
- Become an Affiliate
- Join our Team
- Online Platform Tutorial
- TEFL Courses
- Contact Us / FAQ
Forgot Username or Password
- Active vs. Passive Voice
- Adverbial Clauses
- Adverbial Phrases
- Be Going To Statements
- Be Going To Wh Questions
- Be Going To Yes/No Questions
- Be Going To & Present Continuous
- Comparatives
- Superlatives
- Comparatives & Superlatives
- Zero Conditional
- First Conditional
- Second Conditional
- Third Conditional
- Mixed Conditionals
- Future Continuous
- Future Continuous vs. Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Simple
- Future Tenses
- Future Time Clauses
- Gerunds & Infinitives
- Have Got & Has Got
- I wish & If only
- Imperatives
- Irregular Verbs
- Narrative Tenses
- Noun Clauses
- Noun Phrases
- Passive Voice
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
- Past Perfect Simple & Continuous
- Past Simple Affirmative & Negative
- Past Simple Passive
- Past Simple Regular Verbs
- Past Simple Was and Were
- Past Simple Wh Questions
- Past Simple Yes/No Questions
- Past Simple vs. Past Continuous
- Past Simple vs. Present Perfect
- Past Tense Review
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
- Present Perfect - Ever and Never
- Present Perfect - For and Since
- Present Perfect - Just, Yet & Already
- Present Simple Affirmative & Negative
- Present Simple Passive
- Present Simple vs. Present Continuous
- Present Simple vs. Present Perfect
- Present Simple Wh Questions
- Present Simple Yes/No Questions
- Present Tense Review
- Question Words
- Relative Clauses
- Reported Speech
- Subject-Verb Agreement
- Tag Questions
- There is & There are
- Wh Questions
- Abstract Nouns
- Adjective-Noun Collocations
- Adjectives of Feeling & Emotion
- Adjectives of Opinion
- Adjectives of Quantity
- Adjective Opposites
- Adjective Order
- Adjective-Preposition Collocations
- -ed and -ing Adjectives
- Adverb-Adjective Collocations
- Adverb Order
- Adverbs of Affirmation & Negation
- Adverbs of Degree
- Adverbs of Frequency
- Adverbs of Manner
- Adverbs of Place
- Adverbs of Time
- Articles - a, an, the
- Causative Verbs
- Collective Nouns
- Common & Proper Nouns
- Compound Adjectives
- Compound Nouns
- Concrete Nouns
- Conjunctions
- Countable & Uncountable Nouns
- Demonstrative Adjectives
- Demonstrative Pronouns
- Dependent Prepositions
- Indefinite Pronouns
- Intensifiers & Mitigators
- Interjections
- Modal Verbs of Ability
- Modals of Deduction & Speculation
- Modals of Necessity
- Modals of Obligation & Prohibition
- Modals of Possibility & Certainty
- Onomatopoeia
- Parts of Speech
- Phrasal Verbs
- Possessives
- Prepositions of Movement
- Prepositions of Place
- Prepositions of Time
- Proper Adjectives
- Quantifiers
- Reflexive Pronouns
- Sense Verbs and Adjectives
- Singular & Plural Nouns
- So and Such
- Subject & Object Pronouns
- Too and Enough
- Transition Words
- Verb-Noun Collocations
- Agreeing & Disagreeing
- Asking Permission
- At the Dentist's
- At the Doctor's
- Being Polite
- Classroom Language
- Complaining & Apologizing
- Complimenting
- Critical Thinking & Problem Solving
- Describing Character & Personality
- Describing People's Appearance
- Describing Places
- Describing Things
- Etiquette and Manners
- Getting Around
- Getting to Know You
- Giving Advice
- Giving Directions
- Giving Opinions
- Giving Personal Information
- Greetings & Introductions
- Indirect Questions
- Likes and Dislikes
- Making Arrangements
- Making Decisions
- Making Excuses
- Making Invitations
- Making Offers & Promises
- Making Requests
- Making Suggestions
- Online Communication
- Ordering Food & Drink
- Social Media
- Telephoning
- Times and Dates
- British English vs. American English
- Cities, Towns & Places
- Clothes & Fashion
- Computers & Smartphones
- Countries & Nationalities
- Crime, Law & Punishment
- Cultural Celebrations
- Daily Routines
- Everyday Objects
- Family & Relationships
- Food & Drink
- Going Out & Entertainment
- Health & Fitness
- Hobbies & Free Time
- Houses, Rooms & Furniture
- Jobs & the Workplace
- Love, Romance & Dating
- Modes of Transport
- Parts of the Body
- Reading Comprehension
- Shapes & Measurements
- The Natural World
- Time Expressions
- TV & Film
- Valentine's Day
- Academic Collocations
- Academic Phrasal Verbs
- Academic Reading Comprehension
- AWL Sublist 1 & 2
- Cause and Effect Essays
- Compare and Contrast Essays
- Discussion Essays
- Discussion Skills
- Discussions Practice
- Essay Writing
- Paragraph Writing
- Persuasive Essays
- Presentation Skills
- Problem Solution Essays
- Punctuation
- Reading Skills
- Referenced Essays
- Study Skills
- The Writing Process
- Business Collocations
- Business Emails
- Business Idioms
- Business Meetings
- Business Negotiations
- Business Phrasal Verbs
- Closing a Presentation
- Dealing with Complaints
- Describing Graphs & Charts
- Presentation Language & Structure
- Resumes, CVs & Email Cover Letters
- Starting a Presentation
- Talking about Companies
- Talking About Jobs
- Answer Games
- Brainstorming Games
- Category Games
- Classic Childhood Games
- Counting Games
- Describing Games
- Drawing Games
- Drilling Activity Games
- First Day of Class Games
- Flashcard Games
- Grammar Games
- Hangman Games
- Listening Games
- Miming Games
- Music Games
- Question & Answer Games
- Sentence Race Games
- Spelling Games
- TV Game Shows
- Vocabulary Games
- Word Association Games
- Yes/No Question Games
- Classroom Interaction Patterns
- Classroom Management
- Concept Checking
- Cultural Awareness
- Developing Students' Listening Skills
- Developing Students' Reading Skills
- Developing Students' Speaking Skills
- Eliciting Techniques
- ESL Dictations
- How to Introduce a Lesson
- How to Use Music in ESL Class
- Lesson Planning
- Making Teaching Materials Relevant
- Problems Learning English
- Teaching English Idioms
- Teaching English Vocabulary
- Teaching Large Classes
- Teaching Mixed-Ability Classes
- Teaching Small Classes
- The First Day of Class
- Using Correction in Class
- Using Song Gap Fills
- Online Membership
- ESL Essentials eBook Series

