics tools to gather information on potential customers.
- Assess the scale of the market, both locally and globally, to set realistic goals for your business. Consider factors such as the number of active consumers and the volume of music production in your niche.
- Stay updated on technological advancements and industry innovations that could impact music production, from new software to emerging distribution channels.
- Review economic factors that can affect your business, such as funding opportunities, grants, and changes in consumer spending behavior in the music industry.

Are Music Production businesses profitable?
Yes, depending on the type of services offered, music production businesses can be quite profitable. Many music production businesses specialize in creating music for films, television shows, and other media, which can be quite lucrative. Other types of music production services, such as recording and mixing, can also generate a good income.
Embarking on the journey of starting a music production business requires a well-structured plan to guide your decisions and strategy. A comprehensive business plan is essential for securing funding, understanding your market, and setting clear objectives. Here is a summary of the key elements you should include in your music production business plan:
- Executive Summary: Provide a concise overview of your business, including your mission statement, services offered, and your unique selling proposition.
- Company Description: Detail the nature of your business, the demand for your services, and the markets you intend to serve.
- Market Analysis: Research and analyze your target market, including customer demographics, market size, and competition.
- Organization and Management: Outline your business structure, ownership details, and the profiles of your management team.
- Services Offered: Describe the music production services you plan to offer and how they stand out from the competition.
- Marketing Plan: Detail your strategies for branding, promoting, and selling your services.
- Operational Plan: Explain your process for delivering services, including any equipment or facilities needed.
- Financial Plan: Present financial projections, funding requirements, and revenue models to illustrate the financial viability of your business.
How does a Music Production business make money?
Music production businesses typically make money by charging for their services, such as recording, mixing, mastering, and production. They may also charge for use of their equipment or studio time, or for additional services such as music lessons, artist management, or distribution. Additionally, some music production businesses may offer royalty and publishing deals for their work.
Developing a strong brand is essential for standing out in the competitive music production industry. It's not just about your logo or name; it's about the entire experience your clients have with your business. Here are some key points to consider when developing your music production brand:
- Define Your Brand Identity: Determine the core values, mission, and unique selling points of your brand. Consider what emotions and messages you want to evoke through your brand.
- Create a Visual Identity: Design a memorable logo, choose a color scheme, and develop a consistent visual style that reflects your brand's identity. This will be used across all marketing materials.
- Establish an Online Presence: Build a professional website and maintain active social media profiles. Showcase your portfolio, client testimonials, and provide an insight into your production process.
- Develop a Brand Voice: Decide on the tone and style of communication that reflects your brand's personality. This should be consistent in all written and verbal interactions.
- Network and Collaborate: Partner with artists and other brands that align with your brand identity. This can enhance your brand's visibility and credibility.
How to come up with a name for your Music Production business?
Brainstorming is essential when coming up with a name for your music production business. Consider words that evoke the feeling you want customers to associate with your business and words that reflect the type of music you’ll be producing. Take a look at competitor’s names to get an idea of what works and what doesn’t. Finally, do an online search to make sure the name isn’t already taken and if you’re happy with it, go ahead and register it.

Once you've laid out the foundation for your music production business, it's time to make it official by completing the business registration process. This crucial step legitimizes your company and ensures compliance with local laws and regulations. Follow these guidelines to formalize your business:
- Choose a business structure (e.g., Sole Proprietorship, LLC, Corporation) that best suits your needs for liability protection and tax considerations.
- Register your business name with the appropriate state agency, ensuring it's unique and adheres to state-specific naming requirements.
- Obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS for tax purposes, even if you don't plan to have employees immediately.
- Apply for any required business licenses or permits specific to music production or business operation within your city or county.
- Register for state and local taxes to ensure you can legally operate and are set up to collect sales tax if required.
- Consider consulting with a business attorney or accountant to ensure all legal and financial aspects of your registration are handled correctly.
