Essay on Quality Control of Products: Top 13 Essays
After reading this essay you will learn about:- 1. Meaning and Definitions of Quality Control 2. Quality Control Organisation 3. Advantages of Quality Control 4. Quality Control for Export 5. Indian Standard Institution 6. Quality Assurance 7. Causes of Quality Failures 8. Economics of Quality 9. Product Quality Analysis 10. Quality Planning 11. Quality Improvement 12. Quality Management System 13. Role of Top Management.
- Essay on the Role of Top Management towards Quality

Essay # 1. Meaning and Definitions of Quality Control :
Quality control in its simplest term, is the control of quality during manufacturing. Both quality control and inspection are used to assure quality. Inspection is a determining function which determines raw materials, supplies, parts or finished products etc. as acceptable or unacceptable.
As control becomes effective, the need for inspection decreases. Quality control determines the cause for variations in the characteristics of products and gives solutions by which these variations can be controlled. It is economic in its purpose, objective in its procedure, dynamic in its operation and helpful in its treatment.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Since variations in raw materials have large effects on the quality of in-process materials, quality control includes statistical sampling and testing before acceptance. It also includes the examination of quality characteristics in finished products so as to assure satisfactory outgoing quality.
Cooperation between the quality control group and other departments such as production, planning and inspection is of vital importance. With proper managerial support and co-operation the quality control programme will be more successful.
Definitions :
In current quality control theory and practice, the meaning of “Quality” is closely allied to cost and customer needs. “Quality” may simply be defined as fitness for purpose at lowest cost.
“Quality” of any product is regarded as the degree to which it fulfills the requirements of the customer. “Quality” means degree of perfection. Quality is not absolute but it can only be judged or realized by comparing with standards. It can be determined by some characteristics namely, design, size, material, chemical composition, mechanical functioning, workmanship, finishing and other properties.
Quality of a product depends upon the application of materials, men, machines and manufacturing conditions. The systematic control of these factors is the quality control. The quality of a product differs greatly due to these factors. For example, a skilled worker will produce products of better quality and a less skilled worker will produce poor quality products.
Similarly better machines and better materials with satisfactory manufacturing conditions produce a better quality product. Thus, it is clear that to control the quality of product various factors which are responsible for quality are required to be controlled properly.
In the words of Alford and Beatly, “quality control” may be broadly defined as that “Industrial management technique by means of which products of uniform acceptable quality are manufactured.” Quality control is concerned with making things right rather than discovering and rejecting those made wrong.
“It may also be defined as the function or collection of duties which must be performed throughout the organisation in order to achieve its quality objective” or in the other words ‘Quality is every body’s business and not only the duty of the persons in the Inspection Staff.
Concluding, we can say that quality control is a technique of management for achieving required standard of products.
Factors Affecting Quality :
In addition to men, materials, machines and manufacturing conditions there are some other factors which affect the quality of product as given below:
(i) Market Research i.e. demand of purchaser.
(ii) Money i.e. capability to invest.
(iii) Management i.e. Management policies for quality level.
(iv) Production methods and product design.
Apart from these, poor packing, inappropriate transportation and poor after sales service are the areas which can cause damage to a company’s quality image. There are cases where goods of acceptable quality before transportation were downgraded on receipt by the retailer just because they had been damaged in transportation.
Modern quality control begins with an evaluation of the customer’s requirements and has a part to play at every stage from goods manufactured right through sales to a customer, who remains satisfied.
Essay # 2. Quality Control Organisation :
Over the years, the status of the quality control organisation changed from a function merely responsible for detecting inferior or standard material to a function that establishes what are termed preventive programmes.
These programmes are designed to detect quality problems in the design stage or at any point in the manufacturing process and to follow up on corrective action.
Immediate responsibility for quality products rest with the manufacturing departments. All the activities concerning product quality are usually brought together in the organisation which may be known as inspection, quality control, quality assurance department or any other similar name.
Quality control is a staff activity since it serves the line or production department by assisting them in managing quality. Since the quality control function has authority delegated by management to evaluate material produced by the manufacturing department, it should not be in a position to control or dictate to the quality activity.
The quality control organisation depending upon the type of product, method of quality is sufficient enough to carry out following activities:
1. Inspection of raw material, product or processes.
2. Salvage inspection to determine rejected part and assembly disposition.
3. Records and reports maintenance.
4. Statistical quality control.
5. Gauges for inspection.
6. Design for quality control and inspection.
7. Quality control system maintenance and development.
Functions of Quality Control Department :
Quality control department has the following important functions to perform:
1. Only the products of uniform and standard quality are allowed to be sold.
2. To suggest methods and ways to prevent the manufacturing difficulties.
3. To reject the defective goods so that the products of poor quality may not reach to the customers.
4. To find out the points where the control is breaking down and investigates the causes of it.
5. To correct the rejected goods, if it is possible. This procedure is known as rehabilitation of defective goods.
Essay # 3. Advantages of Quality Control :
There are many advantages by controlling the product quality.
Some of them are listed below:
1. Quality of product is improved which in turn increases sales.
2. Scrap rejection and rework are minimised thus reducing wastage. So the cost of manufacturing reduces.
3. Good quality product improves reputation.
4. Inspection cost reduces to a great extent.
5. Uniformity in quality can be achieved.
6. Improvement in manufacturer and consumer relations.
7. Improvement in technical knowledge and engineering data for process development and manufacturing design.
Essay # 4. Quality Control for Export :
Today we need foreign exchange for our requirements and for repayment of our debts and services. If our products are expensive and are of sub-standard quality then the customers abroad will not buy goods from us.
Therefore, we must be able to supply goods which may meet the requirements of foreign buyers. For this purpose quality and good packing determines to a large extent the continued acceptability of the product.
At present some organisations lite Export Inspection Council of India, the Indian Standards Institution, the Indian Society of Quality Control and the Indian Institute of Foreign Trade are helping about this problem of quality control.
Implementation of the Export Act 1963 and the work of Export Inspection Council (set up under Export Act) have helped in planned approach towards quality control. The advice of Export Inspection Council is very helpful for pre-shipment inspection of exportable goods.
These organisations have been authorised to issue a “Certificate of Quality” after satisfying themselves that the goods fulfill the minimum standards of quality laid down or that they are of the quality claimed by the exporter.
Essay # 5. Indian Standard Institution (I.S.I. Renamed as B.I.S.) :
To protect the interest of the consumers, Indian Standard Institution is serving in India. In most of the western countries, consumers nave formed their own associations to protect their interest. In some countries these associations, receive official support and guidance.
I.S.I, serves the consumers through Certification Marks Scheme. Under this scheme I.S.I, has been vested with the authority to grant licenses to manufacturers to apply the I.S.I, mark on their products in token of their conformity to the desired Indian Standards.
To control the quality, I.S.I, inspectors carry out sudden inspections of the factories of the licensee. Inspectors may check the incoming raw materials, outgoing finished products and may carry out necessary tests at different levels of control during production.
Thus I.S.I, mark gives guarantee to the purchaser that the goods with this mark have been manufactured under a well-defined system of quality control. From first April 1987 it has been renamed as Bureau of Indian Standards.
Essay # 6. Quality Assurance :
Inspection, quality control and quality assurance:.
Inspection is a process of sorting good from a lot. Whereas Quality Control is aimed at prevention of defects at the very source, relies on effective feedback system, and procedure for corrective action.
In Quality control programme, inspection data are used to take prompt corrective action to check the defects. For this purpose, detailed studies are conducted to find out that from where the defect is originated, and how to prevent it, may it be at manufacturing, design, purchase of raw materials, despatch or storage stage.
Quality Assurance means to provide the necessary confidence to the customer as well as to top management that all concerned are carrying out their job effectively and that the product quality is as per customer’s satisfaction with economy. Quality products can be produced only when all the departments fully participate and co-operate.
Presently, customers demand for higher quality and reliability. It has been felt that even a single defect whatever may be the reasons, result in economic loss.
These reasons have necessitated the need for total quality and reliability programmes to cover wide spectrum of functions and various areas of product design, production system design through various states of material, manufacture and commitment to efficient maintenance and operation of the system as a whole. This is necessary for quality assurance and reliability of the product. This assures the continuous failure free system to the customers.
Responsibilities of Quality Assurance Department :
i. Plan, develop and establish Quality policies.
ii. To assure that products of prescribed specification reaches to the customers.
iii. Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of the Quality programmes.
iv. Conduct studies and investigations related to the quality problems.
v. Liaise with different department, in and outside the organisation.
vi. Organise training programmes on quality.
vii. Plan and coordinate vendor quality surveys and evaluate their results.
viii. Develop Quality assurance system and regularly evaluate its effectiveness.
