- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers


The Craft of Writing a Strong Hypothesis

Table of Contents
Writing a hypothesis is one of the essential elements of a scientific research paper. It needs to be to the point, clearly communicating what your research is trying to accomplish. A blurry, drawn-out, or complexly-structured hypothesis can confuse your readers. Or worse, the editor and peer reviewers.
A captivating hypothesis is not too intricate. This blog will take you through the process so that, by the end of it, you have a better idea of how to convey your research paper's intent in just one sentence.
What is a Hypothesis?
The first step in your scientific endeavor, a hypothesis, is a strong, concise statement that forms the basis of your research. It is not the same as a thesis statement , which is a brief summary of your research paper .
The sole purpose of a hypothesis is to predict your paper's findings, data, and conclusion. It comes from a place of curiosity and intuition . When you write a hypothesis, you're essentially making an educated guess based on scientific prejudices and evidence, which is further proven or disproven through the scientific method.
The reason for undertaking research is to observe a specific phenomenon. A hypothesis, therefore, lays out what the said phenomenon is. And it does so through two variables, an independent and dependent variable.
The independent variable is the cause behind the observation, while the dependent variable is the effect of the cause. A good example of this is “mixing red and blue forms purple.” In this hypothesis, mixing red and blue is the independent variable as you're combining the two colors at your own will. The formation of purple is the dependent variable as, in this case, it is conditional to the independent variable.
Different Types of Hypotheses

Types of hypotheses
Some would stand by the notion that there are only two types of hypotheses: a Null hypothesis and an Alternative hypothesis. While that may have some truth to it, it would be better to fully distinguish the most common forms as these terms come up so often, which might leave you out of context.
Apart from Null and Alternative, there are Complex, Simple, Directional, Non-Directional, Statistical, and Associative and casual hypotheses. They don't necessarily have to be exclusive, as one hypothesis can tick many boxes, but knowing the distinctions between them will make it easier for you to construct your own.
1. Null hypothesis
A null hypothesis proposes no relationship between two variables. Denoted by H 0 , it is a negative statement like “Attending physiotherapy sessions does not affect athletes' on-field performance.” Here, the author claims physiotherapy sessions have no effect on on-field performances. Even if there is, it's only a coincidence.
2. Alternative hypothesis
Considered to be the opposite of a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis is donated as H1 or Ha. It explicitly states that the dependent variable affects the independent variable. A good alternative hypothesis example is “Attending physiotherapy sessions improves athletes' on-field performance.” or “Water evaporates at 100 °C. ” The alternative hypothesis further branches into directional and non-directional.
- Directional hypothesis: A hypothesis that states the result would be either positive or negative is called directional hypothesis. It accompanies H1 with either the ‘<' or ‘>' sign.
- Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional hypothesis only claims an effect on the dependent variable. It does not clarify whether the result would be positive or negative. The sign for a non-directional hypothesis is ‘≠.'
3. Simple hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, “Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking.
4. Complex hypothesis
In contrast to a simple hypothesis, a complex hypothesis implies the relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. For instance, “Individuals who eat more fruits tend to have higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.” The independent variable is eating more fruits, while the dependent variables are higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.
5. Associative and casual hypothesis
Associative and casual hypotheses don't exhibit how many variables there will be. They define the relationship between the variables. In an associative hypothesis, changing any one variable, dependent or independent, affects others. In a casual hypothesis, the independent variable directly affects the dependent.
6. Empirical hypothesis
Also referred to as the working hypothesis, an empirical hypothesis claims a theory's validation via experiments and observation. This way, the statement appears justifiable and different from a wild guess.
Say, the hypothesis is “Women who take iron tablets face a lesser risk of anemia than those who take vitamin B12.” This is an example of an empirical hypothesis where the researcher the statement after assessing a group of women who take iron tablets and charting the findings.
7. Statistical hypothesis
The point of a statistical hypothesis is to test an already existing hypothesis by studying a population sample. Hypothesis like “44% of the Indian population belong in the age group of 22-27.” leverage evidence to prove or disprove a particular statement.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis is essential as it can make or break your research for you. That includes your chances of getting published in a journal. So when you're designing one, keep an eye out for these pointers:
- A research hypothesis has to be simple yet clear to look justifiable enough.
- It has to be testable — your research would be rendered pointless if too far-fetched into reality or limited by technology.
- It has to be precise about the results —what you are trying to do and achieve through it should come out in your hypothesis.
- A research hypothesis should be self-explanatory, leaving no doubt in the reader's mind.
- If you are developing a relational hypothesis, you need to include the variables and establish an appropriate relationship among them.
- A hypothesis must keep and reflect the scope for further investigations and experiments.
Separating a Hypothesis from a Prediction
Outside of academia, hypothesis and prediction are often used interchangeably. In research writing, this is not only confusing but also incorrect. And although a hypothesis and prediction are guesses at their core, there are many differences between them.
A hypothesis is an educated guess or even a testable prediction validated through research. It aims to analyze the gathered evidence and facts to define a relationship between variables and put forth a logical explanation behind the nature of events.
Predictions are assumptions or expected outcomes made without any backing evidence. They are more fictionally inclined regardless of where they originate from.
For this reason, a hypothesis holds much more weight than a prediction. It sticks to the scientific method rather than pure guesswork. "Planets revolve around the Sun." is an example of a hypothesis as it is previous knowledge and observed trends. Additionally, we can test it through the scientific method.
Whereas "COVID-19 will be eradicated by 2030." is a prediction. Even though it results from past trends, we can't prove or disprove it. So, the only way this gets validated is to wait and watch if COVID-19 cases end by 2030.
Finally, How to Write a Hypothesis

Quick tips on writing a hypothesis
1. Be clear about your research question
A hypothesis should instantly address the research question or the problem statement. To do so, you need to ask a question. Understand the constraints of your undertaken research topic and then formulate a simple and topic-centric problem. Only after that can you develop a hypothesis and further test for evidence.
2. Carry out a recce
Once you have your research's foundation laid out, it would be best to conduct preliminary research. Go through previous theories, academic papers, data, and experiments before you start curating your research hypothesis. It will give you an idea of your hypothesis's viability or originality.
Making use of references from relevant research papers helps draft a good research hypothesis. SciSpace Discover offers a repository of over 270 million research papers to browse through and gain a deeper understanding of related studies on a particular topic. Additionally, you can use SciSpace Copilot , your AI research assistant, for reading any lengthy research paper and getting a more summarized context of it. A hypothesis can be formed after evaluating many such summarized research papers. Copilot also offers explanations for theories and equations, explains paper in simplified version, allows you to highlight any text in the paper or clip math equations and tables and provides a deeper, clear understanding of what is being said. This can improve the hypothesis by helping you identify potential research gaps.
3. Create a 3-dimensional hypothesis
Variables are an essential part of any reasonable hypothesis. So, identify your independent and dependent variable(s) and form a correlation between them. The ideal way to do this is to write the hypothetical assumption in the ‘if-then' form. If you use this form, make sure that you state the predefined relationship between the variables.
In another way, you can choose to present your hypothesis as a comparison between two variables. Here, you must specify the difference you expect to observe in the results.
4. Write the first draft
Now that everything is in place, it's time to write your hypothesis. For starters, create the first draft. In this version, write what you expect to find from your research.
Clearly separate your independent and dependent variables and the link between them. Don't fixate on syntax at this stage. The goal is to ensure your hypothesis addresses the issue.
5. Proof your hypothesis
After preparing the first draft of your hypothesis, you need to inspect it thoroughly. It should tick all the boxes, like being concise, straightforward, relevant, and accurate. Your final hypothesis has to be well-structured as well.
Research projects are an exciting and crucial part of being a scholar. And once you have your research question, you need a great hypothesis to begin conducting research. Thus, knowing how to write a hypothesis is very important.
Now that you have a firmer grasp on what a good hypothesis constitutes, the different kinds there are, and what process to follow, you will find it much easier to write your hypothesis, which ultimately helps your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace Discover . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
It includes everything you need, including a repository of over 270 million research papers across disciplines, SEO-optimized summaries and public profiles to show your expertise and experience.
If you found these tips on writing a research hypothesis useful, head over to our blog on Statistical Hypothesis Testing to learn about the top researchers, papers, and institutions in this domain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is the definition of hypothesis.
According to the Oxford dictionary, a hypothesis is defined as “An idea or explanation of something that is based on a few known facts, but that has not yet been proved to be true or correct”.
2. What is an example of hypothesis?
The hypothesis is a statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables. An example: "If we increase the number of new users who join our platform by 25%, then we will see an increase in revenue."
3. What is an example of null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between two variables. The null hypothesis is written as H0. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect. For example, if you're studying whether or not a particular type of exercise increases strength, your null hypothesis will be "there is no difference in strength between people who exercise and people who don't."
4. What are the types of research?
• Fundamental research
• Applied research
• Qualitative research
• Quantitative research
• Mixed research
• Exploratory research
• Longitudinal research
• Cross-sectional research
• Field research
• Laboratory research
• Fixed research
• Flexible research
• Action research
• Policy research
• Classification research
• Comparative research
• Causal research
• Inductive research
• Deductive research
5. How to write a hypothesis?
• Your hypothesis should be able to predict the relationship and outcome.
• Avoid wordiness by keeping it simple and brief.
• Your hypothesis should contain observable and testable outcomes.
• Your hypothesis should be relevant to the research question.
6. What are the 2 types of hypothesis?
• Null hypotheses are used to test the claim that "there is no difference between two groups of data".
• Alternative hypotheses test the claim that "there is a difference between two data groups".
7. Difference between research question and research hypothesis?
A research question is a broad, open-ended question you will try to answer through your research. A hypothesis is a statement based on prior research or theory that you expect to be true due to your study. Example - Research question: What are the factors that influence the adoption of the new technology? Research hypothesis: There is a positive relationship between age, education and income level with the adoption of the new technology.
8. What is plural for hypothesis?
The plural of hypothesis is hypotheses. Here's an example of how it would be used in a statement, "Numerous well-considered hypotheses are presented in this part, and they are supported by tables and figures that are well-illustrated."
9. What is the red queen hypothesis?
The red queen hypothesis in evolutionary biology states that species must constantly evolve to avoid extinction because if they don't, they will be outcompeted by other species that are evolving. Leigh Van Valen first proposed it in 1973; since then, it has been tested and substantiated many times.
10. Who is known as the father of null hypothesis?
The father of the null hypothesis is Sir Ronald Fisher. He published a paper in 1925 that introduced the concept of null hypothesis testing, and he was also the first to use the term itself.
11. When to reject null hypothesis?
You need to find a significant difference between your two populations to reject the null hypothesis. You can determine that by running statistical tests such as an independent sample t-test or a dependent sample t-test. You should reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than 0.05.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)

What Is A Research (Scientific) Hypothesis? A plain-language explainer + examples
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
If you’re new to the world of research, or it’s your first time writing a dissertation or thesis, you’re probably noticing that the words “research hypothesis” and “scientific hypothesis” are used quite a bit, and you’re wondering what they mean in a research context .
“Hypothesis” is one of those words that people use loosely, thinking they understand what it means. However, it has a very specific meaning within academic research. So, it’s important to understand the exact meaning before you start hypothesizing.
Research Hypothesis 101
- What is a hypothesis ?
- What is a research hypothesis (scientific hypothesis)?
- Requirements for a research hypothesis
- Definition of a research hypothesis
- The null hypothesis
What is a hypothesis?
Let’s start with the general definition of a hypothesis (not a research hypothesis or scientific hypothesis), according to the Cambridge Dictionary:
Hypothesis: an idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved.
In other words, it’s a statement that provides an explanation for why or how something works, based on facts (or some reasonable assumptions), but that has not yet been specifically tested . For example, a hypothesis might look something like this:
Hypothesis: sleep impacts academic performance.
This statement predicts that academic performance will be influenced by the amount and/or quality of sleep a student engages in – sounds reasonable, right? It’s based on reasonable assumptions , underpinned by what we currently know about sleep and health (from the existing literature). So, loosely speaking, we could call it a hypothesis, at least by the dictionary definition.
But that’s not good enough…
Unfortunately, that’s not quite sophisticated enough to describe a research hypothesis (also sometimes called a scientific hypothesis), and it wouldn’t be acceptable in a dissertation, thesis or research paper . In the world of academic research, a statement needs a few more criteria to constitute a true research hypothesis .
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes – specificity , clarity and testability .
Let’s take a look at these more closely.
Need a helping hand?
Hypothesis Essential #1: Specificity & Clarity
A good research hypothesis needs to be extremely clear and articulate about both what’ s being assessed (who or what variables are involved ) and the expected outcome (for example, a difference between groups, a relationship between variables, etc.).
Let’s stick with our sleepy students example and look at how this statement could be more specific and clear.
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
As you can see, the statement is very specific as it identifies the variables involved (sleep hours and test grades), the parties involved (two groups of students), as well as the predicted relationship type (a positive relationship). There’s no ambiguity or uncertainty about who or what is involved in the statement, and the expected outcome is clear.
Contrast that to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – and you can see the difference. “Sleep” and “academic performance” are both comparatively vague , and there’s no indication of what the expected relationship direction is (more sleep or less sleep). As you can see, specificity and clarity are key.

Hypothesis Essential #2: Testability (Provability)
A statement must be testable to qualify as a research hypothesis. In other words, there needs to be a way to prove (or disprove) the statement. If it’s not testable, it’s not a hypothesis – simple as that.
For example, consider the hypothesis we mentioned earlier:
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
We could test this statement by undertaking a quantitative study involving two groups of students, one that gets 8 or more hours of sleep per night for a fixed period, and one that gets less. We could then compare the standardised test results for both groups to see if there’s a statistically significant difference.
Again, if you compare this to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – you can see that it would be quite difficult to test that statement, primarily because it isn’t specific enough. How much sleep? By who? What type of academic performance?
So, remember the mantra – if you can’t test it, it’s not a hypothesis 🙂

Defining A Research Hypothesis
You’re still with us? Great! Let’s recap and pin down a clear definition of a hypothesis.
A research hypothesis (or scientific hypothesis) is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific and testable.
So, when you write up hypotheses for your dissertation or thesis, make sure that they meet all these criteria. If you do, you’ll not only have rock-solid hypotheses but you’ll also ensure a clear focus for your entire research project.
What about the null hypothesis?
You may have also heard the terms null hypothesis , alternative hypothesis, or H-zero thrown around. At a simple level, the null hypothesis is the counter-proposal to the original hypothesis.
For example, if the hypothesis predicts that there is a relationship between two variables (for example, sleep and academic performance), the null hypothesis would predict that there is no relationship between those variables.
At a more technical level, the null hypothesis proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations and that any differences are due to chance alone.
And there you have it – hypotheses in a nutshell.
If you have any questions, be sure to leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to help you. If you need hands-on help developing and testing your hypotheses, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
17 Comments
Very useful information. I benefit more from getting more information in this regard.
Very great insight,educative and informative. Please give meet deep critics on many research data of public international Law like human rights, environment, natural resources, law of the sea etc
In a book I read a distinction is made between null, research, and alternative hypothesis. As far as I understand, alternative and research hypotheses are the same. Can you please elaborate? Best Afshin
This is a self explanatory, easy going site. I will recommend this to my friends and colleagues.
Very good definition. How can I cite your definition in my thesis? Thank you. Is nul hypothesis compulsory in a research?
It’s a counter-proposal to be proven as a rejection
Please what is the difference between alternate hypothesis and research hypothesis?
It is a very good explanation. However, it limits hypotheses to statistically tasteable ideas. What about for qualitative researches or other researches that involve quantitative data that don’t need statistical tests?
In qualitative research, one typically uses propositions, not hypotheses.
could you please elaborate it more
I’ve benefited greatly from these notes, thank you.
This is very helpful
well articulated ideas are presented here, thank you for being reliable sources of information
Excellent. Thanks for being clear and sound about the research methodology and hypothesis (quantitative research)
I have only a simple question regarding the null hypothesis. – Is the null hypothesis (Ho) known as the reversible hypothesis of the alternative hypothesis (H1? – How to test it in academic research?
this is very important note help me much more
Hi” best wishes to you and your very nice blog”
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is Research Methodology? Simple Definition (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and objectives are confirmatory in nature. For example,…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is a Research Hypothesis: How to Write it, Types, and Examples

Any research begins with a research question and a research hypothesis . A research question alone may not suffice to design the experiment(s) needed to answer it. A hypothesis is central to the scientific method. But what is a hypothesis ? A hypothesis is a testable statement that proposes a possible explanation to a phenomenon, and it may include a prediction. Next, you may ask what is a research hypothesis ? Simply put, a research hypothesis is a prediction or educated guess about the relationship between the variables that you want to investigate.
It is important to be thorough when developing your research hypothesis. Shortcomings in the framing of a hypothesis can affect the study design and the results. A better understanding of the research hypothesis definition and characteristics of a good hypothesis will make it easier for you to develop your own hypothesis for your research. Let’s dive in to know more about the types of research hypothesis , how to write a research hypothesis , and some research hypothesis examples .
Table of Contents
What is a hypothesis ?
A hypothesis is based on the existing body of knowledge in a study area. Framed before the data are collected, a hypothesis states the tentative relationship between independent and dependent variables, along with a prediction of the outcome.
What is a research hypothesis ?
Young researchers starting out their journey are usually brimming with questions like “ What is a hypothesis ?” “ What is a research hypothesis ?” “How can I write a good research hypothesis ?”
A research hypothesis is a statement that proposes a possible explanation for an observable phenomenon or pattern. It guides the direction of a study and predicts the outcome of the investigation. A research hypothesis is testable, i.e., it can be supported or disproven through experimentation or observation.