Resources to help get you started:
Explore vital resources specifically designed for music production entrepreneurs to gain insights into market trends, operational best practices, and strategic growth advice:
- Sound on Sound Magazine: Offers in-depth reviews of music production equipment, software, and techniques. - https://www.soundonsound.com
- Music Business Worldwide: Provides global music industry news and analyses, focusing on trends, deal-making, and behind-the-scenes insights. - https://www.musicbusinessworldwide.com
- Produce Like A Pro: An extensive online resource offering tutorials, tips, and interviews with industry professionals to help producers improve their skills. - https://www.producelikeapro.com
- The Mastering Show Podcast: A resource for advanced production and mastering discussions, hosted by mastering engineer Ian Shepherd. - http://themasteringshow.com
- Splice Insights: Offers trends and statistical analysis on the music industry, particularly useful for beatmakers and electronic music producers. - https://splice.com
- Music Tech Magazine: Covers the latest in music technology, digital music production workshops, and software reviews. - https://www.musictech.net
Launching a music production business involves obtaining licenses and permits related to copyright, business operations, and possibly a studio space. Ensuring legal compliance is crucial for protecting your work and your artists. Key considerations include:
- Business License: Register your music production business with local authorities.
- Copyright Registration: Protect your music and productions by registering copyrights as needed.
- Zoning Permits: If operating a studio, ensure your location complies with local zoning laws for commercial use.
What licenses and permits are needed to run a music production business?
Depending on the type of music production business you are running, you may need various licenses and permits such as an occupational license, a business license, a sound production license, a mechanical rights license, and/or a performance rights (copyright) license. Additionally, depending on the location you plan to conduct your business activities in, you may also need to obtain any required county or city permits.
Having a dedicated business bank account is crucial for managing your music production business's finances, and securing funding can help cover startup costs and keep operations running smoothly. Here's how to approach these important steps:
- Research banks and credit unions: Compare fees, services, and any benefits specific to small businesses or those in the creative industry.
- Choose the right type of account: Decide between checking, savings, or a combination of accounts to suit your business's cash flow needs.
- Prepare the necessary documents: Collect your business registration papers, EIN, and personal identification to open your account.
- Explore funding options: Look into small business loans, grants, investor opportunities, or crowdfunding specific to the music industry.
- Consider credit options: A business credit card or line of credit can be useful for managing expenses and building credit.
- Create a budget: Estimate startup costs, ongoing expenses, and potential income to understand how much funding you'll need.
- Develop a pitch: If seeking investors, prepare a compelling pitch that outlines your business plan, market potential, and financial projections.
Setting the right price for your music production services is crucial to attracting clients while ensuring you're fairly compensated for your time and skills. It's a delicate balance that can determine your business's success. Here are some guidelines to help you establish competitive and sustainable pricing:
- Analyze the Market: Research what other music producers are charging and understand the going rates for various services like mixing, mastering, and beat making.
- Know Your Costs: Tally up your overhead costs, including studio time, equipment, software, and any additional staff, to ensure your rates cover these expenses.
- Value Your Experience: If you have a strong portfolio and years of experience, price your services higher than someone just starting out.
- Offer Packages: Create tiered pricing with bundled services to provide options for different budgets and needs.
- Be Flexible: Be willing to negotiate and adjust prices for larger projects or repeat clients to build long-term relationships.
- Clear Communication: Ensure your pricing is transparent to avoid misunderstandings. Clearly outline what is included in each service package.
- Review Regularly: Reassess your pricing periodically to keep up with changes in the market, your growing expertise, and inflation.
What does it cost to start a Music Production business?
Initiating a music production business can involve substantial financial commitment, the scale of which is significantly influenced by factors such as geographical location, market dynamics, and operational expenses, among others. Nonetheless, our extensive research and hands-on experience have revealed an estimated starting cost of approximately $24000 for launching such an business. Please note, not all of these costs may be necessary to start up your music production business.
Starting a music production business requires not just talent and creativity, but also the right equipment and supplies. Your gear will be the backbone of your operations, capturing, manipulating, and polishing sounds to produce high-quality audio. Here's what you'll need to acquire:
- Computer: A reliable and fast computer is essential for running music production software.
- DAW (Digital Audio Workstation): Choose a DAW that suits your workflow, whether it's Pro Tools, Ableton Live, Logic Pro, or another.
- Audio Interface: Invest in a high-quality audio interface to ensure clear sound input and output.
- Studio Monitors: Accurate monitoring is crucial, so select studio monitors that provide a true representation of sound.
