- Accessories
- Facial Hair
Browse all Get Style
- Program Review
Browse all Get Strong
- Relationships
- Social Skills
Browse all Get Social
- Manly Know-How
- Outdoor/Survival
Browse all Get Skilled
in: Character , Featured , Knowledge of Men
Brett & Kate McKay • August 24, 2020 • Last updated: August 25, 2021

The 35 Greatest Speeches in History

These famous speeches lifted hearts in dark times, gave hope in despair, refined the characters of men, inspired brave feats, gave courage to the weary, honored the dead, and changed the course of history.
How did we compile this list?
Great oratory has three components: style, substance, and impact.
Style: A great speech must be masterfully constructed. The best orators are masters of both the written and spoken word, and use words to create texts that are beautiful to both hear and read.
Substance: A speech may be flowery and charismatically presented, and yet lack any true substance at all. Great oratory must center on a worthy theme; it must appeal to and inspire the audience’s finest values and ideals.
Impact: Great oratory always seeks to persuade the audience of some fact or idea. The very best speeches change hearts and minds and seem as revelatory several decades or centuries removed as when they were first given.
And now for the speeches.
Contents [ hide ]
- 1. Theodore Roosevelt, "Duties of American Citizenship"
- 2. Winston Churchill, "We Shall Fight on the Beaches"
- 3. Lou Gehrig, "Farewell to Baseball Address"
- 4. Demosthenes, "The Third Philippic"
- 5. Chief Joseph, "Surrender Speech"
- 6. John F. Kennedy, "Inauguration Address"
7. Ronald Reagan, "Address to the Nation on the Challenger"
8. "speech of alexander the great", 9. william wilberforce, "abolition speech", 10. theodore roosevelt, "the man with the muck-rake", 11. franklin delano roosevelt, "first inaugural address", 12. charles de gaulle, "the appeal of 18 june", 13. socrates, "apology", 14. george washington, "resignation speech", 15. mahatma gandhi, "quit india", 16. winston churchill, "their finest hour", 17. william faulkner, "nobel prize acceptance speech", 18. dwight d. eisenhower, "farewell address", 19. marcus tullius cicero, "the first oration against catiline", 20. ronald reagan, "remarks at the brandenburg gate", 21. pericles, "funeral oration", 22. general douglas macarthur, "farewell address to congress", 23. theodore roosevelt, "strength and decency", 24. abraham lincoln, "2nd inaugural address", 25. patrick henry, "give me liberty or give me death", 26. ronald reagan, "40th anniversary of d-day".
- 27. John F. Kennedy, "The Decision to Go to the Moon"
28. Frederick Douglass, "What to the Slave is the Fourth of July?"
29. general douglas macarthur, "duty, honor, country", 30. theodore roosevelt, "citizenship in a republic", 31. winston churchill, "blood, sweat, and tears", 32. franklin delano roosevelt, "pearl harbor address to the nation", 33. jesus christ, "the sermon on the mount", 34. martin luther king jr., "i have a dream", 35. abraham lincoln, "the gettysburg address", 1. theodore roosevelt, “duties of american citizenship”.
January 26, 1883; Buffalo , New York
Given while serving as a New York assemblyman, TR's address on the "Duties of American Citizenship" delved into both the theoretical reasons why every man should be involved in politics and the practical means of serving in that capacity. Roosevelt chided those who excused themselves from politics because they were too busy; it was every man's duty to devote some time to maintaining good government.
Worthy Excerpt:
Of course, in one sense, the first essential for a man's being a good citizen is his possession of the home virtues of which we think when we call a man by the emphatic adjective of manly. No man can be a good citizen who is not a good husband and a good father, who is not honest in his dealings with other men and women, faithful to his friends and fearless in the presence of his foes, who has not got a sound heart, a sound mind, and a sound body; exactly as no amount of attention to civil duties will save a nation if the domestic life is undermined, or there is lack of the rude military virtues which alone can assure a country's position in the world. In a free republic the ideal citizen must be one willing and able to take arms for the defense of the flag, exactly as the ideal citizen must be the father of many healthy children. A race must be strong and vigorous; it must be a race of good fighters and good breeders, else its wisdom will come to naught and its virtue be ineffective; and no sweetness and delicacy, no love for and appreciation of beauty in art or literature, no capacity for building up material prosperity can possibly atone for the lack of the great virile virtues. But this is aside from my subject, for what I wish to talk of is the attitude of the American citizen in civic life. It ought to be axiomatic in this country that every man must devote a reasonable share of his time to doing his duty in the Political life of the community. No man has a right to shirk his political duties under whatever plea of pleasure or business; and while such shirking may be pardoned in those of small cleans it is entirely unpardonable in those among whom it is most common--in the people whose circumstances give them freedom in the struggle for life. In so far as the community grows to think rightly, it will likewise grow to regard the young man of means who shirks his duty to the State in time of peace as being only one degree worse than the man who thus shirks it in time of war. A great many of our men in business, or of our young men who are bent on enjoying life (as they have a perfect right to do if only they do not sacrifice other things to enjoyment), rather plume themselves upon being good citizens if they even vote; yet voting is the very least of their duties, Nothing worth gaining is ever gained without effort. You can no more have freedom without striving and suffering for it than you can win success as a banker or a lawyer without labor and effort, without self-denial in youth and the display of a ready and alert intelligence in middle age. The people who say that they have not time to attend to politics are simply saying that they are unfit to live in a free community.
Read full text of speech here .
2. Winston Churchill, “We Shall Fight on the Beaches”
June 4, 1940 ; House of Commons, London

Winston Churchill, one of the greatest orators of the 20th century, was interestingly enough, like Demosthenes and other great orators before him, born with a speech impediment which he worked on until it no longer hindered him. One would never guess this from hearing Churchill's strong and reassuring voice, a voice that would buoy up Britain during some of her darkest hours.
During the Battle of France, Allied Forces became cut off from troops south of the German penetration and perilously trapped at the Dunkirk bridgehead. On May 26, a wholesale evacuation of these troops, dubbed "Operation Dynamo," began. The evacuation was an amazing effort-the RAF kept the Luftwaffe at bay while thousands of ships, from military destroyers to small fishing boats, were used to ferry 338,000 French and British troops to safety, far more than anyone had thought possible. On June 4, Churchill spoke before the House of Commons, giving a report which celebrated the "miraculous deliverance" at Dunkirk, while also seeking to temper a too rosy of view of what was on the whole a "colossal military disaster."
I have, myself, full confidence that if all do their duty, if nothing is neglected, and if the best arrangements are made, as they are being made, we shall prove ourselves once again able to defend our Island home, to ride out the storm of war, and to outlive the menace of tyranny, if necessary for years, if necessary alone. At any rate, that is what we are going to try to do. That is the resolve of His Majesty's Government-every man of them. That is the will of Parliament and the nation. The British Empire and the French Republic, linked together in their cause and in their need, will defend to the death their native soil, aiding each other like good comrades to the utmost of their strength. Even though large tracts of Europe and many old and famous States have fallen or may fall into the grip of the Gestapo and all the odious apparatus of Nazi rule, we shall not flag or fail. We shall go on to the end, we shall fight in France, we shall fight on the seas and oceans, we shall fight with growing confidence and growing strength in the air, we shall defend our Island, whatever the cost may be, we shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender, and even if, which I do not for a moment believe, this Island or a large part of it were subjugated and starving, then our Empire beyond the seas, armed and guarded by the British Fleet, would carry on the struggle, until, in God's good time, the New World, with all its power and might, steps forth to the rescue and the liberation of the old.
Check out my podcast with Churchill biographer Andrew Roberts .
3. Lou Gehrig, “Farewell to Baseball Address”
July 4, 1939; Yankee Stadium

It seemed as if the luminous career of Lou Gehrig would go on forever. The Yankee's first baseman and prodigious slugger was nicknamed the Iron Horse for his durability and commitment to the game. Sadly, his record for suiting up for 2,130 consecutive games came to an end when at age 36, Gehrig was stricken with the crippling disease that now bears his name. On July 4, 1939, the Yankees held a ceremony to honor their teammate and friend. They retired Gehrig's number, spoke of his greatness, and presented him with various gifts, plaques, and trophies. When Gehrig finally addressed the crowd, he did not use the opportunity to wallow in pity. Instead, he spoke of the things he was grateful for and what a lucky guy he was.
Fans, for the past two weeks you have been reading about a bad break I got. Yet today I consider myself the luckiest man on the face of the earth. I have been in ballparks for seventeen years and have never received anything but kindness and encouragement from you fans. Look at these grand men. Which of you wouldn't consider it the highlight of his career to associate with them for even one day? Sure, I'm lucky. Who wouldn't consider it an honor to have known Jacob Ruppert - also the builder of baseball's greatest empire, Ed Barrow - to have spent the next nine years with that wonderful little fellow Miller Huggins - then to have spent the next nine years with that outstanding leader, that smart student of psychology - the best manager in baseball today, Joe McCarthy! Sure, I'm lucky. When the New York Giants, a team you would give your right arm to beat, and vice versa, sends you a gift, that's something! When everybody down to the groundskeepers and those boys in white coats remember you with trophies, that's something. When you have a wonderful mother-in-law who takes sides with you in squabbles against her own daughter, that's something. When you have a father and mother who work all their lives so that you can have an education and build your body, it's a blessing! When you have a wife who has been a tower of strength and shown more courage than you dreamed existed, that's the finest I know. So I close in saying that I might have had a tough break - but I have an awful lot to live for!
4. Demosthenes, “The Third Philippic”
342 B.C.; Athens, Greece

Demosthenes, master statesman and orator, loved his city-state of Athens. He cherished its way of life and abundant freedoms. And he believed in standing strong against anyone who might attempt to infringe on these privileges. This passion, unfortunately, was seldom shared by his fellow Athenians. While Philip the II of Macedon made bolder and bolder incursions into the Greek peninsula, the Athenian people seemed stuck in an apathetic stupor. For years, Demosthenes employed his powerful oratorical skills in attempts to awaken his fellow citizens from sleep to the realization of the imminent danger Philip posed. When Philip advanced on Thrace, the Athenians called an assembly to debate whether or not to finally heed the great orator's advice. Demosthenes was sick of his brethren taking liberty and the Athenian way of life for granted and he boldly called upon them to rise up and take action. After his rousing speech, the assembly all cried out, "To arms! To arms!"
It is this fate, I solemnly assure you, that I dread for you, when the time comes that you make your reckoning, and realize that there is no longer anything that can be done. May you never find yourselves, men of Athens, in such a position! Yet in any case, it were better to die ten thousand deaths, than to do anything out of servility towards Philip [or to sacrifice any of those who speak for your good]. A noble recompense did the people in Oreus receive, for entrusting themselves to Philip's friends, and thrusting Euphraeus aside! And a noble recompense the democracy of Eretria, for driving away your envoys, and surrendering to Cleitarchus! They are slaves, scourged and butchered! A noble clemency did he show to the Olynthians, who elected Lasthenes to command the cavalry, and banished Apollonides! It is folly, and it is cowardice, to cherish hopes like these, to give way to evil counsels, to refuse to do anything that you should do, to listen to the advocates of the enemy's cause, and to fancy that you dwell in so great a city that, whatever happens, you will not suffer any harm.
5. Chief Joseph, “Surrender Speech”
October 5, 1877; Montana Territory
In 1877, the military announced that the Chief Joseph and his tribe of Nez Perce had to move onto a reservation in Idaho or face retribution. Desiring to avoid violence, Chief Joseph advocated peace and cooperation. But fellow tribesmen dissented and killed four white men. Knowing a swift backlash was coming, Joseph and his people began to make their way to Canada, hoping to find amnesty there. The tribe traveled 1700 miles, fighting the pursuing US army along the way. In dire conditions, and after a five day battle, Chief Joseph surrendered to General Nelson A. Miles on Oct. 5, 1877 in the Bear Paw Mountains of Montana Territory, a mere 40 miles from the Canadian border. The Chief knew he was the last of a dying breed, and the moment of surrender was heartbreaking.
Tell General Howard I know his heart. What he told me before, I have it in my heart. I am tired of fighting. Our Chiefs are killed; Looking Glass is dead, Ta Hool Hool Shute is dead. The old men are all dead. It is the young men who say yes or no. He who led on the young men is dead. It is cold, and we have no blankets; the little children are freezing to death. My people, some of them, have run away to the hills, and have no blankets, no food. No one knows where they are - perhaps freezing to death. I want to have time to look for my children, and see how many of them I can find. Maybe I shall find them among the dead. Hear me, my Chiefs! I am tired; my heart is sick and sad. From where the sun now stands I will fight no more forever.
6. John F. Kennedy, “Inauguration Address”
January 20, 1961; Washington, D.C.

Young, handsome, with a glamorous family in tow, John F. Kennedy embodied the fresh optimism that had marked the post-war decade. On January 20, 1961, Kennedy took the oath of office as the 35th President of the United States. The youngest president in United States history, he was the first man born in the 20th century to hold that office. Listening to his inaugural address, the nation felt that a new era and a "new frontier" were being ushered in.
Can we forge against these enemies a grand and global alliance, North and South, East and West, that can assure a more fruitful life for all mankind? Will you join in that historic effort? In the long history of the world, only a few generations have been granted the role of defending freedom in its hour of maximum danger. I do not shrink from this responsibility -- I welcome it. I do not believe that any of us would exchange places with any other people or any other generation. The energy, the faith, the devotion which we bring to this endeavor will light our country and all who serve it -- and the glow from that fire can truly light the world. And so, my fellow Americans: ask not what your country can do for you -- ask what you can do for your country. My fellow citizens of the world: ask not what America will do for you, but what together we can do for the freedom of man.
Listen to the speech.
January 28, 1986; Washington, D.C.

On January 28, 1986, millions of Americans, many of them schoolchildren watching from their classroom desks, tuned in to see 7 Americans, including Christa McAuliffe, a 37 year old schoolteacher and the first ever "civilian astronaut," lift off in the space shuttle Challenger. Just 73 seconds later, the shuttle was consumed in a fireball. All seven aboard perished. These were the first deaths of American astronauts while in flight, and the nation was shocked and heartbroken by the tragedy. Just a few hours after the disaster, President Ronald Reagan took to the radio and airwaves, honoring these "pioneers" and offering comfort and assurance to a rattled people.
We've grown used to wonders in this century. It's hard to dazzle us. But for 25 years the United States space program has been doing just that. We've grown used to the idea of space, and perhaps we forget that we've only just begun. We're still pioneers. They, the members of the Challenger crew, were pioneers. And I want to say something to the school children of America who were watching the live coverage of the shuttle's takeoff. I know it is hard to understand, but sometimes painful things like this happen. It's all part of the process of exploration and discovery. It's all part of taking a chance and expanding man's horizons. The future doesn't belong to the fainthearted; it belongs to the brave. The Challenger crew was pulling us into the future, and we'll continue to follow them...... The crew of the space shuttle Challenger honoured us by the manner in which they lived their lives. We will never forget them, nor the last time we saw them, this morning, as they prepared for the journey and waved goodbye and 'slipped the surly bonds of earth' to 'touch the face of God.'
Check out our podcast with Ronald Regan biographer Bob Sptiz.
326 B.C.; Hydaspes River, India

In 335 B.C., Alexander the Great began his campaign to recapture former Greek cities and to expand his empire. After ten years of undefeated battles, Alexander controlled an empire that included Greece, Egypt, and what had been the massive Persian Empire.
That wasn't enough for Xander. He decided to continue his conquest into India. But after ten years of fighting and being away from home, his men lacked the will to take part in another battle, especially against an opponent like King Porus and his army. Alexander used the talent for oration he had developed while studying under Aristotle to infuse his men with the motivation they needed to continue on, to fight and to win.
I could not have blamed you for being the first to lose heart if I, your commander, had not shared in your exhausting marches and your perilous campaigns; it would have been natural enough if you had done all the work merely for others to reap the reward. But it is not so. You and I, gentlemen, have shared the labour and shared the danger, and the rewards are for us all. The conquered territory belongs to you; from your ranks the governors of it are chosen; already the greater part of its treasure passes into your hands, and when all Asia is overrun, then indeed I will go further than the mere satisfaction of our ambitions: the utmost hopes of riches or power which each one of you cherishes will be far surpassed, and whoever wishes to return home will be allowed to go, either with me or without me. I will make those who stay the envy of those who return.
Check out the AoM podcast about the life of Alexander the Great.
May 12, 1789; House of Commons, London

When William Wilberforce, a member of the British Parliament, converted to Christianity, he began to earnestly seek to reform the evils he found within himself and the world around him. One of the glaring moral issues of the day was slavery, and after reading up on the subject and meeting with anti-slavery activists, Wilberforce became convinced that God was calling him to be an abolitionist. Wilberforce decided to concentrate on ending the slave trade rather than slavery itself, reasoning that the abolition of one would logically lead to the demise of the other. On May 12, 1789, Wilberforce made his first speech on the abolition of the slave trade before the House of Commons. He passionately made his case for why the trade was reprehensible and needed to cease. Wilberforce introduced a bill to abolish the trade, but it failed, a result he would become quite familiar with in the ensuing years. Yet Wilberforce never gave up, reintroducing the bill year after year, and the Slave Trade Act was finally passed in 1807.
When I consider the magnitude of the subject which I am to bring before the House-a subject, in which the interests, not of this country, nor of Europe alone, but of the whole world, and of posterity, are involved: and when I think, at the same time, on the weakness of the advocate who has undertaken this great cause-when these reflections press upon my mind, it is impossible for me not to feel both terrified and concerned at my own inadequacy to such a task. But when I reflect, however, on the encouragement which I have had, through the whole course of a long and laborious examination of this question, and how much candour I have experienced, and how conviction has increased within my own mind, in proportion as I have advanced in my labours;-when I reflect, especially, that however averse any gentleman may now be, yet we shall all be of one opinion in the end;-when I turn myself to these thoughts, I take courage-I determine to forget all my other fears, and I march forward with a firmer step in the full assurance that my cause will bear me out, and that I shall be able to justify upon the clearest principles, every resolution in my hand, the avowed end of which is, the total abolition of the slave trade.
April 14, 1906; Washington, D.C.

Theodore Roosevelt was president during the Progressive Era, a time of great enthusiasm for reform in government, the economy, and society. TR himself held many progressive ideals, but he also called for moderation, not extremism. The "Man with a Muck-rake" in Pilgrim's Progress never looked heavenward but instead constantly raked the filth at his feet. TR thus dubbed the journalists and activists of the day who were intent on exposing the corruption in society as "muckrakers." He felt that they did a tremendous amount of good, but needed to mitigate their constant pessimism and alarmist tone. He worried that the sensationalism with which these exposes were often presented would make citizens overly cynical and too prone to throw out the baby with the bathwater.
To assail the great and admitted evils of our political and industrial life with such crude and sweeping generalizations as to include decent men in the general condemnation means the searing of the public conscience. There results a general attitude either of cynical belief in and indifference to public corruption or else of a distrustful inability to discriminate between the good and the bad. Either attitude is fraught with untold damage to the country as a whole. The fool who has not sense to discriminate between what is good and what is bad is well-nigh as dangerous as the man who does discriminate and yet chooses the bad. There is nothing more distressing to every good patriot, to every good American, than the hard, scoffing spirit which treats the allegation of dishonesty in a public man as a cause for laughter. Such laughter is worse than the crackling of thorns under a pot, for it denotes not merely the vacant mind, but the heart in which high emotions have been choked before they could grow to fruition.
March 4, 1933; Washington, D.C.

Franklin Delano Roosevelt handily beat incumbent Herbert Hoover in the 1932 presidential election. The country was deep into the Great Depression, and the public felt that Hoover did not fully sympathize with their plight and was not doing enough to alleviate it. No one was quite clear on what FDR's plan was, but as in today's election season, "change" was enough of an idea to power a campaign. In his First Inaugural Address, Roosevelt sought to buoy up the injured psyche of the American people and present his case for why he would need broad executive powers to tackle the Depression.
I am certain that my fellow Americans expect that on my induction into the Presidency I will address them with a candor and a decision which the present situation of our Nation impels. This is preeminently the time to speak the truth, the whole truth, frankly and boldly. Nor need we shrink from honestly facing conditions in our country today. This great Nation will endure as it has endured, will revive and will prosper. So, first of all, let me assert my firm belief that the only thing we have to fear is fear itself-nameless, unreasoning, unjustified terror which paralyzes needed efforts to convert retreat into advance. In every dark hour of our national life a leadership of frankness and vigor has met with that understanding and support of the people themselves which is essential to victory. I am convinced that you will again give that support to leadership in these critical days.
Read the full text here .
June 18, 1940; London

In June of 1940, it was clear that France was losing their country to the German invasion. Refusing to sign an armistice, Prime Minister Paul Reynaud was forced to resign. He was succeeded by Marshal Philippe Petain who made clear his intention to seek an accommodation with Germany. Disgusted with this decision, General Charles de Gaulle, leader of the Free French Forces, escaped to England on June 15. De Gaulle asked for, and obtained permission from Winston Churchill to make a speech on BBC radio. De Gaulle exhorted the French to not give up hope and to continue the fight against the German occupation and the Vichy Regime.
But has the last word been said? Must hope disappear? Is defeat final? No! Believe me, I who am speaking to you with full knowledge of the facts, and who tell you that nothing is lost for France. The same means that overcame us can bring us victory one day. For France is not alone! She is not alone! She is not alone! She has a vast Empire behind her. She can align with the British Empire that holds the sea and continues the fight. She can, like England, use without limit the immense industry of the United States. This war is not limited to the unfortunate territory of our country. This war is not over as a result of the Battle of France. This war is a worldwide war. All the mistakes, all the delays, all the suffering, do not alter the fact that there are, in the world, all the means necessary to crush our enemies one day. Vanquished today by mechanical force, in the future we will be able to overcome by a superior mechanical force. The fate of the world depends on it.
399 B.C.; Athens

Socrates is perhaps the greatest teacher in the history of the Western world. He wandered around Athens engaging in dialogues with his fellow citizens that focused on discovering the truth of all things . He taught his pupils that the "unexamined life is not worth living."
The Athenians saw Socrates as a threat, especially to the Athenian youth. Socrates acquired quite a following among the young men of Athens. He taught these impressionable minds to question everything, even Athenian authority. Eventually, Socrates was arrested and put on trial for corrupting the youth, not believing the gods, and creating new deities.
The "Apology" is Socrates' defense to these charges. Instead of crying and pleading for mercy, Socrates accepts his charges and attempts to persuade the jury with reason. He argued that it was his calling from the gods to seek knowledge and that it was through his questions he uncovered truth. To not fulfill his calling would be blasphemy. In the end, Socrates lost and was sentenced to death by hemlock. Socrates accepted this fate willingly and without grudge against his condemners, thus dying as a martyr for free thinking.
Some one will say: Yes, Socrates, but cannot you hold your tongue, and then you may go into a foreign city, and no one will interfere with you? Now I have great difficulty in making you understand my answer to this. For if I tell you that to do as you say would be a disobedience to the God, and therefore that I cannot hold my tongue, you will not believe that I am serious; and if I say again that daily to discourse about virtue, and of those other things about which you hear me examining myself and others, is the greatest good of man, and that the unexamined life is not worth living, you are still less likely to believe me.
Check out our article on the philosophy of Plato .
December 23, 1784; Annapolis, Maryland

As the Revolutionary War drew to a close, there was much speculation that George Washington, then Major General and Commander-in-Chief, would follow in the footsteps of former world leaders by making a grab for supreme power. Some even wished he would do so, hoping he would become the king of a new nation. Yet Washington knew that such a move would wither the fragile beginnings of the new republic. Looking to the Roman general Cincinnatus an exemplar, Washington rejected the temptations of power and resigned his position as Commander-in-Chief. Choosing the right is almost never easy, and as Washington read his speech in front of the Continental Congress, the great statesman trembled so much that he had to hold the parchment with two hands to keep it steady. "The spectators all wept, and there was hardly a member of Congress who did not drop tears. His voice faltered and sunk, and the whole house felt his agitations." When finished, Washington bolted from the door of the Annapolis State House, mounted his horse, and galloped away into the sunset.
While I repeat my obligations to the Army in general, I should do injustice to my own feelings not to acknowledge in this place the peculiar Services and distinguished merits of the Gentlemen who have been attached to my person during the War. It was impossible the choice of confidential Officers to compose my family should have been more fortunate. Permit me Sir, to recommend in particular those, who have continued in Service to the present moment, as worthy of the favorable notice and patronage of Congress. I consider it an indispensable duty to close this last solemn act of my Official life, by commending the Interests of our dearest Country to the protection of Almighty God, and those who have the superintendence of them, to his holy keeping. Having now finished the work assigned me, I retire from the great theater of Action; and bidding an Affectionate farewell to this August body under whose orders I have so long acted, I here offer my Commission, and take my leave of all the employments of public life.
Check out my podcast about the self-education of George Washington.
August 8, 1942; India

While the battle for freedom and democracy raged across the world, the people of India were engaged in their own fight for liberty. For almost a century, India had been under the direct rule of the British crown, and many Indians had had enough. Mahatma Gandhi and the National Indian Congress pushed for a completely non-violent movement aimed at forcing Britain to "Quit India." Gandhi, pioneer of the tactics of non-violent civil disobedience, called for their use on August 8, 1942 with the passing of the Quit India Resolution demanding complete independence from British rule.
I believe that in the history of the world, there has not been a more genuinely democratic struggle for freedom than ours. I read Carlyle's French Resolution while I was in prison, and Pandit Jawaharlal has told me something about the Russian revolution. But it is my conviction that inasmuch as these struggles were fought with the weapon of violence they failed to realize the democratic ideal. In the democracy which I have envisaged, a democracy established by non-violence, there will be equal freedom for all. Everybody will be his own master. It is to join a struggle for such democracy that I invite you today. Once you realize this you will forget the differences between the Hindus and Muslims, and think of yourselves as Indians only, engaged in the common struggle for independence.
June 18, 1940; House of Commons, London

On May 10, 1940, the Germans began their invasion of France. On June 14 Paris fell. In a matter of days, France would surrender and England would stand as Europe's lone bulwark against the twin evils of Fascism and Nazism. At this critical moment, Churchill gave his third and final speech during the Battle of France, once again imparting words meant to bring hope in this dark hour.
What General Weygand called the Battle of France is over. I expect that the Battle of Britain is about to begin. Upon this battle depends the survival of Christian civilization. Upon it depends our own British life, and the long continuity of our institutions and our Empire. The whole fury and might of the enemy must very soon be turned on us. Hitler knows that he will have to break us in this Island or lose the war. If we can stand up to him, all Europe may be free and the life of the world may move forward into broad, sunlit uplands. But if we fail, then the whole world, including the United States, including all that we have known and cared for, will sink into the abyss of a new Dark Age made more sinister, and perhaps more protracted, by the lights of perverted science. Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves that if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, 'This was their finest hour.'
Check out my podcast about how Churchill led during the Blitz.
December 10, 1950; Stockholm, Sweden

A true master of the written word, William Faulkner did not often make public his gift for the spoken variety. So there was some interest as to what he would say when accepting the Nobel Peace Prize for his "powerful and artistically unique contribution to the modern American novel." The year was 1950, the Soviet Union had tapped the potential of the atomic bomb, and the atmosphere in the the United States crackled with the fear of them using it. Faulkner challenged poets, authors, and all mankind to think beyond the questions of "When will I be blown up?" and instead continue to "create out of the materials of the human spirit something which did not exist before."
I decline to accept the end of man. It is easy enough to say that man is immortal because he will endure: that when the last ding-dong of doom has clanged and faded from the last worthless rock hanging tideless in the last red and dying evening, that even then there will still be one more sound: that of his puny inexhaustible voice, still talking. I refuse to accept this. I believe that man will not merely endure: he will prevail. He is immortal, not because he alone among creatures has an inexhaustible voice, but because he has a soul, a spirit capable of compassion and sacrifice and endurance. The poet's, the writer's, duty is to write about these things. It is his privilege to help man endure by lifting his heart, by reminding him of the courage and honor and hope and pride and compassion and pity and sacrifice which have been the glory of his past. The poet's voice need not merely be the record of man, it can be one of the props, the pillars to help him endure and prevail.
January 17, 1961; Washington, D.C.

The 1950's were a time of ever increasing military spending, as the United States sought to fight communism abroad and prevent it at home. As President Dwight D. Eisenhower left office, more than half of the federal budget was allocated for defense purposes. Eisenhower, former General of the Army, was certainly not opposed to the use of military power to keep the peace. Still, he saw fit to use his "Farewell Address" to warn the nation of the dangers posed by the "military-industrial complex," referring to the relationship between the armed forces, the government, and the suppliers of war materials. Eisenhower was wary of the large role defense spending played in the economy, and understood the political and corporate corruption that could result if the public was not vigilant in checking it.
In the councils of government, we must guard against the acquisition of unwarranted influence, whether sought or unsought, by the military-industrial complex . The potential for the disastrous rise of misplaced power exists and will persist. We must never let the weight of this combination endanger our liberties or democratic processes. We should take nothing for granted. Only an alert and knowledgeable citizenry can compel the proper meshing of the huge industrial and military machinery of defense with our peaceful methods and goals, so that security and liberty may prosper together.
63 BC; Rome

Lucius Sergius Catilina (Catiline to his friends) was a very jealous man. Having once run against Cicero for the position of consul and lost, he became determined to win the next election by any devious method necessary. Plan A was to bribe people to vote for him, and when that didn't work, he decided to go for bust and simply knock Cicero off on election day. This plan was ferreted out by the ever vigilant Cicero, the election was postponed, and the Senate established marital law. When the election finally was held, the murderer-cum-candidate was surprisingly trounced at the polls. Now it was time for Catiline's Plan C: raise an army of co-conspirators, create insurrection throughout Italy, overthrow the government, and slice and dice as many Senators as they could get their coo -ky hands on. But Cicero was again one step ahead and discovered the plan. He called the Senate together for a meeting at the Temple of Jupiter in the Capitol, an orifice only used in times of great crisis. Catiline, who seriously didn't know when he was not welcome, decided to crash the party. With his archenemy in attendance, Cicero began his Catiline Orations, a series of speeches covering how he saved Rome from rebellion, the guilt of Catiline, and the need to whack he and his cronies.
I wish, O conscript fathers, to be merciful; I wish not to appear negligent amid such danger to the state; but I do now accuse myself of remissness and culpable inactivity. A camp is pitched in Italy, at the entrance of Etruria, in hostility to the republic; the number of the enemy increases every day; and yet the general of that camp, the leader of those enemies, we see within the walls-aye, and even in the senate-planning every day some internal injury to the republic. If, O Catiline, I should now order you to be arrested, to be put to death, I should, I suppose, have to fear lest all good men should say that I had acted tardily, rather than that any one should affirm that I acted cruelly. But yet this, which ought to have been done long since, I have good reason for not doing as yet; I will put you to death, then, when there shall be not one person possible to be found so wicked, so abandoned, so like yourself, as not to allow that it has been rightly done. As long as one person exists who can dare to defend you, you shall live; but you shall live as you do now, surrounded by my many and trusty guards, so that you shall not be able to stir one finger against the republic; many eyes and ears shall still observe and watch you, as they have hitherto done, tho you shall not perceive them.
June 12, 1987; Brandenburg Gate, Berlin

Since the end of World War II, Germany had been a divided country, the West free and democratic, the East under authoritarian communist control. When President Reagan took office, he was committed not only to uniting that country, but to bringing down the entire "Evil Empire." While the importance of Reagan's role in successfully doing so is endlessly debated, it beyond dispute that he exerted some influence in bringing the Cold War to an end. There is no more memorable and symbolic moment of this influence then when Reagan stood at the Berlin wall, the most visible symbol of the "Iron Curtain," and challenged Gorbachev to "tear down this wall!"
We welcome change and openness; for we believe that freedom and security go together, that the advance of human liberty can only strengthen the cause of world peace. There is one sign the Soviets can make that would be unmistakable, that would advance dramatically the cause of freedom and peace. General Secretary Gorbachev, if you seek peace, if you seek prosperity for the Soviet Union and eastern Europe, if you seek liberalization, come here to this gate. Mr. Gorbachev, open this gate. Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!
Listen to speech.
431 BC; Athens
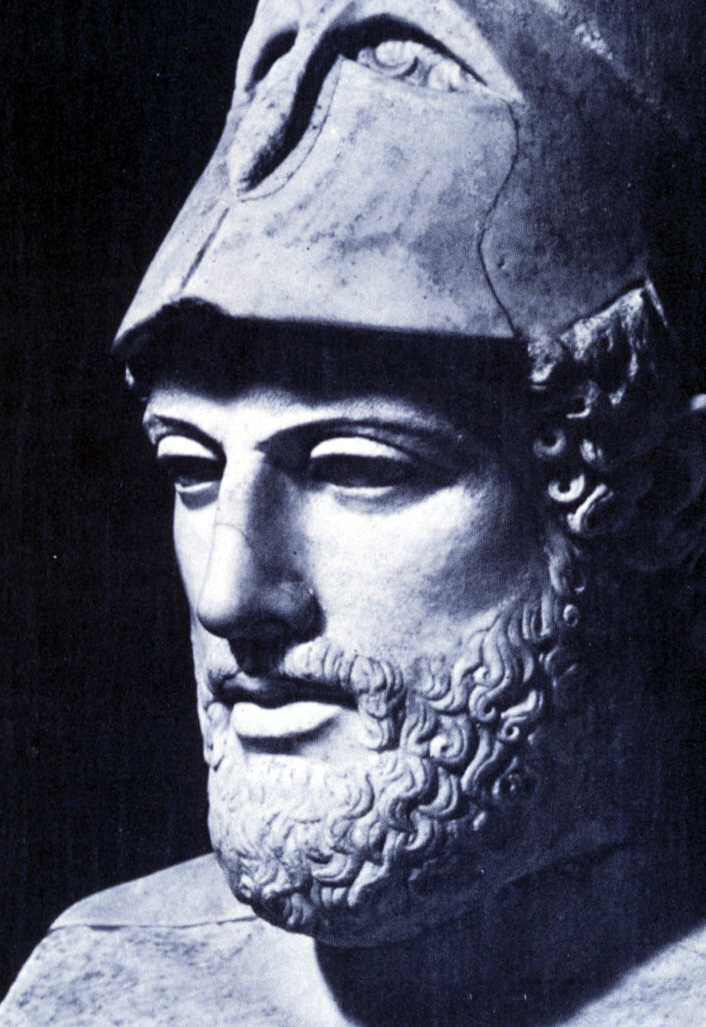

Pericles, master statesman, orator, and general, was truly, as Thuciydies dubbed him, "the first citizen of Athens." Pericles was a product of the Sophists and had been personally tutored by the great philosopher Anaxagoras. His study with the Sophists made Pericles a highly persuasive orator. Through his speeches, he galvanized Athenians to undertake an enormous public works project that created hundreds of temples, including the Pantheon.
Pericles' gift of oration was put to the test during the epic battles of the Peloponnesian War, a civil war between Athens and Sparta. His speeches inspired Athenians to fight to become the number one power in Greece. In February of 431 B.C., Athens had their annual public funeral to honor all those who died in war. Pericles was asked to give the traditional funeral oration. Rather than focus his speech on enumerating the conquests of Athens' fallen heroes, Pericles instead used his funeral oration to laud the glory of Athens itself and inspire the living to make sure the soldiers had not died in vain.
Over 2,000 years later, Pericles' funeral oration inspired Abraham Lincoln's "Gettysburg Address." Like Pericles, Lincoln was a leader during a time of civil war. Like Pericles, Lincoln focused on exhorting the living to live their lives in a way that would make the sacrifice of fallen warriors worthwhile.
So died these men as became Athenians. You, their survivors, must determine to have as unfaltering a resolution in the field, though you may pray that it may have a happier issue. And not contented with ideas derived only from words of the advantages which are bound up with the defense of your country, though these would furnish a valuable text to a speaker even before an audience so alive to them as the present, you must yourselves realize the power of Athens, and feed your eyes upon her from day to day, till love of her fills your hearts; and then, when all her greatness shall break upon you, you must reflect that it was by courage, sense of duty, and a keen feeling of honor in action that men were enabled to win all this, and that no personal failure in an enterprise could make them consent to deprive their country of their valor, but they laid it at her feet as the most glorious contribution that they could offer.
April 19, 1951, Washington; D.C.

During the Korean War, General MacArthur and President Truman clashed over the threat posed by the Chinese People's Liberation Army and their incursion into Korea. MacArthur continually pressed Truman for permission to bomb bases in Manchuria, believing the war needed to be extended in area and scope. Truman refused the General's requests, arguing that directly drawing China into the war would arouse the Soviet Union to action. MacArthur continued to press his case, and Truman, accusing the General of insubordination, made the decision to relieve MacArthur of his command. After serving for 52 years and in three wars, the General's military career was over. MacArthur returned to the United States and gave this farewell address to Congress.
I am closing my 52 years of military service. When I joined the Army, even before the turn of the century, it was the fulfillment of all of my boyish hopes and dreams. The world has turned over many times since I took the oath on theplain at West Point, and the hopes and dreams have long since vanished, but I still remember the refrain of one of the most popular barrack ballads of that day which proclaimed most proudly that "old soldiers never die; they just fade away." And like the old soldier of that ballad, I now close my military career and just fade away, an old soldier who tried to do his duty as God gave him the light to see that duty. Good Bye.

