

साक्षरता पर निबंध हिंदी में । Essay on Literacy in Hindi

आज के युग में लोग ज़मीन से आसमान तक को छूने की बातें करते हैं और ऊंचे ख्वाब देखते हैं। वे यह ख्वाब देख सकते बैन क्योंकि उन्हें शिक्षा और ज्ञान का हथियार मिल गया है।
पूरी दुनिया मे सभी को साक्षरता का महत्व समझ आये इस उद्देश्य से सभी राष्ट्रों की सरकार ने साक्षरता दिवस मनाने की घोषणा की जो हर साल 8 सितम्बर को आता है।
साक्षरता का महत्व
साक्षरता को मनाने कियो शुरुआत सर्व प्रथम संयुक्त राष्ट्र संग के यूनेस्को ने 17 नवम्बर वर्ष 1965 को की थी। यह दिवस पूरे रास्ट्र में सामाजिक तौर पर पर ज्ञान का प्रकाश फैलाएगा जिससे हमारा आने वाला कल सुनहरा हो सके। शिक्षा से सभी रास्ट्र के लोगों में जागरूकता फैलेगी और देश का उद्धार होगा और विकास के मार्ग पर चलेगा।
साक्षरता दिवस को मनाने का उद्देश्य लोगों के बीच शिक्षा क सबसे मूल्यवान करार देना क्योंकि निरक्षता के अंधेरे के डूबकर किसी को भी सोचने व समझने की शक्ती नही रहेगी।
लोगों की जिंदगी को ज्ञान से प्रकाशित करके की हम इस दुनिया का भला कर सकते हैं। एक बेहतर और सभ्य जीवन के लिए एक व्यक्ति का साक्षर होना अति आवश्यक है।
क्यों ज़रूरी है शिक्षा?
एक निरक्षर न तो खुद का कभी भला कर सकता है और न ही दूसरों व समाज का। जो इंसान खुद निरक्षरता के अंधकार में डूबा हुआ है वह दूसरों को क्या गया का प्रकाश देगा और अतः समाज के लिए अपने दायित्व को भी नही निभा पायेगा।
साक्षरता से हम ज़मीन से आसमानों तक पहुंच सकते हैं क्योंकि ज्ञान है तो सब मुमकिन है। साक्षरता हलोगों की विचारधारा को दर्शाती है। आज का आधुनिक काफी तेज और टेक्नोलॉजी से युक्त हो गया है।
शिक्षा से देश का कल्याण
आज लोगों के साथ साथ चलने के किये साक्षर होना बेहद ज़रूरी है। शिक्षा का मूल्य जानना सभी देश की आवश्यकता है क्योंकि हमारी यब हमारे नए विचार को जन्म देती है। आजकल के माँ-बाप बग़ैर शिक्षा पाए अपने बच्चों को भी शिक्षा नही दे सकते। अर्थात साक्षरता देश की आथिक विकास के को तो सही रखता है है इसके अलावा व्यक्तिगत राष्ट्रीय हिट को भी बढ़ावा देता है।
शिक्षा पाना हर उस व्यक्ति के लिए मूल्यवान है जो जीवन में कुछ बड़ा कुछ बड़ा करना चाहते हैं। एक व्यक्ति की इच्छाएं और कामना उसके जिंदगी से भी बड़ी होती है।। एक साक्षर व्यक्ति अपनी शिक्षा के दम पर पूरे रास्ट्र में परिवर्तन ला सकता है और व्यक्ति को एक नेक और अच्छा इंसान भी बना सकता है। पढ़ा लिखा इंसान ही खुद को और समाज की सोच को बदल सकता है।
साक्षरता एक प्रकार का गुण है, जो पीढ़ी दर पीढ़ी पा सकते है। शिक्षा पाना सभी के लिए महत्वपूर्ण और अनिवार्य है क्योंकि इसी के द्वारा एक बेहतर कल का निर्माण हो सकता है।
हर वो इंसान जो इस समाज की नींव मजबूत करता है उसे साक्षर होने की आवश्यकता है। निरक्षता एक रास्ट्र के किये ज़हर के समय है और इससे बार किसी को उबारना चाहिए।
Related Posts
कोरोना वायरस पर निबंध l लक्षण l उपाय l essay on corona virus in hindi, मातृ दिवस पर निबंध। mother’s day, taj mahal essay in english for students & childrens, मेरा गाँव पर निबंध l essay on my village in hindi, विद्यार्थी जीवन के महत्व पर निबंध l essay on importance of students life, बाल दिवस पर लघु निबंध । short essay on children’s day, भ्रष्टाचार की समस्या और समाधान पर निबंध । problem & solution of corruption, essay on diligence, importance of diligence in life, नारी शिक्षा का महत्व । essay on importance of women education, मदर टेरेसा पर निबंध । essay on mother teresa in hindi, 2 thoughts on “साक्षरता पर निबंध हिंदी में । essay on literacy in hindi”.
Pingback: साक्षरता आवश्यक क्यों है ।अर्थ। महत्व। Why Literacy is Important -
Pingback: युद्ध के लाभ और हानियां, Advantages & Disadvantages of War Essay
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
साक्षरता पर अनुच्छेद | Paragraph on Literacy in Hindi
साक्षरता पर अनुच्छेद | Paragraph on Literacy in Hindi!
साक्षरता का अर्थ है – अक्षर ज्ञान होना । दूसरे शब्दों में, पढ़ने-लिखने की क्षमता का होना ही साक्षरता है । आज की दुनिया में सामान्य ज्ञान का बहुत महत्त्व है । इससे युक्त व्यक्ति को ही सफलता मिल सकती है । अनपढ़ व्यक्ति ज्ञान और जानकारी के अथाह भंडार से वंचित रह जाता है । वह कुएँ के मेढक के समान अपनी संकीर्ण दुनिया में ही कैद रह जाता है । वह न तो अधिकारों का सही प्रयोग कर सकता है न ही जनसामान्य के लिए उपलब्ध सुख-सुविधाओं का लाभ उठा सकता है । आज व्यक्ति का साक्षर होना अनिवार्य हो गया है । निरक्षरता एक दुर्गुण बन गया है । इसलिए आजकल हर कोई पढ़ना-लिखना चाहता है । सरकार तथा समाज की ओर से देश के हर नागरिक को साक्षर बनाने के प्रयास किए जा रहे हैं । इसके लिए सभी स्थानों पर स्कूल खोले गए हैं । हर बालक को साक्षर बनाने के लिए अभियान चलाए गए हैं । इस नेक कार्य में जनता की भागीदारी आवश्यक है । इक्कीसवीं सदी में यदि भारत का हर नागरिक साक्षर हो जाए तो यह हमारी महान उपलब्धि होगी ।
Related Articles:
- प्रौढ़ शिक्षा पर अनुच्छेद | Paragraph on Adult Education in Hindi
- स्वास्थ्य ही धन है (अनुच्छेद) | Paragraph on Health is Wealth in Hindi
- इंटरनेट पर अनुच्छेद | Paragraph on Internet in Hindi
- कंप्यूटर पर अनुच्छेद | Paragraph on Computer in Hindi