Reported Speech ESL Games, Activities and Worksheets
- Pre-intermediate ( A2 )
- Intermediate ( B1 )
- Upper-intermediate ( B2 )

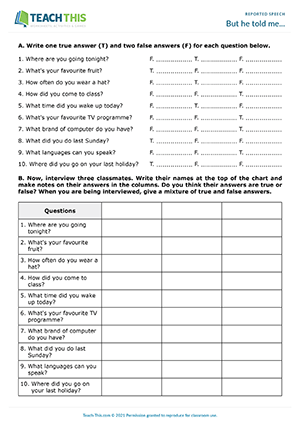
But he told me...
Esl reported speech activity - grammar and speaking: asking and answering questions, forming sentences, true or false, guessing - group work - pre-intermediate (a2) - 40 minutes.
Double Trouble
Esl direct and indirect speech game - grammar and speaking: pelmanism, reforming sentences, controlled practice - group work - pre-intermediate (a2) - 20 minutes.

ESL Reported Speech Game - Grammar and Speaking: Reading and Responding to Statements, Forming Sentences, Controlled Practice - Pre-intermediate (A2) - 35 minutes

You said...
Esl reported speech game - grammar and speaking: miming, guessing, forming sentences - group and pair work - pre-intermediate (a2) - 25 minutes.

Report This
Esl reported speech activity - grammar and speaking: asking and answering questions, forming sentences - pair work - intermediate (b1) - 25 minutes.

Reporting Modal Verbs
Esl reporting modal verbs worksheet - grammar exercises: identifying, matching, gap-fill, rewriting sentences, writing a paragraph - intermediate (b1) - 30 minutes.

Run and Report
Esl reported speech activity - reading, speaking and grammar: running dictation, rewriting sentences - pair work - intermediate (b1) - 25 minutes.

Somebody told me that...
Esl reported speech activities - speaking activity: asking and answering questions - grammar game: forming sentences, guessing - group work - intermediate (b1) - 40 minutes.
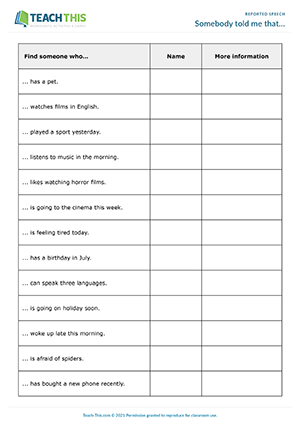
Telephone Messages
Esl reported speech game - grammar and speaking: asking and answering questions from prompts, freer practice - group work - intermediate (b1) - 25 minutes.
Trip Around the World
Esl reported speech activity - grammar, speaking and writing: writing questions and answers, role-play, interview, writing a short article - group and pair work - intermediate (b1) - 45 minutes.

What did they say?
Esl reported speech game - grammar and speaking: asking and answering questions from prompts, writing sentences, controlled and freer practice - group work - intermediate (b1) - 45 minutes.

What did you ask me?
Esl reported speech activity - grammar, speaking and writing: asking and answering questions, writing sentences - pair work - intermediate (b1) - 40 minutes.

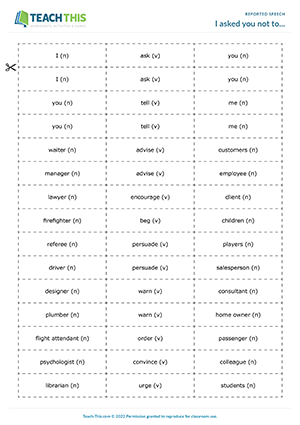
I asked you not to...
Esl reported speech game - grammar: forming sentences from prompts - group work - upper-intermediate (b2) - 45 minutes.
Infinitive Clauses Practice
Esl infinitive clauses worksheet - grammar exercises: binary choice, gap-fill, matching, unscrambling, rewriting sentences - upper-intermediate (b2) - 25 minutes.

Listening In
Esl reported speech game - grammar: sentence completion, guessing - group and pair work - upper-intermediate (b2) - 25 minutes.

