Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples

Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on October 26, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
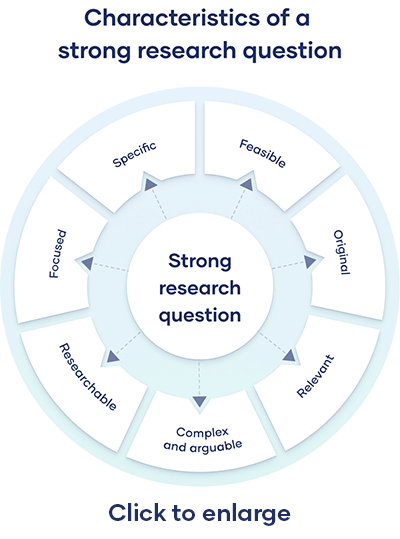
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, using sub-questions to strengthen your main research question, research questions quiz, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
| Research question formulations | |
|---|---|
| Describing and exploring | |
| Explaining and testing | |
| Evaluating and acting | is X |
Using your research problem to develop your research question
| Example research problem | Example research question(s) |
|---|---|
| Teachers at the school do not have the skills to recognize or properly guide gifted children in the classroom. | What practical techniques can teachers use to better identify and guide gifted children? |
| Young people increasingly engage in the “gig economy,” rather than traditional full-time employment. However, it is unclear why they choose to do so. | What are the main factors influencing young people’s decisions to engage in the gig economy? |
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Focused on a single topic | Your central research question should work together with your research problem to keep your work focused. If you have multiple questions, they should all clearly tie back to your central aim. |
| Answerable using | Your question must be answerable using and/or , or by reading scholarly sources on the to develop your argument. If such data is impossible to access, you likely need to rethink your question. |
| Not based on value judgements | Avoid subjective words like , , and . These do not give clear criteria for answering the question. |
Feasible and specific
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Answerable within practical constraints | Make sure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific. |
| Uses specific, well-defined concepts | All the terms you use in the research question should have clear meanings. Avoid vague language, jargon, and too-broad ideas. |
| Does not demand a conclusive solution, policy, or course of action | Research is about informing, not instructing. Even if your project is focused on a practical problem, it should aim to improve understanding rather than demand a ready-made solution. If ready-made solutions are necessary, consider conducting instead. Action research is a research method that aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as it is solved. In other words, as its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time. |
Complex and arguable
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Cannot be answered with or | Closed-ended, / questions are too simple to work as good research questions—they don’t provide enough for robust investigation and discussion. |
| Cannot be answered with easily-found facts | If you can answer the question through a single Google search, book, or article, it is probably not complex enough. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation prior to providing an answer. |
Relevant and original
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Addresses a relevant problem | Your research question should be developed based on initial reading around your . It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline. |
| Contributes to a timely social or academic debate | The question should aim to contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on. |
| Has not already been answered | You don’t have to ask something that nobody has ever thought of before, but your question should have some aspect of originality. For example, you can focus on a specific location, or explore a new angle. |
Chances are that your main research question likely can’t be answered all at once. That’s why sub-questions are important: they allow you to answer your main question in a step-by-step manner.
Good sub-questions should be:
- Less complex than the main question
- Focused only on 1 type of research
- Presented in a logical order
Here are a few examples of descriptive and framing questions:
- Descriptive: According to current government arguments, how should a European bank tax be implemented?
- Descriptive: Which countries have a bank tax/levy on financial transactions?
- Framing: How should a bank tax/levy on financial transactions look at a European level?
Keep in mind that sub-questions are by no means mandatory. They should only be asked if you need the findings to answer your main question. If your main question is simple enough to stand on its own, it’s okay to skip the sub-question part. As a rule of thumb, the more complex your subject, the more sub-questions you’ll need.
Try to limit yourself to 4 or 5 sub-questions, maximum. If you feel you need more than this, it may be indication that your main research question is not sufficiently specific. In this case, it’s is better to revisit your problem statement and try to tighten your main question up.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (“ x affects y because …”).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses . In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.

Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 21). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-questions/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, what is your plagiarism score.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Part 2: Conceptualizing your research project
9. Writing your research question
Chapter outline.
- Empirical vs. ethical questions (4 minute read)
- Characteristics of a good research question (4 minute read)
- Quantitative research questions (7 minute read)
- Qualitative research questions (3 minute read)
- Evaluating and updating your research questions (4 minute read)
Content warning: examples in this chapter include references to sexual violence, sexism, substance use disorders, homelessness, domestic violence, the child welfare system, cissexism and heterosexism, and truancy and school discipline.
9.1 Empirical vs. ethical questions
Learning objectives.
Learners will be able to…
- Define empirical questions and provide an example
- Define ethical questions and provide an example
Writing a good research question is an art and a science. It is a science because you have to make sure it is clear, concise, and well-developed. It is an art because often your language needs “wordsmithing” to perfect and clarify the meaning. This is an exciting part of the research process; however, it can also be one of the most stressful.
Creating a good research question begins by identifying a topic you are interested in studying. At this point, you already have a working question. You’ve been applying it to the exercises in each chapter, and after reading more about your topic in the scholarly literature, you’ve probably gone back and revised your working question a few times. We’re going to continue that process in more detail in this chapter. Keep in mind that writing research questions is an iterative process, with revisions happening week after week until you are ready to start your project.
Empirical vs. ethical questions
When it comes to research questions, social science is best equipped to answer empirical questions —those that can be answered by real experience in the real world—as opposed to ethical questions —questions about which people have moral opinions and that may not be answerable in reference to the real world. While social workers have explicit ethical obligations (e.g., service, social justice), research projects ask empirical questions to help actualize and support the work of upholding those ethical principles.

In order to help you better understand the difference between ethical and empirical questions, let’s consider a topic about which people have moral opinions. How about SpongeBob SquarePants? [1] In early 2005, members of the conservative Christian group Focus on the Family (2005) [2] denounced this seemingly innocuous cartoon character as “morally offensive” because they perceived his character to be one that promotes a “pro-gay agenda.” Focus on the Family supported their claim that SpongeBob is immoral by citing his appearance in a children’s video designed to promote tolerance of all family forms (BBC News, 2005). [3] They also cited SpongeBob’s regular hand-holding with his male sidekick Patrick as further evidence of his immorality.