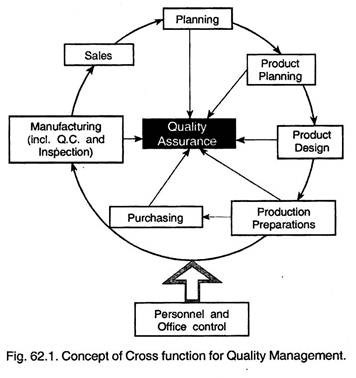
Quality Assurance System :
Quality assurance system should be developed incorporating the following aspects:
i. Formulate the quality control and manufacturing procedures.
ii. Percentage checking be decided.
iii. Procedures and norms for plant performances as regards to quality be developed.
iv. Rejection analysis and immediate feed-back system for corrective action.
v. Prepare a manual for quality assurance.
vi. Formulate plans for quality improvement, quality motivation and quality awareness in the entire organisation.
Essay # 7. Causes of Quality Failures :
Quality failures occur due to various causes, most of them are because of lack of involvement of men concerned with the quality. Studies have indicated that more than 50% of quality failures are due to human errors at various levels, such as understanding of customer’s requirements, manufacturing, inspection, testing, packaging and design etc.
Error affecting quality can be classified into following categories :
(a) Error Due to Inadvertence:
These are due to lack of knowledge of the product, and continue due to lack of information about quality deficiency. Such mistakes can be controlled, if a system for feedback is developed in which quality performance results are analysed in a regular and timely manner.
(b) Errors Due to Lack of Technique:
These errors are due to lack of knowledge, skill, technique etc. In such cases performance of ‘better’ operation are compared with those of ‘poor’ or ‘defect prone’ operations, and the process adopted by them are studied and reasons for errors are investigated.
(c) Willful Errors:
Sometimes quality is compromised due to early delivery schedules, reduction in cost, safety etc.
Reduction of Errors by Improved Motivation :
Quality motivational programmes are developed for getting quality product from the line staff so that they take interest in improving the quality. Motivational programmes are designed after identifying the sources/reasons of failures.
Operators are motivated by designing a campaign to secure alertness, awareness and new actions, and by observing the managers for their behaviours or reactions on any quality problem. Campaign can be launched through mass meetings, quality posters, exhibition of quality deficiencies etc.
Campaign may also invite operators to participate in analysing the causes of defects or the failure on the part of operation and/or systems. Trainings are very helpful in making the operators aware of the technological does and don’ts and the purpose behind each operation.
Essay # 8. Economics of Quality :
The good economic performance is the most essential for survival and growth of any organisation in the highly competitive environment. Therefore, one of the most common objections of every organisation is to attain excellence in its economic performance. The single most important factor which leads to good economic performance is the ‘quality’ of its products or services.
Therefore, in order to achieve economy, quality management system must contribute towards the establishment of customer-oriented quality discipline in the marketing, design, engineering, procurement, production, inspection, testing and other related servicing functions.
Everybody in the organisation must be involved in the production and delivery of quality product or services, consistently to meet the customer needs and satisfaction.
The production of defective output results in the costs of sorting, scrap, rework, dealing with customer complaints, replacement under warranty etc. It is more serious and very difficult to ascertain the cost associated with the loss of goodwill, following the sale of defective or non-conforming products.
Designers of economic models use following costs:
i. Fixed costs of sampling, inspecting, testing and measuring.
ii. Variable cost of sampling, measuring, calculating and plotting each sample value on control charts.
iii. Cost of correcting and assignable cause.
iv. Total loss in profit, when the process is running out of control.
It has been experienced that the savings due to control of poor quality products, better control over the quality of purchased product, use of more economical materials or methods due to their greater reliability, are sometime spectacular.
Quality is a dynamic phenomenon and is being improved continuously with the new developments in technology and management techniques.
Quality and Cost :
Studies have indicated that any reduction in quality results in a reduced level of satisfaction and decrease in customer goodwill toward the producer. This will lead to reduction in return on investment in the long run.
Following are the general principles of quality and cost relationship:
(i) Cost of poor quality are far larger than that had been recognised.
(ii) Appraisal costs are reduced by focussing on preventing errors at the source.
(iii) System be established for reducing the cost rather than reducing the quality.
(iv) By focussing on quality improvement overall, performance of the firm can be improved.
(v) Focus of quality improvement be shifted from product attributes to operational procedure.
Quality Cost (or Costs Associated with Quality) :
Quality cost means cost of poor quality goods or services.
Following are the main quality associated costs:
1. Failure Costs :
(A) Internal Failure Costs:
(i) Scrap and rework cost.
(ii) Costs involved in testing, inspecting and sorting for down-gradation.
(iii) Losses due to avoidable processing.
(iv) Expenditure in failure analysis.
(B) External Failure Costs:
(i) Warranty charges.
(ii) Redressal of complaints.
(iii) Loss of future sales.
(iv). Other expenses on return of materials, failure analysis outside the factory.
2. Appraisal/Detection Costs :
(i) Incoming test and inspection including materials, in-process and final quality sampling.
(ii) Quality audits.
(iii) Equipment calibration.
(iv) Evaluation of performance.
(v) Evaluation of customer satisfaction.
3. Prevention Costs :
(i) Quality planning.
(ii) New product review.
(iii) Process control.
(iv) Training and education.
(v) Process quality planning.
Quality Cost Control :
For the purpose of reducing the cost, when internal and external failure costs are cost down, the appraisal cost and preventive cost may slightly go up. Therefore, it is necessary for optimum balance to reduce failure cost with slight increase in appraisal and preventive cost, with the aim of substantial reduction in total quality cost without compromising with the quality.
Efforts for reducing quality cost must be continuous.
The cost reduction programme must be followed in following stages:
1. Identification of quality cost items.
2. Structuring of quality cost reporting, including related analysis and control, and
3. Maintenance of programme to ensure that the objectives of higher quality at lower cost.
Quality control and quality cost must be directed in such a way so as to provide the firm with major added business value.
Essay # 9. Product Quality Analysis :
It includes:
(i) The various functions to be performed by the manufactured product.
(ii) Life and durability of product.
(iii) Working conditions required during manufacturing.
(iv) Product specifications.
(v) Manufacturing processes and methods.
(vi) Maintenance and installation.
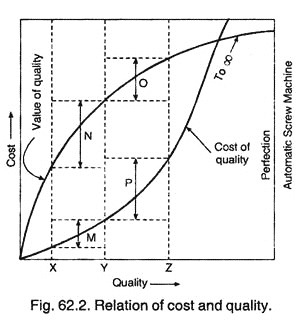
(Quality at level Y is the most economical. A drop of quality to level X reduces the cost by M but also reduces the quality value by N which is greater than M. A rise of quality to level Z increases the quality value by O and increases the cost by P, which is greater than O) — Refer Fig. 62.1.
Essay # 10. Quality Planning :
Quality planning is done keeping the company needs and customer needs in view, and a comprehensive quality plan is prepared for implementation in the company.
Quality plan is a document setting out the specific quality practices, resources and activities relevant to a particular product, process, services, contract or project.
Quality planning is a systematic process for:
(i) Identifying customers,
(ii) Discovering customer needs,
(iii) Designing the responsive products,
(iv) Developing the process for creating and delivering the products, and
(v) Transferring the process and its contents to those who will perform the product or service.
Essay # 11. Quality Improvement :
Quality improvement is a structured process for reducing the deficiencies that are present in products, processes and services and/or improving performance whenever there is an opportunity to improve.
Quality problems are of following two types:
1. Sporadic Problems:
A sporadic problem is a sudden adverse change in the status quo, which requires remedy. The variations due to these problems are so significant that they trigger the alarm signals of the control system.
2. Chronic Problems:
Chronic problem is long-standing adverse situation which requires remedy through changing the status quo. For such problems, by adopting ‘continuous improvement concept’ better and better levels of performance can be achieved. These problems occur for a long time, and are often difficult to solve, as they are accepted as inevitable.
Essay # 12. Quality Management System :
A quality management system organises overall activities of the company in such a way that the technical, administrative and human factors affecting the quality of products or services are under control. The quality management system guides the cooperated actions of the people, machines and information to achieve the quality objectives.
1. Activities:
Activities of quality management system are:
(i) Marketing to evaluate customer needs and use requirements.
(ii) Design and engineering to translate the customer needs into product, process and material specifications.
(iii) Purchasing to select the competent vendors who can supply materials, components, sub-assemblies as per specifications.
(iv) Production to ensure that product is produced under controlled conditions in conformance to standards.
(v) Quality assurance to identify appropriate test methods and exercise quality control techniques.
(vi) Shipping to ensure proper packaging, transportation and distribution of material.
(vii) Documentation to maintain system and progress documents at each stage of operation.
(viii) Product development for innovation and improvement based on customer’s feedback.
(ix) Auditing to identify the non-conforming of the system and product, and follow up the corrective actions.
2. Benefits:
(i) To meet the customer requirements by providing quality products or services to satisfy the customer needs.
(ii) Good reputation helps in better marketability of the company’s products and services.
(iii) Confidence is created.
(iv) Consistivity in quality.
(v) Productivity improvement.
(vi) Better financial performance.
(vii) Brings clarity in working.
(viii) Better documentation.
(ix) Better monitoring.
(x) Increases export potential.
(xi) Human resources development.
3. Quality Function:
(i) Marketing and market research.
(ii) Design and product development.
(iii) Procurement.
(iv) Process planning and development.
(v) Production.