Roosevelt was an advocate of having many children and making sure the next generation would continue to uphold the great virtues of civilization. He was always concerned that young men not be coddled or cowardly, and grow up to live rugged, strenuous, and thoroughly manly lives. But he also strongly believed that being ruggedly manly and being refined in mind and spirit were not incompatible and should in fact go hand and hand. In this speech, he exhorts young men to pursue virtuous manliness. Amen, brother, amen.
It is peculiarly incumbent upon you who have strength to set a right example to others. I ask you to remember that you cannot retain your self-respect if you are loose and foul of tongue, that a man who is to lead a clean and honorable life must inevitably suffer if his speech likewise is not clean and honorable. Every man here knows the temptations that beset all of us in this world. At times any man will slip. I do not expect perfection, but I do expect genuine and sincere effort toward being decent and cleanly in thought, in word, and in deed. As I said at the outset, I hail the work of this society as typifying one of those forces which tend to the betterment and uplifting of our social system. Our whole effort should be toward securing a combination of the strong qualities with those qualities which we term virtues. I expect you to be strong. I would not respect you if you were not. I do not want to see Christianity professed only by weaklings; I want to see it a moving spirit among men of strength. I do not expect you to lose one particle of your strength or courage by being decent. On the contrary, I should hope to see each man who is a member of this society, from his membership in it become all the fitter to do the rough work of the world; all the fitter to work in time of peace; and if, which may Heaven forfend, war should come, all the fitter to fight in time of war. I desire to see in this country the decent men strong and the strong men decent, and until we get that combination in pretty good shape we are not going to be by any means as successful as we should be. There is always a tendency among very young men and among boys who are not quite young men as yet to think that to be wicked is rather smart; to think it shows that they are men. Oh, how often you see some young fellow who boasts that he is going to "see life," meaning by that that he is going to see that part of life which it is a thousandfold better should remain unseen!
March 4, 1865; Washington, D.C.

The Union's victory was but a month away as Abraham Lincoln began his second term as president of a bitterly ruptured United States. Like the Gettysburg Address, Lincoln keeps this speech only as long as needful. While there are those who still debate whether the Civil War was truly fought over slavery or not, Lincoln certainly believed so. To him, slavery was a great national sin, and the blood shed during the war was the atoning sacrifice for that evil.
He does not relish the prospect of coming victory; instead, he appeals to his countrymen to remember that the war was truly fought between brothers. When the war was over and the Confederacy forced to return to the Union, Lincoln was prepared to treat the South with relative leniency. He did not believe secession was truly possible, and thus the South had never truly left the Union. Reconstruction would not mean vengeance, but the return home of a terribly errant son.
Fondly do we hope, fervently do we pray, that this mighty scourge of war may speedily pass away. Yet, if God wills that it continue until all the wealth piled by the bondsman's two hundred and fifty years of unrequited toil shall be sunk, and until every drop of blood drawn with the lash shall be paid by another drawn with the sword, as was said three thousand years ago, so still it must be said "the judgments of the Lord are true and righteous altogether." With malice toward none, with charity for all, with firmness in the right as God gives us to see the right, let us strive on to finish the work we are in, to bind up the nation's wounds, to care for him who shall have borne the battle and for his widow and his orphan, to do all which may achieve and cherish a just and lasting peace among ourselves and with all nations.
March 23, 1775; Richmond , VA

For a decade, revolutionary sentiments had been brewing in Virginia and Patrick Henry had always been in the thick of it, stirring the pot. Henry became particularly enflamed by the Stamp Act of 1764, which prompted him to give his so-called "treason speech," spurring the Burgesses to pass the Virginia Resolves banning the act. Tensions between the colonies and the Crown continued to build, and in 1775, Massachusetts patriots began making preparations for war. Henry believed that Virginia should follow suit. At a meeting held in St. John's Church in Richmond, Henry presented resolutions to make ready Virginia's defenses. Seeking to persuade his fellow delegates of the urgency of his message, he gave a rousing and memorable speech, climaxing is that now famous line, "Give me liberty of give me death!"
The battle, sir, is not to the strong alone; it is to the vigilant, the active, the brave. Besides, sir, we have no election. If we were base enough to desire it, it is now too late to retire from the contest. There is no retreat but in submission and slavery! Our chains are forged! Their clanking may be heard on the plains of Boston! The war is inevitable -- and let it come! I repeat it, sir, let it come! It is in vain, sir, to extenuate the matter. Gentlemen may cry, "Peace! Peace!" -- but there is no peace. The war is actually begun! The next gale that sweeps from the north will bring to our ears the clash of resounding arms! Our brethren are already in the field! Why stand we here idle? What is it that gentlemen wish? What would they have? Is life so dear, or peace so sweet, as to be purchased at the price of chains and slavery? Forbid it, Almighty God! I know not what course others may take; but as for me, give me liberty, or give me death!
June 6, 1984; Pointe du Hoc, France

What the Army Rangers did on D-Day at Pointe Du Hoc is a tale every man worth his salt should be familiar with. Pointe du Hoc was a sheer 100 foot cliff located in-between Omaha and Utah beaches. Perched atop the cliff sat six casemates capable of being manned, armed, and taking out the men on the beaches. As the Germans fired upon them, the Rangers scaled the cliff using ropes and ladders, found the guns (which had been moved from the casemates) and destroyed them. Without reinforcements for two days, the Rangers alone held their position and fended off German counterattacks. These skirmishes proved deadly; only 90 of the original 225 Ranger landing force survived.
On the 40 th anniversary of D-Day, President Reagan gave a moving tribute to these men, many of whom were present at the occasion.
These are the boys of Pointe du Hoc. These are the men who took the cliffs. These are the champions who helped free a continent. These are the heroes who helped end a war. Gentlemen, I look at you and I think of the words of Stephen Spender's poem. You are men who in your 'lives fought for life...and left the vivid air signed with your honor'... Forty summers have passed since the battle that you fought here. You were young the day you took these cliffs; some of you were hardly more than boys, with the deepest joys of life before you. Yet you risked everything here. Why? Why did you do it? What impelled you to put aside the instinct for self-preservation and risk your lives to take these cliffs? What inspired all the men of the armies that met here? We look at you, and somehow we know the answer. It was faith, and belief; it was loyalty and love. The men of Normandy had faith that what they were doing was right, faith that they fought for all humanity, faith that a just God would grant them mercy on this beachhead or on the next. It was the deep knowledge -- and pray God we have not lost it -- that there is a profound moral difference between the use of force for liberation and the use of force for conquest. You were here to liberate, not to conquer, and so you and those others did not doubt your cause. And you were right not to doubt.
27. John F. Kennedy, " The Decision to Go to the Moon"
May 25, 1961; Houston, TX

On April 12, 1961, the Soviets launched the first man into space. Khrushchev used this triumph as prime evidence of communism's superiority over decadent capitalism. Embarrassed, the United States feared it was falling behind the Soviet Union and losing the "space race." After consulting with political and NASA officials, Kennedy decided it was time for America to boldly go where no man had gone before by putting a man on the moon. The feat would not only catapult the nation over the Soviet Union, but also allow man to more fully explore the mysteries of space. And this mission would be accomplished by the end of the 1960's. When was the last time a president had the cajones to publicly issue a straightforward, ambitious goal and set a timeline for its success?
There is no strife, no prejudice, no national conflict in outer space as yet. Its hazards are hostile to us all. Its conquest deserves the best of all mankind, and its opportunity for peaceful cooperation many never come again. But why, some say, the moon? Why choose this as our goal? And they may well ask why climb the highest mountain? Why, 35 years ago, fly the Atlantic? Why does Rice play Texas? We choose to go to the moon. We choose to go to the moon in this decade and do the other things, not because they are easy, but because they are hard, because that goal will serve to organize and measure the best of our energies and skills, because that challenge is one that we are willing to accept, one we are unwilling to postpone, and one which we intend to win, and the others, too.
July 5, 1852; Rochester, NY
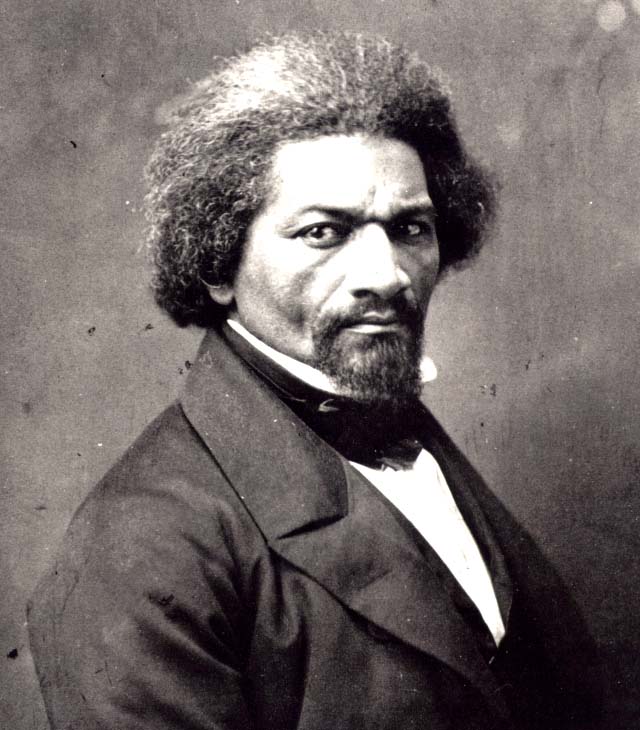
Frederick Douglass, former slave, abolitionist, and engineer on the underground railroad, was a popular speaker on the anti-slavery circuit. He traveled thousands of miles each year, giving hundreds of speeches. Yet the money he earned from lecturing was not enough to become financially comfortable, and he and his family struggled. Douglass was disillusioned by the repercussions of the Fugitive Slave Act, and his abolitionist leanings grew more strident and bold. If the citizens of Rochester, New York had expected to be flattered by Douglass when they asked him to speak on the Fourth, they were soon disavowed of that idea. Douglass took the opportunity to defiantly point out the ripe hypocrisy of a nation celebrating their ideals of freedom and equality while simultaneously mired in the evil of slavery. While the speech surely made even the most liberal audience members squirm; nonetheless, the crowed let loose in "universal applause" when Douglass finished.
I am not included within the pale of this glorious anniversary! Your high independence only reveals the immeasurable distance between us. The blessings in which you this day rejoice are not enjoyed in common. The rich inheritance of justice, liberty, prosperity, and independence bequeathed by your fathers is shared by you, not by me. The sunlight that brought life and healing to you has brought stripes and death to me. This Fourth of July is yours, not mine. Youmay rejoice, I must mourn. To drag a man in fetters into the grand illuminated temple of liberty, and call upon him to join you in joyous anthems, were inhuman mockery and sacrilegious irony. Do you mean, citizens, to mock me, by asking me to speak today?
Read what books had the biggest influence on Frederick Douglass.
May 12, 1962; West Point, New York
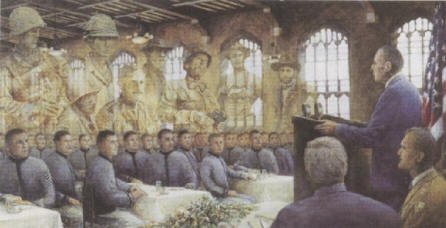
General Douglas MacArthur, General of the Army and a man who fought in three wars, knew something of "Duty, Honor, Country." In 1962, MacArthur was in the twilight of his life and came to West Point to accept the Sylvanus Thayer Award and participate in his final cadet roll call. His address reflects upon and celebrates the brave and courageous men who came before, men he personally led, men who embodied "Duty, Honor, Country."
There are many great speeches in this list, but I hope you will pause to read the entirety of this one. Picking an excerpt was quite difficult, as so many of the passages are inspiring. A must read for all men.
You are the leaven which binds together the entire fabric of our national system of defense. From your ranks come the great captains who hold the nation's destiny in their hands the moment the war tocsin sounds. The Long Gray Line has never failed us. Were you to do so, a million ghosts in olive drab, in brown khaki, in blue and gray, would rise from their white crosses thundering those magic words: Duty, Honor, Country . This does not mean that you are war mongers. On the contrary, the soldier, above all other people, prays for peace, for he must suffer and bear the deepest wounds and scars of war. But always in our ears ring the ominous words of Plato, that wisest of all philosophers: "Only the dead have seen the end of war." The shadows are lengthening for me. The twilight is here. My days of old have vanished, tone and tint. They have gone glimmering through the dreams of things that were. Their memory is one of wondrous beauty, watered by tears, and coaxed and caressed by the smiles of yesterday. I listen vainly, but with thirsty ears, for the witching melody of faint bugles blowing reveille, of far drums beating the long roll. In my dreams I hear again the crash of guns, the rattle of musketry, the strange, mournful mutter of the battlefield. But in the evening of my memory, always I come back to West Point. Always there echoes and re-echoes: Duty, Honor, Country .
April 23, 1910; Paris , France

At the end of Theodore Roosevelt's second term in office, he set out to tour Africa and Europe, hoping to allow his successor, President Taft, to step into the enormous shoes TR had left and become his own man. After a safari in Africa, he traveled throughout Europe. While in France, he was invited to speak at the historic University of Paris. Roosevelt used the opportunity to deliver a powerful address on the requirements of citizenship, the characteristics which would keep democracies like France and the United States robust and strong. This speech is famous for the "man in the arena" quote, but the entire speech is an absolute must read.
Let the man of learning, the man of lettered leisure, beware of that queer and cheap temptation to pose to himself and to others as a cynic, as the man who has outgrown emotions and beliefs, the man to whom good and evil are as one. The poorest way to face life is to face it with a sneer. There are many men who feel a kind of twister pride in cynicism; there are many who confine themselves to criticism of the way others do what they themselves dare not even attempt. There is no more unhealthy being, no man less worthy of respect, than he who either really holds, or feigns to hold, an attitude of sneering disbelief toward all that is great and lofty, whether in achievement or in that noble effort which, even if it fails, comes to second achievement. A cynical habit of thought and speech, a readiness to criticise work which the critic himself never tries to perform, an intellectual aloofness which will not accept contact with life's realities - all these are marks, not as the possessor would fain to think, of superiority but of weakness. They mark the men unfit to bear their part painfully in the stern strife of living, who seek, in the affection of contempt for the achievements of others, to hide from others and from themselves in their own weakness. The rôle is easy; there is none easier, save only the rôle of the man who sneers alike at both criticism and performance. It is not the critic who counts; not the man who points out how the strong man stumbles, or where the doer of deeds could have done them better. The credit belongs to the man who is actually in the arena, whose face is marred by dust and sweat and blood; who strives valiantly; who errs, who comes short again and again, because there is no effort without error and shortcoming; but who does actually strive to do the deeds; who knows great enthusiasms, the great devotions; who spends himself in a worthy cause; who at the best knows in the end the triumph of high achievement, and who at the worst, if he fails, at least fails while daring greatly, so that his place shall never be with those cold and timid souls who neither know victory nor defeat.
May 13, 1940; House of Commons, London

Winston Churchill's first speech to the House of Commons as Britain's new Prime Minister got off to an auspicious start. His welcome to that assembly was quite tepid, while outgoing PM Neville Chamberlain was enthusiastically applauded (the world did not yet know just how disastrous his appeasement policies would prove and did not trust Churchill). But Churchill's first speech, the first of three powerful oratories he gave during the Battle of France, would prove that England was in more than capable hands. A seemingly unstoppable Hitler was advancing rapidly across Europe, and Churchill wasted no time in calling his people to arms. While TR had actually been the first to utter the phrase, "blood, sweat and tears," it was Churchill's use of these words that would leave an inedible and inspiring impression upon the world's mind.
Worthy Excerpt
I say to the House as I said to ministers who have joined this government, I have nothing to offer but blood, toil, tears, and sweat. We have before us an ordeal of the most grievous kind. We have before us many, many months of struggle and suffering. You ask, what is our policy? I say it is to wage war by land, sea, and air. War with all our might and with all the strength God has given us, and to wage war against a monstrous tyranny never surpassed in the dark and lamentable catalogue of human crime. That is our policy. You ask, what is our aim? I can answer in one word. It is victory. Victory at all costs - Victory in spite of all terrors - Victory, however long and hard the road may be, for without victory there is no survival.
December 8, 1941; Washington, D.C.

The attack on Pearl Harbor, December 7, 1941, shocked the United States to its core, outraging a nation that had hoped to stay out of the mounting turmoil in Asia and Europe. Overnight, the country united in desire to enter the war. The day after the attacks, FDR addressed the nation in a brief, but electrifying speech, declaring war on Japan and giving assurance that the United States would attain victory.
Be sure to listen to the audio of the speech. Imagine every American family, rattled and worried, listening around the radio to what their president would say. They knew their whole world was about to change forever. Listen to the reaction of Congress as they applaud and cheer FDR's words. The emotion is so very real and palatable; it truly transports you back to that critical moment in time.
Mr. Vice President, Mr. Speaker, members of the Senate and the House of Representatives: yesterday, December 7, 1941- a date which will live in infamy -the United States of America was suddenly and deliberately attacked by naval and air forces of the Empire of Japan..... But always will our whole nation remember the character of the onslaught against us. No matter how long it may take us to overcome this premeditated invasion, the American people in their righteous might will win through to absolute victory. I believe that I interpret the will of the Congress and of the people when I assert that we will not only defend ourselves to the uttermost but will make it very certain that this form of treachery shall never again endanger us. Hostilities exist. There is no blinking at the fact that our people, our territory and our interests are in grave danger. With confidence in our armed forces-with the unbounding determination of our people-we will gain the inevitable triumph-so help us God.
33 A.D.; Jerusalem

Whether one believes that Jesus of Nazareth was the Son of God or simply a wise teacher, it is impossible to deny the impact of perhaps the world's most famous speech: The Sermon on the Mount. No speech has been more pondered, more influential, or more quoted. It introduced a prayer now familiar the world over and uttered in trenches, churches, and bedsides around the globe. It introduced a code of conduct billions of believers have adopted as their lofty, if not not always attainable, goal. While much of the sermon has roots in Jewish law, the advice given in the Beatitudes represented a dramatic and radical departure from the eye for an eye system of justice known in the ancient world. The standards of behavior outlined in the sermon have given believers and non-believers alike plenty to contemplate and discuss in the two thousand years since it was given.
Blessed are the poor in spirit: for theirs is the kingdom of heaven. Blessed are they that mourn: for they shall be comforted. Blessed are the meek: for they shall inherit the earth. Blessed are they which do hunger and thirst after righteousness: for they shall be filled. Blessed are the merciful: for they shall obtain mercy. Blessed are the pure in heart: for they shall see God. Blessed are the peacemakers: for they shall be called the children of God. Blessed are they which are persecuted for righteousness' sake: for theirs is the kingdom of heaven.
See Matthew Chapter 5-7 for full text.
August 28, 1963; Washington, D.C.

Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a Dream Speech" is hands down one of the greatest, if not the greatest, pieces of oratory in American history. King's charisma, skills in rhetoric, and passion, place him in a league of his own. A century after slavery ended, a century after African-Americans were promised full equality, black children were being hosed down in the streets, spat upon, bused to separate schools, turned away from restaurants, and denied treatment as full human beings. In this midst of this egregious track record, Dr. King voiced a clear, compelling message of hope, a dream that things would not always be as they were, and that a new day was coming.
Many people have seen excerpts of the speech, but a surprisingly number of adults my age I have never sat down and watched the speech in its entirety. I challenge you to do just that. It is just as electrifying and moving today as it was in 1963.
I have a dream that one day down in Alabama, with its vicious racists, with its governor having his lips dripping with the words of interposition and nullification - one day right there in Alabama little black boys and black girls will be able to join hands with little white boys and white girls as sisters and brothers. I have a dream today. I have a dream that one day every valley shall be exalted, and every hill and mountain shall be made low, the rough places will be made plain, and the crooked places will be made straight, and the glory of the Lord shall be revealed and all flesh shall see it together. This is our hope. This is the faith that I go back to the South with. With this faith we will be able to hew out of the mountain of despair a stone of hope. With this faith we will be able to transform the jangling discords of our nation into a beautiful symphony of brotherhood. With this faith we will be able to work together, to pray together, to struggle together, to go to jail together, to stand up for freedom together, knowing that we will be free one day. This will be the day, this will be the day when all of God's children will be able to sing with new meaning "My country 'tis of thee, sweet land of liberty, of thee I sing. Land where my father's died, land of the Pilgrim's pride, from every mountainside, let freedom ring!"
Listen to the speech here .
November 19, 1863; Gettysburg, Pennsylvania

272 words. 3 minutes long. Yet, the Gettysburg Address is unarguably one of the greatest pieces of rhetoric in American history. Dr. J Rufus Fears (one of the great modern orators) argues that the Gettysburg Address, along with the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence, form the three founding documents of American freedom. And I have to agree.
The Battle of Gettysburg left 8,000 men dead. The bodies were too numerous to bury properly and many were at first placed in shallow graves. Weeks after the battle, heads and arms were sticking up through the ground and the smell of rotting flesh was sickening.
Money was raised for a proper reburial, and it was decided that the new cemetery should be dedicated, to sweeten the air of Gettysburg, to solemnize this place of death. As was traditional, a great orator, in this case, Edward Everett, was asked to give a solemn and grand speech as a memorial to the fallen men. Lincoln was asked 2 months later, almost as a causal afterthought. He was to add a few remarks to Everett's, a function much like the man with the ceremonial scissors who cuts the ribbon. Legends has it that Lincoln's remarks were the product of pure inspiration, penned on the back of an envelope on the train chugging its way to the soon-to-be hallowed grounds of Gettysburg.
On the day of the dedication, Everett kept the crowd enthralled for a full two hours. Lincoln got up, gave his speech, and sat down even before the photographer had finished setting up for a picture. There was a long pause before anyone applauded, and then the applause was scattered and polite.
Not everyone immediately realized the magnificence of Lincoln's address. But some did. In a letter to Lincoln, Everett praised the President for his eloquent and concise speech, saying, "I should be glad if I could flatter myself that I came as near to the central idea of the occasion, in two hours, as you did in two minutes."
And of course, in time, we have come to fully appreciate the genius and beauty of the words spoken that day. Dr. Fears argues that Lincoln's address did more than memorialize the fallen soldiers at Gettysburg; it accomplished nothing short of transforming the entire meaning of the Civil War. There were no details of the battle mentioned in the speech, no mentioning of soldier's names, of Gettysburg itself, of the South nor the Union, states rights nor secession. Rather, Lincoln meant the speech to be something far larger, a discourse on the experiment testing whether government can maintain the proposition of equality. At Gettysburg, the Constitution experienced a transformation. The first birth has been tainted by slavery. The men, of both North and South, lying in the graves at Gettysburg had made an atoning sacrifice for this great evil. And the Constitution would be reborn, this time living up to its promises of freedom and equality for all.
Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent, a new nation, conceived in liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal. Now we are engaged in a great civil war, testing whether that nation, or any nation so conceived and so dedicated, can long endure. We are met on a great battlefield of that war. We have come to dedicate a portion of that field, as a final resting place for those who here gave their lives that that nation might live. It is altogether fitting and proper that we should do this. But in a larger sense, we cannot dedicate - we cannot consecrate - we cannot hallow - this ground. The brave men, living and dead, who struggled here, have consecrated it, far above our poor power to add or detract. The world will little note, nor long remember, what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here. It is for us the living, rather, to be dedicated here to the unfinished work which they who fought here have thus far so nobly advanced. It is rather for us to be here dedicated to the great task remaining before us - that from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they gave the last full measure of devotion - that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain - that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom - and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth.
Related Posts