So, can we now conclude that SpongeBob SquarePants is immoral? Not so fast. While your mother or a newspaper or television reporter may provide an answer, a social science researcher cannot. Questions of morality are ethical, not empirical. Of course, this doesn’t mean that social science researchers cannot study opinions about or social meanings surrounding SpongeBob SquarePants (Carter, 2010). [4] We study humans after all, and as you will discover in the following chapters of this textbook, we are trained to utilize a variety of scientific data-collection techniques to understand patterns of human beliefs and behaviors. Using these techniques, we could find out how many people in the United States find SpongeBob morally reprehensible, but we could never learn, empirically, whether SpongeBob is in fact morally reprehensible.
Let’s consider an example from a recent MSW research class I taught. A student group wanted to research the penalties for sexual assault. Their original research question was: “How can prison sentences for sexual assault be so much lower than the penalty for drug possession?” Outside of the research context, that is a darn good question! It speaks to how the War on Drugs and the patriarchy have distorted the criminal justice system towards policing of drug crimes over gender-based violence.
Unfortunately, it is an ethical question, not an empirical one. To answer that question, you would have to draw on philosophy and morality, answering what it is about human nature and society that allows such unjust outcomes. However, you could not answer that question by gathering data about people in the real world. If I asked people that question, they would likely give me their opinions about drugs, gender-based violence, and the criminal justice system. But I wouldn’t get the real answer about why our society tolerates such an imbalance in punishment.
As the students worked on the project through the semester, they continued to focus on the topic of sexual assault in the criminal justice system. Their research question became more empirical because they read more empirical articles about their topic. One option that they considered was to evaluate intervention programs for perpetrators of sexual assault to see if they reduced the likelihood of committing sexual assault again. Another option they considered was seeing if counties or states with higher than average jail sentences for sexual assault perpetrators had lower rates of re-offense for sexual assault. These projects addressed the ethical question of punishing perpetrators of sexual violence but did so in a way that gathered and analyzed empirical real-world data. Our job as social work researchers is to gather social facts about social work issues, not to judge or determine morality.
Key Takeaways
- Empirical questions are distinct from ethical questions.
- There are usually a number of ethical questions and a number of empirical questions that could be asked about any single topic.
- While social workers may research topics about which people have moral opinions, a researcher’s job is to gather and analyze empirical data.
- Take a look at your working question. Make sure you have an empirical question, not an ethical one. To perform this check, describe how you could find an answer to your question by conducting a study, like a survey or focus group, with real people.
9.2 Characteristics of a good research question
- Identify and explain the key features of a good research question
- Explain why it is important for social workers to be focused and clear with the language they use in their research questions
Now that you’ve made sure your working question is empirical, you need to revise that working question into a formal research question. So, what makes a good research question? First, it is generally written in the form of a question. To say that your research question is “the opioid epidemic” or “animal assisted therapy” or “oppression” would not be correct. You need to frame your topic as a question, not a statement. A good research question is also one that is well-focused. A well-focused question helps you tune out irrelevant information and not try to answer everything about the world all at once. You could be the most eloquent writer in your class, or even in the world, but if the research question about which you are writing is unclear, your work will ultimately lack direction.
In addition to being written in the form of a question and being well-focused, a good research question is one that cannot be answered with a simple yes or no. For example, if your interest is in gender norms, you could ask, “Does gender affect a person’s performance of household tasks?” but you will have nothing left to say once you discover your yes or no answer. Instead, why not ask, about the relationship between gender and household tasks. Alternatively, maybe we are interested in how or to what extent gender affects a person’s contributions to housework in a marriage? By tweaking your question in this small way, you suddenly have a much more fascinating question and more to say as you attempt to answer it.
A good research question should also have more than one plausible answer. In the example above, the student who studied the relationship between gender and household tasks had a specific interest in the impact of gender, but she also knew that preferences might be impacted by other factors. For example, she knew from her own experience that her more traditional and socially conservative friends were more likely to see household tasks as part of the female domain, and were less likely to expect their male partners to contribute to those tasks. Thinking through the possible relationships between gender, culture, and household tasks led that student to realize that there were many plausible answers to her questions about how gender affects a person’s contribution to household tasks. Because gender doesn’t exist in a vacuum, she wisely felt that she needed to consider other characteristics that work together with gender to shape people’s behaviors, likes, and dislikes. By doing this, the student considered the third feature of a good research question–she thought about relationships between several concepts. While she began with an interest in a single concept—household tasks—by asking herself what other concepts (such as gender or political orientation) might be related to her original interest, she was able to form a question that considered the relationships among those concepts.
This student had one final component to consider. Social work research questions must contain a target population. Her study would be very different if she were to conduct it on older adults or immigrants who just arrived in a new country. The target population is the group of people whose needs your study addresses. Maybe the student noticed issues with household tasks as part of her social work practice with first-generation immigrants, and so she made it her target population. Maybe she wants to address the needs of another community. Whatever the case, the target population should be chosen while keeping in mind social work’s responsibility to work on behalf of marginalized and oppressed groups.
In sum, a good research question generally has the following features:
- It is written in the form of a question
- It is clearly written
- It cannot be answered with “yes” or “no”
- It has more than one plausible answer
- It considers relationships among multiple variables
- It is specific and clear about the concepts it addresses
- It includes a target population
- A poorly focused research question can lead to the demise of an otherwise well-executed study.
- Research questions should be clearly worded, consider relationships between multiple variables, have more than one plausible answer, and address the needs of a target population.
Okay, it’s time to write out your first draft of a research question.
- Once you’ve done so, take a look at the checklist in this chapter and see if your research question meets the criteria to be a good one.
Brainstorm whether your research question might be better suited to quantitative or qualitative methods.
