
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

Writing Assignments
Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine

Introduction
Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Developing critical thinking and writing skills are also necessary to demonstrate your ability to understand and apply information about your topic. It is not uncommon to be unsure about the processes of writing assignments at university.
- You may be returning to study after a break
- You may have come from an exam based assessment system and never written an assignment before
- Maybe you have written assignments but would like to improve your processes and strategies
This chapter has a collection of resources that will provide you with the skills and strategies to understand assignment requirements and effectively plan, research, write and edit your assignments. It begins with an explanation of how to analyse an assignment task and start putting your ideas together. It continues by breaking down the components of academic writing and exploring the elements you will need to master in your written assignments. This is followed by a discussion of paraphrasing and synthesis, and how you can use these strategies to create a strong, written argument. The chapter concludes with useful checklists for editing and proofreading to help you get the best possible mark for your work.
Task Analysis and Deconstructing an Assignment
It is important that before you begin researching and writing your assignments you spend sufficient time understanding all the requirements. This will help make your research process more efficient and effective. Check your subject information such as task sheets, criteria sheets and any additional information that may be in your subject portal online. Seek clarification from your lecturer or tutor if you are still unsure about how to begin your assignments.
The task sheet typically provides key information about an assessment including the assignment question. It can be helpful to scan this document for topic, task and limiting words to ensure that you fully understand the concepts you are required to research, how to approach the assignment, and the scope of the task you have been set. These words can typically be found in your assignment question and are outlined in more detail in the two tables below (see Table 19.1 and Table 19.2 ).
Table 19.1 Parts of an Assignment Question
| Topic words | These are words and concepts you have to research and write about. |
| Task words | These will tell you how to approach the assignment and structure the information you find in your research (e.g., discuss, analyse). |
| Limiting words | These words define the scope of the assignment, e.g., Australian perspectives, relevant codes or standards or a specific timeframe. |
Make sure you have a clear understanding of what the task word requires you to address.
Table 19.2 Task words
| Give reasons for or explain something has occurred. This task directs you to consider contributing factors to a certain situation or event. You are expected to make a decision about why these occurred, not just describe the events. | the factors that led to the global financial crisis. | |
| Consider the different elements of a concept, statement or situation. Show the different components and show how they connect or relate. Your structure and argument should be logical and methodical. | the political, social and economic impacts of climate change. | |
| Make a judgement on a topic or idea. Consider its reliability, truth and usefulness. In your judgement, consider both the strengths and weaknesses of the opposing arguments to determine your topic’s worth (similar to evaluate). | the efficacy of cogitative behavioural therapy (CBT) for the treatment of depression. | |
| Divide your topic into categories or sub-topics logically (could possibly be part of a more complex task). | the artists studied this semester according to the artistic periods they best represent. Then choose one artist and evaluate their impact on future artists. | |
| State your opinion on an issue or idea. You may explain the issue or idea in more detail. Be objective and support your opinion with reliable evidence. | the government’s proposal to legalise safe injecting rooms. | |
| Show the similarities and differences between two or more ideas, theories, systems, arguments or events. You are expected to provide a balanced response, highlighting similarities and differences. | the efficiency of wind and solar power generation for a construction site. | |
| Point out only the differences between two or more ideas, theories, systems, arguments or events. | virtue ethics and utilitarianism as models for ethical decision making. | |
| (this is often used with another task word, e.g. critically evaluate, critically analyse, critically discuss) | It does not mean to criticise, instead you are required to give a balanced account, highlighting strengths and weaknesses about the topic. Your overall judgment must be supported by reliable evidence and your interpretation of that evidence. | analyse the impacts of mental health on recidivism within youth justice. |
| Provide a precise meaning of a concept. You may need to include the limits or scope of the concept within a given context. | digital disruption as it relates to productivity. | |
| Provide a thorough description, emphasising the most important points. Use words to show appearance, function, process, events or systems. You are not required to make judgements. | the pathophysiology of Asthma. | |
| Highlight the differences between two (possibly confusing) items. | between exothermic and endothermic reactions. | |
| Provide an analysis of a topic. Use evidence to support your argument. Be logical and include different perspectives on the topic (This requires more than a description). | how Brofenbrenner’s ecological system’s theory applies to adolescence. | |
| Review both positive and negative aspects of a topic. You may need to provide an overall judgement regarding the value or usefulness of the topic. Evidence (referencing) must be included to support your writing. | the impact of inclusive early childhood education programs on subsequent high school completion rates for First Nations students. | |
| Describe and clarify the situation or topic. Depending on your discipline area and topic, this may include processes, pathways, cause and effect, impact, or outcomes. | the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the film industry in Australia. | |
| Clarify a point or argument with examples and evidence. | how society’s attitudes to disability have changed from a medical model to a wholistic model of disability. | |
| Give evidence which supports an argument or idea; show why a decision or conclusions were made. Justify may be used with other topic words, such as outline, argue. | Write a report outlining the key issues and implications of a welfare cashless debit card trial and make three recommendations for future improvements. your decision-making process for the recommendations. | |
| A comprehensive description of the situation or topic which provides a critical analysis of the key issues. | Provide a of Australia's asylum policies since the Pacific Solution in 2001. | |
| An overview or brief description of a topic. (This is likely to be part of a larger assessment task.) | the process for calculating the correct load for a plane. |
The criteria sheet , also known as the marking sheet or rubric, is another important document to look at before you begin your assignment. The criteria sheet outlines how your assignment will be marked and should be used as a checklist to make sure you have included all the information required.
The task or criteria sheet will also include the:
- Word limit (or word count)
- Referencing style and research expectations
- Formatting requirements
Task analysis and criteria sheets are also discussed in the chapter Managing Assessments for a more detailed discussion on task analysis, criteria sheets, and marking rubrics.
Preparing your ideas
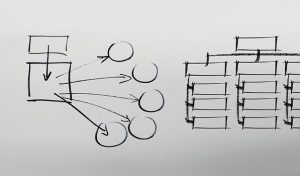
Brainstorm or concept map: List possible ideas to address each part of the assignment task based on what you already know about the topic from lectures and weekly readings.
Finding appropriate information: Learn how to find scholarly information for your assignments which is
See the chapter Working With Information for a more detailed explanation .
What is academic writing?
Academic writing tone and style.
Many of the assessment pieces you prepare will require an academic writing style. This is sometimes called ‘academic tone’ or ‘academic voice’. This section will help you to identify what is required when you are writing academically (see Table 19.3 ). The best way to understand what academic writing looks like, is to read broadly in your discipline area. Look at how your course readings, or scholarly sources, are written. This will help you identify the language of your discipline field, as well as how other writers structure their work.
Table 19.3 Comparison of academic and non-academic writing
| Is clear, concise and well-structured | Is verbose and may use more words than are needed |
| Is formal. It writes numbers under twenty in full. | Writes numbers under twenty as numerals and uses symbols such as “&” instead of writing it in full |
| Is reasoned and supported (logically developed) | Uses humour (puns, sarcasm) |
| Is authoritative (writes in third person- This essay argues…) | Writes in first person (I think, I found) |
| Utilises the language of the field/industry/subject | Uses colloquial language e.g., mate |
Thesis statements
Essays are a common form of assessment that you will likely encounter during your university studies. You should apply an academic tone and style when writing an essay, just as you would in in your other assessment pieces. One of the most important steps in writing an essay is constructing your thesis statement. A thesis statement tells the reader the purpose, argument or direction you will take to answer your assignment question. A thesis statement may not be relevant for some questions, if you are unsure check with your lecturer. The thesis statement:
- Directly relates to the task . Your thesis statement may even contain some of the key words or synonyms from the task description.
- Does more than restate the question.
- Is specific and uses precise language.
- Let’s your reader know your position or the main argument that you will support with evidence throughout your assignment.
- The subject is the key content area you will be covering.
- The contention is the position you are taking in relation to the chosen content.
Your thesis statement helps you to structure your essay. It plays a part in each key section: introduction, body and conclusion.
Planning your assignment structure

When planning and drafting assignments, it is important to consider the structure of your writing. Academic writing should have clear and logical structure and incorporate academic research to support your ideas. It can be hard to get started and at first you may feel nervous about the size of the task, this is normal. If you break your assignment into smaller pieces, it will seem more manageable as you can approach the task in sections. Refer to your brainstorm or plan. These ideas should guide your research and will also inform what you write in your draft. It is sometimes easier to draft your assignment using the 2-3-1 approach, that is, write the body paragraphs first followed by the conclusion and finally the introduction.
Writing introductions and conclusions
Clear and purposeful introductions and conclusions in assignments are fundamental to effective academic writing. Your introduction should tell the reader what is going to be covered and how you intend to approach this. Your conclusion should summarise your argument or discussion and signal to the reader that you have come to a conclusion with a final statement. These tips below are based on the requirements usually needed for an essay assignment, however, they can be applied to other assignment types.
Writing introductions