Characteristics of a good hypothesis
Here are the characteristics of a good hypothesis :
- Clearly formulated and free of language errors and ambiguity
- Concise and not unnecessarily verbose
- Has clearly defined variables
- Testable and stated in a way that allows for it to be disproven
- Can be tested using a research design that is feasible, ethical, and practical
- Specific and relevant to the research problem
- Rooted in a thorough literature search
- Can generate new knowledge or understanding.
How to create an effective research hypothesis
A study begins with the formulation of a research question. A researcher then performs background research. This background information forms the basis for building a good research hypothesis . The researcher then performs experiments, collects, and analyzes the data, interprets the findings, and ultimately, determines if the findings support or negate the original hypothesis.
Let’s look at each step for creating an effective, testable, and good research hypothesis :
- Identify a research problem or question: Start by identifying a specific research problem.
- Review the literature: Conduct an in-depth review of the existing literature related to the research problem to grasp the current knowledge and gaps in the field.
- Formulate a clear and testable hypothesis : Based on the research question, use existing knowledge to form a clear and testable hypothesis . The hypothesis should state a predicted relationship between two or more variables that can be measured and manipulated. Improve the original draft till it is clear and meaningful.
- State the null hypothesis: The null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between the variables you are studying.
- Define the population and sample: Clearly define the population you are studying and the sample you will be using for your research.
- Select appropriate methods for testing the hypothesis: Select appropriate research methods, such as experiments, surveys, or observational studies, which will allow you to test your research hypothesis .
Remember that creating a research hypothesis is an iterative process, i.e., you might have to revise it based on the data you collect. You may need to test and reject several hypotheses before answering the research problem.
How to write a research hypothesis
When you start writing a research hypothesis , you use an “if–then” statement format, which states the predicted relationship between two or more variables. Clearly identify the independent variables (the variables being changed) and the dependent variables (the variables being measured), as well as the population you are studying. Review and revise your hypothesis as needed.
An example of a research hypothesis in this format is as follows:
“ If [athletes] follow [cold water showers daily], then their [endurance] increases.”
Population: athletes
Independent variable: daily cold water showers
Dependent variable: endurance
You may have understood the characteristics of a good hypothesis . But note that a research hypothesis is not always confirmed; a researcher should be prepared to accept or reject the hypothesis based on the study findings.

Research hypothesis checklist
Following from above, here is a 10-point checklist for a good research hypothesis :
- Testable: A research hypothesis should be able to be tested via experimentation or observation.
- Specific: A research hypothesis should clearly state the relationship between the variables being studied.
- Based on prior research: A research hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and previous research in the field.
- Falsifiable: A research hypothesis should be able to be disproven through testing.
- Clear and concise: A research hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner.
- Logical: A research hypothesis should be logical and consistent with current understanding of the subject.
- Relevant: A research hypothesis should be relevant to the research question and objectives.
- Feasible: A research hypothesis should be feasible to test within the scope of the study.
- Reflects the population: A research hypothesis should consider the population or sample being studied.
- Uncomplicated: A good research hypothesis is written in a way that is easy for the target audience to understand.
By following this research hypothesis checklist , you will be able to create a research hypothesis that is strong, well-constructed, and more likely to yield meaningful results.

Types of research hypothesis
Different types of research hypothesis are used in scientific research:
1. Null hypothesis:
A null hypothesis states that there is no change in the dependent variable due to changes to the independent variable. This means that the results are due to chance and are not significant. A null hypothesis is denoted as H0 and is stated as the opposite of what the alternative hypothesis states.
Example: “ The newly identified virus is not zoonotic .”
2. Alternative hypothesis:
This states that there is a significant difference or relationship between the variables being studied. It is denoted as H1 or Ha and is usually accepted or rejected in favor of the null hypothesis.
Example: “ The newly identified virus is zoonotic .”
3. Directional hypothesis :
This specifies the direction of the relationship or difference between variables; therefore, it tends to use terms like increase, decrease, positive, negative, more, or less.
Example: “ The inclusion of intervention X decreases infant mortality compared to the original treatment .”
4. Non-directional hypothesis:
While it does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables, a non-directional hypothesis states the existence of a relationship or difference between variables but not the direction, nature, or magnitude of the relationship. A non-directional hypothesis may be used when there is no underlying theory or when findings contradict previous research.
Example, “ Cats and dogs differ in the amount of affection they express .”
5. Simple hypothesis :
A simple hypothesis only predicts the relationship between one independent and another independent variable.
Example: “ Applying sunscreen every day slows skin aging .”
6 . Complex hypothesis :
A complex hypothesis states the relationship or difference between two or more independent and dependent variables.
Example: “ Applying sunscreen every day slows skin aging, reduces sun burn, and reduces the chances of skin cancer .” (Here, the three dependent variables are slowing skin aging, reducing sun burn, and reducing the chances of skin cancer.)
7. Associative hypothesis:
An associative hypothesis states that a change in one variable results in the change of the other variable. The associative hypothesis defines interdependency between variables.
Example: “ There is a positive association between physical activity levels and overall health .”
8 . Causal hypothesis:
A causal hypothesis proposes a cause-and-effect interaction between variables.
Example: “ Long-term alcohol use causes liver damage .”
Note that some of the types of research hypothesis mentioned above might overlap. The types of hypothesis chosen will depend on the research question and the objective of the study.

Research hypothesis examples
Here are some good research hypothesis examples :
“The use of a specific type of therapy will lead to a reduction in symptoms of depression in individuals with a history of major depressive disorder.”
“Providing educational interventions on healthy eating habits will result in weight loss in overweight individuals.”
“Plants that are exposed to certain types of music will grow taller than those that are not exposed to music.”
“The use of the plant growth regulator X will lead to an increase in the number of flowers produced by plants.”
Characteristics that make a research hypothesis weak are unclear variables, unoriginality, being too general or too vague, and being untestable. A weak hypothesis leads to weak research and improper methods.
Some bad research hypothesis examples (and the reasons why they are “bad”) are as follows:
“This study will show that treatment X is better than any other treatment . ” (This statement is not testable, too broad, and does not consider other treatments that may be effective.)
“This study will prove that this type of therapy is effective for all mental disorders . ” (This statement is too broad and not testable as mental disorders are complex and different disorders may respond differently to different types of therapy.)
“Plants can communicate with each other through telepathy . ” (This statement is not testable and lacks a scientific basis.)
Importance of testable hypothesis
If a research hypothesis is not testable, the results will not prove or disprove anything meaningful. The conclusions will be vague at best. A testable hypothesis helps a researcher focus on the study outcome and understand the implication of the question and the different variables involved. A testable hypothesis helps a researcher make precise predictions based on prior research.
To be considered testable, there must be a way to prove that the hypothesis is true or false; further, the results of the hypothesis must be reproducible.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on research hypothesis
1. What is the difference between research question and research hypothesis ?
A research question defines the problem and helps outline the study objective(s). It is an open-ended statement that is exploratory or probing in nature. Therefore, it does not make predictions or assumptions. It helps a researcher identify what information to collect. A research hypothesis , however, is a specific, testable prediction about the relationship between variables. Accordingly, it guides the study design and data analysis approach.
2. When to reject null hypothesis ?
A null hypothesis should be rejected when the evidence from a statistical test shows that it is unlikely to be true. This happens when the test statistic (e.g., p -value) is less than the defined significance level (e.g., 0.05). Rejecting the null hypothesis does not necessarily mean that the alternative hypothesis is true; it simply means that the evidence found is not compatible with the null hypothesis.
3. How can I be sure my hypothesis is testable?
A testable hypothesis should be specific and measurable, and it should state a clear relationship between variables that can be tested with data. To ensure that your hypothesis is testable, consider the following:
- Clearly define the key variables in your hypothesis. You should be able to measure and manipulate these variables in a way that allows you to test the hypothesis.
- The hypothesis should predict a specific outcome or relationship between variables that can be measured or quantified.
- You should be able to collect the necessary data within the constraints of your study.
- It should be possible for other researchers to replicate your study, using the same methods and variables.
- Your hypothesis should be testable by using appropriate statistical analysis techniques, so you can draw conclusions, and make inferences about the population from the sample data.
- The hypothesis should be able to be disproven or rejected through the collection of data.
4. How do I revise my research hypothesis if my data does not support it?
If your data does not support your research hypothesis , you will need to revise it or develop a new one. You should examine your data carefully and identify any patterns or anomalies, re-examine your research question, and/or revisit your theory to look for any alternative explanations for your results. Based on your review of the data, literature, and theories, modify your research hypothesis to better align it with the results you obtained. Use your revised hypothesis to guide your research design and data collection. It is important to remain objective throughout the process.
5. I am performing exploratory research. Do I need to formulate a research hypothesis?
As opposed to “confirmatory” research, where a researcher has some idea about the relationship between the variables under investigation, exploratory research (or hypothesis-generating research) looks into a completely new topic about which limited information is available. Therefore, the researcher will not have any prior hypotheses. In such cases, a researcher will need to develop a post-hoc hypothesis. A post-hoc research hypothesis is generated after these results are known.
6. How is a research hypothesis different from a research question?
A research question is an inquiry about a specific topic or phenomenon, typically expressed as a question. It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis.
7. Can a research hypothesis change during the research process?
Yes, research hypotheses can change during the research process. As researchers collect and analyze data, new insights and information may emerge that require modification or refinement of the initial hypotheses. This can be due to unexpected findings, limitations in the original hypotheses, or the need to explore additional dimensions of the research topic. Flexibility is crucial in research, allowing for adaptation and adjustment of hypotheses to align with the evolving understanding of the subject matter.
8. How many hypotheses should be included in a research study?
The number of research hypotheses in a research study varies depending on the nature and scope of the research. It is not necessary to have multiple hypotheses in every study. Some studies may have only one primary hypothesis, while others may have several related hypotheses. The number of hypotheses should be determined based on the research objectives, research questions, and the complexity of the research topic. It is important to ensure that the hypotheses are focused, testable, and directly related to the research aims.
9. Can research hypotheses be used in qualitative research?
Yes, research hypotheses can be used in qualitative research, although they are more commonly associated with quantitative research. In qualitative research, hypotheses may be formulated as tentative or exploratory statements that guide the investigation. Instead of testing hypotheses through statistical analysis, qualitative researchers may use the hypotheses to guide data collection and analysis, seeking to uncover patterns, themes, or relationships within the qualitative data. The emphasis in qualitative research is often on generating insights and understanding rather than confirming or rejecting specific research hypotheses through statistical testing.
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

What is IMRaD Format in Research?