100 of the greatest speeches of the 20th century
100 greatest speeches of the 20th century.
The 20th century was one of the most varied, hopeful, and tumultuous in world history. From the Gilded Age to the beginning of the Internet Age—with plenty of stops along the way—it was a century punctuated by conflicts including two World Wars, the Cold War, the War in Vietnam, and the development of nuclear warfare. At the same time, the 20th century was characterized by a push for equality: Women in the United States received the right to vote after decades of activism, while the civil rights movement here ended the era of Jim Crow, inspired marginalized groups to take action, and introduced this country to great leaders like Martin Luther King Jr. and Malcolm X.
Hundreds of people have used their voices along the way to heal, inspire, and enact change with speeches that helped to define these poignant moments in world history. Stacker has curated a list of 100 of the greatest speeches from the 20th century, drawing from research into great American speeches as determined by 137 scholars of American public address , as well as other historical sources. What follows is a gallery of speeches from around the U.S. and the world dealing with the most pressing issues of the day. Not all images show the speech event itself, but do feature the people who gave them.
Read on to discover which American author accepted his Nobel prize under protest and whether an American president accidentally called himself a jelly donut in German.
You may also like: 50 essential civil rights speeches
#100. Maya Angelou's "On the Pulse of Morning"
Delivered Jan. 20, 1993, in Washington D.C.
Maya Angelou, a longtime supporter of the Clinton family , became the second poet (after Robert Frost in 1961), and the first African American poet, to read at a presidential inauguration. She delivered "On the Pulse of Morning" directly after President Bill Clinton gave his first address, a poem that spanned the entire history of America and ended with a hopeful "Good morning." She won the Best Spoken Word Grammy for her performance, and a new audience was introduced to her previous work with the recognition she'd gained from the performance.
#99. Robert M. La Follette's "Free Speech in Wartime"
Delivered Oct. 6, 1917, in Washington D.C.
Wisconsin Senator Robert La Follette was one of just six Senators to oppose U.S. entry into World War I and, after war was declared, an antiwar speech he gave was misleadingly portrayed in the media. As Senators threatened to expel him from the legislative body, he launched a lengthy filibuster that concluded with his rousing defense of "Free Speech in Wartime." He decisively stated that free speech during times of war was not only necessary, but that "the first step toward the prevention of war and the establishment of peace, permanent peace, is to give the people who must bear the brunt of war's awful burden more to say about it." Not everyone in the Senate was convinced, and La Follette was under investigation for treason until the end of the war.
#98. Yasser Arafat's "Gun and Olive Branch"
Delivered Nov. 13, 1974, at the UN General Assembly, New York City, N.Y.
A divisive historical figure at the center of one of the most controversial conflicts, Yasser Arafat served as the Chairman of the Palestinian Liberation Organization for nearly half a century. In 1974, he became the first non-voting member to speak in front of a plenary session of the United Nations. He declared, " Today I have come bearing an olive branch and a freedom fighter's gun . Do not let the olive branch fall from my hand." His "olive branch" appeal to peace in the long-running conflict affected the audience, slightly boosted public support for the Palestinians, and PLO was granted observer status in the international body .
#97. Audre Lorde's "Uses of Anger" keynote address
Delivered June 1981, in Storrs, Conn.
Well-known as a poet, writer, feminist, and civil rights activist, Audre Lorde wasn't afraid to critique the second-wave feminism movement for its disregard for the different ways women of color, particularly black women, suffered under the patriarchy. "Uses of Anger" was her keynote speech at the National Women's Studies Association Conference, but in it, Lorde doesn't only express rage at men and the white feminists who silence those marginalized voices. She also declares , "And I am not free as long as one person of color remains chained. Nor is anyone of you." Here and throughout she echoes the language of more inclusive intersectional feminism but also portends the modern solidarity movements between minority groups we see today.
#96. Charles de Gaulle's "Appeal of June 18"
Broadcast June 18, 19, and 22, 1940, via BBC radio
By 1940, things weren't looking great for Allied powers fighting in Europe, and in June 1940, France, one of the last remaining military powers on the continent, fell to the Nazi army. Escaping the country before a complete Nazi takeover, General Charles de Gaulle declared himself the leader of Free France (based in London), and broadcast several messages calling for resistance in his home country. He knew that "the flame of French resistance must not and shall not die," and ultimately he was proved correct four years later when France was liberated from the Nazi party. He would later become President of the French Republic.
#95. Margaret Sanger's "The Children's Era"
Delivered March 30, 1925, in New York City, N.Y.
The founder of what today is Planned Parenthood, and one of America's most famous birth control advocates, has both the reason and experience to be concerned with the plight of the country's children. In this speech at the Sixth International Neo-Malthusian and Birth Control Conference, Margaret Sanger uses the powerful imagery of turning the world into "a beautiful garden of children." This garden, she suggests, must be cultivated from a fetus' conception and lays out several criteria she thinks parents should be forced to meet before having children—echoing several eugenicist talking points popular before World War II.
#94. George C. Marshall's "Marshall Plan"
Delivered June 5, 1947, at Harvard University, Cambridge, Mass.
Following World War II, the European continent was in shambles, and after failing to negotiate German reconstruction with the Soviet Union, the United States decided it couldn't wait for the USSR to get involved before stepping in. Secretary of State George Marshall doesn't necessarily outline the specifics of the plan that today bears his name, instead calling on European leaders to accept U.S. help to rebuild (and of course, stop the spread of Communism). American journalists were kept as far away from the speech as possible because the Truman administration feared Americans wouldn't like the plan. But it was delivered and later accepted by Europe.
#93. Corazon Aquino's "Speech Before the Joint Session of the United States Congress"
Delivered: Sept. 18, 1986, in Washington D.C.
Corazon Aquino transformed from a self-described "plain housewife" to the presidency of the Philippines after the assassination of her husband Senator Benigno Aquino Jr. He was outspoken about the dictatorial rule of President Ferdinand Marcos, and Corazon took up the mantle, becoming the face of the People Power Revolution that ultimately ousted Marcos and elevated Aquino to the presidency. In this speech, the newly installed president eloquently recalls her journey thus far and reaffirms her commitment to bringing democracy and prosperity to the Filipino people.
#92. Jimmy Carter's "Energy and National Goals: Address to the Nation"
Delivered: July 15, 1979, in Washington D.C.
Energy policy is one of the signature domestic achievements of the Carter administration , reducing U.S. dependence on foreign oil and improving nuclear power in the U.S. However, President Carter's address on energy policy ended up being about more than those policies. Energy is the jumping-off point for those who have lost faith in government—who feel hopeless and fragmented. He tells these frightened people to "have faith in each other, faith in our ability to govern ourselves, and faith in the future of this nation," and that his energy policy is a start in the right direction for healing the nation.
#91. Eva Perón's "Renunciation of the Vice Presidency of Argentina"
Delivered Aug. 31, 1951, on Argentine radio
Immortalized by the people of Argentina, a Broadway musical, and a movie starring Madonna, Eva "Evita" Perón climbed from a childhood of poverty to First Lady when her husband Juan Perón became president in 1946 with the help of her campaigning. She was active as First Lady, helping women earn the right to vote, furthering her husband's Perónist movement, and meeting with the poor. She became something of a celebrity in the country, and in 1951 she announced her candidacy for the vice presidency alongside her husband, to the delight of the poor and working-class citizens she dedicated her time to. Their joy was short-lived; cancer left Perón unable to run for office, as she announces in this speech .
#90. Elizabeth Gurley Flynn's "Statement at the Smith Act Trial"
Delivered April 24, 1952, in New York City, N.Y.
The Smith Act Trial swept up huge numbers of Communist Party members and put them on trial for allegedly trying to overthrow the U.S. government. American Communist Party leader and co-founder of the American Civil Liberties Union, Elizabeth Gurley Flynn, was one of those. She represented herself, made an impassioned statement to the court about her communist beliefs, and argued that she was not, as a communist, advocating for the fall of the government. Despite her remarks, she was found guilty and sentenced to three years in prison.
#89. Ronald Reagan's "Speech on the Challenger Disaster"
Delivered: Jan. 28, 1986, via TV broadcast
The explosion of the Challenger Shuttle just seconds after took off into the sky left seven people dead, including a civilian school teacher, on the same day that President Reagan was to give the State of the Union. Instead, he called in a young speechwriter, Peggy Noonan , to write a new speech that would help the nation process the tragedy they had seen broadcast on live TV. Reagan's speech is lauded even today for its careful balance between honoring the dead while reminding listeners of the importance of exploring the vast and unknown reaches of space, a quest for exploration for which the Challenger astronauts died.
#88. Elizabeth Glaser's "Address at the 1992 Democratic National Convention"
Delivered July 14, 1992, in New York City
Elizabeth Glaser contracted HIV early in the AIDS epidemic after receiving a contaminated transfusion while giving birth; she passed it on to both her children either through breastmilk or in utero. After her daughter passed away at age seven from AIDS, Glasner and two friends started the Pediatric AIDS Foundation, and this activism led to her invitation to speak at the DNC in 1992. There, she described the issue as "not politics" but a "crisis of caring" that led the Republican administration to fail to tackle the AIDS crisis, and she called out Democrats as well to do better. She passed away from complications of the disease two years later.
#87. Theodore Roosevelt's "The Man with the Muckrake"
Delivered April 14, 1906, in Washington D.C.
Investigative journalism was booming in the first decade of the 20th century, as Progressive Era muckraking writers continued to publicize injustices to the country. These journalists had one powerful enemy: President Theodore Roosevelt, as he disliked writers who focused on bad things at the exclusion of all the good that was happening. His speech didn't call for these journalists to stop their practices of uncovering corrupt businessmen but reminded writers that their work affects public outlook and opinion, so only focusing on the worst moments could have a negative impact on the fabric of the nation.
#86. Richard Nixon's "The Great Silent Majority"
Delivered Nov. 3, 1969, in Washington D.C.
Richard Nixon was sworn into office in January 1969 after a wave of anti-Vietnam protests across the country left opposition to the war at a peak. Eleven months after he took office, Nixon gave an Oval Office speech that made clear he believed those protesting the war didn't demonstrate what most Americans actually thought about Vietnam—their opinions were just louder. He called on "the great silent majority of Americans" watching to support him in his decision. It was a gamble, but it paid off as Nixon's approval ratings shot up overnight and popularized the use of the term "silent majority," which is still used in politics today .
#85. John F. Kennedy's "Ich Bin Ein Berliner"
Delivered June 26, 1963, in West Berlin, Germany
Huge crowds thronged around the stage where President John F. Kennedy threw away the speech written by his advisers designed not to offend the Soviet Union and instead read one he'd written himself. The president demonstrated his solidarity with the citizens of the divided city by declaring, "Ich bin ein Berliner," or essentially, "I'm a citizen of Berlin in spirit." (For those who may be wondering, it's a popular myth, but JFK did not accidentally call himself a jelly donut when he called himself a Berliner.) Those who saw the speech in West Berlin, as well as those who watched it around the globe, were inspired.
#84. Rachel Carson's "A New Chapter in Silent Spring"
Delivered Jan. 8, 1963, in New York City, N.Y.
In the '60s and '70s, environmentalism sprang up as a social justice organization inspired by the civil rights movement. A seminal text was Rachel Carson's "Silent Spring," which detailed the effects of the harmful pesticide DDT. In a speech to the Garden Club of America after her book's publication, Carson discusses the importance of raising public awareness of environmental issues, the next steps for those against pesticides, and new environmental dangers emerging on the horizon.
#83. Dwight Eisenhower's "Atoms for Peace"
Delivered Dec. 8, 1953, at the UN General Assembly, New York City, N.Y.
The development of nuclear warfare gave the Cold War higher stakes and led to fears of a potential nuclear holocaust should something go wrong. In his "Atoms for Peace" speech before the UN, Eisenhower admitted that he needed to speak in a " new language...the language of atomic warfare ," and for the first time let the public know what the atomic age actually meant. Ultimately, the speech demonstrated the need for nuclear disarmament due to its destructive power; at the same time, the huge danger offered the U.S. an excuse to continue the arms race with the USSR after the Soviets refused to disarm.
#82. Eugene V. Debs' "Statement to the Court"
Delivered Sept. 18, 1918, in Girard, Kan.
Eugene V. Debs ran for president five times as a candidate for the Socialist Party but ran his final campaign in 1920 from a prison cell. Debs made an enemy of President Woodrow Wilson for his repeated speeches denouncing U.S. entry into World War I and was arrested on 10 charges of sedition. At his trial, Debs was granted permission to testify on his own behalf; the two-hour speech is remembered for its beautiful passages that moved even people who did not support him, such as in his concluding call for listeners everywhere to "take heart of hope, for the cross is bending, the midnight is passing, and joy cometh with the morning." He was sentenced to a decade in prison but only served a few years before his sentence was commuted.
#81. Margaret Chase Smith's "Declaration of Conscience"
Delivered June 1, 1950, in Washington D.C.
Joseph Welch ultimately took down Joseph McCarthy during a 1953 trial investigating communism in the Army, but he was far from the first person to attempt to end the Senator's red-scare fearmongering. Senator Margaret Chase of Maine took aim at him from the Senate to the House floor four months after he became a national figure, with a speech that endorsed " the right to criticize, the right to hold unpopular beliefs, the right to protest, [and] the right of independent thought " as fundamental to American democracy. She was joined by six other moderate Republican Senators in her rebuke, and some publications praised her for taking a stand while others dismissed her concerns. It wasn't until 1954 that the rest of the Senate took her side and formally censured McCarthy .
#80. Gloria Steinem's "Testimony Before Senate Hearings on the Equal Rights Amendment"
Delivered May 6, 1970, in Washington D.C.
While Shirley Chisholm's speech on the Equal Rights Amendment emphasized all the change its passage would bring, Gloria Steinem—a feminist, activist, and journalist—focused on the sex-based myths that she saw as the root of these problems. Among other myths she took down during her testimony, Steinem cited science that proves men aren't biologically superior to women, points out that discrimination keeps women and African Americans from pursuing their dreams as fully as possible, and noted that men, women, and children all benefit when women are treated more equally in the family.
#79. Barbara Bush's "Choices and Change" commencement address
Delivered June 1, 1990, at Wellesley College, Wellesley, Mass.
Unlike most commencement addresses, all three major news networks interrupted their coverage to carry First Lady Barbara Bush's speech to Wellesley College live. Students were unhappy after Bush had replaced author Alice Walker after she withdrew as the speaker, but the First Lady silenced even her most fervent protestors when she showed up with the First Lady of the USSR, Raisa Gorbachev. The speech itself addressed student criticism head-on and exhorted all students, no matter their goals, to prioritize relationships above all .
#78. Lyndon B. Johnson's "The Great Society"
Delivered May 22, 1964, at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Mich.
This speech launched President Lyndon Johnson's ambitious domestic policy agenda and outlined exactly what he meant by a "Great Society." He defined it as "[demanding] an end to poverty and racial injustice," a place where all children can be educated, and "a challenge constantly renewed." Though the rhetoric in the speech is so sweeping it seems impossible to live up to, Johnson's list of accomplishments is long . He signed the Civil Rights Act, integrated schools, started Medicare, gave federal aid to K-12 schools and created federally backed college loans.
#77. Ronald Reagan's "Address at the U.S. Ranger Monument on the 40th Anniversary of D-Day"
Delivered June 6, 1984, in Pointe du Hoc, France
The title of Ronald Reagan's eloquent D-Day memorial address provides a bland package for the stirring—and at times chilling—speech he gave in honor of the storming of Normandy four decades prior. Reagan spoke of the Rangers that climbed the cliffs, remarking that "when one...fell, another would take his place." The focus, however, did not remain on how the men who died there passed away, but rather on the convictions that drove them; speaking directly to the men who died, Reagan praised them : "You all knew that some things are worth dying for...democracy is worth dying for, because it's the most deeply honorable form of government ever devised by man."
#76. Emma Goldman's "Address to the Jury"
Delivered July 9, 1917, in New York City, N.Y.
A Russian-born feminist and anarchist , Emma Goldman went around the country delivering speeches supporting free speech, birth control, women's rights, labor's right to organize, and other progressive causes. In 1917, she and fellow radical Alexander Berkman were arrested for organizing the anti-war No Conscription League because it encouraged men not to register for a draft. At her trial, Goldman invoked the First Amendment , and like many other free speech advocates at the time, pointed out that "if America has entered the war to make the world safe for democracy, she must first make democracy safe in America" by safeguarding free speech protections. The jury was not convinced, and both were found guilty.
#75. Edward Kennedy's "Eulogy for Robert F. Kennedy"
Delivered June 8, 1968, at St. Patrick's Cathedral, New York City, N.Y.
Within a decade, Senator Edward "Ted" Kennedy lost both his brothers to assassination, first President John F. Kennedy in 1963, then Robert "Bobby" Kennedy in 1968, whom he eulogized three days later. His heart-wrenching speech pulled together the past, present, and future , deftly weaving together Bobby's writings, the grief of his family and the nation over his brother's death, and his own vision for the future.
#74. Mario Savio's "Bodies Upon the Gears"
Delivered Dec. 2, 1964, in Berkeley, Calif.
Mario Savio was a student leader during the Berkeley Free Speech Movement, which worked to end the school's restriction on students' political speech. Known for his fiery speeches, Savio delivered his most famous one during a sit-in at Sprout Hall, advocating for civil disobedience: "There is a time when the operation of the machine becomes so odious, makes you so sick at heart, that you can't take part! ... And you've got to put your bodies upon the gears and upon the wheels...and you've got to make it stop." This inspired hundreds to occupy an administrative building overnight , and they continue to inspire countercultural and anti-government movements around the world.
#73. Jesse Jackson's "1984 Democratic National Convention"
Delivered July 18, 1984, in San Francisco, Calif.
Perhaps one of the biggest shifts in 20th-century politics was the "great reversal" of each political party's key constituencies: White Southerners became overwhelmingly Republican while black voters abandoned the party of Lincoln in favor of the Democratic presidents who worked to pass civil rights legislation. In the '80s, Democrats thought they should pivot back to the whites who'd abandoned the party, but civil rights leader Jesse Jackson's 1984 DNC address proposed an alternative: build a "rainbow coalition" that "makes room" for diversity, including black, Latino, young, Native American, environmentalist, activist, union, and LGBTQ+ voters. The strategy seems to have worked, if the diversity of the candidates for the 2020 Democratic nomination is any indication.
#72. John L. Lewis, "Labor and the Nation"
Delivered Sept. 2, 1937, in Washington D.C.
Powerful unions like the American Federation of Labor and the Congress of Industrial Organizations—whose founding president was John L. Lewis —emerged in the 1920s and '30s. Lewis' speech lays out the long, occasionally bloody history of unions that brought them to this point and argues that the labor movement's fight for "peace with justice" shouldn't be seen as communist and should be supported by the people. It seems his speech fell on deaf ears, as unions were significantly weakened in the 1970s and have been on the decline since .
#71. Margaret Sanger's "The Morality of Birth Control"
Delivered Nov. 18, 1921, at Park Theatre, New York
Margaret Sanger, the founder of Planned Parenthood, was one of the most outspoken advocates for every man and woman's right to access birth control and take control of their own family planning. In this speech, she argues that it is not immoral, as some claim, but rather that it's moral for children to be desired and that motherhood should " be the function of dignity and choice ." (She also argues that disabled and impoverished people might not be fit parents, echoing eugenicist ideas of the time , but her fundamental argument is a woman's right to choose.) Open access to birth control for married and unmarried couples wouldn't be realized until the 1965 Griswold v. Connecticut Supreme Court decision established a constitutional right to privacy over reproductive choices.
#70. Shirley Chisholm, "For the Equal Rights Amendment"
Delivered Aug. 10, 1970, in Washington D.C.
Versions of the Equal Rights Amendment (ERA), which would enshrine women's equality into the Constitution, have been proposed since women earned the right to vote, but it didn't take off until the second-wave feminist movement began to push for its passage. Shirley Chisholm, the first black woman in Congress, delivered an eloquent defense of the ERA in the face of arguments that its passage would do nothing to change sexist attitudes. It passed the Senate two years later but was never ratified by enough states—just one more state needs to do so for it to become law .
#69. Edward Kennedy's "Faith, Truth, and Tolerance in America"
Delivered Oct. 3, 1983, at Liberty Baptist College, Lynchburg, Va.
Polls from the 2018 midterms stuck to a trend that's been evident for decades: White Christians, particularly evangelical Protestants, overwhelmingly vote Republican. The rise of the evangelical or "religious" right in the 1970s, and America's increasing polarization, led to this point, but Senator Edward Kennedy's address at the evangelical Liberty University suggested it didn't have to be this way. The devoutly Catholic Kennedy argued that no one's "convictions about religion should command any greater respect than any other faith in this pluralistic society," leading to a robust separation of church and state . The connection between Americans is not, he suggests, a shared faith but rather " individual freedom and mutual respect ."
#68. Mary Church Terrell's "What It Means to Be Colored in the Capital of the United States"
Delivered Oct. 10, 1906, in Washington D.C.
A trailblazer half a century before the full force of the civil rights movement, Mary Church Terrell was one of the first African American women to earn a college degree. She spent her life working in the D.C. education system and the fight for black women's rights. Her hallmark speech detailed the discrimination and racism she and other African Americans experienced in the nation's capital and called on white listeners to realize the impact this oppression has on the future of black people living in D.C. and across the country.
#67. Winston Churchill's "Blood, Toil, Tears, and Sweat"
Delivered May 13, 1940, at the House of Commons, London, England
Winston Churchill replaced Neville Chamberlain as British Prime Minister following Chamberlain's failed attempts to prevent war with Nazi Germany through appeasement. Churchill wasn't an immediately obvious choice as his successor , as his reputation left him with few friends in Parliament, but he was the only man with enough experience willing to take on the job in the middle of a war. In his first speech to Parliament , he offered only his "blood, toil, tears, and sweat...to wage war against [the] monstrous tyranny" that was Nazi Germany. The sentiment won him the support of skeptics in Parliament and was the first in a trio of speeches that unified the country in the early years of the war.
#66. Wilma Mankiller's "On Rebuilding the Cherokee Nation"
Delivered April 2, 1993, in Sweet Briar, Va.
An activist from her early days, Wilma Mankiller became the first woman to be Principal Chief of the Cherokee Nation after decades of community organizing. In her speech at Sweet Briar , Mankiller infuses her story with wry humor and keen insight while at the same time, with gravity, narrating the history of the Cherokee tribe and the deadly removals they faced at the hands of the U.S. government. Mankiller emphasizes trying to rebuild the community that endured within the Cherokee Nation despite all the removals. This theme was made all the more powerful when you remember that Native American children were separated from their communities and forced into assimilationist boarding schools up through the 1970s.
#65. Russell Conwell's "Acres of Diamonds"
Delivered from 1900 to 1925, in multiple locations across the U.S.
The American Dream and the "pull yourself up by your bootstraps" school of thought were popularized in the Gilded Age , creating an ideology of success that proposes any person in the country can succeed, no matter their circumstance, as long as they work hard. Russell Conwell, a former minister, ushered this school of thought into the 20th century with the "Acres of Diamonds" speech, which claims it is "your duty to get rich," and, in general, that impoverished people are unsympathetic because it was their own shortcomings that got them there.
#64. Ellen DeGeneres' "Vigil for Matthew Shepard"
Delivered Oct. 14, 1998, in Washington D.C.
In 1997, Ellen DeGeneres came out, as did the character on her sitcom (becoming the first LGBTQ+ lead on a TV show), paving the way for more LGBTQ+ representation in Hollywood. The following year, Matthew Shepard's murder sent shock waves through the LGBTQ+ community, evident in the angry, tearful speech DeGeneres gave at a celebrity vigil. She called out the hypocrisy of the church and framed Shepard's murder as "a wake-up call" for straight allies "to help us end the hate" and "raise your children with love and non-judgment." Already emerging as a spokesperson for LGBTQ+ rights, she gave voice to the rage and heartbreak many in the community, and across the nation, felt in the wake of the brutal anti-gay hate crime.
#63. Harry Truman's "Statement by the President Announcing the Use of the A-Bomb at Hiroshima"
Delivered Aug. 6, 1945, via radio address
On Aug. 6, 1945, modern warfare changed forever when the atomic bomb was dropped on the Japanese city of Hiroshima. In a radio address to the nation announcing both the development of atomic-bomb technology and the attack, President Harry Truman announced "let there be no mistake; we shall completely destroy Japan's power to make war" using the atomic bomb. Three days later, a bomb was dropped on Nagasaki, Japan, decisively ending the war in the Pacific.
#62. Harold Ickes' "What Is an American?"
Delivered May 1941, in Central Park, New York City, N.Y.
In this speech, Harold Ickes, Secretary of the Interior during the Roosevelt Administration, asks a question that we're still grappling with in one way or another today . Here, Ickes answers the question to advocate for American involvement in World War II, bemoaning the loss of America's "vaunted idealism" . He characterizes an American as someone who "loves justice," "will fight for his freedom" and "in whose heart is engraved the immortal second sentence of the Declaration of Independence." Ickes appeals to these ideals to establish the necessity of fighting the Nazi threat to democracy; however, the bombing of Pearl Harbor a few months later is ultimately what pulled the U.S. into the war.
#61. Golda Meir's "Speech That Made Possible a Jewish State"
Delivered Jan. 2, 1948, in Chicago, Ill.
As the fight between Israelis and Palestinians intensified over the land to form the Jewish state of Israel, David Ben-Gurion (who would become Israel's first Prime Minister) sent Golda Meir (who would become the third) to America to ask for money to finance the fighting from the American Jewish community. The speech, first delivered in Chicago , then across the U.S., appealed to a sense of unity within the community, suggesting that "if you were in Palestine and we were in the United States," the American Jewish community would do the same thing they did. She then asked for between $25 and $30 million to continue the fight; she returned home with $50 million to finance the effort.
#60. Rigoberta Menchú's "Nobel Peace Prize Lecture"
Delivered Dec. 10, 1992, in Oslo, Norway
Rigoberta Menchú is a fierce advocate for the rights of indigenous people, stemming from racism she's experienced in her home country and the violence that caused her to flee her home. She told her story that resulted in the book, "I, Rigoberta Menchú: An Indian Woman in Guatemala," which shaped her into a spokeswoman for indigenous rights in the Western Hemisphere. She makes her universal message clear in her Nobel Lecture , in which she declares her prize "constitutes a sign of hope in the struggle of the indigenous people in the entire Continent."
#59. Robert F. Kennedy's "On the Death of Martin Luther King"
Delivered April 4, 1968, in Indianapolis, Ind.
Brother to John F. Kennedy and candidate for the Democratic nomination for president, Robert F. Kennedy was at a campaign stop in Indiana when news came that Martin Luther King had been shot while marching with striking sanitation workers. His death would lead to marches and protests across the country but when RFK announced the death in Indianapolis, no violence broke out . Instead, in this short and powerful speech, Kennedy empathizes with those hurt by King's death, connecting it with his own brother's murder, and calls for unity and compassion in honor of King's legacy.
#58. Indira Gandhi's "What Educated Women Can Do"
Delivered Nov. 23, 1973, in New Delhi, India
Daughter of India's first prime minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, and the world's longest-serving female PM, Indira Gandhi had the kind of education that most Indian girls would never dream of receiving, especially in the 1930s and 40s. However, her own story doesn't figure into her famous speech on women's education, instead focusing on the need for more scientifically educated people , both men and women, so the country could achieve great things and become truly modern.
#57. Tony Blair's "Address to the Irish Parliament"
Delivered Nov. 26, 1998, in Dublin, Ireland
The relationship between Britain and Ireland had been characterized by centuries of colonialism and violence, culminating in the partition of Ireland and later the Troubles, decades of intense violence between Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland. The two sides had made peace with the Good Friday Agreement in 1998. British Prime Minister Tony Blair's address to the Irish Parliament a few months later marked the first time a British PM addressed an Irish parliament and affirmed that healing had begun and more could be accomplished by both nations when "our voices speak in harmony."
#56. Richard Nixon's "Checkers"
Delivered Sept. 23, 1952, via television broadcast
This speech, delivered when Nixon was a candidate for Vice President, might be named after the Nixon family dog, but the actual subject proves slightly less adorable. In it, Nixon used a television broadcast to directly answer accusations that he'd used political contributions to pay for personal expenses. He denied the allegations, laid out his financial history and proved his political intelligence by turning the question to the Democrats, asking their candidate to do the same. But what about Checkers the dog? Apparently, she was the only political contribution the Nixon's kept.
#55. Nelson Mandela's "Free at Last"
Delivered May 2, 1994, in Pretoria, South Africa
Decades earlier, Nelson Mandela made a name for himself for his anti-apartheid speech while on trial in Pretoria; now, after 27 years in prison, apartheid had officially ended and Mandela had become South Africa's first democratically elected president. "Free at last" is a reference to a Dr. Martin Luther King speech , showing how closely connected the anti-apartheid and civil rights movement were, though the two leaders never met. The speech emphasizes both the joy of the moment and continued work needed to build " a better life for all South Africans ."
#54. Nikita Khrushchev's "The Cult of the Individual"
Delivered Dec. 5, 1956, in Moscow, Russia
Very few men in the Soviet Union dared insult or question Joseph Stalin, a man who ordered the deaths of millions of his own people , including political rivals. It wasn't until after his death that his successor, Nikita Khrushchev, was willing to say that elevating an individual and worshiping a cult of personality went against the kind of communism that Karl Marx and Vladimir Lenin espoused—the communism that formed the foundation of the Soviet Union's political philosophy. Khrushchev's denunciation of his predecessor shocked the world and offered the first thorough account of Stalin's crimes, but his motivations for giving the speech remain unclear.
#53. Franklin D. Roosevelt's "First Inaugural Address"
Delivered March 4, 1933, in Washington D.C.
President Franklin Roosevelt is lauded for guiding the United States through the thick of World War II, but upon first taking office, he was facing down a different kind of war: the one against the Great Depression. When FDR assumed office, the Depression was at its peak, with almost a quarter of the working population unemployed . His inauguration address emphasizes the enormous scale of the project it would take to rebuild the nation; still, he famously invigorated everyone listening by declaring that " the only thing we have to fear is fear itself ."
#52. Betty Friedan's "Farewell to the National Organization of Women"
Delivered Mar. 20, 1970, in Chicago, Ill.
Betty Friedan's best-selling book, "The Feminine Mystique," got women talking about "the problem with no name" and is often credited with helping spark second-wave feminism. Her voice continued to have power even as she stepped down as president from the National Organization of Women. That day, she called for a general women's strike to be held on Aug. 26, 1970. Despite skepticism from media outlets, thousands of women heeded Friedan's call and took to the street that day—a physical manifestation of the feminist movement's enduring power.
#51. Malcolm X's "Message to the Grassroots"
Delivered on Nov. 10, 1963, in Detroit, Mich.
The divisions between the civil rights movement become obvious in "Message to the Grassroots," which contrasted the "Negro revolution" which was nonviolent and ineffectual, and the "black revolution," which was necessarily violent and had proved itself effective across Africa . This stands alongside the powerful but historically flawed distinction he makes between the self-hating "house slaves" loyal their white owners and "field slaves" as illustrative of X's criticism of black activists whom he thought were too eager to acquiesce to the white people whose oppression the movement was trying to overcome.
#50. Martin Luther King Jr.'s "Beyond Vietnam: Breaking the Silence"
Delivered on April 4, 1967, in New York City, N.Y.
Though today Martin Luther King is revered by nearly all Americans as a powerful spokesman for equal rights and integration, not every political opinion was popular among the American public. Exactly one year before he was assassinated, King spoke out against the Vietnam War. He accused America of ignoring conflicts at home in favor of war abroad, pointing out the "cruel irony of watching Negro and white boys on TV screens as they kill and die together for a nation that has been unable to seat them together in the same schools." Delivered several years before popular opinion on the war changed, King lost many of the powerful allies in government and media due to this speech .
#49. Bill Clinton's "Oklahoma Bombing Memorial Prayer Service Address"
Delivered April 23, 1992, in Oklahoma City, Okla.
Before President Bill Clinton became the nation's "consoler-in-chief" during Columbine, he had to face a nation mourning the 168 people killed in the Oklahoma City Bombing by two domestic terrorists angry about the FBI raid in Waco, Texas. The speech he gave at the memorial service reminded those who had lost loved ones that they "have not lost everything" because they "have certainly not lost America, for we will stand with you for as many tomorrows as it takes" to heal from the tragedy. The sentiment struck a chord with the American public, evident in the boosting of Clinton's poll numbers after the speech.
#48. Nora Ephron's "Commencement Address to the Wellesley Class of 1996"
Delivered June 3, 1996, in Wellesley College, Wellesley, Mass.
Commencement speeches are usually uplifting addresses to graduating seniors looking to inspire them before they begin the next chapter of their lives. Journalist, filmmaker, and writer Nora Ephron returned to her alma mater, Wellesley College, to discuss all the ways the world had changed for the better since she graduated but also offered a note of warning for the grads. "Don't underestimate how much antagonism there is toward women and how many people wish we could turn the clock back," she remarked , listing off current events that reminded the Wellesley graduates that feminism was still urgently needed at the close of the 20th century.
#47. Barbara C. Jordan's "Statement on the Articles of Impeachment"
Delivered: July 25, 1974, in Washington D.C.
As a newly minted State Senator in Texas, Barbara Jordan won over segregationists to pass an equal rights amendment in the state and became a hugely popular political figure in her state. She was elected to the House of Representatives in 1973 just as the Watergate investigation was heating up, and there she gave a rousing political speech subtly advocating for the president's impeachment. Grounding her argument in the Constitution, she called on her fellow House members to use "reason, and not passion" to "guide our deliberations, guide our debate, and guide our decision" as she just adeptly demonstrated.
#46. General Douglas MacArthur's "Farewell Address to Congress"
Delivered April 19, 1951, in Washington D.C.
President Harry Truman and five-star general Douglas MacArthur had a combative relationship, which heated up after the President relieved him of command of UN forces in the Korean War for insubordination. General MacArthur's speech before a joint session of Congress questioned Truman's decision not to take on China in the war, commenting that "War's very object is victory, not prolonged indecision." He received 50 standing ovations during the address while Truman's approval rating plummeted after firing a popular general and World War II hero.
#45. Virginia Woolf's "A Room of One's Own" lectures
Delivered October 20 and 26, 1928, at Cambridge University, Cambridge, England
English author Virginia Woolf's lectures at the women's college at Cambridge are not remembered as stirring works of oratory, but rather as a book. "A Room of One's Own" is a foundational piece of feminist literary theory adapted from this pair of lectures that examines the different types of marginalization women have faced throughout history and the impact on their creative productivity. Among other things, she posits that in order for women to write literature , they need a "room of one's own" or a private space and financial independence in order to write well—a revolutionary claim in late-1920s Europe.
#44. Joseph Welch's "Have You No Sense of Decency?" testimony
Delivered June 9, 1953, in Washington D.C.
Though not technically a speech, the exchange between Senator Joseph McCarthy and Joseph Welch, a lawyer hired by the U.S. Army, proved to be the final blow in the Wisconsin Senator's fall from grace . McCarthy had been conducting trials of suspected Communists since 1950 and everyone was beginning to tire of his methods. A heated back-and-forth erupted between the two men when McCarthy questioned whether one of the lawyers at Welch's firm had Communist ties, leading Welch to ask heatedly McCarthy, "Have you no sense of decency, sir?" With these famous lines, Senator McCarthy saw the last of his power evaporate and died three years later.
#43. Carrie Chapman Catt's "The Crisis"
Delivered Sept. 7, 1916, in Atlantic City, N.J.
Carrie Chapman Catt was a leading figure in the late stages of the American women's suffrage movement, founding the International Women's Suffrage Alliance and serving as president of the National American Women's Suffrage Association during the final push to pass the 19th Amendment. In "The Crisis," Catt outlines her plan to make pushing for a federal amendment to the Constitution NAWSA's priority. At the same time, she tied their fight for the vote to World War I in Europe and the broader fight for women's rights around the world. Ultimately, her instinct to focus on federal legislation instead of working state-by-state proved correct; white women gained the right to vote just three years after this address.
#42. Lyndon B. Johnson's "We Shall Overcome"
Delivered March 15, 1965, in Washington D.C.
One of the most stirring pieces of American rhetoric was written by a hungover speechwriter in just eight hours , after President Lyndon B. Johnson decided he wanted to address Congress about the "Bloody Sunday" attacks against protestors in Selma, Ala. In it, Johnson called on all of America to join him in the cause of civil rights. He appealed specifically to white Americans, noting that "it's not just Negroes, but really it's all of us who must overcome the crippling legacy of bigotry and injustice. And we shall overcome." The speech was interrupted for applause 40 times and brought civil rights activists to tears. And overcome they did; five months later, President Johnson signed the Civil Rights Act.
#41. Geraldine Ferraro's "Vice Presidential Nomination Acceptance Address"
Delivered July 19, 1984, in San Francisco, Calif.
In her concession speech in 2016, presidential candidate Hillary Clinton noted that women have yet to shatter the "highest and hardest glass ceiling" of the American presidency or vice presidency. Very few have come close, the first being Geraldine Ferraro, Walter Mondale's VP pick in the 1984 campaign. In her acceptance speech, Ferraro demonstrates her adeptness as a politician, weaving critiques of the Reagan administration together with her career as an avid activist for women's rights. Though they would ultimately lose to the Republicans, Ferraro cemented her place as a prominent voice in the Democratic party and a trailblazer for women in politics .
#40. Richard Nixon's "Resignation Address to the Nation"
Delivered: Aug. 8, 1974, from Washington D.C.
The case against President Richard Nixon had been growing for years as more details about the Watergate scandal emerged. By August 1974, The Supreme Court ordered the release of tapes he made in the Oval Office, articles of impeachment were being drawn up, and Nixon had lost the support of members of his own party. Rather than suffer the shame of being the first president to be removed from office, Nixon opted to be the first president to resign in a speech highlighting his successes and the work that would need to be continued by his successor.
#39. Franklin D. Roosevelt's "Pearl Harbor Address to the Nation"
Delivered Dec. 8, 1941, via radio broadcast
World War II had been raging since 1939 across the Atlantic but America's historic reluctance to enter global conflict barred President Franklin Roosevelt from taking the direct action he wanted to support U.S. allies in Europe. That changed after the Japanese military bombed Pearl Harbor on Dec. 7, 1941, killing thousands of Americans. The next day, FDR took to the radio to report what had happened on this "date which will live in infamy" and called on Congress to declare war on Japan, which they did shortly after.
#38. Huey P. Long's "Share the Wealth"
Delivered Feb. 23, 1934, via radio broadcast
Also called the "Every Man a King" speech, Louisiana Senator Huey P. Long addressed the nation and laid out his radical plan to redistribute wealth between the richest and poorest Americans by capping fortunes and guaranteeing a basic income, among other radical policy proposals . This was a break from the Democratic Party's New Deal policies, which Long felt did not address wealth discrepancies that he believed caused the Great Depression. His embrace of radio to speak directly to the people won him many supporters to his cause; though he was assassinated the following year.
#37. Woodrow Wilson's "Fourteen Points"
Delivered Jan. 8, 1918, in Washington D.C.
Woodrow Wilson and many others who lived through World War I wanted the deadly global conflict to be "the war to end all wars." The idealistic, progressive Wilson turned this desire into his Fourteen Points for world peace, which he later laid out before Congress after other combatants failed to articulate their aims in the war. Cornerstones of Wilson's peace plan included self-determination , free trade, open seas, and a League of Nations to enforce peace around the world—a plan that was ultimately hampered by Congress' refusal to join the League.
#36. Margaret Thatcher's "The Lady's Not for Turning"
Delivered Oct. 10, 1980, in Brighton, England
Margaret Thatcher took over as Prime Minister and leader of the Tory Party at a time when conservatism was becoming politically popular in much of the Western world (Ronald Reagan would be elected a month after this speech was given). In it, Thatcher lays out her opposition to changing the conservative economic policies she'd instituted, one that focuses on curbing inflation and removing economic regulations. It's most famous line, "'You turn [U-turn the economy] if you want to. The lady's not for turning!" fed into her formidable reputation as the Iron Lady of British politics.
#35. Ursula K. Le Guin's "A Left-Handed Commencement Address"
Delivered in 1983, at Mills College, Oakland, Calif.
Feminist science-fiction writer Ursula K. Le Guin wasn't shy about interrogating the complexities of gender in her work, featuring everything from strong female characters to genderfluid aliens. Her famous commencement address is shaped around some of her concerns regarding gender, pointing out that "women as women are largely excluded from, alien to, the self-declared male norms of this society," and that language itself is centered around men. Citing many famous feminists and women leaders of the era, Le Guin's speech provides a powerful call to action for women (and men) to "grow human souls" and work toward gender equality in their own lives.
#34. Harold Macmillan's "Wind of Change"
Delivered Feb. 3, 1960, in Cape Town, South Africa
The list of countries that have never been invaded by the British is shorter than the list of those that have, but by 1960, the British Empire no longer stretched around the world. British Prime Minister Harold Macmillan signaled this by visiting several British colonies in southern Africa before giving a speech to the South African Parliament announcing that England would no longer stand in the way of colonies wishing to become independent. In his opinion, the emergence of these new nations were the result of "the wind of change...blowing through this continent," and there was nothing Parliament could do to stop them.
#33. Mikhail Gorbachev's resignation
Delivered Dec. 25, 1991, in Moscow, Russia
The fall of the Soviet Union marked the end of the Cold War, the conflict which defined almost every aspect of the post-World War II era. The Cold War didn't end with nuclear holocaust, as many had feared during the conflict's peak, but rather the resignation of executive President Mikhail Gorbachev after several Soviet bloc countries broke away from the USSR behind his back. In the speech he warned that though the country had acquired freedom, "we haven't learned to use freedom yet," so it was important to tread carefully—a warning that has a new salience as the country slides back into authoritarian rule under President Vladimir Putin.
#32. Frank James' "Suppressed Speech"
Delivered Nov. 1970, in Plymouth, Mass.
Wampanoag elder Frank James was invited to speak at a celebration at Plymouth in honor of the 350th Thanksgiving. Organizers objected to his portrayal of the Puritan Pilgrims and white settlers as people who "sought to tame the 'savage' and convert him," but James had refused to read the more PR-friendly speech they gave him. James instead held a protest nearby that has since become the annual Day of Mourning , in which indigenous Americans come to protest and speak out about their experiences.
#31. Jawaharlal Nehru's "Tryst with Destiny"
Delivered Aug. 14–15, 1947, in New Delhi, India
The struggle against the British Empire on the Indian subcontinent finally came to a triumphant finish with Jawaharlal Nehru's "Tryst with Destiny" speech just before midnight on the eve of India's independence. He honors Gandhi as the leader of the movement, as well as the victory they achieved. He also alludes to the Partition that split India and Pakistan into two countries, as well as the sectarian divides between Hindus and Muslims—problems that still plague the country today.
#30. Sacheen Littlefeather's speech at the 1972 Academy Award ceremony
Delivered March 27, 1973, in Los Angeles, Calif.
Marlon Brando shocked the Academy Awards when he refused his Oscar for mobster classic "The Godfather." Instead, he sent indigenous activist Sacheen Littlefeather to refuse the award and give her a platform to protest the treatment of Native Americans in Hollywood, and more importantly, bring attention to the standoff between federal agents and Native Americans at Wounded Knee that was under a media blackout. Littlefeather delivered a shortened version of his message amid boos; The New York Times later printed Brando's letter in its entirety , and the media blackout at Wounded Knee was lifted.
#29. Bill Clinton's "Presidential Address to Columbine High School"
Delivered May 20, 1999, at Dakota Ridge High School, Littleton, Colo.
One of the most difficult jobs of the U.S. President is to act as "consoler-in-chief" when tragedy strikes the nation. President Bill Clinton found himself in that position—and, in the eyes of many, set the standard for future American leaders —after the shooting at Columbine High School left 12 students and one teacher dead. In the speech given a month after the tragedy, Clinton traveled to Colorado to offer support to grieving families and try to come to terms with an event that " pierced the soul of America ."
#28. Eleanor Roosevelt's "On the Adoption of the Declaration of Human Rights"
Delivered Dec. 9, 1948, in Paris, France
Eleanor Roosevelt dedicated her life to human rights around the world, serving as the chair of the United Nations Human Rights Commission after World War II. In that position, she pushed for creation of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which lays out 30 articles affirming " that man must have freedom in which to develop his full stature and through common effort to raise the level of human dignity."
#27. Stokely Carmichael's "Black Power"
Delivered Oct. 29, 1966, in Berkeley, Calif.
Stokely Carmichael firmly believed in nonviolent protest in the early days of the civil rights movement, but as the years wore on, he became convinced that "black power for black people" was needed to jump-start the next phase of the civil rights project. Black power, later adopted by groups like the Black Panther Party, required a sense of solidarity between black people and the election of black representatives. As his speech demonstrates , this wasn't an inherently violent concept, but rather questions the notion of nonviolence because, as Carmichael points out, "white people beat up black people every day—don't nobody talk about nonviolence."
#26. Aung San Suu Kyi's "Freedom from Fear"
Delivered Jan. 1 1990, in Myanmar (formerly Burma)
Daughter of the founder of the modern Burmese military and a key figure in Burmese independence, Aung San Suu Kyi followed in her father's footsteps to become a leader in the push for democratic government in the country. The military placed her under house arrest on-and-off for over 20 years while she continued to push for democracy, including in this speech, which calls for "a united determination to persevere in the struggle, to make sacrifices in the name of enduring truths, to resist the corrupting influences of desire, ill will, ignorance and fear." She ascended to governmental power in 2010 with global praise and hope for change, but the recent ethnic cleansing of a minority group in the country threatens her legacy as an advocate for freedom .
#25. Emmeline Pankhurst's "Freedom or Death"
Delivered Nov. 13, 1913, in Hartford, Conn.
The early decades of the 1900s brought new energy and activism to the push for women's suffrage in England, just as it did in the United States and Canada. Emmeline Pankhurst delivered this speech on a fundraising tour of the U.S. after a long period of hunger striking and arrests, using imagery from the American Revolution and other powerful metaphors to justify militant tactics adopted by her group in the push for the vote.
#24. Severn Cullis-Suzuki's "Speech to the UN Summit in Rio"
Delivered in 1992, in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Twelve-year-old Severn Cullis-Suzuki became "The Girl Who Silenced the World for Five Minutes" after she stunned the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development with a plea for older generations to work to improve the environment. Her demand that "If [adults] don't know how to fix it, please stop breaking it!" echoes those of modern child climate activists like Greta Thunberg, who has led a worldwide movement of school strikes pushing for action on the climate crisis.
#23. Nellie McClung's "Should Men Vote?"
Delivered Jan. 29, 1914, in Winnipeg, Canada
The Canadian women's suffrage movement was kicked into high gear when prominent activist Nellie McClung turned a rejection of the request for the vote into a piece of theater. Drawing on humor and showmanship, she presented a mock trial of men asking women legislators for suffrage, arguing that "manhood suffrage has not been a success in the unhappy countries where it has been tried," among other satirical moments. McClung later campaigned against the party that previously denied her the right to vote, finally winning suffrage for white Manitoban women in 1916.
#22. Ronald Reagan's "Remarks at the Brandenburg Gate"
Delivered June 12, 1987, in West Berlin, Germany
It might be hard to believe, but, coming just a few short years before the fall of the Berlin Wall and the Soviet Union, President Ronald Reagan's cry of "Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!" didn't make much of a splash when he first gave his speech. It didn't reach its status as a famous piece of American political rhetoric until the wall actually began to come down in 1989. While some scholars claim it helped Reagan build support for his plans to work with the Soviet Union, others believe the Wall's destruction had far more to do with reforms going on inside the USSR.
#21. William Faulkner's Nobel lecture
Delivered Jan. 10, 1950, in Stockholm, Sweden
Author of stories rooted in the American South, William Faulkner's Nobel lecture ( for a prize he didn't even want! ) spoke to deeply American concerns. He addresses the difficulty in creating art in an age of anxiety over atomic destruction, noting that until a writer relearns their craft under this condition, " he will write as though he stood among and watched the end of man ." He ends the address rejecting this possibility, offering a surprisingly hopeful view in an age characterized by fear of a nuclear holocaust.
#20. John F. Kennedy's Inaugural Address
Delivered Jan. 20, 1961, in Washington D.C.
One line from President John F. Kennedy's Inaugural Address has endured in the American imagination for nearly half a century: "My fellow Americans: Ask not what your country can do for you—ask what you can do for your country." However, Kennedy's call to public service has overshadowed the fact that most of the speech focused on global issues. As Kennedy was elected near the height of tensions in the Cold War, he felt the need to address both the Soviet Union and allies abroad to reassure them of his competency and desire for global peace.
#19. Lou Gehrig's "Farewell to Baseball Address"
Delivered July 4, 1939, at Yankee Stadium, The Bronx, N.Y.
The crowd at Yankee Stadium sat silent as Lou "The Iron Horse" Gehrig addressed his retirement from baseball after being diagnosed with a disease that would later be named after him. Declaring himself "the luckiest man on the face of the earth," he spoke briefly of the "awful lot [of things] to live for," including his fans, his teammates, and his family members. Following the address, he received a two-minute standing ovation and was showered with gifts and praise.
#18. Winston Churchill's "We Shall Fight on the Beaches"
Delivered: June 4, 1940, in London, England
In the first five weeks after he took over as Prime Minister, Winston Churchill gave three major speeches addressing the worsening war in France. The second of these dealt with the intensifying situation in France. Implying that battle might come to Britain, he declared that "we shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets" and never surrender. Parliament praised the rousing address, but the public didn't hear it in Churchill's own words until after the war had ended and caused public pessimism after it was read by broadcasters .
#17. Mahatma Gandhi's "Quit India"
Delivered Aug. 8, 1942, in Bombay (now Mumbai), India
Mohandas "Mahatma" Gandhi became the face of Indian independence as he organized the "Quit India" movement, which, as he laid out in the speech to fellow leaders , would coerce the British to voluntarily leave India using nonviolent protest. His fellow leaders agreed, passing a resolution to that effect, but thousands of arrests followed and Gandhi's speech was suppressed. Underground presses published his speech, and his call to "either free India or die in the attempt" became a rallying point for the movement.
#16. Nelson Mandela's "I am prepared to die"
Delivered April 20, 1964, in Pretoria, South Africa
The address Nelson Mandela gave instead of testimony at his trial for alleged sabotage became the defining speech of the anti-apartheid movement—and of his legacy as an advocate for equality in South Africa. In it, he argues that his cause is correct and explains his views, before launching into his famous conclusion, in which he states a free and equal state is "an ideal for which I am prepared to die." Mandela was sentenced to life in prison but did not die there, instead continuing his advocacy from prison before his release 27 years later.
#15. William Jennings Bryan's "Against Imperialism"
Delivered Aug. 8, 1900, in Indianapolis, Ind.
Perennial presidential candidate (but never winner) William Jennings Bryan advocated against American imperialism shortly after U.S. victory in the Spanish-American War allowed the country to begin building an empire. He appealed to American ideals, pointing out the lack of "full citizenship" offered to Puerto Ricans and Filipinos, and decried the "gun-powder gospel" that argued imperial wars should be fought due to Christianity. Unfortunately, his status as perennial presidential loser continued into the early 1900s and none of his proposed reforms were taken into consideration.
#14. Dolores Huerta's speech at the NFWA march and rally
Delivered April 10, 1966, in Sacramento, Calif.
Dolores Huerta worked alongside César Chávez to establish the National Farm Workers Association and direct the Delano grape strike, where she quickly emerged as a leading feminist figure. Her speech at the NFWA march illustrates her dedication and zeal , exclaiming "La huelga [the strike] and la causa is our cry, and everyone must listen. Viva la huelga!" Huerta's success with the Delano strike led to continued labor organizing and support for feminist causes, activities which she continues today.
#13. Gabriel García Márquez's "The Solitude of Latin America"
Delivered Dec. 8, 1982, in Stockholm, Sweden
Gabriel García Márquez, storied Colombian author whose books "One Hundred Years of Solitude" and "Love in the Time of Cholera" helped fuel the Latin American literature boom, used his Nobel acceptance speech to make a political statement . In it, he spoke of Latin America's isolation in the world, despite decades of imperialism and outside influence in the region. However, with the same magical realism for which his writing was famous, he envisioned " a new and sweeping utopia of life ...where the races condemned to one hundred years of solitude will have, at last and forever, a second opportunity on earth."
#12. Ryan White's "Testimony before the President's Commission on AIDS"
Delivered: March 3, 1988, in Washington D.C.
Born with a rare blood disorder, Ryan White became infected with HIV as a young child because of the factor 8 used for his treatment, which was collected using untested, anonymous blood donors. After his diagnosis in 1984, White attempted to return to school but faced huge stigma and attempts to bar him from the classroom, experiences which formed the basis of his testimony before the commission. This speech, and the court battles over his schooling, led to his becoming a leading HIV/AIDS activist, dispelling myths about the disease for the American public before his death in 1990 at 18.
#11. Elie Wiesel's "The Perils of Indifference"
Delivered April 12, 1999, in Washington D.C.
Eliezer "Elie" Wiesel survived the Holocaust as a teenager, losing his family in the process. The experience fueled his lifelong activism ; he became an educator about the Holocaust and advocate of victims of other atrocities, such as apartheid in South Africa and genocides around the world. His "Perils of Indifference" speech criticized those who ignored the horrors of the Holocaust and reminded listeners that " indifference is not a response " and "in denying [victims] their humanity we betray our own."
#10. Anita Hill's Opening Statement to the Senate Judiciary Committee
Delivered Oct. 11, 1991, in Washington D.C.
Anita Hill's testimony at the Supreme Court confirmation of Clarence Thomas, alleging that he sexually harassed her, proved to be a powerful and occasionally painful day in Washington D.C. Hill, a black woman, shared her experience staring down a Senate Judiciary Committee composed entirely of white men, who have since admitted to mishandling Hill's testimony . Thomas was confirmed to the bench despite Hill's allegations, but her testimony in part spurred record-breaking numbers of women to run for elected office and is seen by some as a precursor to the modern #MeToo movement.
#9. Hillary Rodham Clinton's "Women's Rights are Human Rights"
Delivered Sept. 5, 1995, in Beijing, China
Advisors to then-First Lady Hillary Rodham Clinton advised her to soften her rhetoric in her speech at the United Nations Fourth World Congress on Women , but Clinton refused, seizing the opportunity to shine a spotlight on the abuse of women in China and around the world. Though she is not the first person to declare " human rights are women's rights and women's rights are human rights, once and for all," she popularized use of the phrase on that day, in a speech that defined Clinton's career apart from her husband's. Since then, it's become a rallying cry in the fight for women's rights and became a focal point in Clinton's 2016 bid for president.
#8. Franklin D. Roosevelt's 1941 State of the Union Address
Delivered Jan. 6, 1941, in Washington D.C.
Delivered just under a year before the attack on Pearl Harbor, President Franklin D. Roosevelt's 1941 State of the Union emphasized the value of democracy in a world embroiled in a devastating war. It's most famous for FDR's declaration of the four freedoms : freedom of speech, freedom of worship, freedom from want (meaning economic security), and freedom from fear (meaning global disarmament and prevention of wars).
#7. César Chávez's "The Mexican American and the Church"
Delivered: March 10, 1968, in Delano, Calif.
César Chávez is an iconic figure in movements for labor rights and Latino rights due to his organization and leadership of the National Farm Workers Association (alongside colleague Dolores Huerta), particularly during the five-year Delano grape strike. Chávez adopted historical tactics of nonviolence and resistance, such as fasting; after breaking a 25-day fast, the religious Chávez spoke at a conference about the relationship between Mexican Americans and the church, calling on the ministry to use their " tremendous spiritual and economic power " to support the striking farm workers. His work with the NFWA formed a cornerstone of the Chicano Movement that pushed for Mexican American rights in the 1960s and beyond.
#6. Harvey Milk's "Hope Speech"
Delivered June 25, 1978, in San Francisco, Calif.
Harvey Milk, the first openly gay man to be elected to public office in California, used his "Hope Speech" as his stump speech during his 1977 run for the San Francisco Board of Supervisors; he expanded on it for its final delivery at the San Francisco Gay Freedom Day Parade the following year. The rousing speech emphasizes the importance of electing LGBTQ+ leaders so that young LGBTQ+ people across the country surrounded by homophobia can have those to look up to and regain their hope. Milk's life was cut short when he was assassinated only months later, but he continued to inspire hope as a martyr for the LGBTQ+ movement.
#5. Malcom X's "The Ballot or the Bullet"
Delivered April 12, 1964, at King Solomon Baptist Church, Detroit, Mich. (also delivered nine days earlier in Cleveland)
Malcolm X stands alongside Martin Luther King as one of the leading figures of the civil rights movement, but X's advocacy for black nationalism and defeating racism by "any means necessary" often conflicted with King's support for integration and nonviolent protest. "The Ballot or the Bullet," considered by many to be one of Malcolm X's best orations, urges African Americans to exercise their power at the ballot box in the 1964 election and select leaders who will pass civil rights legislation and care about issues affecting black communities.
#4. Dennis Shepard's "Statement to the Court"
Delivered Nov. 4, 1999, in Laramie, Wyo.
Matthew Shepard, a young gay man attending college in Laramie, Wyo., was beaten to death in an apparent hate crime in October 1998. His father gave an emotional impact statement to the court (since excerpted in several movies and plays about the crime), emphasizing the effect of his son's life and death on his family and the world. After their son's death, Dennis Shepard and his wife, Judy, helped to fulfill the promise he made "to see that this never, ever happens to another person or another family again" by advocating for the passage of hate crime legislation that became the Matthew Shepard and James Byrd, Jr., Hate Crimes Prevention Act of 2009.
#3. Sylvia Rivera's "Y'all Better Quiet Down"
Delivered in 1973, at Washington Square Park, New York City, N.Y.
On June 28, 1969, police raided the Stonewall Inn, a gay bar in New York City, and the riots that resulted jumpstarted the modern LGBTQ+ rights movement. Sylvia Rivera participated in the riots that day (she's said to have thrown one of the first bottles at police) and began a storied career as an activist . Rivera, a transgender Puerto Rican woman, wasn't afraid to call out what she saw as shortcomings in the movement; she delivered her "Y'all Better Quiet Down" to the crowd at the Christopher Street Liberation Rally, decrying white, middle-class gay men and lesbians for ignoring transgender people and other marginalized voices in the fight for LGBTQ+ rights.
#2. John F. Kennedy's "We choose to go to the moon"
Delivered Sept. 12, 1962, at Rice Stadium, Houston, Texas
In 1962, the U.S. and Soviet Union were in the thick of the Space Race, and the U.S. government was fighting over how much money to put into the project to put a man on the moon. With this speech , President Kennedy put an end to the squabbling; he laid out why it was important for the U.S. to lead the way to the stars and famously declared, " We choose to go to the moon in this decade and do the other things, not because they are easy, but because they are hard." This speech inspired the American people, and the Apollo mission was made a priority, leading to Neil Armstrong's first steps on the moon on July 20, 1969.
#1. Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a Dream"
Delivered Aug. 28, 1963, in Washington D.C.
While Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. was giving a speech on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial during the 1963 March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, gospel singer (and King's close friend) Mahalia Jackson spurred him to go off-script , calling out, "Tell them about the dream, Martin! Tell them about the dream!" He did, and today, King's dream that his four children "live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character" is one of the most lauded pieces of American rhetoric. It cemented King's place as the face of the civil rights movement, for which he's still celebrated today. Pictured here is Martin Luther King (center) leading the "March on Washington" the day he gave the speech.
Trending Now
50 best movies of the '60s.