Sign up for our monthly newsletter and keep up-to-date with our latest resources, news and website features.
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Latest Free Resources
Upper-intermediate (B2)
Elementary (A1-A2)
Latest Member Resources
Agreeing and disagreeing, here's what our members are saying....
There are a lot of resources that are useful for teaching English. I downloaded the games which are handy and use them in my classes. With the games, my students never skip class or feel tired to learn English. The resources for teaching English helped my students progress in grammar, vocabulary, writing and comprehension. They also helped me a lot to guide my students to learn in a practical way.
I am an ESOL teacher, and the resources have helped my classes enormously. In particular, the speaking activities were a great help for my intermediate students before their exam. The website is user-friendly, and I will continue to utilise the resources - next term is reading and comprehension, so I will be looking for more resources from you. Thank you for such helpful activities and worksheets. They save me a lot of time in class preparation.
Teach This is an absolutely brilliant website, offering a vast amount of high-quality content, much of it free. Everyone involved in its creation deserves commendation. The leadership's vision has my deepest respect and gratitude. It's undoubtedly the best resource for English teachers, with its clear layout, easy navigation, concise messaging, and lack of invasive advertising - rare qualities that Teach This has perfected.
When I need to add or change an activity from my school’s curriculum, I always turn to TeachThis. While our curriculum is usually very good, it sometimes doesn’t fit well with my students. With TeachThis, I can easily find activities that match my topic and level, and the resources make my classes more interesting and varied. I look forward to the monthly newsletter and exploring new materials for inspiration. Please keep it up!
I like the efficiency and organization of the website. The resources cater to various levels with topic-based options for higher levels. The worksheets are very engaging and the answer keys are particularly helpful for teacher. The resources are also highly specific to levels and outcomes, making planning much easier. Finding what I need is simple and time-saving with the keyword search feature. Everything is clear and straightforward.
The easy and ready-to-go materials have helped me a lot during the last few years. Most of all I like the grammar games that activate my pupils and keep them engaged. My lessons have become way more playful and varied. Additionally, I like the grammar worksheets which I use to consolidate what I have worked on during class. The website is very user-friendly, and I have never had any difficulties finding what I was looking for.
A friend told me about the site, and it's awesome. I have found the Business English resources especially engaging and relevant for my students as the materials help them understand business writing and terms. My teaching experience has also improved from using the games on the site as they allow me to teach in a fun way. The user experience is outstanding. Great job!
I found Teach-This a long time ago when I started teaching. It's always had great resources. I really appreciate the grammar materials, board games, and group activities. They've saved me lots of time on lesson planning. The materials are easy to use and understand, making my job much simpler. The best thing is that many resources can be downloaded for free. I've used it for around 8 years, and it consistently offers great content.
I use the resources from the Games Section as part of my daily 30-minute morning warm-up activities, and I've received rave reviews for using them. The games help me maintain student interest and participation and leave the students feeling happy and awake. I like everything about the site, and customer support is very effective as they respond in time.
Teach-This is one of the best EFL websites I've found. It's extremely user-friendly, and I always find what I need quickly. I like the design, and the content is fun, engaging and original. I am very thankful for all your work and generosity by making some resources free. I always recommend this website to my fellow teachers. Your work is really helpful, and I value it enormously.
I like the grammar-focused resources the most as they save me time. The resources also inspire me. If I see an interesting grammar activity, I often rework it for other grammar rules. I like the fact that I simply pay a flat fee, and I can download whatever I want. Teach-This really is a great timesaver. I know that if I am in need of resources for my students, I can go to Teach-This and find something interesting.
Getting familiar with the site and how to use the resources is not difficult. I found the writing skills resources to be the most valuable as they have enhanced my teaching of this skill. The website is elaborate and full of all types of resources to help me teach English. When I contacted customer support, they were super-fast to deal with my enquiry. So overall, I recommend it.
I have found the grammar and vocabulary resources the most valuable. They have improved my teaching experience because they are easy to use and well-organized. The materials are very engaging for my students. The website is also very user-friendly. The best thing about Teach-This is that it offers ready-made worksheets for busy teachers, and the content is well-organized and full of information.
I'm really glad I found the Teach-This website. The materials in the General English section have proven to be really helpful and made my classes more engaging. The materials are well-structured and cover a wide range of topics, making it easy to keep my students interested and motivated. Overall, my experience using your resources has been great.
My first impression of the website was that it was amazing. The games and activities have really improved my teaching. The resources are engaging and relevant to my students’ needs, and I find the website easy to use and navigate. Thanks.
I discovered the site on Google when I was searching for question games and reading activities. It has been very helpful. The activities are awesome and have benefited me and my students by making my classes more fun. I am now less stressed about preparing for classes as the ready-made resources offer me everything I need. I give the site five out of five for user-friendliness. It is very easy to navigate and find what I need.
I would like to thank you for making a fantastic website. I particularly enjoy teaching the functional language materials, which have been very helpful in my classes. The resources have significantly improved my students' communication skills in daily life, so it was rewarding to see them benefit in this way. It feels great to be able to make a difference in my students' lives. Please keep up the good work.
- Have got & Has got
- Adverbs of Affirmation and Negation
- Concrete nouns
- Sense Verbs & Adjectives
- AWL Sublist 1 and 2
- Talking about Jobs
- TEFL Certification & Courses
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use

COMPLEX GRAMMAR FOR 4th E.S.O.
- Criterios de calificación y evaluación ESO
- Información para familias curso 2020/2021
- Temas interdisciplinares
- Reading worksheets
- Exercises (present and past)
- 3º ESO MARZO/ABRIL 2020
- Activities 2019/20
- 4º ESO MARZO/ABRIL 2020
- Grammar exercises I
- Grammar exercises II
- Reinforcement exercises (RANA, ACIns, Refuerzos...)
- Advanced learners
- University Entrance Examination
- Scholarships and courses in summer
- The Big Challenge
- Anglosaxon culture
- Curiosiosities
- Photos & videos
- Webs at school
CONCURSO EUROESCOLA 2015

Enlace Escuela de idiomas de Jaén

Enlace página para exámenes de Cambridge

Enlace para exámenes de Trinity College
Marisol Aguilar González
Dpto. de Idiomas
Esta página web ha sido creada con Jimdo. ¡Regístrate ahora gratis en https://es.jimdo.com !
Reported Speech
Perfect english grammar.