(vi) Inspection, testing and examination.
(vii) Packaging and storage.
(viii) Sales and distribution.
(ix) Installation and operation.
(x) Technical assistance and maintenance.
(xi) Disposal after use.
4. Quality and Top Management:
Responsibility for and commitment to quality always belong to the highest level of management.
Following action points are necessary to be adopted by top management to achieve quality objectives of the company:
(i) Define and state quality policy.
(ii) Appoint a management representation.
(iii) Define responsibility and authority.
(iv) Establish an internal verification system.
(v) Establish a quality system.
(vi) Review the functioning of quality system at regular intervals.
5. Installing the Quality System :
(A) Preparations:
(i) Analyse the existing status and identify what needs to be done? Prepare an action plan.
(ii) Develop an organisation structure.
(iii) Develop quality system documentation.
(iv) Prepare the material and machinery resources.
(B) Implementation:
(i) Implement the documented quality system.
(ii) Establish internal quality audit system.
(iii) Monitor, control and stabilise the quality system.
(iv) Hormonise the practices with the standards.
Essay # 13. Role of Top Management towards Quality :
Main roles of the top management towards quality are:
1. Define quality Control. Establish a Quality Council.
2. Establish quality policies.
3. Establish quality goals.
4. Provide the resources.
5. Provide problem-oriented training.
6. Serve on quality improvement teams which address chronic problems.
7. Stimulate improvement.
8. Provide for reward and recognition.
9. Top management is required to:
(a) Develop strategies for quality, and
(b) Provide leadership for implementation of these strategies.
Related Articles:
- Essay on Quality Control | Products | Production Management
- Essay on the Pricing of Products: Top 5 Essays | Marketing Management
- Acceptance Sampling: Meaning, Role and Quality Indices
- Essay on Materials Management: Top 7 Essays | Branches | Management
We use cookies
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
122 Quality Assurance Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Quality assurance is an essential aspect of any industry or organization, ensuring that products and services meet the highest standards of excellence. As such, it is crucial for professionals in this field to stay informed about the latest trends and best practices. To help you stay ahead of the curve, we have compiled a list of 122 quality assurance essay topic ideas and examples that you can use for your next research paper or project.
- The importance of quality assurance in the manufacturing industry
- Strategies for implementing a successful quality assurance program
- How to measure the effectiveness of a quality assurance program
- The role of technology in improving quality assurance processes
- Best practices for conducting quality audits
- The impact of quality assurance on customer satisfaction
- The relationship between quality assurance and risk management
- The benefits of implementing a total quality management system
- Quality assurance in the healthcare industry
- Quality assurance in the food industry
- The role of quality assurance in the pharmaceutical industry
- Quality assurance in the automotive industry
- Quality assurance in the aerospace industry
- Quality assurance in the construction industry
- The impact of globalization on quality assurance practices
- The role of quality assurance in ensuring compliance with regulations
- The relationship between quality assurance and continuous improvement
- The challenges of implementing a quality assurance program in a small business
- The role of leadership in promoting a culture of quality assurance
- The impact of quality assurance on employee morale
- The role of training and development in quality assurance
- The role of quality assurance in reducing costs and increasing efficiency
- The impact of quality assurance on brand reputation
- Quality assurance in the service industry
- The impact of quality assurance on supply chain management
- The role of quality assurance in ensuring product safety
- The challenges of implementing a quality assurance program in a global organization
- The impact of quality assurance on product innovation
- The role of quality assurance in new product development
- The relationship between quality assurance and customer loyalty
- The impact of quality assurance on organizational performance
- The role of quality assurance in maintaining competitive advantage
- The challenges of implementing a quality assurance program in a regulated industry
- The role of quality assurance in reducing waste and improving sustainability
- The impact of quality assurance on employee engagement
- The role of quality assurance in fostering a culture of continuous improvement
- The relationship between quality assurance and customer retention
- The impact of quality assurance on organizational resilience
- The role of quality assurance in ensuring product reliability
- The challenges of implementing a quality assurance program in a decentralized organization
- The impact of quality assurance on product differentiation
- The role of quality assurance in ensuring product quality
- The relationship between quality assurance and customer trust
- The impact of quality assurance on cost control
- The role of quality assurance in managing supplier relationships
- The challenges of implementing a quality assurance program in a fast-paced industry
- The impact of quality assurance on organizational culture
- The role of quality assurance in fostering innovation
- The relationship between quality assurance and organizational resilience
- The impact of quality assurance on employee satisfaction
- The role of quality assurance in ensuring product consistency
- The challenges of implementing a quality assurance program in a highly regulated industry
- The impact of quality assurance on product performance
- The role of quality assurance in ensuring customer satisfaction
- The relationship between quality assurance and organizational agility
- The impact of quality assurance on organizational efficiency
- The role of quality assurance in promoting a culture of quality excellence
- The challenges of implementing a quality assurance program in a dynamic industry
- The impact of quality assurance on product competitiveness
- The role of quality assurance in maintaining market leadership
- The relationship between quality assurance and organizational effectiveness
- The impact of quality assurance on product reliability
- The challenges of implementing a quality assurance program in a global supply chain
- The impact of quality assurance on customer loyalty
In conclusion, quality assurance is a critical component of any organization, ensuring that products and services meet the highest standards of excellence. By exploring these 122 quality assurance essay topic ideas and examples, you can gain a deeper understanding of the key issues and trends in this field, enabling you to develop innovative solutions and drive continuous improvement within your organization.
Want to research companies faster?
Instantly access industry insights
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Leverage powerful AI research capabilities
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2024 Pitchgrade
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Quality Control (QC)?
- Understanding QC
- Difference With Quality Assurance
The Bottom Line
- Business Essentials
Quality Control: What It Is, How It Works, and QC Careers
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
Quality control (QC) is a process through which a business seeks to ensure that product quality is maintained or improved. Quality control requires the company to create an environment where management and employees strive for perfection. This is done by training personnel, creating benchmarks for product quality, and testing products to check for statistically significant variations.
A significant aspect of quality control is the establishment of well-defined controls . These controls help standardize both production and reactions to quality issues. Limiting room for error by specifying which production activities are to be completed by which personnel reduces the chance that employees will be involved in tasks for which they do not have adequate training.
Key Takeaways
- Quality control (QC) is a process through which a business seeks to ensure that product quality is maintained or improved.
- Quality control involves testing units and determining if they are within the specifications for the final product.
- The quality control used in a business is highly dependent on the product or industry, and several techniques exist for measuring quality.
- The food industry uses quality control methods to ensure customers do not get sick from their products.
- Quality control creates safe measures that can be implemented to make sure deficient or damaged products do not end up with customers.
Ryan Oakley / Investopedia
Understanding Quality Control (QC)
Quality control involves testing units and determining if they are within the specifications for the final product. The purpose of the testing is to determine any need for corrective actions in the manufacturing process. Good quality control helps companies meet consumer demands for better products.
Why Is QC Needed?
Creating a product is costly, time-consuming, and can be unsafe without controls in place. Additionally, if a company sends defective products out for purchase, it could be held liable for injuries or issues that arise from using its products. Quality control inspectors ensure that defective or unsafe products are identified , and the causes are corrected.
How Is It Done?
Quality testing is generally completed in each step of a manufacturing or business process. Employees often begin by testing raw materials , pulling samples from the manufacturing line, and testing the finished product. Testing at the various stages of manufacturing helps identify where a production problem is occurring and the remedial steps it requires to prevent it in the future.
In a non-manufacturing business, quality testing can involve customer service evaluations, questionnaires, surveys, inspections, or audits. A business can use any process or method to verify that its end product or service meets the customer's needs and is safe and legal.
QC Is Different by Industry
The quality control used in a business is highly dependent on the product or industry. For example, in food and drug manufacturing, quality control includes ensuring the product does not make a consumer sick, so the company performs chemical and microbiological testing of samples from the production line.
In aircraft manufacturing, quality control and assurance is of the utmost importance. Manufacturers are required to document, track, inspect, and reinspect all items and phases of a build to build evidence that everything is completed to very strict standards.
In automobile manufacturing, quality control focuses on parts meeting specifications and tolerances. QC ensures engines, drive trains, and other mechanical parts operate smoothly, efficiently, safely, and as designed.
In electronics, quality testing might involve using meters that measure the flow of electricity and stress testing.
Quality Control vs. Quality Assurance
Quality control and quality assurance are terms often used to define the same thing, but there are distinct differences. Quality control focuses on quality requirements, such as ensuring a part meets specifications. Quality assurance refers to the sum of all actions and processes needed to demonstrate that quality requirements are fulfilled.
What this difference means for quality professionals is that as you move through a quality control career, you might transition from quality control to quality assurance. Quality control is part of quality assurance, which consists of programs and departments that assure upper-level management, customers, and government inspectors that products meet all quality requirements and safety standards .
Quality Control Methods
There are several methods quality control uses to communicate and track inspections and issues. For instance, a quality control chart is a graphic that depicts whether sampled products or processes are meeting their intended specifications—and, if not, the degree by which they vary from those specifications.