50 most meaningful jobs in America

100 best John Wayne movies

Best black and white films of all time


10 of the Most Famous and Inspirational Speeches from History
By Dr Oliver Tearle (Loughborough University)
What makes a great and iconic speech? There are numerous examples of brilliant orators and speechmakers throughout history, from classical times to the present day. What the best speeches tend to have in common are more than just a solid intellectual argument: they have emotive power, or, for want of a more scholarly word, ‘heart’. Great speeches rouse us to action, or move us to tears – or both.
But of course, historic speeches are often also associated with landmark, or watershed, moments in a nation’s history: when Churchill delivered his series of wartime speeches to Britain in 1940, it was against the backdrop of a war which was still in its early, uncertain stages. And when Martin Luther King stood in front of the Lincoln Memorial in 1963, he was addressing a crowd who, like him, were marching for justice, freedom, and civil rights for African Americans.
Let’s take a closer look at ten of the best and most famous speeches from great moments in history.
Abraham Lincoln, ‘ Gettysburg Address ’ (1863).
The Gettysburg Address is one of the most famous speeches in American history, yet it was extremely short – just 268 words, or less than a page of text – and Abraham Lincoln, who gave the address, wasn’t even the top billing .
The US President Abraham Lincoln gave this short address at the dedication of the Soldiers’ National Cemetery in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania on 19 November 1863. At the time, the American Civil War was still raging, and the Battle of Gettysburg had been the bloodiest battle in the war, with an estimated 23,000 casualties.
Lincoln’s speech has been remembered while Edward Everett’s – the main speech delivered on that day – has long been forgotten because Lincoln eschewed the high-flown allusions and wordy style of most political orators of the nineteenth century. Instead, he addresses his audience in plain, homespun English that is immediately relatable and accessible.
Sojourner Truth, ‘ Ain’t I a Woman? ’ (1851).
Sometimes known as ‘Ar’n’t I a Woman?’, this is a speech which Sojourner Truth, a freed African slave living in the United States, delivered in 1851 at the Women’s Convention in Akron, Ohio. The women in attendance were being challenged to call for the right to vote.
In her speech, Sojourner Truth attempts to persuade the audience to give women the vote . As both an ex-slave and a woman, Sojourner Truth knew about the plight of both groups of people in the United States. Her speech shows her audience the times: change is coming, and it is time to give women the rights that should be theirs.
John Ball, ‘ Cast off the Yoke of Bondage ’ (1381).
The summer of 1381 was a time of unrest in England. The so-called ‘Peasants’ Revolt’, led by Wat Tyler (in actual fact, many of the leaders of the revolt were more well-to-do than your average peasant), gathered force until the rebels stormed London, executing a number of high-ranking officials, including the Archbishop of Canterbury and Lord Chancellor, Simon Sudbury.
Alongside Tyler, the priest John Ball was an important leading figure of the rebellion. His famous couplet, ‘When Adam delved and Eve span, / Who was then the gentleman?’ sums up the ethos of the Peasants’ Revolt: social inequality was unheard of until men created it.
Winston Churchill, ‘ We Shall Fight on the Beaches ’ (1940).
Winston Churchill had only recently assumed the role of UK Prime Minister when he gave the trio of wartime speeches which have gone down in history for their rhetorical skill and emotive power. This, for our money, is the best of the three.
Churchill gave this speech in the House of Commons on 4 June 1940. Having brought his listeners up to speed with what has happened, Churchill comes to the peroration of his speech : by far the most famous part. He reassures them that if nothing is neglected and all arrangements are made, he sees no reason why Britain cannot once more defend itself against invasion: something which, as an island nation, it has always been susceptible to by sea, and now by air.
Even if it takes years, and even if Britain must defend itself alone without any help from its allies, this is what must happen. Capitulation to the Nazis is not an option. The line ‘if necessary for years; if necessary, alone’ is sure to send a shiver down the spine, as is the way Churchill barks ‘we shall never surrender!’ in the post-war recording of the speech he made several years later.
William Faulkner, ‘ The Agony and the Sweat ’ (1950).
This is the title sometimes given to one of the most memorable Nobel Prize acceptance speeches: the American novelist William Faulkner’s acceptance of the Nobel Prize for Literature at Stockholm in 1950.
In his speech, Faulkner makes his famous statement about the ‘duty’ of writers: that they should write about ‘the human heart in conflict with itself’, as well as emotions and themes such as compassion, sacrifice, courage, and hope. He also emphasises that being a writer is hard work, and involves understanding human nature in all its complexity. But good writing should also remind readers what humankind is capable of.
Emmeline Pankhurst, ‘ The Plight of Women ’ (1908).
Pankhurst (1858-1928) was the leader of the British suffragettes, campaigning – and protesting – for votes for women. After she realised that Asquith’s Liberal government were unlikely to grand women the vote, the Women’s Social and Political Union, founded by Pankhurst with her daughter Christabel, turned to more militant tactics to shift public and parliamentary opinion.
Her emphasis in this speech is on the unhappy lot most women could face, in marriage and in motherhood. She also shows how ‘man-made’ the laws of England are, when they are biased in favour of men to the detriment of women’s rights.
This speech was given at the Portman Rooms in London in 1908; ten years later, towards the end of the First World War, women over 30 were finally given the vote. But it would be another ten years, in 1928 – the year of Pankhurst’s death – before the voting age for women was equal to that for men (21 years).
Franklin Roosevelt, ‘ The Only Thing We Have to Fear Is Fear Itself ’ (1933).
This is the title by which Roosevelt’s speech at his inauguration in 1933 has commonly become known, and it has attained the status of a proverb. Roosevelt was elected only a few years after the Wall Street Crash of 1929 which ushered in the Great Depression.
Roosevelt’s famous line in the speech, which offered hope to millions of Americans dealing with unemployment and poverty, was probably inspired by a line from Henry David Thoreau, a copy of whose writings FDR had been gifted shortly before his inauguration. The line about having nothing to fear except fear itself was, in fact, only added into the speech the day before the inauguration took place, but it ensured that the speech went down in history.
Marcus Tullius Cicero, ‘ Among Us You Can Dwell No Longer ’ (63 BC).
Of all of the great classical orators, perhaps the greatest of all was the Roman statesman, philosopher, and speechmaker, Cicero (whose name literally means ‘chickpea’).
This is probably his best-known speech. At the Temple of Jupiter in Rome, Cicero addressed the crowd, but specifically directed his comments towards Lucius Catiline, who was accused of plotting a conspiracy to set fire to the capital and stage and insurrection. The speech was considered such a fine example of Roman rhetoric that it was a favourite in classrooms for centuries after, as Brian MacArthur notes in The Penguin Book of Historic Speeches .
Queen Elizabeth I, ‘ The Heart and Stomach of a King ’ (1588).
Queen Elizabeth I’s speech to the troops at Tilbury is among the most famous and iconic speeches in English history. On 9 August 1588, Elizabeth addressed the land forces which had been mobilised at the port of Tilbury in Essex, in preparation for the expected invasion of England by the Spanish Armada.
When she gave this speech, Elizabeth was in her mid-fifties and her youthful beauty had faded. But she had learned rhetoric as a young princess, and this training served her well when she wrote and delivered this speech (she was also a fairly accomplished poet ).
She famously tells her troops: ‘I know I have the body but of a weak and feeble woman; but I have the heart and stomach of a king, and of a king of England too’. She acknowledged the fact that her body was naturally less masculine and strong than the average man’s, but it is not mere physical strength that will win the day. It is courage that matters.
Martin Luther King, ‘ I Have a Dream ’ (1963).
Let’s conclude this selection of the best inspirational speeches with the best-known of all of Martin Luther King’s speeches. The occasion for this piece of oratorical grandeur was the march on Washington , which saw some 210,000 men, women, and children gather at the Washington Monument in August 1963, before marching to the Lincoln Memorial. King reportedly stayed up until 4am the night before he was due to give the speech, writing it out.
King’s speech imagines a collective vision of a better and more equal America which is not only shared by many Black Americans, but by anyone who identifies with their fight against racial injustice, segregation, and discrimination.
Discover more from Interesting Literature
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Type your email…
1 thought on “10 of the Most Famous and Inspirational Speeches from History”
- Pingback: Top Motivational Speeches That Shook the World - Kiiky
Comments are closed.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
- Faculty Experts
- Events Calendar
‘I Have a Dream’ leads top 100 speeches of the century
The mastery and magic of Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.’s famous “I Have a Dream” speech earned it top honors in a new list of the 100 best political speeches of the 20th century.
|
|
Compiled by researchers at UW–Madison and Texas A&M University, the list reflects the opinions of 137 leading scholars of American public address. The experts were asked to recommend speeches on the basis of social and political impact, and rhetorical artistry.
Stephen Lucas, UW–Madison professor of communication arts, and Martin Medhurst, professor of speech communication at Texas A&M, say the new list confirms that excellence in American public oratory has thrived during the last 100 years.
“While it has become fashionable to bemoan the death of eloquence, this list makes it clear that the 20th century has produced public speeches of the highest order,” Lucas says.
King delivered “I Have a Dream” during the civil rights march on Washington Aug. 28, 1963. Says Medhurst, “His eloquent vision of a day when his own children ‘would live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character’ persuasively articulated the American dream within the context of the civil rights struggle.”
Following “I Have a Dream” on the list are John F. Kennedy’s 1961 inaugural address, best known for the famous challenge, “Ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country.” Franklin D. Roosevelt’s first inaugural address, March 4, 1933 and his declaration of war, Dec. 8, 1941, make FDR the only person with two speeches in the top five.
Barbara Jordon’s keynote address to the Democratic National Convention, July 12, 1976, completes the top five. Surveyed scholars cited her eloquence, power and masterful delivery, as well as the historical importance of the first keynote by an African-American woman.
The rest of the top 10 are:
- Richard Nixon’s “Checkers” speech of 1952.
- Malcom X’s 1964 “The Ballot or the Bullet.”
- Ronald Reagan’s 1986 eulogy of the Challenger astronauts.
- JFK’s address to the Houston Ministerial Association during the 1960 presidential campaign.
- Lyndon Johnson’s “We Shall Overcome” speech that helped secure passage of the Voting Rights Act in 1965.
Lucas and Medhurst say the list has yielded some interesting information, including the fact that three of the top 10 speeches were delivered by African Americans, reflecting the importance of the civil rights movement and the black oral tradition.
Twenty-three of the top 100 were delivered by women. Two speeches by women in the 1990s fared especially well: Hillary Rodham Clinton’s 1995 address at the United Nations World Conference on Women (No. 35), well ahead of her husband’s only ranked speech (No. 92), made at a prayer service for Oklahoma City bombing victims. And while George Bush didn’t make the list at all, wife Barbara Bush’s 1990 commencement address at Wellesley College ranked No. 47.
Lucas notes that the list, which also includes speeches by Jesse Jackson, Eleanor Roosevelt, Mario Cuomo, and famed attorney Clarence Darrow, reminds us of the power of the spoken word throughout American history. “Despite our computer age,” he says, “there is still no substitute for public speech to lead, galvanize, console and inspire.”
Tony Dolan, the writer of Ronald Reagan’s “Evil Empire” speech (No. 29), calls the new survey a document of record. “One hundred years from now, historians will see here evidence of both how clearly and how poorly we saw our time,” he says. “The list is sure to cause controversy.”
Tags: research

My Favorite Speeches for Rhetorical Analysis: 10 Speeches for Middle School ELA and High School English
Teaching rhetorical analysis is one of my absolute favorite units to complete with my students. I love teaching my students about rhetorical strategies and devices, analyzing what makes an effective and persuasive argument, and reading critical speeches with my students. Here is a quick list of some of my favorite speeches for rhetorical analysis.

I absolutely LOVE teaching rhetorical analysis. I think it might be one of my favorite units to teach to my high school students. There are just so many different text options to choose from. Here is a list of some of my favorite speeches to include in my rhetorical analysis teaching unit.
10 Speeches for Teaching Rhetorical Analysis
1. the gettysburg address (abraham lincoln).

Some notable things to mention in this speech include allusion and parallel structure. To make your analysis more meaningful, point out these devices to students and explain how these devices enhance the meaning of the text.
Teaching Resource : The Gettysburg Address Rhetorical Analysis Activity Packet
2. Lou Gehrig’s Farewell Speech (Lou Gehrig)
This speech is one that many of my athletes love to analyze, and it is an excellent exemplar text to teach pathos. And like The Gettysburg Address, it is short. This is another speech that you can read, analyze, and even write about in one class period.
When I use this speech in my class, I have students look for examples of pathos. Mainly, I have them look at word choice, tone, and mood. How does Lou Gehrig’s choice of words affect his tone and the overall mood of the speech?
3. I Have a Dream (Martin Luther King, Jr.)

In the classroom, it is important to point out the sermonic feel to the speech and also to have your students look for calls to action and pathos. Have your students look for tone, allusions, and word choice to help them notice these rhetoric expressions throughout it.
Teaching Resource : I Have a Dream Close Read and Rhetorical Analysis
4. Speech at the March on Washington (Josephine Baker)
This is another important speech that held a lot of importance for the changes that needed to be made in America. The speech is a shorter one, so in the classroom, it will not take as long to analyze it, and students can understand the significance of the use of rhetoric in a shorter amount of time than some other speeches.
When teaching this speech, I like to remind my students to search for devices that portray an excellent example of the pathos that is so present in this speech. Some of these devices could be mood, repetition, and diction.
5. Steve Jobs’ Commencement Speech (Steve Jobs)

In class, it is good to have your students annotate and analyze the speech just as they have done for the others. The organization of the speech will help them to notice the similarities and differences between each point Jobs makes.
6. Space Shuttle Challenger (Ronald Reagan)
This speech represents a strong sense of pathos as a movement to help the American people cope with loss after the deaths of the astronauts aboard the Challenger. It is another speech that is not too long, so it should not take a long time to both analyze and annotate the entire speech.
When teaching this speech in class, be sure to mention how pathos is the driving force behind the speech, through the tone and the diction. How does Reagan use emotion to focus on the astronauts as humans, rather than solely focusing on the tragedy?
7. The Perils of Indifference (Elie Wiesel)
This speech is a good one to teach because it both makes students question their own lives, but also how the world works. The speech relies on pathos, and a little ethos too, to get the audience to feel the full effect of the tragedy of the Holocaust and what the speaker went through. It is a long speech so it may take longer for the students to fully grasp all the details that make it such a persuasive speech.
When I teach this speech, I like to have students annotate every place they notice an example of pathos, and then have them explain why in their annotations this makes them feel an emotion. The same with the ethos, and then we can further analyze the rest together.
8. 9/11 Address to the Nation (George W. Bush)
This speech shows another example of the use of pathos in the midst of a tragedy. The President wanted to show the American people how much he was feeling for those lost in the tragedy of 9/11. It is not a long speech, but the amount of emotion within the words is significant for students to notice.
When teaching this speech, it is essential that students look very closely at each part of it, noticing each piece that reveals tone, mood, and other literary devices. How do the different devices add to the pathos of the speech?
FREE TEACHING ACTIVITY : September 11 Address to the Nation Sampler
Teaching Resource : September 11 Address to the Nation Rhetorical Analysis Unit
9. We are Virginia Tech (Nikki Giovanni)
This speech is probably the shortest speech on this list but provides one of the most emotional and pathos-filled rhetoric. This describes another tragedy that is spoken about with pathos to give the audience a safe feeling after such an emotional thing. Students can spend time analyzing the different devices that make the piece so strong in its emotion.
In the classroom, make sure your students make a note of the repetition, and what that does for the speech. Does it make the emotion more impactful? How does it make the audience feel like they are a part of something bigger?
10. Woman’s Right to the Suffrage (Susan B. Anthony)
This is another short speech that holds a lot of power within it. A lot of students will enjoy reading this to see how much the country has changed, and how this speech may have some part in influencing this change. It is a great speech to help teach logos in the classroom, and it will not take a long time to analyze.
Make sure your students notice, and they also understand, the use of allusions within the speech. These allusions help to establish the use of logos, as Anthony wants the use of American historical documents to show how logical her argument is.
Ready-For-You Rhetorical Analysis Teaching Unit

You might also be interested in my blog post about 15 rhetorical analysis questions to ask your students.
Teaching rhetorical analysis and speeches in the classroom is a great way to teach informational text reading standards.
Rhetorical Analysis Teaching Resources:
These resources follow reading standards for informational text and are ideal for secondary ELA teachers.
- Rhetorical Analysis Unit with Sticky Notes
- Ethos, Pathos, Logos: Understanding Rhetorical Appeals\
- Rhetorical Analysis Mini Flip Book
Join the Daring English Teacher community!
Subscribe to receive freebies, teaching ideas, and my latest content by email.
I won’t send you spam. Unsubscribe at any time.
Built with ConvertKit
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

SUBSCRIBE NOW
Uncategorized
40 famous persuasive speeches you need to hear.
Written by Kai Xin Koh