अगर आप पढ़ाई कर रहे है या अंग्रेजी सिख रहे है तो आपने कई बार Literacy शब्द को जरूर पढ़ा होगा। इस Literacy शब्द का हिंदी अर्थ काफी मजेदार है, जो मैं आपको इस आर्टिकल में बताऊंगा। इस आर्टिकल में, मैं आपको Literacy Meaning in Hindi में बताने के अलावा और भी काफी सारी जानकारीयां दूँगा, जैसे- Illiteracy meaning in Hindi, Literacy Rate in India आदि।
Literacy शब्द शिक्षा से जुड़ा एक अहम शब्द है, जिसे अंग्रेजी वाक्यों में Noun के रूप में इस्तेमाल किया जाता है। इस आर्टिकल में आप लिटरेसी का अर्थ, मतलब, अनुवाद, उच्चारण, समानार्थक शब्द, विलोम शब्द इत्यादि के बारे में जानेंगे।
तो चलिए अब मैं आपको Literacy Meaning In Hindi With Example के साथ बताता हूँ।
Literacy Meaning In Hindi
Literacy शब्द का हिंदी अर्थ “ साक्षरता ” होता है, जिसका मतलब है पढ़ना और लिखना जानना। इसे अंग्रेजी वाक्यों में Noun (संज्ञा) के रूप में इस्तेमाल किया जाता है।
उदाहरण:
- The government is working to improve literacy rates in the country. (सरकार देश में साक्षरता दर सुधारने के लिए काम कर रही है।)
- The children are tested in basic literacy. (बच्चों की बुनियादी साक्षरता की परीक्षा ली जाती है।)
Literacy शब्द के हिन्दी अर्थ
- साक्षरता (स्त्रीवाचक)
- पढ़ने लिखने की योग्यता
Literacy शब्द रूप
Literacy एक एकवचन संज्ञा शब्द है जिसे आप वाक्य में बहुवचन संज्ञा के रूप में भी इस्तेमाल कर सकते है।
- Literacies (बहुवचन)
Literacy Meaning In English
The word “ literacy ” has a few different meanings, but it is generally understood to mean the ability to read and write. The original definition of literacy was the ability to read and write at a basic level. However, the definition of literacy has evolved over time to include the ability to understand and use information in a variety of contexts, including print, digital, and visual.
Literacy Pronunciation In Hindi
Literacy का Pronunciation “ लिटरेसी ( li-tuh-ruh-see) ” के रूपय में किया जाता है। कुछ देशों में इसका उच्चारण लितेरैय और लिट्रैसीय के रूप में भी किया जाता है। हालांकि अधिकतर जगह पर Literacy का उच्चारण “लिटरेसी” के रूप में ही किया जाता है।
Literacy Rate Meaning In Hindi
Literacy rate का हिंदी में अर्थ “साक्षरता दर” होता है। इसे साक्षरता प्रतिशत, साक्षरता अनुपात और साक्षरता स्तर भी कहते है।
साक्षरता दर एक जनसंख्या में पढ़ने और लिखने में सक्षम लोगों का प्रतिशत है। साक्षरता दर आमतौर पर 15 वर्ष और उससे अधिक आयु के लोगों के प्रतिशत के रूप में मापी जाती है जो अपनी रोजमर्रा की जिंदगी में थोड़ा बहुत लिखना – पढ़ना जानते हो।
Literacy rate के हिंदी अर्थ:
- साक्षरता प्रतिशत
- साक्षरता दर
- साक्षरता अनुपात
- साक्षरता स्तर
Illiteracy Meaning In Hindi with Example
Illiteracy Literacy शब्द का विलोम शब्द है जिसका हिंदी अर्थ “निरक्षरता” होता है। इलिटरसी को भी अंग्रेजी भाषा में Noun के रूप में इस्तेमाल किया जाता है। उदाहरण:
“भारत में अभी भी बहुत सारे लोग निरक्षर हैं।” (Bahut saare log bharat mein abhi bhi nirakshar hain.)
English Translate: “ There are still many illiterate people in India.”
Illiteracy के कई हिंदी अर्थ है, जैसे:
- निरक्षरता
- विद्याहीनता
- अशिक्षा
निरक्षरता का मतलब पढ़ने और लिखने में असमर्थता है। यह एक गंभीर समस्या है जो लोगों के जीवन को कई तरह से प्रभावित कर सकती है। निरक्षर लोगों को नौकरी पाना, समाज में भाग लेना और अपने स्वास्थ्य की देखभाल करना मुश्किल हो सकता है।
Literacy क्या है, हिंदी अर्थ
हिंदी में, “literacy” का अर्थ “ साक्षरता ” है। साक्षरता पढ़ने और लिखने की क्षमता है। यह एक मौलिक कौशल है जो लोगों को अपने जीवन में सफल होने में मदद करता है।
साक्षरता के कई लाभ हैं, जैसे लोगों को नौकरी पाना, शिक्षा प्राप्त करना, अपने स्वास्थ्य की देखभाल करना, और अपने अधिकारों के बारे में जानना आदि। साक्षरता लोगों को समाज में अधिक पूर्ण रूप से भाग लेने में भी मदद करती है।
दुनिया भर में अभी भी कई लोग निरक्षर हैं। निरक्षरता एक गंभीर समस्या है जो लोगों के जीवन को कई तरह से प्रभावित कर सकती है। निरक्षर की वजह से लोग रोजगार, शिक्षा, और स्वास्थ्य सेवा का लाभ आसानी से नही ले पाते है। निरक्षर लोग अपने अधिकारों के बारे में जानने में भी असमर्थ हो सकते हैं।
सरकारी और गैर-सरकारी संगठन साक्षरता को बढ़ावा देने के लिए कई तरह की योजनाएं चला रही हैं, ताकि ज्यादा से ज्यादा लोग साक्षर बन सके। क्योंकि बिना साक्षरता के लोगों का जीवन काफी कठिन होता है, और निरक्षता देश के विकास को पीछे ले जाती है। इसलिए देश में साक्षरता दर बढ़ाना जरूरी है।
भारत में Literacy Rate क्या है
2023 के आंकड़ो के अनुसार भारत की साक्षरता दर 77.7% है। इसका मतलब है कि भारत में 15 वर्ष और उससे अधिक आयु के लोगों की आबादी का 77.7% पढ़ना और लिखना जानता है। यह एक महत्वपूर्ण प्रगति है, क्योंकि 1947 में भारत की साक्षरता दर केवल 18% थी।
हालांकि, भारत में अभी भी बहुत सारे लोग निरक्षर हैं। 2023 में, भारत की निरक्षरता दर 22.3% है। निरक्षरता दर राज्य के अनुसार भिन्न होती है , केरल में सबसे अधिक साक्षरता दर (96.2%) और बिहार में सबसे कम साक्षरता दर (63.8%) है।
भारत में Literacy Day कब मनाया जाता है
भारत में Literacy Day 15 सितंबर को मनाया जाता है क्योंकि इस दिन भारत के महान इंजीनियर और भारत रत्न सर मोक्षगुंडम विश्वेश्वरैया की जयंती है। विश्वेश्वरैया ने भारत में साक्षरता और शिक्षा को बढ़ावा देने के लिए बहुत काम किया। उन्होंने कई स्कूलों और कॉलेजों की स्थापना की और कई साक्षरता कार्यक्रमों को शुरू किया।
1968 में, भारत सरकार ने 15 सितंबर को Literacy Day के रूप में घोषित किया, जो भारत के लिए महत्वपूर्ण दिन है।
Literacy के अन्य Noun शब्द
Literacy के कुछ अन्य Noun शब्द भी हैं, जो निम्नलिखित हैं-
- Literacy Programs (साक्षरता कार्यक्रम)
- Literacy Education (साक्षरता शिक्षा)
- Literacy Campaign (साक्षरता अभियान)
- Literacy Skills (साक्षरता कौशल)
- Literacy Learning (साक्षरता शिक्षा)
- Literacy Levels (साक्षरता स्तर)
- Literacy Test (साक्षरता परीक्षण)
- Literacy Development (साक्षरता विकास)
- Literacy Programmes (साक्षरता कार्यक्रम)
- Literacy Project (साक्षरता परियोजना)
Literacy के उदाहरण और वाक्य
जैसा की मैने बताया कि Literacy शब्द को अंग्रेजी वाक्यों में Noun (संज्ञा) के रूप में इस्तेमाल कर सकते है। चलिए मैं आपको Literacy शब्द के कुछ उदाहरण देता हूँ।
- The literacy rate in India is 77.7%. (भारत में साक्षरता दर 77.7% है।)
- The program is designed to promote adult literacy . (यह कार्यक्रम वयस्क साक्षरता को बढ़ावा देने के लिए बनाया गया है।)
- The children are tested in basic literacy . (बच्चों की बुनियादी साक्षरता की परीक्षा ली जाती है।)
- The literacy rate in that country is the highest in the region. (उस देश में साक्षरता दर क्षेत्र में सबसे अधिक है।)
- A high standard of literacy is required for this job. (इस कार्य के लिए उच्च स्तर की साक्षरता की आवश्यकता है।)
- Literacy is essential for individual and societal development. (व्यक्तिगत एवं सामाजिक विकास के लिए साक्षरता आवश्यक है।)
- The literacy program has helped to improve the lives of many people. (साक्षरता कार्यक्रम ने कई लोगों के जीवन को बेहतर बनाने में मदद की है।)
- The literacy rate is a key indicator of a country’s development. (साक्षरता दर किसी देश के विकास का एक प्रमुख संकेतक है।)
- The government should invest in literacy programs to improve the lives of its citizens. (सरकार को अपने नागरिकों के जीवन को बेहतर बनाने के लिए साक्षरता कार्यक्रमों में निवेश करना चाहिए।)
Literacy के समानार्थी (Synonyms) शब्द
Literacy के कुछ समानार्थी शब्द निम्नलिखित हैं:
- Education (शिक्षा)
- Articulateness (कलामत्मकता)
- Learning (सीख रहा हूँ)
- Proficiency (प्रवीणता)
- Knowledge (ज्ञान)
Literacy के विलोम (Antonyms) शब्द
Literacy के कुछ विलोम शब्द भी हैं, जैसे-
- Illiteracy (निरक्षरता)
- Ignorance (अज्ञान)
- Crudeness (भोंडापन)
- Analphabetism (वर्णसंकरता)
- Callowness (उदासीनता)
- Denseness (सघनता)
Literacy से जुड़े कुछ FAQs भी पढ़े-
Q1. लिटरेसी का मतलब क्या होता है?
उत्तर: लिटरेसी का शाब्दिक अर्थ है “पढ़ना और लिखना”। इसका मतलब उन लोगों से हैं जो 15 वर्ष की आयु से ऊपर है और उन्हे पढ़ना – लिखना आता है। लिटरेसी का मतलब पढ़ने और लिखने की क्षमता होती है।
Q3. साक्षरता क्या है और इसका उदाहरण क्या है?
उत्तर: साक्षरता वह क्षमता है जिससे व्यक्ति अपनी रोजमर्रा की जिंदगी में आसान चीज़ों को पढ़ना – लिखना जानता हो। यह एक महत्वपूर्ण कौशल है जो लोगों को अपने जीवन में सफल होने में मदद कर सकता है। Literacy को अंग्रेजी भाषा में Noun के रूप में इस्तेमाल करते हैं, उदाहरण: The literacy rate in India is 77.7%.
इसे भी पढ़े:
Dictator meaning in Hindi
Grief Meaning In Hindi
इस आर्टिकल में, मैने Literacy Meaning In Hindi And English में बताया है। मुझे पूरी उम्मीद है कि इस आर्टिकल को पढ़ने के बाद आपको Literacy के बारे में अच्छी जानकारी मिल चुकी होगी। अगर आपको आर्टिकल अच्छा लगा हो तो इसे अपने उन दोस्तों के साथ ज़रूर शेयर करें जो अंग्रेजी सिखना चाहते है।
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Essay on Illiteracy in India
Students are often asked to write an essay on Illiteracy in India in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Illiteracy in India
Introduction.
Illiteracy is a major issue in India, affecting the nation’s development. It refers to the inability to read or write.
Illiteracy is primarily due to poverty, lack of educational facilities, and gender inequality. Many children can’t attend school due to economic hardship.
Illiteracy leads to unemployment and poverty, creating a vicious cycle. It also hampers social and economic growth.
Government initiatives, NGOs, and society can play a crucial role in eradicating illiteracy. Education must be accessible and affordable to all.
250 Words Essay on Illiteracy in India
India, despite its significant advancements in various sectors, continues to grapple with the issue of illiteracy. A sizable portion of the population lacks basic reading and writing skills, which poses a significant barrier to the nation’s socio-economic development.
The Extent of Illiteracy
According to the 2011 census, India’s literacy rate was 74.04%, leaving approximately a quarter of the population illiterate. This figure, however, masks disparities across regions, genders, and social groups. Rural areas, women, and marginalized communities are disproportionately affected, reflecting deep-rooted social inequalities.
Underlying Causes
The causes of illiteracy in India are multifaceted. Poverty plays a significant role, forcing children into labor at a young age and denying them educational opportunities. Additionally, inadequate school infrastructure, particularly in rural areas, contributes to high dropout rates. Furthermore, societal norms and gender biases often restrict girls’ access to education.
The Impact of Illiteracy
Illiteracy hampers individuals’ potential and restricts their access to opportunities. It perpetuates poverty and social inequality, hindering India’s progress towards its development goals. Illiterate individuals are more likely to suffer from poor health, low income, and social exclusion.
Addressing illiteracy requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses improving school infrastructure, promoting gender equality, and alleviating poverty. Only by ensuring that every citizen is literate can India fully harness its human potential and achieve sustainable development. The fight against illiteracy is not just about teaching people to read and write; it’s about creating a more equitable society where everyone has the chance to thrive.
500 Words Essay on Illiteracy in India
Introduction: the landscape of illiteracy in india, the root causes of illiteracy.
The roots of illiteracy in India can be traced back to numerous factors. Socioeconomic disparities, gender inequality, and inadequate infrastructure are among the primary contributors. Poverty often forces children out of school and into labor, thus perpetuating the cycle of illiteracy. Similarly, gender discrimination often leads to the denial of education for girls, contributing to the high rate of female illiteracy.
The lack of quality educational infrastructure, particularly in rural areas, is another significant factor. Many schools lack basic facilities, qualified teachers, and teaching materials, leading to high dropout rates and poor learning outcomes.
The Consequences of Illiteracy
At the societal level, high illiteracy rates impede economic growth and social development. It restricts the country’s human capital and hampers innovation and productivity. Moreover, illiteracy exacerbates social issues such as population growth and health problems, as illiterate individuals often lack awareness about family planning and healthcare practices.
Strategies to Combat Illiteracy
Addressing illiteracy requires multifaceted strategies. Firstly, improving access to quality education is crucial. This involves enhancing the school infrastructure, training teachers, and ensuring availability of teaching materials.
Thirdly, adult education programs need to be strengthened to provide literacy skills to those who missed out on formal education. These programs should be flexible, relevant, and linked to livelihood opportunities to ensure their effectiveness.
Conclusion: The Way Forward
The issue of illiteracy in India is complex and deeply entrenched. However, with concerted efforts from the government, civil society, and individuals, it can be overcome. The key lies in understanding that literacy is not just about reading and writing, but about empowering individuals with the knowledge and skills to improve their lives and contribute to society. As Nelson Mandela rightly said, “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.”
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- At a Glance
Padhna Likhna Abhiyan aims for total literacy in India by 2030