- Describe why your question fits better with quantitative or qualitative methods.
- Provide an alternative research question that fits with the other type of research method.
9.3 Quantitative research questions
- Describe how research questions for exploratory, descriptive, and explanatory quantitative questions differ and how to phrase them
- Identify the differences between and provide examples of strong and weak explanatory research questions
Quantitative descriptive questions
The type of research you are conducting will impact the research question that you ask. Probably the easiest questions to think of are quantitative descriptive questions. For example, “What is the average student debt load of MSW students?” is a descriptive question—and an important one. We aren’t trying to build a causal relationship here. We’re simply trying to describe how much debt MSW students carry. Quantitative descriptive questions like this one are helpful in social work practice as part of community scans, in which human service agencies survey the various needs of the community they serve. If the scan reveals that the community requires more services related to housing, child care, or day treatment for people with disabilities, a nonprofit office can use the community scan to create new programs that meet a defined community need.
Quantitative descriptive questions will often ask for percentage, count the number of instances of a phenomenon, or determine an average. Descriptive questions may only include one variable, such as ours about student debt load, or they may include multiple variables. Because these are descriptive questions, our purpose is not to investigate causal relationships between variables. To do that, we need to use a quantitative explanatory question.

Quantitative explanatory questions
Most studies you read in the academic literature will be quantitative and explanatory. Why is that? If you recall from Chapter 2 , explanatory research tries to build nomothetic causal relationships. They are generalizable across space and time, so they are applicable to a wide audience. The editorial board of a journal wants to make sure their content will be useful to as many people as possible, so it’s not surprising that quantitative research dominates the academic literature.
Structurally, quantitative explanatory questions must contain an independent variable and dependent variable. Questions should ask about the relationship between these variables. The standard format I was taught in graduate school for an explanatory quantitative research question is: “What is the relationship between [independent variable] and [dependent variable] for [target population]?” You should play with the wording for your research question, revising that standard format to match what you really want to know about your topic.
Let’s take a look at a few more examples of possible research questions and consider the relative strengths and weaknesses of each. Table 9.1 does just that. While reading the table, keep in mind that I have only noted what I view to be the most relevant strengths and weaknesses of each question. Certainly each question may have additional strengths and weaknesses not noted in the table. Each of these questions is drawn from student projects in my research methods classes and reflects the work of many students on their research question over many weeks.
| What are the internal and external effects/problems associated with children witnessing domestic violence? | Written as a question | Not clearly focused | How does witnessing domestic violence impact a child’s romantic relationships in adulthood? |
| Considers relationships among multiple concepts | Not specific and clear about the concepts it addresses | ||
| Contains a population | |||
| What causes foster children who are transitioning to adulthood to become homeless, jobless, pregnant, unhealthy, etc.? | Considers relationships among multiple concepts | Concepts are not specific and clear | What is the relationship between sexual orientation or gender identity and homelessness for late adolescents in foster care? |
| Contains a population | |||
| Not written as a yes/no question | |||
| How does income inequality predict ambivalence in the Stereo Content Model using major U.S. cities as target populations? | Written as a question | Unclear wording | How does income inequality affect ambivalence in high-density urban areas? |
| Considers relationships among multiple concepts | Population is unclear | ||
| Why are mental health rates higher in white foster children than African Americans and other races? | Written as a question | Concepts are not clear | How does race impact rates of mental health diagnosis for children in foster care? |
| Not written as a yes/no question | Does not contain a target population |
Making it more specific
A good research question should also be specific and clear about the concepts it addresses. A student investigating gender and household tasks knows what they mean by “household tasks.” You likely also have an impression of what “household tasks” means. But are your definition and the student’s definition the same? A participant in their study may think that managing finances and performing home maintenance are household tasks, but the researcher may be interested in other tasks like childcare or cleaning. The only way to ensure your study stays focused and clear is to be specific about what you mean by a concept. The student in our example could pick a specific household task that was interesting to them or that the literature indicated was important—for example, childcare. Or, the student could have a broader view of household tasks, one that encompasses childcare, food preparation, financial management, home repair, and care for relatives. Any option is probably okay, as long as the researcher is clear on what they mean by “household tasks.” Clarifying these distinctions is important as we look ahead to specifying how your variables will be measured in Chapter 11 .
Table 9.2 contains some “watch words” that indicate you may need to be more specific about the concepts in your research question.
| Factors, Causes, Effects, Outcomes | What causes or effects are you interested in? What causes and effects are important, based on the literature in your topic area? Try to choose one or a handful you consider to be the most important. |
| Effective, Effectiveness, Useful, Efficient | Effective at doing what? Effectiveness is meaningless on its own. What outcome should the program or intervention have? Reduced symptoms of a mental health issue? Better socialization? |
| Etc., and so forth | Don’t assume that your reader understands what you mean by “and so forth.” Remember that focusing on two or a small handful concepts is necessary. Your study cannot address everything about a social problem, though the results will likely have implications on other aspects of the social world. |
It can be challenging to be this specific in social work research, particularly when you are just starting out your project and still reading the literature. If you’ve only read one or two articles on your topic, it can be hard to know what you are interested in studying. Broad questions like “What are the causes of chronic homelessness, and what can be done to prevent it?” are common at the beginning stages of a research project as working questions. However, moving from working questions to research questions in your research proposal requires that you examine the literature on the topic and refine your question over time to be more specific and clear. Perhaps you want to study the effect of a specific anti-homelessness program that you found in the literature. Maybe there is a particular model to fighting homelessness, like Housing First or transitional housing, that you want to investigate further. You may want to focus on a potential cause of homelessness such as LGBTQ+ discrimination that you find interesting or relevant to your practice. As you can see, the possibilities for making your question more specific are almost infinite.