Reported Statements
Here's how it works:
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: I like ice cream.
- Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'. (As I'm sure you know, often, we can choose if we want to use 'that' or not in English. I've put it in brackets () to show that it's optional. It's exactly the same if you use 'that' or if you don't use 'that'.)
But , if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech:
- Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream.
| present simple | I like ice cream | She said (that) she liked ice cream. |
| present continuous | I am living in London | She said (that) she was living in London. |
| past simple | I bought a car | She said (that) she had bought a car OR She said (that) she bought a car. |
| past continuous | I was walking along the street | She said (that) she had been walking along the street. |
| present perfect | I haven't seen Julie | She said (that) she hadn't seen Julie. |
| past perfect* | I had taken English lessons before | She said (that) she had taken English lessons before. |
| will | I'll see you later | She said (that) she would see me later. |
| would* | I would help, but... | She said (that) she would help but... |
| can | I can speak perfect English | She said (that) she could speak perfect English. |
| could* | I could swim when I was four | She said (that) she could swim when she was four. |
| shall | I shall come later | She said (that) she would come later. |
| should* | I should call my mother | She said (that) she should call her mother |
| might* | I might be late | She said (that) she might be late |
| must | I must study at the weekend | She said (that) she must study at the weekend OR She said she had to study at the weekend |
* doesn't change.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
Click here for a mixed tense exercise about practise reported statements. Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.
Reported Questions
So now you have no problem with making reported speech from positive and negative sentences. But how about questions?
- Direct speech: Where do you live?
- Reported speech: She asked me where I lived.
- Direct speech: Where is Julie?
- Reported speech: She asked me where Julie was.
| Where is the Post Office, please? | She asked me where the Post Office was. |
| What are you doing? | She asked me what I was doing. |
| Who was that fantastic man? | She asked me who that fantastic man had been. |
- Direct speech: Do you like chocolate?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
| Do you love me? | He asked me if I loved him. |
| Have you ever been to Mexico? | She asked me if I had ever been to Mexico. |
| Are you living here? | She asked me if I was living here. |
Click here to practise reported 'wh' questions. Click here to practise reported 'yes / no' questions. Reported Requests
There's more! What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)? For example:
- Direct speech: Close the window, please
- Or: Could you close the window please?
- Or: Would you mind closing the window please?
- Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
| Please help me. | She asked me to help her. |
| Please don't smoke. | She asked me not to smoke. |
| Could you bring my book tonight? | She asked me to bring her book that night. |
| Could you pass the milk, please? | She asked me to pass the milk. |
| Would you mind coming early tomorrow? | She asked me to come early the next day. |
- Direct speech: Please don't be late.
- Reported speech: She asked us not to be late.
Reported Orders
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
| Go to bed! | He told the child to go to bed. |
| Don't worry! | He told her not to worry. |
| Be on time! | He told me to be on time. |
| Don't smoke! | He told us not to smoke. |
- Click here for an exercise to practise reported requests and orders.
| now | then / at that time |
| today | yesterday / that day / Tuesday / the 27th of June |
| yesterday | the day before yesterday / the day before / Wednesday / the 5th of December |
| last night | the night before, Thursday night |
| last week | the week before / the previous week |
| tomorrow | today / the next day / the following day / Friday |
- Click here for an exercise about using 'say' and 'tell'.
- Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
Reported Speech 4th eso
(ING) Loreto Cascales Martínez
Created on April 5, 2022
More creations to inspire you
Presentation
ENGLISH IRREGULAR VERBS
Visual communication and storytelling, growth mindset, blended learning, intro innovate, summer zine 2018.
Discover more incredible creations here
REPORTED SPEECH
Difference between direct and indirect speech
- The questions have a different word order to direct questions, but we change the tenses in the same way:
- DIRECT QUESTION: 'HOW OLD ARE YOU?' , she asked.
- SUBJECT QUESTION: She asked me HOW OLD I WAS.
REPORTING QUESTIONS
*SUGGEST/RECOMMEND We can use different structures:'We should go to the beach' he advised.1. He suggested (that) we / she (should/shouldn't) go to the beach2. He suggested going to the beach. (+polite and to avoid IO)1. He recommended (that) we (should) go the beach.2. He recommended going to the beach. (neg: not going)*ADVISE and INVITE is used as follows: He advise me to go to the beach.
*We use verbs such as SUGGEST, RECOMMEND, ADVISE OR INVITE
how to report suggestions:
Present perf. cont.--Past perf. continuous
Past continuous--Past perfect continuous
Will--wouldCan--couldMust--had to
2. Most modal do not change form in reported spech. However, WILL, CAN and MUST do change.
**We don't change the Past Perfect Simple.'Ex: 'They have eaten´ She said that they had eaten.
am/is/ are going to--was/were/going to
Past simple--Past perfect simple
Present perfect simple --Past perfect
Present continuous--Past continuous
Present simple--Past simple
1. We change direct speech into reported speech by putting the main verb further into the past.
***We can omit THAT after SAY and TELLThey said they had lived in GuardamarThey told me they had lived in GuardamarThey said (that) they had lived in Guardamar.
SAY+ to me(THAT)+REPORTED SPEECHThey said to me (that) they had lived in Guardamar.
TELL+INDIRECT OBJECT+(THAT)+ Report. SpeechThey told me (that) they had lived in Guardamar
SAY+ (THAT)+REPORTED SPEECHThey said (that) they had lived in Guardamar.
Nombre del autor/a
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh
We don't use questions words. We use IF or WHETHER in the reported questions as follows:'Are you hungry?' Mum asked us.Mum asked us if /whether we were hungry.
DIRECT QUESTIONS:
WH-QUESTIONS:
Such as WHO, WHY, WHEN, HOW OR WHAT, we repeat the question word in the reported question as follows:HOW TALL IS HE?She asked me HOW TALL HE WAS?
TYPES OF QUESTIONS:
Escribe un titular aquí
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh euismod tincidunt ut laoreet dolore magna aliquam erat volutpat amet elit.
Escribe un titular
Time and place expressions
We also change the pronouns and posssessive adjectives which refer to 'who' the speaker is talking about.'We arrived early', he said.He said that they had arrived early.
Time expressionsnow.............................then, at that momenttoday/tonight...........that day/nightthis (wek/month).....that(week/month)yesterday...................the day beforelast(week/month)....the(week/month)before(two days) ago..........(two days) earliertomorrow...................the next/following daynext(week).................the next/following weekPlace expressionsthis.............................thatthese..........................thosehere............................there
Pronouns and possessive adjectives changes
*NEGATIVE: S+verb+object+NOT TO INFINITIVE'Don't forget to send me a text'She reminded him not to forget to send her a text.
*AFFIRMATIVE: S+verb+object+TO INFINITIVE'Sit down!´---He ordered them all to sit down.
how to report commands, offers and requests:
*We use verbs such as ASK, TELL, ORDER, OFFER, PROMISE, PLEASE
REPORTING VERBS & STRUCTURES
My friend said that she would improve her health.
WHEN WE CHANGE THE WORDS USED BY THE SPEAKER
My friend said: "I will improve my health".
WHEN WE UTILIZE THE SAME WORDS THE SPEAKERS USED
INDIRECT SPEECH
DIRECT SPEECH
ask, beg, etc.
explain, announce, add, admit, promise, answer, apologise, complain, etc
order, warn, instruct, remind, shout, demand, etc
ask, want to know, wonder, enquire, request,etc
Depending on the intention of the sentence, we can use different types of reporting verbs
different reporting verbs
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh euismod.