The government’s new literacy scheme, ‘Padhna Likhna Abhiyan’, will be a leap forward for achieving the goal of total literacy by 2030, Union Education Minister Ramesh Pokhriyal ‘Nishank’ said.
The principal target of the programme is to impart functional literacy and numeracy to 55 lakh non-literate and non-numerate adults in both rural and urban areas across the country in the age group of 15 years and above.
The ministry of education has made efforts for eradication of illiteracy in the country over the years resulting in achieving substantial progress towards improving access to adult education and learning. However, India still has a sizeable number of illiterates.
Illiteracy in India
The main focus of adult education has been on its very bottom tier, which is, basic literacy. Reason being that, at the time of Independence in 1947, 86 per cent of India’s population was illiterate.
As per Census 2011, the absolute number of illiterates of the country in the 15+ age group is 25.76 crore (male-9.08 crore, female-16.68 crore).
In India, literacy and particularly adult literacy has been a national priority. India has been celebrating International Literacy Day on September 8 to reaffirm its national commitment to achieve the goal and objectives of literacy and express solidarity with the international community in its efforts to eradicate illiteracy.
Earlier efforts for eradication of illiteracy
A series of programmes for promotion of adult literacy were launched by the government since 1951.
Social Education (1951-56): Programme gave importance to literacy, extension, general education, leadership training and social consciousness.
Gram Shikshan Mohim (1959): A movement for literacy in the rural areas aimed at imparting basic literacy skills within a period of four months.
Farmer’s Functional Literacy Project (1967-68): An inter-ministerial project for farmers’ training and functional literacy.
Functional Literacy for Adult Women (1975-76): Scheme included a component which enabled illiterate adult women to acquire functional skills along with literacy, to gain better awareness of health, hygiene, child care practices and in the process to facilitate attitudinal changes.
National Adult Education Programme (1978): First nationwide literacy programme taken up at macro level to eradicate illiteracy through project approach. Massive programme aimed at educating 100 million non-literate adults in the age-group of 15-35 years within a time frame of five years.
Rural Functional Literacy Project & Mass Programme of Functional Literacy (1986): To impart functional literacy to all illiterate persons in the 15-35 age group who were living in the rural areas by organising specified number of literacy centres. Launched on May 1, 1986 by involving National Service Scheme (NSS) and other students in colleges and universities.
National Literacy Mission (1988): On May 5, 1988 a mission mode programme for promoting adult literacy was launched as National Literacy Mission (NLM) countrywide to impart functional literacy to non-literates in the country in the age group of 15-35 years in a time bound manner.
It aimed at imparting functional literacy to non-literates in a time bound manner. Since the inception of the NLM in 1988, 127.45 million persons were made literate, of which, 60 per cent were females while 23 per cent belonged to the categories of Scheduled Castes and 12 per cent to Scheduled Tribes.
The scheme of National Literacy Mission was concluded in September, 2009 on account of launch of a new variant of the scheme under the name of Saakshar Bharat (Literate India).
Saakshar Bharat (2009): During 11th Five Year Plan, a need was felt to modify the strategy of NLM programme. Accordingly Saakshar Bharat was launched on September 8, 2009 as a new variant of NLM. Saakshar Bharat programme was sanctioned in phased manner since 2009 in 404 eligible districts of 26 states and one Union Territory and was given an interim extension till March 31, 2018 by Department of Expenditure.
Padhna Likhna Abhiyan
In order to ensure complete eradication of illiteracy, the main objective of the scheme of adult education will be basic literacy.
The scheme shall have a flexible approach and innovative methodologies such as involving school and college students and other volunteers of such schemes as NCC, NSS and NYKS, for imparting basic literacy. It will also enable creation of digital e-material, mobile app, etc.
The principal target of the abhiyan is to impart functional literacy to 55 lakh adult illiterates in the age group of 15 years and above under basic literacy programme in a period of one year (2020-21).
Within these targets, the abhiyan will focus on women, Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs) minorities, and other disadvantaged groups. The states/UTs will distribute the allotted target to districts selected by them.
The programme entails identification of non-literates through a survey, area wise mapping of their learning needs and imparting them instructor based teaching of about 120 hours, spread over four months or beyond, depending on motivation of the learner and local conditions. A certificate will be issued to every successful learner based on a Basic Literacy Assessment Test against learning outcomes. This will open up opportunities for further education through Open Learning Systems.
National Literacy Mission Authority (NLMA) constituted under the National Literacy Mission will continue to formulate policies, administer and supervise the scheme at the national level.
It has proposed to set up a National Centre for Literacy (to be housed in NCERT) at national level and State Centre for Literacy (within SCERTs/SIEs) in states/UTs. Both national and state centres will be assisted by the Technical Support Group.
Manorama Yearbook app is now available on Google Play Store and iOS App Store
Add to Flashcards
- Select a Deck
- Create New Deck
- hrd ministry
- Ramesh Pokhriyal ‘Nishank’
- {{stories.sectionName}} {{stories.title}}

- Classroom Programme
- Interview Guidance
- Online Programme
- Drishti Store
- My Bookmarks
- My Progress
- Change Password
- From The Editor's Desk
- How To Use The New Website
- Help Centre
Achievers Corner
- Topper's Interview
- About Civil Services
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus
- GS Prelims Strategy
- Prelims Analysis
- GS Paper-I (Year Wise)
- GS Paper-I (Subject Wise)
- CSAT Strategy
- Previous Years Papers
- Practice Quiz
- Weekly Revision MCQs
- 60 Steps To Prelims
- Prelims Refresher Programme 2020
Mains & Interview
- Mains GS Syllabus
- Mains GS Strategy
- Mains Answer Writing Practice
- Essay Strategy
- Fodder For Essay
- Model Essays
- Drishti Essay Competition
- Ethics Strategy
- Ethics Case Studies
- Ethics Discussion
- Ethics Previous Years Q&As
- Papers By Years
- Papers By Subject
- Be MAINS Ready
- Awake Mains Examination 2020
- Interview Strategy
- Interview Guidance Programme
Current Affairs
- Daily News & Editorial
- Daily CA MCQs
- Sansad TV Discussions
- Monthly CA Consolidation
- Monthly Editorial Consolidation
- Monthly MCQ Consolidation
Drishti Specials
- To The Point
- Important Institutions
- Learning Through Maps
- PRS Capsule
- Summary Of Reports
- Gist Of Economic Survey
Study Material
- NCERT Books
- NIOS Study Material
- IGNOU Study Material
- Yojana & Kurukshetra
- Chhatisgarh
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
Test Series
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Mains Test Series
- UPPCS Prelims Test Series
- UPPCS Mains Test Series
- BPSC Prelims Test Series
- RAS/RTS Prelims Test Series
- Daily Editorial Analysis
- YouTube PDF Downloads
- Strategy By Toppers
- Ethics - Definition & Concepts
- Mastering Mains Answer Writing
- Places in News
- UPSC Mock Interview
- PCS Mock Interview
- Interview Insights
- Prelims 2019
- Product Promos
Drishti IAS Blog
- Literacy as a Tool for Empowerment and Social Change
Literacy as a Tool for Empowerment and Social Change Blogs Home
- 20 Nov 2023