When one chart analyzes a specific product attribute, it is called a univariate chart. A chart that measures variances in several product attributes is called a multivariate chart. Tracking variances allows businesses to see how many defects per production unit they produce and what types of defects are occurring. Here are a few examples of some methods used.
X-Bar Chart
Randomly selected products are tested for the given attributes the chart is tracking. A common form of a quality control chart is the X-bar chart, where the y-axis on the graph tracks the degree to which the variance of the tested attribute is acceptable. The x-axis tracks the samples tested. Analyzing the variance pattern on this chart helps you determine if defects are occurring randomly or systematically.
Taguchi Method
The Taguchi Method of quality control is another approach that emphasizes the roles of research and development, product design, and product development in reducing the occurrence of defects and failures in products. The Taguchi Method considers design more important than the manufacturing process in quality control and tries to eliminate variances in production before they can occur.
100% Inspection Method
This 100% inspection method is a quality control process involving looking at and assessing all product parts. This type of quality control is done to rule out flaws in products. This method is often used to evaluate valuable metals. The 100% inspection method calls for data about the manufacturing process and software to analyze inventory.
The challenge of using this method is that looking at every single item used to build a product is expensive and could destabilize or render the product unusable. For example, if you use this method to examine organic strawberries, you risk damaging the berries, rendering them unsellable.
Quality control methods help standardize production and reactions to quality issues in various industries, from food production to automobile manufacturing.
Quality Control Careers
Quality control can be a rewarding career if you enjoy working with people, communicating, presenting results, and working to make products better and safer. To become a quality control inspector, you'll need (depending on the industry):
- A high school diploma for entry-level positions
- A bachelor's degree, depending on the industry
- Experience in an industry
- Licenses and certifications for some industries and businesses
Other qualities that are necessary for quality control professionals are:
- Attention to detail
- Mechanical and math skills
- Physical abilities and strength
- Technical skills
- Performance under pressure
Career Path
The route to a career in quality control and assurance varies by industry, so there may be differences. However, you'll generally need several years of experience in your industry. Typically, you begin by being hired as a quality assurance or control associate after meeting educational and work experience requirements.
Once you gain work experience as a quality specialist or associate, you may move into a senior specialist position and begin managing teams of quality control specialists. You may attend professional development courses sponsored by your employer or be required to gain certifications such as Six Sigma. You might also need to earn a professional designation such as Certified Quality Inspector.
Moving up the career path, you have more options. You may be able to choose from or be selected to be a:
- QA Systems Manager
- QA Operations Manager
- QA Compliance Manager
These positions can lead up to upper-level management or executive levels within quality control:
- Director of Quality
- Head of Compliance
- Vice President of Quality
Quality Control Salaries
The average pay for quality control professionals differs by industry, experience, and position. Pay increases as you gain more experience and move into management positions. As of May 2023, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reports average salaries as:
- Professional, scientific and technical services: $48,680
- Manufacturing: $46,390
- Wholesale trade: $43,880
- Administrative and support services: $35,940

What Does Quality Control Mean?
Quality control means how a company measures product quality and improves it if need be. Quality control can be done in many ways, from testing products, reviewing manufacturing processes, and creating benchmarks. This is all done to monitor significant variations in a product.
What Are the 4 Types of Quality Control?
There are several methods of quality control. These include an x-bar chart, Six Sigma, 100% inspection mode, and the Taguchi Method.
Why Is Quality Control Important?
Quality control ensures that defective goods do not go out to the public. Companies that have quality control methods in place often have employees who pay close attention to their work.
In food and drug manufacturing, quality control prevents products that make customers sick, and in manufacturing, quality control can ensure that accidents don't happen when people use a product.
What Are 3 Examples of Quality Control?
Three examples of quality control could be in the food industry; overseeing the ingredient specifications, reviewing supplier lists, and ensuring the facility where the food product is made is sanitary.
Having quality control in place within a business helps ensure product quality and the overall success of a business. The quality control environment influences employees' attitudes about the workplace and creates a sense of ownership of the products and company.
Quality control can be done in various ways, from training personnel to creating data-driven tools to test products and set standards. Quality control methods help create a safe work environment and products that are safe to use and meet customers' needs. Additionally, it is a rewarding career for someone who enjoys investigating issues and improving outcomes.
American Society for Quality. " Quality Assurance & Quality Control ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " How to Become a Quality Control Inspector ."
The Council for Six Sigma Certification (S.S.C.). " Six Sigma Certifications ."
American Society for Quality. " Quality Inspector Certification CQI ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Quality Control Inspectors | Pay ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/young-woman--in-factory--inspecting-conveyor-belt-961181850-d82276e0629a404e85fd02777333b7ef.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Quality Control Essays
Project selection: dmha, quality training plan, starbucks coffee’s operations management practices, company’s performance metrics, healthcare ethics committee project-inadequate staffing, a comparative analysis of baldrige’s core values and deming’s principles, apple customer focus practices, tesla technical challenges, popular essay topics.
- American Dream
- Artificial Intelligence
- Black Lives Matter
- Bullying Essay
- Career Goals Essay
- Causes of the Civil War
- Child Abusing
- Civil Rights Movement
- Community Service
- Cultural Identity
- Cyber Bullying
- Death Penalty
- Depression Essay
- Domestic Violence
- Freedom of Speech
- Global Warming
- Gun Control
- Human Trafficking
- I Believe Essay
- Immigration
- Importance of Education
- Israel and Palestine Conflict
- Leadership Essay
- Legalizing Marijuanas
- Mental Health
- National Honor Society
- Police Brutality
- Pollution Essay
- Racism Essay
- Romeo and Juliet
- Same Sex Marriages
- Social Media
- The Great Gatsby
- The Yellow Wallpaper
- Time Management
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Violent Video Games
- What Makes You Unique
- Why I Want to Be a Nurse
- Send us an e-mail
Table of Contents
What is quality control (qc), key components of quality control, types of quality control, why is quality control important what are the benefits, quality control roles and responsibilities, quality control vs. quality assurance, quality control careers, what does quality control mean, what are 3 examples of quality control, train to assess quality with lean today.

In today’s world, it’s not uncommon that we take the reliability and quality of products and services for granted. At the start of the 20th century, however, quality control in manufacturing was not exactly a reliable process.
Now, decades after early pioneers created business problem-solving processes and analysis frameworks to determine and control consistency and value, it’s possible more than ever for a business to implement and scale best practices.
Quality does not have a singular definition. Despite the relative meaning of “value,” quality control is the process by which products/services are tested and measured to ensure they meet a standard. Through this process, a business can evaluate, maintain, and improve product quality. The primary objective of Quality Control is to identify and correct any deviations from the established quality standards. This process involves monitoring and inspecting products or services at various stages of production or delivery to ensure that they meet the desired level of quality. QC is also concerned with preventing defects or errors from occurring in the first place by implementing measures to control and improve the production or service delivery processes.
Ultimately, there are two crucial goals of quality control: (1) to ensure that products are as uniform as possible and (2), to minimize errors and inconsistencies within them.
Key components of Quality Control may include:
Inspection: Regularly examining products, materials, or services to identify defects, non-compliance, or deviations from quality standards.
Testing: Conducting various tests and measurements to assess the performance, functionality, or characteristics of products or services.
Statistical Process Control (SPC): Employing statistical techniques to monitor and control the production processes, ensuring that they remain within acceptable quality limits.
Documentation and Records: Keeping detailed records of inspections, tests, and corrective actions taken to maintain traceability and accountability.
Corrective Action: Implementing appropriate measures to address any identified quality issues and prevent their recurrence.
Training and Education: Providing employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to maintain quality standards effectively.
Continuous Improvement: Constantly analyzing data and feedback to identify areas for improvement and enhancing the overall quality management system.
Quality Control is closely related to another quality management concept called Quality Assurance (QA). While QC focuses on detecting and correcting defects, QA concentrates on preventing them from occurring in the first place by setting up robust processes and procedures.
Together, QC and QA form the backbone of an organization's quality management system, helping to ensure that products and services consistently meet or exceed customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Quality Control Process
Normally, quality testing is part of every stage of a manufacturing or business process. Employees frequently begin testing using samples collected from the production line, finished products, and raw materials. Testing during various production phases can help identify the cause of a production problem and the necessary corrective actions to prevent it from happening again.
Customer service reviews, questionnaires, surveys, inspections, and audits are a few examples of quality testing procedures that can be used in non-manufacturing businesses. A company can use any procedure or technique to ensure that the final product or service is safe, compliant, and meets consumer demands.
QC Is Different by Industry
Quality Control (QC) is an indispensable aspect of various industries, ensuring that products and services adhere to predefined standards. In the manufacturing sector, QC involves rigorous inspection and testing of raw materials, intermediate components, and final products to maintain consistent quality and minimize defects. In the food industry, QC guarantees the safety and integrity of consumables through thorough testing for contaminants and adherence to health regulations. In the pharmaceutical sector, QC plays a critical role in verifying the potency and purity of drugs, ensuring they are safe for consumption. Additionally, in the software industry, QC involves extensive testing of applications and programs to identify bugs and errors before release, guaranteeing a smooth user experience. Across all industries, QC is a fundamental process that enhances customer satisfaction, boosts efficiency, and fosters a reputation for reliability.