- Headphones: A good pair of closed-back headphones will be essential for detailed listening and mixing.
- Microphones: Depending on your needs, you might require various types of microphones, such as condenser, dynamic, and ribbon mics.
- MIDI Controller: A MIDI keyboard or pad controller will be useful for programming instruments and beats.
- Cables and Stands: Ensure you have all the necessary cables for your equipment, as well as mic stands and monitor stands.
- Acoustic Treatment: Proper acoustic panels and bass traps will help control room reflections and provide accurate sound.
- External Storage: High-capacity hard drives or SSDs are important for backing up projects and storing samples and recordings.
List of Software, Tools and Supplies Needed to Start a Music Production Business:
- Music Production Software
- Digital Audio Workstation (DAW)
- Audio/MIDI Interface
- MIDI Controllers
- Synthesizers/Samplers
- Microphones
- Studio Monitors
- Mixing Console/Mixer
- Recording Media
- Computer/Laptop
- External Hard Drives
Ensuring that your music production business is protected against potential risks is crucial for its longevity and success. Business insurance can safeguard against unforeseen events that could otherwise be financially devastating. Here are some key steps to obtain the right business insurance:
- Assess Your Risks: Identify the types of risks your music production business could face, such as property damage, theft of equipment, or legal liabilities.
- Research Insurance Providers: Look for insurance companies with experience in the entertainment or music industry. Compare their coverage options, premiums, and customer reviews.
- Choose the Right Coverage: Common insurance policies for music production businesses include general liability, professional liability, and property insurance. You may also need workers' compensation if you have employees.
- Consult with an Expert: Speak with an insurance broker or legal advisor who specializes in the music industry to ensure you're getting appropriate coverage for your specific needs.
- Review and Update Regularly: As your business grows and changes, your insurance needs may evolve. Make sure to review and update your policies accordingly to maintain adequate protection.
Now that you've honed your skills and set up your music production business, it's time to attract clients. Marketing your services effectively is crucial to building your brand and establishing a client base. Here are some strategies to get the word out and start generating business:
- Develop a Strong Online Presence: Create a professional website showcasing your portfolio, services, and contact information. Utilize social media platforms to engage with potential clients and share your work.
- Networking: Attend industry events, join music production forums, and connect with artists and other professionals on platforms like LinkedIn. Word-of-mouth can be a powerful tool.
- Create Content: Produce tutorial videos, write blog posts, or start a podcast to share your expertise and attract attention from potential clients interested in learning more about music production.
- Offer Promotions: Consider offering introductory rates or package deals to new clients to encourage them to try your services.
- Collaborate: Work with established artists or producers and ask for referrals. Collaborations can also lead to shared audiences and increased visibility.
- Paid Advertising: Invest in targeted online advertisements on platforms like Google, Facebook, or Instagram to reach potential clients actively searching for music production services.
Once you've established your music production business and have a solid workflow and client base, it's time to think about expansion. Growing your business can take many forms, from increasing your client list to offering new services. Here are some strategies to consider for expanding your music production business:
- Network and Collaborate: Build relationships with more artists, producers, and industry professionals to expand your reach and opportunities.
- Enhance Online Presence: Invest in a professional website, SEO, and social media marketing to attract a wider audience.
- Expand Services: Offer additional services such as songwriting, mixing, mastering, or sound design to become a one-stop-shop for clients.
- Invest in Education: Keep up with industry trends and new technology by attending workshops, courses, or obtaining certifications.
- Upgrade Equipment: Invest in higher quality or additional equipment to improve the production value and attract more clients.
- Hire Talent: Bring on additional producers, engineers, or administrative staff to handle increased workload and bring in fresh ideas.
- Seek Partnerships: Form partnerships with labels, studios, or media companies to secure a steady stream of projects.
- Diversify Income: Look into passive income streams like selling sample packs, beats, or offering online courses.

- Development
How to Create a Production Company Business Plan [FREE Template]
H ighly successful video companies start with a strong production company business plan. Whether your company has been around for a while, or you’re a freelancer ready to take your services to the next level, this post will provide you with actionable strategies for success to compete more effectively right now.