In our fast-paced world, literacy is a vital tool for personal growth and societal progress. From 1820's 12% global literacy to today's 87% (2022), its importance is evident. Developed nations boast a 99% literacy rate. In 2018, Brazil reached 93%, China 97%, and India 74% (UIS 2018a, 2018b). Literacy opens doors, enabling access to information and active societal engagement. This blog explores literacy's roles in individual empowerment and fostering positive social change.
Transformation of Global Literacy Rates Over Time
According to data compiled by Our World in Data and the World Bank, the global literacy rate for individuals aged secondary school and above was merely 12 percent in 1820, equivalent to approximately one in ten people. By 1900, it had only marginally increased, barely surpassing 20 percent. The trend shifted from the 1950s onward, witnessing a substantial rise, reaching 42 percent in 1960 and a significant 70 percent in 1983. As of 2022, the worldwide literacy rate has climbed to 87 percent, meaning nearly nine out of ten individuals globally are literate.
Most developed countries, including those in Europe, the former CIS nations, as well as Argentina and Uruguay, have achieved a 99 percent literacy rate. Meanwhile, developing countries, particularly emerging markets, have made notable progress.
Historical Context and Social Change
Throughout history, improved literacy rates have driven transformative societal changes. The invention of the printing press during the Renaissance stands as a pivotal example. Before Gutenberg's innovation, books were scarce and expensive due to manual copying. The printing press democratised knowledge, making books more accessible and fueling an intellectual renaissance. This era of enlightenment spurred a culture of learning, debate, and innovation, laying the groundwork for the modern world.
Literacy's impact extends to social reform movements. In the women's suffrage movement, written materials played a crucial role in educating and mobilising women, leading to significant political and social shifts. Similarly, global civil rights movements leveraged literacy to empower marginalised communities, advocating for equal rights. The historical trajectory showcases literacy as a catalyst for widespread positive change.
Education and Economic Empowerment
The connection between literacy and economic empowerment is undeniable. Education, which is built upon literacy skills, opens doors to opportunities for employment and entrepreneurship. Regions that have significantly improved literacy rates have witnessed a subsequent reduction in poverty and enhanced economic growth.
For example, countries like South Korea and Singapore invested heavily in education and literacy, transforming themselves from low-income to high-income economies within a single generation. These success stories underscore the transformative power of literacy in addressing economic disparities.
Gender Equality and Women's Empowerment
Literacy plays a pivotal role in promoting gender equality . Educating women is not only about their individual well-being but also has broader societal implications. Literate women are better equipped to make informed decisions about their health, family planning, and overall empowerment.
Across the globe, countless inspirational stories of women have harnessed the power of literacy to break barriers and achieve leadership positions. From Malala Yousafzai advocating for girls' education to women in leadership roles across various sectors, literacy has been the cornerstone of their empowerment.
Political Participation and Civic Engagement
In democratic societies, literacy is crucial for political participation, fostering informed decision-making. Higher literacy rates, indicative of informed citizenry, correlate with robust political systems. In these societies, public discourse and accountable governance thrive. For instance, countries with high literacy rates boast more discerning voters who critically assess political candidates. This elevated engagement enhances democracy, relying on an informed citizenry making judicious voting choices.
Social Inclusion and Empowerment of Marginalised Communities
Literacy programs have the potential to bridge gaps in education and empower marginalised communities, including indigenous populations and ethnic minorities. These initiatives often focus on improving literacy rates among marginalised groups, leading to increased social integration and empowerment.
One such success story is the " Ekal Vidyalaya " initiative in India, which aims to provide basic literacy education to remote and tribal areas. This program has improved literacy rates and empowered these communities by enhancing their access to opportunities and information.
Challenges and Barriers to Literacy
While literacy holds immense potential for empowerment, it's essential to recognise and address the challenges and barriers that hinder progress. Some regions lack infrastructure, including schools and libraries, which limits access to education. Innovative solutions, such as mobile libraries and community-based learning centres, can make a significant difference.
Gender disparities in access to education continue to persist in many parts of the world. To promote gender equality, targeted efforts are needed to ensure that girls and women have equal access to quality education. Initiatives like scholarships for girls and the construction of female-friendly schools have effectively broken down these barriers.
Role of Government and NGOs
Governments and non-governmental organisations (NGOs) have a vital role in promoting literacy and creating supportive learning environments. They allocate resources, develop policies, and implement programs to enhance literacy rates. Reputable organisations like the United Nations (UN), the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), and the Wildlife Trust of India (WTI) work diligently to promote literacy as a means to empower individuals and protect the environment.
One noteworthy example is the " Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan" in India, a government program aimed at universalising elementary education. Through initiatives like these, governments and NGOs raise literacy rates and foster social change.
Technological Literacy and Digital Empowerment
In today's digital age, technological literacy is increasingly vital. It equips individuals with the skills needed to navigate the digital world, access online information, and seize digital opportunities. Digital literacy , a subset of technological literacy, empowers people with the skills necessary for understanding and utilising digital technologies effectively.
Consider the rapid digitisation of information and services that has become the hallmark of our times. From online education platforms offering access to knowledge from around the world to e-commerce platforms transforming the way we shop and telemedicine services bridging healthcare gaps, digital literacy has become the key to unlocking these modern conveniences.
Digital Literacy and Navigating the Information Age
Digital literacy has emerged as a critical component of modern literacy. It equips individuals with the skills to navigate the digital realm effectively, including using search engines, discerning credible information from misinformation, and safeguarding their online privacy and security. In today's information age, digital literacy empowers individuals to harness the vast resources available on the internet for education, work, and personal growth.
Media Literacy- Decoding Information in a Digital World
Media literacy has gained prominence with the proliferation of news and information sources. It involves critically analysing media messages, including news articles, advertisements, and social media content. It enables individuals to distinguish between reliable and biased information, promoting a more informed and discerning citizenry.

Data Literacy- Understanding the Language of Numbers
Data literacy is another dimension of modern literacy. In an increasingly data-driven world, understanding and interpreting data is a valuable skill. Data literacy empowers individuals to make informed decisions based on quantitative information, whether in their personal finances, healthcare choices, or understanding complex societal issues.
Environmental Literacy- Fostering Sustainability
As the world faces environmental challenges, environmental literacy has gained importance. It involves understanding ecological systems, the impact of human activities on the environment, and sustainability principles. Environmental literacy empowers individuals to make eco-conscious choices and advocate for environmental preservation.
Global Literacy- Navigating a Connected World
In a globalised world, global literacy is essential. It encompasses knowledge of diverse cultures, global issues, and an understanding of interconnectedness. Global literacy enables individuals to engage in cross-cultural communication, appreciate cultural diversity, and contribute to global problem-solving.
Literacy Trends in India
As per the 2011 Population Census of India, there has been a notable improvement in India's literacy rate , witnessing an increase of approximately 9.2 per cent over the past decade. The literacy rate ascended from 64.83 per cent in 2001 to 74.04 per cent in 2011.
India also grapples with a significant gender disparity in literacy. The data reveals that men exhibit a higher literacy rate at 82.14 per cent, whereas women lag with a literacy rate of 65.46 per cent in 2011.
Furthermore, a study conducted by the National Statistical Office between July 2017 and June 2018 underscores the gender gap in literacy nationwide. The research indicates that male literacy rates stand at 84.7 per cent, surpassing female literacy rates at 70.3 per cent.
To sum up, literacy is undeniably a transformative force that empowers individuals and fosters positive social change. It has historical significance as a catalyst for intellectual and societal revolutions. Today, literacy continues to drive progress in areas such as health, economics, gender equality, political participation, social inclusion, and environmental awareness.
As we move forward, it is imperative to recognise literacy as an investment in the future. By addressing barriers, promoting education, and embracing technological advancements, we can ensure that literacy remains a powerful tool for empowerment and social change. Through literacy, we empower individuals to write their own stories of success and contribute to the betterment of society.
References:
- https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2022/09/reading-writing-global-literacy-rate-changed/
- https://www.epw.in/journal/2021/34/special-articles/inconvenient-truth-illiteracy-inequality.html
- https://www.education.gov.in/sites/upload_files/mhrd/files/DRAFT_MERITE_ESMF.pdf
- https://ncert.nic.in/pdf/publication/journalsandperiodicals/journalofindianeducation/JIEfeb2014.pdf
- https://pib.gov.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=71383
- https-//www.globalasia.org/v10no2/cover/education-in-a-high-income-society-lessons-from-singapore-and-south-korea_s-gopinathancatherine-ramos
- https-//www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK310967/
- https-//www.ekal.org/education-in-india-ekal-s-role
Comments (0)