What is a Review Article? How to Write it?
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Choosing a Title
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The title summarizes the main idea or ideas of your study. A good title contains the fewest possible words needed to adequately describe the content and/or purpose of your research paper.
Importance of Choosing a Good Title
The title is the part of a paper that is read the most, and it is usually read first . It is, therefore, the most important element that defines the research study. With this in mind, avoid the following when creating a title:
- If the title is too long, this usually indicates there are too many unnecessary words. Avoid language, such as, "A Study to Investigate the...," or "An Examination of the...." These phrases are obvious and generally superfluous unless they are necessary to covey the scope, intent, or type of a study.
- On the other hand, a title which is too short often uses words which are too broad and, thus, does not tell the reader what is being studied. For example, a paper with the title, "African Politics" is so non-specific the title could be the title of a book and so ambiguous that it could refer to anything associated with politics in Africa. A good title should provide information about the focus and/or scope of your research study.
- In academic writing, catchy phrases or non-specific language may be used, but only if it's within the context of the study [e.g., "Fair and Impartial Jury--Catch as Catch Can"]. However, in most cases, you should avoid including words or phrases that do not help the reader understand the purpose of your paper.
- Academic writing is a serious and deliberate endeavor. Avoid using humorous or clever journalistic styles of phrasing when creating the title to your paper. Journalistic headlines often use emotional adjectives [e.g., incredible, amazing, effortless] to highlight a problem experienced by the reader or use "trigger words" or interrogative words like how, what, when, or why to persuade people to read the article or click on a link. These approaches are viewed as counter-productive in academic writing. A reader does not need clever or humorous titles to catch their attention because the act of reading research is assumed to be deliberate based on a desire to learn and improve understanding of the problem. In addition, a humorous title can merely detract from the seriousness and authority of your research.
- Unlike everywhere else in a college-level social sciences research paper [except when using direct quotes in the text], titles do not have to adhere to rigid grammatical or stylistic standards. For example, it could be appropriate to begin a title with a coordinating conjunction [i.e., and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet] if it makes sense to do so and does not detract from the purpose of the study [e.g., "Yet Another Look at Mutual Fund Tournaments"] or beginning the title with an inflected form of a verb such as those ending in -ing [e.g., "Assessing the Political Landscape: Structure, Cognition, and Power in Organizations"].
Appiah, Kingsley Richard et al. “Structural Organisation of Research Article Titles: A Comparative Study of Titles of Business, Gynaecology and Law.” Advances in Language and Literary Studies 10 (2019); Hartley James. “To Attract or to Inform: What are Titles for?” Journal of Technical Writing and Communication 35 (2005): 203-213; Jaakkola, Maarit. “Journalistic Writing and Style.” In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication . Jon F. Nussbaum, editor. (New York: Oxford University Press, 2018): https://oxfordre.com/communication.
Structure and Writing Style
The following parameters can be used to help you formulate a suitable research paper title:
- The purpose of the research
- The scope of the research
- The narrative tone of the paper [typically defined by the type of the research]
- The methods used to study the problem
The initial aim of a title is to capture the reader’s attention and to highlight the research problem under investigation.
Create a Working Title Typically, the final title you submit to your professor is created after the research is complete so that the title accurately captures what has been done . The working title should be developed early in the research process because it can help anchor the focus of the study in much the same way the research problem does. Referring back to the working title can help you reorient yourself back to the main purpose of the study if you find yourself drifting off on a tangent while writing. The Final Title Effective titles in research papers have several characteristics that reflect general principles of academic writing.
- Indicate accurately the subject and scope of the study,
- Rarely use abbreviations or acronyms unless they are commonly known,
- Use words that create a positive impression and stimulate reader interest,
- Use current nomenclature from the field of study,
- Identify key variables, both dependent and independent,
- Reveal how the paper will be organized,
- Suggest a relationship between variables which supports the major hypothesis,
- Is limited to 5 to 15 substantive words,
- Does not include redundant phrasing, such as, "A Study of," "An Analysis of" or similar constructions,
- Takes the form of a question or declarative statement,
- If you use a quote as part of the title, the source of the quote is cited [usually using an asterisk and footnote],
- Use correct grammar and capitalization with all first words and last words capitalized, including the first word of a subtitle. All nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs that appear between the first and last words of the title are also capitalized, and
- Rarely uses an exclamation mark at the end of the title.
The Subtitle Subtitles are frequently used in social sciences research papers because it helps the reader understand the scope of the study in relation to how it was designed to address the research problem. Think about what type of subtitle listed below reflects the overall approach to your study and whether you believe a subtitle is needed to emphasize the investigative parameters of your research.
1. Explains or provides additional context , e.g., "Linguistic Ethnography and the Study of Welfare Institutions as a Flow of Social Practices: The Case of Residential Child Care Institutions as Paradoxical Institutions." [Palomares, Manuel and David Poveda. Text & Talk: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Language, Discourse and Communication Studies 30 (January 2010): 193-212]
2. Adds substance to a literary, provocative, or imaginative title or quote , e.g., "Listen to What I Say, Not How I Vote": Congressional Support for the President in Washington and at Home." [Grose, Christian R. and Keesha M. Middlemass. Social Science Quarterly 91 (March 2010): 143-167]
3. Qualifies the geographic scope of the research , e.g., "The Geopolitics of the Eastern Border of the European Union: The Case of Romania-Moldova-Ukraine." [Marcu, Silvia. Geopolitics 14 (August 2009): 409-432]
4. Qualifies the temporal scope of the research , e.g., "A Comparison of the Progressive Era and the Depression Years: Societal Influences on Predictions of the Future of the Library, 1895-1940." [Grossman, Hal B. Libraries & the Cultural Record 46 (2011): 102-128]
5. Focuses on investigating the ideas, theories, or work of a particular individual , e.g., "A Deliberative Conception of Politics: How Francesco Saverio Merlino Related Anarchy and Democracy." [La Torre, Massimo. Sociologia del Diritto 28 (January 2001): 75 - 98]
6. Identifies the methodology used , e.g. "Student Activism of the 1960s Revisited: A Multivariate Analysis Research Note." [Aron, William S. Social Forces 52 (March 1974): 408-414]
7. Defines the overarching technique for analyzing the research problem , e.g., "Explaining Territorial Change in Federal Democracies: A Comparative Historical Institutionalist Approach." [ Tillin, Louise. Political Studies 63 (August 2015): 626-641.
With these examples in mind, think about what type of subtitle reflects the overall approach to your study. This will help the reader understand the scope of the study in relation to how it was designed to address the research problem.
Anstey, A. “Writing Style: What's in a Title?” British Journal of Dermatology 170 (May 2014): 1003-1004; Balch, Tucker. How to Compose a Title for Your Research Paper. Augmented Trader blog. School of Interactive Computing, Georgia Tech University; Bavdekar, Sandeep B. “Formulating the Right Title for a Research Article.” Journal of Association of Physicians of India 64 (February 2016); Choosing the Proper Research Paper Titles. AplusReports.com, 2007-2012; Eva, Kevin W. “Titles, Abstracts, and Authors.” In How to Write a Paper . George M. Hall, editor. 5th edition. (Oxford: John Wiley and Sons, 2013), pp. 33-41; Hartley James. “To Attract or to Inform: What are Titles for?” Journal of Technical Writing and Communication 35 (2005): 203-213; General Format. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Kerkut G.A. “Choosing a Title for a Paper.” Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Physiology 74 (1983): 1; “Tempting Titles.” In Stylish Academic Writing . Helen Sword, editor. (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 2012), pp. 63-75; Nundy, Samiran, et al. “How to Choose a Title?” In How to Practice Academic Medicine and Publish from Developing Countries? A Practical Guide . Edited by Samiran Nundy, Atul Kakar, and Zulfiqar A. Bhutta. (Springer Singapore, 2022), pp. 185-192.
- << Previous: Applying Critical Thinking
- Next: Making an Outline >>
- Last Updated: Jul 30, 2024 10:20 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Null and Alternative Hypothesis: Research Guidelines
- Icon Calendar 17 June 2024
- Icon Page 2753 words
- Icon Clock 13 min read
When undertaking a qualitative or quantitative research project, researchers must first formulate a research question, from which they develop their theories. By definition, an assumption is a prediction that a researcher makes about an actual research question and can either be affirmative or negative. In this case, writing a research question has three main components: variables (independent and dependent), a population sample, and the relation between these variables. To find null and alternative hypotheses, scholars identify a specific research question, determine the variables involved, and state H0 as no effect or difference and H1 or Ha as a significant effect or difference. When the prediction contradicts the research question, it is referred to as a null assumption. In short, an initial theory is a statement that implies there is no relationship between independent and dependent variables. Hence, researchers need to learn how to write a good null and alternative hypothesis to present quality studies.
General Aspects
Students with qualitative or quantitative research assignments must learn how to formulate and write good research questions and proposition statements. In essence, hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to determine if there is enough evidence to reject an initial theory and support an alternative assumption based on sample data. By definition, a research proposition is an assumption or prediction that a scholar makes before undertaking an experimental investigation. Basically, academic standards require such a prediction to be a precise and testable statement, meaning that researchers must prove or disapprove of it in the course of their assignment and provide alternatives if possible. In this case, the main components of a typical research assumption are variables (independent and dependent), a population sample, and the relation between these variables. To formulate a null hypothesis (H0) in quantitative research, researchers state there is no effect or difference between variables (e.g., µ1 = µ2), and, for an alternative hypothesis (H1 or Ha), they posit there is a significant effect or difference (e.g., µ1 ≠ µ2). Therefore, a research proposition is a prediction that scholars write about the relationship between two or more variables. In turn, a standard research inquiry is a particular process that seeks to answer a specific research question and, in the process, test a particular theory by confirming or disapproving it.

Types of Hypotheses
There are several types of hypotheses, including null, alternative, directional, and non-directional assumptions. Basically, a directional hypothesis is a prediction of how an independent variable affects a dependent variable. In contrast, a non-directional hypothesis predicts that an independent variable influences a dependent variable but does not specify how. Regardless of the type, all propositions are about predicting the relationship between independent and dependent variables. To write H0 (null assumption) and H1 or Ha (alternative prediction), researchers clearly state H0 as a central assumption of no effect or no difference (e.g., µ1 = µ2) and H1 or Ha as a secondary assumption of a significant effect or difference (e.g., µ1 ≠ µ2).
What Is a Null Hypothesis (H0) and Its Purpose
According to its definition, a null hypothesis is a foundational statement in statistical testing that posits there is no significant effect, relationship, or difference between groups or variables within a given study. In simple words, a null hypothesis, usually symbolized as “H0,” is a statement that contradicts an actual research theory (Watt & Collins, 2019). The main purpose of writing a null hypothesis is to provide a basis for comparison, allowing researchers to determine whether there is sufficient evidence to reject this assumption in favor of an alternative theory, which suggests a real effect or relationship. As such, it is a negative statement, indicating that there is no relationship or connection between independent and dependent variables (Harrison et al., 2020). By starting with a null proposition, researchers can also employ various statistical tests to evaluate an entire data, ensuring the objectivity of findings and minimizing their bias. The process helps to ensure the validity of scientific research, minimizing the likelihood of drawing incorrect conclusions from the data collected. Moreover, by testing an initial theory, researchers can determine whether the inquiry results are due to the chance or the effect of manipulating a dependent variable (McNulty, 2022). In most instances, a null assumption corresponds with an alternative theory, a positive statement that covers a relationship that exists between independent and dependent variables. Finally, it is highly recommended that researchers should write an alternative assumption first before a null proposition.
What Is an Alternative Hypothesis (H1 or Ha) and Its Purpose
According to its definition and opposite to a null assumption, an alternative hypothesis in research is another statement in statistical testing that suggests there is a significant effect, relationship, or difference between groups or variables in a given study. Basically, this statement contrasts with what a null theory posits, which asserts that no such effect or relationship exists (Baker, 2021). The main purpose of writing an alternative hypothesis is to guide researchers in testing and validating new theories or effects and determine whether the observed data can provide evidence against a null proposition. The process involves comparing observed results to what would be expected under a null assumption. When statistical tests provide enough evidence to reject an initial postulation, an alternative theory becomes true, indicating that the observed effect or relationship is likely real and not due to random variation (Jawlik, 2016). By framing their research around an alternative hypothesis, scientists can focus their investigations on discovering meaningful effects and relationships, thereby advancing knowledge and understanding in their study fields. Hence, writing good null and alternative hypotheses is important because they provide a structured framework for statistical testing, allowing researchers to objectively evaluate evidence and draw conclusions about the presence of significant effects or relationships in an entire data.
Null vs. Alternative Hypothesis Formats
| Aspect | Null Assumption (H0) | Alternative Prediction (H1 or Ha) |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Assumes no effect or relationship | Assumes a significant effect or relationship |
| Purpose | Serves as a default or baseline assumption | Provides a specific direction for research |
| Claim | No difference or effect exists | A difference or effect exists |
| Statistical Testing | Basis for comparison | Sought to be supported by rejecting H0 |
| Example (Means) | µ1 = µ2 | µ1 ≠ µ2, µ1 > µ2, or µ1 < µ2 |
| Example (Proportions) | p1 = p2 | p1 ≠ p2, p1 > p2, or p1 < p2 |
| Role in Research | Used to test for significance of results | Indicates a presence of an effect if H0 is rejected |
| Decision Making | Retain H0 if there is insufficient evidence to reject | Accept H1 or Ha as an alternative option if there is sufficient evidence to reject H0 |
| Result Interpretation | Observed effect is due to chance | Observed effect is real and not due to chance |
| Scientific Inquiry | Maintains objectivity and prevents false positives | Provides alternative discovery and theory testing |
Steps on How to Write a Good Null and Alternative Hypothesis
- Identify a Specific Research Question: Start with clearly defining a particular problem or phenomenon you want to study.
- Determine Key Variables: Identify independent and dependent variables involved in your study.
- State a Specific Null Hypothesis (H0): Formulate a concrete statement that suggests no effect, no difference, or no relationship between your variables. This is usually a statement of equality (e.g., µ1 = µ2).
- State a Clear Alternative Hypothesis (H1 or Ha): Formulate another statement that suggests a significant effect, difference, or relationship between your variables. This is usually a statement of inequality (e.g., µ1 ≠ µ2, µ1 > µ2, or µ1 < µ2).
- Means: H0: µ1 = µ2 vs. H1: µ1 ≠ µ2
- Proportions: H0: p1 = p2 vs. H1: p1 ≠ p2
- One-tailed test: If you are testing for a specific direction of effect (e.g., H1: µ1 > µ2).
- Two-tailed test: If you are testing for any difference, regardless of direction (e.g., H1: µ1 ≠ µ2).
- Consult Literature: Review existing research to see how similar or alternative theories have been formulated. This can provide guidance and ensure your expectations are aligned with standard practices in your field.
- Write in Simple Terms: Ensure both null and alternative theories are stated clearly and concisely, making them easy to understand.
- Review and Refine: Double-check your propositions for clarity and correctness. Make sure they are mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive, covering all possible outcomes.
- Seek Feedback: Discuss your approaches with peers or advisors to ensure they are logical, relevant, and testable. Adjust as necessary based on their input.
Note: A null hypothesis is a specific statement assuming no effect or difference, while other hypotheses refer to general statements that include writing null and alternative hypotheses and proposing possible outcomes to be tested.
Written Examples of Research Questions With H0 and H1 Hypotheses
Before developing any study proposition, a researcher must formulate a specific research question. In this case, a research hypothesis is a broad, testable statement about the expected relationship between variables, while a statistical hypothesis specifically refers to writing null and alternative hypotheses used in statistical testing to validate or refute an initial study assumption (O’Donnell et al., 2023). Then, the next step is to transform this study question into a negative statement that claims the lack of a relationship between independent and dependent variables. Alternatively, researchers can change the question into a positive statement that includes a relationship that exists between the variables. In turn, this latter statement becomes an alternative hypothesis and is symbolized as H1 or Ha. Hence, some of the examples of research questions and hull and alternative hypotheses are as follows:
Research Question (RQ) 1: Do physical exercises help individuals to age gracefully?
- A Null Hypothesis (H0): Physical exercises are not a guarantee for graceful old age.
- An Alternative Hypothesis (H1): Engaging in physical exercises enables individuals to remain healthy and active into old age.
RQ 2: What are the implications of therapeutic interventions in the fight against substance abuse?
- H0: Therapeutic interventions are of no help in the fight against substance abuse.
- H1: Exposing individuals with substance abuse disorders to therapeutic interventions helps to control and even stop their addictions.
RQ 3: How do sexual orientation and gender identity affect the experiences of late adolescents in foster care?
- H0: Sexual orientation and gender identity have no effects on the experiences of late adolescents in foster care.
- H1: The reality of stereotypes in society makes sexual orientation and gender identity factors complicate the experiences of late adolescents in foster care.
RQ 4: Does income inequality contribute to crime in high-density urban areas?
- H0: There is no correlation between income inequality and incidences of crime in high-density urban areas.
- H1: The high crime rates in high-density urban areas are due to the incidence of income inequality in those areas.
RQ 5: Does placement in foster care impact individuals’ mental health?
- H0: There is no correlation between being in foster care and having mental health problems.
- H1: Individuals placed in foster care experience anxiety and depression at one point in their life.
RQ 6: Do assistive devices and technologies lessen the mobility challenges of older adults with a stroke?
- H0: Assistive devices and technologies do not provide any assistance to the mobility of older adults diagnosed with a stroke.
- H1: Assistive devices and technologies enhance the mobility of older adults diagnosed with a stroke.
RQ 7: Does race identity undermine classroom participation?
- H0: There is no correlation between racial identity and the ability to participate in classroom learning.
- H1: Students from racial minorities are not as active as white students in classroom participation.
RQ 8: Do high school grades determine future success?
- H0: There is no correlation between how one performs in high school and their success level in life.
- H1: Attaining high grades in high school positions one for greater success in the future personal and professional lives.
RQ 9: Does critical thinking predict academic achievement?
- H0: There is no correlation between critical thinking and academic achievement.
- H1: Being a critical thinker is a pathway to academic success.
RQ 10: What benefits does group therapy provide to victims of domestic violence?
- H0: Group therapy does not help victims of domestic violence because individuals prefer to hide rather than expose their shame.
- H1: Group therapy provides domestic violence victims with a platform to share their hurt and connect with others with similar experiences.
Symbols and Signs in Writing
| Aspect | Null Theory (H0) | Alternative Proposition (H1 or Ha) |
|---|---|---|
| Symbols | H0 | H1 or Ha |
| Equality Sign | = | ≠ |
| Greater Than Sign | Not used | > |
| Less Than Sign | Not used | < |
| Means | µ1 = µ2: No difference in population means | µ1 ≠ µ2: Population means are different |
| Proportions | p1 = p2: No difference in population proportions | p1 ≠ p2: Population proportions are different |
| p1 > p2: Proportion of population 1 is greater than proportion of population 2 | ||
| p1 < p2: Proportion of population 1 is less than proportion of population 2 | ||
| Testing Approach | Serves as a default assumption; tested to be retained or rejected | Provides an alternative claim to be tested for evidence |
| Outcome if Accepted | Indicates that the observed data is due to chance in a null theory | Indicates that the observed data shows a true effect or relationship as an alternative to a null statement |
Common Mistakes
- Ambiguity in Theories: Writing vague or unclear null and alternative assumptions.
- Directional vs. Non-Directional Confusion: Confusing one-tailed (directional) and two-tailed (non-directional) claims.
- Using Sample Statistics: Stating initial and alternative propositions in terms of sample statistics instead of population parameters.
- Overlapping Assumptions: Creating null and alternative statements that are not mutually exclusive.
- Testing Multiple Variables: Including multiple variables or conditions in a single theory.
- Misinterpreting a Null Proposition: Assuming an initial statement is what you want to prove.
- Incorrect Symbols and Signs: Using incorrect or inconsistent symbols and signs for writing null and alternative propositions.
- Ignoring Context: Writing initial and alternative theories that are not relevant to an assigned research question or context.
- Not Testable Hypotheses: Formulating null and alternative statements that are not testable with the available data or methods.
- Confusing Null and Alternative Hypotheses: Swapping the roles of null and alternative assumptions.
The formulation of research questions in qualitative and quantitative assignments helps students to develop a specific theory for their experiments. In this case, learning how to write a good null and alternative hypothesis helps students and researchers to make their research relevant. Basically, the difference between a null and alternative hypothesis is that the former contradicts an entire research question, while the latter affirms it. In short, an initial proposition is a negative statement relative to a particular research question, and an alternative theory is a positive assumption. Moreover, it is important to note that developing a null hypothesis at the beginning of the assignment is for prediction purposes. As such, the research work must answer a specific research question and confirm or disapprove of an initial proposition. Hence, some of the tips that students and researchers need to know when developing any theory include:
- Formulate a research question that specifies the relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable.
- Develop an alternative assumption that says a relationship exists between the variables.
- Develop a null proposition that says a relationship does not exist between the variables.
- Conduct an experiment to answer a research question under analysis, which allows the confirmation of a disapproval of a null theory or considering alternative options.
Baker, L. (2021). Hypothesis testing: How to choose the correct test (Getting started with statistics) . Chi-Squared Innovations.
Harrison, A. J., McErlain-Naylor, S. A., Bradshaw, E. J., Dai, B., Nunome, H., Hughes, G. T. G., Kong, P. W., Vanwanseele, B., Vilas-Boas, J. P., & Fong, D. T. (2020). Recommendations for statistical analysis involving null hypothesis significance testing. Sports Biomechanics , 19 (5), 561–568. https://doi.org/10.1080/14763141.2020.1782555
Jawlik, A. (2016). Statistics from A to Z: Confusing concepts clarified . John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
McNulty, R. (2022). A logical analysis of null hypothesis significance testing using popular terminology. BMC Medical Research Methodology , 22 (1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-022-01696-5
O’Donnell, C. T., Fielding-Singh, V., & Vanneman, M. W. (2023). The art of the null hypothesis — Considerations for study design and scientific reporting. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia , 37 (6), 867–869. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2023.02.026
Watt, R., & Collins, E. (2019). Null hypothesis testing . SAGE Publications Ltd.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