It all beings with formulating the business plan that will get you where you want to go. If you don’t have a business plan, don’t worry. We provide a free business plan template below and will walk you through it.
Step by step.
- Production Company Business Plan
- The Executive Summary
- Perform a Video Company Self Assessment
- How to Get Started
- Financing a Video Production Company
- Marketing Plan
- Day to Day Operations
Freebie: Business Plan Template for Video Production

Download your FREE printable business plan template for your video production. Just enter your email address and we'll instantly send it to you!
business plan template
1. what is a production company business plan.
Essentially it's a tool for raising funds, creating a roadmap, or altering course and plotting out the next steps.
One purpose of any business plan to so convey to investors, or a bank, why they should put money into this business.

Think of creating a business plan you could bring to them
What does that mean?
It means you need this business plan for a production company to prove that you will make money. To prove it to you, but also to any investors.
After all, nobody invests to lose money. Or break even. So with that in mind, let's forge ahead into the actual writing of the business plan.
how to make a business plan
2. what is an executive summary.
Every business plan starts from the top down, with an executive summary.
What is that, exactly?
An executive summary is a short part of a larger proposal or report that summarizes the main points so the reader can become quickly educated on the whole document without having to read it all.
So it’s a detailed overview.
Of course, "executive summary" has a nice ring to it...
Your job here is to lay out the big picture of your plan. Some questions to ask yourself: Why do you want this business in the first place?
Similarly, what inspired you to start it? What's going to make it work?
Next, start to answer the questions your investors might have. Try getting into their head-space.
"Why would YOU invest in this business?"
You might want to write about the competition. The targeted demographic. Be specific here.
What need does your business fill? Which kinds of customers and clients are you targeting?
Think about your target market
Furthermore, what else sets you and your business apart?
Especially relevant is using concrete examples and not only ideas. Can you cite previous work you've done?
This brings us to...
Your production companies competition
What does the rest of the field looks like. Your investor will want to know if they don't already.
What sets this company and this production company business plan apart from others?
Knowing the entire field of competitors you have is a good idea, even if it's a very long list.
Your production company business plan must factor in what else is being offered. That way you can adjust, and target a more specific niche.
Or, you can figure out what you can do better.
For example: what can you identify in your competitor's list of services that you know you can nail?
This is what your video company plan needs to convey.
Finally, remember to think of it from the investor's standpoint. How is this an opportunity for them?
how to create a business plan
3. why a video company self-assessment.
This step is easy to do, but hard to do well.
Can you take a good long look at your video production studio? With the intent to circle problems? Areas that need improvement?
The second part of this step might be easier. Find the areas where your video production studio can really shine.
In contrast, you don't want to elaborate on weaknesses in your video production company business plan. Rather, you want to identify them so you can find ways to address them.
You need to have answers to the questions these flaws might bring to the mind of your investors.

You are not required to sing “Man in the Mirror”
Then go beyond looking in the mirror.
Look back at the field before you.
This is a business plan for a production company. What opportunities exist for that?
Most of all, try and tailor this production house business plan to specific needs.
Here are a few methods of company self-analysis:
This is a way to identify changes in your industry, to target potential growth opportunities. The acronym stands for:
P olitical Factors
E conomic Factors
S ocial Factors
T echnological Factors
P roduction company business plan would include a PEST
We've mentioned elements of SWOT:
W eaknesses
O pportunities
The one to focus in on here is threats. Don't assume everything will work out for the plan just the why you'd like it to.
Because it won't. Investors will know that. You should not only know it, you should expect it.
Most important of all: prove that you're prepared for whatever may happen.
Here's a cool way to approach your SWOT analysis. Try applying your strengths to your opportunities and see what kind of leverage you can create.
Then theoretically expose your weaknesses to your threats. Are you in trouble? Do you need to address something to better protect your company?
Think of this as planning for a battle. Therefore, you don't want to ignore cracks in the wall if your enemy is bringing a battering ram.
Business plan can benefit from SWOT
Strategy, structure, systems, style, shared values, staff, and skills. The 7S model was developed by business consultants Robert H. Waterman Jr. and Tom Peters . It's also known as the McKinsey 7S framework.
The idea here is that your business needs these elements to be aligned and "mutually reinforcing". Let's go over each "S".