- Website Inauguration Function.
- Vocational Placement Cell Inauguration
- Media Coverage.
- Certificate & Recommendations
- Privacy Policy
- Science Project Metric
- Social Studies 8 Class
- Computer Fundamentals
- Introduction to C++
- Programming Methodology
- Programming in C++
- Data structures
- Boolean Algebra
- Object Oriented Concepts
- Database Management Systems
- Open Source Software
- Operating System
- PHP Tutorials
- Earth Science
- Physical Science
- Sets & Functions
- Coordinate Geometry
- Mathematical Reasoning
- Statics and Probability
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political Science
- English (Sr. Secondary)
Hindi (Sr. Secondary)
- Punjab (Sr. Secondary)
- Accountancy and Auditing
- Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Technology
- Automobile Technology
- Electrical Technology
- Electronics Technology
- Hotel Management and Catering Technology
- IT Application
- Marketing and Salesmanship
- Office Secretaryship
- Stenography
- Hindi Essays
- English Essays
Letter Writing
- Shorthand Dictation
Essay on “Illiteracy in India” Complete Essay for Class 10, Class 12 and Graduation and other classes.
Illiteracy in India
Essay No. 01
Illiteracy has been the bane of independent India. It is a shame to note that, the country that gave Epics like the Ramayana and the Mahabharata to the world should, in the let Century turn out to be one among the most illiterate countries of the world. How this has come to be is of course not far to seek. Even in the understanding of a layman, it is clear that India has remained so very illiterate because it has, for centuries been slave to someone or the other. The rulers, whoever they may have been never wanted the Indians to be educated as, an educated mass of men would be difficult to reign, and so they never wanted them to raise their heads, and so, kept them away from the light of education. So much of course can be understood but, the sad story of the Indian masses is that even their own rulers, the Indians had no different attitude, they also wanted the Indians to remain mostly illiterate for much the same reason as the foreigners had wished. Just like the foreign rulers the Indian rulers also thought that an educated public may not be so easy to control so they also followed the track laid by their predecessors. Besides this, if the masses remained uneducated, any kind of manipulation could be easily managed in the favour of the rulers. Thus, since the Indian rulers also wanted to keep the Indian masses away from the light of knowledge, the result is for all of us to see that, even after fifty years of independence, India is still lagging behind the world in its ratio of educated / literate and the illiterate.
This goes without saying that, educated gentry is far more difficult to handle and to satisfy than an uncouth uneducated lot. For this simple reason the Indian rulers deemed it fit to keep education a far off dream for the majority, and the image that the foreigners had established has been maintained by our Indian rulers for simple selfish reasons that are obvious. For this reason I feel that, the rate of literacy in India is no surprise. This has been the definite policy of the Indian rulers just to suit their vicious designs, and their own inefficient policies. Illiterate masses can be led like sheep and goats very easily however and wherever they are taken. They can be very easily aroused on any emotional issues, they can be easily convinced into understanding and thinking as their rulers want them to. If the masses were to be educated it would not have been so easy for the politician to do what and how he wants to do on any issue. People would have to be convinced with genuine reasoning to the correctness of all that is being done or being planned. For this simple reason, even the dawn of the 21 st , Century finds India listed among the countries with the lowest ratio of education.
Now, after a little over fifty years, the Government has seen and understood the folly of such a lame policy of education. Now the Government is re-scheduling its literacy programmes and making a mark of the fundamental right of each resident of India to the right of education. If the masses had not been kept illiterate, they would have in so many years, raised a hue and cry about their right to education and the Governments of the past years would not have found it all so very smooth sailing. However, at least now the Government has awakened to the fact and need of correct education but, let us remember that the decades already lost cannot come back or regained. For, to complete the task in hand and to manage the huge backlog makes the job rather cumbersome and time consuming, besides being difficult to achieve.
It is hoped that, if the direction taken is continued we will in the course of another decade be higher on the grade of educated/ literate countries.
Essay No. 02
Illiteracy is a social problem in India. Illiteracy is the state of being not able to read or write. A. country’s progress depends much or literacy. Illiteracy is a curse on mankind in this age of science. An illiterate person doesn’t understand value of life. He is unaware of the modern day developments.
34 percent of the population of India is illiterate. According to the Global Education Monitoring Report of 2005, India ranks 106 out of the 127 countries. The average adult literacy rate is 76 percent for developing countries and 81.7 percent global the adult literacy rate in India is 61.3 percent.
But over the decades, literacy rates have shown a considerable improvement. The total literacy rate in 1951 was only 18.33 percent. It rose to 52.21 percent in 1991 an: 65.4 7ercent in 2001. According to the 2001 census report, the male literacy rate is 75.85 percent and the female literacy rate is 54.16 percent.
The rate of illiteracy is the highest among the agricultural, laborers. The main cause of illiteracy is poverty. Poor parents cannot afford to give education to their children. These children work in industries. They are subject to various types of exploitations. The rate of child laborers very high in India
Before 1976, education was the responsibility of the States. After the Constitutional Amendment of 1976, the Central Government accepts a larger responsibility in this field. The Central Government monitors educational policies and programmes. The most-notable of these are the National Policy of Education (NPE), 1986 and the Programme of Action (POA), 1986 as updated in 1992.
These policies bring about uniformity in education and make adult education programmes a mass movement. They lay special emphasis on education of girls, establishment of schools like Navodaya Vidyalaya in each district, encouraging sports, etc.
The Parliament has passed the Constitution. Amendment Act in 2002. This Act has made elementary education a fundamental right for children in the age group of 6-14 years. The Shiksha Sarva Abhiyan (SSA) covers the entire country and addresses the needs of 192 million children in 11 lakh habitations. It seeks to open new schools in areas which do not have schooling facilities.
Literacy is essential ‘for productivity. Illiterate farmers and workers cannot make proper use of the modern technologies both in the agriculture and the industrial sectors. Children are the asset of the nation. They are the citizens of tomorrow. If they remain illiterate, nothing good can be expected from them in the near future.
Literate people have a creative mind to think. They can choose a career. They have more employment opportunities as compared to the illiterates.
About evirtualguru_ajaygour

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Quick Links

Popular Tags
Visitors question & answer.
- Jayprakash on Hindi Essay on “Aitihasik Sthal ki Yatra” , ”ऐतिहासिक स्थल की यात्रा” Complete Hindi Essay for Class 10, Class 12 and Graduation and other classes.
- Diksha on Official Letter Example “Write a letter to Superintendent of Police for theft of your bicycle. ” Complete Official Letter for all classes.
- Anchal Sharma on Write a letter to the Postmaster complaining against the Postman of your locality.
- rrrr on Hindi Essay on “Pratahkal ki Sair” , ”प्रातःकाल की सैर ” Complete Hindi Essay for Class 10, Class 12 and Graduation and other classes.
- Mihir on CBSE ASL “Listening Test Worksheet” (ASL) 2017 for Class 11, Listening Test Audio Script 1
Download Our Educational Android Apps

Latest Desk
- Contemporary Indian Women-English Essay, Paragraph, Speech for Class 9, 10, 11 and 12 Students.
- Privatisation: Strengths and Weaknesses-English Essay, Paragraph, Speech for Class 9, 10, 11 and 12 Students.
- Greater political power alone will not improve women’s plight-English Essay, Paragraph, Speech for Class 9, 10, 11 and 12 Students.
- Casteism and Electoral Politics in India-English Essay, Paragraph, Speech for Class 9, 10, 11 and 12 Students.
- Wither Indian Democracy?-English Essay, Paragraph, Speech for Class 9, 10, 11 and 12 Students.
- Do Not Put Off till Tomorrow What You Can Do Today, Complete English Essay, Paragraph, Speech for Class 9, 10, 11, 12, Graduation and Competitive Examination.
- Shabd Shakti Ki Paribhasha aur Udahran | शब्द शक्ति की परिभाषा और उदाहरण
- Shabd Gun Ki Paribhasha aur Udahran | शब्द गुण की परिभाषा और उदाहरण
- Example Letter regarding election victory.
- Example Letter regarding the award of a Ph.D.
- Example Letter regarding the birth of a child.
- Example Letter regarding going abroad.
- Letter regarding the publishing of a Novel.
Vocational Edu.
- English Shorthand Dictation “East and Dwellings” 80 and 100 wpm Legal Matters Dictation 500 Words with Outlines.
- English Shorthand Dictation “Haryana General Sales Tax Act” 80 and 100 wpm Legal Matters Dictation 500 Words with Outlines meaning.
- English Shorthand Dictation “Deal with Export of Goods” 80 and 100 wpm Legal Matters Dictation 500 Words with Outlines meaning.
- English Shorthand Dictation “Interpreting a State Law” 80 and 100 wpm Legal Matters Dictation 500 Words with Outlines meaning.
HiHindi.Com
HiHindi Evolution of media
निरक्षरता एक अभिशाप पर निबंध | Essay On Illiteracy In Hindi
Essay On Illiteracy In Hindi प्रिय विद्यार्थियों आज हम निरक्षरता एक अभिशाप पर निबंध शेयर कर रहे हैं. निरक्षरता हिंदी निबंध लेखन का महत्वपूर्ण विषय हैं.
स्टूडेंट्स अपने प्रोजेक्ट के लिए अथवा परीक्षा की तैयारी के उद्देश्य से निरक्षरता पर यहाँ दिए गये निबंध का उपयोग कर सकते हैं.
निरक्षरता एक अभिशाप पर निबंध Essay On Illiteracy In Hindi