Just as quality is a relative word with many interpretations, quality control itself doesn’t have a uniform, universal process. Some methods depend on the industry. Take food and drug products, for instance, where errors can put people at risk and create significant liability. These industries may rely more heavily on scientific measures, whereas others (such as education or coaching) may require a more holistic, qualitative method.
At its core, quality control requires attention to detail and research methodology.
So, what is quality control? There are a wide range of quality control methods , including:
Control Charts:
A graph or chart is used to study how processes are changing over time. Using statistics, the business and manufacturing processes are analyzed for being “in control.”
Process Control:
Processes are monitored and adjusted to ensure quality and improve performance. This is typically a technical process using feedback loops, industrial-level controls, and chemical processes to achieve consistency.
Acceptance Sampling:
A statistical measure is used to determine if a batch or sample of products meets the overall manufacturing standard.
Process Protocol:
A mapping methodology that improves the design and implementation processes by creating evaluative indicators for each step.
There are other quality control factors to consider when selecting a method in addition to types of processes.
Some companies establish internal quality control divisions when defining what is quality control. They do this to monitor products and services, while others rely on external bodies to track products and performance. These controls may be largely dependent on the industry of the business. Due to the strict nature of food inspections, for example, it may be in a company’s best interest to sample products internally and verify these results in a third-party lab.
Become a Quality Management Professional
- 10% Growth In Jobs Of Quality Managers Profiles By 2025
- 11% Revenue Growth For Organisations Improving Quality
Certified Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
- 4 hands-on projects to perfect the skills learnt
- 4 simulation test papers for self-assessment
Lean Six Sigma Expert
- IASSC® Lean Six Sigma Green Belt and Black Belt certification
- 13 Projects, 12 Simulation exams, 18 Case Studies & 114 PDUs
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Xueting Liu
Mechanical engineer student at sargents pty. ltd. ,.
A great training and proper exercise with step-by-step guide! I'll give a rating of 10 out of 10 for this training.
Abdus Salam
Completing Simplilearn's Lean Six Sigma Expert Master’s Program empowered me to excel in new projects, enhancing my performance significantly. Consequently, my research position's average pay rate surged by 21%.
Quality Control (QC) is essential for various reasons, and its importance lies in the numerous benefits it brings to both businesses and consumers. Here are some key reasons why QC is crucial:
Customer Satisfaction: QC ensures that products and services meet or exceed customer expectations, leading to higher satisfaction levels and increased customer loyalty.
Defect Prevention: By identifying and correcting issues early in the production or service delivery process, QC helps prevent defects, reducing the likelihood of expensive recalls or rework.
Cost Reduction: Implementing QC measures can lead to reduced waste, lower production costs, and improved operational efficiency, contributing to overall cost savings.
Compliance and Regulations: QC ensures that products and services adhere to industry standards and regulatory requirements, avoiding legal issues and penalties.
Brand Reputation: Consistent high-quality products or services build a positive brand image, enhancing the company's reputation and competitiveness in the market.
Increased Efficiency: QC optimizes processes and identifies areas for improvement, leading to increased productivity and streamlined operations.
Risk Mitigation: Through rigorous testing and inspections, QC helps identify potential risks and hazards, enabling businesses to address them proactively.
Continuous Improvement: QC encourages a culture of continuous improvement, where organizations strive to enhance their products, services, and processes constantly.
International Competitiveness: High-quality products can open doors to global markets, increasing a company's competitiveness on an international scale.
Customer Retention and Loyalty: Satisfied customers are more likely to remain loyal and recommend the brand to others, contributing to long-term business success.
Overall, Quality Control is crucial for maintaining high standards, minimizing risks, and fostering a competitive advantage in today's dynamic and demanding business environment. It serves as the foundation for delivering superior products and services while ensuring customer satisfaction and loyalty.
When answering what is quality control, it is critical to understand that it consists of multifaceted responsibilities and roles. Moreover, it shouldn’t be confused with quality assurance. Whereas quality assurance looks at the processes used to prevent defects, quality control is focused specifically on the measurement and analysis processes involved with determining product quality.
Quality control uses specific research tools to accomplish fact-finding processes and conduct analyses. A quality control professional is tasked with analyzing these measurements against some sort of standard determined by the quality management department, company policies, and industries or regulatory bodies. Based on this evidence-gathering, quality control will recommend changes.
We can see from this roadmap, too, how quality assurance and quality control differ. Quality assurance looks at the holistic picture to prevent a product from becoming defective. Quality control, on the other hand, later determines if a product is, in fact, defective or not. Both roles fit under the broad umbrella of quality management.
Thus, an individual in quality control is tasked with communicating results to stakeholders and significant parties. A good quality control specialist will be able to disseminate scientific and research-based thinking to a business community and assist with the problem-solving process. These specialists are a key component of a product’s design process, as they determine whether a company’s creation is truly acceptable for the market.
Even though the terms quality control and quality assurance are sometimes used interchangeably, they have some key differences. Quality criteria, such as ensuring an item complies with specifications, are the main emphasis of quality control. Quality assurance is the sum of all processes and actions necessary to demonstrate that the requirements for quality are satisfied.
Quality control can be a fulfilling job if you enjoy dealing with people, talking, presenting results, and trying to make things better and safer. Depending on the sector, you may need the following qualifications to work as a quality control inspector:
- Entry-level positions require a high school diploma.
- Depending on the business, a bachelor's degree
- A background in the industry
- Certain businesses and sectors require licenses and certifications.
Additional characteristics required by quality control specialists include:
- Observation of details
- Talents in math and mechanics
- Physical prowess and power
- Technical expertise
- Pressured performance
Career Path
There may be discrepancies because the path to quality assurance and control job varies by industry. However, you'll typically require a number of years of professional expertise in your field. After completing the necessary educational qualifications and gaining the necessary work experience, you are often hired as a quality assurance or control associate.
As you gain job experience, you can advance to the position of senior specialist and start leading groups of quality control specialists.
Your employer may require you to take professional development classes or obtain certifications like Six Sigma . A professional designation like Certified Quality Inspector may also be required.
Quality Control Salaries
Depending on the role, expertise, and industry, quality control specialists make a variety of salaries. As you get more expertise and advance into management positions, your pay rises. The average wage, as reported by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, is:
- Services rendered by experts in science and technology: $46,280
- Production: $40,020
- Trade in bulk: $37,800
- $30,070 for office supplies and support services
Quality control refers to a company's methods for assessing product quality and, if necessary, improving it. There are various ways to perform quality control, including benchmarking, examining manufacturing procedures, and testing products. All of this is done to keep track of significant product differences.
Three examples of quality control in the food sector are monitoring ingredient standards, verifying supplier lists, and making sure the manufacturing facility is hygienic.
Learn how to define what is quality control with Simplilearn’s Post Graduate Program in Lean Six Sigma , offered in partnership with the University of Massachusetts Amherst. This Lean Six Sigma green belt certification program will help you gain key skills to lead tranformational projects by improving overall quality and delivering the best results.
With the Six Sigma Black Belt certification , you'll be equipped to mentor Green Belts, guide projects, and drive substantial ROI for your organization. Elevate your career with this program's in-depth curriculum, designed to mold you into a proficient Six Sigma Black Belt capable of orchestrating impactful change and delivering excellence.
This course focuses on two important management methodologies — Lean practices and Six Sigma — that will enable you to accelerate business improvement.
1. What is Quality Control (QC)?
Quality control is the process by which services/products are measured and tested to ensure they are as uniform as possible and meet a standard. It helps businesses minimize inconsistencies and improve product quality.
2. What are the four types of Quality Control?
The four types of quality control are process control, control charts, acceptance sampling, and product quality control. While a control chart helps study changing processes over time, process control and product quality control help monitor and adjust products as per the standards. Acceptance sampling is a unique type that involves a statistical measure to determine whether a batch or sample of products satisfies the standards.
3. Why is Quality Control important?
Quality control is important to safeguard the company’s reputation, prevent products from being unreliable, and increase trust on the side of consumers. It ensures that the company looks at evidence-based data and research rather than anecdotal observations to ensure that the services/products live up to the standards. It reduces cost and maximizes profit, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
4. What are three examples of Quality Control?
Some examples of quality control are: a high-speed car manufacturer runs thorough tests for every component, including manual and automated verifications; websites study the average response time per page for customer interactions and generate tickets when the service gets unacceptably slow; retail store owners employ secret shoppers to test the customer service of their stores.
5. What are the four steps of Quality Control?
The first step for quality control is to set your quality standards and decide which ones to focus on. Secondly, you must establish operational processes to deliver optimal quality and implement them. The third step is to review your results and identify gaps. Lastly, get feedback and make improvisations.
6. What are quality control techniques?
Inspection and Statistical quality control (SQC) are the two major techniques of Quality Control. Inspection checks the performance of items as per the pre-decided specifications. It involves periodic checking before, during and on completion of the process. It can be categorized into two types: Centralized and Floor Inspection. Statistical Quality Control relies on laws of probability. It controls the production quality within tolerance limits via sample procedure.