Strategy: How does this business plan to gain an advantage.
Structure: How do you divide the various operations of the company.
Systems: Procedure for measurement, reward and resource allocation.
Skills: the companies core and distinctive capabilities.
Staff: Human resources.
Style: Behavior patterns of the key groups like managers.
Shared values are in the middle of them all on the diagram. It's somewhat self-explanatory.
In theory, using these methods of self-analysis will help you a great deal. Due to them you'll know, and decide, all sorts of things about your production company.
The 7 S model of analysis
Start putting these ideas onto paper now! If you haven’t already…
Gentlemen, start your engines
4. how to get started.
A business plan for a production company must lay out how you will get started. This is also referred to as a "roll out plan".
How you engineer your beginning is critical to your cash flow. What do you need to get started?
And can you start at a sustainable level?
Will you open a physical office space right off the bat?
Overhead is a major cost. If this is more of a production house business plan then you’ll want to factor that in.
Do you have existing clients?
Equipment or gear already in place?
A video production business plan suggests that your focus will be on video production. Things like equipment will be critical.
In addition to considering this an entertainment production company business plan you may also want to focus on creative development.
How you want to focus effects how you want to phrase things. And it matters almost immediately.
START FEES YOU CAN AVOID
It's a good idea to propose that you start small.
There are two reasons for this.
The first is that you will scare away investors if you ask for too much up front, almost without fail they can tell if you are asking for more than it seems like you need.
It also throws into question how serious you are about sustaining success.
Which leads to the second reason.
It'll be much harder for you to sustain success if you ask for big upfront funding that you aren't sure you can earn back plus profit.
Let's say because you know of a few jobs you'll have early on, that you ask for less up front.
You'll be able to get rolling right away, earning back the initial investments and then some.
Above all you want to start off with easy wins.
Or as close to easy wins as you can get when launching or re-launching a video production business plan.
Seems like it would somewhat obvious not to ask for more than you can earn back...
Rather, it's a mistake people make all the time.
Speaking of which...
do have the capital?
5. financing a company.
Any business needs capital. As a result, you need a section where you lay out the cash flow for the production house business plan.
What kind of money do you expect to have coming in, and how much do you expect to be spending?
Make the budget, while also estimating how you'll be earning.
If you can't demonstrate this, then you need to go back to the drawing board.

Just pose like this and you’ll reassure any investor
You will want to get involved with an accountant at some point soon.
But remember, this is a business plan for a production company. So you may have a lot of costs coming at you early just to get started.
What is a marketing plan?
Your video production business plan is almost complete. Another section worth including would be one on marketing.
Here is a good additional resource on small business accounting .
You want to prove that business will be coming in, and not assume it will on faith alone.
Building a strong portfolio is a must. Consider again what niche you may be able to serve best. Find a solid "bread and butter" to start with.
Remember, good businesses expand when they need to. They don't bite off more than they can chew right out of the gate.
INVEST IN A GOOD WEBSITE
Do some research on how you’ll be building the best website for your product.
Get your production company a few social media accounts, and start trying to create a presence there. You'll need to find many ways to attract clients, and show your work.
Do some additional research on how to market a production company.
All this needs to find its way into the marketing section of your production company business plan.
what's your daily workflow?
7. day to day operations.
The day to day operations are a critical part of the plan. Have you visualized what the daily workflow will be?
Now is the time to do that. Who is going to be on your team, and how will it grow and change over time?
Determine what tasks will take priority each day, and how to best utilize your resources and finances.
This will be a key step in determining if your production company business plan is sustainable.
Ask yourself a few of the following questions:
How much time per day will you spend building your client base? What elements of each job will you tackle in-house? Which tasks might you outsource?
What equipment and gear do you own?
When will it need to be replaced and/or upgraded?
Are you going to hire anyone to start? Will they be full-time employees?
Will you hire independent contractors per project? How many, roughly?
As mentioned in the finance section, you need to know how you'll plan your reporting for taxes and your bookkeeping process.
These questions will help you start to determine what each "day at the office" will look like.
The clearer a picture you can paint here, the better.
Write a Business Plan
Get as specific as possible in each section of your entertainment company business plan. The more you know... right?