SAT Essay Examples With Explanations and Recommendations
- Icon Calendar 29 July 2020
- Icon Page 3990 words


How to Cite Lecture Notes in APA: Basic Guidelines
- Icon Calendar 27 July 2020
- Icon Page 2390 words

6 Important Tips on Writing a Research Paper Title
When you are searching for a research study on a particular topic, you probably notice that articles with interesting, descriptive research titles draw you in. By contrast, research paper titles that are not descriptive are usually passed over, even though you may write a good research paper with interesting contents. This shows the importance of coming up with a good title for your research paper when drafting your own manuscript.
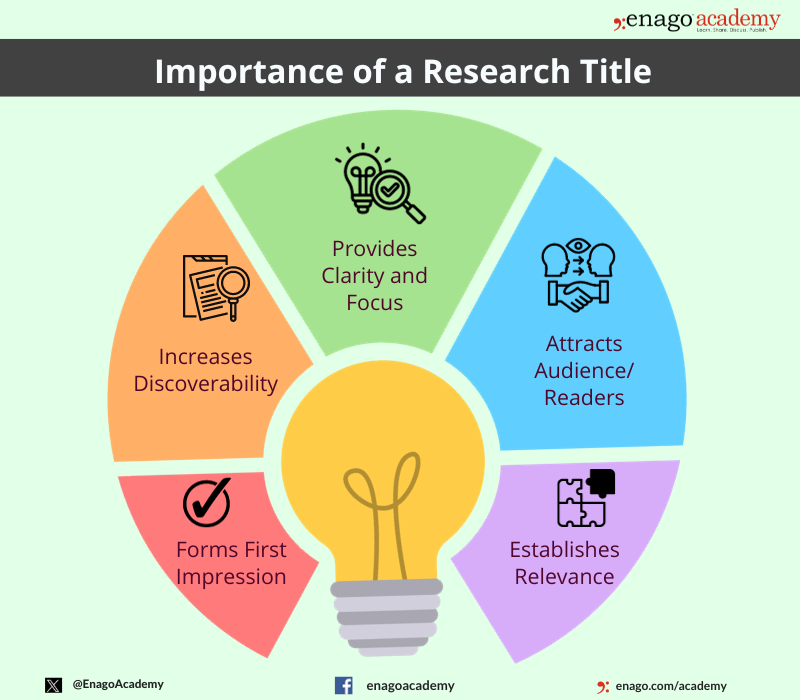
Importance of a Research Title
The research title plays a crucial role in the research process, and its importance can be summarized as follows:
Why do Research Titles Matter?
Before we look at how to title a research paper, let’s look at a research title example that illustrates why a good research paper should have a strong title.
Imagine that you are researching meditation and nursing, and you want to find out if any studies have shown that meditation makes nurses better communicators. You conduct a keyword search using the keywords “nursing”, “communication”, and “meditation.” You come up with results that have the following titles:
- Benefits of Meditation for the Nursing Profession: A Quantitative Investigation
- Why Mindful Nurses Make the Best Communicators
- Meditation Gurus
- Nurses on the Move: A Quantitative Report on How Meditation Can Improve Nurse Performance
All four of these research paper titles may describe very similar studies—they could even be titles for the same study! As you can see, they give very different impressions.
- Title 1 describes the topic and the method of the study but is not particularly catchy.
- Title 2 partly describes the topic, but does not give any information about the method of the study—it could simply be a theoretical or opinion piece.
- Title 3 is somewhat catchier but gives almost no information at all about the article.
- Title 4 begins with a catchy main title and is followed by a subtitle that gives information about the content and method of the study.
As we will see, Title 4 has all the characteristics of a good research title.
Characteristics of a Good Research Title
According to rhetoric scholars Hairston and Keene, making a good title for a paper involves ensuring that the title of the research accomplishes four goals as mentioned below:
- It should predict the content of the research paper .
- It should be interesting to the reader .
- It should reflect the tone of the writing .
- It should contain important keywords that will make it easier to be located during a keyword search.
Let’s return to the examples in the previous section to see how to make a research title.
| Title | Predicts content? | Interesting? | Reflects tone? | Important keywords? |
|
| Yes | No | No | Yes |
|
| No | Yes | Yes | No |
|
| No | Yes | No | No |
|
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
As you can see in the table above, only one of the four example titles fulfills all of the criteria of a suitable research paper title.
Related: You’ve chosen your study topic, but having trouble deciding where to publish it? Here’s a comprehensive course to help you identify the right journal .
Tips for Writing an Effective Research Paper Title
When writing a research title, you can use the four criteria listed above as a guide. Here are a few other tips you can use to make sure your title will be part of the recipe for an effective research paper :
- Make sure your research title describes (a) the topic, (b) the method, (c) the sample, and (d) the results of your study. You can use the following formula:
[ Result ]: A [ method ] study of [ topic ] among [ sample ] Example : Meditation makes nurses perform better: a qualitative study of mindfulness meditation among German nursing students
- Avoid unnecessary words and jargons. Keep the title statement as concise as possible. You want a title that will be comprehensible even to people who are not experts in your field. Check our article for a detailed list of things to avoid when writing an effective research title .
- Make sure your title is between 5 and 15 words in length.
- If you are writing a title for a university assignment or for a particular academic journal, verify that your title conforms to the standards and requirements for that outlet. For example, many journals require that titles fall under a character limit, including spaces. Many universities require that titles take a very specific form, limiting your creativity.
- Use a descriptive phrase to convey the purpose of your research efficiently.
- Most importantly, use critical keywords in the title to increase the discoverability of your article.

Resources for Further Reading
In addition to the tips above, there are many resources online that you can use to help write your research title. Here is a list of links that you may find useful as you work on creating an excellent research title:
- The University of Southern California has a guide specific to social science research papers: http://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/title
- The Journal of European Psychology Students has a blog article focusing on APA-compliant research paper titles: http://blog.efpsa.org/2012/09/01/how-to-write-a-good-title-for-journal-articles/
- This article by Kristen Hamlin contains a step-by-step approach to writing titles: http://classroom.synonym.com/choose-title-research-paper-4332.html
Are there any tips or tricks you find useful in crafting research titles? Which tip did you find most useful in this article? Leave a comment to let us know!
- Hairston, M., & Keene, M. 2003. Successful writing . 5th ed. New York: Norton.
- University of Southern California. 2017. Organizing your social sciences research paper: choosing a title . [Online] Available at: http://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/title
Thank you so much:) Have a nice day!
Thank you so much, it helped me.. God bless..
Thank you for the excellent article and tips for creating a research work, because I always forget about such an essential element as the keywords when forming topics. In particular, I have found a rapid help with the formation of informative and sound titles that also conforms to the standards and requirements.
I am doing a research work on sales girls or shop girls using qualititative method. Basicly I am from Pakistan and writing on the scenario of mycountry. I am really confused about my research title can you kindly give some suggestions and give me an approperaite tilte

Hi Zubair, Thank you for your question. However, the information you have provided is insufficient for drafting an appropriate title. Information on what exactly you intend to study would be needed in order to draft a meaningful title. Meanwhile, you can try drafting your own title after going through the following articles our website: https://www.enago.com/academy/top-10-tips-on-choosing-an-attractive-research-title/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/writing-a-good-research-title-things-to-avoid/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/write-irresistible-research-paper-title/ We would be happy to give you feedback and suggest changes if required. Did you get a chance to install our free Mobile App? https://www.enago.com/academy/mobile-app/ . Make sure you subscribe to our weekly newsletter https://www.enago.com/academy/subscribe-now/ .
thanks for helping me like this!!
Thank you for this. It helped me improve my research title. I just want to verify to you the title I have just made. “Ensuring the safety: A Quantitative Study of Radio Frequency Identification system among the selected students of ( school’s name ).
(I need your reply asap coz we will be doing the chap. 1 tomorrow. Thank u in advance. 🙂 )
I am actually doing a research paper title. I want to know more further in doing research title. Can you give me some tips on doing a research paper?
Hi Joan, Thank you for your question. We are glad to know that you found our resources useful. Your feedback is very valuable to us. You can try drafting your own title after going through the following articles on our website: https://www.enago.com/academy/top-10-tips-on-choosing-an-attractive-research-title/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/writing-a-good-research-title-things-to-avoid/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/write-irresistible-research-paper-title/
We would be happy to give you feedback and suggest changes if required. Did you get a chance to install our free Mobile App? https://www.enago.com/academy/mobile-app/ . Make sure you subscribe to our weekly newsletter https://www.enago.com/academy/subscribe-now/ .
That really helpful. Thanks alot
Thank you so much. It’s really help me.
Thanks for sharing this tips. Title matters a lot for any article because it contents Keywords of article. It should be eye-catchy. Your article is helpful to select title of any article.
nice blog that you have shared
This blog is very informative for me. Thanks for sharing.
nice information that you have shared
i’m found in selecting my ma thesis title ,so i’m going to do my final research after the proposal approved. Your post help me find good title.
I need help. I need a research title for my study about early mobilization of the mechanically ventilated patients in the ICU. Any suggestions would be highly appreciated.
Thank you for posting your query on the website. When writing manuscripts, too many scholars neglect the research title. This phrase, along with the abstract, is what people will mostly see and read online. Title research of publications shows that the research paper title does matter a lot. Both bibliometrics and altmetrics tracking of citations are now, for better or worse, used to gauge a paper’s “success” for its author(s) and the journal publishing it. Interesting research topics coupled with good or clever yet accurate research titles can draw more attention to your work from peers and the public alike. You can check through the following search results for titles on similar topics: https://www.google.com/search?q=early+mobilization+of+the+mechanically+ventilated+patients+in+the+icu&rlz=1C1GCEU_enIN907IN907&oq=&aqs=chrome.0.69i59.4920093j0j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8 .
We hope this would be helpful in drafting an attractive title for your research paper.
Please let us know in case of any other queries.
I’ve been surfing online more than 3 hours these days, but I never found any interesting article like yours. It is lovely worth enough for me. In my opinion, if all website owners and bloggers made just right content material as you did, the internet will be much more helpful than ever before.
Wonderful article! We will bee linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the good writing.
Wow that was odd. I just wrote an very long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyhow, just wanted to say fantastic blog!
In case the topic is new research before you’re writing. And then to stand out, you end up being different.and be inclined to highlight yourself.
There are many free directories, and more paid lists.
To be honest your article is informative. I search many site to know about writing but I didn’t get the information I needed. I saw your site and I read it. I got some new information from here. I think some of your tips can be applied to those too! Thank you so very much for such informative and useful content.
Nice and well written content you have shared with us. thanks a lot!
Thanks for sharing these tips… Rockwide
Its helpful. a person can grab knowledge through it.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Industry News
- Publishing Research
- Promoting Research
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer-Review Week 2023
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

In your opinion, what is the most effective way to improve integrity in the peer review process?
Hypothesis Maker Online
Looking for a hypothesis maker? This online tool for students will help you formulate a beautiful hypothesis quickly, efficiently, and for free.
Are you looking for an effective hypothesis maker online? Worry no more; try our online tool for students and formulate your hypothesis within no time.
- 🔎 How to Use the Tool?
- ⚗️ What Is a Hypothesis in Science?
👍 What Does a Good Hypothesis Mean?
- 🧭 Steps to Making a Good Hypothesis
🔗 References
📄 hypothesis maker: how to use it.
Our hypothesis maker is a simple and efficient tool you can access online for free.
If you want to create a research hypothesis quickly, you should fill out the research details in the given fields on the hypothesis generator.
Below are the fields you should complete to generate your hypothesis:
- Who or what is your research based on? For instance, the subject can be research group 1.
- What does the subject (research group 1) do?
- What does the subject affect? - This shows the predicted outcome, which is the object.
- Who or what will be compared with research group 1? (research group 2).
Once you fill the in the fields, you can click the ‘Make a hypothesis’ tab and get your results.
⚗️ What Is a Hypothesis in the Scientific Method?
A hypothesis is a statement describing an expectation or prediction of your research through observation.
It is similar to academic speculation and reasoning that discloses the outcome of your scientific test . An effective hypothesis, therefore, should be crafted carefully and with precision.
A good hypothesis should have dependent and independent variables . These variables are the elements you will test in your research method – it can be a concept, an event, or an object as long as it is observable.
You can observe the dependent variables while the independent variables keep changing during the experiment.
In a nutshell, a hypothesis directs and organizes the research methods you will use, forming a large section of research paper writing.
Hypothesis vs. Theory
A hypothesis is a realistic expectation that researchers make before any investigation. It is formulated and tested to prove whether the statement is true. A theory, on the other hand, is a factual principle supported by evidence. Thus, a theory is more fact-backed compared to a hypothesis.
Another difference is that a hypothesis is presented as a single statement , while a theory can be an assortment of things . Hypotheses are based on future possibilities toward a specific projection, but the results are uncertain. Theories are verified with undisputable results because of proper substantiation.
When it comes to data, a hypothesis relies on limited information , while a theory is established on an extensive data set tested on various conditions.
You should observe the stated assumption to prove its accuracy.
Since hypotheses have observable variables, their outcome is usually based on a specific occurrence. Conversely, theories are grounded on a general principle involving multiple experiments and research tests.
This general principle can apply to many specific cases.
The primary purpose of formulating a hypothesis is to present a tentative prediction for researchers to explore further through tests and observations. Theories, in their turn, aim to explain plausible occurrences in the form of a scientific study.
It would help to rely on several criteria to establish a good hypothesis. Below are the parameters you should use to analyze the quality of your hypothesis.
| Testability | You should be able to test the hypothesis to present a true or false outcome after the investigation. Apart from the logical hypothesis, ensure you can test your predictions with . |
|---|---|
| Variables | It should have a dependent and independent variable. Identifying the appropriate variables will help readers comprehend your prediction and what to expect at the conclusion phase. |
| Cause and effect | A good hypothesis should have a cause-and-effect connection. One variable should influence others in some way. It should be written as an “if-then” statement to allow the researcher to make accurate predictions of the investigation results. However, this rule does not apply to a . |
| Clear language | Writing can get complex, especially when complex research terminology is involved. So, ensure your hypothesis has expressed as a brief statement. Avoid being vague because your readers might get confused. Your hypothesis has a direct impact on your entire research paper’s quality. Thus, use simple words that are easy to understand. |
| Ethics | Hypothesis generation should comply with . Don’t formulate hypotheses that contravene taboos or are questionable. Besides, your hypothesis should have correlations to published academic works to look data-based and authoritative. |
🧭 6 Steps to Making a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis becomes way simpler if you follow a tried-and-tested algorithm. Let’s explore how you can formulate a good hypothesis in a few steps:
Step #1: Ask Questions
The first step in hypothesis creation is asking real questions about the surrounding reality.
Why do things happen as they do? What are the causes of some occurrences?
Your curiosity will trigger great questions that you can use to formulate a stellar hypothesis. So, ensure you pick a research topic of interest to scrutinize the world’s phenomena, processes, and events.
Step #2: Do Initial Research
Carry out preliminary research and gather essential background information about your topic of choice.
The extent of the information you collect will depend on what you want to prove.
Your initial research can be complete with a few academic books or a simple Internet search for quick answers with relevant statistics.
Still, keep in mind that in this phase, it is too early to prove or disapprove of your hypothesis.
Step #3: Identify Your Variables
Now that you have a basic understanding of the topic, choose the dependent and independent variables.
Take note that independent variables are the ones you can’t control, so understand the limitations of your test before settling on a final hypothesis.
Step #4: Formulate Your Hypothesis
You can write your hypothesis as an ‘if – then’ expression . Presenting any hypothesis in this format is reliable since it describes the cause-and-effect you want to test.
For instance: If I study every day, then I will get good grades.
Step #5: Gather Relevant Data
Once you have identified your variables and formulated the hypothesis, you can start the experiment. Remember, the conclusion you make will be a proof or rebuttal of your initial assumption.
So, gather relevant information, whether for a simple or statistical hypothesis, because you need to back your statement.
Step #6: Record Your Findings
Finally, write down your conclusions in a research paper .
Outline in detail whether the test has proved or disproved your hypothesis.
Edit and proofread your work, using a plagiarism checker to ensure the authenticity of your text.
We hope that the above tips will be useful for you. Note that if you need to conduct business analysis, you can use the free templates we’ve prepared: SWOT , PESTLE , VRIO , SOAR , and Porter’s 5 Forces .
❓ Hypothesis Formulator FAQ
Updated: Jul 19th, 2024
- How to Write a Hypothesis in 6 Steps - Grammarly
- Forming a Good Hypothesis for Scientific Research
- The Hypothesis in Science Writing
- Scientific Method: Step 3: HYPOTHESIS - Subject Guides
- Hypothesis Template & Examples - Video & Lesson Transcript
- Free Essays
- Writing Tools
- Lit. Guides
- Donate a Paper
- Q&A by Experts
- Referencing Guides
- Free Textbooks
- Tongue Twisters
- Editorial Policy
- Job Openings
- Video Contest
- Writing Scholarship
- Discount Codes
- Brand Guidelines
- IvyPanda Shop
- Online Courses
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Copyright Principles
- DMCA Request
- Service Notice
IvyPanda's free online hypothesis maker will help you formulate a hypothesis for your study. With this easy-to-use tool, you just need to provide basic info about the focus of your research, its variables, and predicted outcomes. The rest is on us. Get a perfect hypothesis fast!
Frequently asked questions
Should i use a research question, hypothesis, or thesis statement.
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Frequently asked questions: Writing a research paper
A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question . Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative , descriptive , longitudinal , experimental , or correlational . What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them.
In general, they should be:
- Focused and researchable
- Answerable using credible sources
- Complex and arguable
- Feasible and specific
- Relevant and original
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly

A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
Your research objectives indicate how you’ll try to address your research problem and should be specific:
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in Chicago style are to:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Use 1 inch margins or larger
- Apply double line spacing
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch
- Include a title page
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center
- Cite your sources with author-date citations or Chicago footnotes
- Include a bibliography or reference list
To automatically generate accurate Chicago references, you can use Scribbr’s free Chicago reference generator .
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Set 1 inch page margins
- Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page
- Center the paper’s title
- Use title case capitalization for headings
- Cite your sources with MLA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a Works Cited page at the end
To format a paper in APA Style , follow these guidelines:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial
- If submitting for publication, insert a running head on every page
- Apply APA heading styles
- Cite your sources with APA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a reference page at the end
No, it’s not appropriate to present new arguments or evidence in the conclusion . While you might be tempted to save a striking argument for last, research papers follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the results and discussion sections if you are following a scientific structure). The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
The conclusion of a research paper has several key elements you should make sure to include:
- A restatement of the research problem
- A summary of your key arguments and/or findings
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
Where to Find The Hypothesis in a Research Article

The question of “Where to Find The Hypothesis in a Research Article” can only be answered by exploring how research articles represent scientific methods.
Table of Contents
Introduction
A research article represents a compilation of information by a scientist concerning an original research idea. It is characterized by a wide range of information including, the purpose of the study, the thesis statement, hypothesis, literature review, methodology, results and conclusion.
The examination of a research article is an important process, and the ability to identify crucial elements of research is paramount for the effective analysis of a research article.
Research articles are usually arranged in specific ways. A hypothesis in a research article is usually located in a specific position in an article. The ability to quickly pinpoint where the hypothesis is located is crucial in becoming an expert in exploring research articles as well as formulating them.

What is a hypothesis
A hypothesis represents a scientific guess that is stated in research. It is a speculative statement concerning the relationship between two or more variables in research.
Therefore, a good hypothesis is a prediction that is testable, specific, and explores what a researcher expects to find in the study.
Formulating a Hypothesis
The creation of a hypothesis represents a critical part of the scientific method. Formulating a hypothesis is important, especially when testing a theory. Most scientific research involves testing theories. Theories, in this case, refer to ideas about the way things relate to one another. For one to formulate a hypothesis to be used in research, they have to be to predict the outcome of the research.
If one cannot predict the outcome, then the research does not need the formulating of a hypothesis because it is either exploratory or descriptive. These forms of research cannot have a hypothesis, and the reason is that there is a limited base of knowledge concerning the subject matter for the prediction of the outcome to be possible.
A good Hypothesis
A good hypothesis has to have two or more variables. These variables have to be measurable or have the potential to be measured. The hypothesis also has to specify how the variables are related to one another.
Where to Find the Hypothesis in a Research Article
The scientific method is characterized by several steps. They include:
- Coming up with a question or the problem that needs to be solved.
- Conducting background research on the problem
- Formulating a hypothesis
- Establishing how the research will be conducted using a research design
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the data and coming up with results
- Provide conclusions
- Presenting the information through a research article.
Based on the above structure, it is evident that the hypothesis is located in the introduction section of a research article. One should look out for “if-then” statements. However, for such statements to be hypotheses, they need to:
- Demonstrates the relationship between variables,
- The relationship needs to be testable and
- The prediction needs to be measurable
A hypothesis is not always clearly labeled. This means that the statement can appear in different forms apart from when formulated using the “if-then” statements. One should, therefore, look out for a statement that offers a prediction of what readers need to expect from the research.
The ability to identify where to find a hypothesis is located in a research article is very important in several ways:
- One can quickly know what the researcher wants to prove using the research.
- It makes individuals effective in reading research articles.
- It enhances an individual’s ability to formulate their own hypothesis when conducting research
Entrust your assignments to our expert writers for excellent results!
Eagle Academics prides itself in providing quality custom papers for many students around the world. We guarantee exceptional standards, and this is based on the selection of highly professional and experienced tutors and writers in different fields. Our experts can handle any work regardless of the deadline.
You must choose what you do with your time. Let our experts help you with your schoolwork while you focus on other essential things in your life. Talk to us, and we will give you the help that you need.
Calculate the price of your paper
Free features.
- Formatting (APA, MLA, Harvard, Chicago/Turabian)
- Bibliography
- Upload custom grading criteria
Additional services
- Part-by-part payment
- Links to used sources
- Review your writer’s samples
- Charts and PowerPoint slides
Don’t look far for academic help. We have you covered
Money back guarantee.
Our goal is to give the best services to our clients. However, if for one reason or the other a client is not satisfied, we will refund your money. So the funds paid to us are safe.
Confidentiality
We value our clients’ privacy. No single information of our clients can be shared by third parties.
Our service is legit
Our services follow the laid down academic guidelines. We cannot blackmail our clients, but only strive to offer them the best academic assistance they need.
Get a plagiarism-free paper
Our writers work hand in hand with the quality assurance department to ensure whatever paper you get is totally plagiarism-free.
We can help with urgent tasks
We have standby writers who can handle papers even within 6 hours. Just get in touch and let us know.
Pay a fair price
We have competitive prices that are pocket friendly. In addition, we have plenty of discounts to offer.
Need a better grade? We've got you covered.
- Privacy Policy

Home » 500+ Quantitative Research Titles and Topics
500+ Quantitative Research Titles and Topics
Table of Contents

Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships among variables. This method is widely used in social sciences, psychology , economics , and other fields where researchers aim to understand human behavior and phenomena through statistical analysis. If you are looking for a quantitative research topic, there are numerous areas to explore, from analyzing data on a specific population to studying the effects of a particular intervention or treatment. In this post, we will provide some ideas for quantitative research topics that may inspire you and help you narrow down your interests.
Quantitative Research Titles
Quantitative Research Titles are as follows:
Business and Economics
- “Statistical Analysis of Supply Chain Disruptions on Retail Sales”
- “Quantitative Examination of Consumer Loyalty Programs in the Fast Food Industry”
- “Predicting Stock Market Trends Using Machine Learning Algorithms”
- “Influence of Workplace Environment on Employee Productivity: A Quantitative Study”
- “Impact of Economic Policies on Small Businesses: A Regression Analysis”
- “Customer Satisfaction and Profit Margins: A Quantitative Correlation Study”
- “Analyzing the Role of Marketing in Brand Recognition: A Statistical Overview”
- “Quantitative Effects of Corporate Social Responsibility on Consumer Trust”
- “Price Elasticity of Demand for Luxury Goods: A Case Study”
- “The Relationship Between Fiscal Policy and Inflation Rates: A Time-Series Analysis”
- “Factors Influencing E-commerce Conversion Rates: A Quantitative Exploration”
- “Examining the Correlation Between Interest Rates and Consumer Spending”
- “Standardized Testing and Academic Performance: A Quantitative Evaluation”
- “Teaching Strategies and Student Learning Outcomes in Secondary Schools: A Quantitative Study”
- “The Relationship Between Extracurricular Activities and Academic Success”
- “Influence of Parental Involvement on Children’s Educational Achievements”
- “Digital Literacy in Primary Schools: A Quantitative Assessment”
- “Learning Outcomes in Blended vs. Traditional Classrooms: A Comparative Analysis”
- “Correlation Between Teacher Experience and Student Success Rates”
- “Analyzing the Impact of Classroom Technology on Reading Comprehension”
- “Gender Differences in STEM Fields: A Quantitative Analysis of Enrollment Data”
- “The Relationship Between Homework Load and Academic Burnout”
- “Assessment of Special Education Programs in Public Schools”
- “Role of Peer Tutoring in Improving Academic Performance: A Quantitative Study”
Medicine and Health Sciences
- “The Impact of Sleep Duration on Cardiovascular Health: A Cross-sectional Study”
- “Analyzing the Efficacy of Various Antidepressants: A Meta-Analysis”
- “Patient Satisfaction in Telehealth Services: A Quantitative Assessment”
- “Dietary Habits and Incidence of Heart Disease: A Quantitative Review”
- “Correlations Between Stress Levels and Immune System Functioning”
- “Smoking and Lung Function: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “Influence of Physical Activity on Mental Health in Older Adults”
- “Antibiotic Resistance Patterns in Community Hospitals: A Quantitative Study”
- “The Efficacy of Vaccination Programs in Controlling Disease Spread: A Time-Series Analysis”
- “Role of Social Determinants in Health Outcomes: A Quantitative Exploration”
- “Impact of Hospital Design on Patient Recovery Rates”
- “Quantitative Analysis of Dietary Choices and Obesity Rates in Children”
Social Sciences
- “Examining Social Inequality through Wage Distribution: A Quantitative Study”
- “Impact of Parental Divorce on Child Development: A Longitudinal Study”
- “Social Media and its Effect on Political Polarization: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “The Relationship Between Religion and Social Attitudes: A Statistical Overview”
- “Influence of Socioeconomic Status on Educational Achievement”
- “Quantifying the Effects of Community Programs on Crime Reduction”
- “Public Opinion and Immigration Policies: A Quantitative Exploration”
- “Analyzing the Gender Representation in Political Offices: A Quantitative Study”
- “Impact of Mass Media on Public Opinion: A Regression Analysis”
- “Influence of Urban Design on Social Interactions in Communities”
- “The Role of Social Support in Mental Health Outcomes: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “Examining the Relationship Between Substance Abuse and Employment Status”
Engineering and Technology
- “Performance Evaluation of Different Machine Learning Algorithms in Autonomous Vehicles”
- “Material Science: A Quantitative Analysis of Stress-Strain Properties in Various Alloys”
- “Impacts of Data Center Cooling Solutions on Energy Consumption”
- “Analyzing the Reliability of Renewable Energy Sources in Grid Management”
- “Optimization of 5G Network Performance: A Quantitative Assessment”
- “Quantifying the Effects of Aerodynamics on Fuel Efficiency in Commercial Airplanes”
- “The Relationship Between Software Complexity and Bug Frequency”
- “Machine Learning in Predictive Maintenance: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “Wearable Technologies and their Impact on Healthcare Monitoring”
- “Quantitative Assessment of Cybersecurity Measures in Financial Institutions”
- “Analysis of Noise Pollution from Urban Transportation Systems”
- “The Influence of Architectural Design on Energy Efficiency in Buildings”
Quantitative Research Topics
Quantitative Research Topics are as follows:
- The effects of social media on self-esteem among teenagers.
- A comparative study of academic achievement among students of single-sex and co-educational schools.
- The impact of gender on leadership styles in the workplace.
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic performance of students.
- The effect of mindfulness meditation on stress levels in college students.
- The relationship between employee motivation and job satisfaction.
- The effectiveness of online learning compared to traditional classroom learning.
- The correlation between sleep duration and academic performance among college students.
- The impact of exercise on mental health among adults.
- The relationship between social support and psychological well-being among cancer patients.
- The effect of caffeine consumption on sleep quality.
- A comparative study of the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy and pharmacotherapy in treating depression.
- The relationship between physical attractiveness and job opportunities.
- The correlation between smartphone addiction and academic performance among high school students.
- The impact of music on memory recall among adults.
- The effectiveness of parental control software in limiting children’s online activity.
- The relationship between social media use and body image dissatisfaction among young adults.
- The correlation between academic achievement and parental involvement among minority students.
- The impact of early childhood education on academic performance in later years.
- The effectiveness of employee training and development programs in improving organizational performance.
- The relationship between socioeconomic status and access to healthcare services.
- The correlation between social support and academic achievement among college students.
- The impact of technology on communication skills among children.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction programs in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- The relationship between employee turnover and organizational culture.
- The correlation between job satisfaction and employee engagement.
- The impact of video game violence on aggressive behavior among children.
- The effectiveness of nutritional education in promoting healthy eating habits among adolescents.
- The relationship between bullying and academic performance among middle school students.
- The correlation between teacher expectations and student achievement.
- The impact of gender stereotypes on career choices among high school students.
- The effectiveness of anger management programs in reducing violent behavior.
- The relationship between social support and recovery from substance abuse.
- The correlation between parent-child communication and adolescent drug use.
- The impact of technology on family relationships.
- The effectiveness of smoking cessation programs in promoting long-term abstinence.
- The relationship between personality traits and academic achievement.
- The correlation between stress and job performance among healthcare professionals.
- The impact of online privacy concerns on social media use.
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating anxiety disorders.
- The relationship between teacher feedback and student motivation.
- The correlation between physical activity and academic performance among elementary school students.
- The impact of parental divorce on academic achievement among children.
- The effectiveness of diversity training in improving workplace relationships.
- The relationship between childhood trauma and adult mental health.
- The correlation between parental involvement and substance abuse among adolescents.
- The impact of social media use on romantic relationships among young adults.
- The effectiveness of assertiveness training in improving communication skills.
- The relationship between parental expectations and academic achievement among high school students.
- The correlation between sleep quality and mood among adults.
- The impact of video game addiction on academic performance among college students.
- The effectiveness of group therapy in treating eating disorders.
- The relationship between job stress and job performance among teachers.
- The correlation between mindfulness and emotional regulation.
- The impact of social media use on self-esteem among college students.
- The effectiveness of parent-teacher communication in promoting academic achievement among elementary school students.
- The impact of renewable energy policies on carbon emissions
- The relationship between employee motivation and job performance
- The effectiveness of psychotherapy in treating eating disorders
- The correlation between physical activity and cognitive function in older adults
- The effect of childhood poverty on adult health outcomes
- The impact of urbanization on biodiversity conservation
- The relationship between work-life balance and employee job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) in treating trauma
- The correlation between parenting styles and child behavior
- The effect of social media on political polarization
- The impact of foreign aid on economic development
- The relationship between workplace diversity and organizational performance
- The effectiveness of dialectical behavior therapy in treating borderline personality disorder
- The correlation between childhood abuse and adult mental health outcomes
- The effect of sleep deprivation on cognitive function
- The impact of trade policies on international trade and economic growth
- The relationship between employee engagement and organizational commitment
- The effectiveness of cognitive therapy in treating postpartum depression
- The correlation between family meals and child obesity rates
- The effect of parental involvement in sports on child athletic performance
- The impact of social entrepreneurship on sustainable development
- The relationship between emotional labor and job burnout
- The effectiveness of art therapy in treating dementia
- The correlation between social media use and academic procrastination
- The effect of poverty on childhood educational attainment
- The impact of urban green spaces on mental health
- The relationship between job insecurity and employee well-being
- The effectiveness of virtual reality exposure therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between childhood trauma and substance abuse
- The effect of screen time on children’s social skills
- The impact of trade unions on employee job satisfaction
- The relationship between cultural intelligence and cross-cultural communication
- The effectiveness of acceptance and commitment therapy in treating chronic pain
- The correlation between childhood obesity and adult health outcomes
- The effect of gender diversity on corporate performance
- The impact of environmental regulations on industry competitiveness.
- The impact of renewable energy policies on greenhouse gas emissions
- The relationship between workplace diversity and team performance
- The effectiveness of group therapy in treating substance abuse
- The correlation between parental involvement and social skills in early childhood
- The effect of technology use on sleep patterns
- The impact of government regulations on small business growth
- The relationship between job satisfaction and employee turnover
- The effectiveness of virtual reality therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic motivation in adolescents
- The effect of social media on political engagement
- The impact of urbanization on mental health
- The relationship between corporate social responsibility and consumer trust
- The correlation between early childhood education and social-emotional development
- The effect of screen time on cognitive development in young children
- The impact of trade policies on global economic growth
- The relationship between workplace diversity and innovation
- The effectiveness of family therapy in treating eating disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and college persistence
- The effect of social media on body image and self-esteem
- The impact of environmental regulations on business competitiveness
- The relationship between job autonomy and job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of virtual reality therapy in treating phobias
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic achievement in college
- The effect of social media on sleep quality
- The impact of immigration policies on social integration
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee well-being
- The effectiveness of psychodynamic therapy in treating personality disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and executive function skills
- The effect of parental involvement on STEM education outcomes
- The impact of trade policies on domestic employment rates
- The relationship between job insecurity and mental health
- The effectiveness of exposure therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and social mobility
- The effect of social media on intergroup relations
- The impact of urbanization on air pollution and respiratory health.
- The relationship between emotional intelligence and leadership effectiveness
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between early childhood education and language development
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in STEM fields
- The impact of trade policies on income inequality
- The relationship between workplace diversity and customer satisfaction
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and civic engagement in adolescents
- The effect of social media on mental health among teenagers
- The impact of public transportation policies on traffic congestion
- The relationship between job stress and job performance
- The effectiveness of group therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between early childhood education and cognitive development
- The effect of parental involvement on academic motivation in college
- The impact of environmental regulations on energy consumption
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee engagement
- The effectiveness of art therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in vocational education
- The effect of social media on academic achievement in college
- The impact of tax policies on economic growth
- The relationship between job flexibility and work-life balance
- The effectiveness of acceptance and commitment therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and social competence
- The effect of parental involvement on career readiness in high school
- The impact of immigration policies on crime rates
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee retention
- The effectiveness of play therapy in treating trauma
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in online learning
- The effect of social media on body dissatisfaction among women
- The impact of urbanization on public health infrastructure
- The relationship between job satisfaction and job performance
- The effectiveness of eye movement desensitization and reprocessing therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between early childhood education and social skills in adolescence
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in the arts
- The impact of trade policies on foreign investment
- The relationship between workplace diversity and decision-making
- The effectiveness of exposure and response prevention therapy in treating OCD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in special education
- The impact of zoning laws on affordable housing
- The relationship between job design and employee motivation
- The effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation therapy in treating traumatic brain injury
- The correlation between early childhood education and social-emotional learning
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in foreign language learning
- The impact of trade policies on the environment
- The relationship between workplace diversity and creativity
- The effectiveness of emotion-focused therapy in treating relationship problems
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in music education
- The effect of social media on interpersonal communication skills
- The impact of public health campaigns on health behaviors
- The relationship between job resources and job stress
- The effectiveness of equine therapy in treating substance abuse
- The correlation between early childhood education and self-regulation
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in physical education
- The impact of immigration policies on cultural assimilation
- The relationship between workplace diversity and conflict resolution
- The effectiveness of schema therapy in treating personality disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in career and technical education
- The effect of social media on trust in government institutions
- The impact of urbanization on public transportation systems
- The relationship between job demands and job stress
- The correlation between early childhood education and executive functioning
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in computer science
- The effectiveness of cognitive processing therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in homeschooling
- The effect of social media on cyberbullying behavior
- The impact of urbanization on air quality
- The effectiveness of dance therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and math achievement
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in health education
- The impact of global warming on agriculture
- The effectiveness of narrative therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in character education
- The effect of social media on political participation
- The impact of technology on job displacement
- The relationship between job resources and job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of art therapy in treating addiction
- The correlation between early childhood education and reading comprehension
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in environmental education
- The impact of income inequality on social mobility
- The relationship between workplace diversity and organizational culture
- The effectiveness of solution-focused brief therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in physical therapy education
- The effect of social media on misinformation
- The impact of green energy policies on economic growth
- The relationship between job demands and employee well-being
- The correlation between early childhood education and science achievement
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in religious education
- The impact of gender diversity on corporate governance
- The relationship between workplace diversity and ethical decision-making
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in dental hygiene education
- The effect of social media on self-esteem among adolescents
- The impact of renewable energy policies on energy security
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in social studies
- The impact of trade policies on job growth
- The relationship between workplace diversity and leadership styles
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in online vocational training
- The effect of social media on self-esteem among men
- The impact of urbanization on air pollution levels
- The effectiveness of music therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between early childhood education and math skills
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in language arts
- The impact of immigration policies on labor market outcomes
- The effectiveness of hypnotherapy in treating phobias
- The effect of social media on political engagement among young adults
- The impact of urbanization on access to green spaces
- The relationship between job crafting and job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of exposure therapy in treating specific phobias
- The correlation between early childhood education and spatial reasoning
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in business education
- The impact of trade policies on economic inequality
- The effectiveness of narrative therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in nursing education
- The effect of social media on sleep quality among adolescents
- The impact of urbanization on crime rates
- The relationship between job insecurity and turnover intentions
- The effectiveness of pet therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and STEM skills
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in culinary education
- The impact of immigration policies on housing affordability
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee satisfaction
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction in treating chronic pain
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in art education
- The effect of social media on academic procrastination among college students
- The impact of urbanization on public safety services.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