Most writing at university will require a strong and logically structured introduction. An effective introduction should provide some background or context for your assignment, clearly state your thesis and include the key points you will cover in the body of the essay in order to prove your thesis.
Usually, your introduction is approximately 10% of your total assignment word count. It is much easier to write your introduction once you have drafted your body paragraphs and conclusion, as you know what your assignment is going to be about. An effective introduction needs to inform your reader by establishing what the paper is about and provide four basic things:
- A brief background or overview of your assignment topic
- A thesis statement (see section above)
- An outline of your essay structure
- An indication of any parameters or scope that will/ will not be covered, e.g. From an Australian perspective.
The below example demonstrates the four different elements of an introductory paragraph.
1) Information technology is having significant effects on the communication of individuals and organisations in different professions. 2) This essay will discuss the impact of information technology on the communication of health professionals. 3) First, the provision of information technology for the educational needs of nurses will be discussed. 4) This will be followed by an explanation of the significant effects that information technology can have on the role of general practitioner in the area of public health. 5) Considerations will then be made regarding the lack of knowledge about the potential of computers among hospital administrators and nursing executives. 6) The final section will explore how information technology assists health professionals in the delivery of services in rural areas . 7) It will be argued that information technology has significant potential to improve health care and medical education, but health professionals are reluctant to use it.
1 Brief background/ overview | 2 Indicates the scope of what will be covered | 3-6 Outline of the main ideas (structure) | 7 The thesis statement
Note : The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing conclusions
You should aim to end your assignments with a strong conclusion. Your conclusion should restate your thesis and summarise the key points you have used to prove this thesis. Finish with a key point as a final impactful statement. Similar to your introduction, your conclusion should be approximately 10% of the total assignment word length. If your assessment task asks you to make recommendations, you may need to allocate more words to the conclusion or add a separate recommendations section before the conclusion. Use the checklist below to check your conclusion is doing the right job.
Conclusion checklist
- Have you referred to the assignment question and restated your argument (or thesis statement), as outlined in the introduction?
- Have you pulled together all the threads of your essay into a logical ending and given it a sense of unity?
- Have you presented implications or recommendations in your conclusion? (if required by your task).
- Have you added to the overall quality and impact of your essay? This is your final statement about this topic; thus, a key take-away point can make a great impact on the reader.
- Remember, do not add any new material or direct quotes in your conclusion.
This below example demonstrates the different elements of a concluding paragraph.
1) It is evident, therefore, that not only do employees need to be trained for working in the Australian multicultural workplace, but managers also need to be trained. 2) Managers must ensure that effective in-house training programs are provided for migrant workers, so that they become more familiar with the English language, Australian communication norms and the Australian work culture. 3) In addition, Australian native English speakers need to be made aware of the differing cultural values of their workmates; particularly the different forms of non-verbal communication used by other cultures. 4) Furthermore, all employees must be provided with clear and detailed guidelines about company expectations. 5) Above all, in order to minimise communication problems and to maintain an atmosphere of tolerance, understanding and cooperation in the multicultural workplace, managers need to have an effective knowledge about their employees. This will help employers understand how their employee’s social conditioning affects their beliefs about work. It will develop their communication skills to develop confidence and self-esteem among diverse work groups. 6) The culturally diverse Australian workplace may never be completely free of communication problems, however, further studies to identify potential problems and solutions, as well as better training in cross cultural communication for managers and employees, should result in a much more understanding and cooperative environment.
1 Reference to thesis statement – In this essay the writer has taken the position that training is required for both employees and employers . | 2-5 Structure overview – Here the writer pulls together the main ideas in the essay. | 6 Final summary statement that is based on the evidence.
Note: The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing paragraphs
Paragraph writing is a key skill that enables you to incorporate your academic research into your written work. Each paragraph should have its own clearly identified topic sentence or main idea which relates to the argument or point (thesis) you are developing. This idea should then be explained by additional sentences which you have paraphrased from good quality sources and referenced according to the recommended guidelines of your subject (see the chapter Working with Information ). Paragraphs are characterised by increasing specificity; that is, they move from the general to the specific, increasingly refining the reader’s understanding. A common structure for paragraphs in academic writing is as follows.
Topic Sentence
This is the main idea of the paragraph and should relate to the overall issue or purpose of your assignment is addressing. Often it will be expressed as an assertion or claim which supports the overall argument or purpose of your writing.
Explanation/ Elaboration
The main idea must have its meaning explained and elaborated upon. Think critically, do not just describe the idea.
These explanations must include evidence to support your main idea. This information should be paraphrased and referenced according to the appropriate referencing style of your course.
Concluding sentence (critical thinking)
This should explain why the topic of the paragraph is relevant to the assignment question and link to the following paragraph.
Use the checklist below to check your paragraphs are clear and well formed.
Paragraph checklist
- Does your paragraph have a clear main idea?
- Is everything in the paragraph related to this main idea?
- Is the main idea adequately developed and explained?
- Do your sentences run together smoothly?
- Have you included evidence to support your ideas?
- Have you concluded the paragraph by connecting it to your overall topic?
Writing sentences
Make sure all the sentences in your paragraphs make sense. Each sentence must contain a verb to be a complete sentence. Avoid sentence fragments . These are incomplete sentences or ideas that are unfinished and create confusion for your reader. Avoid also run on sentences . This happens when you join two ideas or clauses without using the appropriate punctuation. This also confuses your meaning (See the chapter English Language Foundations for examples and further explanation).
Use transitions (linking words and phrases) to connect your ideas between paragraphs and make your writing flow. The order that you structure the ideas in your assignment should reflect the structure you have outlined in your introduction. Refer to transition words table in the chapter English Language Foundations.
Paraphrasing and Synthesising
Paraphrasing and synthesising are powerful tools that you can use to support the main idea of a paragraph. It is likely that you will regularly use these skills at university to incorporate evidence into explanatory sentences and strengthen your essay. It is important to paraphrase and synthesise because:
- Paraphrasing is regarded more highly at university than direct quoting.
- Paraphrasing can also help you better understand the material.
- Paraphrasing and synthesising demonstrate you have understood what you have read through your ability to summarise and combine arguments from the literature using your own words.
What is paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing is changing the writing of another author into your words while retaining the original meaning. You must acknowledge the original author as the source of the information in your citation. Follow the steps in this table to help you build your skills in paraphrasing (see Table 19.4 ).
Table 19.4 Paraphrasing techniques
| 1 | Make sure you understand what you are reading. Look up keywords to understand their meanings. |
| 2 | Record the details of the source so you will be able to cite it correctly in text and in your reference list. |
| 3 | Identify words that you can change to synonyms (but do not change the key/topic words). |
| 4 | Change the type of word in a sentence (for example change a noun to a verb or vice versa). |
| 5 | Eliminate unnecessary words or phrases from the original that you don’t need in your paraphrase. |
| 6 | Change the sentence structure (for example change a long sentence to several shorter ones or combine shorter sentences to form a longer sentence). |
Example of paraphrasing
Please note that these examples and in text citations are for instructional purposes only.
Original text
Health care professionals assist people often when they are at their most vulnerable . To provide the best care and understand their needs, workers must demonstrate good communication skills . They must develop patient trust and provide empathy to effectively work with patients who are experiencing a variety of situations including those who may be suffering from trauma or violence, physical or mental illness or substance abuse (French & Saunders, 2018).
Poor quality paraphrase example
This is a poor example of paraphrasing. Some synonyms have been used and the order of a few words changed within the sentences however the colours of the sentences indicate that the paragraph follows the same structure as the original text.
Health care sector workers are often responsible for vulnerable patients. To understand patients and deliver good service , they need to be excellent communicators . They must establish patient rapport and show empathy if they are to successfully care for patients from a variety of backgrounds and with different medical, psychological and social needs (French & Saunders, 2018).
A good quality paraphrase example
This example demonstrates a better quality paraphrase. The author has demonstrated more understanding of the overall concept in the text by using the keywords as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up to see how much the structure has changed from the original text.
Empathetic communication is a vital skill for health care workers. Professionals in these fields are often responsible for patients with complex medical, psychological and social needs. Empathetic communication assists in building rapport and gaining the necessary trust to assist these vulnerable patients by providing appropriate supportive care (French & Saunders, 2018).
The good quality paraphrase example demonstrates understanding of the overall concept in the text by using key words as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up, which indicates how much the structure has changed from the original text.
What is synthesising?
Synthesising means to bring together more than one source of information to strengthen your argument. Once you have learnt how to paraphrase the ideas of one source at a time, you can consider adding additional sources to support your argument. Synthesis demonstrates your understanding and ability to show connections between multiple pieces of evidence to support your ideas and is a more advanced academic thinking and writing skill.
Follow the steps in this table to improve your synthesis techniques (see Table 19.5 ).
Table 19.5 Synthesising techniques
| 1 | Check your referencing guide to learn how to correctly reference more than one author at a time in your paper. |
| 2 | While taking notes for your research, try organising your notes into themes. This way you can keep similar ideas from different authors together. |
| 3 | Identify similar language and tone used by authors so that you can group similar ideas together. |
| 4 | Synthesis can not only be about grouping ideas together that are similar, but also those that are different. See how you can contrast authors in your writing to also strengthen your argument. |
Example of synthesis
There is a relationship between academic procrastination and mental health outcomes. Procrastination has been found to have a negative effect on students’ well-being (Balkis, & Duru, 2016). Yerdelen, McCaffrey, and Klassens’ (2016) research results suggested that there was a positive association between procrastination and anxiety. This was corroborated by Custer’s (2018) findings which indicated that students with higher levels of procrastination also reported greater levels of the anxiety. Therefore, it could be argued that procrastination is an ineffective learning strategy that leads to increased levels of distress.
Topic sentence | Statements using paraphrased evidence | Critical thinking (student voice) | Concluding statement – linking to topic sentence
This example demonstrates a simple synthesis. The author has developed a paragraph with one central theme and included explanatory sentences complete with in-text citations from multiple sources. Note how the blocks of colour have been used to illustrate the paragraph structure and synthesis (i.e., statements using paraphrased evidence from several sources). A more complex synthesis may include more than one citation per sentence.
Creating an argument
What does this mean.
Throughout your university studies, you may be asked to ‘argue’ a particular point or position in your writing. You may already be familiar with the idea of an argument, which in general terms means to have a disagreement with someone. Similarly, in academic writing, if you are asked to create an argument, this means you are asked to have a position on a particular topic, and then justify your position using evidence.
What skills do you need to create an argument?
In order to create a good and effective argument, you need to be able to:
- Read critically to find evidence
- Plan your argument
- Think and write critically throughout your paper to enhance your argument
For tips on how to read and write critically, refer to the chapter Thinking for more information. A formula for developing a strong argument is presented below.
A formula for a good argument
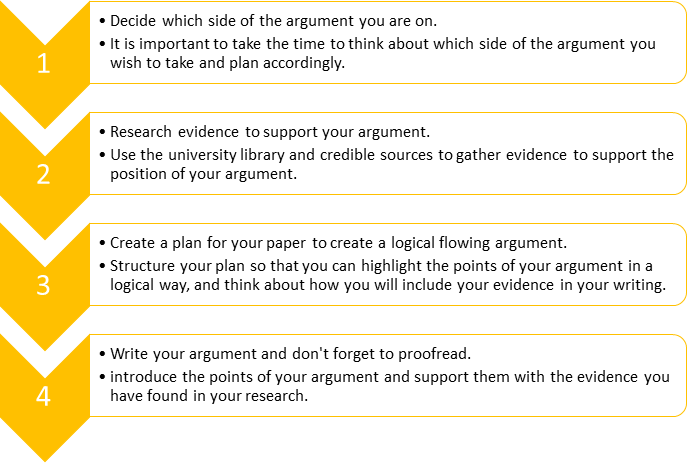
What does an argument look like?
As can be seen from the figure above, including evidence is a key element of a good argument. While this may seem like a straightforward task, it can be difficult to think of wording to express your argument. The table below provides examples of how you can illustrate your argument in academic writing (see Table 19.6 ).
Table 19.6 Argument
| Introducing your argument | • This paper will argue/claim that... • ...is an important factor/concept/idea/ to consider because... • … will be argued/outlined in this paper. |
| Introducing evidence for your argument | • Smith (2014) outlines that.... • This evidence demonstrates that... • According to Smith (2014)… • For example, evidence/research provided by Smith (2014) indicates that... |
| Giving the reason why your point/evidence is important | • Therefore this indicates... • This evidence clearly demonstrates.... • This is important/significant because... • This data highlights... |
| Concluding a point | • Overall, it is clear that... • Therefore, … are reasons which should be considered because... • Consequently, this leads to.... • The research presented therefore indicates... |
Editing and proofreading (reviewing)
Once you have finished writing your first draft it is recommended that you spend time revising your work. Proofreading and editing are two different stages of the revision process.
- Editing considers the overall focus or bigger picture of the assignment
- Proofreading considers the finer details
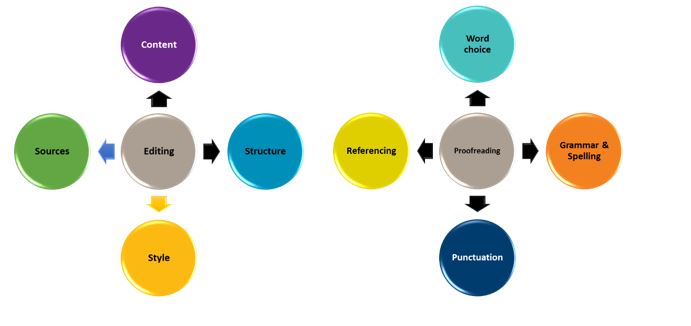
As can be seen in the figure above there are four main areas that you should review during the editing phase of the revision process. The main things to consider when editing include content, structure, style, and sources. It is important to check that all the content relates to the assignment task, the structure is appropriate for the purposes of the assignment, the writing is academic in style, and that sources have been adequately acknowledged. Use the checklist below when editing your work.
Editing checklist
- Have I answered the question accurately?
- Do I have enough credible, scholarly supporting evidence?
- Is my writing tone objective and formal enough or have I used emotive and informal language?
- Have I written in the third person not the first person?
- Do I have appropriate in-text citations for all my information?
- Have I included the full details for all my in-text citations in my reference list?
There are also several key things to look out for during the proofreading phase of the revision process. In this stage it is important to check your work for word choice, grammar and spelling, punctuation and referencing errors. It can be easy to mis-type words like ‘from’ and ‘form’ or mix up words like ‘trail’ and ‘trial’ when writing about research, apply American rather than Australian spelling, include unnecessary commas or incorrectly format your references list. The checklist below is a useful guide that you can use when proofreading your work.
Proofreading checklist
- Is my spelling and grammar accurate?
- Are they complete?
- Do they all make sense?
- Do they only contain only one idea?
- Do the different elements (subject, verb, nouns, pronouns) within my sentences agree?
- Are my sentences too long and complicated?
- Do they contain only one idea per sentence?
- Is my writing concise? Take out words that do not add meaning to your sentences.
- Have I used appropriate discipline specific language but avoided words I don’t know or understand that could possibly be out of context?
- Have I avoided discriminatory language and colloquial expressions (slang)?
- Is my referencing formatted correctly according to my assignment guidelines? (for more information on referencing refer to the Managing Assessment feedback section).
This chapter has examined the experience of writing assignments. It began by focusing on how to read and break down an assignment question, then highlighted the key components of essays. Next, it examined some techniques for paraphrasing and summarising, and how to build an argument. It concluded with a discussion on planning and structuring your assignment and giving it that essential polish with editing and proof-reading. Combining these skills and practising them, can greatly improve your success with this very common form of assessment.
- Academic writing requires clear and logical structure, critical thinking and the use of credible scholarly sources.
- A thesis statement is important as it tells the reader the position or argument you have adopted in your assignment. Not all assignments will require a thesis statement.
- Spending time analysing your task and planning your structure before you start to write your assignment is time well spent.
- Information you use in your assignment should come from credible scholarly sources such as textbooks and peer reviewed journals. This information needs to be paraphrased and referenced appropriately.
- Paraphrasing means putting something into your own words and synthesising means to bring together several ideas from sources.
- Creating an argument is a four step process and can be applied to all types of academic writing.
- Editing and proofreading are two separate processes.
Academic Skills Centre. (2013). Writing an introduction and conclusion . University of Canberra, accessed 13 August, 2013, http://www.canberra.edu.au/studyskills/writing/conclusions
Balkis, M., & Duru, E. (2016). Procrastination, self-regulation failure, academic life satisfaction, and affective well-being: underregulation or misregulation form. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 31 (3), 439-459.
Custer, N. (2018). Test anxiety and academic procrastination among prelicensure nursing students. Nursing education perspectives, 39 (3), 162-163.
Yerdelen, S., McCaffrey, A., & Klassen, R. M. (2016). Longitudinal examination of procrastination and anxiety, and their relation to self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: Latent growth curve modeling. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice, 16 (1).
Writing Assignments Copyright © 2021 by Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Academic writing
- A step-by-step guide to the writing process
The Writing Process | 5 Steps with Examples & Tips
Published on April 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on December 8, 2023.