Across eras of calamity and peace in our world’s history, a great many leaders, writers, politicians, theorists, scientists, activists and other revolutionaries have unveiled powerful rousing speeches in their bids for change. In reviewing the plethora of orators across tides of social, political and economic change, we found some truly rousing speeches that brought the world to their feet or to a startling, necessary halt. We’ve chosen 40 of the most impactful speeches we managed to find from agents of change all over the world – a diversity of political campaigns, genders, positionalities and periods of history. You’re sure to find at least a few speeches in this list which will capture you with the sheer power of their words and meaning!
1. I have a dream by MLK
“I have a dream that one day down in Alabama, with its vicious racists, with its governor having his lips dripping with the words of interposition and nullification – one day right there in Alabama little black boys and black girls will be able to join hands with little white boys and white girls as sisters and brothers. I have a dream today. I have a dream that one day every valley shall be exalted, and every hill and mountain shall be made low, the rough places will be made plain, and the crooked places will be made straight, and the glory of the Lord shall be revealed and all flesh shall see it together. This is our hope. This is the faith that I go back to the South with. With this faith we will be able to hew out of the mountain of despair a stone of hope. With this faith we will be able to transform the jangling discords of our nation into a beautiful symphony of brotherhood. With this faith we will be able to work together, to pray together, to struggle together, to go to jail together, to stand up for freedom together, knowing that we will be free one day. This will be the day, this will be the day when all of God’s children will be able to sing with new meaning “My country ’tis of thee, sweet land of liberty, of thee I sing. Land where my father’s died, land of the Pilgrim’s pride, from every mountainside, let freedom ring!”
Unsurprisingly, Martin Luther King’s speech comes up top as the most inspiring speech of all time, especially given the harrowing conditions of African Americans in America at the time. In the post-abolition era when slavery was outlawed constitutionally, African Americans experienced an intense period of backlash from white supremacists who supported slavery where various institutional means were sought to subordinate African American people to positions similar to that of the slavery era. This later came to be known as the times of Jim Crow and segregation, which Martin Luther King powerfully voiced his vision for a day when racial discrimination would be a mere figment, where equality would reign.
2. Tilbury Speech by Queen Elizabeth I
“My loving people, We have been persuaded by some that are careful of our safety, to take heed how we commit our selves to armed multitudes, for fear of treachery; but I assure you I do not desire to live to distrust my faithful and loving people. Let tyrants fear. I have always so behaved myself that, under God, I have placed my chiefest strength and safeguard in the loyal hearts and good-will of my subjects; and therefore I am come amongst you, as you see, at this time, not for my recreation and disport, but being resolved, in the midst and heat of the battle, to live and die amongst you all; to lay down for my God, and for my kingdom, and my people, my honour and my blood, even in the dust. I know I have the body of a weak, feeble woman; but I have the heart and stomach of a king, and of a king of England too, and think foul scorn that Parma or Spain, or any prince of Europe, should dare to invade the borders of my realm; to which rather than any dishonour shall grow by me, I myself will take up arms, I myself will be your general, judge, and rewarder of every one of your virtues in the field. I know already, for your forwardness you have deserved rewards and crowns; and We do assure you on a word of a prince, they shall be duly paid. In the mean time, my lieutenant general shall be in my stead, than whom never prince commanded a more noble or worthy subject; not doubting but by your obedience to my general, by your concord in the camp, and your valour in the field, we shall shortly have a famous victory over these enemies of my God, of my kingdom, and of my people.”
While at war with Spain, Queen Elizabeth I was most renowned for her noble speech rallying the English troops against their comparatively formidable opponent. Using brilliant rhetorical devices like metonymy, meronymy, and other potent metaphors, she voiced her deeply-held commitment as a leader to the battle against the Spanish Armada – convincing the English army to keep holding their ground and upholding the sacrifice of war for the good of their people. Eventually against all odds, she led England to victory despite their underdog status in the conflict with her confident and masterful oratory.
3. Woodrow Wilson, address to Congress (April 2, 1917)
“The world must be made safe for democracy. Its peace must be planted upon the tested foundations of political liberty. We have no selfish ends to serve. We desire no conquest, no dominion. We seek no indemnities for ourselves, no material compensation for the sacrifices we shall freely make. We are but one of the champions of the rights of mankind. We shall be satisfied when those rights have been made as secure as the faith and the freedom of nations can make them. Just because we fight without rancor and without selfish object, seeking nothing for ourselves but what we shall wish to share with all free peoples, we shall, I feel confident, conduct our operations as belligerents without passion and ourselves observe with proud punctilio the principles of right and of fair play we profess to be fighting for. … It will be all the easier for us to conduct ourselves as belligerents in a high spirit of right and fairness because we act without animus, not in enmity toward a people or with the desire to bring any injury or disadvantage upon them, but only in armed opposition to an irresponsible government which has thrown aside all considerations of humanity and of right and is running amuck. We are, let me say again, the sincere friends of the German people, and shall desire nothing so much as the early reestablishment of intimate relations of mutual advantage between us—however hard it may be for them, for the time being, to believe that this is spoken from our hearts. We have borne with their present government through all these bitter months because of that friendship—exercising a patience and forbearance which would otherwise have been impossible. We shall, happily, still have an opportunity to prove that friendship in our daily attitude and actions toward the millions of men and women of German birth and native sympathy who live among us and share our life, and we shall be proud to prove it toward all who are in fact loyal to their neighbors and to the government in the hour of test. They are, most of them, as true and loyal Americans as if they had never known any other fealty or allegiance. They will be prompt to stand with us in rebuking and restraining the few who may be of a different mind and purpose. If there should be disloyalty, it will be dealt with with a firm hand of stern repression; but, if it lifts its head at all, it will lift it only here and there and without countenance except from a lawless and malignant few. It is a distressing and oppressive duty, gentlemen of the Congress, which I have performed in thus addressing you. There are, it may be, many months of fiery trial and sacrifice ahead of us. It is a fearful thing to lead this great peaceful people into war, into the most terrible and disastrous of all wars, civilization itself seeming to be in the balance. But the right is more precious than peace, and we shall fight for the things which we have always carried nearest our hearts—for democracy, for the right of those who submit to authority to have a voice in their own governments, for the rights and liberties of small nations, for a universal dominion of right by such a concert of free peoples as shall bring peace and safety to all nations and make the world itself at last free. To such a task we can dedicate our lives and our fortunes, everything that we are and everything that we have, with the pride of those who know that the day has come when America is privileged to spend her blood and her might for the principles that gave her birth and happiness and the peace which she has treasured. God helping her, she can do no other.”
On April 2, 1917, President Woodrow Wilson of the USA delivered his address to Congress, calling for declaration of war against what was at the time, a belligerent and aggressive Germany in WWI. Despite his isolationism and anti-war position earlier in his tenure as president, he convinced Congress that America had a moral duty to the world to step out of their neutral observer status into an active role of world leadership and stewardship in order to liberate attacked nations from their German aggressors. The idealistic values he preached in his speech left an indelible imprint upon the American spirit and self-conception, forming the moral basis for the country’s people and aspirational visions to this very day.
4. Ain’t I A Woman by Sojourner Truth
“That man over there says that women need to be helped into carriages, and lifted over ditches, and to have the best place everywhere. Nobody ever helps me into carriages, or over mud-puddles, or gives me any best place! And ain’t I a woman? Look at me! Look at my arm! I have ploughed and planted, and gathered into barns, and no man could head me! And ain’t I a woman? I could work as much and eat as much as a man – when I could get it – and bear the lash as well! And ain’t I a woman? I have borne thirteen children, and seen most all sold off to slavery, and when I cried out with my mother’s grief, none but Jesus heard me! And ain’t I a woman? … If the first woman God ever made was strong enough to turn the world upside down all alone, these women together ought to be able to turn it back , and get it right side up again! And now they is asking to do it, the men better let them.”
Hailing from a background of slavery and oppression, Sojourner Truth was one of the most revolutionary advocates for women’s human rights in the 1800s. In spite of the New York Anti-Slavery Law of 1827, her slavemaster refused to free her. As such, she fled, became an itinerant preacher and leading figure in the anti-slavery movement. By the 1850s, she became involved in the women’s rights movement as well. At the 1851 Women’s Rights Convention held in Akron, Ohio, she delivered her illuminating, forceful speech against discrimination of women and African Americans in the post-Civil War era, entrenching her status as one of the most revolutionary abolitionists and women’s rights activists across history.
5. The Gettsyburg Address by Abraham Lincoln
“Fondly do we hope, fervently do we pray, that this mighty scourge of war may speedily pass away. Yet, if God wills that it continue until all the wealth piled by the bondsman’s two hundred and fifty years of unrequited toil shall be sunk, and until every drop of blood drawn with the lash shall be paid by another drawn with the sword, as was said three thousand years ago, so still it must be said “the judgments of the Lord are true and righteous altogether.” With malice toward none, with charity for all, with firmness in the right as God gives us to see the right, let us strive on to finish the work we are in, to bind up the nation’s wounds, to care for him who shall have borne the battle and for his widow and his orphan, to do all which may achieve and cherish a just and lasting peace among ourselves and with all nations.”
President Abraham Lincoln had left the most lasting legacy upon American history for good reason, as one of the presidents with the moral courage to denounce slavery for the national atrocity it was. However, more difficult than standing up for the anti-slavery cause was the task of unifying the country post-abolition despite the looming shadows of a time when white Americans could own and subjugate slaves with impunity over the thousands of Americans who stood for liberation of African Americans from discrimination. He urged Americans to remember their common roots, heritage and the importance of “charity for all”, to ensure a “just and lasting peace” among within the country despite throes of racial division and self-determination.
6. Woman’s Rights to the Suffrage by Susan B Anthony
“For any State to make sex a qualification that must ever result in the disfranchisement of one entire half of the people is to pass a bill of attainder, or an ex post facto law, and is therefore a violation of the supreme law of the land. By it the blessings of liberty are for ever withheld from women and their female posterity. To them this government has no just powers derived from the consent of the governed. To them this government is not a democracy. It is not a republic. It is an odious aristocracy; a hateful oligarchy of sex; the most hateful aristocracy ever established on the face of the globe; an oligarchy of wealth, where the right govern the poor. An oligarchy of learning, where the educated govern the ignorant, or even an oligarchy of race, where the Saxon rules the African, might be endured; but this oligarchy of sex, which makes father, brothers, husband, sons, the oligarchs over the mother and sisters, the wife and daughters of every household–which ordains all men sovereigns, all women subjects, carries dissension, discord and rebellion into every home of the nation. Webster, Worcester and Bouvier all define a citizen to be a person in the United States, entitled to vote and hold office. The only question left to be settled now is: Are women persons? And I hardly believe any of our opponents will have the hardihood to say they are not. Being persons, then, women are citizens; and no State has a right to make any law, or to enforce any old law, that shall abridge their privileges or immunities. Hence, every discrimination against women in the constitutions and laws of the several States is today null and void, precisely as in every one against Negroes.”
Susan B. Anthony was a pivotal leader in the women’s suffrage movement who helped to found the National Woman Suffrage Association with Elizabeth Cady Stanton and fight for the constitutional right for women to vote. She courageously and relentlessly advocated for women’s rights, giving speeches all over the USA to convince people of women’s human rights to choice and the ballot. She is most well known for her act of righteous rebellion in 1872 when she voted in the presidential election illegally, for which she was arrested and tried unsuccessfully. She refused to pay the $100 fine in a bid to reject the demands of the American system she denounced as a ‘hateful oligarchy of sex’, sparking change with her righteous oratory and inspiring many others in the women’s suffrage movement within and beyond America.
7. Vladimir Lenin’s Speech at an International Meeting in Berne, February 8, 1916
“It may sound incredible, especially to Swiss comrades, but it is nevertheless true that in Russia, also, not only bloody tsarism, not only the capitalists, but also a section of the so-called or ex-Socialists say that Russia is fighting a “war of defence,” that Russia is only fighting against German invasion. The whole world knows, however, that for decades tsarism has been oppressing more than a hundred million people belonging to other nationalities in Russia; that for decades Russia has been pursuing a predatory policy towards China, Persia, Armenia and Galicia. Neither Russia, nor Germany, nor any other Great Power has the right to claim that it is waging a “war of defence”; all the Great Powers are waging an imperialist, capitalist war, a predatory war, a war for the oppression of small and foreign nations, a war for the sake of the profits of the capitalists, who are coining golden profits amounting to billions out of the appalling sufferings of the masses, out of the blood of the proletariat. … This again shows you, comrades, that in all countries of the world real preparations are being made to rally the forces of the working class. The horrors of war and the sufferings of the people are incredible. But we must not, and we have no reason whatever, to view the future with despair. The millions of victims who will fall in the war, and as a consequence of the war, will not fall in vain. The millions who are starving, the millions who are sacrificing their lives in the trenches, are not only suffering, they are also gathering strength, are pondering over the real cause of the war, are becoming more determined and are acquiring a clearer revolutionary understanding. Rising discontent of the masses, growing ferment, strikes, demonstrations, protests against the war—all this is taking place in all countries of the world. And this is the guarantee that the European War will be followed by the proletarian revolution against capitalism”
Vladimir Lenin remains to this day one of the most lauded communist revolutionaries in the world who brought the dangers of imperialism and capitalism to light with his rousing speeches condemning capitalist structures of power which inevitably enslave people to lives of misery and class stratification. In his genuine passion for the rights of the working class, he urged fellow comrades to turn the “imperialist war” into a “civil” or class war of the proletariat against the bourgeoisie. He encouraged the development of new revolutionary socialist organisations, solidarity across places in society so people could unite against their capitalist overlords, and criticised nationalism for its divisive effect on the socialist movement. In this speech especially, he lambasts “bloody Tsarism” for its oppression of millions of people of other nationalities in Russia, calling for the working class people to revolt against the Tsarist authority for the proletariat revolution to succeed and liberate them from class oppression.
8. I Have A Dream Speech by Mary Wollstonecraft
“If, I say, for I would not impress by declamation when Reason offers her sober light, if they be really capable of acting like rational creatures, let them not be treated like slaves; or, like the brutes who are dependent on the reason of man, when they associate with him; but cultivate their minds, give them the salutary, sublime curb of principle, and let them attain conscious dignity by feeling themselves only dependent on God. Teach them, in common with man, to submit to necessity, instead of giving, to render them more pleasing, a sex to morals. Further, should experience prove that they cannot attain the same degree of strength of mind, perseverance, and fortitude, let their virtues be the same in kind, though they may vainly struggle for the same degree; and the superiority of man will be equally clear, if not clearer; and truth, as it is a simple principle, which admits of no modification, would be common to both. Nay, the order of society as it is at present regulated would not be inverted, for woman would then only have the rank that reason assigned her, and arts could not be practised to bring the balance even, much less to turn it.”
In her vindication of the rights of women, Mary Wollstonecraft was one of the pioneers of the feminist movement back in 1792 who not only theorised and advocated revolutionarily, but gave speeches that voiced these challenges against a dominantly sexist society intent on classifying women as irrational less-than-human creatures to be enslaved as they were. In this landmark speech, she pronounces her ‘dream’ of a day when women would be treated as the rational, deserving humans they are, who are equal to man in strength and capability. With this speech setting an effective precedent for her call to equalize women before the law, she also went on to champion the provision of equal educational opportunities to women and girls, and persuasively argued against the patriarchal gender norms which prevented women from finding their own lot in life through their being locked into traditional institutions of marriage and motherhood against their will.
9. First Inaugural Speech by Franklin D Roosevelt
“So, first of all, let me assert my firm belief that the only thing we have to fear is…fear itself — nameless, unreasoning, unjustified terror which paralyzes needed efforts to convert retreat into advance. In every dark hour of our national life a leadership of frankness and of vigor has met with that understanding and support of the people themselves which is essential to victory. And I am convinced that you will again give that support to leadership in these critical days. … More important, a host of unemployed citizens face the grim problem of existence, and an equally great number toil with little return. Only a foolish optimist can deny the dark realities of the moment. Our greatest primary task is to put people to work. This is no unsolvable problem if we face it wisely and courageously. There are many ways in which it can be helped, but it can never be helped merely by talking about it. We must act and act quickly. … I am prepared under my constitutional duty to recommend the measures that a stricken Nation in the midst of a stricken world may require. These measures, or such other measures as the Congress may build out of its experience and wisdom, I shall seek, within my constitutional authority, to bring to speedy adoption. But in the event that the Congress shall fail to take one of these two courses, and in the event that the national emergency is still critical, I shall not evade the clear course of duty that will then confront me. I shall ask the Congress for the one remaining instrument to meet the crisis — broad Executive power to wage a war against the emergency, as great as the power that would be given to me if we were in fact invaded by a foreign foe.”
Roosevelt’s famous inaugural speech was delivered in the midst of a period of immense tension and strain under the Great Depression, where he highlighted the need for ‘quick action’ by Congress to prepare for government expansion in his pursuit of reforms to lift the American people out of devastating poverty. In a landslide victory, he certainly consolidated the hopes and will of the American people through this compelling speech.
10. The Hypocrisy of American Slavery by Frederick Douglass
“What to the American slave is your Fourth of July? I answer, a day that reveals to him more than all other days of the year, the gross injustice and cruelty to which he is the constant victim. To him your celebration is a sham; your boasted liberty an unholy license; your national greatness, swelling vanity; your sounds of rejoicing are empty and heartless; your shouts of liberty and equality, hollow mock; your prayers and hymns, your sermons and thanksgivings, with all your religious parade and solemnity, are to him mere bombast, fraud, deception, impiety, and hypocrisy – a thin veil to cover up crimes which would disgrace a nation of savages. There is not a nation of the earth guilty of practices more shocking and bloody than are the people of these United States at this very hour. Go search where you will, roam through all the monarchies and despotisms of the Old World, travel through South America, search out every abuse and when you have found the last, lay your facts by the side of the everyday practices of this nation, and you will say with me that, for revolting barbarity and shameless hypocrisy, America reigns without a rival.”
On 4 July 1852, Frederick Douglass gave this speech in Rochester, New York, highlighting the hypocrisy of celebrating freedom while slavery continues. He exposed the ‘revolting barbarity and shameless hypocrisy’ of slavery which had gone unabolished amidst the comparatively obscene celebration of independence and liberty with his potent speech and passion for the anti-abolition cause. After escaping from slavery, he went on to become a national leader of the abolitionist movement in Massachusetts and New York with his oratory and incisive antislavery writings. To this day, his fierce activism and devotion to exposing virulent racism for what it was has left a lasting legacy upon pro-Black social movements and the overall sociopolitical landscape of America.
11. Still I Rise by Maya Angelou
“You may write me down in history With your bitter, twisted lies, You may trod me in the very dirt But still, like dust, I’ll rise. Does my sassiness upset you? Why are you beset with gloom? ’Cause I walk like I’ve got oil wells Pumping in my living room. Just like moons and like suns, With the certainty of tides, Just like hopes springing high, Still I’ll rise. Did you want to see me broken? Bowed head and lowered eyes? Shoulders falling down like teardrops, Weakened by my soulful cries? Does my haughtiness offend you? Don’t you take it awful hard ’Cause I laugh like I’ve got gold mines Diggin’ in my own backyard. You may shoot me with your words, You may cut me with your eyes, You may kill me with your hatefulness, But still, like air, I’ll rise. Does my sexiness upset you? Does it come as a surprise That I dance like I’ve got diamonds At the meeting of my thighs? Out of the huts of history’s shame I rise Up from a past that’s rooted in pain I rise I’m a black ocean, leaping and wide, Welling and swelling I bear in the tide. Leaving behind nights of terror and fear I rise Into a daybreak that’s wondrously clear I rise Bringing the gifts that my ancestors gave, I am the dream and the hope of the slave. I rise I rise I rise.”
With her iconic poem Still I Rise , Maya Angelou is well-known for uplifting fellow African American women through her empowering novels and poetry and her work as a civil rights activist. Every bit as lyrical on the page, her recitation of Still I Rise continues to give poetry audiences shivers all over the world, inspiring women of colour everywhere to keep the good faith in striving for equality and peace, while radically believing in and empowering themselves to be agents of change. A dramatic reading of the poem will easily showcase the self-belief, strength and punch that it packs in the last stanza on the power of resisting marginalization.
12. Their Finest Hour by Winston Churchill
“What General Weygand called the Battle of France is over. I expect that the Battle of Britain is about to begin. Upon this battle depends the survival of Christian civilization. Upon it depends our own British life, and the long continuity of our institutions and our Empire. The whole fury and might of the enemy must very soon be turned on us. Hitler knows that he will have to break us in this Island or lose the war. If we can stand up to him, all Europe may be free and the life of the world may move forward into broad, sunlit uplands. But if we fail, then the whole world, including the United States, including all that we have known and cared for, will sink into the abyss of a new Dark Age made more sinister, and perhaps more protracted, by the lights of perverted science. Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves that, if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, “This was their finest hour.””
In the darkest shadows cast by war, few leaders have been able to step up to the mantle and effectively unify millions of citizens for truly sacrificial causes. Winston Churchill was the extraordinary exception – lifting 1940 Britain out of the darkness with his hopeful, convicted rhetoric to galvanise the English amidst bleak, dreary days of war and loss. Through Britain’s standalone position in WWII against the Nazis, he left his legacy by unifying the nation under shared sacrifices of the army and commemorating their courage.
13. A Room of One’s Own by Virginia Woolf
“Life for both sexes – and I looked at them (through a restaurant window while waiting for my lunch to be served), shouldering their way along the pavement – is arduous, difficult, a perpetual struggle. It calls for gigantic courage and strength. More than anything, perhaps, creatures of illusion as we are, it calls for confidence in oneself. Without self-confidence we are babes in the cradle. And how can we generate this imponderable quality, which is yet so invaluable, most quickly? By thinking that other people are inferior to oneself. By feeling that one has some innate superiority – it may be wealth, or rank, a straight nose, or the portrait of a grandfather by Romney – for there is no end to the pathetic devices of the human imagination – over other people. Hence the enormous importance to a patriarch who has to conquer, who has to rule, of feeling that great numbers of people, half the human race indeed, are by nature inferior to himself. It must indeed be one of the great sources of his power….Women have served all these centuries as looking-glasses possessing the magic and delicious power of reflecting the figure of man at twice its natural size. Without that power probably the earth would still be swamp and jungle. The glories of all our wars would be on the remains of mutton bones and bartering flints for sheepskins or whatever simple ornament took our unsophisticated taste. Supermen and Fingers of Destiny would never have existed. The Czar and the Kaiser would never have worn their crowns or lost them. Whatever may be their use in civilised societies, mirrors are essential to all violent and heroic action. That is why Napoleon and Mussolini both insist so emphatically upon the inferiority of women, for if they were not inferior, they would cease to enlarge. That serves to explain in part the necessity that women so often are to men. And it serves to explain how restless they are under her criticism; how impossible it is for her to say to them this book is bad, this picture is feeble, or whatever it may be, without giving far more pain and rousing far more anger than a man would do who gave the same criticism. For if she begins to tell the truth, the figure in the looking-glass shrinks; his fitness in life is diminished. How is he to go on giving judgment, civilising natives, making laws, writing books, dressing up and speechifying at banquets, unless he can see himself at breakfast and at dinner at least twice the size he really is?”
In this transformational speech , Virginia Woolf pronounces her vision that ‘a woman must have money and a room of her own if she is to write fiction’. She calls out the years in which women have been deprived of their own space for individual development through being chained to traditional arrangements or men’s prescriptions – demanding ‘gigantic courage’ and ‘confidence in oneself’ to brave through the onerous struggle of creating change for women’s rights. With her steadfast, stolid rhetoric and radical theorization, she paved the way for many women’s rights activists and writers to forge their own paths against patriarchal authority.
14. Inaugural Address by John F Kennedy
“In the long history of the world, only a few generations have been granted the role of defending freedom in its hour of maximum danger. I do not shrink from this responsibility–I welcome it. I do not believe that any of us would exchange places with any other people or any other generation. The energy, the faith, the devotion which we bring to this endeavor will light our country and all who serve it–and the glow from that fire can truly light the world. And so, my fellow Americans: ask not what your country can do for you–ask what you can do for your country. My fellow citizens of the world: ask not what America will do for you, but what together we can do for the freedom of man. Finally, whether you are citizens of America or citizens of the world, ask of us here the same high standards of strength and sacrifice which we ask of you. With a good conscience our only sure reward, with history the final judge of our deeds, let us go forth to lead the land we love, asking His blessing and His help, but knowing that here on earth God’s work must truly be our own.”
For what is probably the most historically groundbreaking use of parallelism in speech across American history, President JFK placed the weighty task of ‘asking what one can do for their country’ onto the shoulders of each American citizen. Using an air of firmness in his rhetoric by declaring his commitment to his countrymen, he urges each American to do the same for the broader, noble ideal of freedom for all. With his crucial interrogation of a citizen’s moral duty to his nation, President JFK truly made history.
15. Atoms for Peace Speech by Dwight Eisenhower
“To pause there would be to confirm the hopeless finality of a belief that two atomic colossi are doomed malevolently to eye each other indefinitely across a trembling world. To stop there would be to accept helplessly the probability of civilization destroyed, the annihilation of the irreplaceable heritage of mankind handed down to us from generation to generation, and the condemnation of mankind to begin all over again the age-old struggle upward from savagery towards decency, and right, and justice. Surely no sane member of the human race could discover victory in such desolation. Could anyone wish his name to be coupled by history with such human degradation and destruction?Occasional pages of history do record the faces of the “great destroyers”, but the whole book of history reveals mankind’s never-ending quest for peace and mankind’s God-given capacity to build. It is with the book of history, and not with isolated pages, that the United States will ever wish to be identified. My country wants to be constructive,not destructive. It wants agreements, not wars, among nations. It wants itself to live in freedom and in the confidence that the peoples of every other nation enjoy equally the right of choosing their own way of life. So my country’s purpose is to help us to move out of the dark chamber of horrors into the light, to find a way by which the minds of men, the hopes of men, the souls of men everywhere, can move forward towards peace and happiness and well-being.”
On a possibility as frightful and tense as nuclear war, President Eisenhower managed to convey the gravity of the world’s plight in his measured and persuasive speech centred on the greater good of mankind. Using rhetorical devices such as the three-part paratactical syntax which most world leaders are fond of for ingraining their words in the minds of their audience, he centers the discourse of the atomic bomb on those affected by such a world-changing decision in ‘the minds, hopes and souls of men everywhere’ – effectively putting the vivid image of millions of people’s fates at stake in the minds of his audience. Being able to make a topic as heavy and fraught with moral conflict as this as eloquent as he did, Eisenhower definitely ranks among some of the most skilled orators to date.
16. The Transformation of Silence into Language and Action by Audre Lorde
“I was going to die, if not sooner then later, whether or not I had ever spoken myself. My silences had not protected me. Your silence will not protect you. But for every real word spoken, for every attempt I had ever made to speak those truths for which I am still seeking, I had made contact with other women while we examined the words to fit a world in which we all believed, bridging our differences. What are the words you do not have yet? What do you need to say? What are the tyrannies you swallow day by day and attempt to make your own, until you will sicken and die of them, still in silence? Perhaps for some of you here today, I am the face of one of your fears. Because I am a woman, because I am black, because I am myself, a black woman warrior poet doing my work, come to ask you, are you doing yours?”
Revolutionary writer, feminist and civil rights activist Audre Lorde first delivered this phenomenal speech at Lesbian and Literature panel of the Modern Language Association’s December 28, 1977 meeting, which went on to feature permanently in her writings for its sheer wisdom and truth. Her powerful writing and speech about living on the margins of society has enlightened millions of people discriminated across various intersections, confronting them with the reality that they must speak – since their ‘silence will not protect’ them from further marginalization. Through her illuminating words and oratory, she has reminded marginalized persons of the importance of their selfhood and the radical capacity for change they have in a world blighted by prejudice and division.
17. 1965 Cambridge Union Hall Speech by James Baldwin
“What is dangerous here is the turning away from – the turning away from – anything any white American says. The reason for the political hesitation, in spite of the Johnson landslide is that one has been betrayed by American politicians for so long. And I am a grown man and perhaps I can be reasoned with. I certainly hope I can be. But I don’t know, and neither does Martin Luther King, none of us know how to deal with those other people whom the white world has so long ignored, who don’t believe anything the white world says and don’t entirely believe anything I or Martin is saying. And one can’t blame them. You watch what has happened to them in less than twenty years.”
Baldwin’s invitation to the Cambridge Union Hall is best remembered for foregrounding the unflinching differences in white and African Americans’ ‘system of reality’ in everyday life. Raising uncomfortable truths about the insidious nature of racism post-civil war, he provides several nuggets of thought-provoking wisdom on the state of relations between the oppressed and their oppressors, and what is necessary to mediate such relations and destroy the exploitative thread of racist hatred. With great frankness, he admits to not having all the answers but provides hard-hitting wisdom on engagement to guide activists through confounding times nonetheless.
18. I Am Prepared to Die by Nelson Mandela
“Above all, My Lord, we want equal political rights, because without them our disabilities will be permanent. I know this sounds revolutionary to the whites in this country, because the majority of voters will be Africans. This makes the white man fear democracy. But this fear cannot be allowed to stand in the way of the only solution which will guarantee racial harmony and freedom for all. It is not true that the enfranchisement of all will result in racial domination. Political division, based on colour, is entirely artificial and, when it disappears, so will the domination of one colour group by another. The ANC has spent half a century fighting against racialism. When it triumphs as it certainly must, it will not change that policy. This then is what the ANC is fighting. Our struggle is a truly national one. It is a struggle of the African people, inspired by our own suffering and our own experience. It is a struggle for the right to live. During my lifetime I have dedicated my life to this struggle of the African people. I have fought against white domination, and I have fought against black domination. I have cherished the ideal of a democratic and free society in which all persons will live together in harmony and with equal opportunities. It is an ideal for which I hope to live for and to see realised. But, My Lord, if it needs be, it is an ideal for which I am prepared to die.”
Apartheid is still considered one of these most devastating events of world history, and it would not have ended without the crucial effort and words of Nelson Mandela during his courageous political leadership. In this heartbreaking speech , he voices his utter devotion to the fight against institutionalised racism in African society – an ideal for which he was ‘prepared to die for’. Mandela continues to remind us today of his moral conviction in leading, wherein the world would likely to be a better place if all politicians had the same resolve and genuine commitment to human rights and the abolition of oppression as he did.
19. Critique on British Imperialism by General Aung San
“Do they form their observations by seeing the attendances at not very many cinemas and theatres of Rangoon? Do they judge this question of money circulation by paying a stray visit to a local bazaar? Do they know that cinemas and theatres are not true indicators, at least in Burma, of the people’s conditions? Do they know that there are many in this country who cannot think of going to these places by having to struggle for their bare existence from day to day? Do they know that those who nowadays patronise or frequent cinemas and theatres which exist only in Rangoon and a few big towns, belong generally to middle and upper classes and the very few of the many poor who can attend at all are doing so as a desperate form of relaxation just to make them forget their unsupportable existences for the while whatever may be the tomorrow that awaits them?”
Under British colonial rule, one of the most legendary nationalist leaders emerged from the ranks of the thousands of Burmese to boldly lead them towards independence, out of the exploitation and control under the British. General Aung San’s speech criticising British social, political and economic control of Burma continues to be scathing, articulate, and relevant – especially given his necessary goal of uniting the Burmese natives against their common oppressor. He successfully galvanised his people against the British, taking endless risks through nationalist speeches and demonstrations which gradually bore fruit in Burma’s independence.
20. Nobel Lecture by Mother Teresa
“I believe that we are not real social workers. We may be doing social work in the eyes of the people, but we are really contemplatives in the heart of the world. For we are touching the Body Of Christ 24 hours. We have 24 hours in this presence, and so you and I. You too try to bring that presence of God in your family, for the family that prays together stays together. And I think that we in our family don’t need bombs and guns, to destroy to bring peace–just get together, love one another, bring that peace, that joy, that strength of presence of each other in the home. And we will be able to overcome all the evil that is in the world. There is so much suffering, so much hatred, so much misery, and we with our prayer, with our sacrifice are beginning at home. Love begins at home, and it is not how much we do, but how much love we put in the action that we do. It is to God Almighty–how much we do it does not matter, because He is infinite, but how much love we put in that action. How much we do to Him in the person that we are serving.”
In contemporary culture, most people understand Mother Teresa to be the epitome of compassion and kindness. However, if one were to look closer at her speeches from the past, one would discover not merely her altruistic contributions, but her keen heart for social justice and the downtrodden. She wisely and gracefully remarks that ‘love begins at home’ from the individual actions of each person within their private lives, which accumulate into a life of goodness and charity. For this, her speeches served not just consolatory value or momentary relevance, as they still inform the present on how we can live lives worth living.
21. June 9 Speech to Martial Law Units by Deng Xiaoping
“This army still maintains the traditions of our old Red Army. What they crossed this time was in the true sense of the expression a political barrier, a threshold of life and death. This was not easy. This shows that the People’s Army is truly a great wall of iron and steel of the party and state. This shows that no matter how heavy our losses, the army, under the leadership of the party, will always remain the defender of the country, the defender of socialism, and the defender of the public interest. They are a most lovable people. At the same time, we should never forget how cruel our enemies are. We should have not one bit of forgiveness for them. The fact that this incident broke out as it did is very worthy of our pondering. It prompts us cool-headedly to consider the past and the future. Perhaps this bad thing will enable us to go ahead with reform and the open policy at a steadier and better — even a faster — pace, more speedily correct our mistakes, and better develop our strong points.”
Mere days before the 4 June 1989 Tiananmen Square uprising, Chinese Communist Party leader Deng Xiaoping sat with six party elders (senior officials) and the three remaining members of the Politburo Standing Committee, the paramount decision-making body in China’s government. The meeting was organised to discuss the best course of action for restoring social and political order to China, given the sweeping economic reforms that had taken place in the past decade that inevitably resulted in some social resistance from the populace. Deng then gave this astute and well-regarded speech, outlining the political complexities in shutting down student protests given the context of reforms encouraging economic liberalization already taking place, as aligned with the students’ desires. It may not be the most rousing or inflammatory of speeches, but it was certainly persuasive in voicing the importance of taking a strong stand for the economic reforms Deng was implementing to benefit Chinese citizens in the long run. Today, China is an economic superpower, far from its war-torn developing country status before Deng’s leadership – thanks to his foresight in ensuring political stability would allow China to enjoy the fruits of the massive changes they adapted to.
22. Freedom or Death by Emmeline Pankhurst
“You won your freedom in America when you had the revolution, by bloodshed, by sacrificing human life. You won the civil war by the sacrifice of human life when you decided to emancipate the negro. You have left it to women in your land, the men of all civilised countries have left it to women, to work out their own salvation. That is the way in which we women of England are doing. Human life for us is sacred, but we say if any life is to be sacrificed it shall be ours; we won’t do it ourselves, but we will put the enemy in the position where they will have to choose between giving us freedom or giving us death. Now whether you approve of us or whether you do not, you must see that we have brought the question of women’s suffrage into a position where it is of first rate importance, where it can be ignored no longer. Even the most hardened politician will hesitate to take upon himself directly the responsibility of sacrificing the lives of women of undoubted honour, of undoubted earnestness of purpose. That is the political situation as I lay it before you today.”
In 1913 after Suffragette Emily Davison stepped in front of King George V’s horse at the Epsom Derby and suffered fatal injuries, Emmeline Pankhurst delivered her speech to Connecticut as a call to action for people to support the suffragette movement. Her fortitude in delivering such a sobering speech on the state of women’s rights is worth remembering for its invaluable impact and contributions to the rights we enjoy in today’s world.
23. Quit India by Mahatma Gandhi
“We shall either free India or die in the attempt; we shall not live to see the perpetuation of our slavery. Every true Congressman or woman will join the struggle with an inflexible determination not to remain alive to see the country in bondage and slavery. Let that be your pledge. Keep jails out of your consideration. If the Government keep me free, I will not put on the Government the strain of maintaining a large number of prisoners at a time, when it is in trouble. Let every man and woman live every moment of his or her life hereafter in the consciousness that he or she eats or lives for achieving freedom and will die, if need be, to attain that goal. Take a pledge, with God and your own conscience as witness, that you will no longer rest till freedom is achieved and will be prepared to lay down your lives in the attempt to achieve it. He who loses his life will gain it; he who will seek to save it shall lose it. Freedom is not for the coward or the faint-hearted.”
Naturally, the revolutionary activist Gandhi had to appear in this list for his impassioned anti-colonial speeches which rallied Indians towards independence. Famous for leading non-violent demonstrations, his speeches were a key element in gathering Indians of all backgrounds together for the common cause of eliminating their colonial masters. His speeches were resolute, eloquent, and courageous, inspiring the hope and admiration of many not just within India, but around the world.
24. 1974 National Book Award Speech by Adrienne Rich, Alice Walker, Audre Lorde
“The statement I am going to read was prepared by three of the women nominated for the National Book Award for poetry, with the agreement that it would be read by whichever of us, if any, was chosen.We, Audre Lorde, Adrienne Rich, and Alice Walker, together accept this award in the name of all the women whose voices have gone and still go unheard in a patriarchal world, and in the name of those who, like us, have been tolerated as token women in this culture, often at great cost and in great pain. We believe that we can enrich ourselves more in supporting and giving to each other than by competing against each other; and that poetry—if it is poetry—exists in a realm beyond ranking and comparison. We symbolically join together here in refusing the terms of patriarchal competition and declaring that we will share this prize among us, to be used as best we can for women. We appreciate the good faith of the judges for this award, but none of us could accept this money for herself, nor could she let go unquestioned the terms on which poets are given or denied honor and livelihood in this world, especially when they are women. We dedicate this occasion to the struggle for self-determination of all women, of every color, identification, or derived class: the poet, the housewife, the lesbian, the mathematician, the mother, the dishwasher, the pregnant teen-ager, the teacher, the grandmother, the prostitute, the philosopher, the waitress, the women who will understand what we are doing here and those who will not understand yet; the silent women whose voices have been denied us, the articulate women who have given us strength to do our work.”
Adrienne Rich, Audre Lorde, and Alice Walker wrote this joint speech to be delivered by Adrienne Rich at the 1974 National Book Awards, based on their suspicions that the first few African American lesbian women to be nominated for the awards would be snubbed in favour of a white woman nominee. Their suspicions were confirmed, and Adrienne Rich delivered this socially significant speech in solidarity with her fellow nominees, upholding the voices of the ‘silent women whose voices have been denied’.
25. Speech to 20th Congress of the CPSU by Nikita Khruschev
“Considering the question of the cult of an individual, we must first of all show everyone what harm this caused to the interests of our Party. Vladimir Ilyich Lenin had always stressed the Party’s role and significance in the direction of the socialist government of workers and peasants; he saw in this the chief precondition for a successful building of socialism in our country. Pointing to the great responsibility of the Bolshevik Party, as ruling Party of the Soviet state, Lenin called for the most meticulous observance of all norms of Party life; he called for the realization of the principles of collegiality in the direction of the Party and the state. Collegiality of leadership flows from the very nature of our Party, a Party built on the principles of democratic centralism. “This means,” said Lenin, “that all Party matters are accomplished by all Party members – directly or through representatives – who, without any exceptions, are subject to the same rules; in addition, all administrative members, all directing collegia, all holders of Party positions are elective, they must account for their activities and are recallable.””
This speech is possibly the most famed Russian speech for its status as a ‘secret’ speech delivered only to the CPSU at the time, which was eventually revealed to the public. Given the unchallenged political legacy and cult of personality which Stalin left in the Soviet Union, Nikita Khruschev’s speech condemning the authoritarian means Stalin had resorted to to consolidate power as un-socialist was an important mark in Russian history.
26. The Struggle for Human Rights by Eleanor Roosevelt
“It is my belief, and I am sure it is also yours, that the struggle for democracy and freedom is a critical struggle, for their preservation is essential to the great objective of the United Nations to maintain international peace and security. Among free men the end cannot justify the means. We know the patterns of totalitarianism — the single political party, the control of schools, press, radio, the arts, the sciences, and the church to support autocratic authority; these are the age-old patterns against which men have struggled for three thousand years. These are the signs of reaction, retreat, and retrogression. The United Nations must hold fast to the heritage of freedom won by the struggle of its people; it must help us to pass it on to generations to come. The development of the ideal of freedom and its translation into the everyday life of the people in great areas of the earth is the product of the efforts of many peoples. It is the fruit of a long tradition of vigorous thinking and courageous action. No one race and on one people can claim to have done all the work to achieve greater dignity for human beings and great freedom to develop human personality. In each generation and in each country there must be a continuation of the struggle and new steps forward must be taken since this is preeminently a field in which to stand still is to retreat.”
Eleanor Roosevelt has been among the most well-loved First Ladies for good reason – her eloquence and gravitas in delivering every speech convinced everyone of her suitability for the oval office. In this determined and articulate speech , she outlines the fundamental values that form the bedrock of democracy, urging the rest of the world to uphold human rights regardless of national ideology and interests.
27. The Ballot or The Bullet by Malcolm X
“And in this manner, the organizations will increase in number and in quantity and in quality, and by August, it is then our intention to have a black nationalist convention which will consist of delegates from all over the country who are interested in the political, economic and social philosophy of black nationalism. After these delegates convene, we will hold a seminar; we will hold discussions; we will listen to everyone. We want to hear new ideas and new solutions and new answers. And at that time, if we see fit then to form a black nationalist party, we’ll form a black nationalist party. If it’s necessary to form a black nationalist army, we’ll form a black nationalist army. It’ll be the ballot or the bullet. It’ll be liberty or it’ll be death.”
Inarguably, the revolutionary impact Malcolm X’s fearless oratory had was substantial in his time as a radical anti-racist civil rights activist. His speeches’ emancipatory potential put forth his ‘theory of rhetorical action’ where he urges Black Americans to employ both the ballot and the bullet, strategically without being dependent on the other should the conditions of oppression change. A crucial leader in the fight for civil rights, he opened the eyes of thousands of Black Americans, politicising and convincing them of the necessity of fighting for their democratic rights against white supremacists.
28. Living the Revolution by Gloria Steinem
“The challenge to all of us, and to you men and women who are graduating today, is to live a revolution, not to die for one. There has been too much killing, and the weapons are now far too terrible. This revolution has to change consciousness, to upset the injustice of our current hierarchy by refusing to honor it, and to live a life that enforces a new social justice. Because the truth is none of us can be liberated if other groups are not.”
In an unexpected commencement speech delivered at Vassar College in 1970, Gloria Steinem boldly makes a call to action on behalf of marginalized groups in need of liberation to newly graduated students. She proclaimed it the year of Women’s Liberation and forcefully highlighted the need for a social revolution to ‘upset the injustice of the current hierarchy’ in favour of human rights – echoing the hard-hitting motto on social justice, ‘until all of us are free, none of us are free’.
29. The Last Words of Harvey Milk by Harvey Milk
“I cannot prevent some people from feeling angry and frustrated and mad in response to my death, but I hope they will take the frustration and madness and instead of demonstrating or anything of that type, I would hope that they would take the power and I would hope that five, ten, one hundred, a thousand would rise. I would like to see every gay lawyer, every gay architect come out, stand up and let the world know. That would do more to end prejudice overnight than anybody could imagine. I urge them to do that, urge them to come out. Only that way will we start to achieve our rights. … All I ask is for the movement to continue, and if a bullet should enter my brain, let that bullet destroy every closet door…”
As the first openly gay elected official in the history of California, Harvey Milk’s entire political candidature was in itself a radical statement against the homophobic status quo at the time. Given the dangerous times he was in as an openly gay man, he anticipated that he would be assassinated eventually in his political career. As such, these are some of his last words which show the utter devotion he had to campaigning against homophobia while representing the American people, voicing his heartbreaking wish for the bullet that would eventually kill him to ‘destroy every closet door’.
30. Black Power Address at UC Berkeley by Stokely Carmichael
“Now we are now engaged in a psychological struggle in this country, and that is whether or not black people will have the right to use the words they want to use without white people giving their sanction to it; and that we maintain, whether they like it or not, we gonna use the word “Black Power” — and let them address themselves to that; but that we are not going to wait for white people to sanction Black Power. We’re tired waiting; every time black people move in this country, they’re forced to defend their position before they move. It’s time that the people who are supposed to be defending their position do that. That’s white people. They ought to start defending themselves as to why they have oppressed and exploited us.”
A forceful and impressive orator, Stokely Carmichael was among those at the forefront of the civil rights movement, who was a vigorous socialist organizer as well. He led the Black Power movement wherein he gave this urgent, influential speech that propelled Black Americans forward in their fight for constitutional rights in the 1960s.
31. Speech on Vietnam by Lyndon Johnson
“The true peace-keepers are those men who stand out there on the DMZ at this very hour, taking the worst that the enemy can give. The true peace-keepers are the soldiers who are breaking the terrorist’s grip around the villages of Vietnam—the civilians who are bringing medical care and food and education to people who have already suffered a generation of war. And so I report to you that we are going to continue to press forward. Two things we must do. Two things we shall do. First, we must not mislead the enemy. Let him not think that debate and dissent will produce wavering and withdrawal. For I can assure you they won’t. Let him not think that protests will produce surrender. Because they won’t. Let him not think that he will wait us out. For he won’t. Second, we will provide all that our brave men require to do the job that must be done. And that job is going to be done. These gallant men have our prayers-have our thanks—have our heart-felt praise—and our deepest gratitude. Let the world know that the keepers of peace will endure through every trial—and that with the full backing of their countrymen, they are going to prevail.”
During some of the most harrowing periods of human history, the Vietnam War, American soldiers were getting soundly defeated by the Vietnamese in guerrilla warfare. President Lyndon Johnson then issued this dignified, consolatory speech to encourage patriotism and support for the soldiers putting their lives on the line for the nation.
32. A Whisper of AIDS by Mary Fisher
“We may take refuge in our stereotypes, but we cannot hide there long, because HIV asks only one thing of those it attacks. Are you human? And this is the right question. Are you human? Because people with HIV have not entered some alien state of being. They are human. They have not earned cruelty, and they do not deserve meanness. They don’t benefit from being isolated or treated as outcasts. Each of them is exactly what God made: a person; not evil, deserving of our judgment; not victims, longing for our pity people, ready for support and worthy of compassion. We must be consistent if we are to be believed. We cannot love justice and ignore prejudice, love our children and fear to teach them. Whatever our role as parent or policymaker, we must act as eloquently as we speak else we have no integrity. My call to the nation is a plea for awareness. If you believe you are safe, you are in danger. Because I was not hemophiliac, I was not at risk. Because I was not gay, I was not at risk. Because I did not inject drugs, I was not at risk. The lesson history teaches is this: If you believe you are safe, you are at risk. If you do not see this killer stalking your children, look again. There is no family or community, no race or religion, no place left in America that is safe. Until we genuinely embrace this message, we are a nation at risk.”
Back when AIDS research was still undeveloped, the stigma of contracting HIV was even more immense than it is today. A celebrated artist, author and speaker, Mary Fisher became an outspoken activist for those with HIV/AIDS, persuading people to extend compassion to the population with HIV instead of stigmatizing them – as injustice has a way of coming around to people eventually. Her bold act of speaking out for the community regardless of the way they contracted the disease, their sexual orientation or social group, was an influential move in advancing the human rights of those with HIV and spreading awareness on the discrimination they face.
33. Freedom from Fear by Aung San Suu Kyi
“The quintessential revolution is that of the spirit, born of an intellectual conviction of the need for change in those mental attitudes and values which shape the course of a nation’s development. A revolution which aims merely at changing official policies and institutions with a view to an improvement in material conditions has little chance of genuine success. Without a revolution of the spirit, the forces which produced the iniquities of the old order would continue to be operative, posing a constant threat to the process of reform and regeneration. It is not enough merely to call for freedom, democracy and human rights. There has to be a united determination to persevere in the struggle, to make sacrifices in the name of enduring truths, to resist the corrupting influences of desire, ill will, ignorance and fear. Saints, it has been said, are the sinners who go on trying. So free men are the oppressed who go on trying and who in the process make themselves fit to bear the responsibilities and to uphold the disciplines which will maintain a free society. Among the basic freedoms to which men aspire that their lives might be full and uncramped, freedom from fear stands out as both a means and an end. A people who would build a nation in which strong, democratic institutions are firmly established as a guarantee against state-induced power must first learn to liberate their own minds from apathy and fear.”
Famous for her resoluteness and fortitude in campaigning for democracy in Burma despite being put under house arrest by the military government, Aung San Suu Kyi’s speeches have been widely touted as inspirational. In this renowned speech of hers, she delivers a potent message to Burmese to ‘liberate their minds from apathy and fear’ in the struggle for freedom and human rights in the country. To this day, she continues to tirelessly champion the welfare and freedom of Burmese in a state still overcome by vestiges of authoritarian rule.
34. This Is Water by David Foster Wallace
“Our own present culture has harnessed these forces in ways that have yielded extraordinary wealth and comfort and personal freedom. The freedom all to be lords of our tiny skull-sized kingdoms, alone at the centre of all creation. This kind of freedom has much to recommend it. But of course there are all different kinds of freedom, and the kind that is most precious you will not hear much talk about much in the great outside world of wanting and achieving…. The really important kind of freedom involves attention and awareness and discipline, and being able truly to care about other people and to sacrifice for them over and over in myriad petty, unsexy ways every day. That is real freedom. That is being educated, and understanding how to think. The alternative is unconsciousness, the default setting, the rat race, the constant gnawing sense of having had, and lost, some infinite thing.”
Esteemed writer David Foster Wallace gave a remarkably casual yet wise commencement speech at Kenyon College in 2005 on the importance of learning to think beyond attaining a formal education. He encouraged hundreds of students to develop freedom of thought, a heart of sacrificial care for those in need of justice, and a consciousness that would serve them in discerning the right choices to make within a status quo that is easy to fall in line with. His captivating speech on what it meant to truly be ‘educated’ tugged at the hearts of many young and critical minds striving to achieve their dreams and change the world.
35. Questioning the Universe by Stephen Hawking
“This brings me to the last of the big questions: the future of the human race. If we are the only intelligent beings in the galaxy, we should make sure we survive and continue. But we are entering an increasingly dangerous period of our history. Our population and our use of the finite resources of planet Earth are growing exponentially, along with our technical ability to change the environment for good or ill. But our genetic code still carries the selfish and aggressive instincts that were of survival advantage in the past. It will be difficult enough to avoid disaster in the next hundred years, let alone the next thousand or million. Our only chance of long-term survival is not to remain inward-looking on planet Earth, but to spread out into space. The answers to these big questions show that we have made remarkable progress in the last hundred years. But if we want to continue beyond the next hundred years, our future is in space. That is why I am in favor of manned — or should I say, personned — space flight.”
Extraordinary theoretical physicist, cosmologist, and author Stephen Hawking was a considerable influence upon modern physics and scientific research at large, inspiring people regardless of physical ability to aspire towards expanding knowledge in the world. In his speech on Questioning the Universe, he speaks of the emerging currents and issues in the scientific world like that of outer space, raising and answering big questions that have stumped great thinkers for years.
36. 2008 Democratic National Convention Speech by Michelle Obama
“I stand here today at the crosscurrents of that history — knowing that my piece of the American dream is a blessing hard won by those who came before me. All of them driven by the same conviction that drove my dad to get up an hour early each day to painstakingly dress himself for work. The same conviction that drives the men and women I’ve met all across this country: People who work the day shift, kiss their kids goodnight, and head out for the night shift — without disappointment, without regret — that goodnight kiss a reminder of everything they’re working for. The military families who say grace each night with an empty seat at the table. The servicemen and women who love this country so much, they leave those they love most to defend it. The young people across America serving our communities — teaching children, cleaning up neighborhoods, caring for the least among us each and every day. People like Hillary Clinton, who put those 18 million cracks in the glass ceiling, so that our daughters — and sons — can dream a little bigger and aim a little higher. People like Joe Biden, who’s never forgotten where he came from and never stopped fighting for folks who work long hours and face long odds and need someone on their side again. All of us driven by a simple belief that the world as it is just won’t do — that we have an obligation to fight for the world as it should be. That is the thread that connects our hearts. That is the thread that runs through my journey and Barack’s journey and so many other improbable journeys that have brought us here tonight, where the current of history meets this new tide of hope. That is why I love this country.”
Ever the favourite modern First Lady of America, Michelle Obama has delivered an abundance of iconic speeches in her political capacity, never forgetting to foreground the indomitable human spirit embodied in American citizens’ everyday lives and efforts towards a better world. The Obamas might just have been the most articulate couple of rhetoricians of their time, making waves as the first African American president and First Lady while introducing important policies in their period of governance.
37. The Audacity of Hope by Barack Obama
“I’m not talking about blind optimism here — the almost willful ignorance that thinks unemployment will go away if we just don’t think about it, or the health care crisis will solve itself if we just ignore it. That’s not what I’m talking about. I’m talking about something more substantial. It’s the hope of slaves sitting around a fire singing freedom songs; the hope of immigrants setting out for distant shores; the hope of a young naval lieutenant bravely patrolling the Mekong Delta; the hope of a millworker’s son who dares to defy the odds; the hope of a skinny kid with a funny name who believes that America has a place for him, too. Hope — Hope in the face of difficulty. Hope in the face of uncertainty. The audacity of hope! In the end, that is God’s greatest gift to us, the bedrock of this nation. A belief in things not seen. A belief that there are better days ahead.”
Now published into a book, Barack Obama’s heart-capturing personal story of transformational hope was first delivered as a speech on the merits of patriotic optimism and determination put to the mission of concrete change. He has come to be known as one of the most favoured and inspiring presidents in American history, and arguably the most skilled orators ever.
38. “Be Your Own Story” by Toni Morrison
“But I’m not going to talk anymore about the future because I’m hesitant to describe or predict because I’m not even certain that it exists. That is to say, I’m not certain that somehow, perhaps, a burgeoning ménage a trois of political interests, corporate interests and military interests will not prevail and literally annihilate an inhabitable, humane future. Because I don’t think we can any longer rely on separation of powers, free speech, religious tolerance or unchallengeable civil liberties as a matter of course. That is, not while finite humans in the flux of time make decisions of infinite damage. Not while finite humans make infinite claims of virtue and unassailable power that are beyond their competence, if not their reach. So, no happy talk about the future. … Because the past is already in debt to the mismanaged present. And besides, contrary to what you may have heard or learned, the past is not done and it is not over, it’s still in process, which is another way of saying that when it’s critiqued, analyzed, it yields new information about itself. The past is already changing as it is being reexamined, as it is being listened to for deeper resonances. Actually it can be more liberating than any imagined future if you are willing to identify its evasions, its distortions, its lies, and are willing to unleash its secrets.”
Venerated author and professor Toni Morrison delivered an impressively articulate speech at Wellesley College in 2004 to new graduates, bucking the trend by discussing the importance of the past in informing current and future ways of living. With her brilliance and eloquence, she blew the crowd away and renewed in them the capacity for reflection upon using the past as a talisman to guide oneself along the journey of life.
39. Nobel Speech by Malala Yousafzai
“Dear brothers and sisters, the so-called world of adults may understand it, but we children don’t. Why is it that countries which we call “strong” are so powerful in creating wars but so weak in bringing peace? Why is it that giving guns is so easy but giving books is so hard? Why is it that making tanks is so easy, but building schools is so difficult? As we are living in the modern age, the 21st century and we all believe that nothing is impossible. We can reach the moon and maybe soon will land on Mars. Then, in this, the 21st century, we must be determined that our dream of quality education for all will also come true. So let us bring equality, justice and peace for all. Not just the politicians and the world leaders, we all need to contribute. Me. You. It is our duty. So we must work … and not wait. I call upon my fellow children to stand up around the world. Dear sisters and brothers, let us become the first generation to decide to be the last. The empty classrooms, the lost childhoods, wasted potential-let these things end with us.”
At a mere 16 years of age, Malala Yousafzai gave a speech on the severity of the state of human rights across the world, and wowed the world with her passion for justice at her tender age. She displayed tenacity and fearlessness speaking about her survival of an assassination attempt for her activism for gender equality in the field of education. A model of courage to us all, her speech remains an essential one in the fight for human rights in the 21st century.
40. Final Commencement Speech by Michelle Obama
“If you are a person of faith, know that religious diversity is a great American tradition, too. In fact, that’s why people first came to this country — to worship freely. And whether you are Muslim, Christian, Jewish, Hindu, Sikh — these religions are teaching our young people about justice, and compassion, and honesty. So I want our young people to continue to learn and practice those values with pride. You see, our glorious diversity — our diversities of faiths and colors and creeds — that is not a threat to who we are, it makes us who we are. So the young people here and the young people out there: Do not ever let anyone make you feel like you don’t matter, or like you don’t have a place in our American story — because you do. And you have a right to be exactly who you are. But I also want to be very clear: This right isn’t just handed to you. No, this right has to be earned every single day. You cannot take your freedoms for granted. Just like generations who have come before you, you have to do your part to preserve and protect those freedoms. … It is our fundamental belief in the power of hope that has allowed us to rise above the voices of doubt and division, of anger and fear that we have faced in our own lives and in the life of this country. Our hope that if we work hard enough and believe in ourselves, then we can be whatever we dream, regardless of the limitations that others may place on us. The hope that when people see us for who we truly are, maybe, just maybe they, too, will be inspired to rise to their best possible selves.”
Finally, we have yet another speech by Michelle Obama given in her final remarks as First Lady – a tear-inducing event for many Americans and even people around the world. In this emotional end to her political tenure, she gives an empowering, hopeful, expressive speech to young Americans, exhorting them to take hold of its future in all their diversity and work hard at being their best possible selves.
Amidst the bleak era of our current time with Trump as president of the USA, not only Michelle Obama, but all 40 of these amazing speeches can serve as sources of inspiration and hope to everyone – regardless of their identity or ambitions. After hearing these speeches, which one’s your favorite? Let us know in the comments below!
Article Written By: Kai Xin Koh
You may also like….