Now, let's get a little more advanced. In our next post we'll dive into writing a 4 part business plan.
Up Next: Write a 4-Part Business Plan →
Project management for video creatives. tasks, file sharing, calendars and more..
Manage video production timelines, tasks, storyboards, shot lists, breakdowns, call sheets. Made for video creatives, new media and film.
Learn More ➜
1.1 CHAPTER TITLE HERE...
Short, actionable h3 phrase....
Marshmallow pie sweet roll gummies candy icing. I love candy canes soufflé I love jelly beans biscuit. Marshmallow pie sweet roll gummies candy icing.
- Pricing & Plans
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- 24 Best Storyboarding Software of 2024
- What is Tone? — A Guide for Storytellers
- What is Symbolism? Definition & Examples
- Film Coverage — A Step-by-Step Guide to Shot Listing Efficiently
- What Is a Plot? Types of Plot, Definitions, and Examples
- 1.2K Facebook
- 44 Pinterest
- 20 LinkedIn

How To Write a Winning Music Production Business Plan + Template

Creating a business plan is essential for any business, but it can be especially helpful for music production businesses that want to improve their strategy and/or raise funding.
A well-crafted business plan not only outlines the vision for your company, but also documents a step-by-step roadmap of how you are going to accomplish it. In order to create an effective business plan, you must first understand the components that are essential to its success.
This article provides an overview of the key elements that every music production business owner should include in their business plan.
Download the Ultimate Business Plan Template
What is a Music Production Business Plan?
A music production business plan is a formal written document that describes your company’s business strategy and its feasibility. It documents the reasons you will be successful, your areas of competitive advantage, and it includes information about your team members. Your business plan is a key document that will convince investors and lenders (if needed) that you are positioned to become a successful venture.
Why Write a Music Production Business Plan?
A music production business plan is required for banks and investors. The document is a clear and concise guide of your business idea and the steps you will take to make it profitable.
Entrepreneurs can also use this as a roadmap when starting their new company or venture, especially if they are inexperienced in starting a business.
Writing an Effective Music Production Business Plan
The following are the key components of a successful music production business plan:
Executive Summary
The executive summary of a music production business plan is a one to two page overview of your entire business plan. It should summarize the main points, which will be presented in full in the rest of your business plan.
- Start with a one-line description of your music production company
- Provide a short summary of the key points in each section of your business plan, which includes information about your company’s management team, industry analysis, competitive analysis, and financial forecast among others.
Company Description
This section should include a brief history of your company. Include a short description of how your company started, and provide a timeline of milestones your company has achieved.
If you are just starting your music production business, you may not have a long company history. Instead, you can include information about your professional experience in this industry and how and why you conceived your new venture. If you have worked for a similar company before or have been involved in an entrepreneurial venture before starting your music production firm, mention this.
You will also include information about your chosen music production business model and how, if applicable, it is different from other companies in your industry.
Industry Analysis
The industry or market analysis is an important component of a music production business plan. Conduct thorough market research to determine industry trends and document the size of your market.
Questions to answer include:
- What part of the music production industry are you targeting?
- How big is the market?
- What trends are happening in the industry right now (and if applicable, how do these trends support the success of your company)?
You should also include sources for the information you provide, such as published research reports and expert opinions.
Customer Analysis
This section should include a list of your target audience(s) with demographic and psychographic profiles (e.g., age, gender, income level, profession, job titles, interests). You will need to provide a profile of each customer segment separately, including their needs and wants.
For example, the clients of a music production business may include:
- Recording studios
- Independent record labels
You can include information about how your customers make the decision to buy from you as well as what keeps them buying from you.
Develop a strategy for targeting those customers who are most likely to buy from you, as well as those that might be influenced to buy your products or music production services with the right marketing.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis helps you determine how your product or service will be different from competitors, and what your unique selling proposition (USP) might be that will set you apart in this industry.
For each competitor, list their strengths and weaknesses. Next, determine your areas of competitive differentiation and/or advantage; that is, in what ways are you different from and ideally better than your competitors.