Good academic writing requires effective planning, drafting, and revision.
The writing process looks different for everyone, but there are five basic steps that will help you structure your time when writing any kind of text.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Table of contents
Step 1: prewriting, step 2: planning and outlining, step 3: writing a first draft, step 4: redrafting and revising, step 5: editing and proofreading, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about the writing process.
Before you start writing, you need to decide exactly what you’ll write about and do the necessary research.
Coming up with a topic
If you have to come up with your own topic for an assignment, think of what you’ve covered in class— is there a particular area that intrigued, interested, or even confused you? Topics that left you with additional questions are perfect, as these are questions you can explore in your writing.
The scope depends on what type of text you’re writing—for example, an essay or a research paper will be less in-depth than a dissertation topic . Don’t pick anything too ambitious to cover within the word count, or too limited for you to find much to say.
Narrow down your idea to a specific argument or question. For example, an appropriate topic for an essay might be narrowed down like this:
Doing the research
Once you know your topic, it’s time to search for relevant sources and gather the information you need. This process varies according to your field of study and the scope of the assignment. It might involve:
- Searching for primary and secondary sources .
- Reading the relevant texts closely (e.g. for literary analysis ).
- Collecting data using relevant research methods (e.g. experiments , interviews or surveys )
From a writing perspective, the important thing is to take plenty of notes while you do the research. Keep track of the titles, authors, publication dates, and relevant quotations from your sources; the data you gathered; and your initial analysis or interpretation of the questions you’re addressing.
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
Especially in academic writing , it’s important to use a logical structure to convey information effectively. It’s far better to plan this out in advance than to try to work out your structure once you’ve already begun writing.
Creating an essay outline is a useful way to plan out your structure before you start writing. This should help you work out the main ideas you want to focus on and how you’ll organize them. The outline doesn’t have to be final—it’s okay if your structure changes throughout the writing process.
Use bullet points or numbering to make your structure clear at a glance. Even for a short text that won’t use headings, it’s useful to summarize what you’ll discuss in each paragraph.
An outline for a literary analysis essay might look something like this:
- Describe the theatricality of Austen’s works
- Outline the role theater plays in Mansfield Park
- Introduce the research question: How does Austen use theater to express the characters’ morality in Mansfield Park ?
- Discuss Austen’s depiction of the performance at the end of the first volume
- Discuss how Sir Bertram reacts to the acting scheme
- Introduce Austen’s use of stage direction–like details during dialogue
- Explore how these are deployed to show the characters’ self-absorption
- Discuss Austen’s description of Maria and Julia’s relationship as polite but affectionless
- Compare Mrs. Norris’s self-conceit as charitable despite her idleness
- Summarize the three themes: The acting scheme, stage directions, and the performance of morals
- Answer the research question
- Indicate areas for further study
Once you have a clear idea of your structure, it’s time to produce a full first draft.
This process can be quite non-linear. For example, it’s reasonable to begin writing with the main body of the text, saving the introduction for later once you have a clearer idea of the text you’re introducing.
To give structure to your writing, use your outline as a framework. Make sure that each paragraph has a clear central focus that relates to your overall argument.
Hover over the parts of the example, from a literary analysis essay on Mansfield Park , to see how a paragraph is constructed.
The character of Mrs. Norris provides another example of the performance of morals in Mansfield Park . Early in the novel, she is described in scathing terms as one who knows “how to dictate liberality to others: but her love of money was equal to her love of directing” (p. 7). This hypocrisy does not interfere with her self-conceit as “the most liberal-minded sister and aunt in the world” (p. 7). Mrs. Norris is strongly concerned with appearing charitable, but unwilling to make any personal sacrifices to accomplish this. Instead, she stage-manages the charitable actions of others, never acknowledging that her schemes do not put her own time or money on the line. In this way, Austen again shows us a character whose morally upright behavior is fundamentally a performance—for whom the goal of doing good is less important than the goal of seeming good.
When you move onto a different topic, start a new paragraph. Use appropriate transition words and phrases to show the connections between your ideas.
The goal at this stage is to get a draft completed, not to make everything perfect as you go along. Once you have a full draft in front of you, you’ll have a clearer idea of where improvement is needed.
Give yourself a first draft deadline that leaves you a reasonable length of time to revise, edit, and proofread before the final deadline. For a longer text like a dissertation, you and your supervisor might agree on deadlines for individual chapters.
Now it’s time to look critically at your first draft and find potential areas for improvement. Redrafting means substantially adding or removing content, while revising involves making changes to structure and reformulating arguments.
Evaluating the first draft
It can be difficult to look objectively at your own writing. Your perspective might be positively or negatively biased—especially if you try to assess your work shortly after finishing it.
It’s best to leave your work alone for at least a day or two after completing the first draft. Come back after a break to evaluate it with fresh eyes; you’ll spot things you wouldn’t have otherwise.
When evaluating your writing at this stage, you’re mainly looking for larger issues such as changes to your arguments or structure. Starting with bigger concerns saves you time—there’s no point perfecting the grammar of something you end up cutting out anyway.
Right now, you’re looking for:
- Arguments that are unclear or illogical.
- Areas where information would be better presented in a different order.
- Passages where additional information or explanation is needed.
- Passages that are irrelevant to your overall argument.
For example, in our paper on Mansfield Park , we might realize the argument would be stronger with more direct consideration of the protagonist Fanny Price, and decide to try to find space for this in paragraph IV.
For some assignments, you’ll receive feedback on your first draft from a supervisor or peer. Be sure to pay close attention to what they tell you, as their advice will usually give you a clearer sense of which aspects of your text need improvement.
Redrafting and revising
Once you’ve decided where changes are needed, make the big changes first, as these are likely to have knock-on effects on the rest. Depending on what your text needs, this step might involve:
- Making changes to your overall argument.
- Reordering the text.
- Cutting parts of the text.
- Adding new text.
You can go back and forth between writing, redrafting and revising several times until you have a final draft that you’re happy with.
Think about what changes you can realistically accomplish in the time you have. If you are running low on time, you don’t want to leave your text in a messy state halfway through redrafting, so make sure to prioritize the most important changes.
Editing focuses on local concerns like clarity and sentence structure. Proofreading involves reading the text closely to remove typos and ensure stylistic consistency. You can check all your drafts and texts in minutes with an AI proofreader .
Editing for grammar and clarity
When editing, you want to ensure your text is clear, concise, and grammatically correct. You’re looking out for:
- Grammatical errors.
- Ambiguous phrasings.
- Redundancy and repetition .
In your initial draft, it’s common to end up with a lot of sentences that are poorly formulated. Look critically at where your meaning could be conveyed in a more effective way or in fewer words, and watch out for common sentence structure mistakes like run-on sentences and sentence fragments:
- Austen’s style is frequently humorous, her characters are often described as “witty.” Although this is less true of Mansfield Park .
- Austen’s style is frequently humorous. Her characters are often described as “witty,” although this is less true of Mansfield Park .
To make your sentences run smoothly, you can always use a paraphrasing tool to rewrite them in a clearer way.
Proofreading for small mistakes and typos
When proofreading, first look out for typos in your text:
- Spelling errors.
- Missing words.
- Confused word choices .
- Punctuation errors .
- Missing or excess spaces.
Use a grammar checker , but be sure to do another manual check after. Read through your text line by line, watching out for problem areas highlighted by the software but also for any other issues it might have missed.
For example, in the following phrase we notice several errors:
- Mary Crawfords character is a complicate one and her relationships with Fanny and Edmund undergoes several transformations through out the novel.
- Mary Crawford’s character is a complicated one, and her relationships with both Fanny and Edmund undergo several transformations throughout the novel.
Proofreading for stylistic consistency
There are several issues in academic writing where you can choose between multiple different standards. For example:
- Whether you use the serial comma .
- Whether you use American or British spellings and punctuation (you can use a punctuation checker for this).
- Where you use numerals vs. words for numbers.
- How you capitalize your titles and headings.
Unless you’re given specific guidance on these issues, it’s your choice which standards you follow. The important thing is to consistently follow one standard for each issue. For example, don’t use a mixture of American and British spellings in your paper.
Additionally, you will probably be provided with specific guidelines for issues related to format (how your text is presented on the page) and citations (how you acknowledge your sources). Always follow these instructions carefully.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Revising, proofreading, and editing are different stages of the writing process .
- Revising is making structural and logical changes to your text—reformulating arguments and reordering information.
- Editing refers to making more local changes to things like sentence structure and phrasing to make sure your meaning is conveyed clearly and concisely.
- Proofreading involves looking at the text closely, line by line, to spot any typos and issues with consistency and correct them.
Whether you’re publishing a blog, submitting a research paper , or even just writing an important email, there are a few techniques you can use to make sure it’s error-free:
- Take a break : Set your work aside for at least a few hours so that you can look at it with fresh eyes.
- Proofread a printout : Staring at a screen for too long can cause fatigue – sit down with a pen and paper to check the final version.
- Use digital shortcuts : Take note of any recurring mistakes (for example, misspelling a particular word, switching between US and UK English , or inconsistently capitalizing a term), and use Find and Replace to fix it throughout the document.
If you want to be confident that an important text is error-free, it might be worth choosing a professional proofreading service instead.
If you’ve gone over the word limit set for your assignment, shorten your sentences and cut repetition and redundancy during the editing process. If you use a lot of long quotes , consider shortening them to just the essentials.
If you need to remove a lot of words, you may have to cut certain passages. Remember that everything in the text should be there to support your argument; look for any information that’s not essential to your point and remove it.
To make this process easier and faster, you can use a paraphrasing tool . With this tool, you can rewrite your text to make it simpler and shorter. If that’s not enough, you can copy-paste your paraphrased text into the summarizer . This tool will distill your text to its core message.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, December 08). The Writing Process | 5 Steps with Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved July 31, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-writing/writing-process/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to create a structured research paper outline | example, quick guide to proofreading | what, why and how to proofread, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Utility Menu
- Writing Center
- Writing Program
- Designing Essay Assignments
by Gordon Harvey
Students often do their best and hardest thinking, and feel the greatest sense of mastery and growth, in their writing. Courses and assignments should be planned with this in mind. Three principles are paramount:
1. Name what you want and imagine students doing it
However free students are to range and explore in a paper, the general kind of paper you’re inviting has common components, operations, and criteria of success, and you should make these explicit. Having satisfied yourself, as you should, that what you’re asking is doable, with dignity, by writers just learning the material, try to anticipate in your prompt or discussions of the assignment the following queries:
- What is the purpose of this? How am I going beyond what we have done, or applying it in a new area, or practicing a key academic skill or kind of work?
- To what audience should I imagine myself writing?
- What is the main task or tasks, in a nutshell? What does that key word (e.g., analyze, significance of, critique, explore, interesting, support) really mean in this context or this field?
- What will be most challenging in this and what qualities will most distinguish a good paper? Where should I put my energy? (Lists of possible questions for students to answer in a paper are often not sufficiently prioritized to be helpful.)
- What misconceptions might I have about what I’m to do? (How is this like or unlike other papers I may have written?) Are there too-easy approaches I might take or likely pitfalls? An ambitious goal or standard that I might think I’m expected to meet but am not?
- What form will evidence take in my paper (e.g., block quotations? paraphrase? graphs or charts?) How should I cite it? Should I use/cite material from lecture or section?
- Are there some broad options for structure, emphasis, or approach that I’ll likely be choosing among?
- How should I get started on this? What would be a helpful (or unhelpful) way to take notes, gather data, discover a question or idea? Should I do research?
2. Take time in class to prepare students to succeed at the paper
Resist the impulse to think of class meetings as time for “content” and of writing as work done outside class. Your students won’t have mastered the art of paper writing (if such a mastery is possible) and won’t know the particular disciplinary expectations or moves relevant to the material at hand. Take time in class to show them:
- discuss the assignment in class when you give it, so students can see that you take it seriously, so they can ask questions about it, so they can have it in mind during subsequent class discussions;
- introduce the analytic vocabulary of your assignment into class discussions, and take opportunities to note relevant moves made in discussion or good paper topics that arise;
- have students practice key tasks in class discussions, or in informal writing they do in before or after discussions;
- show examples of writing that illustrates components and criteria of the assignment and that inspires (class readings can sometimes serve as illustrations of a writing principle; so can short excerpts of writing—e.g., a sampling of introductions; and so can bad writing—e.g., a list of problematic thesis statements);
- the topics of originality and plagiarism (what the temptations might be, how to avoid risks) should at some point be addressed directly.
3. Build in process
Ideas develop over time, in a process of posing and revising and getting feedback and revising some more. Assignments should allow for this process in the following ways:
- smaller assignments should prepare for larger ones later;
- students should do some thinking and writing before they write a draft and get a response to it (even if only a response to a proposal or thesis statement sent by email, or described in class);
- for larger papers, students should write and get response (using the skills vocabulary of the assignment) to a draft—at least an “oral draft” (condensed for delivery to the class);
- if possible, meet with students individually about their writing: nothing inspires them more than feeling that you care about their work and development;
- let students reflect on their own writing, in brief cover letters attached to drafts and revisions (these may also ask students to perform certain checks on what they have written, before submitting);
- have clear and firm policies about late work that nonetheless allow for exception if students talk to you in advance.
|
A PDF version of the text above. Provides guidance on creating carefully crafted and explicit paper assignments that encourage students to write better papers
|
- Pedagogy Workshops
- Responding to Student Writing
- Commenting Efficiently
- Vocabulary for Discussing Student Writing
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- HarvardWrites Instructor Toolkit
- Additional Resources for Teaching Fellows
Module 4: Writing in College
Writing assignments, learning objectives.
- Describe common types and expectations of writing tasks given in a college class

Figure 1 . All college classes require some form of writing. Investing some time in refining your writing skills so that you are a more confident, skilled, and efficient writer will pay dividends in the long run.
What to Do With Writing Assignments
Writing assignments can be as varied as the instructors who assign them. Some assignments are explicit about what exactly you’ll need to do, in what order, and how it will be graded. Others are more open-ended, leaving you to determine the best path toward completing the project. Most fall somewhere in the middle, containing details about some aspects but leaving other assumptions unstated. It’s important to remember that your first resource for getting clarification about an assignment is your instructor—they will be very willing to talk out ideas with you, to be sure you’re prepared at each step to do well with the writing.
Writing in college is usually a response to class materials—an assigned reading, a discussion in class, an experiment in a lab. Generally speaking, these writing tasks can be divided into three broad categories: summary assignments, defined-topic assignments, and undefined-topic assignments.
Link to Learning
Empire State College offers an Assignment Calculator to help you plan ahead for your writing assignment. Just plug in the date you plan to get started and the date it is due, and the calculator will help break it down into manageable chunks.
Summary Assignments
Being asked to summarize a source is a common task in many types of writing. It can also seem like a straightforward task: simply restate, in shorter form, what the source says. A lot of advanced skills are hidden in this seemingly simple assignment, however.
An effective summary does the following:
- reflects your accurate understanding of a source’s thesis or purpose
- differentiates between major and minor ideas in a source
- demonstrates your ability to identify key phrases to quote
- shows your ability to effectively paraphrase most of the source’s ideas
- captures the tone, style, and distinguishing features of a source
- does not reflect your personal opinion about the source
That last point is often the most challenging: we are opinionated creatures, by nature, and it can be very difficult to keep our opinions from creeping into a summary. A summary is meant to be completely neutral.
In college-level writing, assignments that are only summary are rare. That said, many types of writing tasks contain at least some element of summary, from a biology report that explains what happened during a chemical process, to an analysis essay that requires you to explain what several prominent positions about gun control are, as a component of comparing them against one another.
Writing Effective Summaries
Start with a clear identification of the work.
This automatically lets your readers know your intentions and that you’re covering the work of another author.
- In the featured article “Five Kinds of Learning,” the author, Holland Oates, justifies his opinion on the hot topic of learning styles — and adds a few himself.
Summarize the Piece as a Whole
Omit nothing important and strive for overall coherence through appropriate transitions. Write using “summarizing language.” Your reader needs to be reminded that this is not your own work. Use phrases like the article claims, the author suggests, etc.
- Present the material in a neutral fashion. Your opinions, ideas, and interpretations should be left in your brain — don’t put them into your summary. Be conscious of choosing your words. Only include what was in the original work.
- Be concise. This is a summary — it should be much shorter than the original piece. If you’re working on an article, give yourself a target length of 1/4 the original article.
Conclude with a Final Statement
This is not a statement of your own point of view, however; it should reflect the significance of the book or article from the author’s standpoint.
- Without rewriting the article, summarize what the author wanted to get across. Be careful not to evaluate in the conclusion or insert any of your own assumptions or opinions.
Understanding the Assignment and Getting Started

Figure 2 . Many writing assignments will have a specific prompt that sends you first to your textbook, and then to outside resources to gather information.
Often, the handout or other written text explaining the assignment—what professors call the assignment prompt —will explain the purpose of the assignment and the required parameters (length, number and type of sources, referencing style, etc.).
Also, don’t forget to check the rubric, if there is one, to understand how your writing will be assessed. After analyzing the prompt and the rubric, you should have a better sense of what kind of writing you are expected to produce.
Sometimes, though—especially when you are new to a field—you will encounter the baffling situation in which you comprehend every single sentence in the prompt but still have absolutely no idea how to approach the assignment! In a situation like that, consider the following tips:
- Focus on the verbs . Look for verbs like compare, explain, justify, reflect , or the all-purpose analyze . You’re not just producing a paper as an artifact; you’re conveying, in written communication, some intellectual work you have done. So the question is, what kind of thinking are you supposed to do to deepen your learning?
- Put the assignment in context . Many professors think in terms of assignment sequences. For example, a social science professor may ask you to write about a controversial issue three times: first, arguing for one side of the debate; second, arguing for another; and finally, from a more comprehensive and nuanced perspective, incorporating text produced in the first two assignments. A sequence like that is designed to help you think through a complex issue. If the assignment isn’t part of a sequence, think about where it falls in the span of the course (early, midterm, or toward the end), and how it relates to readings and other assignments. For example, if you see that a paper comes at the end of a three-week unit on the role of the Internet in organizational behavior, then your professor likely wants you to synthesize that material.
- Try a free-write . A free-write is when you just write, without stopping, for a set period of time. That doesn’t sound very “free”; it actually sounds kind of coerced, right? The “free” part is what you write—it can be whatever comes to mind. Professional writers use free-writing to get started on a challenging (or distasteful) writing task or to overcome writer’s block or a powerful urge to procrastinate. The idea is that if you just make yourself write, you can’t help but produce some kind of useful nugget. Thus, even if the first eight sentences of your free write are all variations on “I don’t understand this” or “I’d really rather be doing something else,” eventually you’ll write something like “I guess the main point of this is…,” and—booyah!—you’re off and running.
- Ask for clarification . Even the most carefully crafted assignments may need some verbal clarification, especially if you’re new to a course or field. Professors generally love questions, so don’t be afraid to ask. Try to convey to your instructor that you want to learn and you’re ready to work, and not just looking for advice on how to get an A.
Defined-Topic Assignments
Many writing tasks will ask you to address a particular topic or a narrow set of topic options. Defined-topic writing assignments are used primarily to identify your familiarity with the subject matter. (Discuss the use of dialect in Their Eyes Were Watching God , for example.)
Remember, even when you’re asked to “show how” or “illustrate,” you’re still being asked to make an argument. You must shape and focus your discussion or analysis so that it supports a claim that you discovered and formulated and that all of your discussion and explanation develops and supports.
Undefined-Topic Assignments
Another writing assignment you’ll potentially encounter is one in which the topic may be only broadly identified (“water conservation” in an ecology course, for instance, or “the Dust Bowl” in a U.S. History course), or even completely open (“compose an argumentative research essay on a subject of your choice”).