7. What is the difference QA and QC?
Quality Assurance (QA) focuses on preventing defects and maintaining the overall quality management system through process implementation and improvement. It ensures that proper processes are in place to avoid issues. On the other hand, Quality Control (QC) involves detecting and correcting defects through inspections and testing. QC ensures that products or services meet specific quality standards. While QA is proactive, emphasizing prevention, QC is reactive, emphasizing identification and correction of issues after they occur.
Our Quality Management Courses Duration And Fees
Explore our top Quality Management Courses and take the first step towards career success
| Program Name | Duration | Fees |
|---|---|---|
| Cohort Starts: | 12 weeks | € 2,250 |
| 10 weeks | € 1,249 |
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Quality Management
Lean Management
Learn from Industry Experts with free Masterclasses
Digital marketing.
The Top 10 AI Tools You Need to Master Marketing in 2024
Career Trends: AI-Proof Your Digital Marketing Career: Future-Ready Roles You Can Count On
SEO vs. PPC: Which Digital Marketing Career Path Fits You Best in 2024?
Recommended Reads
Free eBook: Quality Management Professionals Salary Report
Quality Control Manager Job Description
The Ultimate Guide to Understand Everything on Control Statements in C
Free eBook: Top 25 Interview Questions and Answers: Quality Management
Project Quality Management: Perform Quality Assurance Vs Perform Quality Control
What is Version Control and What Are Its Benefits?
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
4.3 – Achieving Quality Production
Quality means to produce a good or service which meets customer expectations. The products should be free of faults or defects. Quality is important because it:
- establishes a brand image
- builds brand loyalty
- maintains good reputation
- increase sales
- attract new customers
If there is no quality, the firm will
- lose customers to other brands
- have to replace faulty products and repeat poor service, increasing costs
- bad reputation leading to low sales and profits
There are three methods a business can implement to achieve quality: quality control, quality assurance and total quality management.
Quality Control
Quality control is the checking for quality at the end of the production process , whether a good or a service. Advantages:
- Eliminates the fault or defect before the customer receives it, so better customer satisfaction
- Not much training required for conducting this quality check
Disadvantages:
- Still expensive to hire employees to check for quality
- Quality control may find faults and errors but doesn’t find out why the fault has occurred , so the it’s difficult to solve the problem
- if product has to be replaced and reworked , then it is very expensive for the firm
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is the checking for quality throughout the production process of a good or service.
Advantages:
- Since each stage of production is checked for quality, f aults and errors can be easily identified and solved
- Products don’t have to be scrapped or reworked as often, so less expensive than quality control
- Expensive to carry out since quality checks have to be carried throughout the entire process, which will require manpower and appropriate technology at every stage.
- How well will employees follow quality standards? The firm will have to ensure that every employee follows quality standards consistently and prudently, and knows how to address quality issues.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management or TQM is the continuous improvement of products and production processes by focusing on quality at each stage of production . There is great emphasis on ensuring that customers are satisfied. In TQM, customers just aren’t the consumers of the final product. It is every worker at each stage of production. Workers at one stage have to ensure the quality standards are met for the product in production at their stage before they are passed onto the next stage and so on. Thus, quality is maintained throughout production and products are error-free.
TQM also involves quality circles and like Kaizen, workers come together and discuss issues and solutions, to reduce waste ensure zero defects.
- quality is built into every part of the production process and becomes central to the workers principles
- eliminates all faults before the product gets to the final customer
- no customer complaints and so improved brand image
- products don’t have to be scrapped or reworked , so lesser costs
- waste is removed and efficiency is improved
- Expensive to train employees all employees
- Relies on all employees following TQM – how well are they motivated to follow the procedures?
How can customers be assured of the quality of a product or service?
They can look for a quality mark on the product like ISO (International Organization for Standardization). The business with these quality marks would have followed certain quality procedures to keep the quality mark. For services, a good reputation and positive customer reviews are good indicators of the service’s quality.
Notes submitted by Lintha
Click here to go to the next topic
Click here to go back to the previous topic
Click here to go back to the Business Studies menu
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
2 thoughts on “ 4.3 – Achieving Quality Production ”
Can please include some detailed explanation on disadvatnages of quility assurance.
Also this site is very useful to revise for revision. So im really thankful to the hard working team behind the site.
Done. I hope it will suffice.
What Do You Think? Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- Manage subscriptions
- Call to +1 844 889-9952
Quality Control Root Cause Analysis
| 📄 Words: | 1108 |
|---|---|
| 📝 Subject: | |
| 📑 Pages: | 3 |
| ✍️ Type: | Essay |
Laboratory report problems
Clearance problems, poor transportation and distribution.
This is an in-depth investigation into the identified problems and their main causes. The main problems that face this company are customer complaints, nonconformance, unfulfilled requirements, and undesirable conditions. Basically, root cause analysis is a method that is used to undertake corrective actions on issues affecting this organization; indeed, it is a component of the quality management system. In a situation where the company is facing problems with the shipment, there is a great need to perform problem-solving at all times.
Any inconsistencies in any department may be costly to the business, thus there is a need to address nonconformance. Moreover, in RCA, the executive tries to uncover the main cause of the problem and what can be done to avoid reoccurrence. Among the many problems that Denver Facility is facing are; a problem with a delay of laboratory reports, a problem with the clearance of trucks on the front gate, and transportation and distribution difficulties. This research paper is aimed at analyzing the root cause of each of the above main problems.
In Denver Facility, the automotive customers have been insisting that the laboratory testing report department is very slow at releasing the reports. Ideally, it is vital to avoid some questions like ‘who made a mistake?’ as this frustrates those involved. The investigative process should dispel anxieties concerning the assigning of blame that frequently intimidates and frustrates those involved.
Your analysis should redirect participants away from the convenient human error cliché towards more probing questions concerning the obstacles that prevented an individual or group from successfully completing a task. A thorough RCA should establish why an individual failed to perform his or her job in accordance with defined procedures, for instance, not adhering to the health and safety measures in the plant. As an analyst, you need to understand that initiating a complete corrective action is not a momentary human lapse, an isolated incident or an inconsequential matter. Thus, it is significant to make inquiries into what caused the individual to make a mistake.
A RCA is a prerequisite to any viable corrective plan, thus it is important to ascertain the actual cause of a problem before developing a plan to address it. The RCA process helps an analyst to specifically connect elements of the corrective action plan to the identified causes. For instance, if the analysis comes up with the conclusion that one of the factors that contributed to the problem was the lack of a controlled distribution list for engineering change notices, then one will know that a part of the corrective action plan must address documentation and practices relative to this process.
For processes that do not match with the identified cause and a corresponding action to correct it, there are high chances of overlooking the less contributing factors. In this case, the input to the corrective action process becomes the output of the RCA process, while the output of the corrective action process ought to be the fulfillment of the defined requirement, which is the elimination of the cause that was identified as the input.
Analyzing the distribution problem and the quality of the products is vital and focuses on effective management in an organization. Effective supply chains should be developed that have clear programs on how goods are going to be transported and methods of clearing the shipment. This will also entail good check-up methods so that trucks do not have to wait for so long before being cleared. The result of this will be an improvement in the movement of people as well as vehicles in the company. Therefore, the problem of vehicles blocking the streets in front of the plant awaiting clearance to enter the plant will be resolved.
Effective supply chain management is a significant factor that lowers the cost of inventory, transportation, packaging and warehousing. The distribution entails both the physical movement of products and the establishment of relationships that guide the movement of products from producer to user. If there is ineffective distribution, this indicates that the individuals who are concerned are not working effectively, thus the analyst should discus with them to develop the cause of the problem and come up with the best way to end the mishap. This implies that the departments that deal with transportation, material handling, storage, inventory as well as delivery ought to be thoroughly scrutinized so as to iron out the challenging problems (Moore, 2008, p. 392).
About 20% of the trucks arriving at the company do not have the advance notice or even order on file; they are only accompanied by purchase orders. As an analyst of Product Quality and Distribution Problems at the Denver facility, you need first to understand the root cause of the shipment and distribution problems in the plant and the address the existing nonconformance, particularly within the context of the corrective action process. This will help to investigate the source of potential problems to avoid their occurrences; thus you deal with distribution problem causes and their effects. For instance, it has been noted that at Denver, the transportation operation group – the dispatching and scheduling team – in many times do not know when the trucks will arrive at the front gate.
The analyst ought to involve the people responsible in the department and positively influence their working system. Normally, the reoccurrence of nonconformance is a result of failure to research their fundamental causes. Therefore, as an analyst with the task of performing corrective action, you note that people frequently identify the root cause of a problem by simply restarting it, a task that is normally done by offering corrective action request (CAR). Once you take your time to generate a request for corrective action, you need to understand that the problem is either a critical issue that requires further investigation or may be an isolated anomaly and is therefore probably indicative of a systemic problem (Robitaille, 2004, p. 3).