Quantitative exploratory questions
In exploratory research, the researcher doesn’t quite know the lay of the land yet. If someone is proposing to conduct an exploratory quantitative project, the watch words highlighted in Table 9.2 are not problematic at all. In fact, questions such as “What factors influence the removal of children in child welfare cases?” are good because they will explore a variety of factors or causes. In this question, the independent variable is less clearly written, but the dependent variable, family preservation outcomes, is quite clearly written. The inverse can also be true. If we were to ask, “What outcomes are associated with family preservation services in child welfare?”, we would have a clear independent variable, family preservation services, but an unclear dependent variable, outcomes. Because we are only conducting exploratory research on a topic, we may not have an idea of what concepts may comprise our “outcomes” or “factors.” Only after interacting with our participants will we be able to understand which concepts are important.
Remember that exploratory research is appropriate only when the researcher does not know much about topic because there is very little scholarly research. In our examples above, there is extensive literature on the outcomes in family reunification programs and risk factors for child removal in child welfare. Make sure you’ve done a thorough literature review to ensure there is little relevant research to guide you towards a more explanatory question.
- Descriptive quantitative research questions are helpful for community scans but cannot investigate causal relationships between variables.
- Explanatory quantitative research questions must include an independent and dependent variable.
- Exploratory quantitative research questions should only be considered when there is very little previous research on your topic.
- Identify the type of research you are engaged in (descriptive, explanatory, or exploratory).
- Create a quantitative research question for your project that matches with the type of research you are engaged in.
Preferably, you should be creating an explanatory research question for quantitative research.

9.4 Qualitative research questions
- List the key terms associated with qualitative research questions
- Distinguish between qualitative and quantitative research questions
Qualitative research questions differ from quantitative research questions. Because qualitative research questions seek to explore or describe phenomena, not provide a neat nomothetic explanation, they are often more general and openly worded. They may include only one concept, though many include more than one. Instead of asking how one variable causes changes in another, we are instead trying to understand the experiences , understandings , and meanings that people have about the concepts in our research question. These keywords often make an appearance in qualitative research questions.
Let’s work through an example from our last section. In Table 9.1, a student asked, “What is the relationship between sexual orientation or gender identity and homelessness for late adolescents in foster care?” In this question, it is pretty clear that the student believes that adolescents in foster care who identify as LGBTQ+ may be at greater risk for homelessness. This is a nomothetic causal relationship—LGBTQ+ status causes changes in homelessness.
However, what if the student were less interested in predicting homelessness based on LGBTQ+ status and more interested in understanding the stories of foster care youth who identify as LGBTQ+ and may be at risk for homelessness? In that case, the researcher would be building an idiographic causal explanation . The youths whom the researcher interviews may share stories of how their foster families, caseworkers, and others treated them. They may share stories about how they thought of their own sexuality or gender identity and how it changed over time. They may have different ideas about what it means to transition out of foster care.

Because qualitative questions usually center on idiographic causal relationships, they look different than quantitative questions. Table 9.3 below takes the final research questions from Table 9.1 and adapts them for qualitative research. The guidelines for research questions previously described in this chapter still apply, but there are some new elements to qualitative research questions that are not present in quantitative questions.
- Qualitative research questions often ask about lived experience, personal experience, understanding, meaning, and stories.
- Qualitative research questions may be more general and less specific.
- Qualitative research questions may also contain only one variable, rather than asking about relationships between multiple variables.
| How does witnessing domestic violence impact a child’s romantic relationships in adulthood? | How do people who witness domestic violence understand its effects on their current relationships? |
| What is the relationship between sexual orientation or gender identity and homelessness for late adolescents in foster care? | What is the experience of identifying as LGBTQ+ in the foster care system? |
| How does income inequality affect ambivalence in high-density urban areas? | What does racial ambivalence mean to residents of an urban neighborhood with high income inequality? |
| How does race impact rates of mental health diagnosis for children in foster care? | How do African-Americans experience seeking help for mental health concerns? |
Qualitative research questions have one final feature that distinguishes them from quantitative research questions: they can change over the course of a study. Qualitative research is a reflexive process, one in which the researcher adapts their approach based on what participants say and do. The researcher must constantly evaluate whether their question is important and relevant to the participants. As the researcher gains information from participants, it is normal for the focus of the inquiry to shift.
For example, a qualitative researcher may want to study how a new truancy rule impacts youth at risk of expulsion. However, after interviewing some of the youth in their community, a researcher might find that the rule is actually irrelevant to their behavior and thoughts. Instead, their participants will direct the discussion to their frustration with the school administrators or the lack of job opportunities in the area. This is a natural part of qualitative research, and it is normal for research questions and hypothesis to evolve based on information gleaned from participants.
However, this reflexivity and openness unacceptable in quantitative research for good reasons. Researchers using quantitative methods are testing a hypothesis, and if they could revise that hypothesis to match what they found, they could never be wrong! Indeed, an important component of open science and reproducability is the preregistration of a researcher’s hypotheses and data analysis plan in a central repository that can be verified and replicated by reviewers and other researchers. This interactive graphic from 538 shows how an unscrupulous research could come up with a hypothesis and theoretical explanation after collecting data by hunting for a combination of factors that results in a statistically significant relationship. This is an excellent example of how the positivist assumptions behind quantitative research and intepretivist assumptions behind qualitative research result in different approaches to social science.
- Qualitative research questions often contain words or phrases like “lived experience,” “personal experience,” “understanding,” “meaning,” and “stories.”
- Qualitative research questions can change and evolve over the course of the study.
- Using the guidance in this chapter, write a qualitative research question. You may want to use some of the keywords mentioned above.
9.5 Evaluating and updating your research questions
- Evaluate the feasibility and importance of your research questions
- Begin to match your research questions to specific designs that determine what the participants in your study will do
Feasibility and importance
As you are getting ready to finalize your research question and move into designing your research study, it is important to check whether your research question is feasible for you to answer and what importance your results will have in the community, among your participants, and in the scientific literature
Key questions to consider when evaluating your question’s feasibility include:
- Do you have access to the data you need?
- Will you be able to get consent from stakeholders, gatekeepers, and others?
- Does your project pose risk to individuals through direct harm, dual relationships, or breaches in confidentiality? (see Chapter 6 for more ethical considerations)
- Are you competent enough to complete the study?