500+ Statistics Research Topics

500+ Cyber Security Research Topics

1000+ Sociology Research Topics

300+ Mental Health Research Topics

300+ Chemistry Research Topics

300+ Interesting Research Topics
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.53(4); 2010 Aug

Research questions, hypotheses and objectives
Patricia farrugia.
* Michael G. DeGroote School of Medicine, the
Bradley A. Petrisor
† Division of Orthopaedic Surgery and the
Forough Farrokhyar
‡ Departments of Surgery and
§ Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont
Mohit Bhandari
There is an increasing familiarity with the principles of evidence-based medicine in the surgical community. As surgeons become more aware of the hierarchy of evidence, grades of recommendations and the principles of critical appraisal, they develop an increasing familiarity with research design. Surgeons and clinicians are looking more and more to the literature and clinical trials to guide their practice; as such, it is becoming a responsibility of the clinical research community to attempt to answer questions that are not only well thought out but also clinically relevant. The development of the research question, including a supportive hypothesis and objectives, is a necessary key step in producing clinically relevant results to be used in evidence-based practice. A well-defined and specific research question is more likely to help guide us in making decisions about study design and population and subsequently what data will be collected and analyzed. 1
Objectives of this article
In this article, we discuss important considerations in the development of a research question and hypothesis and in defining objectives for research. By the end of this article, the reader will be able to appreciate the significance of constructing a good research question and developing hypotheses and research objectives for the successful design of a research study. The following article is divided into 3 sections: research question, research hypothesis and research objectives.
Research question
Interest in a particular topic usually begins the research process, but it is the familiarity with the subject that helps define an appropriate research question for a study. 1 Questions then arise out of a perceived knowledge deficit within a subject area or field of study. 2 Indeed, Haynes suggests that it is important to know “where the boundary between current knowledge and ignorance lies.” 1 The challenge in developing an appropriate research question is in determining which clinical uncertainties could or should be studied and also rationalizing the need for their investigation.
Increasing one’s knowledge about the subject of interest can be accomplished in many ways. Appropriate methods include systematically searching the literature, in-depth interviews and focus groups with patients (and proxies) and interviews with experts in the field. In addition, awareness of current trends and technological advances can assist with the development of research questions. 2 It is imperative to understand what has been studied about a topic to date in order to further the knowledge that has been previously gathered on a topic. Indeed, some granting institutions (e.g., Canadian Institute for Health Research) encourage applicants to conduct a systematic review of the available evidence if a recent review does not already exist and preferably a pilot or feasibility study before applying for a grant for a full trial.
In-depth knowledge about a subject may generate a number of questions. It then becomes necessary to ask whether these questions can be answered through one study or if more than one study needed. 1 Additional research questions can be developed, but several basic principles should be taken into consideration. 1 All questions, primary and secondary, should be developed at the beginning and planning stages of a study. Any additional questions should never compromise the primary question because it is the primary research question that forms the basis of the hypothesis and study objectives. It must be kept in mind that within the scope of one study, the presence of a number of research questions will affect and potentially increase the complexity of both the study design and subsequent statistical analyses, not to mention the actual feasibility of answering every question. 1 A sensible strategy is to establish a single primary research question around which to focus the study plan. 3 In a study, the primary research question should be clearly stated at the end of the introduction of the grant proposal, and it usually specifies the population to be studied, the intervention to be implemented and other circumstantial factors. 4
Hulley and colleagues 2 have suggested the use of the FINER criteria in the development of a good research question ( Box 1 ). The FINER criteria highlight useful points that may increase the chances of developing a successful research project. A good research question should specify the population of interest, be of interest to the scientific community and potentially to the public, have clinical relevance and further current knowledge in the field (and of course be compliant with the standards of ethical boards and national research standards).
FINER criteria for a good research question
| Feasible | ||
| Interesting | ||
| Novel | ||
| Ethical | ||
| Relevant |
Adapted with permission from Wolters Kluwer Health. 2
Whereas the FINER criteria outline the important aspects of the question in general, a useful format to use in the development of a specific research question is the PICO format — consider the population (P) of interest, the intervention (I) being studied, the comparison (C) group (or to what is the intervention being compared) and the outcome of interest (O). 3 , 5 , 6 Often timing (T) is added to PICO ( Box 2 ) — that is, “Over what time frame will the study take place?” 1 The PICOT approach helps generate a question that aids in constructing the framework of the study and subsequently in protocol development by alluding to the inclusion and exclusion criteria and identifying the groups of patients to be included. Knowing the specific population of interest, intervention (and comparator) and outcome of interest may also help the researcher identify an appropriate outcome measurement tool. 7 The more defined the population of interest, and thus the more stringent the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the greater the effect on the interpretation and subsequent applicability and generalizability of the research findings. 1 , 2 A restricted study population (and exclusion criteria) may limit bias and increase the internal validity of the study; however, this approach will limit external validity of the study and, thus, the generalizability of the findings to the practical clinical setting. Conversely, a broadly defined study population and inclusion criteria may be representative of practical clinical practice but may increase bias and reduce the internal validity of the study.
PICOT criteria 1
| Population (patients) | ||
| Intervention (for intervention studies only) | ||
| Comparison group | ||
| Outcome of interest | ||
| Time |
A poorly devised research question may affect the choice of study design, potentially lead to futile situations and, thus, hamper the chance of determining anything of clinical significance, which will then affect the potential for publication. Without devoting appropriate resources to developing the research question, the quality of the study and subsequent results may be compromised. During the initial stages of any research study, it is therefore imperative to formulate a research question that is both clinically relevant and answerable.
Research hypothesis
The primary research question should be driven by the hypothesis rather than the data. 1 , 2 That is, the research question and hypothesis should be developed before the start of the study. This sounds intuitive; however, if we take, for example, a database of information, it is potentially possible to perform multiple statistical comparisons of groups within the database to find a statistically significant association. This could then lead one to work backward from the data and develop the “question.” This is counterintuitive to the process because the question is asked specifically to then find the answer, thus collecting data along the way (i.e., in a prospective manner). Multiple statistical testing of associations from data previously collected could potentially lead to spuriously positive findings of association through chance alone. 2 Therefore, a good hypothesis must be based on a good research question at the start of a trial and, indeed, drive data collection for the study.
The research or clinical hypothesis is developed from the research question and then the main elements of the study — sampling strategy, intervention (if applicable), comparison and outcome variables — are summarized in a form that establishes the basis for testing, statistical and ultimately clinical significance. 3 For example, in a research study comparing computer-assisted acetabular component insertion versus freehand acetabular component placement in patients in need of total hip arthroplasty, the experimental group would be computer-assisted insertion and the control/conventional group would be free-hand placement. The investigative team would first state a research hypothesis. This could be expressed as a single outcome (e.g., computer-assisted acetabular component placement leads to improved functional outcome) or potentially as a complex/composite outcome; that is, more than one outcome (e.g., computer-assisted acetabular component placement leads to both improved radiographic cup placement and improved functional outcome).
However, when formally testing statistical significance, the hypothesis should be stated as a “null” hypothesis. 2 The purpose of hypothesis testing is to make an inference about the population of interest on the basis of a random sample taken from that population. The null hypothesis for the preceding research hypothesis then would be that there is no difference in mean functional outcome between the computer-assisted insertion and free-hand placement techniques. After forming the null hypothesis, the researchers would form an alternate hypothesis stating the nature of the difference, if it should appear. The alternate hypothesis would be that there is a difference in mean functional outcome between these techniques. At the end of the study, the null hypothesis is then tested statistically. If the findings of the study are not statistically significant (i.e., there is no difference in functional outcome between the groups in a statistical sense), we cannot reject the null hypothesis, whereas if the findings were significant, we can reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternate hypothesis (i.e., there is a difference in mean functional outcome between the study groups), errors in testing notwithstanding. In other words, hypothesis testing confirms or refutes the statement that the observed findings did not occur by chance alone but rather occurred because there was a true difference in outcomes between these surgical procedures. The concept of statistical hypothesis testing is complex, and the details are beyond the scope of this article.
Another important concept inherent in hypothesis testing is whether the hypotheses will be 1-sided or 2-sided. A 2-sided hypothesis states that there is a difference between the experimental group and the control group, but it does not specify in advance the expected direction of the difference. For example, we asked whether there is there an improvement in outcomes with computer-assisted surgery or whether the outcomes worse with computer-assisted surgery. We presented a 2-sided test in the above example because we did not specify the direction of the difference. A 1-sided hypothesis states a specific direction (e.g., there is an improvement in outcomes with computer-assisted surgery). A 2-sided hypothesis should be used unless there is a good justification for using a 1-sided hypothesis. As Bland and Atlman 8 stated, “One-sided hypothesis testing should never be used as a device to make a conventionally nonsignificant difference significant.”
The research hypothesis should be stated at the beginning of the study to guide the objectives for research. Whereas the investigators may state the hypothesis as being 1-sided (there is an improvement with treatment), the study and investigators must adhere to the concept of clinical equipoise. According to this principle, a clinical (or surgical) trial is ethical only if the expert community is uncertain about the relative therapeutic merits of the experimental and control groups being evaluated. 9 It means there must exist an honest and professional disagreement among expert clinicians about the preferred treatment. 9
Designing a research hypothesis is supported by a good research question and will influence the type of research design for the study. Acting on the principles of appropriate hypothesis development, the study can then confidently proceed to the development of the research objective.
Research objective
The primary objective should be coupled with the hypothesis of the study. Study objectives define the specific aims of the study and should be clearly stated in the introduction of the research protocol. 7 From our previous example and using the investigative hypothesis that there is a difference in functional outcomes between computer-assisted acetabular component placement and free-hand placement, the primary objective can be stated as follows: this study will compare the functional outcomes of computer-assisted acetabular component insertion versus free-hand placement in patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. Note that the study objective is an active statement about how the study is going to answer the specific research question. Objectives can (and often do) state exactly which outcome measures are going to be used within their statements. They are important because they not only help guide the development of the protocol and design of study but also play a role in sample size calculations and determining the power of the study. 7 These concepts will be discussed in other articles in this series.
From the surgeon’s point of view, it is important for the study objectives to be focused on outcomes that are important to patients and clinically relevant. For example, the most methodologically sound randomized controlled trial comparing 2 techniques of distal radial fixation would have little or no clinical impact if the primary objective was to determine the effect of treatment A as compared to treatment B on intraoperative fluoroscopy time. However, if the objective was to determine the effect of treatment A as compared to treatment B on patient functional outcome at 1 year, this would have a much more significant impact on clinical decision-making. Second, more meaningful surgeon–patient discussions could ensue, incorporating patient values and preferences with the results from this study. 6 , 7 It is the precise objective and what the investigator is trying to measure that is of clinical relevance in the practical setting.
The following is an example from the literature about the relation between the research question, hypothesis and study objectives:
Study: Warden SJ, Metcalf BR, Kiss ZS, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound for chronic patellar tendinopathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Rheumatology 2008;47:467–71.
Research question: How does low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) compare with a placebo device in managing the symptoms of skeletally mature patients with patellar tendinopathy?
Research hypothesis: Pain levels are reduced in patients who receive daily active-LIPUS (treatment) for 12 weeks compared with individuals who receive inactive-LIPUS (placebo).
Objective: To investigate the clinical efficacy of LIPUS in the management of patellar tendinopathy symptoms.
The development of the research question is the most important aspect of a research project. A research project can fail if the objectives and hypothesis are poorly focused and underdeveloped. Useful tips for surgical researchers are provided in Box 3 . Designing and developing an appropriate and relevant research question, hypothesis and objectives can be a difficult task. The critical appraisal of the research question used in a study is vital to the application of the findings to clinical practice. Focusing resources, time and dedication to these 3 very important tasks will help to guide a successful research project, influence interpretation of the results and affect future publication efforts.
Tips for developing research questions, hypotheses and objectives for research studies
- Perform a systematic literature review (if one has not been done) to increase knowledge and familiarity with the topic and to assist with research development.
- Learn about current trends and technological advances on the topic.
- Seek careful input from experts, mentors, colleagues and collaborators to refine your research question as this will aid in developing the research question and guide the research study.
- Use the FINER criteria in the development of the research question.
- Ensure that the research question follows PICOT format.
- Develop a research hypothesis from the research question.
- Develop clear and well-defined primary and secondary (if needed) objectives.
- Ensure that the research question and objectives are answerable, feasible and clinically relevant.
FINER = feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, relevant; PICOT = population (patients), intervention (for intervention studies only), comparison group, outcome of interest, time.
Competing interests: No funding was received in preparation of this paper. Dr. Bhandari was funded, in part, by a Canada Research Chair, McMaster University.
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Author Biographies
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
Impacts of generative artificial intelligence in higher education: research trends and students’ perceptions.