Figure 3 . For open-ended assignments, it’s best to pick something that interests you personally.
Where defined-topic essays demonstrate your knowledge of the content , undefined-topic assignments are used to demonstrate your skills— your ability to perform academic research, to synthesize ideas, and to apply the various stages of the writing process.
The first hurdle with this type of task is to find a focus that interests you. Don’t just pick something you feel will be “easy to write about” or that you think you already know a lot about —those almost always turn out to be false assumptions. Instead, you’ll get the most value out of, and find it easier to work on, a topic that intrigues you personally or a topic about which you have a genuine curiosity.
The same getting-started ideas described for defined-topic assignments will help with these kinds of projects, too. You can also try talking with your instructor or a writing tutor (at your college’s writing center) to help brainstorm ideas and make sure you’re on track.
Getting Started in the Writing Process
Writing is not a linear process, so writing your essay, researching, rewriting, and adjusting are all part of the process. Below are some tips to keep in mind as you approach and manage your assignment.
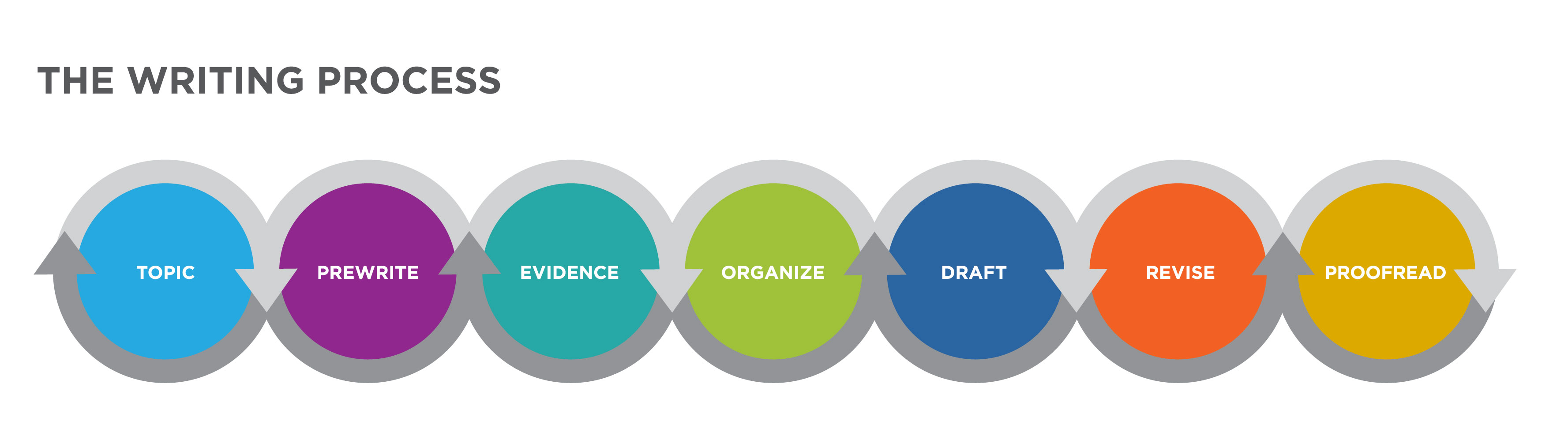
Figure 4 . Writing is a recursive process that begins with examining the topic and prewriting.
Write down topic ideas. If you have been assigned a particular topic or focus, it still might be possible to narrow it down or personalize it to your own interests.
If you have been given an open-ended essay assignment, the topic should be something that allows you to enjoy working with the writing process. Select a topic that you’ll want to think about, read about, and write about for several weeks, without getting bored.

Figure 5 . Just getting started is sometimes the most difficult part of writing. Freewriting and planning to write multiple drafts can help you dive in.
If you’re writing about a subject you’re not an expert on and want to make sure you are presenting the topic or information realistically, look up the information or seek out an expert to ask questions.
- Note: Be cautious about information you retrieve online, especially if you are writing a research paper or an article that relies on factual information. A quick Google search may turn up unreliable, misleading sources. Be sure you consider the credibility of the sources you consult (we’ll talk more about that later in the course). And keep in mind that published books and works found in scholarly journals have to undergo a thorough vetting process before they reach publication and are therefore safer to use as sources.
- Check out a library. Yes, believe it or not, there is still information to be found in a library that hasn’t made its way to the Web. For an even greater breadth of resources, try a college or university library. Even better, research librarians can often be consulted in person, by phone, or even by email. And they love helping students. Don’t be afraid to reach out with questions!
Write a Rough Draft
It doesn’t matter how many spelling errors or weak adjectives you have in it. Your draft can be very rough! Jot down those random uncategorized thoughts. Write down anything you think of that you want included in your writing and worry about organizing and polishing everything later.
If You’re Having Trouble, Try F reewriting
Set a timer and write continuously until that time is up. Don’t worry about what you write, just keeping moving your pencil on the page or typing something (anything!) into the computer.
- Outcome: Writing in College. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Writing in College: From Competence to Excellence. Authored by : Amy Guptill. Provided by : SUNY Open Textbooks. Located at : http://textbooks.opensuny.org/writing-in-college-from-competence-to-excellence/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of man writing. Authored by : Matt Zhang. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/pAg6t9 . License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- Writing Strategies. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/lumencollegesuccess/chapter/writing-strategies/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of woman reading. Authored by : Aaron Osborne. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/dPLmVV . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of sketches of magnifying glass. Authored by : Matt Cornock. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/eBSLmg . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- How to Write a Summary. Authored by : WikiHow. Located at : http://www.wikihow.com/Write-a-Summary . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- How to Write. Provided by : WikiHow. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of typing. Authored by : Kiran Foster. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/9M2WW4 . License : CC BY: Attribution

- Mailing List
- Search Search
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Resources for Teachers: Creating Writing Assignments
This page contains four specific areas:
Creating Effective Assignments
Checking the assignment, sequencing writing assignments, selecting an effective writing assignment format.
Research has shown that the more detailed a writing assignment is, the better the student papers are in response to that assignment. Instructors can often help students write more effective papers by giving students written instructions about that assignment. Explicit descriptions of assignments on the syllabus or on an “assignment sheet” tend to produce the best results. These instructions might make explicit the process or steps necessary to complete the assignment. Assignment sheets should detail:
- the kind of writing expected
- the scope of acceptable subject matter
- the length requirements
- formatting requirements
- documentation format
- the amount and type of research expected (if any)
- the writer’s role
- deadlines for the first draft and its revision
Providing questions or needed data in the assignment helps students get started. For instance, some questions can suggest a mode of organization to the students. Other questions might suggest a procedure to follow. The questions posed should require that students assert a thesis.
The following areas should help you create effective writing assignments.
Examining your goals for the assignment
- How exactly does this assignment fit with the objectives of your course?
- Should this assignment relate only to the class and the texts for the class, or should it also relate to the world beyond the classroom?
- What do you want the students to learn or experience from this writing assignment?
- Should this assignment be an individual or a collaborative effort?
- What do you want students to show you in this assignment? To demonstrate mastery of concepts or texts? To demonstrate logical and critical thinking? To develop an original idea? To learn and demonstrate the procedures, practices, and tools of your field of study?
Defining the writing task
- Is the assignment sequenced so that students: (1) write a draft, (2) receive feedback (from you, fellow students, or staff members at the Writing and Communication Center), and (3) then revise it? Such a procedure has been proven to accomplish at least two goals: it improves the student’s writing and it discourages plagiarism.
- Does the assignment include so many sub-questions that students will be confused about the major issue they should examine? Can you give more guidance about what the paper’s main focus should be? Can you reduce the number of sub-questions?
- What is the purpose of the assignment (e.g., review knowledge already learned, find additional information, synthesize research, examine a new hypothesis)? Making the purpose(s) of the assignment explicit helps students write the kind of paper you want.
- What is the required form (e.g., expository essay, lab report, memo, business report)?
- What mode is required for the assignment (e.g., description, narration, analysis, persuasion, a combination of two or more of these)?
Defining the audience for the paper
- Can you define a hypothetical audience to help students determine which concepts to define and explain? When students write only to the instructor, they may assume that little, if anything, requires explanation. Defining the whole class as the intended audience will clarify this issue for students.
- What is the probable attitude of the intended readers toward the topic itself? Toward the student writer’s thesis? Toward the student writer?
- What is the probable educational and economic background of the intended readers?
Defining the writer’s role
- Can you make explicit what persona you wish the students to assume? For example, a very effective role for student writers is that of a “professional in training” who uses the assumptions, the perspective, and the conceptual tools of the discipline.
Defining your evaluative criteria
1. If possible, explain the relative weight in grading assigned to the quality of writing and the assignment’s content:
- depth of coverage
- organization
- critical thinking
- original thinking
- use of research
- logical demonstration
- appropriate mode of structure and analysis (e.g., comparison, argument)
- correct use of sources
- grammar and mechanics
- professional tone
- correct use of course-specific concepts and terms.
Here’s a checklist for writing assignments:
- Have you used explicit command words in your instructions (e.g., “compare and contrast” and “explain” are more explicit than “explore” or “consider”)? The more explicit the command words, the better chance the students will write the type of paper you wish.
- Does the assignment suggest a topic, thesis, and format? Should it?
- Have you told students the kind of audience they are addressing — the level of knowledge they can assume the readers have and your particular preferences (e.g., “avoid slang, use the first-person sparingly”)?
- If the assignment has several stages of completion, have you made the various deadlines clear? Is your policy on due dates clear?
- Have you presented the assignment in a manageable form? For instance, a 5-page assignment sheet for a 1-page paper may overwhelm students. Similarly, a 1-sentence assignment for a 25-page paper may offer insufficient guidance.
There are several benefits of sequencing writing assignments:
- Sequencing provides a sense of coherence for the course.
- This approach helps students see progress and purpose in their work rather than seeing the writing assignments as separate exercises.
- It encourages complexity through sustained attention, revision, and consideration of multiple perspectives.
- If you have only one large paper due near the end of the course, you might create a sequence of smaller assignments leading up to and providing a foundation for that larger paper (e.g., proposal of the topic, an annotated bibliography, a progress report, a summary of the paper’s key argument, a first draft of the paper itself). This approach allows you to give students guidance and also discourages plagiarism.
- It mirrors the approach to written work in many professions.
The concept of sequencing writing assignments also allows for a wide range of options in creating the assignment. It is often beneficial to have students submit the components suggested below to your course’s STELLAR web site.
Use the writing process itself. In its simplest form, “sequencing an assignment” can mean establishing some sort of “official” check of the prewriting and drafting steps in the writing process. This step guarantees that students will not write the whole paper in one sitting and also gives students more time to let their ideas develop. This check might be something as informal as having students work on their prewriting or draft for a few minutes at the end of class. Or it might be something more formal such as collecting the prewriting and giving a few suggestions and comments.
Have students submit drafts. You might ask students to submit a first draft in order to receive your quick responses to its content, or have them submit written questions about the content and scope of their projects after they have completed their first draft.
Establish small groups. Set up small writing groups of three-five students from the class. Allow them to meet for a few minutes in class or have them arrange a meeting outside of class to comment constructively on each other’s drafts. The students do not need to be writing on the same topic.
Require consultations. Have students consult with someone in the Writing and Communication Center about their prewriting and/or drafts. The Center has yellow forms that we can give to students to inform you that such a visit was made.
Explore a subject in increasingly complex ways. A series of reading and writing assignments may be linked by the same subject matter or topic. Students encounter new perspectives and competing ideas with each new reading, and thus must evaluate and balance various views and adopt a position that considers the various points of view.
Change modes of discourse. In this approach, students’ assignments move from less complex to more complex modes of discourse (e.g., from expressive to analytic to argumentative; or from lab report to position paper to research article).
Change audiences. In this approach, students create drafts for different audiences, moving from personal to public (e.g., from self-reflection to an audience of peers to an audience of specialists). Each change would require different tasks and more extensive knowledge.
Change perspective through time. In this approach, students might write a statement of their understanding of a subject or issue at the beginning of a course and then return at the end of the semester to write an analysis of that original stance in the light of the experiences and knowledge gained in the course.
Use a natural sequence. A different approach to sequencing is to create a series of assignments culminating in a final writing project. In scientific and technical writing, for example, students could write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic. The next assignment might be a progress report (or a series of progress reports), and the final assignment could be the report or document itself. For humanities and social science courses, students might write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic, then hand in an annotated bibliography, and then a draft, and then the final version of the paper.
Have students submit sections. A variation of the previous approach is to have students submit various sections of their final document throughout the semester (e.g., their bibliography, review of the literature, methods section).
In addition to the standard essay and report formats, several other formats exist that might give students a different slant on the course material or allow them to use slightly different writing skills. Here are some suggestions:
Journals. Journals have become a popular format in recent years for courses that require some writing. In-class journal entries can spark discussions and reveal gaps in students’ understanding of the material. Having students write an in-class entry summarizing the material covered that day can aid the learning process and also reveal concepts that require more elaboration. Out-of-class entries involve short summaries or analyses of texts, or are a testing ground for ideas for student papers and reports. Although journals may seem to add a huge burden for instructors to correct, in fact many instructors either spot-check journals (looking at a few particular key entries) or grade them based on the number of entries completed. Journals are usually not graded for their prose style. STELLAR forums work well for out-of-class entries.
Letters. Students can define and defend a position on an issue in a letter written to someone in authority. They can also explain a concept or a process to someone in need of that particular information. They can write a letter to a friend explaining their concerns about an upcoming paper assignment or explaining their ideas for an upcoming paper assignment. If you wish to add a creative element to the writing assignment, you might have students adopt the persona of an important person discussed in your course (e.g., an historical figure) and write a letter explaining his/her actions, process, or theory to an interested person (e.g., “pretend that you are John Wilkes Booth and write a letter to the Congress justifying your assassination of Abraham Lincoln,” or “pretend you are Henry VIII writing to Thomas More explaining your break from the Catholic Church”).
Editorials . Students can define and defend a position on a controversial issue in the format of an editorial for the campus or local newspaper or for a national journal.
Cases . Students might create a case study particular to the course’s subject matter.
Position Papers . Students can define and defend a position, perhaps as a preliminary step in the creation of a formal research paper or essay.
Imitation of a Text . Students can create a new document “in the style of” a particular writer (e.g., “Create a government document the way Woody Allen might write it” or “Write your own ‘Modest Proposal’ about a modern issue”).
Instruction Manuals . Students write a step-by-step explanation of a process.
Dialogues . Students create a dialogue between two major figures studied in which they not only reveal those people’s theories or thoughts but also explore areas of possible disagreement (e.g., “Write a dialogue between Claude Monet and Jackson Pollock about the nature and uses of art”).
Collaborative projects . Students work together to create such works as reports, questions, and critiques.
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
The writing process, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
Understanding Your Assignment