Get Here Free Short And Long Length Essay On Illiteracy In Hindi Language For School & College Students.
अक्सर कक्षा 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 के स्टूडेंट्स को Essay On Illiteracy In Hindi अथवा illiteracy in india पर छोटा बड़ा निबंध विविध शब्दसीमा
जैसे 5, 10 लाइन, 100, 200, 250, 300 ,400, 500 शब्दों में निरक्षरता पर निबंध अनुच्छेद लिखने को कहा जाता हैं. आप हमारे द्वारा सरल भाषा में लिखे गये इस निबंध का उपयोग कर सकते हैं.
निरक्षरता एक अभिशाप निबंध 1
भले ही हमारे देश को आजादी हुए 70 वर्ष से अधिक का समय हो गया हो गया हो, मगर देश में आज भी ऐसे बच्चों की संख्या सैकड़ों हजारों में नहीं बल्कि करोड़ों में हैं जिन्होंने कभी स्कूल नहीं देखा.
ये बच्चें भी अन्य की तरह ही जीवन में कुछ बड़ा बनने का सपना रखते है मगर कमजोर सामाजिक आर्थिक प्रष्ठभूमि के चलते वे अपने स्वप्न को साकार नहीं कर पाते हैं.
ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में इस प्रकार के बच्चों की संख्या ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में अधिक है. इन क्षेत्रों में बालिकाओं की शिक्षा की स्थिति भी दयनीय हैं. मात्र अल्पायु में ही इन्हें घर तथा खेत के काम में लगा दिया जाता हैं. लडकों की तुलना में लड़कियों के लिए शिक्षा के अवसर बेहद सीमित हैं.
निरक्षरता का शाब्दिक अर्थ होता है अक्षरों की पहचान न होना . एक अनपढ़ व्यक्ति के लिए हर लिखा गया काला अक्षर भैस के बराबर ही होता हैं.
वह न तो संख्या को पहचान पाता हैं न शब्दों को. यहाँ तक कि वह अपना नाम भी लिखना नही जाता हैं. वह लिखने पढने की इस दुनियां से स्वयं को कटा सा महसूस करता हैं.
एक समय था जब निरक्षरों की तादाद बहुत अधिक थी. इक्के दुक्के ही लोग पढ़ी हुई सामग्री पढ़ पाते थे. जब कभी उनके लिए कोई चिट्टी या कागज आता तो वे गाँव के पंडित या किसी पढ़े लिखे व्यक्ति के पास बचवाने के लिए जाया करते थे.
मगर आज समय बहुत आगे बढ़ रहा हैं. लोग इंटरनेट की इस दुनियां में सब कुछ ऑनलाइन ही करते हैं. ऐसे दौर में अनपढ़ रहकर जीवन बिताना किसी अभिशाप से कम नही हैं.
अब शिक्षा प्राप्ति के लिए तमाम रास्ते हर किसी के लिए खुले हैं. सरकार द्वारा बच्चों को निशुल्क शिक्षा दी जा रही हैं. उनके समस्त खर्च का वहन सरकार द्वारा किया जाता हैं.
सुबह शाम की कक्षाओं में बच्चें अपनी सुविधा के अनुसार शिक्षा अर्जित कर सकते हैं. जीवन में निरक्षरता के बहुत से नुक्सान हैं. उन्हें समाज में आए दिन विषमताओं का सामना करना पड़ता हैं.
हर समय किसी से ठगे जाने का भय उसे सताता रहता हैं. वही वह हर समय औरों पर निर्भर हो जाने की शुरुआत हो जाती हैं. यदि हम अपनी प्रगति तथा विकास के कार्यों अपने अधिकारों का समुचित उपभोग करना चाहते है तो हमें साक्षरता का स्तर बढ़ाना होगा तथा समाज के हर नागरिक को साक्षर बनाना होगा.
निरक्षरता निबंध 2
भारतीय दार्शनिकों ने अक्षर को साक्षात् ब्रह्मा कहा है और इसे शब्द रूप में समस्त सृष्टि में व्यास बतलाया है. सामान्य रूप से यह अक्षर ज्ञान का वाची और बौद्धिक विकास का सूचक है. मानव समाज में जो व्यक्ति ज्ञानवान तथा बौद्धिक विकास से वंचित रहता है उसे निरक्षर कहते है.
निरक्षर का आशय है कि वह पढ़ा लिखा नही होता है, उसे अक्षर ज्ञान नही रहता है और उसके लिए ”काला अक्षर भैस बराबर” कहावत चरितार्थ होती है. निरक्षर या अनपढ़ व्यक्ति में सामान्य लौकिक बुद्धि भले ही रहती हो, परन्तु पुस्तकीय राशि ज्ञान से वंचित रहता है.
इस कारण वह ज्ञान भंडार से अपरिचित, अनजान तथा अविगज्ञ रहता है. ऐसें लोग अपने व्यक्तित्व का उचित विकास नही कर पाते है. साथ ही वे सामाजिक एवं राष्ट्रीय विकास में भी उचित सहयोग नही दे पाते है. इसलिए निरक्षरता को व्यक्ति और समाज दोनों के लिए अभिशाप कहा गया है.
निरक्षरता के दुष्परिणाम (what are the bad effects of illiteracy)
हमारे देश में पराधीनता के काल में शिक्षण सुविधाओं का नितांत अभाव था. निरक्षरता के कारण उस समय बंधुआ मजदूर, जमीदारी प्रथा , शोषण उत्पीड़न, आर्थिक विषमता, अंधविश्वास एवं रूढ़ियों की अधिकता थी.
देश का गुलामी में जकड़े रहना भी एक निरक्षरता का अहम कारण था. भारत के सामाजिक जीवन का समग्र विकास नही हो रहा था. फलस्वरूप आजादी मिलने पर साक्षरता के अनेक कार्यक्रम चलाए गये.
हमारे देश में निरक्षरता ग्रामीण क्षेत्र में अधिक है. स्त्रियों, अनुसूचित जातियों, जनजातियों तथा गिरिजनों में निरक्षरता का प्रतिशत सबसे ज्यादा है. शहरी क्षेत्रों में निरक्षरता का प्रतिशत कम है. राजस्थान में लगभग 65 प्रतिशत लोग ही साक्षर है. शेष सभी निरक्षर है.
देखा जाए तो निरक्षरता की अधिकता के कारण ही हमारा राजस्थान अन्य राज्यों की अपेक्षा अधिक पिछड़ा हुआ है और यहाँ बेरोजगारी तथा विषमता इसी कारण अधिक है. यह निरक्षरता का एक दुष्परिणाम ही है.
निरक्षरता दूर करने के उपाय (how reduce illiteracy rates india)
स्वतंत्रता प्राप्ति के बाद सन 1951 में जो जनगणना हुई, उनमे लगभग 18 प्रतिशत जनता ही साक्षर थी. इस तरह उस समय भारत में साक्षरता बहुत ही कम थी. इस कारण सरकारी स्तर पर निरक्षरता को दूर करने के प्रयास किये जाते रहे.
इस दृष्टि से शिक्षण संस्थाओं का विस्तार किया गया तथा राष्ट्रीय स्तर पर प्रौढ़ शिक्षा निति घोषित की गई. इस निति के अनुसार अनेक स्तरों पर साक्षरता कार्यक्रम चलाए गये.
ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में अधिक विद्यालय खोले गये तथा प्राथमिक शिक्षा का खूब प्रचार किया गया. गाँवों में बेरोजगार शिक्षित युवकों को पंचायत स्तर पर साक्षरता अभियान में लगाया गया और समाज कल्याण विभाग के सहयोग से साक्षरता अभियान को आगे बढ़ाया गया.
इस अभियान में महाविद्यालयों और विश्वविद्यालयों के छात्रों एवं सेवानिवृत कर्मचारियों का भी सहयोग लिया गया. अब उच्च माद्यमिक शिक्षा के अंतर्गत सामाजिक सेवा के रूप में इस अभियान का समावेश किया गया है.
अब राजस्थान में राजीव गांधी पाठशाला योजना, लोक जुम्बिश परिषद् और संधान संस्थान के द्वारा पिछड़े ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में विद्यालय खोले जा रहे है.
आठ से पन्द्रह वर्ष के बालक बालिकाओं को साक्षर बनाने का लक्ष्य रखा गया है. वर्तमान में प्रचलित सर्वशिक्षा अभियान के द्वारा साक्षरता के लक्ष्य के प्रति काफी आशाएं है.
निरक्षरता निवारण के लिए सुझाव (Suggestions for illiteracy prevention)
हमारे देश से निरक्षरता का कलंक तभी मिट सकता है. जब सारे देश में प्राथमिक शिक्षा अनिवार्य कर दी जाए और बालकों को अशिक्षित रखना कानूनी अपराध माना जाए.
इसके लिए जगह जगह पर विद्यालय खोले जाए और गरीब जनता के बालकों को हर तरह की सुविधा उपलब्ध करवाई जाए.
वयस्कों के लिए प्रौढ़ शिक्षा के कार्यक्रम को प्रभावी बनाया जावे. सरकार भी इस दिशा में अधिक से अधिक धन खर्च करने का प्रावधान रखे.
सरकारी कर्मचारियों के लिए प्रोत्साहन का प्रावधान रखा जाए ताकि वे साक्षरता अभियान में अपना अधिकाधिक सहयोग दे सके.
वर्तमान में राष्ट्रीय स्तर पर प्रचलित सर्वशिक्षा अभियान को अधिक प्रभावशाली बनाया जावे तथा प्रचार साधनों एवं दूरदर्शन का इसके लिए पूरा उपयोग किया जावे.
निरक्षरता की समस्या और समाधान (Hindi Essay on Niraksharta ek Abhishap)
निरक्षरता समाज में अज्ञान और अन्धकार का प्रतीक है. जो समाज और राष्ट्र निरक्षर नागरिकों से रहित है, जिनमे निरक्षरता नही है. और सर्वत्र ज्ञान का प्रकाश फैला हुआ है, वह समाज तथा राष्ट्र सभी प्रकार से उन्नत माना जाता है.
सुशिक्षित नागरिकों से ही सभ्य तथा सम्पन्न राष्ट्र का निर्माण होता है. परन्तु अशिक्षित नागरिकों वाला देश असभ्य माना जाता है.
निरक्षरता मानव समाज का एक कलंक है. यह मानवता के लिए एक अभिशाप है. इस कारण अभिशाप से मुक्ति आवश्यक है और यह कार्य साक्षरता के आलोक से ही हो सकता है.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Your Article Library
Essay on illiteracy in india (416 words).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Essay on Illiteracy in India!
While India is still struggling to eradicate illiteracy, it is heartening to note that our literacy rate has gone up from 25 per cent in 1951 to 64.8 per cent in 2001. It is true that this percentage includes everyone who knows how to read and write a few alphabets, and may not be considered a true indicator of education; however, the rise in the percentage is quite noticeable.
It indicates how much still remains to be done to achieve 100 per cent literacy. It also shows the magnitude of demand that is likely to be made on the education system for higher learning. Infrastructure will have to be expanded to accommodate the burgeoning number of students seeking admission to secondary, higher secondary, and tertiary education.
The classrooms, teachers, libraries and laboratory facilities, hostels, and playfields needed for the rising number of student clientele will have to be provided. Already we know that the existing system is unable to meet the rising demand.
As a consequence, many surrogate institutions have sprung up outside of the education system to train aspiring students. Coaching centre’s, tuition classes, ‘institutes’ and ‘universities’ have been set up in the private sector, not all of which are of acceptable standards. Such institutions have commercialized education and put it beyond the reach of the poor and the deprived.
A continuing worry is the lower rate of literacy among women. Sixty per cent of the non-literates in India are women, although the female literacy rate has gone up from 9 per cent in the 1950s to 54 per cent in 2001. But the gender gap in literacy is enormous; the difference between the male and female literacy rate is 22 percentage points – that is, there are more male literates than female.
Some states and some areas within the states have shown higher rates of illiteracy among women, and efforts are afoot to improve the situation through the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan of the government of India. As is expected, the literacy rate in the urban areas is higher than in the rural. Table 1 illustrates this.
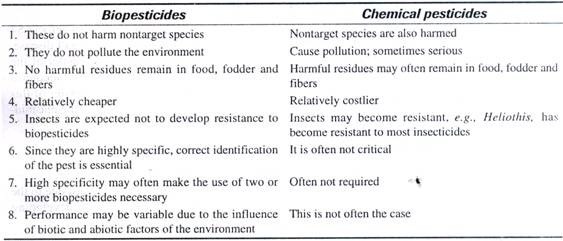
It is clear that change has occurred in the literacy profile on both variables, namely gender and settlement, and the change is for the better. Because of the changes in literacy, one can expect changes in other aspects of the life of the people in terms of job opportunities, marriage, and mobility. It might also bring about changes in interpersonal and inter-group relations.
Related Articles:
- Illiteracy in Hindi Belt
- Essay on Illiteracy in India
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Essays in Hindi /
Essay on Financial Literacy : वित्तीय साक्षरता पर निबंध पर निबंध