1. Introduction
2. materials and methods.
- “Generative Artificial Intelligence” or “Generative AI” or “Gen AI”, AND;
- “Higher Education” or “University” or “College” or “Post-secondary”, AND;
- “Impact” or “Effect” or “Influence”.
- Q1— Does GenAI have more positive or negative effects on higher education? Options (to choose one): 1. It has more negative effects than positives; 2. It has more positive effects than negative; 3. There is a balance between positive and negative effects; 4. Don’t know.
- Q2— Identify the main positive effect of Gen AI in an academic context . Open-ended question.
- Q3— Identify the main negative effect of Gen AI in an academic context . Open-ended question.
3.1. Impacts of Gen AI in HE: Research Trends
3.1.1. he with gen ai, the key role that pedagogy must play, new ways to enhance the design and implementation of teaching and learning activities.
- Firstly, prompting in teaching should be prioritized as it plays a crucial role in developing students’ abilities. By providing appropriate prompts, educators can effectively guide students toward achieving their learning objectives.
- Secondly, configuring reverse prompting within the capabilities of Gen AI chatbots can greatly assist students in monitoring their learning progress. This feature empowers students to take ownership of their education and fosters a sense of responsibility.
- Furthermore, it is essential to embed digital literacy in all teaching and learning activities that aim to leverage the potential of the new Gen AI assistants. By equipping students with the necessary skills to navigate and critically evaluate digital resources, educators can ensure that they are prepared for the digital age.
The Student’s Role in the Learning Experience
The key teacher’s role in the teaching and learning experience, 3.1.2. assessment in gen ai/chatgpt times, the need for new assessment procedures, 3.1.3. new challenges to academic integrity policies, new meanings and frontiers of misconduct, personal data usurpation and cheating, 3.2. students’ perceptions about the impacts of gen ai in he.
- “It harms the learning process”: ▪ “What is generated by Gen AI has errors”; ▪ “Generates dependence and encourages laziness”; ▪ “Decreases active effort and involvement in the learning/critical thinking process”.
4. Discussion
- Training: providing training for both students and teachers on effectively using and integrating Gen AI technologies into teaching and learning practices.
- Ethical use and risk management: developing policies and guidelines for ethical use and risk management associated with Gen AI technologies.
- Incorporating AI without replacing humans: incorporating AI technologies as supplementary tools to assist teachers and students rather than replacements for human interaction.
- Continuously enhancing holistic competencies: encouraging the use of AI technologies to enhance specific skills, such as digital competence and time management, while ensuring that students continue to develop vital transferable skills.
- Fostering a transparent AI environment: promoting an environment in which students and teachers can openly discuss the benefits and concerns associated with using AI technologies.
- Data privacy and security: ensuring data privacy and security using AI technologies.
- The dynamics of technological support to align with the most suitable Gen AI resources;
- The training policy to ensure that teachers, students, and academic staff are properly trained to utilize the potential of Gen AI and its tools;
- Security and data protection policies;
- Quality and ethical action policies.
5. Conclusions
- Database constraints: the analysis is based on existing publications in SCOPUS and the Web of Science, potentially omitting relevant research from other sources.
- Inclusion criteria: due to the early stage of scientific production on this topic, all publications were included in the analysis, rather than focusing solely on articles from highly indexed journals and/or with a high number of citations as recommended by bibliometric and systematic review best practices.
- Dynamic landscape: the rate of publications on Gen AI has been rapidly increasing and diversifying in 2024, highlighting the need for ongoing analysis to track trends and changes in scientific thinking.
Author Contributions
Institutional review board statement, informed consent statement, data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
- Akakpo, Martin Gameli. 2023. Skilled for the Future: Information Literacy for AI Use by University Students in Africa and the Role of Librarians. Internet Reference Services Quarterly 28: 19–26. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- AlAfnan, Mohammad Awad, Samira Dishari, Marina Jovic, and Koba Lomidze. 2023. ChatGPT as an Educational Tool: Opportunities, Challenges, and Recommendations for Communication, Business Writing, and Composition Courses. Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Technology 3: 60–68. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Almaraz-López, Cristina, Fernando Almaraz-Menéndez, and Carmen López-Esteban. 2023. Comparative Study of the Attitudes and Perceptions of University Students in Business Administration and Management and in Education toward Artificial Intelligence. Education Sciences 13: 609. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Al-Zahrani, Abdulrahman. 2023. The impact of generative AI tools on researchers and research: Implications for academia in higher education. Innovations in Education and Teaching International , 1–15. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Athilingam, Ponrathi, and Hong-Gu He. 2023. ChatGPT in nursing education: Opportunities and challenges. Teaching and Learning in Nursing 19: 97–101. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Álvarez-Álvarez, Carmen, and Samuel Falcon. 2023. Students’ preferences with university teaching practices: Analysis of testimonials with artificial intelligence. Educational Technology Research and Development 71: 1709–24. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bannister, Peter, Elena Alcalde Peñalver, and Alexandra Santamaría Urbieta. 2023. Transnational higher education cultures and generative AI: A nominal group study for policy development in English medium instruction. Journal for Multicultural Education . ahead-of-print . [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bearman, Margaret, and Rola Ajjawi. 2023. Learning to work with the black box: Pedagogy for a world with artificial intelligence. British Journal of Educational Technology 54: 1160–73. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Boháček, Matyas. 2023. The Unseen A+ Student: Evaluating the Performance and Detectability of Large Language Models in the Classroom. CEUR Workshop Proceedings 3487: 89–100. Available online: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=9ZKJLYg5EQ (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Chan, Cecilia Ka Yuk. 2023. A comprehensive AI policy education framework for university teaching and learning. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education 20: 38. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chan, Cecilia Ka Yuk, and Wenjie Hu. 2023. Students’ voices on generative AI: Perceptions, benefits, and challenges in higher education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education 20: 43. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chan, Cecilia Ka Yuk, and Wenxin Zhou. 2023. An expectancy value theory (EVT) based instrument for measuring student perceptions of generative AI. Smart Learning Environments 10: 64. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chang, Daniel H., Michael Pin-Chuan Lin, Shiva Hajian, and Quincy Q. Wang. 2023. Educational Design Principles of Using AI Chatbot That Supports Self-Regulated Learning in Education: Goal Setting, Feedback, and Personalization. Sustainability 15: 12921. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chiu, Thomas. 2023. The impact of Generative AI (GenAI) on practices, policies and research direction in education: A case of ChatGPT and Midjourney. Interactive Learning Environments , 1–17. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chun, John, and Katherine Elkins. 2023. The Crisis of Artificial Intelligence: A New Digital Humanities Curriculum for Human-Centred AI. International Journal of Humanities and Arts Computing 17: 147–67. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Cowling, Michael, Joseph Crawford, Kelly-Ann Allen, and Michael Wehmeyer. 2023. Using leadership to leverage ChatGPT and artificial intelligence for undergraduate and postgraduate research supervision. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology 39: 89–103. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Crawford, Joseph, Carmen Vallis, Jianhua Yang, Rachel Fitzgerald, Christine O’Dea, and Michael Cowling. 2023a. Editorial: Artificial Intelligence is Awesome, but Good Teaching Should Always Come First. Journal of University Teaching & Learning Practice 20: 01. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Crawford, Joseph, Michael Cowling, and Kelly-Ann Allen. 2023b. Leadership is needed for ethical ChatGPT: Character, assessment, and learning using artificial intelligence (AI). Journal of University Teaching & Learning Practice 20: 02. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Currie, Geoffrey. 2023a. A Conversation with ChatGPT. Journal of Nuclear Medicine Technology 51: 255–60. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Currie, Geoffrey. 2023b. GPT-4 in Nuclear Medicine Education: Does It Outperform GPT-3.5? Journal of Nuclear Medicine Technology 51: 314–17. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Currie, Geoffrey, and Kym Barry. 2023. ChatGPT in Nuclear Medicine Education. Journal of Nuclear Medicine Technology 51: 247–54. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Currie, Geoffrey, Clare Singh, Tarni Nelson, Caroline Nabasenja, Yazan Al-Hayek, and Kelly Spuur. 2023. ChatGPT in medical imaging higher education. Radiography 29: 792–99. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dai, Yun, Ang Liu, and Cher P. Lim. 2023. Reconceptualizing Chatgpt and Generative AI as a Student-driven Innovation in Higher Education. Procedia CIRP Volume 119: 84–90. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dogru, Tarik, Nathana Line, Lydia Hanks, Fulya Acikgoz, Je’Anna Abbott, Selim Bakir, Adiyukh Berbekova, Anil Bilgihan, Ali Iskender, Murat Kizildag, and et al. 2023. The implications of generative artificial intelligence in academic research and higher education in tourism and hospitality. Tourism Economics 30: 1083–94. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Duong, Cong Doanh, Trong Nghia Vu, and Thi Viet Nga Ngo. 2023. Applying a modified technology acceptance model to explain higher education students’ usage of ChatGPT: A serial multiple mediation model with knowledge sharing as a moderator. The International Journal of Management Education 21: 100883. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Eager, Bronwyn, and Ryan Brunton. 2023. Prompting Higher Education Towards AI-Augmented Teaching and Learning Practice. Journal of University Teaching & Learning Practice 20: 5. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Elkhodr, Mahmoud, Ergun Gide, Robert Wu, and Omar Darwish. 2023. ICT students’ perceptions towards ChatGPT: An experimental reflective lab analysis. STEM Education 3: 70–88. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Farrelly, Tom, and Nick Baker. 2023. Generative Artificial Intelligence: Implications and Considerations for Higher Education Practice. Education Sciences 13: 1109. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Farrokhnia, Mohammadreza, Seyyed Banihashem, Seyyed Kazem Banihashem, Omid Noroozi, and Arjen Wals. 2023. A SWOT analysis of ChatGPT: Implications for educational practice and research. Innovations in Education and Teaching International 61: 460–74. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gong, Furong. 2023. The Impact of Generative AI like ChatGPT on Digital Literacy Education in University Libraries. Documentation, Information & Knowledge 40: 97–106, 156. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Han, Bingyi, Sadia Nawaz, George Buchanan, and Dana McKay. 2023. Ethical and Pedagogical Impacts of AI in Education. In Artificial Intelligence in Education . Edited by Ning Wang, Genaro Rebolledo-Mendez, Noboru Matsuda, Olga Santos and Vania Dimitrova. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer, pp. 667–73. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hassoulas, Athanasios, Ned Powell, Lindsay Roberts, Katja Umla-Runge, Laurence Gray, and Marcus J. Coffey. 2023. Investigating marker accuracy in differentiating between university scripts written by students and those produced using ChatGPT. Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching 6: 71–77. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hernández-Leo, Davinia. 2023. ChatGPT and Generative AI in Higher Education: User-Centered Perspectives and Implications for Learning Analytics. CEUR Workshop Proceedings , 1–6. Available online: https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-3542/paper2.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Hidayat-ur-Rehman, Imdadullah, and Yasser Ibrahim. 2023. Exploring factors influencing educators’ adoption of ChatGPT: A mixed method approach. Interactive Technology and Smart Education . ahead-of-print . [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ilieva, Galina, Tania Yankova, Stanislava Klisarova-Belcheva, Angel Dimitrov, Marin Bratkov, and Delian Angelov. 2023. Effects of Generative Chatbots in Higher Education. Information 14: 492. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Javaid, Mohd, Abid Haleem, Ravi Pratap Singh, Shahbaz Khan, and Haleem Ibrahim. 2023. Unlocking the opportunities through ChatGPT Tool towards ameliorating the education system. Bench Council Transactions on Benchmarks, Standards and Evaluations 3: 100115. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kaplan-Rakowski, Regina, Kimberly Grotewold, Peggy Hartwick, and Kevin Papin. 2023. Generative AI and Teachers’ Perspectives on Its Implementation in Education. Journal of Interactive Learning Research 34: 313–38. Available online: https://www.learntechlib.org/primary/p/222363/ (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Karunaratne, Thashmee, and Adenike Adesina. 2023. Is it the new Google: Impact of ChatGPT on Students’ Information Search Habits. Paper presented at the European Conference on e-Learning (ECEL 2023), Pretoria, South Africa, October 26–27; pp. 147–55. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kelly, Andrew, Miriam Sullivan, and Katrina Strampel. 2023. Generative artificial intelligence: University student awareness, experience, and confidence in use across disciplines. Journal of University Teaching & Learning Practice 20: 12. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kohnke, Lucas, Benjamin Luke Moorhouse, and Di Zou. 2023. Exploring generative artificial intelligence preparedness among university language instructors: A case study. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence 5: 100156. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Laker, Lauren, and Mark Sena. 2023. Accuracy and detection of student use of ChatGPT in business analytics courses. Issues in Information Systems 24: 153–63. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lemke, Claudia, Kathrin Kirchner, Liadan Anandarajah, and Florian Herfurth. 2023. Exploring the Student Perspective: Assessing Technology Readiness and Acceptance for Adopting Large Language Models in Higher Education. Paper presented at the European Conference on e-Learning, (ECEL 2023), Pretoria, South Africa, October 26–27; pp. 156–64. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Limna, Pongsakorn, Tanpat Kraiwanit, Kris Jangjarat, and Prapasiri Klayklung. 2023a. The use of ChatGPT in the digital era: Perspectives on chatbot implementation. Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching 6: 64–74. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Limna, Pongsakorn, Tanpat Kraiwanit, Kris Jangjarat, and Yarnaphat Shaengchart. 2023b. Applying ChatGPT as a new business strategy: A great power comes with great responsibility [Special issue]. Corporate & Business Strategy Review 4: 218–26. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lopezosa, Carlos, Carles Lluís Codina, Carles Pont-Sorribes, and Mari Vállez. 2023. Use of Generative Artificial Intelligence in the Training of Journalists: Challenges, Uses and Training Proposal. Profesional De La información Information Professional 32: 1–12. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Martineau, Kim. 2023. What Is Generative AI? IBM Research Blog . April 20. Available online: https://research.ibm.com/blog/what-is-generative-AI (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Mondal, Himel, Shaikat Mondal, and Indrashis Podder. 2023. Using ChatGPT for Writing Articles for Patients’ Education for Dermatological Diseases: A Pilot Study. Indian Dermatology Online Journal 14: 482–86. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Moorhouse, Benjamin, Marie Alina Wan, and Yuwei Wan. 2023. Generative AI tools and assessment: Guidelines of the world’s top-ranking universities. Computers and Education Open 5: 100151. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Overono, Acacia L., and Annie Ditta. 2023. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence: A Clarion Call for Higher Education to Redefine Learning and Reimagine Assessment. College Teaching , 1–4. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Page, Matthew J., Joanne E. McKenzie, Patrick M. Bossuyt, Isabelle Boutron, Tammy C. Hoffmann, Cynthia D. Mulrow, Larissa Shamseer, Jennifer M. Tetzlaff, Elie A. Akl, Sue E. Brennan, and et al. 2021. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372: n71. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pechenkina, Ekaterina. 2023. Artificial intelligence for good? Challenges and possibilities of AI in higher education from a data justice perspective. In Higher Education for Good: Teaching and Learning Futures . Edited by Laura Czerniewicz and Catherine Cronin. Cambridge, UK: Open Book Publishers, pp. 239–66. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Perkins, Mike, Jasper Roe, Darius Postma, James McGaughran, and Don Hickerson. 2023. Detection of GPT-4 Generated Text in Higher Education: Combining Academic Judgement and Software to Identify Generative AI Tool Misuse. Journal of Academic Ethics 22: 89–113. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pitso, Teboho. 2023. Post-COVID-19 Higher Learning: Towards Telagogy, A Web-Based Learning Experience. IAFOR Journal of Education 11: 39–59. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Plata, Sterling, Maria Ana De Guzman, and Arthea Quesada. 2023. Emerging Research and Policy Themes on Academic Integrity in the Age of Chat GPT and Generative AI. Asian Journal of University Education 19: 743–58. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Rudolph, Jürgen, Samson Tan, and Shannon Tan. 2023a. War of the chatbots: Bard, Bing Chat, ChatGPT, Ernie and beyond. The new AI gold rush and its impact on higher education. Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching 6: 364–89. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Rudolph, Jürgen, Samson Tan, and Shannon Tan. 2023b. ChatGPT: Bullshit spewer or the end of traditional assessments in higher education? Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching 6: 342–63. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ryall, Adelle, and Stephen Abblitt. 2023. “A Co-Pilot for Learning Design?”: Perspectives from Learning Designers on the Uses, Challenges, and Risks of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education. In People, Partnerships and Pedagogies. Proceedings ASCILITE 2023 . Edited by Thomas Cochrane, Vickel Narayan, Cheryl Brown, MacCallum Kathryn, Elisa Bone, Christopher Deneen, Robert Vanderburg and Brad Hurren. Christchurch: Te Pae Conference Center, pp. 525–30. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Santiago, Cereneo S., Steve I. Embang, Ricky B. Acanto, Kem Warren P. Ambojia, Maico Demi B. Aperocho, Benedicto B. Balilo, Erwin L. Cahapin, Marjohn Thomas N. Conlu, Samson M. Lausa, Ester Y. Laput, and et al. 2023. Utilization of Writing Assistance Tools in Research in Selected Higher Learning Institutions in the Philippines: A Text Mining Analysis. International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research 22: 259–84. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Solopova, Veronika, Eiad Rostom, Fritz Cremer, Adrian Gruszczynski, Sascha Witte, Chengming Zhang, Fernando Ramos López, Lea Plößl, Florian Hofmann, Ralf Romeike, and et al. 2023. PapagAI: Automated Feedback for Reflective Essays. In KI 2023: Advances in Artificial Intelligence. KI 2023 . Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics). Cham: Springer, vol. 14236, pp. 198–206. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sridhar, Pragnya, Aidan Doyle, Arav Agarwal, Christopher Bogart, Jaromir Savelka, and Majd Sakr. 2023. Harnessing LLMs in Curricular Design: Using GPT-4 to Support Authoring of Learning Objectives. CEUR Workshop Proceedings 3487: 139–50. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sullivan, Miriam, Andrew Kelly, and Paul McLaughlan. 2023. ChatGPT in higher education: Considerations for academic integrity and student learning. Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching 6: 31–40. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tominc, Polona, and Maja Rožman. 2023. Artificial Intelligence and Business Studies: Study Cycle Differences Regarding the Perceptions of the Key Future Competences. Education Sciences 13: 580. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- van den Berg, Geesje, and Elize du Plessis. 2023. ChatGPT and Generative AI: Possibilities for Its Contribution to Lesson Planning, Critical Thinking and Openness in Teacher Education. Education Sciences 13: 998. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Walczak, Krzysztof, and Wojciech Cellary. 2023. Challenges for higher education in the era of widespread access to Generative AI. Economics and Business Review 9: 71–100. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, Ting, Brady D. Lund, Agostino Marengo, Alessandro Pagano, Nishith Reddy Mannuru, Zoë A. Teel, and Jenny Pange. 2023. Exploring the Potential Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on International Students in Higher Education: Generative AI, Chatbots, Analytics, and International Student Success. Applied Sciences 13: 6716. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Watermeyer, Richard, Lawrie Phipps, Donna Lanclos, and Cathryn Knight. 2023. Generative AI and the Automating of Academia. Postdigital Science and Education 6: 446–66. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wolf, Leigh, Tom Farrelly, Orna Farrell, and Fiona Concannon. 2023. Reflections on a Collective Creative Experiment with GenAI: Exploring the Boundaries of What is Possible. Irish Journal of Technology Enhanced Learning 7: 1–7. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yilmaz, Ramazan, and Fatma Gizem Karaoglan Yilmaz. 2023. The effect of generative artificial intelligence (AI)-based tool use on students’ computational thinking skills, programming self-efficacy and motivation. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence 4: 100147. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zawiah, Mohammed, Fahmi Y. Al-Ashwal, Lobna Gharaibeh, Rana Abu Farha, Karem H. Alzoubi, Khawla Abu Hammour, Qutaiba A. Qasim, and Fahd Abrah. 2023. ChatGPT and Clinical Training: Perception, Concerns, and Practice of Pharm-D Students. Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare 16: 4099–110. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
Click here to enlarge figure
| Selected Group of Students | Students Who Answered the Questionnaire | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | F | M | F | |
| 1st year | 59 | 5 | 34 | 2 |
| 2nd year | 36 | 5 | 29 | 4 |
| 1st year | 39 | 3 | 24 | 2 |
| 2nd year | 21 | 2 | 15 | 2 |
| Country | N. | Country | N. | Country | N. | Country | N. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | 16 | Italy | 2 | Egypt | 1 | South Korea | 1 |
| United States | 7 | Saudi Arabia | 2 | Ghana | 1 | Sweden | 1 |
| Singapore | 5 | South Africa | 2 | Greece | 1 | Turkey | 1 |
| Hong Kong | 4 | Thailand | 2 | India | 1 | United Arab Emirates | 1 |
| Spain | 4 | Viet Nam | 2 | Iraq | 1 | Yemen | 1 |
| United Kingdom | 4 | Bulgaria | 1 | Jordan | 1 | ||
| Canada | 3 | Chile | 1 | Malaysia | 1 | ||
| Philippines | 3 | China | 1 | Mexico | 1 | ||
| Germany | 2 | Czech Republic | 1 | New Zealand | 1 | ||
| Ireland | 2 | Denmark | 1 | Poland | 1 |
| Country | N. | Country | N. | Country | N. | Country | N. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singapore | 271 | United States | 15 | India | 2 | Iraq | 0 |
| Australia | 187 | Italy | 11 | Turkey | 2 | Jordan | 0 |
| Hong Kong | 37 | United Kingdom | 6 | Denmark | 1 | Poland | 0 |
| Thailand | 33 | Canada | 6 | Greece | 1 | United Arab Emirates | 0 |
| Philippines | 31 | Ireland | 6 | Sweden | 1 | Yemen | 0 |
| Viet Nam | 29 | Spain | 6 | Saudi Arabia | 1 | ||
| Malaysia | 29 | South Africa | 6 | Bulgaria | 1 | ||
| South Korea | 29 | Mexico | 3 | Czech Republic | 0 | ||
| China | 17 | Chile | 3 | Egypt | 0 | ||
| New Zealand | 17 | Germany | 2 | Ghana | 0 |
| Categories | Subcategories | Nr. of Documents | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| HE with Gen AI | 15 | ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ). | |
| 15 | ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ). | ||
| 14 | ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ). | ||
| 8 | ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ). | ||
| Assessment in Gen AI/ChatGPT times | 8 | ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ). | |
| New challenges to academic integrity policies | 4 | ( ); ( ); ( ); ( ). |
| Have You Tried Using a Gen AI Tool? | Nr. | % |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | 52 | 46.4% |
| No | 60 | 53.6% |
| Categories and Subcategories | % | Unit of Analysis (Some Examples) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Learning support: | ||
| 1.1. Helpful to solve doubts, to correct errors | 34.6% | |
| 1.2. Helpful for more autonomous and self-regulated learning | 19.2% | |
| 2. Helpful to carry out the academic assignments/individual or group activities | 17.3% | |
| 3. Facilitates research/search processes | ||
| 3.1. Reduces the time spent with research | 13.5% | |
| 3.2. Makes access to information easier | 9.6% | |
| 4. Reduction in teachers’ workload | 3.9% | |
| 5. Enables new teaching methods | 1.9% | |
| Categories and Subcategories | % | Unit of Analysis (Some Examples) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Harms the learning process: | ||
| 1.1. What is generated by Gen AI has errors | 13.5% | |
| 1.2. Generates dependence and encourages laziness | 15.4% | |
| 1.3. Decreases active effort and involvement in the learning/critical thinking process | 28.8% | |
| 2. Encourages plagiarism and incorrect assessment procedures | 17.3% | |
| 3. Reduces relationships with teachers and interpersonal relationships | 9.6% | |
| 4. No negative effect—as it will be necessary to have knowledge for its correct use | 7.7% | |
| 5. Don’t know | 7.7% | |
| The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
Share and Cite
Saúde, S.; Barros, J.P.; Almeida, I. Impacts of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: Research Trends and Students’ Perceptions. Soc. Sci. 2024 , 13 , 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci13080410
Saúde S, Barros JP, Almeida I. Impacts of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: Research Trends and Students’ Perceptions. Social Sciences . 2024; 13(8):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci13080410
Saúde, Sandra, João Paulo Barros, and Inês Almeida. 2024. "Impacts of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: Research Trends and Students’ Perceptions" Social Sciences 13, no. 8: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci13080410
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals
Health & Environmental Research Online (HERO)
- Learn about HERO
- Search HERO
- Projects in HERO
- Risk Assessment
- Transparency & Integrity