“What is expected of me?” Writing a strong paper requires that you fully understand your assignment, and answering this question is the first crucial step in the academic writing process. What is your professor asking of you? The suggestions below will assist you as you determine what is expected of you.
Assignment Comprehension Tips
Click on the tabs below for tips on how to fully understand what is expected of you.
- STUDY THE DETAILS
- CREATE A TANGIBLE RESOURCE
- IMPLEMENT A TIMETABLE
- HIGHLIGHT KEY WORDS
- STAY WITHIN CLOSE PROXIMITY OF DETAILS
- RELY ON SUPPORT
Read the instructions line-by-line to familiarize yourself initially. Reading them aloud helps too.
Print out the instructions if necessary and highlight key information, such as the due date, word count, format, or citation style. Print and study the rubric, if available. The rubric reveals how you will be graded for each part of your essay and will give you clues on how exactly to structure your writing.
Plug the due date into your smartphone calendar and request a reminder notification. In addition, work backward from the due date and schedule specific weeks for planning, prewriting, researching, writing, getting feedback, and rewriting.
Circle any key phrases that can guide your actions.
Keep your assignment instructions next to you as you work on informal prewriting exercises and planning so you avoid getting off track.
When in doubt, ask your professor. Your professors want you to succeed and welcome any remaining questions about assignment expectations.
Finding Purpose and Meaning
The purpose of the preparative steps above is to create a foundation for nuanced writing. Some additional questions can help you reach a deeper understanding of the assignment. Ask yourself the following questions:
What is the purpose of this assignment and why is it important?
Who is my audience my professor classmates professionals in my field of study, how will this contribute to my knowledge and growth as a writer, what timeline should i assign myself for the gradual development of this work.
Table 2.1 below shows you how to identify keywords and expectations from the directive wording of the assignment. These key phrases are often associated with essay questions, as well as informal and formal papers. As a note, the table is based on Benjamin Bloom’s cognitive objectives.
Table 2.1 Assignment Wording and Expectations
| Define, label, list, name, repeat, order, arrange, memorize | Memorize, recall, and present information |
| Describe, indicate, restate, explain, review, summarize, classify | Interpret information in your own words |
| Apply, illustrate, prepare, solve, use, sketch, operate, practice, calculate | Apply knowledge to new situations |
| Analyze, categorize, compare, test, distinguish, examine, contrast | Break down knowledge into parts and show relationships among parts |
| Arrange, compose, formulate, organize, plan, assemble, construct | Bring together parts of knowledge to form a whole; build relationships for new situations |
| Appraise, evaluate, conclude, judge, predict, compare, score | Make judgments based on criteria; support, confirm preferences |
| Use supporting examples, cite passages from the text, paraphrase, summarize | Quote or paraphrase to support what you have written |
| Provide corroborating evidence, reference other works, research, cite examples from case studies | Use outside research to support your thesis or hypothesis |
Once you understand your assignment and decide on what approach to take, you can move on to identifying and targeting your audience.
Key Takeaways
If you take the steps to retain, plan, and understand the meaning behind your writing assignment, you will increase your confidence and success as a writer.
Focusing on key words and phrases will provide clues on what actions to take while planning the structure and content of your essay.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
- Utility Menu
GA4 Tracking Code
Gen ed writes, writing across the disciplines at harvard college, teaching the elements of writing assignments.
Overview: How Unpacking the Elements Translates into Lesson Planning
In Unpacking the Elements we try to break down prompts into the essential features common to nearly every assignment (writing or not), and in doing so the goal was primarily two-fold: to help instructors identify the role of each element in their own assignments and how clearly each element is communicated in their prompts; and to give students and instructors a shared, simple vocabulary for talking about the goals and expectations of assignments. In this section, the goal is to move from designing effective prompts and sharing them with students to using prompts as a road map for teaching in the classroom. If you’ve done the assignment prompt decoder and thought about elements in a specific prompt, you were maybe left with a few questions. For example:
- What does it look like to teach each element and give students practice with them?
- What is the best order to teach the elements in?
- How can I scaffold smaller exercises or give students feedback along the way?
- What’s the timing of all of this look like within the framework of a real term?
In the pages of this section we take up these questions, first laying out more generally how teaching through the elements looks in the classroom before taking a deeper dive into a handful of the more common—and increasingly complex—types of academic writing assignments. For each kind of assignment, you’ll find sample timelines and sequences, along with out-of-the-box activities and generalizable advice on teaching with writing (“tips” and “pitfalls to avoid”).
The advice and examples in this section are meant to be flexible enough to adapt to a wide range of real-life teaching scenarios and pedagogical approaches, but they all reflect a handful of guiding principles about the interrelated ways that assignment prompts "work": they create the context for learning experiences by serving as a touchstone for student-teacher discussions about the specific goals and expectations of the learning experience at hand, and they help keep instructors and students alive to what those goals and expectations are—and how their time together is an ongoing, well-supported engagement with them.
Three Key Principles for Teaching Writing in the Classroom
Students should always be “writing the paper”.
If your lesson plan is drawn from the actual assignment students are working on at any point in the term (whether it’s a smaller “now” response paper or a smaller part of a “bigger” project due in six weeks), then nearly every homework assignment or in-class activity is writing the paper. The purpose of section will always be more clear if students recognize that every meeting is a chance to practice relevant skills or make progress on an assignment. And of course, that recognition is only possible if students understand what the goals of the assignment they're working on are, what skills are relevant to meeting those goals, and what kinds of steps reflect progress toward them. With that in mind, it’s helpful to start with the Assignment Decoder for Students .
Prompts don’t (and shouldn’t be asked to) speak for themselves
The assignment prompt decoders linked throughout this site are meant to give course heads, TFs & TAs, and students a way of assessing how clearly a prompt is communicating its elements. For course heads and instructors, this might lead to a revision of the prompt or clarifications in class or meetings of the teaching team. For students, it might lead to questions in section, emails to an instructor, or asking a fellow student for input. Whatever doing the decoder leads to—and whether or not the decoder is used at all—it’s crucial to keep in mind that prompts don’t speak for themselves, no matter how clear they are: they’re a framework for, and hopefully an invitation to discussion about what it will look and feel like to do an assignment well. But what about a really clear prompt—doesn’t it save class time if students can just read it on their own? It’s a fair question, and the fair response is that we can’t know whether students have understood the really clear prompt unless we have a discussion with them about it. At that point, of course, we’re back to discussing the prompt, and the upside is this: spending class time working through prompts is actually a reliably efficient way to make subsequent classes more effective.
You can’t do it all, and you don’t need to
If you and your students are on the same page about the goals and priorities of an assignment, then you’re freed up to engage in some backward design triage: How much time is there until the likely deadline? How many sections are there to work with? What are the essential elements that need teaching and practice? What’s a good place to start? When giving feedback, it’s almost as unhelpful to just write “A-” without comments as it is to fill the margins with comments or append a novella’s worth of reflection to the end of a student’s essay. In both cases, it’s unclear what the rubric for feedback is and how they reflect the priorities of this assignment. And the same goes for teaching this assignment: You should find the sequence of in-class activities and formative assessments that best balance what’s necessary for students to succeed with what’s possible given the time and bandwidth available to you and your students. The general advice and sample trajectories for assignments in this section are meant to make that balance feel both attainable and much more than “good enough”—it’s what great teachers aim for.
- DIY Guides for Analytical Writing Assignments

- Types of Assignments
- Unpacking the Elements of Writing Prompts
- The Steps of Teaching the Most Common Types of Writing Assignments
- Giving Feedback to Students
Assignment Decoder
Search form
You are here.
- Implementing Writing in Your Course
How to Design Successful Writing Assignments