- Do you have the resources and time needed to carry out the project?
Key questions to consider when evaluating the importance of your question include:
- Can we answer your research question simply by looking at the literature on your topic?
- How does your question add something new to the scholarly literature? (raises a new issue, addresses a controversy, studies a new population, etc.)
- How will your target population benefit, once you answer your research question?
- How will the community, social work practice, and the broader social world benefit, once you answer your research question?
- Using the questions above, check whether you think your project is feasible for you to complete, given the constrains that student projects face.
- Realistically, explore the potential impact of your project on the community and in the scientific literature. Make sure your question cannot be answered by simply reading more about your topic.
Matching your research question and study design
This chapter described how to create a good quantitative and qualitative research question. In Parts 3 and 4 of this textbook, we will detail some of the basic designs like surveys and interviews that social scientists use to answer their research questions. But which design should you choose?
As with most things, it all depends on your research question. If your research question involves, for example, testing a new intervention, you will likely want to use an experimental design. On the other hand, if you want to know the lived experience of people in a public housing building, you probably want to use an interview or focus group design.
We will learn more about each one of these designs in the remainder of this textbook. We will also learn about using data that already exists, studying an individual client inside clinical practice, and evaluating programs, which are other examples of designs. Below is a list of designs we will cover in this textbook:
- Surveys: online, phone, mail, in-person
- Experiments: classic, pre-experiments, quasi-experiments
- Interviews: in-person or via phone or videoconference
- Focus groups: in-person or via videoconference
- Content analysis of existing data
- Secondary data analysis of another researcher’s data
- Program evaluation
The design of your research study determines what you and your participants will do. In an experiment, for example, the researcher will introduce a stimulus or treatment to participants and measure their responses. In contrast, a content analysis may not have participants at all, and the researcher may simply read the marketing materials for a corporation or look at a politician’s speeches to conduct the data analysis for the study.
I imagine that a content analysis probably seems easier to accomplish than an experiment. However, as a researcher, you have to choose a research design that makes sense for your question and that is feasible to complete with the resources you have. All research projects require some resources to accomplish. Make sure your design is one you can carry out with the resources (time, money, staff, etc.) that you have.
There are so many different designs that exist in the social science literature that it would be impossible to include them all in this textbook. The purpose of the subsequent chapters is to help you understand the basic designs upon which these more advanced designs are built. As you learn more about research design, you will likely find yourself revising your research question to make sure it fits with the design. At the same time, your research question as it exists now should influence the design you end up choosing. There is no set order in which these should happen. Instead, your research project should be guided by whether you can feasibly carry it out and contribute new and important knowledge to the world.
- Research questions must be feasible and important.
- Research questions must match study design.
- Based on what you know about designs like surveys, experiments, and interviews, describe how you might use one of them to answer your research question.
- You may want to refer back to Chapter 2 which discusses how to get raw data about your topic and the common designs used in student research projects.
Media Attributions
- patrick-starfish-2062906_1920 © Inspired Images is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- financial-2860753_1920 © David Schwarzenberg is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- target-group-3460039_1920 © Gerd Altmann is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- Not familiar with SpongeBob SquarePants? You can learn more about him on Nickelodeon’s site dedicated to all things SpongeBob: http://www.nick.com/spongebob-squarepants/ ↵
- Focus on the Family. (2005, January 26). Focus on SpongeBob. Christianity Today . Retrieved from http://www.christianitytoday.com/ct/2005/januaryweb-only/34.0c.html ↵
- BBC News. (2005, January 20). US right attacks SpongeBob video. Retrieved from: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/4190699.stm ↵
- In fact, an MA thesis examines representations of gender and relationships in the cartoon: Carter, A. C. (2010). Constructing gender and relationships in “SpongeBob SquarePants”: Who lives in a pineapple under the sea . MA thesis, Department of Communication, University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL. ↵
research questions that can be answered by systematically observing the real world
unsuitable research questions which are not answerable by systematic observation of the real world but instead rely on moral or philosophical opinions
the group of people whose needs your study addresses
attempts to explain or describe your phenomenon exhaustively, based on the subjective understandings of your participants
"Assuming that the null hypothesis is true and the study is repeated an infinite number times by drawing random samples from the same populations(s), less than 5% of these results will be more extreme than the current result" (Cassidy et al., 2019, p. 233).
whether you can practically and ethically complete the research project you propose
the impact your study will have on participants, communities, scientific knowledge, and social justice
Graduate research methods in social work Copyright © 2021 by Matthew DeCarlo, Cory Cummings, Kate Agnelli is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.

How to Write a Research Proposal: (with Examples & Templates)

Table of Contents
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers’ plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed research that you intend to undertake. It provides readers with a snapshot of your project by describing what you will investigate, why it is needed, and how you will conduct the research.
Your research proposal should aim to explain to the readers why your research is relevant and original, that you understand the context and current scenario in the field, have the appropriate resources to conduct the research, and that the research is feasible given the usual constraints.
This article will describe in detail the purpose and typical structure of a research proposal , along with examples and templates to help you ace this step in your research journey.
What is a Research Proposal ?
A research proposal¹ ,² can be defined as a formal report that describes your proposed research, its objectives, methodology, implications, and other important details. Research proposals are the framework of your research and are used to obtain approvals or grants to conduct the study from various committees or organizations. Consequently, research proposals should convince readers of your study’s credibility, accuracy, achievability, practicality, and reproducibility.
With research proposals , researchers usually aim to persuade the readers, funding agencies, educational institutions, and supervisors to approve the proposal. To achieve this, the report should be well structured with the objectives written in clear, understandable language devoid of jargon. A well-organized research proposal conveys to the readers or evaluators that the writer has thought out the research plan meticulously and has the resources to ensure timely completion.
Purpose of Research Proposals
A research proposal is a sales pitch and therefore should be detailed enough to convince your readers, who could be supervisors, ethics committees, universities, etc., that what you’re proposing has merit and is feasible . Research proposals can help students discuss their dissertation with their faculty or fulfill course requirements and also help researchers obtain funding. A well-structured proposal instills confidence among readers about your ability to conduct and complete the study as proposed.