For an executive or the analyst to come up with the solution to the issues that are affecting distribution, he should establish the right internal team that comprises representation from the affected areas – human resources, financial, production, as well as distribution. It is also vital to establish clear objectives by identifying the needs so that he may know what he is trying to accomplish. Having a clear objective, like redesigning your critical business systems or implementing technology to double production, will serve as a benchmark for evaluating the success or failure of implementation. This will help the organization to overcome the problems of clearance, laboratory and shipment (Radhakrishnan and Balasubramanian, 2008, p. 42).
Moore, C. W. (2008). Managing small business : an entrepreneurial emphasis. London, Cengage Learning EMEA. Web.
Radhakrishnan, R. and Balasubramanian, S. (2008). Business Process Reengineering : Text and Cases . New Delhi, PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd. Web.
Robitaille, D. (2004). Root Cause Analysis: Basic Tools and Techniques . CA, Paton Professional. Web.
Cite this paper
Select style
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
BusinessEssay. (2022, December 8). Quality Control Root Cause Analysis. https://business-essay.com/quality-control-root-cause-analysis/
"Quality Control Root Cause Analysis." BusinessEssay , 8 Dec. 2022, business-essay.com/quality-control-root-cause-analysis/.
BusinessEssay . (2022) 'Quality Control Root Cause Analysis'. 8 December.
BusinessEssay . 2022. "Quality Control Root Cause Analysis." December 8, 2022. https://business-essay.com/quality-control-root-cause-analysis/.
1. BusinessEssay . "Quality Control Root Cause Analysis." December 8, 2022. https://business-essay.com/quality-control-root-cause-analysis/.
Bibliography
BusinessEssay . "Quality Control Root Cause Analysis." December 8, 2022. https://business-essay.com/quality-control-root-cause-analysis/.
- Influences upon Purchasing Shipping Container Houses
- Wal-Mart: The Inventory Management
- Change as an Important Aspect in Any Kind of Organization
- Micro Learning: Is It the Future of Workplace Training?
- Consultative Change Recommendation
- Leadership in an Organization’s Transformational Change
- Publix: Strategy Formulation
- The Management Science Approach
- Integrated Supply Chain in Business
- A Case Management Model Use to Work With Ryan
Quality Assurance and Quality Control – Is There a Difference? Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
History of qc and qa, aviation perspectives on qa and qc, qa, qc, and inspection, qa, qc, and auditing functions, qa, qc, safety, and compliance.
Often, the terms QC and QA are used interchangeably in the wrong manner. QA is a term that has dominated the corporate industry and world for many years. It refers to the standard that something holds as compared to other things within the same scope (Baker, 2018). It may also refer to the degree or quality of excellence that may be needed to realize efficiency of a product. The critical focus of QA is on aspects such as processes, techniques, approaches, and planning within a specific field. On the other hand, QC may be a portion of the overall quality management scheme that emphasizes or realizes the quality requirements. While QA is based on how a technique is performed, QC focuses on the inspection attribute of quality management.
QC should not be regarded as the real alternative in typical quality management processes. However, it may be adopted to test the working efficiency of the adopted QA process. In the case of failure detection within the adopted QA process during the QC inspection test, it is clear that there was an error in the QA process being used (Baker, 2018). Therefore, there is usually a need for the QA processes to be reviewed to establish the cause of poor functioning. This paper aims to analyze the various vital roles that QA and QC play in the maintenance operation, focusing on aspects such as inspection, auditing, safety, and compliance.
Quality has been a focus in many industries from the early ages till now. When Hammurabi controlled Babylonia in ancient times, there were allusions to QC in the code he issued (Baker, 2018). The QC used to be as easy as drawing a picture of the intended object. Tolerance limitations were created around 1840 when manufacturers realized it was impractical and expensive to build items precisely like their portrayal; hence, a design would work provided its pieces were measured to be within limits (Z et al., 2019). As a result, tools like plug and ring gauges were used to quantify quality accurately.
Since the dawn of human civilization, people have sought to improve the quality of their products and services. From the standards for ancient Greek structures to the Egyptian pyramids, it can be traced back in time. The ideas of current QA, based on medieval guilds’ efforts to improve product quality, initially emerged in the late Middle Ages (Baker, 2018). In part, guilds were founded to ensure that the quality of specific crafts, such as blacksmithing, met the standards set by kings. Other guild leaders would check all goods to ensure the quality was upheld by the guild’s participants (Zio et al., 2019). It was also necessary to produce exceptional quality work before being considered an expert in a specific field. After the late 19th century, guilds mostly disappeared due to the Industrial Revolution, at least in part.
For different firms within the aviation industry, the idea of QC may appear to be irrelevant due to the lack of specific tangible products to be controlled or inspected. Similarly, QA in the aviation industry is regarded as an effective system that helps monitor and inspect procedures, programs, and aviation equipment to ensure state civil and ICAO aviation regulatory requirements are adhered to (Nsien, 2020). Both QA and QC provide essential background for inspecting the various aviation equipment, programs, and procedures to ensure that all maintenance in the aviation sector is undertaken correctly based on the manufacturer’s needs.
People may travel for both work and pleasure thanks to the convenience of commercial aviation. Aviation QA and QC are critical to fostering customer confidence and delight. Before delivery, it guarantees that the items or services meet the customer’s expectations (Zio et al., 2019). Flight Operations, Aircraft Maintenance (checks, repairs, and inspections), and employee training are all under the watchful eye of the QA department in the airline sector.
To determine whether or not a product or service meets specified standards, inspectors measure, examine, and test the product or service in question. Products, processes, and many other results can be reviewed to ensure that the product or service being produced or given is proper and satisfies the requirements (Nsien, 2020). QA plays a vital role in the inspection of the airlines in the aviation industry. Usually, aviation firms deploy a QA Inspector tasked with inspecting aircraft, thus ensuring that there is the maintenance of procedures and aiding in the air navigation processes within the aviation sector (Baker, 2018). Additionally, QA is significant in maintaining traffic controls and communication tools to realize conformance with the regulated rules by the federal safety regulatory body.
The aviation sector requires a QCl strategy that includes external and internal inspections. QC in aviation primarily focuses on monitoring the organization’s operation while testing the resulting products and equipment (Nsien, 2020). This aims at realizing compliance with the needs of the customers. Often, aviation industries deploy an Aircraft QC inspector who is tasked with inspecting the different systems and components of the aircraft (Zio et al., 2019). Suppose they need to find out what has to be repaired. In that case, they may conduct functional inspections, verify that all repair work is done under safety regulations, and calibrate their inspection instruments to the necessary standards.
It is part of the QA process to conduct audits. It is critical to assure quality since it is used to compare factual circumstances with requirements and to communicate those results to management within the aviation industry. Aviation organizations are now guided and regulated by formal management systems (Nsien, 2020). For example, quality management systems (QMSs) can also include management or environmental systems (Zio et al., 2019). An ACA Quality Audit is a planned and formal assessment to determine whether or not the aviation processes, policies, procedures, and contractual obligations are in accordance with ACA’s quality standards. Internal ACA operations, as well as contract service provider activities, are the focus of quality audits.
The QA role includes auditing. In order to assure quality in the aviation sector, it is necessary to compare factual circumstances to requirements and report those results to management. The notion of QA auditing is frequently utilized in internal, external, and customer audits to measure the level of QA in the aviation industry. Effective QA auditing relies heavily on ensuring procedures are in line with established standards. QA is vital in the aviation sector as it helps to realize compliance risk management and provides consistent advancement for the adopted auditing plan.
QA covers all aspects of aviation QC, from equipment and systems inspection to process audits to guarantee compliance to all ICAO and state-level civil aviation regulation bodies’ standard criteria, thus ensuring safety. The Aerospace industry has always had to demonstrate a high degree of safety and quality to compete in today’s marketplace (Baker, 2018). Providing high-quality products is essential to consumer pleasure, and if quality falters, there might be profound implications. QA’s aviation safety services include research, education, and the design of aircraft and aviation infrastructure to reduce aviation accidents and mishaps.
On the other hand,QC, compliance, and safety are intertwined in the aviation sector. Aviation QA safety and compliance are critical to foster consumer confidence and delight. Pre-delivery checks verify that the items or services meet the customer’s expectations. The aerospace industry has always had to show that it complies with FAA and ACA regulations regarding safety and quality (Zio et al., 2019). Customer satisfaction is dependent on the timely delivery of high-quality items, and if quality falters, there can be profound implications.
In conclusion, the paper has analyzed the various vital roles that QA and QC play in the maintenance operation, focusing on aspects such as inspection, auditing, safety, and compliance. In a review, QA is necessary for aircraft inspection, thus ensuring that there is the maintenance of procedures and aiding in the air navigation processes. At the same time, QC helps in monitoring the operation within the organization while testing the physical conditions of the resulting products and equipment. Additionally, An ACA QA and QC Audit is a planned and formal assessment to determine whether or not the aviation processes, policies, procedures, and contractual obligations are in accordance with ACA’s quality standards. QA and QC procedures are also essential in maintaining safety and compliance of the aviation practices to the FAA and ACA policies.