Reported Speech: Important Grammar Rules and Examples
Reported speech is a very common aspect of the English language. You use it nearly every day, both in conversations and in writing. This reference covers key sections about reported speech, including what it is, examples, rules, and verb tense changes. You’ll also learn about modal verbs, changes in time and place, and different reporting verbs.
Reported Speech

What Is Reported Speech?
Reported speech is simply when you tell somebody what someone else said. You can do this in your writing, or in speech. Reported speech is very different from direct speech , which is when you show what somebody said in the exact way that they said it . In reported speech though, you do not need to quote somebody directly.
Instead, you use a reporting verb, such as ‘say’ or ‘ask’. These reporting verbs are used to report the speech to someone else. There are many different reporting verbs that can be used.
In short, reported speech is the linguistic technique that you use to tell somebody what someone else’s direct speech was. In reported speech though, you may need to make certain changes to the grammar to make the sentence make sense. Some examples below highlight what needs to be changed.
Reported Speech Examples
When using reported speech, you are usually talking about the past. The verbs, therefore, usually have to be in the past too.
For example :
- Direct speech: I’ve lost my umbrella .
- Reported speech: He said (that) he had lost his umbrella.
Another example :
- Direct speech: She is doing her homework .
- Reported speech: He said (that) she was doing her homework.
Table of Changes :
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| I am | He said he was |
| I have | She said she had |
| I will | They said they would |
Reported Speech Rules
Verb tense changes in reported speech.
When the reporting verb is in the present tense, only small changes are needed.
- Direct speech: I like dogs.
- Reported speech: She says she likes dogs.
When the reporting verb is in the past tense, you need to change the tense of both the reporting verb and the main verb.
- Reported speech: She said she liked dogs.
The tenses generally move backward as follows:
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Past Simple | |
| Present Continuous | Past Continuous |
| Past Perfect | |
| Past Simple | Past Perfect |
| Past Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous |
| Past Perfect | Past Perfect (remains unchanged) |
For sentences about the future, you also need to change the future verbs.
- Direct speech: I shall leave in a moment.
- Reported speech: She said that she would leave in a moment.
Here are the changes for future tenses:
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Will | Would |
| Will be | Would be |
| Will have | Would have |
| Will have been | Would have been |
Modal Verbs and Reported Speech
Modal verbs also change when used in reported speech.
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Can | Could |
| Could | Could (unchanged) |
| Have to | Had to |
| Must | Must/Had to |
| May | Might |
| Might | Might (unchanged) |
| Should | Should (unchanged) |
- Direct speech: Will I see you later?
- Reported speech: He asked if he would see me later.
Some modal verbs do not need to change tense because they fit naturally.
- Direct speech: I should go to the park.
- Reported speech: He told me he should go to the park.
Here are both correct and incorrect examples of reported speech for clarity:
- Reported speech: He told me he should go to the park.
- Reported speech: He said he should go to the park.
- Incorrect reported speech: He told he should go to the park.
- Incorrect reported speech: He said me he should go to the park.
To correct these:
- Add ‘me’: He told me he should go to the park.
- Remove ‘me’ or add ‘to’: He said he should go to the park or He said to me he should go to the park.
Direct and Indirect Speech
Changes in time and place in reported speech.
References to time and place often need to change when you use indirect speech. Here is a useful guide to these changes:
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
|---|---|
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| Here | There |
| This | That |
| Tomorrow | The following day/ The next day |
| Next week | The following week/ The week after |
| Yesterday | The previous day/ The day before |
| Last week | The previous week/ The week before |
| Ago | Previously/ Before |
| Tonight | That night |
No Change in Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
In some cases, verb tenses do not change when you report speech indirectly. Here are the key instances:
- When the introductory verb is in the present , present perfect , or future .
- When the reported sentence deals with a fact or general truth .
- When the reported sentence contains a time clause .
- If the verb of the sentence is in the unreal past (the second or the third conditional ).
- The subjunctive stays unchanged in the subordinate clause .
- Had better , could , would , used to , should , might , ought to , and mustn’t remain unchanged.
- If the speaker reports something immediately or soon after it was said .
Reporting Verbs in Indirect Speech
Reporting verbs are crucial in indirect speech. Here is a list categorized by their usage:
- Basic Verbs : Tell, say, ask
- Verb + that + clause : Complain, deny, explain, exclaim, remark, promise, boast, inform somebody, claim, agree, suggest
- Verb + to + infinitive : Agree, offer, refuse, demand, threaten, promise, claim
- Verb + indirect object + to + infinitive : Advise, allow, beg, command, encourage, forbid, invite, want, instruct, permit, urge, order, remind, warn
- Verb + “ing” form : Admit (to), accuse somebody of, apologize for, boast about/of, complain to somebody of, deny, insist on, suggest
- Verb + how : Explain to somebody
Reported Questions
When converting questions from direct to indirect speech, you follow rules similar to those for statements. Verbs used include inquire, wonder, want to know, ask.
Reported Commands and Requests
Commands and requests in Indirect Speech are formed using the to-infinitive and not to-infinitive . Common reporting verbs include order, shout, demand, warn, beg, command, tell, insist, beseech , threaten, implore, ask, propose, forbid.
Pronoun and tense changes are needed when shifting from direct to indirect speech.
Reported Speech Video
- Latest Posts
- Active vs. Passive Voice Exercises – Active vs. Passive Voice Worksheet - December 25, 2023
- Phrase Exercises – Phrase Worksheet - December 23, 2023
- Sentence Exercises – Sentence Worksheet - December 23, 2023
ESL Activities
ESL Games, Activities, Lesson Plans, Jobs & More
in Listening · Reading · Speaking
Reported Speech Games, Activities, Worksheets and Lesson Plans
If you’re looking for some of the best reported speech games and activities, then you’re certainly in the right place. Keep on reading for our top picks, along with worksheets, lesson plans and more.
Reported speech activities
ESL Reported Speech Games
Let’s get into the best activities and games for English learners.