How To Prepare An Awesome Business Presentation
by Kai Xin Koh
Business presentations are inescapable in today’s world, where entrepreneurship and innovation are at the heart of businesses. With limited...
Sign Up for Winning With Stories!
- First Name *
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Why “I Have A Dream” Remains One Of History’s Greatest Speeches

Monday will mark the holiday in honor of Rev. Martin Luther King Jr. and Texas A&M University Professor of Communication Leroy Dorsey is reflecting on King’s celebrated “I Have a Dream” speech, one which he said is a masterful use of rhetorical traditions.
King delivered the famous speech as he stood before a crowd of 250,000 people in front of the Lincoln Memorial on Aug. 28, 1963 during the “March on Washington.” The speech was televised live to an audience of millions.
“He was not just speaking to African Americans, but to all Americans” ~ Leroy Dorsey
Dorsey , associate dean for inclusive excellence and strategic initiatives in the College of Liberal Arts, said one of the reasons the speech stands above all of King’s other speeches – and nearly every other speech ever written – is because its themes are timeless. “It addresses issues that American culture has faced from the beginning of its existence and still faces today: discrimination, broken promises, and the need to believe that things will be better,” he said.
Powerful Use of Rhetorical Devices
Dorsey said the speech is also notable for its use of several rhetorical traditions, namely the Jeremiad, metaphor-use and repetition.
The Jeremiad is a form of early American sermon that narratively moved audiences from recognizing the moral standard set in its past to a damning critique of current events to the need to embrace higher virtues.
“King does that with his invocation of several ‘holy’ American documents such as the Emancipation Proclamation and Declaration of Independence as the markers of what America is supposed to be,” Dorsey said. “Then he moves to the broken promises in the form of injustice and violence. And he then moves to a realization that people need to look to one another’s character and not their skin color for true progress to be made.”
Second, King’s use of metaphors explains U.S. history in a way that is easy to understand, Dorsey said.
“Metaphors can be used to connect an unknown or confusing idea to a known idea for the audience to better understand,” he said. For example, referring to founding U.S. documents as “bad checks” transformed what could have been a complex political treatise into the simpler ideas that the government had broken promises to the American people and that this was not consistent with the promise of equal rights.
The third rhetorical device found in the speech, repetition, is used while juxtaposing contrasting ideas, setting up a rhythm and cadence that keeps the audience engaged and thoughtful, Dorsey said.
“I have a dream” is repeated while contrasting “sons of former slaves and the sons of former slave owners” and “judged by the content of their character” instead of “judged by the color of their skin.” The device was used also with “let freedom ring” which juxtaposes states that were culturally polar opposites – Colorado, California and New York vs. Georgia, Tennessee and Mississippi.

Words That Moved A Movement
The March on Washington and King’s speech are widely considered turning points in the Civil Rights Movement, shifting the demand and demonstrations for racial equality that had mostly occurred in the South to a national stage.
Dorsey said the speech advanced and solidified the movement because “it became the perfect response to a turbulent moment as it tried to address past hurts, current indifference and potential violence, acting as a pivot point between the Kennedy administration’s slow response and the urgent response of the ‘marvelous new militancy’ [those fighting against racism].”
What made King such an outstanding orator were the communication skills he used to stir audience passion, Dorsey said. “When you watch the speech, halfway through he stops reading and becomes a pastor, urging his flock to do the right thing,” he said. “The cadence, power and call to the better nature of his audience reminds you of a religious service.”
Lessons For Today
Dorsey said the best leaders are those who can inspire all without dismissing some, and that King in his famous address did just that.
“He was not just speaking to African Americans in that speech, but to all Americans, because he understood that the country would more easily rise together when it worked together,” he said.
“I Have a Dream” remains relevant today “because for as many strides that have been made, we’re still dealing with the elements of a ‘bad check’ – voter suppression, instances of violence against people of color without real redress, etc.,” Dorsey said. “Remembering what King was trying to do then can provide us insight into what we need to consider now.”
Additionally, King understood that persuasion doesn’t move from A to Z in one fell swoop, but it moves methodically from A to B, B to C, etc., Dorsey said. “In the line ‘I have a dream that one day ,’ he recognized that things are not going to get better overnight, but such sentiment is needed to help people stay committed day-to-day until the country can honestly say, ‘free at last!'”
Media contact: Lesley Henton, 979-845-5591, [email protected].
Related Stories

MSC SCOLA Illuminates Path To Success
The three-day Student Conference on Latinx Affairs offers opportunities for learning, leadership and growth.

Asian Pacific Islander Desi American Heritage Month Events
A variety of campus organizations are inviting the Aggie community for unique cultural experiences.

MSC SCOLA 2023: ‘Focusing On The Present To Ensure Our Future’
The MSC Student Conference On Latinx Affairs (SCOLA) will challenge student leaders to focus on the influence of the Latinx community.
Recent Stories

Every Third Friday In Downtown Bryan Is ‘Maroon And White Night’ Starting Aug. 16
Texas A&M and System employees and their families are invited for festivities and special deals in historic Downtown Bryan.

Texas A&M Kicks Off Fall 2024 With Global Welcome Party
Enjoy music, food and prizes at Aggie Park Aug. 23 as the Department of Global Engagement celebrates Aggieland's international community.

Texas A&M Names Director Of Veteran Resources
John Fleming becomes only the second director in the department’s history, replacing Jerry Smith, who has retired.

Subscribe to the Texas A&M Today newsletter for the latest news and stories every week.
Explore the Constitution
- The Constitution
- Read the Full Text
Dive Deeper
Constitution 101 course.
- The Drafting Table
- Supreme Court Cases Library
- Founders' Library
- Constitutional Rights: Origins & Travels

Start your constitutional learning journey
- News & Debate Overview
Constitution Daily Blog
- America's Town Hall Programs
- Special Projects
Media Library

America’s Town Hall
Watch videos of recent programs.
- Education Overview
Constitution 101 Curriculum
- Classroom Resources by Topic
- Classroom Resources Library
- Live Online Events
- Professional Learning Opportunities
- Constitution Day Resources

Explore our new 15-unit high school curriculum.
- Explore the Museum
- Plan Your Visit
- Exhibits & Programs
- Field Trips & Group Visits
- Host Your Event
- Buy Tickets

New exhibit
The first amendment, looking at 10 great speeches in american history.
August 28, 2017 | by NCC Staff
Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have A Dream” speech certainly ranks highly in the pantheon of public speaking. Here is a look at the Dream speech and other addresses that moved people – and history.

King’s “Dream” speech from August 28, 1963 topped the list, followed by John F. Kennedy’s 1961 inaugural address and Franklin Roosevelt’s first inaugural address in 1933. In fact, three of King’s speeches were included in the top 50 speeches listed by the experts.
The eclectic list included public speeches from Barbara Jordan, Richard Nixon, Malcom X and Ronald Reagan in the top 10 of the rankings.
Link : Read The List
Public speaking has played an important role in our country’s story. Here is a quick look at some of the landmark speeches that often pop up in the discussion about public rhetoric.
1. Patrick Henry. “ Give Me Liberty Or Give Me Death .” In March 1775, Henry spoke to a Virginia convention considering a breakaway from British rule. “The war is actually begun. The next gale that sweeps from the north will bring to our ears the clash of resounding arms,” said Henry, who spoke without notes. “I know not what course others may take; but as for me, give me liberty, or give me death!”
2. George Washington’s first inaugural address . In 1789, the First President addressed the First Congress after his inauguration, setting the precedent for all inaugural speeches to follow. Washington enforced the need for the Constitution, concluding that “Parent of the Human Race … has been pleased to favor the American people with opportunities for deliberating in perfect tranquillity, and dispositions for deciding with unparalleled unanimity on a form of government for the security of their union and the advancement of their happiness.”
3. Frederick Douglass. “ The Hypocrisy Of American Slavery .” In 1852, Douglass was invited to speak at a public Fourth of July celebration in Rochester, N.Y. Instead of talking about the celebration, Douglass addressed the issue that was dividing the nation. “I will, in the name of humanity, which is outraged, in the name of liberty, which is fettered, in the name of the Constitution and the Bible, which are disregarded and trampled upon, dare to call in question and to denounce, with all the emphasis I can command, everything that serves to perpetuate slavery,” he said.
4. Abraham Lincoln. “ The Gettysburg Address .” The best known of Lincoln’s speeches was one of his shortest. Lincoln was asked to make a few remarks in November 1863 after featured speaker Edward Everett spoke for about two hours. “Fourscore and seven years ago our fathers brought forth, upon this continent, a new nation, conceived in liberty and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal,” Lincoln said in his opening paragraph. He spoke for two minutes.
5. William Jennings Bryan. “ Cross of Gold Speech .” A lesser-known contender for the Democratic presidential nomination in 1896, Bryan created a sensation with his speech that condemned the gold standard and held the promise of debt relief for farmers. “We shall answer their demands for a gold standard by saying to them, you shall not press down upon the brow of labor this crown of thorns. You shall not crucify mankind upon a cross of gold,” Bryan said with his arms spread in a crucifix-like position.
6. FDR’s first inaugural address . In 1933, the new President faced a nation in the grips of a deep economic recession. “First of all, let me assert my firm belief that the only thing we have to fear is fear itself -- nameless, unreasoning, unjustified terror which paralyzes needed efforts to convert retreat into advance,” Roosevelt said as he opened his powerful speech. The inaugural set the agenda for FDR’s 12 years in office.
7. Richard Nixon’s Checkers speech . Facing controversy as a vice presidential candidate, Nixon showed how television could be used as a powerful communications tool. In a stroke of political genius, Nixon spoke to the nation about his family finances, and then said the only gift he wouldn’t return was Checkers, the family dog.
8. JFK’s first inaugural address . The well-written 1961 speech is considered one of the best inaugural speeches ever. Rhetoric expert Dr. Max Atkinson told the BBC in 2011 what made the Kennedy speech special. “Tt was the first inaugural address by a U.S. president to follow the first rule of speech-preparation: analyze your audience - or, to be more precise at a time when mass access to television was in its infancy, analyze your audiences.”
9. Dr. King’s “I Have A Dream” speech . King’s speech at the Lincoln Memorial in August 1963, in front of 250,000 people, is also one of the most-analyzed speeches in modern history. But King hadn’t included the sequence about the “Dream” in his prepared remarks. Singer Mahalia Jackson yelled for King to speak about “the Dream,” and King improvised based on remarks he had made in earlier speeches.
10. Ronald Reagan in Berlin . President Reagan appeared at the 750 th birthday celebration for Berlin in 1987, speaking about 100 yards away from the Berlin Wall. Reagan first cited President Kennedy’s famous 1963 speech in Berlin, and then asked, “General Secretary Gorbachev, if you seek peace, if you seek prosperity for the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe, if you seek liberalization: Come here to this gate! Mr. Gorbachev, open this gate! Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!” A Reagan speech writer later said the State Department didn’t want Reagan to use the famous line, but Reagan decided to do it anyway.
More from the National Constitution Center

Constitution 101
Explore our new 15-unit core curriculum with educational videos, primary texts, and more.

Search and browse videos, podcasts, and blog posts on constitutional topics.

Founders’ Library
Discover primary texts and historical documents that span American history and have shaped the American constitutional tradition.
Modal title
Modal body text goes here.
Share with Students
- Material Detail: American Rhetoric: Top 100 Speeches
Material Detail
American Rhetoric: Top 100 Speeches
- Humanities / English / Language / Communications

- User Rating
- Comments (1) Comments
- Learning Exercises
- Bookmark Collections (9) Bookmark Collections
- Course ePortfolios
- Accessibility Info
- Report Broken Link
- Report as Inappropriate
More about this material
Disciplines with similar materials as american rhetoric: top 100 speeches, people who viewed this also viewed, other materials like american rhetoric: top 100 speeches.

Renee Young (Faculty)
This is a very good collection of speeches complete with recordings and text for most of them.
Edit Comment
Edit comment for material American Rhetoric: Top 100 Speeches
Delete Comment
This will delete the comment from the database. This operation is not reversible. Are you sure you want to do it?
Report a Broken Link
Thank you for reporting a broken "Go to Material" link in MERLOT to help us maintain a collection of valuable learning materials.
Would you like to be notified when it's fixed?
Do you know the correct URL for the link?
Link Reported as Broken
Link report failed, report an inappropriate material.
If you feel this material is inappropriate for the MERLOT Collection, please click SEND REPORT, and the MERLOT Team will investigate. Thank you!
Material Reported as Inappropriate
Material report failed, comment reported as inappropriate, leaving merlot.
You are being taken to the material on another site. This will open a new window.
Do not show me this again
Rate this Material
Search by ISBN?
It looks like you have entered an ISBN number. Would you like to search using what you have entered as an ISBN number?
Searching for Members?
You entered an email address. Would you like to search for members? Click Yes to continue. If no, materials will be displayed first. You can refine your search with the options on the left of the results page.
Tap into the power to persuade by using these 6 techniques of clear and compelling speech
Share this idea.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)

Politicians and other public figures deploy particular rhetorical devices to communicate their ideas and to convince people, and it’s time that we all learned how to use them, says speechwriter Simon Lancaster.
This post is part of TED’s “How to Be a Better Human” series, each of which contains a piece of helpful advice from someone in the TED community; browse through all the posts here.
There is a secret language of leadership — and it’s one that anyone can learn, says UK speechwriter Simon Lancaster in a TEDxVerona talk . He has made a career out of crafting addresses, remarks and talks for top politicians and CEOs of international corporations such as Nestle and Unilever, and continues to do so . Refreshingly, rather than clinging Gollum-like to what he’s learned and knows, he believes everyone should have access to the same tools that he and his colleagues use.
By tools, he’s not talking about special software or databases — he’s referring to rhetoric. Rhetoric has its roots in ancient Greece ( think: Aristotle ) as clear, convincing speech was seen as an essential component of communication and participation in a democracy. Instruction in rhetoric remained part of the curriculum in many secondary schools in Europe and the US until the 19th century.
“The reason we all used to learn rhetoric at school was because it was seen as a basic entry point to society,” explains Lancaster, who is based in London. “How could society be fair, unless everyone had equal ability to articulate and express themselves? Without it, your legal systems, your political systems, your financial systems are not fair.”
Yes, the power to persuade is just that — power.
Lancaster states there is only one school in England that still teaches rhetoric: Eton, the alma mater of 20 Prime Ministers (including current officeholder, Boris Johnson). He adds, “It should be of intense concern to all of us that education in this has been narrowed to a very small … elite.”
While Lancaster can’t send the world to Eton, he can share the 6 rhetorical building blocks needed to speak persuasively. Here they are:
Building block #1: Breathless sentences or phrases
Barack Obama gave an acceptance speech for the ages in 2008 after he was first elected president of the US. He spoke vividly of the challenges that lay ahead for the country: “Even as we celebrate tonight, we know that the challenges tomorrow will bring are the greatest of our lifetime: Two wars, a planet in peril, the worst financial crisis in a century.”
Lancaster wants us to pay special attention to the last part of that sentence, the “two wars, a planet in peril, the worst financial crisis in a century” part. Yes, it’s a stressful mouthful — not just because of the content but because of how it’s delivered. Short, staccato phrases like these mimic how we speak when we’re anxious and in a hurry. This technique helps communicate urgency to an audience.
Building block #2: Speaking in 3s
What’s the other rhetorical trick underlying “two wars, a planet in peril, the worst financial crisis in a century”? The rule of 3.
Humans are accustomed to things coming in 3s: whether it’s judges on American Idol , bowls of porridge in a fairy tale , or sides in a triangle. Our minds and ears have been trained by speeches (Abraham Lincoln’s “government of the people, for the people, by the people”); slogans (reduce, reuse, recycle); and book titles ( Elizabeth Gilbert ‘s memoir Eat, Pray, Love ). “You put your argument in 3s, it makes it sound more compelling, more convincing, more credible. Just like that,” says Lancaster.
Recall British PM Winston Churchill’s stirring triplet from the speech he delivered to Parliament on June 4, 1940 : “We shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight on the fields and in the streets.” Besides the rule of 3, he gave the line additional rhetorical firepower by repeating the opening clause.
Lancaster explains, “When we are emotional about things, our perspective distorts, and this then manifests in our speech. So this is the authentic sound of passion.” Doing this can catch an audience in the speaker’s enthusiasm.
Building block #3: Balanced statements
“Ask not what your country can do for you — ask what you can do for your country.” It’s a line from president John F Kennedy’s inspiring 1961 inaugural address , and one that’s stood the test of time. Why? Its balanced construction, says Lancaster. “If the sentence sounds as if it’s balanced, we imagine that the underlying thinking is balanced and our brain is tuned to like things that are balanced.”
Grouping balanced statements in 3s further amplifies the effect:
“We’re looking to the future, not the past.
We’re working together, not against one another.
We’re thinking about what we can do, not what we can’t.”
Building block #4: Metaphor
According to Lancaster, people use a metaphor once every 16 words on average ( side question: Where do statistics like this even come from? ). He declares, “Metaphor is probably the most powerful piece of political communication.”
Metaphors are rich in imagery and awake immediate feelings in people, so it follows that politicians love them and sprinkle them like birdseed (“like birdseed” is a simile, not a metaphor , and similes are other strong rhetorical tools to have in your kit). At times, they can employ them to point us to an ideal or aspiration. For example, in his farewell address , president Ronald Reagan movingly invoked America, h/t to John Winthrop, as a “shining city upon the hill.”
Too often, however, metaphors are used to manipulate, incite and denigrate. Politicians and talking heads could have called the 2015-16 refugee encampment in Calais, France, a “refugee camp” or “refugee settlement.” Instead, they deployed this loaded word: “jungle.” Lancaster says,“It’s planting in your mind the idea that migrants are like wild animals to be afraid of, that they are dangerous, that they represent a threat to you. This is a very dangerous metaphor because this is the language of genocide; it’s the language of hate.” Unfortunately, media outlets picked up “Calais jungle” and used it as their shorthand identifier of the camp, extending the metaphor’s reach.
Building block #5: Exaggeration
In the same way that we get breathless when they’re speaking with passion, our speech distorts in another significant way. We exaggerate. So when we’re sitting down to a meal after having eaten little that day, we tell our family and friends: “I love this pizza.” But when we say things like this to each other, we also realize it’s a bit of distortion: We do not love the pizza in the same way that we love our children or parents or the planet, and everyone present knows that.
Similarly, politicians and leaders might say things like “I’ve waited my whole life to say these words” or “I will work to achieve this with all my heart and soul.” These utterances are indeed over the top, but because they’re acceptable and even welcome since they echo how we speak.
Building block #6: Rhyming
Starting from childhood, many of us are taught concepts through rhymes — such as “an apple a day keeps the doctor away” or “i before e except after c.” With their musicality, they’re a pleasing informational snack that sticks in memories like a musical earworm .
Rhymes can seem corny, but sprinkled in at the right time, they can be incredibly potent. We all remember the pithy “If it doesn’t fit, you must acquit” from defense attorney Johnnie Cochran during O.J. Simpson’s 1995 murder trial.
Rhyming’s appeal comes “down to what linguists talk about as the processing fluency of language — how easy is language to swallow?” says Lancaster. “If you speak using long words and long sentences, it’s like giving someone a steak and asking them to swallow it. Whereas if you give them something pithy, like a rhyme, it’s like asking them to just sip on some Prosecco.”
These six tricks can help us speak directly to people’s instinctive, emotional and logical brains, and they are extremely effective, says Lancaster. There’s no need for us to be in the public eye to use them in order to sway others or make our words stay in people’s minds. Even if we never employ them in our own lives, it’s equally important for us to recognize them. Politicians, con artists and advertisers utilize them to win votes, spread opinions, or sell products people don’t need. By being alert to these rhetorical devices, we can be better citizens and consumers.
To learn more about rhetoric, watch this:
Watch Simon Lancaster’s TEDxVerona talk here:
About the author
Daryl Chen is the Ideas Editor at TED.
- how to be a better human
- public speaking
- simon lancaster
TED Talk of the Day

How to make radical climate action the new normal

3 strategies for effective leadership, from a former astronaut

Feeling unseen by your boss? Here’s what you can do

Let’s stop calling them “soft skills” -- and call them “real skills” instead

There’s a know-it-all at every job — here’s how to deal

The 7 types of people you need in your life to be resilient

Perfectionism holding you back? 3 ways to shift the habit

The unseen forces that can cause your great new idea to crash and burn

Have you quietly quit? Your next step: Go to the neutral zone

6 ways to give that aren't about money
How one scientist is growing miniature brains in her lab

A simple trick to help you speak in public without showing your nerves

One effective way to manage stage fright: Make it a habit

A political party for the whole world -- and you're invited to join
.
, , , , .
4 Ways to Use Rhetorical Devices to Make Powerful Speeches (with Examples)
Hrideep barot.
- Speech Writing

I am certain all of us have come across powerful speeches, novels, or presentations that left us speechless at some point. But have you wondered how the speaker or the author managed to do so?
How did they manage to make almost everyone in the audience riveted? You might have attributed this skill of captivating the audience to good public speaking, which is partially true but the other half of this lies in their use of magic tools which are referred to as rhetorical devices.
A rhetorical device is a technique that is used by a speaker or an author for conveying a particular message to the audience in such a way that it provokes an emotional response to a particular action. It is a linguistic tool, whose employment can be used to construct an argument or make an existing one more compelling .
To put it simply, rhetorical devices are devices used to spice up your conversations, work presentations, and speeches. They are often used to provoke an emotional response and make the matter of the speech more compelling, with the goal of persuading the audience.
Why are rhetorical techniques important?
Why should rhetorical devices be used? What impact do they have? Well, here’s why,
There is one common thing between the world’s famous speeches and presentations, which is their ability to create an emotional connection with the audience. The way in which a speaker makes the audience feel is very important as that feeling will stay with the audience long after the speech or the presentation is over. This emotional response is evoked with the help of rhetorical devices.
Apart from this, rhetorical devices help you become more persuasive. It also aids in composing successful presentations and writings. It helps you make your speech crisp and improves the understanding of the audience.
Moreover, with the correct rhetorical devices, it enables you to make stronger arguments and a way of handling controversial topics. It also has a powerful impact on the audience helping them remember the ideas better through repetition or grammatical manipulation.
Most used rhetorical devices
In order to know how to use these magic tools, it is crucial to know some of these most used rhetorical devices and also its application in a speech.
1. Alliteration
This is the repetition of sounds of two or more neighboring words. This is usually used to put emphasis and to draw attention. For instance, safety and security Ate apples all afternoon
2. Anadiplosis
Repetition of the last word in a phrase at the beginning of the next phrase or sentence. For example, Fear leads to anger, anger leads to hate and hate leads to suffering –Yoda, Star Wars
3. Antistrophe
This is repetition of words at the end of consecutive phrases/clauses. It can be termed as a specific type of repetition. “What lies behind us and what lies before us are tiny compared to what lies within us.”
The above sentence is quoted by Ralph Waldo Emerson, a prominent essayist. Here, the words ‘What lies’ is repeated leading to the creation of a poetic effect.
4. Antithesis
In this, two opposite and contrasting ideas are juxtaposed. For example, “Ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country.”
Here, two contrasting ideas are proposed in the same sentence in such a way that it shows the strikingly different ideas showing a compare and contrast kind of situation.
A repeated word or phrase split up by another word, to display strong emotion. Understanding it with an example, Free at last! Free at last! Thank god we are free at last!
6. Ellipsis
In this, few words are depicting an event is omitted making the readers ponder about the narrative gaps. For instance, “Fourscore and seven years ago our fathers brought forth…the proposition that all men are created equal.”
This is the start of Abraham Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address, where the three dots are ellipsis points suggesting a time lapse.
This is a simple method of double negatives that present a positive statement. It is often used to express irony. This is commonly used in conversations as well.
For example, ‘She is not thin’ OR ‘You are not unfamiliar with poetry’.
8. Hyperbole
This is an expression of mere exaggeration, often used to draw attention to the severity of the matter or to make a strong point. This is also frequently used in day to day language.
For instance,
‘I called her a thousand times’
‘It raining cats and dogs’.
9. Epistrophe
Repetition of words at the end of successive phrases for a poetic effect. An example of this could be the famous definition of democracy given by Abraham Lincoln, “… and that the government of the people, by the people and for the people shall not perish from the earth.”
10. Personification
Attributing human qualities to inanimate objects. It aids in a better explanation of ideas and concepts.
For instance, ‘The thunder roared in the evening’
‘The brutal wind bullied the trees compelling them into giving up their leaves’
11. Epiphora
Repetition of a word/phrase at the end of every clause. An instance of this could be a speech given by Steve Jobs where this technique is effectively used,
“Well, these are their home screens . And again, as you recall, this is the iPhone’s homescreen. This is what their contacts look like . This is what iPhone’s contacts look like .”
12. Anaphora
This is slightly different from Epiphora in the sense that the repetition of the word/phrase is at the beginning of the two or more sentences or clauses.
For instance, “They’re the women whose names we’ll never know. They are domestic workers and farm workers. They are working in factories and they work in restaurants and in academia, and engineering, medicine and science. They are part of the world of tech and politics and in business. They are athletes in the Olympics and they are soldiers in the military.”
This is a small chunk of a speech made by Oprah Winfrey at the Golden Globes awards. Here, she tries to draw attention of the audience by emphasising on the word ‘They are’ highlighting the role of women in different parts of life.
13. Germinatio
This is repetition of a word in the same sentence for more than once. For instance, “And so I’ve got voice mail how I wanna listen to it, when I wanna listen to it, in any order I wanna listen to it with visual voicemail.”
The technique of germinatio was used by Steve Jobs in his speech in order to create a compelling effect on the listeners.
These are just a few commonly used rhetorical devices from an ocean of such magic tools. (Take a guess at what device is used here!)
How to use rhetorical devices in speeches?
Before we dive in to how to use rhetorical devices, we made a fun video on how these tools are the one simple thing that helps take your speech to the next level. There are a bunch of examples and tips here that will help you incorporate rhetorical devices for your next presentation. Highly recommend you check it out:
To know how to implement these rhetorical devices in your speech is also of utmost importance, apart from knowing them. Here’s a way of incorporating them in your speech.