- Updated on
- जून 15, 2024

वित्तीय साक्षरता का अर्थ है वित्तीय प्रबंधन सिद्धांतों को जानना और उन्हें अपने जीवन में लागू करना। वित्तीय रूप से साक्षर व्यक्ति जिम्मेदारी से अपना कार्य कर सकता है। हर व्यक्ति, युवा और वृद्ध को पता होना चाहिए कि वित्तीय साक्षरता क्या है। यह हमें बजट और धन प्रबंधन के काॅंसेप्ट्स समझने में आसान बनाती है। स्टूडेंट्स के लिए भी वित्तीय साक्षरता का टाॅपिक बेहद महत्वपूर्ण है, इसलिए इस ब्लाॅग में हम छात्रों के लिए वित्तीय साक्षरता पर निबंध (Essay on Financial Literacy in Hindi) दे रहे हैं।
This Blog Includes:
वित्तीय साक्षरता पर निबंध 100 शब्दों में, वित्तीय साक्षरता पर निबंध 200 शब्दों में, वित्तीय साक्षरता क्या है, वित्तीय साक्षरता का महत्व, वित्तीय साक्षरता इतनी महत्वपूर्ण क्यों है, वित्तीय साक्षरता के लाभ.
100 शब्दों में Essay on Financial Literacy in Hindi इस प्रकार हैः
किसी भी इंसान के लिए वित्तीय साक्षरता बेहद ही महत्वपूर्ण है। हम अपनी शिक्षा पूरी करने के लिए स्कूल, कॉलेज और विश्वविद्यालय जाते हैं। शिक्षा पूरी करने के साथ ही हमें वित्तीय साक्षर होना होता है क्योंकि पढ़ाई के बाद हम नौकरी करते हैं या फिर कोई भी पेशा अपनाते हैं या फि अपना खुद का व्यवसाय शुरू करते हैं ताकि हम अपनी आजीविका चला सके। किसी भी काम के लिए व्यवस्थित बजट बनाकर, क्रय-विक्रय संबंधी निर्णय लेकर और वित्तीय रूप से आत्मनिर्भर बनकर अपने धन का प्रभावी प्रबंधन करने की हमारी क्षमता को वित्तीय साक्षरता के रूप में जाना जाता है।
200 शब्दों में Essay on Financial Literacy in Hindi इस प्रकार हैः
वित्तीय साक्षरता किसी व्यक्ति को एक बजटीय मार्गदर्शिका बनाने में सक्षम बना सकती है वित्तीय साक्षरता लोगों को स्वतंत्र और आत्मनिर्भर बनने में मदद करती है। यह आपको निवेश विकल्पों, वित्तीय बाजारों, पूंजी बजट आदि के बारे में साक्षर करती है।
हम सभी को पैसे खर्च करना और अपने और अपने प्रियजनों के लिए नई चीजें खरीदना बहुत पसंद है। बहुत से लोग अपनी पूरी ज़िंदगी बहुत मेहनत करते हैं और बहुत सारा पैसा बचाते हैं, लेकिन वे इसे मैनेज नहीं कर पाते। ऐसा इसलिए है क्योंकि हममें से बहुत से लोग वित्तीय साक्षरता के बारे में नहीं जानते हैं। जब आप वित्तीय रूप से साक्षर होते हैं, तो आपके पास पैसे के साथ एक स्मार्ट रिश्ते के लिए आवश्यक आधार होता है।
यह ध्यान रखना महत्वपूर्ण है कि अच्छी वित्तीय स्थिति का मतलब अमीर होना नहीं है। बल्कि, इसका मतलब है अपनी स्थिति के बारे में जागरूक होना और उसे सुधारने की योजना बनाना। यह विश्वास करना कठिन है कि लोग इतना बचत कर सकते हैं, जबकि उन्हें नहीं पता कि अपने पैसे को कैसे खर्च करना है या कैसे प्रबंधित करना है। किसी भी व्यक्ति के लिए उसके जीवन में चीजें व्यवस्थित करने के लिए वित्तीय साक्षरता महत्वपूर्ण है।
वित्तीय साक्षरता पर निबंध 500 शब्दों में
500 शब्दों में Essay on Financial Literacy in Hindi इस प्रकार हैः
वित्तीय साक्षर होना हर किसी के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है। कई बार हम देखते हैं कि हमारे घरों में बचपन से सिखाया जाता है कि कोई भी काम करो तो उसका लेखा-जोखा रखो। इसे पैसे से भी जोड़ा जाता है और इसका सही उदाहरण हम तब देखते हैं जब हम अपनी शिक्षा पूरी करने के बाद नौकरी या फिर बिजनेस करते हैं तो हमारे लिए वित्तीय साक्षरता काम आती है और हम अपने सामने आने वाली चुनौतियों से निपटते हैं।
सरल शब्दों में कहें तो वित्तीय साक्षरता का मतलब है अपने पैसे को समझदारी से सभांलना और इसे कैसे कमाया और खर्च किया जाता है। वित्तीय साक्षरता स्किल और नाॅलेज का वह गुण है जो किसी व्यक्ति को पैसे के बारे में निर्णय लेने में सक्षम बनाता है। वित्तीय साक्षरता हमें अपनी आमदनी का उचित प्रबंधन करने के लिए रास्ता बताती है। अगर हम वित्तीय साक्षर नहीं होंगे तो कुछ चीजों में हमें परेशानी हो सकती है।
वित्तीय साक्षरता को हम शिक्षा जितना ही महत्वपूर्ण मान सकते हैं। हम जानते हैं कि एक बार खर्च किया गया पैसा वापस नहीं मिल सकता है, और यहीं पर वित्तीय साक्षरता हमारी मदद करती है। वित्तीय साक्षरता के महत्व को समझने का पहला कदम खुद से यह सवाल पूछना है, ‘अगर आप पैसे खर्च नहीं कर सकते तो पैसा क्यों कमाएं’। वित्तीय साक्षरता हमें बजट बनाने के कौशल विकसित करने में मदद कर सकती है। वित्तीय साक्षरता के साथ, हम बजट बना सकते हैं, खर्च करने के पैटर्न का विश्लेषण कर सकते हैं और बचत और निवेश के बारे में सूचित निर्णय ले सकते हैं।
वित्तीय साक्षरता महत्वपूर्ण है क्योंकि यह व्यक्तियों को अपने वित्त का कुशलतापूर्वक प्रबंधन करने के लिए आवश्यक जानकारी और कौशल प्रदान करती है। वित्तीय साक्षरता के बिना, बचत और निवेश के संबंध में व्यक्ति के कार्य प्रभावित हो सकते हैं। यह वित्तीय अवधारणाओं की बेहतर समझ और धन के प्रभावी प्रबंधन में सहायता करता है। वित्तीय साक्षरता उचित धन प्रबंधन, वित्तीय निर्णय लेने और वित्तीय स्थिरता में सहायता करता है। यह फाइनेंस शिक्षा और फाइनेंस विकास और सफलता के लिए आवश्यक कई तकनीकों की समझ प्रदान करती है।
वित्तीय साक्षरता के लाभ कई प्रकार से देखे गए हैं। इनमें सबसे पहले वित्तीय निर्णय लेने की क्षमता और धन व ऋण का प्रभावी प्रबंधन शामिल है। इसके अलावा वित्तीय लक्ष्यों को कैसे प्राप्त किया जाए, इसकी बेहतर समझ होना, बेहतर नियंत्रण के माध्यम से व्यय में कमी, वित्तीय चिंता और बीमा, ऋण, निवेश और क्रेडिट कार्ड का उपयोग करते समय नैतिक निर्णय लेने में वृद्धि आदि शामिल है।
अर्थशास्त्रियों का कहना है कि डिजिटल दुनिया में वित्तीय साक्षरता एक महत्वपूर्ण स्किल के रूप में है। वित्तीय साक्षरता से ही हम हमारे पैसे को प्रभावी ढंग से प्रबंधित करने और वित्तीय रूप से स्वतंत्र, आर्थिक रूप से स्थिर कर सकते हैं। वित्तीय साक्षरता आज के समय में हम सबकी जरूरत बन चुकी है।
संबंधित ब्लाॅग्स
वित्तीय साक्षरता से का अर्थ किसी भी व्यक्ति को वित्तीय रूप से साक्षर होना है।
वित्तीय साक्षरता हमें अपनी आमदनी का उचित प्रबंधन करने के लिए रास्ता बताती है।
मीडिया रिपोर्ट्स और कई सर्वे से पता चलता है कि भारत की केवल 27-30 प्रतिशत आबादी ही वित्तीय रूप से साक्षर है।
उम्मीद है कि आपको Essay on Financial Literacy in Hindi के संदर्भ में हमारा यह ब्लॉग पसंद आया होगा। निबंध लेखन के अन्य ब्लॉग्स पढ़ने के लिए Leverage Edu के साथ बने रहें।
Team Leverage Edu
प्रातिक्रिया दे जवाब रद्द करें
अगली बार जब मैं टिप्पणी करूँ, तो इस ब्राउज़र में मेरा नाम, ईमेल और वेबसाइट सहेजें।
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.