#1: Reported Speech Board Game
I love to play board games in real life which is why I also like to play them with my students! It’s super easy to make your own to use for just about any grammatical point, including this concept.
In this case, fill the board with a bunch of statements like the following:
- Sister-has boyfriend
- Friend-fired from job
- Dad-playing golf tomorrow
Then, students have to make a reported speech statement using the information. It’s fun, engaging and a nice way to give students some practice with this important concept.
Check out this simple ESL board game so you can see how easy it is to make your own:
ESL Board Game .
#2: Ball Toss
This is a simple but versatile activity that’s perfect for reported speech. I write down a number of questions on the beach ball. Then, students take turns tossing the ball to each other and the person that catches it has to answer the question under their right thumb.
To add a reported speech element, have another student (the one who threw the ball?) report on that student’s answer. It’s simple but effective! Check it out:
Ball Toss Activity .
#3: Is that Sentence Correct
If you want to focus on forms, then consider using this simple error correction activity. Write some sentences that use the target grammar. Some have errors while others do not. Students have to find the incorrect ones and make the required changes.
It’s possible to do this in class, or for a homework activity. Have a look here:
Is that Sentence Correct?
#4: Running Dictation
Please enable JavaScript
#5: Mixed Up Sentences
Making good sentences using reported speech can be a little bit tricky. If you want to focus on forms, consider using this simple activity.
Write some sentences on the board of PowerPoint, but mix them up in terms of the order. Students have to work quickly to put them in the correct order and the first time to finish is the winner. It also makes a nice homework assignment. Try it out for yourself:
Mixed Up Sentences .
- Amazon Kindle Edition
- Bolen, Jackie (Author)
- English (Publication Language)
- 92 Pages - 09/27/2020 (Publication Date)
#6: Man/Woman on the Street Interview Activity
If you want to level up the typical ESL interview activity, consider using Man or Woman on the Street. Then, to make it into a reported speech activity, have students tell someone else about what they heard. It’s fun, engaging, and lends itself well to this grammar point. Find out more:
Man/Woman on the Street Activity .
#7: Concentration
This is a fun memory game that’s ideal for a whole bunch of different grammar or vocabulary points. On one card, write down a statement, and then on the other, write down the correct form.
- I have a boyfriend (She told me that she has a boyfriend).
Make a number of these sets. I usually do 8 of them per group of 4. Then, students play a matching memory game. Learn more here:
Concentration Game .
#8: Vocabulary Auction
#9: find someone who bingo game.
This is a nice icebreaker activity that can also be used for some practice with this grammar point. Students have to circulate around the class, asking their classmates questions to find people to fill their Bingo grid.
To make this into a reported speech activity, have students report some of the things they learned about their classmates to a partner (bigger classes) or to the entire class (smaller classes). Find out more about it:
Find Someone Who Bingo Game .
#10: More Ideas for Teaching English
#11: dictogloss and reported speech.
This is a challenging ESL activity that’s perfect for developing listening skills. It also lends itself to almost any vocabulary set or grammatical point, including this one.
Find (or write) a passage of people talking about something that they heard.. Then, put students into pairs and read it out at a faster than normal pace. Students take notes and then attempt to recreate what they heard. Repeat the process again. Finally, they can compare what they have with the original. Check it out:
Dictogloss Activity .
#12: Surveys and Reported Speech
I love to use surveys and questionnaires in my classes. They’re engaging, student-centred and cover a range of skills in a single activity. They’re also great for working on this concept if you get each student to tell their partner some of the things they learned about their classmates.
This is a simple way to cover a new concept but have a quick review of this grammar point as well. Take a look at this activity:
ESL Surveys .
ESL games and activities
#13: Brochure Scanning Activity
This is a nice activity if you have a bunch of different travel brochures. Have students quickly scan them to find important information. For example:
- number of days
Then, have students use reported speech to tell their partner about the trip. Find out more:
Brochure Scanning Activity .
#14: ESL Review Games and Activities
#15: daily routine activities and reported speech.
In terms of topics to combine with this concept, daily routine is one of the best. It’s very simple to set up activities that lead to sentences like the following:
- Tim told me that he gets up at 7 am.
- Jenny said that she usually sleeps in on the weekends.
For some more ideas, have a look here:
Daily Routine ESL Activities .
#16: Error Correction Relay Race
This is a simple activity that takes something old (error correction) and makes it new again. Students have to work in teams to fix errors in a number of reported speech sentences. The first team to make all the corrections is the winner!
Want to give it a try? Learn more:
Error Correction Relay Race .
#17: Dialogue Substitution
#18: news reporting.
Provide students with news headlines or short news articles. Ask them to transform from direct speech (quoted speech) to reported speech (indirect speech) when retelling the news. This activity helps students practice the appropriate changes in verb tenses, pronouns, and time and place references.
#19: Interview and Report
Pair students up and ask them to conduct mock interviews. Afterward, have them report the interview to a different partner using reported speech. This activity allows students to practice converting direct speech into reported while maintaining the meaning and context of the conversation.
#20: Picture Stories
Provide students with a series of pictures that depict a sequence of events. Ask them to create a story using reported speech to describe what is happening in each picture. This activity encourages students to use this language in a narrative context and practice converting direct speech into reported speech.
#21: Role Plays
Create role play scenarios where students take on different roles and engage in conversations. Afterward, ask them to report the conversations to another person using reported speech. This activity allows students to practice converting direct speech into reported speech in a context that mimics real-life situations.
#22: Song Lyrics Transformation
Choose a song that contains direct speech and ask students to rewrite the lyrics using reported speech. This activity helps students practice converting direct speech in songs into reported speech while exploring the meaning and context of the lyrics.
Online Practice for Reported Speech
There are a number of sites for online practice and quizzes that cover this. They are excellent resources to recommend to students who want a little bit of extra practice. Check it out here:
Perfect English Grammar
Exam English
My English Pages
Reported Speech ESL Lesson Plans
There are lots of nice lesson plans. Here are some of the best ones to consider using:
Lingua House