Research proposals can be written for several reasons:³
- To describe the importance of research in the specific topic
- Address any potential challenges you may encounter
- Showcase knowledge in the field and your ability to conduct a study
- Apply for a role at a research institute
- Convince a research supervisor or university that your research can satisfy the requirements of a degree program
- Highlight the importance of your research to organizations that may sponsor your project
- Identify implications of your project and how it can benefit the audience
What Goes in a Research Proposal?
Research proposals should aim to answer the three basic questions—what, why, and how.
The What question should be answered by describing the specific subject being researched. It should typically include the objectives, the cohort details, and the location or setting.
The Why question should be answered by describing the existing scenario of the subject, listing unanswered questions, identifying gaps in the existing research, and describing how your study can address these gaps, along with the implications and significance.
The How question should be answered by describing the proposed research methodology, data analysis tools expected to be used, and other details to describe your proposed methodology.
Research Proposal Example
Here is a research proposal sample template (with examples) from the University of Rochester Medical Center. 4 The sections in all research proposals are essentially the same although different terminology and other specific sections may be used depending on the subject.

Structure of a Research Proposal
If you want to know how to make a research proposal impactful, include the following components:¹
1. Introduction
This section provides a background of the study, including the research topic, what is already known about it and the gaps, and the significance of the proposed research.
2. Literature review
This section contains descriptions of all the previous relevant studies pertaining to the research topic. Every study cited should be described in a few sentences, starting with the general studies to the more specific ones. This section builds on the understanding gained by readers in the Introduction section and supports it by citing relevant prior literature, indicating to readers that you have thoroughly researched your subject.
3. Objectives
Once the background and gaps in the research topic have been established, authors must now state the aims of the research clearly. Hypotheses should be mentioned here. This section further helps readers understand what your study’s specific goals are.
4. Research design and methodology
Here, authors should clearly describe the methods they intend to use to achieve their proposed objectives. Important components of this section include the population and sample size, data collection and analysis methods and duration, statistical analysis software, measures to avoid bias (randomization, blinding), etc.
5. Ethical considerations
This refers to the protection of participants’ rights, such as the right to privacy, right to confidentiality, etc. Researchers need to obtain informed consent and institutional review approval by the required authorities and mention this clearly for transparency.
6. Budget/funding
Researchers should prepare their budget and include all expected expenditures. An additional allowance for contingencies such as delays should also be factored in.
7. Appendices
This section typically includes information that supports the research proposal and may include informed consent forms, questionnaires, participant information, measurement tools, etc.
8. Citations

Important Tips for Writing a Research Proposal
Writing a research proposal begins much before the actual task of writing. Planning the research proposal structure and content is an important stage, which if done efficiently, can help you seamlessly transition into the writing stage. 3,5
The Planning Stage
- Manage your time efficiently. Plan to have the draft version ready at least two weeks before your deadline and the final version at least two to three days before the deadline.
- What is the primary objective of your research?
- Will your research address any existing gap?
- What is the impact of your proposed research?
- Do people outside your field find your research applicable in other areas?
- If your research is unsuccessful, would there still be other useful research outcomes?
The Writing Stage
- Create an outline with main section headings that are typically used.
- Focus only on writing and getting your points across without worrying about the format of the research proposal , grammar, punctuation, etc. These can be fixed during the subsequent passes. Add details to each section heading you created in the beginning.
- Ensure your sentences are concise and use plain language. A research proposal usually contains about 2,000 to 4,000 words or four to seven pages.
- Don’t use too many technical terms and abbreviations assuming that the readers would know them. Define the abbreviations and technical terms.
- Ensure that the entire content is readable. Avoid using long paragraphs because they affect the continuity in reading. Break them into shorter paragraphs and introduce some white space for readability.
- Focus on only the major research issues and cite sources accordingly. Don’t include generic information or their sources in the literature review.
- Proofread your final document to ensure there are no grammatical errors so readers can enjoy a seamless, uninterrupted read.
- Use academic, scholarly language because it brings formality into a document.
- Ensure that your title is created using the keywords in the document and is neither too long and specific nor too short and general.
- Cite all sources appropriately to avoid plagiarism.
- Make sure that you follow guidelines, if provided. This includes rules as simple as using a specific font or a hyphen or en dash between numerical ranges.
- Ensure that you’ve answered all questions requested by the evaluating authority.
Key Takeaways
Here’s a summary of the main points about research proposals discussed in the previous sections:
- A research proposal is a document that outlines the details of a proposed study and is created by researchers to submit to evaluators who could be research institutions, universities, faculty, etc.
- Research proposals are usually about 2,000-4,000 words long, but this depends on the evaluating authority’s guidelines.
- A good research proposal ensures that you’ve done your background research and assessed the feasibility of the research.
- Research proposals have the following main sections—introduction, literature review, objectives, methodology, ethical considerations, and budget.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How is a research proposal evaluated?
A1. In general, most evaluators, including universities, broadly use the following criteria to evaluate research proposals . 6
- Significance —Does the research address any important subject or issue, which may or may not be specific to the evaluator or university?
- Content and design —Is the proposed methodology appropriate to answer the research question? Are the objectives clear and well aligned with the proposed methodology?
- Sample size and selection —Is the target population or cohort size clearly mentioned? Is the sampling process used to select participants randomized, appropriate, and free of bias?
- Timing —Are the proposed data collection dates mentioned clearly? Is the project feasible given the specified resources and timeline?
- Data management and dissemination —Who will have access to the data? What is the plan for data analysis?
Q2. What is the difference between the Introduction and Literature Review sections in a research proposal ?
A2. The Introduction or Background section in a research proposal sets the context of the study by describing the current scenario of the subject and identifying the gaps and need for the research. A Literature Review, on the other hand, provides references to all prior relevant literature to help corroborate the gaps identified and the research need.
Q3. How long should a research proposal be?