Baker, B. (2018). Project quality management practice & theory. American Journal of Management , 18 (3), 10-17. Web.
Zio, E., Fan, M., Zeng, Z., & Kang, R (2019). Application of reliability technologies in civil aviation: Lessons learned and perspectives. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics , 32 (1), 143-158. Web.
Nsien, C. B. (2020). TQM and the Role of Customers’ Orientation in Organizational Performance. FULafia Journal of Social Sciences , 3 (4), 119-133. Web.
- The PwC India Project Management and Maturity Model
- Implications of Cultural Differences in International Projects
- Plan of Assessing Learner Performances
- DevOps Application: Advantages and Disadvantages
- Integrating CQI in the Health Care Organization
- Farcargo’s System Implementation Document
- A Web-Based Information Project Feasibility Analysis
- Project Management in Information Technology Sphere
- E-Cloth Online Store's Project Management
- A Food Truck Business: Project Summary
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, January 12). Quality Assurance and Quality Control – Is There a Difference? https://ivypanda.com/essays/quality-assurance-and-quality-control-is-there-a-difference/
"Quality Assurance and Quality Control – Is There a Difference?" IvyPanda , 12 Jan. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/quality-assurance-and-quality-control-is-there-a-difference/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Quality Assurance and Quality Control – Is There a Difference'. 12 January.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Quality Assurance and Quality Control – Is There a Difference?" January 12, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/quality-assurance-and-quality-control-is-there-a-difference/.
1. IvyPanda . "Quality Assurance and Quality Control – Is There a Difference?" January 12, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/quality-assurance-and-quality-control-is-there-a-difference/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Quality Assurance and Quality Control – Is There a Difference?" January 12, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/quality-assurance-and-quality-control-is-there-a-difference/.

Salesforce is closed for new business in your area.
Advertisement
Where Tim Walz Stands on the Issues
As governor of Minnesota, he has enacted policies to secure abortion protections, provide free meals for schoolchildren, allow recreational marijuana and set renewable energy goals.
- Share full article

By Maggie Astor
- Aug. 6, 2024
Gov. Tim Walz of Minnesota, the newly announced running mate to Vice President Kamala Harris, has worked with his state’s Democratic-controlled Legislature to enact an ambitious agenda of liberal policies: free college tuition for low-income students, free meals for schoolchildren, legal recreational marijuana and protections for transgender people.
“You don’t win elections to bank political capital,” Mr. Walz wrote last year about his approach to governing. “You win elections to burn political capital and improve lives.”
Republicans have slammed these policies as big-government liberalism and accused Mr. Walz of taking a hard left turn since he represented a politically divided district in Congress years ago.
Here is an overview of where Mr. Walz stands on some key issues.
Mr. Walz signed a bill last year that guaranteed Minnesotans a “fundamental right to make autonomous decisions” about reproductive health care on issues such as abortion, contraception and fertility treatments.
Abortion was already protected by a Minnesota Supreme Court decision, but the new law guarded against a future court reversing that precedent as the U.S. Supreme Court did with Roe v. Wade, and Mr. Walz said this year that he was also open to an amendment to the state’s Constitution that would codify abortion rights.
Another bill he signed legally shields patients, and their medical providers, if they receive an abortion in Minnesota after traveling from a state where abortion is banned.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
To help you get started, here are 113 quality control essay topic ideas and examples: The importance of quality control in manufacturing. How quality control can improve customer satisfaction. The role of quality control in ensuring product safety. The impact of quality control on a company's reputation.
Quality control is commonly utilized to promote quality of business products. Golden Age Hospital: Quality Control and Accreditation. GAH's core competencies include professionalism, evidence-based practices, effective communication, patient safety, patient-centered approaches and quality improvement.
To help you get started, here are 118 total quality management essay topic ideas and examples that you can use as inspiration: The impact of TQM on organizational performance. Implementing TQM in a small business. TQM tools and techniques: a case study. The role of leadership in TQM implementation.
Essay # 1. Meaning and Definitions of Quality Control: Quality control in its simplest term, is the control of quality during manufacturing. Both quality control and inspection are used to assure quality. Inspection is a determining function which determines raw materials, supplies, parts or finished products etc. as acceptable or unacceptable.
The relationship between quality assurance and organizational resilience. The impact of quality assurance on employee engagement. In conclusion, quality assurance is a critical component of any organization, ensuring that products and services meet the highest standards of excellence. By exploring these 122 quality assurance essay topic ideas ...
Quality control essentially represents a means to develop a procedure for contemporary organizations to tackle the multifaceted challenges they come across in this era. Its basis is that, in the health/healthcare sector, quality improvement, in truth, deals with process management (Haughom, 2016). Use of Performance Improvement Tools.
Learn More. As a part of quality management, the feedback is taken and incorporated in the design of new products that are aimed at raising customer satisfaction. Quality management spans from creating a design and lifecycle plan for a product or service to its production and distribution. The activity involves identifying and measuring process ...
Quality control is a process through which a business seeks to ensure that product quality is maintained or improved and manufacturing errors are reduced or eliminated. Quality control requires ...
Quality Control Essays. Project Selection: DMHA. ... Introduction Given the dynamic nature of business, Sionyx appreciates the crucial function of quality training in securing a competitive advantage. ... an American scholar in management, and has been an effective quality control method since the 1930s (Smith, 2021). On the other hand, the ...
Total quality management (TQM) is defined as a strategic approach to quality which permeates the entire organization. TQM is a top-down management philosophy that focuses on the needs of the customer. It comprises a quality plan which offers a structured, disciplined approach to quality and incorporates a number of tools and techniques.
Quality control ensures that products meet predefined specifications and customer requirements. It helps: - Eliminate defects and non-conformance. - Enhance customer satisfaction by providing products that perform as expected. 2. Process Optimization: Quality control identifies inefficiencies and areas for improvement in production processes.
Quality Control (QC) is an indispensable aspect of various industries, ensuring that products and services adhere to predefined standards. In the manufacturing sector, QC involves rigorous inspection and testing of raw materials, intermediate components, and final products to maintain consistent quality and minimize defects.
Quality control paper Quality control is a critical concept in every industry and profession. The survival of your job and of your company depends on your ability to produce a quality product or service. For most people, quality is associated with the idea of a product or service that's well done, looks good, and does its job well.
Business essay sample: Cultural changes in Coca-Cola hinder the efforts to implement quality control. Hence, there is a need to set up controls that respect the cultural values of all people. Call to +1 844 889-9952
Learners must be able to: Define the following: Quality. Quality control. Quality assurance. managementQuality performance Quality management systemsExpl. n the advantages/benefits of a good quality management system.Explain/Discuss how the quality of performance can. ontribute to success and/or failure of each business f.
There are three methods a business can implement to achieve quality: quality control, quality assurance and total quality management. Quality Control. Quality control is the checking for quality at the end of the production process, whether a good or a service. Advantages:
Introduction. Statistical quality control (SQC) or statistical process control (SPC) refers to a group of analytical instruments and techniques used by process engineers to guarantee the quality of a process or product. Statistical quality control helps process managers to evaluate the quality of manufacturing course and solve emerging problems ...
Primary Quality Control Issues. It is possible to identify three central issues related to quality control during the production of Fallout 76: a lack of time in which to conduct the procedures, insufficient quality standards and lacking employee engagement. The game was announced in May 2018 and released in October 2018, and the variety of ...
Business essay sample: This is an in-depth investigation into the problems and their main causes in Denver Facility: customers complaints, nonconformance, unfulfilled requirements. undesirable conditions.
There are four steps in the control process according to R. Daft (1991) ,namely establish standards, measure actual performance, compare performance to standards and take corrective action. Firstly, establishing standards precisely provides a guide to workers and managers so that they can determine whether the product or service Is on target.
THE Forex Scalping Guide - PDF Room. Topic 9 Questions - no des. Business Development Schedule. Chapter 4 Outline - The Business Environment. 180530 CVP Summary OF Framework. This will help you study more about quality control. businebeimoaded from stanmorephysics.com march 2023 common test guideline grade 10 question business.
Quality Control and Business. Description of business The I-TEC Corporation is runned as a partnership of fifteen people. The numbers are important to guide the business to the right path of success. Ideas from each partner contribute to the growth of the business to new heights. The objective of the business is to provide low cost computers.
QA is a term that has dominated the corporate industry and world for many years. It refers to the standard that something holds as compared to other things within the same scope (Baker, 2018). It may also refer to the degree or quality of excellence that may be needed to realize efficiency of a product. The critical focus of QA is on aspects ...
In many ways, sales is a game of chance, and many people struggle understanding how to generate leads. Figuring out how to generate leads and handle lead management can be a tough task, but it doesn't have to be if you create your luck and follow proven best practices. In reality, there's more skill than luck in sales, especially when you follow proven lead generation strategies and ...
Officials had braced for more unrest on Wednesday, but the night's anti-immigration protests were smaller, with counterprotesters dominating the streets instead.
As governor of Minnesota, he has enacted policies to secure abortion protections, provide free meals for schoolchildren, allow recreational marijuana and set renewable energy goals.