Reported Speech Worksheets
If you’re a busy teacher then you’re going to know what a huge time saver it can be to use worksheets that other teachers have made. Here are some of the top picks:
ISL Collective
English Grammar
There are a number of common questions that people have about using this method of speech. Here are the answers to some of the most popular ones.
What is reported speech ESL?
Reported speech ESL is when we tell someone what another person said. You often have to use a tense that is further back in time (backshift) and may also need to change the pronouns.
What are some examples of reported speech?
Some examples of reported speech are the following:
- They said you didn’t want to come.
- My mom told me that she was angry at my dad.
- I asked her what her plans were.
How do you teach reported speech?
To teach reported speech, first set the context with a short video clip, discussion question, etc. Then, explain the grammar rules for it and do some controlled practice. Finally, use an ESL game or activity that allows students to practice further.
What are the types of reported speech?
The types of reported speech are direct speech and indirect speech.
Tips for Teaching Reported Speech To English Learners
Teaching reported speech to ESL learners can be challenging, as it involves a shift in verb tense and pronoun usage. Here are some tips to make the teaching process more effective and engaging.
Start with Direct Speech
Begin by introducing and reviewing direct speech, which is the original statement or question spoken by someone. Ensure students are familiar with the use of quotation marks and the appropriate verb tenses in direct speech.
Introduce Reporting Verbs
Teach students a variety of reporting verbs such as say, tell, ask, explain, suggest, etc. Explain the different patterns that follow these reporting verbs, including the use of direct objects, indirect objects, and prepositions.
Present Tense Changes
Demonstrate how to change verb tenses when reporting speech. Provide clear examples of how present simple changes to past simple, present continuous changes to past continuous, and so on. Reinforce the importance of maintaining accuracy in verb tense changes.
Practice Conversion of Pronouns
Show students how pronouns change when reporting speech. Explain the transformation from the speaker’s pronouns (I, you, we) to the appropriate pronouns in reported speech (he, she, they). Emphasize the use of possessive pronouns when necessary.
Provide Contextualized Examples
Use authentic materials, such as dialogues, interviews, or news articles, to provide meaningful examples of reported speech. This helps students understand the purpose and practical application in real-life situations.
Use Reporting Structures
Teach students reporting structures, such as reporting statements, reporting questions, and reporting commands. Practice transforming direct speech into reported speech using these structures and provide opportunities for students to generate their own examples.
Focus on Reporting Verbs of Perception
Highlight reporting verbs of perception like see, hear, feel, notice, etc., which require a change in verb tense but do not require reporting the exact words. Provide examples to help students understand the difference between reporting statements and reporting verbs of perception.
Incorporate Speaking and Writing Activities
Encourage students to practice reported speech through role-plays, interviews, or storytelling activities. Assign writing tasks where students report a conversation or summarize an article using reported speech.
Address Common Errors
Be aware of common errors students make when learning reported speech, such as incorrect verb tense changes or pronoun usage. Provide corrective feedback and offer opportunities for targeted practice to overcome these challenges.
Review and Reinforce
Regularly review with students and provide opportunities for reinforcement through quizzes, games, or interactive exercises. Repetition and reinforcement are key to solidifying understanding and application of this language.
Did you like these Reported Speech Activities?
- 87 Pages - 10/24/2019 (Publication Date)
Yes? Thought so. Then you’re going to love this book on Amazon: 39 No-Prep/Low-Prep ESL Grammar Activities for Teenagers and Adults . It’s the book you need if you want to have more engaging and interactive grammar lessons.
You can find the book in both digital and print formats. Keep a copy on the bookshelf in your office to use as a handy reference guide. Or, take the e-version with you to your favourite coffee shop for some lesson planning on the go.
Whatever the case, get ready for some ESL grammar teaching awesome in your life. Head over to Amazon to find out more about it:
Have your Say about Reported Speech Games and Activities
What do you think about these activities? Are they a winner, or do you have another one that you’d like to recommend? Leave a comment below and let us know what you think. We’d love to hear from you.
Also, be sure to give this article a share on Facebook, Pinterest, or Twitter. It’ll help other busy English teachers, like yourself find this useful resource.
Last update on 2022-07-17 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API
About Jackie
Jackie Bolen has been teaching English for more than 20 years to students in South Korea and Canada. She's taught all ages, levels and kinds of TEFL classes. She holds an MA degree, along with the Celta and Delta English teaching certifications.
Jackie is the author of more than 100 books for English teachers and English learners, including Business English Vocabulary Builder , 67 ESL Conversation Topics ,and 39 No-Prep/Low-Prep ESL Speaking Activities for Teenagers and Adults . She loves to share her ESL games, activities, teaching tips, and more with other teachers throughout the world.
You can find her on social media at: YouTube Facebook Instagram
Top Selling ESL Activity Book
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
More ESL Activities and Games
Requesting games & asking for help activities for esl, musical instruments names with pictures: top 25, esl weather activities: make your esl weather lesson fun, 20 most common adjectives that start with b, about, contact, privacy policy.
Best-selling author and English teacher Jackie Bolen has been talking ESL activities and games since 2015. The goal is to bring you the best ideas, lesson plans, and activity recommendations for your TEFL classes.
Get in touch: About + Contact
Privacy Policy and Terms of Use
Email: [email protected]
Address: 2436 Kelly Ave, Port Coquitlam, Canada