Below are sample competitive advantages your music production business may have:
- Proven industry experience
- Unique production process
- Strong customer loyalty
- Extensive music library
- Personalized service
Marketing Plan
This part of the business plan is where you determine and document your marketing plan. . Your plan should be clearly laid out, including the following 4 Ps.
- Product/Service : Detail your product/service offerings here. Document their features and benefits.
- Price : Document your pricing strategy here. In addition to stating the prices for your products/services, mention how your pricing compares to your competition.
- Place : Where will your customers find you? What channels of distribution (e.g., partnerships) will you use to reach them if applicable?
- Promotion : How will you reach your target customers? For example, you may use social media, write blog posts, create an email marketing campaign, use pay-per-click advertising, launch a direct mail campaign. Or, you may promote your music production business via a public relations campaign.
Operations Plan
This part of your music production business plan should include the following information:
- How will you deliver your product/service to customers? For example, will you do it in person or over the phone only?
- What infrastructure, equipment, and resources are needed to operate successfully? How can you meet those requirements within budget constraints?
The operations plan is where you also need to include your company’s business policies. You will want to establish policies related to everything from customer service to pricing, to the overall brand image you are trying to present.
Finally, and most importantly, in your Operations Plan, you will lay out the milestones your company hopes to achieve within the next five years. Create a chart that shows the key milestone(s) you hope to achieve each quarter for the next four quarters, and then each year for the following four years. Examples of milestones for a music production business include reaching $X in sales. Other examples include adding new production equipment, opening a second location, or hiring new personnel.
Management Team
List your team members here including their names and titles, as well as their expertise and experience relevant to your specific music production industry. Include brief biography sketches for each team member.
Particularly if you are seeking funding, the goal of this section is to convince investors and lenders that your team has the expertise and experience to execute on your plan. If you are missing key team members, document the roles and responsibilities you plan to hire for in the future.
Financial Plan
Here you will include a summary of your complete and detailed financial plan (your full financial projections go in the Appendix).
This includes the following three financial statements:
Income Statement
Your income statement should include:
- Revenue : how much revenue you generate.
- Cost of Goods Sold : These are your direct costs associated with generating revenue. This includes labor costs, as well as the cost of any equipment and supplies used to deliver the product/service offering.
- Net Income (or loss) : Once expenses and revenue are totaled and deducted from each other, this is the net income or loss.
Sample Income Statement for a Startup Music Production Firm
Balance sheet.
Include a balance sheet that shows your assets, liabilities, and equity. Your balance sheet should include:
- Assets : All of the things you own (including cash).
- Liabilities : This is what you owe against your company’s assets, such as accounts payable or loans.
- Equity : The worth of your business after all liabilities and assets are totaled and deducted from each other.
Sample Balance Sheet for a Startup Music Production Firm
Cash flow statement.
Include a cash flow statement showing how much cash comes in, how much cash goes out and a net cash flow for each year. The cash flow statement should include:
- Cash Flow From Operations
- Cash Flow From Investments
- Cash Flow From Financing
Below is a sample of a projected cash flow statement for a startup music production business.
Sample Cash Flow Statement for a Startup Music Production Firm
You will also want to include an appendix section which will include:
- Your complete financial projections
- A complete list of your company’s business policies and procedures related to the rest of the business plan (marketing, operations, etc.)
- Any other documentation which supports what you included in the body of your business plan.
Writing a good business plan gives you the advantage of being fully prepared to launch and/or grow your music production company. It not only outlines your business vision but also provides a step-by-step process of how you are going to accomplish it.
Remember to keep your business plan updated as your company grows and changes. Review it at least once a year to make sure it is still relevant and accurate.
Finish Your Music Production Business Plan in 1 Day!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Need to write a convincing business plan for your music video production company fast? Discover which tool to use and what to write in our complete guide.
A music business plan provides a snapshot of your music business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also …
Music production can be a profitable business, but success and profitability depend on various factors, such as the producer’s skills, industry connections, reputation, demand for their services, and the ability to adapt to …
Download your FREE printable business plan template for your video production. Just enter your email address and we'll instantly send it to you!
Ready? Let’s get started! In this guide: Understanding how a music video production company works. Assembling your music video production company's founding team. Conducting …
Learn how to successfully write a music production business plan to help you start, grow, and/or raise funding for your music production company.