A3. Research proposal lengths vary with the evaluating authority like universities or committees and also the subject. Here’s a table that lists the typical research proposal lengths for a few universities.
| Arts programs | 1,000-1,500 | |
| University of Birmingham | Law School programs | 2,500 |
| PhD | 2,500 | |
| 2,000 | ||
| Research degrees | 2,000-3,500 |
Q4. What are the common mistakes to avoid in a research proposal ?
A4. Here are a few common mistakes that you must avoid while writing a research proposal . 7
- No clear objectives: Objectives should be clear, specific, and measurable for the easy understanding among readers.
- Incomplete or unconvincing background research: Background research usually includes a review of the current scenario of the particular industry and also a review of the previous literature on the subject. This helps readers understand your reasons for undertaking this research because you identified gaps in the existing research.
- Overlooking project feasibility: The project scope and estimates should be realistic considering the resources and time available.
- Neglecting the impact and significance of the study: In a research proposal , readers and evaluators look for the implications or significance of your research and how it contributes to the existing research. This information should always be included.
- Unstructured format of a research proposal : A well-structured document gives confidence to evaluators that you have read the guidelines carefully and are well organized in your approach, consequently affirming that you will be able to undertake the research as mentioned in your proposal.
- Ineffective writing style: The language used should be formal and grammatically correct. If required, editors could be consulted, including AI-based tools such as Paperpal , to refine the research proposal structure and language.
Thus, a research proposal is an essential document that can help you promote your research and secure funds and grants for conducting your research. Consequently, it should be well written in clear language and include all essential details to convince the evaluators of your ability to conduct the research as proposed.
This article has described all the important components of a research proposal and has also provided tips to improve your writing style. We hope all these tips will help you write a well-structured research proposal to ensure receipt of grants or any other purpose.
References
- Sudheesh K, Duggappa DR, Nethra SS. How to write a research proposal? Indian J Anaesth. 2016;60(9):631-634. Accessed July 15, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5037942/
- Writing research proposals. Harvard College Office of Undergraduate Research and Fellowships. Harvard University. Accessed July 14, 2024. https://uraf.harvard.edu/apply-opportunities/app-components/essays/research-proposals
- What is a research proposal? Plus how to write one. Indeed website. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/research-proposal
- Research proposal template. University of Rochester Medical Center. Accessed July 16, 2024. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/MediaLibraries/URMCMedia/pediatrics/research/documents/Research-proposal-Template.pdf
- Tips for successful proposal writing. Johns Hopkins University. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://research.jhu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Tips-for-Successful-Proposal-Writing.pdf
- Formal review of research proposals. Cornell University. Accessed July 18, 2024. https://irp.dpb.cornell.edu/surveys/survey-assessment-review-group/research-proposals
- 7 Mistakes you must avoid in your research proposal. Aveksana (via LinkedIn). Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/7-mistakes-you-must-avoid-your-research-proposal-aveksana-cmtwf/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
How to write a phd research proposal.
- What are the Benefits of Generative AI for Academic Writing?
- How to Avoid Plagiarism When Using Generative AI Tools
- What is Hedging in Academic Writing?
How to Write Your Research Paper in APA Format
The future of academia: how ai tools are changing the way we do research, you may also like, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements.

Discovery and description of gammanonin: a widely distributed natural product from Gammaproteobacteria
- Find this author on Google Scholar
- Find this author on PubMed
- Search for this author on this site
- ORCID record for Jonas Henrique Costa
- ORCID record for Chad W Johnston
- For correspondence: [email protected]
- Info/History
- Supplementary material
- Preview PDF
Antibiotics are essential for modern medicine, but their use drives the evolution of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) that limits the long-term efficacy of any one drug. To keep pace with AMR and preserve our ability to treat bacterial infections, it is essential that we identify antibiotics with new structures and targets that are not affected by clinical resistance. Historically, most developmental candidates for antibiotics have come from microbial natural products, as they feature chemical structures and biological activities that have been honed over millions of years of evolution. Unfortunately, as classical bioactivity screens for natural product discovery are blind to the pharmacological properties of their hits, they often identify molecules with functional groups that limit their utility as drugs. One prominent example is actinonin, an inhibitor of bacterial peptide deformylase (PDF) whose activity is dependent on a hydroxamate moiety associated with toxicity in vivo. The abundance of bacterial genomes now presents an opportunity for target-based natural product discovery, where biosynthetic pathways can be mined for molecules that possess desired activities but lack toxic moieties. Here, we use bioinformatics to lead a chemotype-sensitive, target-based search for natural product inhibitors of bacterial PDF that lacks the conserved and problematic metal chelating group. We describe the discovery, heterologous expression, biosynthesis, total synthesis, and activity of the molecule gammanonin: an apparent actinonin homologue from Gammaproteobacteria. Moving forward, we hope this chemotype and target-driven methodology will help to expedite the discovery of new leads for antibiotic development.
Competing Interest Statement
The authors have declared no competing interest.
View the discussion thread.
Supplementary Material
Thank you for your interest in spreading the word about bioRxiv.
NOTE: Your email address is requested solely to identify you as the sender of this article.

Citation Manager Formats
- EndNote (tagged)
- EndNote 8 (xml)
- RefWorks Tagged
- Ref Manager
- Tweet Widget
- Facebook Like
- Google Plus One
Subject Area
- Biochemistry
- Animal Behavior and Cognition (5521)
- Biochemistry (12563)
- Bioengineering (9419)
- Bioinformatics (30795)
- Biophysics (15836)
- Cancer Biology (12906)
- Cell Biology (18502)
- Clinical Trials (138)
- Developmental Biology (9993)
- Ecology (14949)
- Epidemiology (2067)
- Evolutionary Biology (19147)
- Genetics (12729)
- Genomics (17525)
- Immunology (12668)
- Microbiology (29695)
- Molecular Biology (12360)
- Neuroscience (64671)
- Paleontology (479)
- Pathology (2000)
- Pharmacology and Toxicology (3449)
- Physiology (5322)
- Plant Biology (11071)
- Scientific Communication and Education (1728)
- Synthetic Biology (3063)
- Systems Biology (7681)
- Zoology (1728)

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The following are examples of qualita tive research questions drawn from several types of strategies. 131 Example 7.1 A Qualitative Central Question From an Ethnography Finders (1996) used ethnographic procedures to document the reading of teen magazines by middle-class European American seventh-grade girls. By exam-
Formulating a Research Question. Every research project starts with a question. Your question will allow you to select, evaluate and interpret your sources systematically. The question you start with isn't set in stone, but will almost certainly be revisited and revised as you read. Every discipline allows for certain kinds of questions to be ...