- All topics A-Z
- Grammar
- Vocabulary
- Speaking
- Reading
- Listening
- Writing
- Pronunciation
- Virtual Classroom
- Worksheets by season
- 600 Creative Writing Prompts
- Warmers, fillers & ice-breakers
- Coloring pages to print
- Flashcards
- Classroom management worksheets
- Emergency worksheets
- Revision worksheets
- Resources we recommend










COMMENTS
Some exercises to practise reported speech (statements, questions, orders, requests and suggestions)
My mother asked me who I had been talking to the day before. (Reported S.) - Otros verbos:demandshoutwarn. - Órdenes:"Please, be quiet now!" (Direct Speech)The teacher asked us to be quiet then. (Reported S.)- Peticiones y Avisos:"Please, don't send homework today, teacher!" (Direct Sp.) The students begged the teacher not to send homework ...
Liveworksheets transforms your traditional printable worksheets into self-correcting interactive exercises that the students can do online and send to the teacher.
Fun ESL reported speech games, activities and worksheets to help you teach your students how to use indirect speech to report back what other people said.
REPORTED SPEECH I Here, you can find grammar explanations and some exercises about reported speech Apuntes + ejercicios Reported Speech.doc Documento Microsoft Word 63.0 KB Descarga
Practise reported speech - clear explanations and lots of exercises.
Present simple--Past simple. 1. We change direct speech into reported speech by putting the main verb further into the past. ***We can omit THAT after SAY and TELLThey said they had lived in GuardamarThey told me they had lived in GuardamarThey said (that) they had lived in Guardamar. SAY+ to me (THAT)+REPORTED SPEECHThey said to me (that) they ...
Learn about reported speech in English language: what it is, examples, rules, verb tense changes, modal verbs, time/place changes, and reporting verbs.
Find out all the top picks for reported speech games and activities, along with worksheets, lesson plans, online practice and more.
Reported Speech Card Games For some students, the best way to learn Reported Speech is by reading the statements they have to report. This is why we often write them on the board. Try these card games instead! For the first game, prepare a set of index card each with a direct speech statement on one side and the indirect statement on the other. Divide students into pairs. Student A picks up a ...
Liveworksheets transforms your traditional printable worksheets into self-correcting interactive exercises that the students can do online and send to the teacher.
3. "Will you help organise the party for Jim next week?" asked Taylor. Taylor asked us if we ................................
Liveworksheets transforms your traditional printable worksheets into self-correcting interactive exercises that the students can do online and send to the teacher.
Reported speech - indirect speech. Reporting statements, questions and commands. Reporting verbs. English intermediate grammar exercises.
REPORTED SPEECH - EXPLANATION AND PRACTICE Mark as done Descargar carpeta
We use reported speech when we want to tell someone what someone said. We usually use a reporting verb (e.g. say, tell, ask, etc.) and then change the tense of what was actually said in direct speech. So, direct speech is what someone actually says? Like 'I want to know about reported speech'?
Reported speech is when you tell somebody what you or another person said before. When reporting a speech, some changes are necessary.
The document contains examples of reported speech, with sentences in direct speech followed by the same sentences rewritten in reported or indirect speech. In the first section, direct speech quotes are rewritten by changing pronouns, tense, and sometimes words to report rather than quote what was said. The second section asks the reader to complete reported speech versions of questions and ...
Reported speech is the name we give to the set of grammatical structures we use to tell someone what another person said or thought. A statement that reports speech always has two main parts: a reporting verb No definition set for verb Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
Liveworksheets transforms your traditional printable worksheets into self-correcting interactive exercises that the students can do online and send to the teacher.
If we report what another person has said, we usually do not use the speaker's exact words (direct speech), but reported (indirect) speech. Therefore, you need to learn how to transform direct speech into reported speech. The structure is a little different depending on whether you want to transform a statement, question or request.
9/11 live updates: Biden and Harris attend wreath-laying ceremony at the Pentagon
Liveworksheets transforms your traditional printable worksheets into self-correcting interactive exercises that the students can do online and send to the teacher.