- Population Density
- Literacy Rate
Madhya Pradesh Literacy Rate
| S.No. | District Name | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Jabalpur | |||
| 2. | Indore | |||
| 3. | Bhopal | |||
| 4. | Balaghat | |||
| 5. | Gwalior | |||
| 6. | Sagar | |||
| 7. | Narsimhapur | |||
| 8. | Hoshangabad | |||
| 9. | Bhind | |||
| 10. | Raisen | |||
| 11. | Datia | |||
| 12. | Harda | |||
| 13. | Ujjain | |||
| 14. | Satna | |||
| 15. | Seoni | |||
| 16. | Katni | |||
| 17. | Mandsaur | |||
| 18. | Rewa | |||
| 19. | Chhindwara | |||
| 20. | Morena | |||
| 21. | Neemuch | |||
| 22. | Vidisha | |||
| 23. | Sehore | |||
| 24. | Damoh | |||
| 25. | Dewas | |||
| 26. | Shajapur | |||
| 27. | Betul | |||
| 28. | Anuppur | |||
| 29. | Mandla | |||
| 30. | Ratlam | |||
| 31. | Shahdol | |||
| 32. | Ashoknagar | |||
| 33. | East Nimar | |||
| 34. | Umaria | |||
| 35. | Panna | |||
| 36. | Sidhi | |||
| 37. | Burhanpur | |||
| 38. | Dindori | |||
| 39. | Chhattarpur | |||
| 40. | Guna | |||
| 41. | West Nimar | |||
| 42. | Shivpuri | |||
| 43. | Tikamgarh | |||
| 44. | Rajgarh | |||
| 45. | Singrauli | |||
| 46. | Dhar | |||
| 47. | Sheopur | |||
| 48. | Barwani | |||
| 49. | Jhabua | |||
| 50. | Alirajpur | |||
Madhya Pradesh Population Facts
Most populous districts.
| District | Population in 2011 | Population in 2024 |
|---|---|---|
Least Populous Districts
Highest literate districts.
| District | Per |
|---|---|
Lowest Literacy Districts
Highest sex ratio districts.
| District | Sex Ratio |
|---|---|
Lowest Sex Ratio Districts
© 2024 Copyright India Census | All Rights Reserved
- Learn English Online Classes
- Learn Foreign Languages
- Learn Indian Languages
- Live Online Classes for Kids
- See Other Live Online Classes
- Books to Learn French
- Books to learn Spanish
- Books to learn German
- Books to learn Chinese
- Books to learn Japanese
- Books to learn Korean
- Books to learn Portuguese
- Books to learn Persian
- Books to learn Tibetan
- Books to learn Italian
- Books to learn Russian
- Best Books to learn Arabic from in 2021
- English Dictionary
- English – Hindi Dictionary
- English – Kannada Dictionary
- English – Telugu Dictionary
- English – Tamil Dictionary
- Learn English Articles
- Learn Hindi Articles
- Learn Kannada Articles
- Learn Tamil Articles
- Learn Gujarati Articles
- Translation Services
- Localization Services
- Voice Over Services
- Transcription Services
- Digital Marketing Services
- Vernacular Language Service Offerings
- Case Studies
- For Business / Enterprises
literacy meaning in Hindi | literacy का हिन्दी अर्थ

literacy साक्षरता

literacy = साक्षरता
Pronunciation = 🔊 bb1.onclick = function(){ if(responsivevoice.isplaying()){ responsivevoice.cancel(); }else{ responsivevoice.speak("literacy", "uk english female"); } }; literacy, pronunciation in hindi = लिटरेसी, literacy in hindi : साक्षरता, part of speech : noun , definition in english : the ability to read and write , definition in hindi : पढ़ने और लिखने की क्षमता, examples in english :.
- Kerala has achieved a literacy rate of 93.9%
Examples in Hindi :
- केरल ने साक्षरता दर 93.9% हासिल की है
Synonyms of literacy
| Synonyms in Hindi | कौशल शिक्षा |
| Synonyms in English | skill education schooling |
Antonyms of literacy
| Antonyms in Hindi | निरक्षरता अशिक्षित |
| Antonyms in English | illiteracy uneducated |
About English Hindi Dictionary
Multibhashi’s Hindi-English Dictionary will help you find the meaning of different words from Hindi to English like meaning of Kshamta meaning of nipun and from English to Hindi like meaning of Ability, The meaning of capability etc. Use this free dictionary to get the definition of capability in Hindi and also the definition of capability in English. Also see the translation in Hindi or translation in English, synonyms, antonyms, related words, image and pronunciation for helping spoken English improvement or spoken Hindi improvement.
About English Language
English is one of the most widely spoken languages across the globe and a common language of choice for people from different backgrounds trying to communicate with each other. This is the reason why English is the second language learned by most of the people.
About the Hindi Language
Hindi is among the oldest languages to be discovered by mankind, which has its roots laid back in around the 10th Century AD. It is a descendant of Sanskrit, which was the earliest speech of the Aryans in India. Hindi- also known as Hindustani or Khari-Boli, is written in the Devanagari script, which is the most scientific writing system in the world and is widely spoken by over ten million people across the globe as their first or second language, which makes it 3rd most widely spoken language in the world.

- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Translation of literacy – English–Hindi dictionary
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
(Translation of literacy from the Cambridge English–Hindi Dictionary © Cambridge University Press)
Examples of literacy
Translations of literacy.
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
a very short holiday

Trial, judge, and jury: talking about what happens when a criminal is caught

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English–Hindi Noun
- Translations
- All translations
To add literacy to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add literacy to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
2 Comments / Essay, Hindi Essay / Essay on Literacy in Hindi, साक्षरता पर निबंध हिंदी में. यदि हमें समाज के अंदर अच्छाई व बदलाव का बीज रखना है तो इस समाज को साक्षरता से ...
Literacy rate in India The working definition of literacy in the Indian census since 1991 is as follows: [ 10] Literacy rate Also called the "effective literacy rate"; the total percentage of the population of an area at a particular time aged seven years or above who can read and write with understanding.
नव भारत साक्षरता कार्यक्रम 17 Feb 2022 7 min read टैग्स: सामान्य अध्ययन-II शिक्षा सरकारी नीतियाँ और हस्तक्षेप
Article shared by: साक्षरता पर अनुच्छेद | Paragraph on Literacy in Hindi! साक्षरता का अर्थ है - अक्षर ज्ञान होना । दूसरे शब्दों में, पढ़ने-लिखने की क्षमता का होना ही ...
It is based on the National Statistical Office (NSO) survey and provides for state-wise detail of literacy rate among the persons aged seven years and above. The report comes before the International Literacy Day which is celebrated on 8th September every year.
Read this article in Hindi to learn about the literacy in India and its spatial patterns. साक्षरता की अवधारणा जो एक देश से दूसरे देश में भिन्न होती है- सामान्यत: न्यूनतम शिक्षण स्तर का उल्लेख करती है । यह ...
विश्व साक्षरता दिवस पर निबंध Essay On World Literacy Day In Hindi. माना जाता हैं कि अधिकतर सामाजिक समस्याओं की जड़ अशिक्षा हैं. साक्षरता के अभाव में किसी भी ...
In this blog, we will look at the literacy rates of various Indian states, understand the factors affecting them, and trace the efforts made to improve education and eradicate illiteracy.
The National Policy of Education has been declared that the whole nation has to commit itself and help in eradicating illiteracy, especially among the young population. The National Literacy Mission of 1988 made literacy a community endeavour. It has aimed to attain a literacy rate of 41% by 2035.
Literacy Rate Meaning In Hindi Literacy rate का हिंदी में अर्थ "साक्षरता दर" होता है। इसे साक्षरता प्रतिशत, साक्षरता अनुपात और साक्षरता स्तर भी कहते है।
The literacy rate of India has been recorded 64.84% (2001 census) against 52.21% in 1991. It has been increased by more than 12% in a decade. Also, the literacy rate is supposed to be around 70-72% by the end of 2010 (As estimated by National Sample Survey). But the goal is yet to be achieved completely (i.e. to obtain 100% literacy).
High-quality essay on the topic of "Illiteracy in India" for students in schools and colleges.
The government's new literacy scheme, 'Padhna Likhna Abhiyan', will be a leap forward for achieving the goal of total literacy by 2030, Union Education Minister Ramesh Pokhriyal 'Nishank' said.
In our fast-paced world, literacy is a vital tool for personal growth and societal progress. From 1820's 12% global literacy to today's 87% (2022), its importance is evident. Developed nations boast a 99% literacy rate. In 2018, Brazil reached 93%, China 97%, and India 74% (UIS 2018a, 2018b). Literacy opens doors, enabling access to information and active societal engagement. This blog ...
According to Census 2011, India managed to achieve a literacy rate of 74.04% as opposed to 64.80% in 2001. This. notable shift also highlights an increase in female literacy over the years. While ...
The average adult literacy rate is 76 percent for developing countries and 81.7 percent global the adult literacy rate in India is 61.3 percent. But over the decades, literacy rates have shown a considerable improvement. The total literacy rate in 1951 was only 18.33 percent. It rose to 52.21 percent in 1991 an: 65.4 7ercent in 2001.
Essay On Illiteracy In Hindi प्रिय विद्यार्थियों आज हम निरक्षरता एक अभिशाप पर निबंध शेयर कर रहे हैं. निरक्षरता हिंदी निबंध लेखन का महत्वपूर्ण विषय ...
Essay on Illiteracy in India (416 Words) Essay on Illiteracy in India! While India is still struggling to eradicate illiteracy, it is heartening to note that our literacy rate has gone up from 25 per cent in 1951 to 64.8 per cent in 2001. It is true that this percentage includes everyone who knows how to read and write a few alphabets, and ...
How to say literacy rate in Hindi and what is the meaning of literacy rate in Hindi? literacy rate Hindi meaning, translation, pronunciation, synonyms and example sentences are provided by Hindlish.com.
वित्तीय साक्षरता का टाॅपिक बेहद महत्वपूर्ण है, इसलिए इस ब्लाॅग में हम (Essay on Financial Literacy in Hindi) दे रहे हैं।
Here is the literacy rate in Madhya Pradesh (2024), including the literacy rate of all districts in Madhya Pradesh.
Get the meaning of literacy in Hindi with Usage, Synonyms, Antonyms & Pronunciation. Sentence usage examples & English to Hindi translation (word meaning).
LITERACY translate: साक्षरता, किसी खास विषय या खास तरह की जानकारी. Learn more in the Cambridge English-Hindi Dictionary.