This paper, on writing research questions, is the first in a series that aims to support novice researchers within clinical education, particularly those undertaking their first qualitative study ...
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
arch Questions A research question is a clear, concise, and open-ended question that centers your research for a paper, project, or. literature review. It forms the foundation of a research-based assignment and helps guide the entir. research process. A well-made research question is essential to define the scope and direction of your paper ...
esearch question for a study, depending on the complex-ity and breadth of your proposed work. Each question should be clear and specific, refer to the problem or phenomenon, reflect an inter. ention in experimental work, and note the target population or participants (see Figure 2.1). Identifying a research question will provide greater focus ...
arch questions:1. A good question is about the who, what, where, when, why, or. ow. of social life.2. A good question requires data that can be obtained through the senses using the methods. f. ocial research.3. A good question is sensitive to the characteristics of the person. oi.
Central Question Guidelines. 1. Begin with "How" or "What". Avoid "Why". 2. List the central phenomenon you plan to explore. 3. Identify the participants and research site [this is a quantitative term that implies cause and effect] Qualitative Central Question Script:
In a research paper, the emphasis is on generating a unique question and then synthesizing diverse sources into a coherent essay that supports your argument about the topic. In other words, you integrate information from publications with your own thoughts in order to formulate an argument. Your topic is your starting place: from here, you will ...
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
In essence, the research question that guides the sciences and social sciences should do the following three things:2. 1) Post a problem. 2) Shape the problem into a testable hypothesis. 3) Report the results of the tested hypothesis. There are two types of data that can help shape research questions in the sciences and social sciences ...
the research. For example, if the study begins with a quantitative phase, the investigator might introduce hypotheses. Later in the study, when the qualitative phase is addressed, the qualitative research questions appear. When writing these questions or hypotheses, follow the guidelines in this chapter for scripting good questions or hypotheses.
research question. Using the Anatomy, your question will embody the structural components of a well-crafted study. You will be poised to propose and conduct your study that I hope will illuminate your world. To help you become familiar with the Anatomy, throughout this book, I reference and deconstruct a sample research question. The sample is ...
Some Predictions are Better at Distinguishing among Hypotheses. Hypotheses : Monkeys prefer tree types with foliage that provides the best camouflage from lions. Monkeys prefer trees with a specific insect/leaf that they like to eat. Monkeys prefer trees that are comfortable to sleep in.
Experiments using sounds suggest that we are less responsive during stages 3 and 4 sleep (deep sleep) than during stages 1, 2, or REM sleep (lighter sleep). Thus, the researcher predicts that research participants will be less responsive to odors during stages 3 and 4 sleep than during the other stages of sleep.
question may develop into a series of questions that lead to your conclusion. These steps are used to. connect the dots for your reader, s howing the way to your solutions. Taking the time to ...
DEFINING THE research question is a particularly significant step in research as it narrows the research aim and objective down to specific areas the study will address (Creswell 2014, Johnson and Christensen 2014). Research questions are vital as they guide the choice of methodology, methods, sample, sample size, data collection instrument and
It is a. Prediction: It predicts the anticipated outcome of the experiment. Testable: Once you have collected and evaluated your data (i.e. observations of what the monkeys eat when all five types of leaves are offered), you know whether or not they ate more B leaves than the other types.
Summary. Research question begins with an idea which is then transformed into a research question. A research question: clear, focused, and concise statement that conveys the objectives of the research and its potential findings. Should be expressed in a simple, straight-forward language.
Be 'open' questions (This means that they cannot be answered with a simple 'yes' or 'no' answer. Usually this means starting the question with: who, what, when, where, why, or how) Incorporate terms and concepts that you learnt during your background research. Offer a roadmap to break up your PhD into manageable pieces.
PDF | On Jan 1, 2005, E.M. Khoo published Research questions and research objectives. | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
3) Evaluate and compare two theories, models, or hypotheses. 4) Prove that a certain method is more effective than other methods. Moreover, the research question should address what the variables of the experiment are, their relationship, and state something about the testing of those relationships.
Chapter Outline. Empirical vs. ethical questions (4 minute read); Characteristics of a good research question (4 minute read); Quantitative research questions (7 minute read); Qualitative research questions (3 minute read); Evaluating and updating your research questions (4 minute read); Content warning: examples in this chapter include references to sexual violence, sexism, substance use ...
1. Early questions should be easy and pleasant to answer, and should build rapport between the respondent and the researcher. 2. Questions at the very beginning of a questionnaire should explicitly address the topic of the survey, as it was described to the respondent prior to the interview. 3. Questions on the same topic should be grouped ...
Examples of research questions and hypotheses 1. What is a research question? For project 2, your research question takes the form of, "What is the feasibility of [goal] by [specific method]?" Example: Our research is guided by the question— 1.1. What is the feasibility of [reducing the cost of tuition at public universities in Minnesota] by [increasing state funding]?
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers' plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed ...
to find the examples in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). More information on references and reference examples are in Chapters 9 and 10 of the Publication Manual as well as the Concise Guide to APA Style (7th ed.). Also see the Reference Examples pages on the APA Style website.
One prominent example is actinonin, an inhibitor of bacterial peptide deformylase (PDF) whose activity is dependent on a hydroxamate moiety associated with toxicity in vivo. The abundance of bacterial genomes now presents an opportunity for target-based natural product discovery, where biosynthetic pathways can be mined for molecules that ...