As writing instructors ourselves, we are all too familiar with the many difficulties that come with assigning writing. It’s difficult to create meaningful assignments that help students learn what you want them to learn. And despite all the labor we put into it, students can still express frustration and confusion over writing assignments. It is tempting to ask, “Why bother?”
However, while thoughtful writing instruction tied to learning outcomes takes time to implement, that initial effort can lead to a huge time savings over the long run. Some writing you do not even need to grade! Once you know some of the key components of writing assignment design, you will be able to create a collection of high-value teaching materials that you can adapt for years to come. Also, your students will learn more, and will be better equipped to handle complexity. With regular writing practice and targeted feedback, over time they will become more authoritative participants and contributors in your field.
Designing successful writing assignments involves some or all of the following six strategies:
- Explicitly State Assignment Goals
- Tie Assignment Goals to Course Goals
- Create Antiracist Writing Assignments
- Offer Clear Instructions for Completion
- Clarify Expectations About Genre, Audience, and Formatting
- Provide Examples of the Kinds of Writing You Assign
- Asses Your Own Work
1. Explicitly State Assignment Goals
Are students “writing to learn” key course concepts from course materials or “learning to write” a new and specific form of communication in the class, such as a lab report or business memo? Or do you want your assignment to do some of both? Try to be as specific as possible when thinking about the assignment’s purpose. We encourage you to even jot down some of your desired outcomes. Being detailed about what you want students to gain from completing the assignment will help you create clear instructions for the assignment.
The example below is a strong example of a “writing to learn” assignment. In this assignment the instructor uses words such as "read," “explore,” “shape,” and “reflect” to clearly indicate that the act of composing in this assignment is more about attaining knowledge than it is about the creation of a final product.
From a prompt for a personal narrative in a science writing course:
All scientists have intellectual, cultural, and linguistic histories. For the sake of “neutrality” and “objectivity,” apprentices are often trained to separate themselves from these histories, especially when it comes to conducting and communicating research. This assignment asks you to read examples of scientists’ memoirs in various genres and then you will compose your own narrative in the mode of your choice, exploring how your identities, investments, and intellectual interests have shaped your science training and your trajectory as a scientist. This assignment serves as a form of reflection, orientation to/within a scientific field, and even as a professional credential (if desirable).
Back to top
2. Tie Assignment Goals to Course Goals
While you know why you are assigning a particular writing assignment, your students may not. Being clear about how completing the writing assignment will help your students learn can help create expectations and motivation for students. Without a clear understanding of how a writing assignment will help them learn, students may feel that they are being assigned useless "busywork."
Example 1 :
The example below is drawn from the final paper assignment for a course called “Imagining and Dreaming: Indigenous Futures,” taught by Lydia Heberling. In this assignment, the instructor not only clearly shows students how the assignment aligns with the course content, but it also reminds students how the third section of the course builds upon content learned in earlier units.
Throughout the quarter we have examined various writing practices that affirm the ongoing existence of American Indian peoples in spite of settler colonial attempts to remove, erase, and eradicate them. In our first sequence, we reflected on the relationship between place and identity and learned from Momaday that the land possesses stories from the past that can be accessed through interaction with and memories of those places.
In our second sequence, we examined a contemporary activist moment to deepen our understanding of the ongoing relational formations between Indigenous peoples and how those relations revitalize cultures from the brink of extinction. In learning about how various tribes worked together to protect a valuable natural resource by employing media and storytelling practices to garner support and attention, we learned that regardless of the outcome, activist moments like Standing Rock demonstrate a strong trans-Indigenous community that continues to survive in spite of ongoing settler colonial tactics of dispossession and erasure.
In this third, and last sequence, we are focusing on imagining, or dreaming about, vibrant Indigenous futures. Athabascan poet and scholar (and UW professor) Dian Million defines dreaming the following way [. . .]
Your task i n this next assignment is to return to the place you described in Paper 1, imagine what that place looks like 100 years from now. . .
Example 2 :
Here’s a second example of a writing assignment, created by Jen Malone for a course on writing in environmental science, which clearly demonstrates to students how the writing assignment both builds on previous course content and how it will help students cultivate research skills that they will be able to use in future writing assignments.
Thus far in this class, we’ve written an Op-Ed about ecotourism, and we will be moving into writing a short research paper on the topic of your choice later on in the quarter. But first, we’re going to do something a bit different.
Learning to research well is largely about practice—both in terms of growing accustomed to search engines (particularly scholarly ones) and library databases, and in terms of learning to plug different versions of your research terms into these search engines/databases until you find useful sources. Using research well is largely about figuring out how to analyze your sources--particularly in combination with one another, as a body of research. In order to practice both of these skills (which will totally help us to prepare for Paper #3, later on in the quarter), for Paper #2 we will. . .
3. Create Antiracist Writing Assignments
Antiracist writing instruction is usually discussed in relation to assessment, but it should be considered earlier than that, during assignment creation (just as it should be considered as key elements of curriculum and class culture). Antiracist writing assignment design can be pursued in two ways: through the subject matter, or content, of the writing assignments; and through your values around language use. Some brief suggestions for each follow.
Promoting antiracist subject matter in writing assignments:
Take a step back and discuss knowledge frameworks in your course and in your field. Every discipline has knowledge traditions and methods that can be problematic. How did these traditions come to be? Who do they serve, and who do they harm?
Avoid reductionist binaries when discussing complex questions. For example, framing a question like "What are the pros and cons of conducting medical research without subjects' knowledge or consent?" may lead students to consider both sides as having equal moral weight. A more specific (so a particular context can be considered) and open-ended (so students are not led to one or the other answer) question might work better. For example, "What are some of the ethical considerations of conducting flu vaccine clinical trials without participants' consent?"
Give students opportunities to explore their own identities in relation to the course content. Drawing personal connections not only helps foster deeper learning, but it can also cultivate a student’s sense of belonging in the field. It may also help you see how your field might serve some but not others.
Encourage students to engage academic and non-academic source material. Have discussions about what “counts” as authoritative information in your field, and why.
Promoting linguistic justice in writing assignments:
As this site from Wesleyan College recommends, “Centralize rhetorical situations and writing contexts rather than language standards in your writing classroom.” If you show that all language use (content, structure, syntax, vocabulary, style) is based on authorial choices made in particular contexts and for particular audiences, then you can help bust the myth of the universal standard of “academic English.”
Encourage students to use their own linguistic traditions whenever possible. For example, let students freewrite in a native language or dialect. Encourage them to draw connections between their own language backgrounds and the disciplinary discourse you are teaching. This is called translanguaging, and it can be a powerful tool for learning.
Avoid penalizing language use. If there is a certain style or vocabulary you want students to use, be explicit about why discourse is used that way, and how it conveys discipline-specific knowledge.
Further reading: 10 Ways to Tackle Linguistic Bias in Our Classrooms (Inside HigherEd)
4. Offer Clear Instructions for Completion
Investigative or writing techniques that seem obvious to you—such as making an argument, analyzing, evaluating—might mean something different to students from outside your specific discipline. Being clear about what you mean when you use certain terms can help students navigate an assignment more successfully. While it might feel clunky or obvious, including this information in an assignment will help steer your students in the right direction and minimize miscommunication.
In the following excerpt from a prompt for a writing-in-history course taught by Sumyat Thu, the instructor asks students to use research in their papers, and then clearly describes, and supports with examples from the class and library resources, what counts as appropriate source material.
This essay is based on research. Students are expected to use primary sources and secondary works in developing their essays. We do not frown on the use of on-line resources ; indeed, some very good reference works ( identified on the history librarian Ms. Mudrock's research guide) are available as on-line books, and the library has e-book versions of Paul Spickard's Almost All Aliens . Nonetheless, we strongly urge students to utilize the very rich materials available in the UW Libraries, particularly scholarly books and articles. The UW Libraries' on-line catalog can be explored with keyword searches, and such indexes as America: History and Life (again, see Ms. Mudrock’s website) are very helpful as well.
In this second example, again by Jen Malone, we see how the instructor not only indicates what chronological steps students must take to complete the assignment, but also how she includes thorough and clear instructions for how students can complete each step.
So, the first step you’ll need to take will be to choose a topic . You may wish to choose the same topic you’ll be using for your research paper in ENVIR 100 (if you’ve chosen that option—if so, please follow any instructions they’ve given you for choosing a topic for that), or something related to environmental science that simply interests you, or a topic from the following list of suggestions:
- GMOs (particularly with regards to the ecosystem and/or biodiversity),
- The environmental impact of meat production
- Bees and Colony Collapse Disorder
The second step you’ll need to take will be to do the research —you’ll need to find some sources (via library search engines, Google scholar, etc.). Keep some notes or a log of this process, since you’ll have to talk about how this went for you in your final report. Then you’ll need to read/skim the sources you’ve selected, and then you’ll need to create an annotated bibliography in which you list and briefly summarize those sources. An annotated bibliography is a particularly handy step when performing research, or when writing a paper that involves research. Basically, it is a list of the sources you intend to use for your paper (like a Works Cited page, you may use either MLA or APA format), but with the addition of a substantial paragraph (or two, if you wish) beneath each entry in which you summarize, and often evaluate, the source. This will help you to consider the sources you find as a body of research, and this makes using sources easier because you’ll have these initial notes handy as you write your report.
After you find and skim through your sources, the third step you’ll need to take will be to write the report .
- In the first section of the report, you’ll want to talk about your research process (What was this like? What was easy for you and what was difficult? What did you learn? What search terms did you use? How did those terms change?).
- In the second section of the report, you’ll want to talk about the body of research as a whole (How would you describe the issues/terms/debates surrounding the topic? What did you find? What do these sources indicate—both in terms of conclusions drawn and questions raised? How do these sources fit together and/or differ? What did you find most interesting?)
- In the third section of the report, you’ll want to take a moment to consider how this body of research fits it with what you’re learning in ENVIR 100 and where you might take the topic in a future paper (How do you see what you found regarding this topic as relating to what has been discussed in class thus far? What are the stakes of this topic and for whom? What aspects of this topic do we seem to know little about? What are the questions you still have about this topic? And, finally, now that you’ve read through this body of research, if you were going to write a paper on this topic, what might your basic argument be?). We’ll discuss this all in more detail next week, after you’ve compiled your sources.
Note: the second example may be a lot longer of a writing prompt than many of us are used to. This is not a bad thing. In fact, students tend to really appreciate such clear instruction and it reduces the amount of time you will spend clarifying confusion about what is expected. Also, instructions like these can be easily re-purposed for other, similar assignments in the future so you will not have to reinvent the wheel each time.
5. Clarify Expectations About Genre, Audience, and Formatting
Students will approach your writing assignment with varying knowledge and experience. Unless you have already instructed students explicitly in class about the knowledge and skills needed to complete a writing assignment, you cannot assume that students will already possess that knowledge. While clear, explicit prompts are essential, we also strongly urge you to discuss in class the genre you are assigning as well. Offer examples, both from professionals in the field, and from former students. The more exposure students have to the kinds of writing you want to see, the the more inclusive and accessible your assignments will be. We know of a history TA who said that one of her students, an engineering major, wasn't clear on the nature of a historiography, so he turned in his paper formatted like a technical report! This is an understandable mistake for a student to make, and providing examples can prevent mistakes like this from happening in your own classroom.
Below are two examples of how instructors communicate their expectations about genre, audience, and formatting to students. The first example is less helpful for students because it leaves key parts of the instructor’s expectations vague. (What is the writing assignment’s audience? What citation style does the instructor prefer? Is the works cited page part of the assignment or not?) The second example provides more detail for students.
Example 1: Paper must be 4-5 pages double spaced and must include a works cited page.
Example 2 : T he business memo should be fo rmatted according to the parameters we have discussed: no more than two pages long , typed, single-spaced with one space between paragraphs , with standard margins, in Times New Roman font (12 point), written for an audience of industry professionals.
6. Provide Examples of the Kinds of Writing You Assign
Studies have shown that examples can be a powerful learning tool in writing instruction. We recommend that instructors distribute examples of both successful and unsuccessful student writing to their students and explain why the examples are successful or unsuccessful.
Ask students who have submitted successful assignments if you can borrow their work as examples for future classes. Be sure to remove students’ identifying information from the assignments before they are given to future students.
If you do not have examples of unsuccessful writing (remember, sharing even anonymized student writing without the author's consent would be unethical), you can alternatively create a list of common pitfalls and mistakes to avoid when completing the writing assignment. Distribute the list to your students. Be sure to ground these pitfalls in terms of higher order issues specific to this genre, rather than just distributing a one-size-fits-all personal list of writing pet peeves.
Ask students which examples help them learn the genre, and which do not. Over time your students will help you curate a really great collection of samples.
Create occasional reading assignments where you ask students to find and analyze examples of writing by professionals in the field. What makes them effective or ineffective examples of the genre? What are some of the text's defining characteristics? These kinds of analyses can really help students improve their own writing.
7. Assess Your Own Work
Assessment is not just for student writing: it’s also important to assess the efficacy of the assignments you create. If student work is disappointing or students have struggled with an assignment, it most likely a result of ineffective assignment design. Please remember: everyone , even seasoned writing instructors, has assignments that do not go well initially. That is normal and ok!
We recommend that you engage in self-reflection as to why your assignment did not turn out well, and make tweaks to the assignment and/or grading criteria as needed. Here are some questions to ask yourself to reflect on your writing assignments.
Did many students turn in work which did not meet your expectations? In what specific ways did they fall short?
Did many students struggle with the assignment or a particular piece of the assignment? Where, exactly, did they struggle and how do you know?
Were many students surprised or dissatisfied by their grades on the assignment? Why do you think this happened?
Strategies for understanding what went wrong
Ask your students, either in class, on Canvas, or in a survey like a Google Form, to debrief the assignment. What was easy for them about the assignment? What did they learn from it? What was challenging? What was unclear?
Take writing assignments to writing centers such as OWRC or CLUE to get student feedback on updated or streamlined assignments. Student writing tutors can be a great resource-- they've seen hundreds of writing assignments!
Next guide: Supporting Academic Integrity
What Makes a Good Writing Assignment?
Getting Started
Why include writing in my courses?
What is writing to learn?
WTL Activities
What is writing to engage?
What is writing in the disciplines?
WID Assignments
Useful Knowledge
What should I know about rhetorical situations?
Do I have to be an expert in grammar to assign writing?
What should I know about genre and design?
What should I know about second-language writing?
What teaching resources are available?
What should I know about WAC and graduate education?
Assigning Writing
What makes a good writing assignment?
How can I avoid getting lousy student writing?
What benefits might reflective writing have for my students?
Using Peer Review
Why consider collaborative writing assignments?
Do writing and peer review take up too much class time?
How can I get the most out of peer review?
Responding to Writing
How can I handle responding to student writing?
Sample Grading Sheets
How can writing centers support writing in my courses?
What writing resources are available for my students?
Using Technology
How can computer technologies support writing in my classes?
Designing and Assessing WAC Programs
What is a WAC program?
What designs are typical for WAC programs?
How can WAC programs be assessed?
More on WAC
Where can I learn more about WAC?
Surprisingly, teachers have been known to assign writing tasks without articulating to themselves what the task is supposed to do for students. Good writing assignments always start with a clear goal that the teacher can express, usually on the assignment sheet so that students understand the goal as well.
Good writing assignments also often take shape by thinking backwards. In effect, teachers ask themselves, "What do I want to read at the end of this assignment?" By working from what they anticipate the final product to look like, teachers can give students detailed guidelines about both the writing task and the final written product.
Five Principles
As you think about making up writing assignments, use these five principles:
- Tie the writing task to specific pedagogical goals, particularly those articulated in the overall course goals.
- Note rhetorical aspects of the task, i.e., audience, purpose, writing situation.
- Break down the task into manageable steps.
- Make all elements of the task clear.
- Include grading criteria on the assignment sheet.
Principle 1. Writing Should Meet Teaching Goals
Asking questions like these about your assignment will help guarantee that writing tasks tie directly to your teaching goals in the class:
- What specific course objectives will the writing assignment meet?
- Will informal or formal writing better meet teaching goals?
- Will students be writing to learn course material or writing conventions in the discipline or both?
- Does the assignment make sense?