1. Know the rhetorical appeals
It is important to know the types of rhetorical appeals as rhetorical devices fall into these categories. Make a rough draft and then insert rhetorical devices accordingly depending on the tone of the speech. Figure out the mode of persuasion, that is, whether it is Logos, Pathos, Ethos or Kairos.
This refers to giving logical and intellectual arguments and reasoning, supporting it with credible evidence. An example of logos can be a speech by Donald Trump, where he states a few figures regarding the illegal immigration,
“So here are just a few statistics on the human toll of illegal immigration. According to a 2011 government report, the arrests attached to the criminal alien population included an estimated 25,000 people for homicide, 42,000 for robbery, nearly 70,000 for sex offenses, and nearly 15,000 for kidnapping. In Texas alone, within the last seven years, more than a quarter-million criminal aliens have been arrested and charged with over 600,000 criminal offenses. … Sixty-three thousand Americans since 9/11 have been killed by illegal aliens. This isn’t a problem that’s going away; it’s getting bigger.”
This refers to making an appeal to the audience’s emotions. This includes using language in such a way that creates an empathetic feeling towards the speaker. Given below is an example of Martin Luther King Jr. “I have a dream” speech.
“Let us not wallow in the valley of despair, I say to you today, my friends. And so even though we face the difficulties of today and tomorrow, I still have a dream. It is a dream deeply rooted in the American dream.”
This refers to persuading the audience about the speaker’s credibility and the fact that his arguments carry weight.
An example of this could be the speech made by Mitt Romney, senator of the United States. In this speech, accepting the presidential nominee Mitt Romney points out to the fact that his business success would prove useful if he were to take the office.
“I learned the real lessons about how America works from experience. When I was 37, I helped start a small company. My partners and I had been working for a company that was in the business of helping other businesses. So some of us had this idea that if we really believed our advice was helping companies, we should invest in companies. We should bet on ourselves and on our advice. So we started a new business called Bain Capital…That business we started with 10 people has now grown into a great American success story. Some of the companies we helped start are names you know. An office supply company called Staples – where I’m pleased to see the Obama campaign has been shopping; The Sports Authority, which became a favorite of my sons. We started an early childhood learning center called Bright Horizons that First Lady Michelle Obama rightly praised.”
This involves an appeal to the timing of the argument, meaning that the argument has to be made in a suitable context making the audience receptive to it. An instance of Kairos can be Martin Luther King’s ‘I Have a Dream’ speech,
“This is no time to engage in the luxury of cooling off or to take the tranquilizing drug of gradualism. Now is the time to make real the promises of democracy. Now is the time to make to rise from the dark and desolate valley of segregation to the sunlit path of racial justice.”
One can use these rhetorical appeals in such a way that a combination of all 4 appeals is made simultaneously.
Making the speech highly logos specific, that is giving only facts, will make the audience bored, whereas making it too pathos oriented will make the speech very emotional and lacking in rational thinking.
If you would like some more information on ETHOS, PATHOS and LOGOS, you can check out the same in this short video we made:
2. A rhetorical question

Rhetorical questions can be used to control the thoughts of the audience. These questions may have obvious answers or may not have a clear cut answer.
One technique of using such questions is inserting them in the start of the speech and then carrying on with the speech in such a way that the rhetorical question is answered in the content of your presentation.
Another way is by inserting a rhetorical question, which as an obvious answer to it at the end of the speech- making sure that the question is related to what the speech entails.
The election speech of Ronald Reagan for the 1980 presidential debate between Governor Ronald Reagan and President Jimmy Carter, where the governor ended with a bunch of rhetorical questions is a perfect example for this,
“Next Tuesday is Election Day. Next Tuesday all of you will go to the polls, will stand there in the polling place and make a decision. I think when you make that decision, it might be well if you would ask yourself, are you better off than you were four years ago? Is it easier for you to go and buy things in the stores than it was four years ago? Is there more or less unemployment in the country than there was four years ago? Is America as respected throughout the world as it was? Do you feel that our security is as safe, that we’re as strong as we were four years ago? And if you answer all of those questions yes, why then, I think your choice is very obvious as to whom you will vote for. If you don’t agree, if you don’t think that this course that we’ve been on for the last four years is what you would like to see us follow for the next four, then I could suggest another choice that you have.”
Check it out in action, here:
3. A powerful beginning
It is rightly said that the first impression is the last impression and hence a powerful beginning is very important. To capture the audience it is important to insert some rhetorical devices at the start of your speech which create some poetic effect that helps you engage the audience. It may also include the use of diacope or anadiplosis which focus on repetition of the words of phrases creating emphasis and a strong display of emotions.
An example of anadiplosis can be: “Tonight, we are a country awakened to danger and called to defend freedom. Our grief has turned to anger, and anger to resolution.” This was used by the George W. Bush

4. A powerful end
Climax is the most important part, be it a speech or a movie! What you say in the end is what stays with the audience hence, ending the speech with impactful rhetorical devices is advisable.
These may include inserting a rhetorical question making the audience ponder a little as mentioned above. It may also include the use of Epistrophe.
For instance, while addressing the nation about terrorism George Bush ends his speech in a powerful way assuring people that he will take the necessary actions to prevent terrorism, with appropriate use of Epistrophe:
“I will not forget the wound to our country and those who inflicted it. I will not yield, I will not rest, I will not relent in waging this struggle for freedom and security for the American people.”
Watch the full speech here:
Use of rhetorical devices by Frederick Douglass

The credit for developing the basics of rhetoric goes to Aristotle and since then there has been extensive use of these literary tools. A prominent figure who is well known for his use of rhetorical devices is also Frederick Douglass, who was a slave who had escaped and went on to become an activist, author and public speaker.
He is known not only for his idea of abolition of slavery but also his superior skill of rhetoric and the art of persuading the audience. In his memoir called the ‘Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave’, a number of rhetorical devices are used to argue against the heinous act of slavery.
Here is a look at how he used some of them to make his communication all the more poewrful:
It involves persuading the audience about the author’s qualifications and credibility pointing to the fact that the speaker’s arguments carry weight.
In the memoir, Frederick Douglass talks about his first-hand experience with slavery by talking about being oblivious about his birthday unlike other people in the first chapter itself, building his ethos.
In order to make an appeal to the audience’s emotions, Douglass talks about his experience of watching his aunt being whipped by the slaveholder until she is covered in blood.
Frederick writes, ‘He would at times seem to take great pleasure in whipping a slave. I have often been awakened at the dawn of day by the most heart-rending shrieks of an own aunt of mine, whom he used to tie up to a joist, and whip upon her naked back till she was literally covered with blood. No words, no tears, no prayers, from his gory victim, seemed to move his iron heart from its bloody purpose. The louder she screamed, the harder he whipped; and where the blood ran fastest, there he whipped longest. He would whip her to make her scream, and whip her to make her hush; and not until overcome by fatigue, would he cease to swing the blood-clotted cow skin.’
Frederick talks about how animals were treated better than humans by the slaveholder.
He writes about the condition of the slaves by saying:
‘Everything depended upon the looks of the horses, and the state of Colonel Lloyd’s own mind when his horses were brought to him for use. If a horse did not move fast enough, or hold his head high enough, it was owing to some fault of his keepers. It was painful to stand near the stable-door, and hear the various complaints against the keepers when a horse was taken out for use. To all the complaints, no matter how unjust, the slave must answer never a word. Colonel Lloyd could not brook any contradiction from a slave. When he spoke, a slave must stand, listen, and tremble; and such was literally the case. I have seen Colonel Lloyd make old Barney, a man between fifty and sixty years of age, uncover his bald head, kneel down upon the cold, damp ground, and receive upon his naked and toil-worn shoulders more than thirty lashes at the time.’
In Fredrick Douglass’s speech- “What to the Slave Is the Fourth of July?”, he also makes a similar appeal through the use of ethos, pathos and logos . To begin with, he makes an appeal to ethos, by initiating his speech with modesty and meekness. For example, “He who could address this audience without a quailing sensation, has stronger nerves than I have.”
To steer emotions among the audience, he also uses metaphors such as “A horrible reptile is coiled up in your nation’s bosom; the venomous creature is nursing at the tender breast of your youthful republic . “
“From the round top of your ship of state, dark and threatening clouds may be seen.” This is an example of an extended metaphor where he is comparing the United States to a ship at sea and the dark and threatening clouds are compared to the ongoing threats and troubles.
There has also been use of simile , where the speaker makes a direct comparison of the slaves to animals sold in the market. For example, “I hear the doleful wail of fettered humanity, on the way to the slave-markets, where the victims are to be sold like horses, sheep, and swine.”
Other Rhetorical Devices used by Douglas
Moreover, through the phrase ‘ doleful wail of fettered humanity ’ the speaker is trying to give the human quality of being fettered to an abstract noun of humanity, pointing out to the use of personification .
Apart from these rhetorical devices, Frederick Douglass also uses rhetorical questions to make the audience ponder about the situation of slavery by asking them, “Is slavery among them? Is it at the gateway? Or is it in the temple?”
“What would be thought of an instrument, drawn up, legally drawn up, for the purpose of entitling the city of Rochester to a tract of land, in which no mention of land was made?”
Another important rhetorical device used by him was that of allusion . Allusion is when the author or the speaker refers to an event, object, person or to a work of art either directly or indirectly. In his speech, Frederick alludes to biblical material, knowing that the audience mostly comprises of Christians.
For instance, “ The arm of the Lord is not shortened, and the doom of slavery is certain.” Through this, the speaker makes an analogy between the Lord sending the Israelites back to their homeland and the hope that slavery will perish. Frederick Douglass has made such allusions in order to support his arguments, knowing that words from the bible would carry weight and have a strong impact.
Use of rhetorical devices in famous speeches
1. michelle obama – anaphora.
“I trust Hillary to lead this country because I’ve seen her lifelong devotion to our nation’s children – not just her own daughter, who she has raised to perfection but every child who needs a champion: Kids who take the long way to school to avoid the gangs. Kids who wonder how they’ll ever afford college. Kids whose parents don’t speak a word of English but dream of a better life. Kids who look to us to determine who and what they can be.”
This is a small part of a speech made by Michelle Obama. In this, it is seen the word “ Kids ” is used more than once to start sentences that follow each other, pointing out to the use of anaphora.
Here’s the video for the speech made by the former first lady:
2. Steve Jobs – Germination
“That’s 58 songs every second of every minute of every hour of every day.”
This is an instance from the speech of Steve Jobs, where he puts emphasis on the word “ every ” by repeating it frequently in the same sentence.
See the entire speech here:
3. Barack Obama – Antistrophe
“It was a creed written into the founding documents that declared the destiny of a nation: Yes, we can. It was whispered by slaves and abolitionists as they blazed a trail towards freedom through the darkest of nights: Yes, we can. It was sung by immigrants as they struck out from distant shores and pioneers who pushed westward against an unforgiving wilderness: Yes, we can.”
Here, the phrase “Yes, we can” is used repeatedly at the end of every sentence in order to put emphasis on the subject.
Watch the video of the speech here:
4. Martin Luther King, Jr – Antithesis
“I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the colour of their skin but by the content of their character.”
Here, the speaker uses antithesis by inverting the statements to show that America will have a day when people are judged by their character and not their skin colour.
Given below is the historic speech made at the Lincoln Memorial by Martin Luther King Jr :
5. John Kennedy – Ellipsis
“This much we pledge — and more.”
Here the former President uses “and more” instead of listing more ideas. He also compels the audience to keep thinking about the ideas they should pledge to, instead of listing them.

In order to use a wide variety of rhetorical devices, it is important to know the different types of these literary techniques. A powerful speech is not just about a good orator or good public speaking skills but much more than that! And these rhetorical devices constitute an integral part of the components which make your speech extraordinary.
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

How to Brag Like a Pro as a Speaker

Less is More! Tips to Avoid Overwhelming Your Audience

What does it mean to Resonate with the Audience- Agreement, Acceptance, Approval

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved

Brand Consultation & Market Analysis
- Brand Audit & Strategy
- Competitor Analysis
- Consumer Interviews
- Google Analytics Review
- Persona Development
- SEO Audit & Strategy
- SEO Keyword Research
- Site Mapping & Content Architecture
- Technical Strategy & Roadmapping

Creative Design & Branding
- Copywriting & Storytelling
- Event & Exhibition
- Inbound Marketing
- Logo & Brand Development
- Mobile App Design & Development
- Presentation Design
- Print Design
- Website Design & Development

Custom Web & App Development
- API Development
- Augmented Reality App Development
- Front-End Design & Development
- Virtual Reality App Development
- Web App Development
- WordPress Theme Customization
- WordPress Theme Development

Immersive Reality & New Technologies
- 3D Environment Creation
- Advanced 3D Modeling
- Immersive Story Telling
- Mixed Reality App Development
- Photogrammetry
- Prototyping
- Quantified Biometrics
Video Production & Animation
- Drone Video
- Film Production
- Mixed Reality Video
- Motion Graphics
- Post Production & Editing
- Script Writing & Story Telling
- Storyboards & Shotlists
- Voiceover & Audio Sourcing

25 Examples of Rhetorical Strategies in Famous Speeches

I’m not trying to be cheesy! An emotional response is a meaningful response, and that reaction stays with you long after the presentation is over. Whenever you think of that speaker or of that topic, your brain will bring back those feelings for you- whether they be of motivation, inspiration, sadness, empathy, or otherwise.
Rhetorical strategies use language to convey special meaning and/or to persuade someone. Basically, these strategies can be used to intentionally invoke feelings in others.
If your first reaction to all this is “Huh?” that’s okay- so was mine. Here’s how I understand it now: rhetorical strategies = emotional connection = memorability.
If you’ve ever considered becoming a master presenter (no judgement if you have), you need these tools in your repertoire ASAP. They’re just so effective!

Don’t believe me? All the cool kids are using (or used) them – I’m talking about thought leader Simon Sinek , technology guru Steve Jobs, past American president Barack Obama, civil rights leader Martin Luther King Jr., and even good old William Shakespeare.
Unless you’re above any of these greatly respected people, I’m betting that you could benefit from a little rhetorical strategy in your next speech!
25 rhetorical strategies from the best minds
We’ve compiled 25 rhetorical strategies from the most memorable presentations on the planet so that your next presentation is undeniably memorable. Ready to begin?
1. Alliteration:
Two or more words in a row that start with the same sound.
“They are part of the finest fighting force that the world has ever known. They have served tour after tour of duty in distant, different, and difficult places.” – Barack Obama
2. Allusion:
A statement that hints at something instead of being direct about it.
“You must borrow me Gargantua’s mouth first. ‘Tis a word too great for any mouth of this age’s size” – Shakespeare
3. Anadiplosis:
Repeating the last word (or words) of a sentence at the beginning of the next sentence.
“Tonight, we are a country awakened to danger and called to defend freedom. Our grief has turned to anger, and anger to resolution.” – George W. Bush
4. Analogy:
A literal comparison of two things.
“A good speech should be like a woman’s skirt: long enough to cover the subject and short enough to create interest.” – Winston Churchill
5. Anaphora:
Using the same word (or words) to begin 2 or more sentences (or paragraphs) that follow each other.
“I trust Hillary to lead this country because I’ve seen her lifelong devotion to our nation’s children – not just her own daughter, who she has raised to perfection but every child who needs a champion: Kids who take the long way to school to avoid the gangs. Kids who wonder how they’ll ever afford college. Kids whose parents don’t speak a word of English but dream of a better life. Kids who look to us to determine who and what they can be.” – Michelle Obama
6. Anastrophe:
A reversal of the typical ordering of a sentence.
“This much we pledge, and more” – JF Kennedy
7. Antistrophe:
Repeating one (or more) words at the end of a sentence.
“It was a creed written into the founding documents that declared the destiny of a nation: Yes, we can. It was whispered by slaves and abolitionists as they blazed a trail towards freedom through the darkest of nights: Yes, we can. It was sung by immigrants as they struck out from distant shores and pioneers who pushed westward against an unforgiving wilderness: Yes, we can” – Barack Obama
8. Antithesis:
A contrast of thoughts.
“That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.” – Neil Armstrong
9. Asyndeton:
Leaving out conjunction words (as or and) from a sentence.
“…and that government of the people, by the people, for the people shall not perish from the earth.” – Abraham Lincoln
10. Assonance:
Repeating a vowel sound in a sentence.
“I feel the need, the need for speed” – Tom Cruise (from the movie Top Gun)
11. Chiasmus:
The reversal of the latter of two parallel sentences.
“And so, my fellow Americans, ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country” – John F. Kennedy
12. Diacope/Tmesis:
Inserting a word (or more) between the components of a compound word.
“Free at last, free at last; thank God almighty, free at last!” – Martin Luther King
13. Epistrophe:
Another name for antistrophe (see above).
“…and that government of the people, by the people, for the people shall not perish from the earth” – Abraham Lincoln
14. Expletive:
Using a word or phrase only to fill out a sentence for grammar, rhythm or balance.
“… we shall never surrender, and even if, which I do not for a moment believe, this Island or a large part of it were subjugated and starving …” – Winston Churchill
15. Germinatio:
The repetition of a word within the sentence.
“That’s 58 songs every second of every minute of every hour of every day.” – Steve Jobs
16. Hyperbole:
Exaggerating a description for emphasis.
“Best version of Google Maps on the planet, widgets, and all with Edge and Wi-Fi networking.” – Steve Jobs
17. Hypophora:
Posing a question that you will answer yourself.
“When the enemy struck on that June day of 1950, what did America do? It did what it always has done in all its times of peril. It appealed to the heroism of its youth” – Dwight D. Eisenhower
18. Litotes:
An understatement that expresses an affirmative by negating its opposite.
“I am not unmindful that some of you have come here out of great trials and tribulations.” – Martin Luther King, Jr.
19. Meiosis:
A massive understatement.
“The situation has developed, not necessarily to our advantage” – Emperor Hirohito, announcing to the Japanese people that atomic bombs had been dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki
20. Metaphor:
Comparing two unlike objects to provide a clearer description.
“All the world’s a stage, and all the men and women merely players.” – William Shakespeare
21. Parallelism:
using a sequence of identical constructions in writing
“Tell me and I forget. Teach me and I may remember. Involve me and I will learn.” – Benjamin Franklin
22. Scesis Onomaton:
Repeating two (or more) different words with identical or similar meaning within the same sentence.
“That is heart-breaking, it is wrong, and no one should be treated that way in the United States of America” – Barack Obama
23. Simile:
Comparing two unlike things using the words “like” or “as” with an example.
“We will not be satisfied until justice rolls down like waters, and righteousness like a mighty stream.” – Martin Luther King, Jr.
24. Symploce:
Repeating one (or more) words at the beginning and end of successive sentences.
“In the struggle for peace and justice, we cannot walk alone. In the struggle for opportunity and equality, we cannot walk alone. In the struggle to heal this nation and repair this world, we cannot walk alone” – Barack Obama
25. Tricolon:
A sentence with three clearly defined parts of equal length
Rhetorical strategies improve audience engagement
If you got a little lost amidst the English jargon, here are the 2 main takeaways you need to know:
- Repetition emphasizes meaning Repetition is perhaps the most common rhetorical strategy. Whether it be the repetition of a word, a phrase, or a specific sound, it is incredibly effective. Use this strategy to build meaning behind the essential points you need to get across.
- Comparisons facilitate understanding Comparisons are also an extremely popular strategy, likely because they make the subject matter more relatable. If your audience can identify with what you’re saying, that creates an opportunity for you to cultivate a connection with them.

In sum, the best designed presentations , a slick new outfit, or a commanding voice may impress an audience initially, and can be important to gain their attention, but they lack true substance for any long-term retention. Rhetorical strategies are the single greatest tool for memorability. If you recognized even one of these examples, you just proved that rhetoric strategies are memorable. Why not start using them to your advantage?
Incorporating rhetorical strategies is kind of like learning how to ride a bike – you’re going to think you look unsure the first few times you try and you’re probably going to walk away with some scrapes and bruises. But, once you gain confidence, you’ll be able to ride circles around everyone else.
See what I did there? Here’s to being memorable!
Note: All definitions have been adapted from Your Dictionary .
Looking for more presentation insights?
Check out our Top 30 Most Popular Presentations of All Time , 16 Strategies Used by Pitch Deck Designers , 10 Things to Never Do When Presenting , or read our Top 10 Presentation Tips .
Looking for some creative help for your next presentation? Our team of talented ninja designers would love to assist!

Previous Post The Ultimate Guide to VR Videos
Next post 52 creative infographics that will inspire, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Brand Consultation & Market Analysis
- Creative Design & Branding
- Custom Web & App Development
- Immersive Reality & New Technologies
- Video Production & Animation
- View All Services
- 1-888-77-NINJA
You can see how this popup was set up in our step-by-step guide: https://wppopupmaker.com/guides/auto-opening-announcement-popups/

Need a Ninja?

VisualStory®
- Duarte DataStory®
- Presentation Principles™
Slide:ology®
- Slide Design
Speaker Coaching
- Presenting Virtually™
- Illuminate™
- Adaptive Listening™
- Team training
- Learning journeys
- Brand and product storytelling
- Keynotes and events
- Sales enablement
- Communication systems
- Accelerator Lab™
- Our culture
- Our leaders
- Case studies
- Media mentions
- Guides and tools
- Learner support
17 rhetorical devices that will make you sound like Steve Jobs

Nancy Duarte
Image source: Bob Stanfield
Ask anyone who the best contemporary speakers are, and there’s a pretty good chance they’ll rank Steve Jobs in the top five.
The late, great mind behind Apple didn’t just dream up a company that changed the way humans interact. He was also a visionary and an unparalleled communicator. He knew exactly how to deliver his ideas in a way that moved audiences and left long-lasting impressions.
A number of Jobs’ speeches have garnered attention for being stirring, inspirational, and well-written. Jobs’ Stanford commencement speech, “ Stay Hungry, Stay Foolish ,” given in 2005, is often cited as one of the most powerful speeches of the last few decades, and one of the best graduation speeches ever given (the video has more than 44 million unique views on YouTube.)
There are several reasons that Jobs became such a legendary speaker . First, Jobs wasn’t afraid to be theatrical and dramatic. He used props , included shocking statistics and facts, and illustrated his words visually.

Second, Jobs also knew how to structure a presentation , which included:
- Building suspense
- Keeping listeners engaged
- And helping them envision what their future could look like if they embraced his ideas
We at Duarte call that structure a Presentation Sparkline ™.
Finally, Jobs’ speeches were so powerful because of the way he used rhetorical devices to deliver his message.
What are rhetorical devices?
Rhetoric — which people sometimes call “ the art of language ” — uses figures of speech and persuasive strategies to elevate language and make it more engaging, memorable, and entertaining.
When used properly, rhetorical devices in speeches can be a powerful tool for crafting speeches that stick. By couching his messages using rhetorical techniques, Jobs was able to deliver ideas that would go on to shape the world.
17 rhetorical devices Steve Jobs used in the Macworld 2007 iPhone launch
One of Jobs’ best speeches was given at Macworld 2007 — during the original iPhone launch. In this speech for this product launch , he announced a new tech device that would change the world forever.
Throughout his talk, he used powerful communication tricks and tools:
- He repeated sound bites to make an impression
- He showed the audience the new product in order to shock them
- And he also painted a picture of the future that got people excited about what was coming
But what made this speech one of his best was his use of rhetorical techniques, which made the announcement beautiful to listen to and moving to grasp. Take a look at the 17 most brilliant rhetorical devices used by Jobs during the iPhone launch:
Rhetorical device No. 1: Anaphora (means carrying up or back)
The repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of every clause.
“ As you know, we’ve got the iPod, best music player in the world. We’ve got the iPod Nano’s, brand new models, colors are back. We’ve got the amazing new iPod Shuffle .”
Rhetorical device No. 2: Epiphora
The repetition of a word or phrase at the end of every clause.
“ Well, these are their home screens . And again, as you recall, this is the iPhone’s home screen .”
“ This is what their contacts look like . This is what iPhone’s contacts look like .”
Rhetorical device No. 3: Symploke
The combination of multiple rhetorical techniques, involving one or several anaphora(s) with one or several epiphora(s).
“ In 1984, we introduced the Macintosh, it didn’t just change Apple, it changed the whole computer industry. In 2001, we introduced the first iPods, and … it didn’t just change the way we all listen to music, it changed the entire music industry .”*
*With parallelism and germination.

Rhetorical device No. 4. Germination
The repetition of a word or word group within one sentence.
“ That’s 58 songs every second of every minute of every hour of every day .”
“ And so I’ve got voice mail how I wanna listen to it , when I wanna listen to it , in any order I wanna listen to it with visual voice mail .”
Rhetorical device No. 5. Anadiplosis
This rhetorical technique involves the repetition of the last word of a sentence which is also the first word of the following sentence or sequence.
“ And they garnered two percent market share . Two percent market share . iPod had 62 percent market share, and the rest had 36 .”
Rhetorical device No. 6. Asyndeton
Sequence or words or similar expressions without the use of conjunctions.
“ We’ve got movies, TV shows, music, podcasts, photos .”
Rhetorical device No. 7. Polysyndeton
Repetition of conjunctions in a series of coordinated words, phrases, or clauses.
“ It’s got everything from Cocoa and the graphics, and it’s got core animation built in and it’s got the audio and video that OSX is famous for .”
Rhetorical device No. 8. Interrogation
A rhetorical question in which the answer is self-evident.
“ Isn’t that incredible ?” “ Want to see that again ?” “ Pretty cool, huh ?”
Rhetorical device No. 9. Exclamation
An exclamation that expresses the emotional affection of the speaker.
“ I just take my unit here, and I turn it into landscape mode, oh, look what happens! I’m in cover flow .”
“ Wha, whoa, what is this ?”
Rhetorical device No. 10. Aporia
A feigned statement of doubt by the speaker and a question to the audience about how he should act.
“ Now, how are we gonna communicate this? We don’t wanna carry around a mouse, right? What are we gonna do ?”
Rhetorical device No. 11. Hyperbole
An exaggeration of the characteristics of an object or circumstance.
“ Best version of Google Maps on the planet, widgets, and all with Edge and Wi-Fi networking .”

Rhetorical device No. 12. Simile
An explicit comparison between two things, usually using “as” or “like.”
“ It works like magic .”
Rhetorical device No. 13. Antitheton
The opposition of two facts of contrasting content.
“ The kind of things you would find on a typical phone, but in a very untypical way now .”
Rhetorical device No. 14. Metaphor
A comparison made by referring to one thing as another, perhaps one of the most popular rhetorical techniques out there.
“ A huge heart transplant to Intel microprocessors .”
Rhetorical device No. 15. Climax
The increase from a weaker expression to a stronger one. Thus, a word sequence is arranged in ascending order.
“ First was the mouse. The second was the click wheel. And now, we’re gonna bring multi-touch to the market .”
Rhetorical device No. 16. Personification
The attribution of human properties toward things or animals, a great rhetorical technique.
“ It already knows how to power manage … and if there’s a new message it will tell me .”
Rhetorical device No. 17. Slogans
Short and striking or memorable phrases used in advertising.
Mr. Jobs also had specific phrases he wanted to repeat over and over. According to Carmine Gallo, this was all intentional since “reinvent the phone” was in the press release Apple sent out before the keynote.
“ Today, Apple is going to reinvent the phone , and here it is .”
“ So, we’re gonna reinvent the phone .”
“ We wanna reinvent the phone .”
“ … You’ll agree, we have reinvented the phone .”
“ Today, Apple is reinventing the phone .”
Want help with rhetorical devices in your speeches?
If you have a big speech coming up, the communication coaches at Duarte can help. From working on your pauses and vocal variety to removing filler words or inserting rhetorical devices into your speeches, our team of executive speaker coaches can help!
They have worked on many C-suite speeches for some of the world’s top performing brands, and can help you nail your high-stakes moment, too.

Blog post inspired by the work of Bernhard Kast.
This article was originally published on February 15, 2018. It has been updated in August 2024 for relevancy.
Check out these related courses
Captivate™
Improve your public speaking
Overcome bad habits, conquer fears, and increase your confidence in any speaking setting. Discover your strengths and build on them to improve your delivery.
Structure and storyboard a talk
Analyze your audience and organize your ideas into a story structure that will move them. Transform content into visual concepts and build a storyboard for your presentation.
Personalized help for speakers
Up-level your speaking skills with one-on-one support. We’ll help you rehearse your talk, polish your presence, and transform your message delivery.
Craft a persuasive talk
Learn how the world’s greatest speakers use story to persuade. Develop a story structure that powerfully expresses your ideas, applying the principles of empathy, contrast, and variety.
Presentation Principles™
Learn presentation basics
Follow a step-by-step method to write compelling stories, amplify ideas visually, and present with confidence while learning at your own pace.
Turn ideas into visuals
Use visual thinking and design principles to transform information into effective and memorable graphics for presentations.
Create “skimmable” documents
Build helpful pre-reads and impactful leave-behinds with presentation software to support knowledge sharing and decision-making.
Check out these related resources

Why you should absolutely avoid using filler words (and how to actually stop)
Want to learn what are filler words and how to stop using them for good? Use these expert public speaking tips to nail your next board meeting, presentation or keynote and learn to embace the “pause for effect.”

The ultimate guide to contrast: What your presentation is missing
Need to deliver a great presentation? Master the art of contrast to make sure it’s unforgettable and met with success, every time.

The secret to writing a call to action in a persuasive speech
Struggling to write a call-to-action for your speech or presentation? Make sure you address the 4 audience types so your CTAs are met with success.

Your top 6 storytelling questions (Answered by an expert storyteller)
Can you “over story” in a business setting? Can you be clunky in your story deliver? Find common storytelling questions and answers in this deep-dive on storytelling.

Everything you need to know about using speaker notes in PowerPoint®
Learn all the Powerpoint hacks with speaker notes from an expert presentation designer. Easily design and prepare for your next presentation with ease.

Good business communication demands a 3 act story structure
Learn why effective business communication needs a storytelling framework to influence and inspire. The 3 act structure is a timeless principle to employ in your next presentation or big-stage moment.

How to Write and Deliver a Compelling Narrative Speech (With Examples)
- The Speaker Lab
- August 8, 2024
Table of Contents
If you want to elevate your public speaking game, storytelling is one of the best ways to do so. By weaving captivating tales into your presentations, you’ll forge a powerful emotional bond with your audience in a way you can’t with mere data and statistics. Not sure where to begin? Look no further than these narrative speech examples , designed to spark your creativity and help you craft your own compelling narratives.
From personal anecdotes to historical tales, these examples will demonstrate the power of storytelling to engage, persuade, and inspire. You’ll also see how great speakers use vivid language, descriptive details, and relatable characters to draw their listeners in and keep them hanging on every word. So get ready to take notes, because you’re about to unleash your inner storyteller!
What Is a Narrative Speech?
If you’ve ever been captivated by a great story, then you know the power of storytelling. A narrative speech is a type of speech that uses a personal story or narrative to engage the audience and illustrate a point. It’s one of the most effective ways to connect with your listeners on an emotional level.
Elements of a Good Narrative Speech
So, what makes a good narrative speech? First and foremost, it needs to have a clear beginning, middle, and end. Your story should have a strong opening that hooks the audience, a compelling middle that builds tension and keeps them engaged, and a satisfying conclusion that ties everything together.
If you want your story to pack a punch, don’t skimp on the specifics. Describe what you experienced using the five senses: sight, hearing, smell, touch, and taste. When you paint a vivid picture with your words, your audience will feel like they’re right there with you, experiencing every thrilling moment firsthand.
Benefits of Giving a Narrative Speech
But why bother with a narrative speech in the first place? Because stories have the power to change hearts and minds. They allow you to connect with your audience on a personal level, making your message more memorable and impactful. Think about it—when was the last time a list of facts and figures moved you to tears or inspired you to take action? Probably never. But a well-told story? That can stay with you for a lifetime.
Find Out Exactly How Much You Could Make As a Paid Speaker
Use The Official Speaker Fee Calculator to tell you what you should charge for your first (or next) speaking gig — virtual or in-person!
How to Choose a Topic for Your Narrative Speech
Now that you’ve unlocked the potential of narrative speeches, the next step is selecting the perfect topic. Look for a narrative that not only resonates with you on a personal level but will also strike a chord with your audience.
Brainstorming Ideas
Start by brainstorming speech topics that are meaningful to you. Think about pivotal moments in your life, lessons you’ve learned, or challenges you’ve overcome. Consider stories that highlight your values, passions, or unique experiences.
One brainstorming technique is to make a list of “firsts”—first love, first job, first big failure, etc. These moments often make for compelling stories because they’re relatable and emotionally charged.
Narrowing Down Your Options
Once you have a list of potential topics, it’s time to narrow them down. Ask yourself which stories are most relevant to your audience and the message you want to convey. Which ones have the most dramatic arc or the most valuable lessons?
You also want to consider your comfort level with each story. Some stories may be too personal or emotionally raw to share in a public setting. Others may not have enough substance to sustain a full speech. Trust your gut and choose the story that feels right for you.
Ensuring Your Topic Is Engaging
Finally, make sure your chosen topic is engaging and compelling. A good story should have some sort of conflict or tension that keeps the audience on the edge of their seats. It should also have a clear theme or message that resonates with listeners.
To determine if your story is a crowd-pleaser, put it to the test by sharing it with your inner circle. As you weave your narrative, watch closely for signs of engagement or boredom. Then, afterwards, ask for feedback on how you can improve your narrative speech—and don’t be afraid to ask for examples of how you might re-write specific sections. Jot down these suggestions and use them to fine-tune your story, ensuring it’s a hit with any audience.
Crafting an Outline for Your Narrative Speech
Now that you’ve nailed down your topic, it’s time to roll up your sleeves and craft a speech outline . Trust us, having a clear roadmap will make all the difference when it comes to delivering your message with confidence and clarity.
Introduction
Begin your speech with a hook, something that will pique your audience’s interest and encourage them to keep listening. Oftentimes, speakers like to use a shocking statistic or a captivating anecdote to kick things off.
For example, if your narrative speech is about overcoming a fear of public speaking , you might start with something like, “Imagine standing in front of a room full of people, your heart racing, your palms sweating, your mind going blank. That was me, just a few years ago.”
The body of your speech is where you’ll tell your actual story. Break it down into clear, chronological segments with smooth transitions between each part. Use vivid details and sensory language to bring the story to life.
As you’re writing, consider incorporating dialogue, humor , or suspense to keep the audience engaged. You might also use rhetorical devices like repetition or metaphor to drive home your key points.
As you wrap up your story, consider the bigger picture. What insights did this journey reveal to you? How have you grown as a person because of it? Think about the key takeaway you want to leave with your readers—something that will stick with them long after they’ve walked away.
End with a call-to-action or a thought-provoking question that encourages the audience to reflect on your message. You might also circle back to the opening anecdote or question to create a sense of closure.
Incorporating Characterization Techniques
To make your story more engaging, consider incorporating characterization techniques. This means giving your characters distinct personalities, motivations, and quirks that make them feel like real people.
Firstly, bring your characters to life through their conversations. The words they choose, their facial expressions, and even their body language can speak volumes about who they are and what makes them tick.
Secondly, to help your audience visualize your characters, use rich descriptions of their physical attributes, fashion choices, and distinct behaviors. Paint a picture of what they look like, how they present themselves through their attire, and any idiosyncrasies that define who they are. By bringing your characters to life, you’ll make your story more relatable and memorable for the audience.
In order to create a narrative speech that truly stands out , you’ll need to put in the time and effort to refine your craft. The reward? An opportunity to share a personal story that not only entertains but also motivates and inspires your audience, forging a connection that lasts long after the final word is spoken.
Delivering Your Narrative Speech Effectively
Before we get to narrative speech examples, let’s take a look at speech delivery. Speech delivery isn’t just about the words you say, but how you say them. Your body language, eye contact, and vocal delivery all play crucial roles in engaging your audience and making your story memorable.
In addition, practice until you can recite your story in your sleep. When you know your content like the back of your hand, you can focus on engaging with your listeners and making your words come alive.
Practicing Your Speech
Rehearsing your speech is of utmost importance. It’s a step that many speakers overlook, but it can make a world of difference in your delivery. When you practice, you familiarize yourself with the flow of your story, allowing you to speak more naturally and confidently.
One technique you find particularly helpful is recording yourself delivering the speech. When you watch the playback, you can identify areas where you need to improve your vocal variety, adjust your speaking rate , or refine your body language. It’s a powerful tool for self-critique and growth as a speaker.
Engaging Your Audience
When you take the stage, your focus should be squarely on those who have gathered to hear you. Eye contact is just the beginning; truly engaging your audience means creating a genuine connection and making them feel like they’re right there with you, experiencing your story firsthand. Try using words like “we” and “us” to make your audience feel included. Asking questions can also get them thinking about what you’re saying.
Using Props and Visual Aids
Your narrative speech may revolve around your words, but don’t underestimate the impact of a carefully selected prop or visual aid. These tools can make abstract ideas tangible, evoke strong emotional responses, and ensure your message lingers long after you’ve left the stage.
However, it’s important to use these tools judiciously. Overreliance on props or visuals can distract from your message and undermine your credibility as a speaker. When selecting props or creating visual aids, always ask yourself: does this add value to my story, or is it just a gimmick?
Overcoming Nervousness
Even seasoned speakers get the jitters sometimes. Before stepping up to the mic, take a moment to ground yourself with some breathing exercises. Visualize yourself delivering your story with confidence and poise, and watch as that nervous energy transforms into pure charisma on stage.
Remember, your listeners are your biggest supporters. They’ve gathered to hear your unique perspective and leave feeling uplifted. Rely on the effort you’ve put in, breathe deeply, and allow your fervor for your message to radiate throughout the room.
Examples of Compelling Narrative Speeches
Great speakers have always known the secret to capturing an audience’s attention: storytelling. Whether it’s an ancient Greek orator spinning a yarn or a modern-day TED Talker sharing a personal journey, the ability to craft a compelling narrative is what sets the best speakers apart. So, what do these narrative speeches look like in action? Let’s dive into some narrative speech examples that have educated, inspired, and motivated people across the ages.
Inspirational Stories
Inspirational stories are those that uplift and motivate us to be our best selves. They often involve overcoming adversity, achieving a seemingly impossible goal, or making a positive difference in the world. Take, for example, Amy Purdy’s narrative speech about the power of imagination. In case you aren’t familiar with the name, Amy Purdy is a Paralympic snowboarder who lost both her legs below the knee due to bacterial meningitis. In her TED talk, she shares her journey of resilience and adaptation, showing how she turned a devastating setback into an opportunity to inspire others.
Humorous Anecdotes
Want to instantly connect with your audience? Try sprinkling in some humor. A well-timed joke or absurd anecdote can break the ice and leave your listeners in stitches. Keep them on their toes with unexpected twists, and they’ll be hanging on your every word.
Darren LaCroix, a professional speaker, frequently uses humorous stories in his talks. Take a look at how he uses his stories of failure in this speech to motivate his crowd to chase their dreams.
Emotional Tales
Emotional tales have a way of grabbing our hearts and not letting go. These stories frequently revolve around individual challenges, the pain of loss, or powerful moments of clarity that reshape a person’s path forward.
One example of an emotional narrative speech is Steve Jobs’ 2005 Stanford Commencement Address , in which he shares three personal stories that shaped his philosophy on life and work. From his adoption story to his battle with cancer, Jobs’ tales are raw, honest, and deeply moving.
Motivational Narratives
Ever heard a story that made you want to jump up and take on the world? That’s the power of a motivational narrative. These inspiring tales feature everyday people doing incredible things—conquering challenges, chasing their passions, and proving that with hard work and determination, anything is possible.
If you want to hear an inspiring tale, check out J.K. Rowling’s Harvard Commencement Speech . She shares her personal journey of failure and resilience, and how she used her imagination to create one of the most adored book series ever. It’s a beautiful story about the power of storytelling and never giving up on your dreams.
Want to hook your audience, tug at their heartstrings, and spur them to action? Take a look at some narrative speech examples from those who’ve mastered the craft. But as you do, don’t forget: your story, told in your unique voice, is the most powerful tool you have. Share it boldly, and watch as it transforms lives.
Ready to Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig?
Download our free 26-page guide and get the 14 exact steps you can follow to book a paid speaking gig right now!
FAQs on Narrative Speech Examples
How do you start a narrative speech.
Kick off with a hook that grabs attention. Maybe share an unexpected fact, ask a thought-provoking question, or launch into the heart of your tale.
What is an example of storytelling?
An example would be recounting how overcoming acute anxiety before a big job interview taught resilience and self-confidence.
Dive straight into setting the scene or introduce your main character in action. Let listeners feel they’re right there with you from the get-go.
What are examples of narrative speech?
Narrative speeches might explore personal growth through volunteering experiences or share humorous anecdotes about learning to drive. They weave personal stories to engage and enlighten audiences.
Storytelling is a timeless art that has the power to captivate, inspire, and transform. By studying these narrative speech examples, you’ve seen firsthand how weaving narratives into your presentations can create an emotional connection with your audience and make your message unforgettable.
In order to engage your audience, focus on your characters. Additionally, include details that engage the senses. And don’t be afraid to get a little personal. After all, your own experiences can be the most powerful stories of all.
With these tips in mind, go forth and tell your stories with passion, authenticity, and purpose. Your audience is waiting to be inspired by the narratives only you can tell. Happy storytelling!
- Last Updated: August 6, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.