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
3. Simple hypothesis. A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, "Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking. 4.
Developing a hypothesis (with example) Step 1. Ask a question. Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project. Example: Research question.
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes - specificity, clarity and testability. Let's take a look at these more closely.
It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis. 7.
A snapshot analysis of citation activity of hypothesis articles may reveal interest of the global scientific community towards their implications across various disciplines and countries. As a prime example, Strachan's hygiene hypothesis, published in 1989,10 is still attracting numerous citations on Scopus, the largest bibliographic database ...
The title and abstracts are the only sections of the research paper that are often freely available to the readers on the journal websites, search engines, and in many abstracting agencies/databases, whereas the full paper may attract a payment per view or a fee for downloading the pdf copy.[1,2,3,7,8,10,11,13,14] The abstract is an independent ...
RESEARCH HYPOTHESIS A research hypothesis is a statement of expectation or prediction that will be tested by research. ... • As a title for your paper Your hypothesis will become part of your research proposal. Sample Student Hypotheses 2008-2009 Senior Seminar Note how each student, in the samples below, began with a general topic or area of ...
The null hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is no significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as a starting point for testing the research hypothesis, and if the results of the study reject the null hypothesis, it suggests that there is a significant difference or relationship between variables.
The following parameters can be used to help you formulate a suitable research paper title: The purpose of the research; The scope of the research; The narrative tone of the paper [typically defined by the type of the research] The methods used to study the problem; The initial aim of a title is to capture the reader's attention and to ...
There are seven different types of research hypotheses. Simple Hypothesis. A simple hypothesis predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable. Complex Hypothesis. A complex hypothesis predicts the relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables. Directional Hypothesis.
Steps on How to Write a Good Null and Alternative Hypothesis. Identify a Specific Research Question: Start with clearly defining a particular problem or phenomenon you want to study. Determine Key Variables: Identify independent and dependent variables involved in your study. State a Specific Null Hypothesis (H0): Formulate a concrete statement that suggests no effect, no difference, or no ...
Make sure your research title describes (a) the topic, (b) the method, (c) the sample, and (d) the results of your study. You can use the following formula: [ Result ]: A [ method] study of [ topic] among [ sample] Example: Meditation makes nurses perform better: a qualitative study of mindfulness meditation among German nursing students. Avoid ...
Correlative research questions might lead to hypothesis testing in order to show that a change in one variable is associated (what we fre-quently statistically call "correlated") with a change in a second variable, but they do not explicitly aim to test causality. As we will learn later in this chapter, correlation does not
3. Content of the Title. The main elements of a title include intervention, end-point or outcome, study population, and its specific conditions, design, and setting, which refers to a situation or a place that study was conducted at ().The main elements in a hypothesis-testing paper, are (1) the independent variable(s) (X), (2) dependent variable(s) (Y), and (3) the study subjects (i.e. animal ...
In a nutshell, a hypothesis directs and organizes the research methods you will use, forming a large section of research paper writing. Hypothesis vs. Theory. A hypothesis is a realistic expectation that researchers make before any investigation. It is formulated and tested to prove whether the statement is true.
A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement. A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
What is a hypothesis. A hypothesis represents a scientific guess that is stated in research. It is a speculative statement concerning the relationship between two or more variables in research.. Therefore, a good hypothesis is a prediction that is testable, specific, and explores what a researcher expects to find in the study.
ABSTRACT. Criteria are briefly proposed for final conclusions, research problems, and research hypotheses in quantitative research. Moreover, based on a proposed definition of applied and basic/general research, it is argued that (1) in applied quantitative research, while research problems are necessary, research hypotheses are unjustified, and that (2) in basic/general quantitative ...
A good research paper title: So here are three basic tips to keep in mind while writing a title: 1] Keep it simple, brief and attractive: The primary function of a title is to provide a precise summary of the paper's content. So keep the title brief and clear. Use active verbs instead of complex noun-based phrases, and avoid unnecessary details.
Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships among variables. This method is widely used in social sciences, psychology, economics, and other fields where researchers aim to understand human behavior and phenomena through statistical analysis.
Research question. Interest in a particular topic usually begins the research process, but it is the familiarity with the subject that helps define an appropriate research question for a study. 1 Questions then arise out of a perceived knowledge deficit within a subject area or field of study. 2 Indeed, Haynes suggests that it is important to know "where the boundary between current ...
In this paper, the effects of the rapid advancement of generative artificial intelligence (Gen AI) in higher education (HE) are discussed. A mixed exploratory research approach was employed to understand these impacts, combining analysis of current research trends and students' perceptions of the effects of Gen AI tools in academia. Through bibliometric analysis and systematic literature ...
Health & Environmental Research Online (HERO) Contact Us; Print Feedback Export to File . Search: ... Tags; HERO ID. 3615659 Reference Type. Journal Article Title. Biological autoxidation. I. Decontrolled iron: an ultimate carcinogen and toxicant: an hypothesis Author(s) Kon, SH Year. 1978 Is Peer Reviewed? 1 Journal. Medical Hypotheses ISSN ...