Work Backward from Goals
Although it might seem awkward at first, working backwards from what you hope the final drafts will look like often produces the best assignment sheets. We recommend jotting down several points that will help you with this step in writing your assignments:
- Why should students write in your class? State your goals for the final product as clearly and concretely as possible.
- Determine what writing products will meet these goals and fit your teaching style/preferences.
- Note specific skills that will contribute to the final product.
- Sequence activities (reading, researching, writing) to build toward the final product.
Beyond the Basics
Writing tasks fill many different roles for students, so defining good writing assignments begins with the specific instructional context. For that reason, the first key to writing a good assignment is tying the task to the specific course goals. After taking your class and its goals into account, though, several other principles can improve the writing tasks you assign and the writing you get from students.
Principle 2. Consider the Rhetorical Situation
Perhaps most important, as noted in the five principles section, is to consider the rhetorical situation. By this, writing experts mean that you should think carefully about the audience you want students to write to as well as the particular genre or format for the final document and the larger context for the document.
Setting up your writing assignment so that the target reader is someone other than you, the teacher, might result in the most improvement in student writing. Students, after all, have had extensive experience writing to teachers, and students know that teachers are a "captive" audience. Your job mandates that you read carefully and respond to their texts. Chinn & Hilgers (2000) explain this role for the teachers as often limited to "corrector." However, instructors can move beyond the corrector role into a "collaborator" role by varying writing tasks, encouraging peer collaboration, and emphasizing professional contexts for writing. So for students, the teacher is not necessarily a reader or audience that will motivate the best possible work on a writing task. Indeed, Hilgers et al . (1999) report that their interview research with 33 upper-division students yielded an intriguing statistic: "56% of the interviewees also described one or more nonteacher audiences" (328) for their academic tasks. In many instances, the assignment called for a hypothetical audience other than the teacher, but even when the assignment didn't prompt students to write for readers other than the teacher, students directed their work toward "an individual they believed has specific content knowledge such as a CEO, coworker, or technician" (328).
Although some experts (Freedman et al ., 1994) argue that setting up a fictitious scenario with a specified audience does not motivate students any more highly than simply writing for the teacher, other practitioners across the disciplines have seen improvement in student writing when they use cases with embedded audiences for students' documents. (See, for instance, Brumberger, 2004; Cass & Fernandez, 2008; Stevens, 2005; Sulewski, 2003.)
A further extension of this move toward providing rich writing contexts beyond the teacher involves writing tasks that actually target real readers. Many senior design projects and management projects in engineering and natural resources involve pairing students with actual clients so that students must take into account the particular needs of their readers. Across many disciplines, teachers are investigating alternative methods to connect undergraduate writers with real audiences, including client-based partnerships (Kiefer & Leff, 2008; Kreth, 2005; Planken & Kreps, 2006;) and service-learning opportunities (Addams et al ., 2010; Bourelle, 2012), among other options.
But even if your particular class doesn't allow you to pair students with actual clients or other readers, consider ways in which you can create a meaningful context with readers beyond the teacher in the classroom (see, for example, Ward, 2009). Chamely-Wiik et al . (2012), for instance, describe in detail how, drawing on materials from The Council of Writing Program Administrators and The Foundation for Critical Thinking, they developed a case study writing context for first-year general chemistry students. As they explain,
Our initial case-study assignment, used for the first two years of the course, required students to explore the scientific principles involved in the Bhopal disaster where thousands of people died in an industrial chemical accident.... The second assignment, used in the third year, required students to formulate and defend an argument whether research in the field of cold fusion should continue to be supported. (504)
Students write with a local audience of classmates and a larger institutional context of the university community in mind. Students responded positively on affective surveys, a typical reaction to carefully designed writing tasks. More significantly, "students in this chemistry course outperformed the majority of students across all undergraduate levels at the university" (506). (For other examples of science students writing to lay audiences, see Martin, 2010; McDermott& Kuhn, 2011; Moni et al ., 2007; Sivey & Lee, 2008).
In addition to audience concerns, students also benefit from understanding how and why a particular format or genre helps them communicate with a target audience (especially when we think of genres as those recurring rhetorical reactions to typical communicative situations). From YouTube videos in organic chemistry (Franz, 2012) to position papers in public relations (Powell, 2012) to posters in physiology (Mulnix, 2003), teachers are helping students to write in genres that immediately connect them with the real readers of their future professional settings. (See also Blakeslee, 2001; Guilford, 2001; Jebb, 2005; LeBigot & Rouet, 2007; Mizrahi, 2003; Motavalli et al ., 2007; Schwartz et al ., 2004; Wald et al ., 2009.)
Why does this attention to audience and genre seem to matter so much to student writing? In recent years, several studies (Adam, 2000; Beaufort, 2004; Belfiore et al ., 2004; Freedman & Adam, 2000; Spinuzzi, 2010) have explored the reasons why writers attentive to specific contexts are more successful. In particular, workplace literacy and socio-cognitive apprenticeship theory (among related theoretical perspectives) both emphasize the role that knowledgeable mentors within a workplace play as they initiate newcomers to the communicative context. (See especially Beaufort, 2000, and Ding, 2008, for social apprenticeship studies and Paretti, 2008, on situated learning and activity theory.) As Dias et al . (1999) explain, writing is not a fixed set of skills that we learn once and then simply plug into as we need to communicate. Rather,
Written discourse... is regularized but not fixed; fluid, flexible, and dynamic; emerging and evolving in exigency and action; reflecting and incorporating social needs, demands, and structures, and responsive to social interpretations and reinterpretations of necessarily shifting, complex experiences. (23)
And, as a result of the fluidity of discourse in varied workplace settings, writers themselves should be prepared for major development of their communication skills when they enter new workplaces. MacKinnon's qualitative study (2000) of new analysts and economists at the Bank of Canada showed that
Overall, the writing-related changes were considerable, consequential, and a shock for some participants: "It's like going to China," said one. For most of the ten participants, the complex totality of the writing-related changes they experienced added up to a "sea change": a major shift in their understanding of what writing is an does in an organization, a revised understanding of the roles they saw for themselves as writing workers and as working writers, and often major changes in various aspects of the macro writing process. (50)
When students have opportunities as undergraduates or graduate/professional students to anticipate these major shifts, then the transitions to workplaces of all sorts become easier. For the most part, moreover, students recognize that apprenticeship learning in academic settings provides both more structured scaffolding of writing tasks and lower-stakes learning. They thus embrace the learning opportunities when offered to them in academic classes.
Principle 3. Break Down the Task into Manageable Steps
The fifth principle noted in the general section on "what makes a good writing assignment?" is to break down the task into manageable steps. Many teachers approach this element of good assignment design by thinking carefully about assignment sequence. One particularly thorough explanation of this process appears in Leydens & Santi (2006). This writing specialist and geoscientist take up the details of designing assignments with an eye to course goals. They also consider the importance of not overwhelming teachers and students (the Less is More approach) as they explain their specific process of questioning their assignments (pp. 493-497). (See also Lord, 2009, and Greasley & Cassidy, 2010.)
Scaffolded assignments, such as the agricultural economics assignment noted in the Additional Resources section, help students reach a larger goal by asking them to collect resources in stages. A final stage requires that students transform each of the earlier stages in a final document. Sequenced assignments, on the other hand, each stand independently, but each task builds on particular skills and challenges to enable students to meet a larger set of goals. Herrington (1997) describes a scaffolded assignment (71-72) with a preliminary plan for a major project followed by an annotated bibliography, early draft (with cover note focused on successes and challenges thus far) and final draft (with cover note). Mulnix & Mulnix (2010) also describe a similar argumentative assignment that uses sequenced tasks to repeat and reinforce critical thinking skills. See also Sin et al . (2007) for a sequence in accounting, Howell (2007) in materials science, Fencl (2010) on a sequence in physics, Zlatic et al . (2000) on pharmaceutical education, and Harding (2005) on freshman mechanical engineering. Coe (2011), on the other hand, describes a series of scaffolded writing tasks to help students build argument skills in philosophy, Alaimo et al . (2009) explain their project for sophomore organic chemistry students, and Lillig (2008) looks at upper-division chemistry.
Principles 4 and 5. Make the Assignment Clear to Students
A well-designed assignment will make the elements of the task clear to students. This includes identifying relevant intermediate assignments and activities, such as topic proposals or literature reviews for longer assignments, as well as providing information about relevant writing, research, and collaboration processes. In general, it is also advisable to list grading criteria on the assignment sheet. Making the assignment clear to students will help them better understand the scope and challenge of the assignment. It also is likely to produce better learning and performance.
Resource: Sample Assignment from an Advanced Undergraduate Agricultural Economics Seminar
Good analytical writing is a rigorous and difficult task. It involves a process of editing and rewriting, and it is common to do a half dozen or more drafts. Because of the difficulty of analytical writing and the need for drafting, we will be completing the assignment in four stages. A draft of each of the sections described below is due when we finish the class unit related to that topic (see due dates on syllabus). I will read the drafts of each section and provide comments; these drafts will not be graded but failure to pass in a complete version of a section will result in a deduction in your final assignment grade. Because of the time both you and I are investing in the project, it will constitute one-half of your semester grade.
Content, Concepts and Substance
Papers will focus on the peoples and policies related to population, food, and the environment of your chosen country. As well as exploring each of these subsets, papers need to highlight the interrelations among them. These interrelations should form part of your revision focus for the final draft. Important concepts relevant to the papers will be covered in class; therefore, your research should be focused on the collection of information on your chosen country or region to substantiate your themes. Specifically, the paper needs to address the following questions.
1. Population
Developing countries have undergone large changes in population. Explain the dynamic nature of this continuing change in your country or region and the forces underlying the changes. Better papers will go beyond description and analyze the situation at hand. That is, go behind the numbers to explain what is happening in your country with respect to the underlying population dynamics: structure of growth, population momentum, rural/urban migration, age structure of population, unanticipated populations shocks, etc. DUE: WEEK 4.
What is the nature of food consumption in your country or region? Is the average daily consumption below recommended levels? Is food consumption increasing with economic growth? What is the income elasticity of demand? Use Engel's law to discuss this behavior. Is production able to stay abreast with demand given these trends? What is the nature of agricultural production: traditional agriculture or green revolution technology? Is the trend in food production towards self-sufficiency? If not, can comparative advantage explain this? Does the country import or export food? Is the politico-economic regime supportive of a progressive agricultural sector? DUE: WEEK 8.
3. Environment
This is the third issue to be covered in class. It is crucial to show in your paper the environmental impact of agricultural production techniques as well as any direct impacts from population changes. This is especially true in countries that have evolved from traditional agriculture to green revolution techniques in the wake of population pressures. While there are private benefits to increased production, the use of petroleum-based inputs leads to environmental and human health related social costs which are exacerbated by poorly defined property rights. Use the concepts of technological externalities, assimilative capacity, property rights, etc., to explain the nature of this situation in your country or region. What other environmental problems are evident? Discuss the problems and methods for economically measuring environmental degradation. DUE: WEEK 12.
4. Final Draft
The final draft of the project should consider the economic situation of agriculture in your specified country or region from the three perspectives outlined above. Key to such an analysis are the interrelationships of the three perspectives. How does each factor contribute to an overall analysis of the successes and problems in agricultural policy and production of your chosen country or region? The paper may conclude with recommendations, but, at the very least, it should provide a clear summary statement about the challenges facing your country or region. DUE: WEEK15.
Adam, C. (2000). "What do we learn from the readers? Factors in determining successful transitions between academic and workplace writing." In P. Dias and A. Paré (Eds.), Transitions: Writing in Academic and Workplace Settings ; pp. 167-182. Cresskill, NJ: Hampton Press.
Addams, L.H., Woodbury, D., Allred, T., & Addams, J. (2010). Developing Student Communication Skills while Assisting Nonprofit Organizations. Business Communication Quarterly, 73 (3), 282-290.
Alaimo, P.J., Bean, J.C., Langenhan, J.M., & Nichols, L. (2009). Eliminating Lab Reports: A Rhetorical Approach for Teaching the Scientific Paper in Sophomore Organic Chemistry. The WAC Journal, 20 , 17-32.
Beaufort, A. (2004). Developmental gains of a history major: A case for building a theory of disciplinary writing expertise. Research in the Teaching of English, 39 (2), 136-185.
Beaufort, A. (2000). Learning the trade: A social apprenticeship model for gaining writing expertise. Written Communication, 17 (2), 185-224.
Belfiore, M.E., Defoe, T.A., Folinsbee, S., Hunter, J., & Jackson, N.S. (2004). Reading Work: Literacies in the New Workplace. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Blakeslee, A.M. (2001). Bridging the workplace and the academy: Teaching professional genres through classroom-workplace collaborations. Technical Communication Quarterly, 10 (2), 169-192.
Bourelle, T. (2012). Bridging the Gap between the Technical Communication Classroom and the Internship: Teaching Social Consciousness and Real-World Writing. Journal of Technical Writing and Communication, 42 (2), 183-197.
Brumberger, E.R. (2004). The "Corporate Correspondence Project": Fostering Audience Awareness and Extended Collaboration. Business Communication Quarterly, 67 (3), 349-58.
Cass, A.G., & Fernandes, C.S.T. (2008). Simulated conference submissions: A technique to improve student attitudes about writing. 2008 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference, Vols. 1-3 ; pp. 1535-1540.
Chamely,Wiik, D.M., Kaky, J.E., & Galin, J. (2012). From Bhopal to cold fusion: A case-study approach to writing assignments in honors general chemistry. Journal of Chemical Education, 89 (4), 502-508.
Chinn, P.W.U., & Hilgers. T.L. (2000). From corrector to collaborator: The range of instructor roles in writing-based natural and applied science classes. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 37 (1), 3-25.
Coe, C.D. (2011). Scaffolded writing as a tool for critical thinking: Teaching beginning students how to write arguments. Teaching Philosophy, 34 (1), 33-50.
Dias, P., Freedman, A., Medway, P., & Paré. (1999). "Introduction: Researching Writing at School and at Work." Worlds Apart: Acting and Writing in Academic and Workplace Contexts; pp. 3-13. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Dias, P., Freedman, A., Medway, P., & Paré. (1999). "Situating Writing." Worlds Apart: Acting and Writing in Academic and Workplace Contexts; pp. 17-41. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Ding, H. (2008). The use of cognitive and social apprenticeship to teach a disciplinary genre: Initiation of graduate students into NIH grant writing. Written Communication, 25 (1), 3-52.
Fencl, H.S. (2010). Development of Students' Critical-Reasoning Skills through Content-Focused Activities in a General Education Course. Journal of College Science Teaching, 39 (5), 56-62.
Franz, A.K. (2012). Organic chemistry YouTube writing assignment for large lecture classes. Journal of Chemical Education, 89 (4), 497-501.
Freedman, A., & Adam, C. (2000). "Write where you are: Situating learning to write in university and workplace settings." In P. Dias and A. Paré (Eds.), Transitions: Writing in Academic and Workplace Settings ; pp. 31-60. Cresskill, NJ: Hampton Press.
Freedman, A., Adam, C., & Smart, G. (1994). Wearing suits to class: Simulating genres and simulations as genre. Written Communication, 11 (2), 193-226.
Greasley, P., & Cassidy, A. (2010). When it comes round to marking assignments: how to impress and how to 'distress' lecturers. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 35 (2), 173-189.
Guildford, W.H. (2001). Teaching peer review and the process of scientific writing. Advances in Physiology Education, 25 (3), 167-175.
Harding, B.A. (2005). "A simple mechanism to teach a complex practitioner knowledge set." Innovations in Engineering Education 2005 ; pp. 479-486. ASME.
Herrington, A. (1997). "Developing and responding to major writing projects ." In M.D. Sorcinelli & P. Elbow (Eds.), Writing to learn: Strategies for assigning and responding to writing across the disciplines , pp. 67-75. New directions for teaching the learning, No. 69 . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Hilgers, T.L., Hussey, E.L., & Stitt-Bergh, M. (1999). "As you're writing, you have these epiphanies": What college students say about writing and learning in their majors. Written Communication, 16 (3), 317-353.
Howell, P.R. (2007). "Writing to specification: An approach to teaching scientific literacy, and a prelude to writing 'The World of Materials' essays." In J.E.E. Baglin (Ed.), Proceedings of the Symposium and Forum Education in Materials Science, Engineering and Technology ; pp. 247-289.
Kiefer, K., & Leff, A. (2008). "Client-based writing about science: Immersing science students in real writing contexts." Across the Disciplines , vol. 5 .
Kreth, M.L. (2005). A Small-Scale Client Project for Business Writing Students: Developing a Guide for First-Time Home Buyers. Business Communication Quarterly, 68 (1), 52-59.
LeBigot, L., & Rouet, J.F. (2007). The impact of presentation format, task assignment, and prior knowledge on students' comprehension of multiple online documents. Journal of Literacy Research, 39 (4), 445-470.
Leydens, J., & Santi, P. (2006). Optimizing faculty use of writing as a learning tool in geoscience education. Journal of Geoscience Education , 54 (4), 491-502.
Lillig, J.W. (2008). Writing across the semester: A non-standard term paper that encourages critical data analysis in the upper-division chemistry classroom. Journal of Chemical Education, 85 (10), 1392-1394.
Lord, S.M. (2009). Integrating effective "writing to communicate" experiences in engineering courses: Guidelines and examples. International Journal of Engineering Education, 25 (1), 196-204.
MacKinnon, J. (1993). "Becoming a rhetor: Developing writing ability in a mature, writing-intensive organization." In R. Spilka (Ed.), Writing in the Workplace: New Research Perspectives ; pp. 41-55. Carbondale: Southern Illinois UP.
Martin, A.M. (2010). "Astronomy and writing: A first-year cosmology course for nonmajors." In J. Barnes, D.A. Smith, M.G. Gibbs, and J.G. Manning (Eds.), Science Education and Outreach: Forging a Path to the Future . Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series, Vol. 431; pp. 368-371. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
McDermott, M., & Kuhn, M. (2011). Using writing for alternative audiences in a college integrated science course. Journal of College Science Teaching, 41 (1), 40-45.
Mizrahi, J. (2003). Teaching technical writing to university students using the medical report. STC's 50 th Annual Conference Proceedings ; 190-193.
Moni, R.W., Hryciw, D.H., Poronnik, P., & Moni, K.B. (2007). Using explicit teaching to improve how bioscience students write to the lay public. Advances in Physiology Education, 31 (2), 167-75.
Motavalli, P.P., Patton, M.D., & Miles, R.J. (2007). Use of web-based student extension publications to improve undergraduate student writing skills. Journal of Natural Resources and Life Sciences Education, 36 : 95-102.
Mulnix, A.B. (2003). Investigations of Protein Structure and Function Using the Scientific Literature: An Assignment for an Undergraduate Cell Physiology Course. Cell Biology Education, 2 (4), 248-255.
Mulnix, J.W., & Mulnix, M.J. (2010). Using a writing portfolio project to teach critical thinking skills. Teaching Philosophy, 33 (1), 27-54.
Paretti, M.C. (2008). Teaching communication in capstone design: The role of the instructor in situated learning. Journal of Engineering Education, 97 (4), 491-503.
Planken, B., & Kreps, A.J. Raising Students' Awareness of the Implications of Multimodality for Content Design and Usability: The Web Site Project. Business Communication Quarterly, 69 (4), 421-425.
Powell, V. (2012). Revival of the Position Paper: Aligning Curricula and Professional Competencies. Communication Teacher, 26 (2), 96-103.
Schwartz, R.S., Lederman, N.G., & Crawford, B.A. (2004). Developing view of nature of science in an authentic context: An explicit approach to bridging the gap between nature of science and scientific inquiry. Science Education, 88 (4), 610-645.
Sin, S., Jones, A., & Petocz, P. (2007). Evaluating a method of integrating generic skills with accounting content based on a functional theory of meaning. Accounting and Finance, 47 (1), 143-163.
Sivey, J.D., & Lee, C.M. (2008). Using popular magazine articles to teach the art of writing for nontechnical audiences. Journal of Chemical Education, 85 (1), 55-58.
Spinuzzi, C. (2010). Secret sauce and snake oil: Writing monthly reports in a highly contingent environment. Written Communication, 27 (4), 363-409.
Stevens, B. (2005). The Car Accident: An Exercise in Persuasive Writing. Communication Teacher, 19 (2), 62-67.
Sulewski, R. (2003). Integrating communication and technical material int eh first-year engineering curriculum: The role of the laboratory. STC's 50 th Annual Conference Proceedings ; 176-178.
Wald, H.S., Davis, S.W., Reis, S.P., Monroe, A.D., & Borkan, J.M. (2009). Reflecting on reflections: Enhancement of medical education curriculum with structured field notes and guided feedback. Academic Medicine, 84 (7), 830-837.
Ward, M., Sr. (2009). Squaring the learning circle: Cross-classroom collaborations and the impact of audience on student outcomes in professional writing. Journal of Business and Technical Communication, 23 (1), 61-82.
Zlatic, T.D., Nowak, D.M., & Sylvester, D. (2000). Integrating general and professional education through a study of herbal products: An intercollegiate collaboration. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 64 (1), 83-94.
Related Web Sites
WAC@NIU ( http://www.engl.niu.edu/wac/ ) has two useful items in their archives under "Ccomputer-intensive assignments" in the first Key Web Sites section of links:
- "checklist, a series of questions to help plan writing assignments"
(If the questions under rhetorical situation confuse you, call our Writing Center for a quick explanation.)
- "setting up a writing assignment"
Writing@CSU includes a much more detailed explanation of how and why to design writing assignments at http://writing.colostate.edu/guides/teaching/fys/assignmentwriting.cfm .
- MyU : For Students, Faculty, and Staff
Writing Across the Curriculum
Ask a question
- Research & Assessment
- Writing Plans
- WEC Liaisons
- Academic Units
- Engage with WEC
- Teaching Resources
- Teaching Consultations
- Faculty Writing Resources