ONLINE SPEECH BANK
Database of and index to 5000+ full text, audio, and video versions of public speeches, sermons, legal proceedings, lectures, debates, interviews, other recorded media events, and a declaration or two.
Index links alphabetized by first name. Available mediums flagged with [T] (text), [A] (audio), [V] (video).
RECENT ADDITIONS
► Pete Sampras: International Tennis Hall of Fame Induction Address [Entire Video Added]
► John Kerry: Tokyo Institute of Technology Address on a 21st Century Pacific Partnership [w/ Video]
► Donald J. Trump: Address to the 75th Session of the UN General Assembly [w/ AudioXE and Video]
► Robert F. Kennedy: On the Death of Martin Luther King, Jr. [Entire Video Added]
SPEECH OF THE WEEK

"The Dream Shall Never Die"
TOP 100 SPEECHES OF THE 20TH CENTURY

Full text, audio, and video database of the 100 most significant American political speeches of the 20th century, according to 137 leading scholars of American public address, as compiled by Stephen E. Lucas (University of Wisconsin-Madison) and Martin J. Medhurst (Baylor University). Discover who made the cut and experience the power of rhetorical eloquence in this provocative list of "who's who" in American public address.
OBAMA SPEECHES

475+ Campaign, First and Second Term Speeches in full text, enhanced audioXE and HD video. Popular artifacts include the Audacity of Hope, Yes We Can, A More Perfect Union, President-Elect Victory, First Presidential Inaugural, A New Beginning, Together We Thrive, Newtown Prayer Vigil addresses, and many more.

MOVIE SPEECHES

Full text, audio and video database of some 275+ Hollywood movie speeches.
Included are military movie speeches, sports-oriented movie speeches, forensic movie speeches, and social-political movie speeches, among others.

RHETORICAL FIGURES

200+ short audio and video clips illustrating stylistic figures of speech ranging from alliteration to synecdoche. Clips are taken from speeches, movies, sermons, and sensational media events and delivered by politicians, actors, preachers, athletes, and other notable personalities.
Main Site Areas
For scholars, cool exercises.
© Copyright 2001-Present. American Rhetoric.
Home > Blog > Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples and Best Practices

Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples and Best Practices
- Smodin Editorial Team
- Updated: August 13, 2024
- General Guide About Content and Writing
Are you having trouble creating a high-quality rhetorical analysis essay? Then you’ll love the rhetorical analysis essay examples and best practices in this article. We’ll share the best ways to improve the quality of your content and get top marks with your assignment.
Let’s dive in!

What Is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Examples and Key Elements
A rhetorical analysis essay examines how authors or speakers use rhetoric to persuade, inform, or entertain their audience. It is not a persuasive essay . It involves breaking down a piece of communication, such as a speech, article, or advertisement. This helps you to understand the strategies employed to achieve its purpose.
Still want more details about what is a rhetorical analysis essay? No problem! The essay typically focuses on three primary elements, which are as follows:
- Ethos: Ethos refers to the credibility and character of the speaker or writer. You can use it to establish trust and authority. It helps convince the audience of the speaker’s reliability and expertise on the subject. Furthermore, you can convey ethos through the speaker’s qualifications, reputation, ethical behavior, and the use of credible sources.
- Pathos: Pathos appeals to the audience’s emotions. It aims to evoke feelings that will lead the audience to accept the speaker’s viewpoint. You can achieve this through storytelling, vivid imagery, emotionally charged language, and personal anecdotes. Also, pathos is effective in creating a connection with the audience and making the argument more relatable and impactful.
- Logos: Logos is the appeal to logic and reason. It involves the use of evidence, facts, statistics, and logical arguments to support a claim. Therefore, you can add a rhetorical analysis body paragraph about the extent of evidence the author provides.
To write a rhetorical analysis essay, one must first identify the purpose and audience of the text. Next, analyze the rhetorical strategies the author decided to use. This includes considering how effectively they contribute to the overall message. Also, examine the use of language, tone, imagery, and structure.
An Example of a Rhetorical Analysis
Let’s take Martin Luther King Jr’s speech, “I have a dream” as our rhetorical analysis example. The speech masterfully uses rhetorical strategies to inspire action for civil rights. Martin Luther King Jr establishes his credibility (ethos) by aligning with historical figures and documents, which enhances his moral authority.
Furthermore, he evokes strong emotions (pathos) through vivid imagery and the repetitive phrase “I have a dream.” This creates a hopeful vision for the future. Additionally, he employs logical arguments (logos) by highlighting broken promises and referencing American ideals of liberty and equality.
This blend of ethos, pathos, and logos makes his speech a powerful, and a call for justice and equality.

How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Best Practices and Top Tips
Now, let’s look at some of the key rhetorical concepts to create an essay that will get you top marks. The idea is to use these best practices to save time and simplify the writing process. Also, they ensure you don’t miss out on important points that deliver on what you shared in the thesis statement.
So, consider the following if you want to know how to write a rhetorical analysis essay and what to include in each section of your essay.
Understand the Text
Thoroughly read and understand the text before you begin the analysis stage. After all, how can you create a rhetorical essay on a piece of literature you don’t fully understand? You may feel like saving time by skimming the content, but it will lead to an inaccurate and slower writing process.
You’ll need to identify the author’s purpose, audience, and the main argument. Additionally, take notes on key points, recurring themes, and the overall tone. Understanding the context in which the text was created is crucial for an accurate analysis. Hence, pay attention to the historical, cultural, and social factors.
Identify Rhetorical Strategies
Focus on the three primary rhetorical appeals, which are ethos, pathos, and logos. Make sure to analyze how the author uses these strategies to persuade the audience. Then look for specific examples, such as language choices, emotional anecdotes, or logical arguments that illustrate these techniques.
Organize Your Essay
Create a clear rhetorical analysis essay outline that includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion format . The rhetorical analysis introduction should present the text being analyzed and your thesis statement. Also, each body paragraph should focus on a specific rhetorical strategy or element by providing evidence and analysis.
You’ll need to create a rhetorical analysis conclusion by summarizing your main points and restating the significance of your analysis. Make sure you summarize the main points in a way that is easy to understand. Also, leave the reader with a few final thoughts you want them to take away from the academic writing.

Use Textual Evidence
Support your analysis with direct quotes and detailed examples from the text. When citing evidence, explain how it illustrates the rhetorical strategy being discussed and its effect on the audience. Additionally, ensure that each piece of evidence is relevant and strengthens your overall argument.
However, don’t add too many direct quotes since it can clutter the flow and feel of the essay. Instead, select a few quotes that allow you to convey the key concepts of the literature piece. Generally, it’s a good idea to focus on a few key concepts rather than covering many in a shallow fashion.
Proofread and Revise
Carefully proofread your essay for grammatical and structural errors. Also, ensure that your analysis is coherent and logically organized. Revising allows you to refine your arguments, improve clarity, and ensure that your essay effectively communicates your analysis.
Furthermore, you may want to use tools that help you proofread and write a good rhetorical analysis essay. They can help you with aspects of the writing process, such as creating a clear thesis statement and logical reasoning.
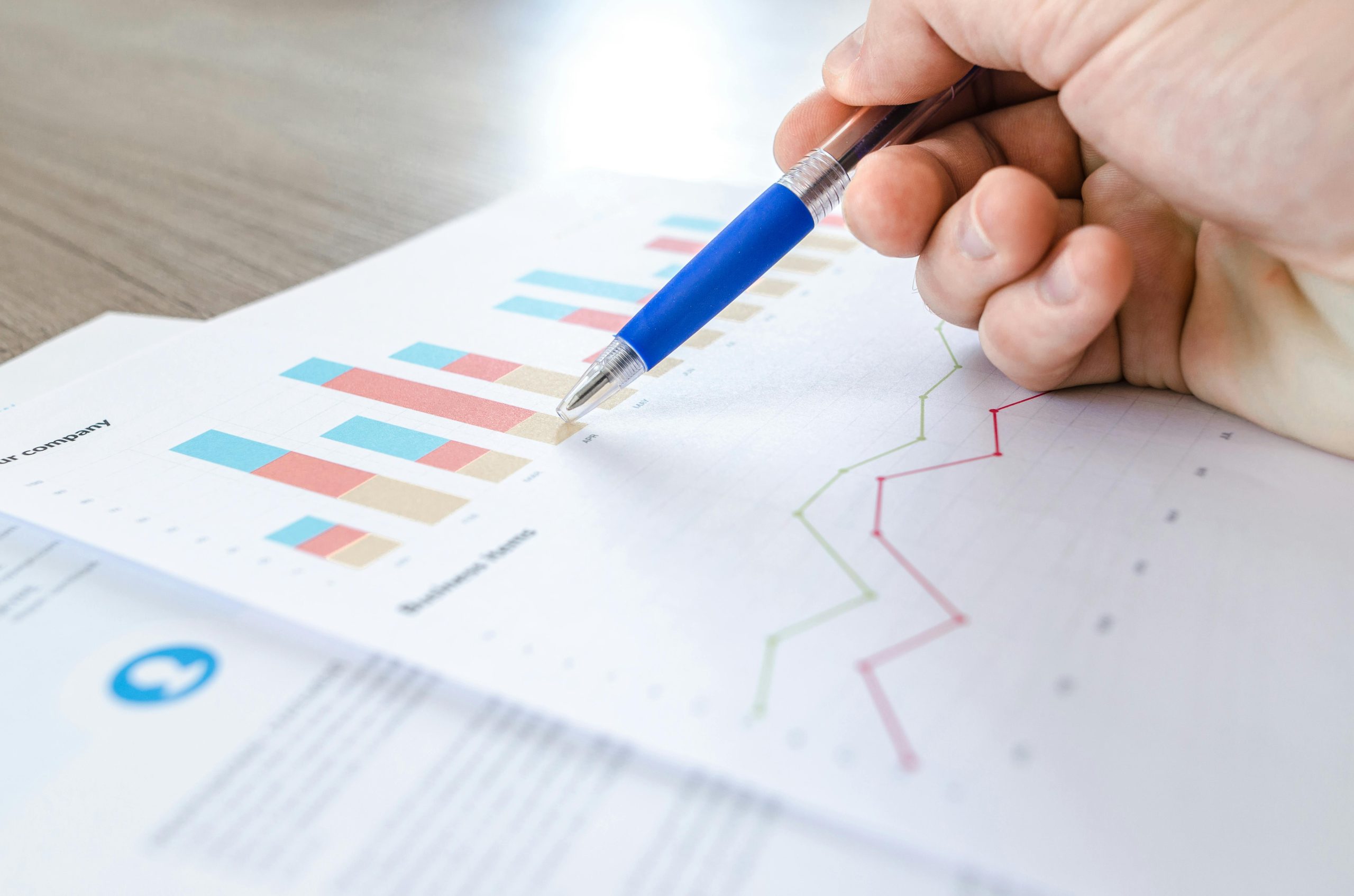

Contextual Analysis
You can place the text within its broader context. This means discussing the historical, cultural, or social background that influences the text. Also, understanding the context can provide deeper insights into the rhetorical choices made by the author and how they resonate with the audience.
Maintain an Analytical Tone
Write in an objective and analytical tone for the best results. Avoid summarizing the text and instead focus on analyzing how the rhetorical strategies contribute to the author’s purpose. You’ll need to be critical and insightful, which shows a deep understanding of the text’s rhetorical techniques and their impact.
Are you unsure of how to strike the right analytical tone? Then it’s a good idea to look at different examples to learn the best practices. For example, you can look at a rhetorical analysis introduction example to get going.

How To Start a Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Examples To Help You
Do you want to know how to start a rhetorical analysis essay? We’ll now cover the basics of how you can start to get the best results. This ensures that you hit the ground running and finish the project in time for the deadline.
Here’s the step-by-step process about how to start a rhetorical analysis essay with an example to show you how it’s done:
- Understand the purpose: The goal of a rhetorical analysis essay is to examine how an author or speaker uses rhetoric to persuade, inform, or entertain an audience. For example, in analyzing Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I have a dream” speech, you would explore how King used rhetorical strategies to advocate for civil rights and inspire action.
- Read and annotate the text: Carefully read the text you are analyzing. Also, annotate key passages and note examples of rhetorical devices such as ethos, pathos, logos, diction, syntax, and imagery. For instance, you might highlight King’s use of metaphors like “the manacles of segregation and the chains of discrimination.”
- Formulate a thesis statement: Develop a clear thesis that presents your main argument about how the text uses rhetoric. For example, Martin Luther King Jr. effectively uses ethos, pathos, and logos to inspire his audience to pursue racial equality.

How To Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Factors To Consider
You may need to look at many different examples to craft the best essay for your assignment. This ensures that you can figure out what works to get top marks. However, you shouldn’t directly copy from the example you come across. Instead, use them for inspiration to write an essay with a great writing flow that’s unique.
Here are the top things to consider when looking at a rhetorical analysis essay:
- Thesis statement example: Pay attention to the thesis statement example to better understand the type of issues you may need to address. This allows you to craft your own statement, which makes for a good topic to tackle.
- Analytical depth: Evaluate the depth of analysis in explaining how rhetorical strategies contribute to the text’s purpose. That’s because a strong essay goes beyond surface-level observations to provide insightful commentary on the effectiveness of these strategies.
- Logical organization: Check for a clear and logical structure, with each paragraph focusing on a specific aspect of the analysis. The organization should help guide the reader through the argument in a coherent and systematic way. You can emulate this organizational structure to improve the readability of your own essay.
- Conclusive summary: Look for a strong conclusion that summarizes the main points and reiterates the significance of the analysis. Furthermore, the conclusion should tie together the essay’s arguments and reflect on the overall impact of the rhetorical strategies.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
To write an AP Lang rhetorical analysis essay, start by carefully reading the text and identifying the author’s purpose, audience, and main argument. You’ll need to begin your essay with an introduction that includes the title, author, and context of the text. Also, don’t forget about the clear thesis statement.
In the body paragraphs, focus on specific rhetorical strategies such as ethos, pathos, and logos. you’ll also need to focus on using ethos, pathos, and logos, which we covered above.
Maintain an objective and analytical tone throughout your essay. You can achieve this by organizing your paragraphs logically, with each focusing on a different strategy or element.
Finally, conclude by summarizing your main points and reiterating the significance of the rhetorical strategies in achieving the author’s purpose. Make sure to proofread your essay for clarity and coherence to ensure a polished final piece. If you are unsure of how to structure your essay, you can always check out AP Lang rhetorical analysis essay examples online .

Frequently Asked Questions
What should i include in a rhetorical analysis essay introduction.
The introduction to the rhetorical analysis essay should provide background information on the text. This includes the author, title, and context. Also, it should present the purpose of the rhetorical analysis and your thesis statement.
Make sure that the thesis briefly mentions the main rhetorical strategies you will discuss to guide the reader on what to expect in the essay body. You’ll get better at doing this with practice and keep it brief.
How do I analyze ethos in a rhetorical analysis essay?
To analyze ethos in a rhetorical analysis essay, you need to evaluate how the author establishes credibility and authority. Look for references to their qualifications, experience, or reputation. Additionally, consider the tone and language used to build trust and rapport with the audience.
Discuss how these elements contribute to the overall persuasiveness of the text, which means you’ll need to read it in detail. It’s handy to make notes with regard to ethos evaluation as you work on the project.
How do I analyze logos in a rhetorical analysis essay?
To analyze logos in a rhetorical analysis essay, focus on the logical structure and evidence presented in the text. Also, identify examples of facts, statistics, logical arguments, and reasoning used to support the author’s claims.
You’ll also need to evaluate the clarity and coherence of these arguments and how they contribute to the overall persuasiveness of the text. This latter part is more tricky and takes practice before you can get it right.
What are common mistakes to avoid when writing a rhetorical analysis essay?
Common mistakes to avoid when writing a rhetorical analysis essay include summarizing the text instead of analyzing it. This is not the point of the content, and you need to avoid doing this since it can result in a low grade.
Furthermore, you need to avoid neglecting to support claims with evidence and failing to address the effectiveness of rhetorical strategies. Also, avoid focusing too much on one type of appeal (ethos, pathos, or logos) to the detriment of others.
Can I use a first-person perspective in a rhetorical analysis essay?
While rhetorical analysis essays are typically written in the third person to maintain an objective tone, there are instances where a first-person perspective might be appropriate. However, it is essential to use it sparingly and ensure that the focus remains on the text and its rhetorical strategies.
You may want to look at a rhetorical analysis essay example that uses the first person to learn. You can use your findings to improve the quality of your essay and make sure you strike the right balance.

Use Smodin AI To Write Your Rhetorical Analysis Essay
The best practices in this article will help you create a high-quality rhetorical analysis essay. Therefore, you can get top marks in your class or improve on your personal best. You’ll see that there’s a method to the madness, such as following the right structure.
Now that you know how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, you can begin the process. Make sure that you remember the rules about ethos, logos, and pathos to write the best content. This will also help you craft the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion sections.
Do you still need help with your visual rhetorical analysis essay? Then you can use Smodin AI to improve the overall quality of your essay. The tool can proofread your work or help generate text that meets your exact requirements.
So what are you waiting for? Give Smodin AI a try today and craft top-quality essays!
Commentary | 5 takeaways from a Trump speech focused on the…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
Baltimore Sun eNewspaper
- Readers Respond
Commentary | 5 takeaways from a Trump speech focused on the wrong numbers | STAFF COMMENTARY

But the minute he took the stage in battleground North Carolina, it was clear he would focus too much on the wrong numbers. He was supposed to talk about the economy and eventually did — but with disputable claims. Trump started off by focusing on polling numbers, 2020 Democratic Primary results and one sketch of Harris on the cover of Time magazine.
Trump filled the first 20 minutes with personal attacks and false claims—the opposite of what many supporters and allies have been asking him to do. They’ve asked him to stay on message, but he continues to make the race about personalities.
Perhaps the biggest blunder was when he noted he was there to speak about the economy but questioned its importance: “They say it’s the most important subject. I’m not sure it is, but they say it is the most important.”
Trump and Harris polls and crowd sizes
I’ve never met a voter, especially a voter in a battleground state, who cares about a candidate’s crowd size. Trump has measured his success in the number of buildings bearing his name, TV ratings and crowd sizes, so I understand why it matters to him. But I don’t know any American craving a data point in their life to show a politician’s crowd sizes. And while some Americans like to see polling results, the percentages don’t change their lives. Every second that Trump talked about polls in North Carolina Wednesday afternoon was a second he wasted. He should have devoted all of his time to talking about numbers that matter to Americans — not numbers that matter to him.
Trump can’t get out of the high 40s
Part of Trump’s obsession with polls lately is because Harris is gaining points, and he’s not. That’s partially because he’s not offering voters anything new. He’s focused on the past. The future he does mention is a dystopian wasteland, a third-world country where everything is bad and nothing is good.
“The American dream is dead,” Trump said in North Carolina.
Who will that inspire? Is that message more likely to make people support him or ask themselves why they should bother voting at all?
This is where he contrasts sharply with Harris, who paints a picture of a hopeful future. It seems to be working for her. She’s climbing into the low 50s in polls, and he’s been stuck in the high 40s.
Trump went high on promises, low on plans
He didn’t say how, but Trump promised to “rapidly drive prices down and make America affordable again.” The former president also said he would cut energy and electricity prices in half within 18 months of taking office. Trump said Americans would be better off overall if he’s elected in November.
“Vote Trump and your incomes will soar. Your savings will grow. Young people will be able to afford a home. And we will bring back the American dream bigger, better and stronger than ever before,” he said, without laying out an economic plan.
Trump also renewed his call to eliminate taxes seniors pay on their Social Security benefits. He didn’t explain how the plan would work, but critics say it would cost more than a trillion dollars and exhaust federal programs faster.
Trump doesn’t realize 2024 isn’t 2016
Eight years ago, Trump ran against Hillary Clinton, a well-known entity from a powerful political family and part of the Washington establishment. He didn’t have to work hard to get half the country to hate her. Many people did, whether justified or not, long before his name appeared on a ballot. So, in 2016, the “lock her up” chants and making the race about personality worked for him.
But this year is not 2016. Harris is not Clinton. And she didn’t come into this race with half the country hating her. Spending multiple paragraphs of a speech on her laugh fills time, but it doesn’t move his campaign forward.
Trump is right on the crises, wrong on the causes
Trump said he gave President Joe Biden and Harris “an economic miracle” when he left office. “Now, you have an economic nightmare,” he said to his crowd in Asheville, North Carolina.
Renters and homeowners are burdened by higher prices. High interest rates have driven up monthly mortgage payments to sometimes double what they were five years ago, pushing homeownership out of reach for many. That has forced more renters into the market, and the competition has increased prices.
But Trump claimed the “colossal influx of migrants is driving rent absolutely through the roof.”
He also pointed to higher car insurance rates, which increased about 19%, according to Consumer Price Index numbers released earlier Wednesday. Rates haven’t increased that much since the 1970s, but they’re still lower than they were in March.
On a day when the Biden administration got some of its best numbers, with inflation reaching its lowest levels in three years, Trump could have emphasized that inflation is slowing down, but it’s not over. He could have focused his speech on how people feel at home when they go to the grocery store, pay the monthly bills and have little left over — if at all — for savings. But he resorted to old, tired insults and meaningless claims, putting the focus on his thoughts and feelings instead of those of the American people who are still struggling to make ends meet.
Candy Woodall is the opinion editor at The Baltimore Sun. She wants to know what you think of the presidential race and can be reached at [email protected].
More in Commentary

Advice | Asking Eric: Husband’s sister invades social plans

Commentary | Trump’s anti-immigrant rhetoric is harmful — and false | GUEST COMMENTARY

Commentary | 5 takeaways from Trump’s interview with Elon Musk | STAFF COMMENTARY

Commentary | Investing in mental health recovery helps everyone in Baltimore | GUEST COMMENTARY
Independence Day 2024: Powerful speech ideas for flag hoisting ceremony

The struggles and sacrifices of our freedom fighters

South Korea's Yoon calls for unification with North, offers new dialogue channel

SEOUL, Aug. 15 (UPI) -- South Korean President Yoon Suk Yeol on Thursday outlined a vision for unification with North Korea and offered to open a working group for dialogue, even as tensions with Pyongyang remain precariously high.
Yoon laid out his plan in an address marking South Korea's Liberation Day, which celebrates the 1945 end of Japan's colonial rule, saying that "complete liberation remains an unfinished task for us." Advertisement
"The freedom we enjoy must be extended to the frozen kingdom of the North, where people are deprived of freedom and suffer from poverty and starvation," Yoon said. "Only when a unified free and democratic nation rightfully owned by the people is established across the entire Korean Peninsula will we finally have complete liberation."
Yoon's blueprint for unification includes sparking change within North Korea through human rights improvements and access to information from the outside world. Advertisement
"It is also important to help awaken the people of North Korea to the value of freedom," Yoon said. "Testimonials from numerous North Korean defectors show that our radio and TV broadcasts helped make them aware of the false propaganda and instigations emanating from the North Korean regime."
The South Korean president called for building international support for unification among allies and proposed establishing an "Inter-Korean Working Group" for dialogue with the North.
"This body could take up any issue ranging from relieving tensions to economic cooperation, people-to-people and cultural exchanges and disaster and climate-change responses," Yoon said.
The plan comes at a time when prospects for unification appear to be at a nadir. In February, North Korean leader Kim Jong Un declared the South the "principal enemy" and publicly called for a constitutional change rejecting the long-held official goal of reunification.
The South Korean public has also lost enthusiasm for becoming one country with the North, especially younger generations. In one recent poll , more than 60% of respondents in their 20s and 30s said unification was unnecessary.
Analysts said that Seoul's offer was unlikely to entice North Korea to the discussion table.
"The creation of an Inter-Korean North/South Working Group will surely fall on deaf ears in Pyongyang," said Sean King, senior vice president and East Asia expert at New York-based consulting firm Park Strategies. Advertisement
"Yoon's clearly proposing unification by absorption, not a coming together of two equals," King told UPI. "This speech was largely about rhetorical positioning on Yoon's part -- well intended but not feasible under current realities."
Pyongyang has kept up a steady stream of weapons tests and hostile rhetoric over the past three years, while back-and-forth Cold War-style psychological warfare has emerged in border areas in recent months.
North Korea has sent thousands of balloons carrying scrap paper, shredded clothing and manure into the South since early June, including one that spilled trash on Yoon's presidential compound. Seoul, meanwhile, has resumed propaganda loudspeaker broadcasts near the DMZ, blasting K-pop songs and South Korean news and information across the border.
Earlier this week, North Korean state-run media decried the growing trilateral security relationship among the United States, South Korea and Japan, warning that the Asian allies would become "cannon fodder" for a nuclear attack.
- Time is ripe for a new approach: Human rights up front in support of a free and unified Korea
- North Korea warns South Korea, Japan will be nuclear 'cannon fodder'
- U.S., South Korea to start joint military drills next week amid mounting North Korea threats
- North Korea
- Kim Jong Un
Latest Headlines

Trending Stories

Advertisement
Where Kamala Harris Stands on the Issues: Abortion, Immigration and More
She wants to protect the right to abortion nationally. Here’s what else to know about her positions.
- Share full article

By Maggie Astor
- Published July 21, 2024 Updated Aug. 11, 2024
With Vice President Kamala Harris poised to replace President Biden on the Democratic ticket, her stances on key issues will be scrutinized by both parties and the nation’s voters.
She has a long record in politics: as district attorney of San Francisco, as attorney general of California, as a senator, as a presidential candidate and as vice president.
Here is an overview of where she stands.
Ms. Harris supports legislation that would protect the right to abortion nationally, as Roe v. Wade did before it was overturned in 2022, in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization.
After the Dobbs ruling, she became central to the Biden campaign’s efforts to keep the spotlight on abortion, given that Mr. Biden — with his personal discomfort with abortion and his support for restrictions earlier in his career — was a flawed messenger. In March, she made what was believed to be the first official visit to an abortion clinic by a president or vice president.
She consistently supported abortion rights during her time in the Senate, including cosponsoring legislation that would have banned common state-level restrictions, like requiring doctors to perform specific tests or have hospital admitting privileges in order to provide abortions.
As a presidential candidate in 2019, she argued that states with a history of restricting abortion rights in violation of Roe should be subject to what is known as pre-clearance for new abortion laws — those laws would have to be federally approved before they could take effect. That proposal is not viable now that the Supreme Court has overturned Roe.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Speech Bank: Top 100 Speeches: Great New Speeches: Obama Speeches: GWB Speeches: Movie Speeches: Rhetorical Figures: Christian Rhetoric: 9/11 Speeches: News and Research: For Scholars: Rhetoric Defined: Corax v. Tisias: Plato on Rhetoric: Aristotle on Rhetoric: Comm Journals: Comm Associations: Cool Exercises: Rodman & de Ref: Speech Quiz #1 ...
THE TOP 100 SPEECHES is an index to and substantial database of full text transcriptions of the 100 most significant American political speeches of the 20th century, according to a list compiled by Professors Stephen E. Lucas and Martin J. Medhurst.Dr. Lucas is Evjue-Bascom Professor in the Humanities and Professor of Communication Arts at the University of Wisconsin at Madison.
But Churchill's first speech, the first of three powerful oratories he gave during the Battle of France, would prove that England was in more than capable hands. ... Yet, the Gettysburg Address is unarguably one of the greatest pieces of rhetoric in American history. Dr. J Rufus Fears (one of the great modern orators) argues that the Gettysburg ...
13. Dwayne The Rock Johnson's eulogy for father Rocky Johnson, 'The show must go on'. Dwayne 'The Rock' Johnson was the source of two of the great speeches of 2020, one political, his 'where are you' critique of Trump in the aftermath of George Floyd's death, and one personal, an emotional tribute to father Rocky.
Speech Bank: Top 100 Speeches: Great New Speeches: Obama Speeches: GWB Speeches: Movie Speeches: Rhetorical Figures: Christian Rhetoric: 9/11 Speeches: News and Research: For Scholars: Rhetoric Defined: Corax v. Tisias: Plato on Rhetoric: Aristotle on Rhetoric: Comm Journals: Comm Associations: Cool Exercises: Rodman & de Ref: Speech Quiz #1 ...
Instead, in this short and powerful speech, Kennedy empathizes with those hurt by King's death, connecting it with his own brother's murder, ... One of the most stirring pieces of American rhetoric was written by a hungover speechwriter in just eight hours, after President Lyndon B. Johnson decided he wanted to address Congress about the ...
Let's take a closer look at ten of the best and most famous speeches from great moments in history. Abraham Lincoln, ' Gettysburg Address ' (1863). The Gettysburg Address is one of the most famous speeches in American history, yet it was extremely short - just 268 words, or less than a page of text - and Abraham Lincoln, who gave the ...
The experts were asked to recommend speeches on the basis of social and political impact, and rhetorical artistry. Stephen Lucas, UW-Madison professor of communication arts, and Martin Medhurst, professor of speech communication at Texas A&M, say the new list confirms that excellence in American public oratory has thrived during the last 100 ...
Teaching rhetorical analysis is one of my absolute favorite units to complete with my students. I love teaching my students about rhetorical strategies and devices, analyzing what makes an effective and persuasive argument, and reading critical speeches with my students. Here is a quick list of some of my favorite speeches for rhetorical analysis.
Using brilliant rhetorical devices like metonymy, meronymy, and other potent metaphors, she voiced her deeply-held commitment as a leader to the battle against the Spanish Armada - convincing the English army to keep holding their ground and upholding the sacrifice of war for the good of their people. ... Her powerful writing and speech about ...
Powerful Use of Rhetorical Devices Dorsey said the speech is also notable for its use of several rhetorical traditions, namely the Jeremiad, metaphor-use and repetition. The Jeremiad is a form of early American sermon that narratively moved audiences from recognizing the moral standard set in its past to a damning critique of current events to ...
Here is a quick look at some of the landmark speeches that often pop up in the discussion about public rhetoric. 1. Patrick Henry. " Give Me Liberty Or Give Me Death .". In March 1775, Henry spoke to a Virginia convention considering a breakaway from British rule. "The war is actually begun.
THE TOP 100 SPEECHES is an index to and partial database of full text transcriptions of the 100 most significant American political speeches of the 20th century, according to a list compiled by Professors Stephen E. Lucas and Martin J. Medhurst. Dr. Lucas is Evjue-Bascom Professor in the Humanities and Professor of Communication Arts at the University of Wisconsin at Madison. Dr. Medhurst is ...
By tools, he's not talking about special software or databases — he's referring to rhetoric. Rhetoric has its roots in ancient Greece (think: Aristotle) as clear, convincing speech was seen as an essential component of communication and participation in a democracy. Instruction in rhetoric remained part of the curriculum in many secondary ...
Rhetoric, according to Aristotle, is the art of seeing the available means of persuasion. Today we apply it to any form of communication. Aristotle focused on oration, though, and he described three types of persuasive speech. Forensic, or judicial, rhetoric establishes facts and judgments about the past, similar to detectives at a crime scene.
4. A powerful end. Climax is the most important part, be it a speech or a movie! What you say in the end is what stays with the audience hence, ending the speech with impactful rhetorical devices is advisable. These may include inserting a rhetorical question making the audience ponder a little as mentioned above.
Though not a real-life speech, Mark Antony's funeral oration in Shakespeare's Julius Caesar is a fictional example of rhetorical mastery. Antony's speech is a brilliant manipulation of the crowd's emotions, turning them against Brutus and the other conspirators and inciting them to riot. One of Antony's key techniques is irony.
8. Antithesis: A contrast of thoughts. "That's one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.". - Neil Armstrong. 9. Asyndeton: Leaving out conjunction words (as or and) from a sentence. "…and that government of the people, by the people, for the people shall not perish from the earth.".
17 rhetorical devices Steve Jobs used in the Macworld 2007 iPhone launch. One of Jobs' best speeches was given at Macworld 2007—during the original iPhone launch. In this speech, he announced a new tech device that would change the world forever. Throughout his talk, he used powerful tricks and tools.
Martin Luther King Jr.'s famous "I Have a Dream" speech is a powerful example of anaphora. The repetition of the said "I have a dream" emphasizes his vision for a more equal and just society. Example 3: Metaphor. "Our life is like a journey on a train, with its stations, with changes of routes, and with accidents!".
If you've ever been captivated by a great story, then you know the power of storytelling. A narrative speech is a type of speech that uses a personal story or narrative to engage the audience and illustrate a point. It's one of the most effective ways to connect with your listeners on an emotional level. Elements of a Good Narrative Speech
Full text, audio, and video database of the 100 most significant American political speeches of the 20th century, according to 137 leading scholars of American public address, as compiled by Stephen E. Lucas (University of Wisconsin-Madison) and Martin J. Medhurst (Baylor University). Discover who made the cut and experience the power of rhetorical eloquence in this provocative list of "who's ...
The speech masterfully uses rhetorical strategies to inspire action for civil rights. Martin Luther King Jr establishes his credibility (ethos) by aligning with historical figures and documents, which enhances his moral authority. ... This blend of ethos, pathos, and logos makes his speech a powerful, and a call for justice and equality.
Victory-night speeches are not complicated. You thank the voters and supporters, the brilliant campaign staff, the long-suffering spouse and children. You celebrate the triumphs so far, express ...
During a Veterans Day speech, Mr. Trump used language that echoed authoritarian leaders who rose to power in Germany and Italy in the 1930s, degrading his political adversaries as "vermin" who ...
Eight years ago, Trump ran against Hillary Clinton, a well-known entity from a powerful political family and part of the Washington establishment. He didn't have to work hard to get half the ...
Beyond simply being a rich and powerful bully who can waste his own money on vexatious, performative litigation, Musk's theory of "free speech" is a censorship wolf in sheep's clothing.
Independence Day is a celebration of India's freedom, providing students a platform to express patriotism through speeches. Suggested topics include the struggles of freedom fighters, India's ...
South Korean President Yoon Suk Yeol on Thursday outlined a vision for unification with North Korea and offered to open a working group for dialogue, even as tensions with Pyongyang remain high.
She has condemned former President Donald J. Trump's efforts to overturn the 2020 election results. In a speech in 2022 marking the anniversary of the Jan. 6, 2021, attack on the Capitol, she ...