- Scaffolding and Sequencing Writing Assignments
Effective writing assignments, aligned with core learning goals, can help students build on their prior knowledge, apply key concepts introduced in lectures, labs, readings, and discussions, and anticipate future learning. While it is important to make the why behind the assignment clear to students, it’s also important to consider the when of the assignment. This page offers some guidelines for scaffolding and sequencing writing assignments.
Scaffolding and sequencing are closely related terms. Scaffolding assignments entails breaking longer writing activities into shorter tasks. Sequencing assignments refers to the specific ordering of those writing tasks. Scaffolding and sequencing can be used to establish discrete stages within one longer assignment, and they can be used more broadly to organize an entire semester of writing.
Options for Scaffolding and Sequencing
While it may not always be feasible to scaffold and sequence writing assignments, here are four options for how one might do so:
1. Scaffold and sequence assignments to move from smaller, discrete tasks to more complex ones. For example, a literature review is a complex writing assignment—often assigned in capstone-level courses—that requires the integration of multiple skills, such as careful reading, annotating, summarizing, and synthesizing. To support student writers in their development of a literature review, an instructor might scaffold the project into shorter tasks focused on reading, summarizing, and synthesizing. These short tasks provide an opportunity for the instructor to offer formative feedback and identify potential problems or challenges. Those tasks might then be sequenced into writing assignments that begin with a summary of a source, followed by an annotated bibliography, before culminating in the literature review. As seen in this example, complex tasks can be scaffolded by:
- Writing short, single-task papers (e.g. a methods section of a scientific paper) before writing longer ones with multiple dimensions (e.g. a scientific paper that includes the IMRAD structure.)
- Summarizing a text before analyzing, interpreting, or criticizing a text.
- Summarizing multiple readings before comparing or synthesizing two or more readings.
- Explaining a basic concept before applying that concept to new problems or cases.
- Explaining one or more author’s argument or theory and evidence before putting these arguments and theories into discussion and/or before developing one’s own position on the issue.
2. Scaffold and sequence a key assignment into parts with which students might struggle that you can schedule as times for targeted writing instruction. For example, is there a research component? If so, schedule times for students to bring in critiques of their sources to discuss in groups. Are you asking them to analyze a problem? Schedule time to explain the methods of analysis in your field and have them apply it to their developing paper in a quick, informal writing assignment .
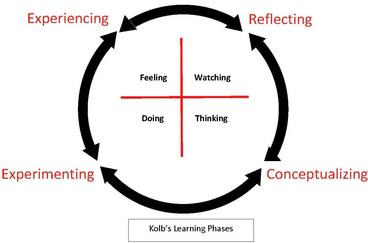
3. Scaffold and sequence assignments so they begin with concrete tasks before moving into reflective, abstract, and active ones. Drawing on David Kolb’s work (1985) with learning phases , John Bean (2011) offers a useful overview of the kinds of writing assignments that might align with ways of thinking, learning, and knowing about your course topic:
Concrete Experience Assignments: Learners are introduced to new concepts and issues through watching a film or demonstration, playing a game, doing field observations, and so forth.
These may include non- or minimally graded writing that provides practice with expected critical and/or innovative thinking or records the learner’s personal observations, thoughts, and feelings during the initial experiences; raises questions; and expresses puzzlement. Read more about informal writing assignments .
Reflective Observation Assignments: Learners reconsider concepts and issues after reading, listening to lectures, participating in class discussions, and hearing different points of view.
These may include exploratory writing, such as journal entries, that allow students to connect new material to their personal experiences and what they’ve learned previously; personal pieces based on autobiographical experiences with a topic, problem, or concept; personal reflections that encourage a questioning, open-ended, thinking-aloud-on-paper approach. Read more about informal, out-of-class writing and reflective writing .
Abstract Conceptualization Assignments: Learners try to achieve an abstract understanding of the concepts and issues by mastering and internalizing their components and seeing the relationship between new material and other concepts and issues.
These may include academic, argument-based, analytical, thesis-driven papers; concept maps; role-playing assignments.
Active Conceptualization Assignments: Learners actively use newly acquired concepts to solve problems by applying them to new situations.
These may include position papers based on cases that use new concepts; write-ups of students’ laboratory or field research using the concepts; proposals applying new concepts and knowledge to solve real-world problems; creative pieces demonstrating understanding of new material.
It’s important to note that these learning phases involving concrete, reflective, and abstract thinking are not meant to imply a hierarchy of value for each activity and the forms of writing associated with it. Rather, the sequencing of such tasks may be more productive for writers by moving from local to outward concerns.
4. Scaffold and sequence assignments to repeat and measure progress. There are very few skills that can be mastered in one writing assignment. Having learners write more than one case study, more than one technical memo, or more than one explication essay will allow them to develop increased control over the term.
Scaffolding and Sequencing across the Semester
The following writing assignments were developed for a course on medical anthropology. Here the instructor has scaffolded and sequenced the writing tasks, so that student writers will first define a key concept (structural violence), then analyze the key concept in a specific context, and then apply it to a course of action.
Writing Assignment 1 (Definition Essay): Paul Farmer introduces the idea of “structural violence,” a useful concept for thinking about the diagnosis of poor health and injustice around the world. Yet the term is not widely recognized or understood. In this paper, define and describe the concept of structural violence, and illustrate it with an example. Include a textual quote (of your choice) from Farmer’s essay that provides support for your definition and description.

Writing Assignment 2 (Op-Ed Essay): For the second essay cycle, imagine that you are invited to write a 3-page guest editorial for a newspaper or magazine of your choosing. Your Op-Ed must concern a contemporary issue involving health injustice and structural violence.
Writing Assignment 3 (An Action Alert): Write an action alert essay that does not exceed five typed pages. While your essay needs to be coherent, it does not have to “look” like a conventional essay; for example, you may organize your paper according to categories, ones that will help your readers to find the information they want when they reread your alert. As with your op-ed, your action alert should target a specific audience of readers; however, unlike the op-ed, you are now writing to an audience that is generally sympathetic to your views. Your purpose for writing is to inform readers of the issue and to offer a specific course of action you think will help begin to solve the problem.
- African American & African Studies
- Agronomy and Plant Genetics
- Animal Science
- Anthropology
- Applied Economics
- Art History
- Carlson School of Management
- Chemical Engineering and Materials Science
- Civil, Environmental, and Geo- Engineering
- College of Biological Sciences
- Communication Studies
- Computer Science & Engineering
- Construction Management
- Curriculum and Instruction
- Dental Hygiene
- Apparel Design
- Graphic Design
- Product Design
- Retail Merchandising
- Earth Sciences
- Electrical and Computer Engineering
- Environmental Sciences, Policy and Management
- Family Social Science
- Fisheries, Wildlife, and Conservation Biology
- Food Science and Nutrition
- Geography, Environment and Society
- German, Nordic, Slavic & Dutch
- Health Services Management
- Horticultural Science
- Hubbard School of Journalism and Mass Communication
- Industrial and Systems Engineering
- Information Technology Infrastructure
- Mathematics
- Mechanical Engineering
- Medical Laboratory Sciences
- Mortuary Science
- Organizational Leadership, Policy, and Development
- Political Science
- School of Architecture
- School of Kinesiology
- School of Public Health
- Spanish and Portuguese Studies
- Speech-Language-Hearing Sciences
- Theatre Arts & Dance
- Youth Studies
- New Enrollments for Departments and Programs
- Legacy Program for Continuing Units
- Writing in Your Course Context
- Syllabus Matters
- Mid-Semester Feedback Strategies
- Designing Effective Writing Assignments
- Writing Assignment Checklist
- Informal, Exploratory Writing Activities
- 5-Minute Revision Workshops
- Reflective Memos
- Conducting In-Class Writing Activities: Notes on Procedures
- Now what? Responding to Informal Writing
- Teaching Writing with Quantitative Data
- Commenting on Student Writing
- Supporting Multilingual Learners
- Teaching with Effective Models of Writing
- Peer Response Protocols and Procedures
- Using Reflective Writing to Deepen Student Learning
- Conferencing with Student Writers
- Designing Inclusive Writing Assigments
- Addressing a Range of Writing Abilities in Your Courses
- Effective Grading Strategies
- Designing and Using Rubrics
- Running a Grade-Norming Session
- Working with Teaching Assistants
- Managing the Paper Load
- Teaching Writing with Sources
- Preventing Plagiarism
- Grammar Matters
- What is ChatGPT and how does it work?
- Incorporating ChatGPT into Classes with Writing Assignments: Policies, Syllabus Statements, and Recommendations
- Restricting ChatGPT Use in Classes with Writing Assignments: Policies, Syllabus Statements, and Recommendations
- What do we mean by "writing"?
- How can I teach writing effectively in an online course?
- What are the attributes of a "writing-intensive" course at the University of Minnesota?
- How can I talk with students about the use of artificial intelligence tools in their writing?
- How can I support inclusive participation on team-based writing projects?
- How can I design and assess reflective writing assignments?
- How can I use prewritten comments to give timely and thorough feedback on student writing?
- How can I use online discussion forums to support and engage students?
- How can I use and integrate the university libraries and academic librarians to support writing in my courses?
- How can I support students during the writing process?
- How can I use writing to help students develop self-regulated learning habits?
- Submit your own question
- Short Course: Teaching with Writing Online
- Five-Day Faculty Seminar
- Past Summer Hunker Participants
- Resources for Scholarly Writers
- Consultation Request
- Faculty Writing Groups
- Further Writing Resources
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1-College Writing
Common Types of Writing Assignments
While much of the writing you did in high school may have been for an English or literature class, in college, writing is a common form of expression and scholarship in many fields and thus in many courses.
You may have to write essays, reflections, discussion board posts, or research papers in your history, biology, psychology, art history, or computer science classes.
Writing assignments in college vary in length, purpose, and the relationship between the writer (you) and the topic. Sometimes you may be asked to gather information and write a report on your findings . Sometimes you may be asked to compare opinions expressed by experts. You might be asked to answer a question or state your position and defend it with evidence . Some assignments require a mixture of several of these tasks.
When a writing assignment is mentioned in the syllabus of a course, make sure you understand the assignment long before you begin to do it. The university’s Writing Center recommends that you note the vocabulary used in assignment descriptions and make sure you understand what actions certain words suggest or require. You should also talk to peers in your class to compare understandings and expectations.
The university’s Writing Center consultants will help you with questions about an assignment and how to ask your instructor for more information if necessary. They will help you strengthen your writing, give you feedback on your ideas, and offer suggestions for organizing your content. They can tell you if you are appropriately using sources.
The Writing Center is not only for students who have questions or are puzzled about assignments. It offers support to experienced writers, too. Faculty and graduate students routinely schedule sessions with Writing Center consultants.
Strong, experienced writers enjoy conversation about their writing decisions and find it helpful to have an outside reader for their work.
Conferences with a writing consultant can be face-to-face or online.
If you are uneasy about talking with your instructor, make an appointment at the Writing Center: https://cstw.osu.edu/writing-center
Common characteristics of writing in college:
- Based on evidence
- Is written for a very or moderately knowledgeable audience rather than general public
- Style is formal, objective, often technical
- Uses conventional formatting
- Documents evidence using a professional citation style
(From: Lunsford & Ruszkiewicz, p. 367)
| : Explain why something typically happens or may have happened in the past. | |
| Write about someone’s work by comparing it to another work (or works). Discuss the significance of the similarities. | |
| Write about someone’s work by comparing and contrasting it to another work (or works) and discuss the significance of these similarities and differences. | |
| Write about the argument or reasoning of an author’s work. Evaluate. | |
| Write about your interpretation of the meaning or significance of literary work (novel, play, poem, short story). In the visual arts, we use the term “critique,” for writing that does this about films, paintings, etc. | |
| Explain the steps involved in producing something. | |
| Write about the strategies an author used to express meaning or achieve certain results. | |
| Write a summary/evaluation of each source that you used in a project or paper. Summarize the main point(s) or arguments, and the topics covered. Next, evaluate (assess) its value to the field or to your topic. | |
| (Review of the Literature) | Write about several works that contribute to your topic. Discuss how they contribute by summarizing their main points. (At the graduate-level, the literature review provides important background information, with a focus on existing publications, for a research topic.)
|
| Write about a work studied in class changed your thinking or challenges your assumptions. This writing is personal, drawing on your reactions, feelings, or experiences, in a way that shows a change or progression in thinking. | |
| Write a (usually lengthy) paper in which you answer a question, support a position or argument on an issue, or propose a solution to a problem. Your writing is based on your own ideas as well as research (opinions, facts, interviews, information) collected from sources). | |
| Write what you think based on your own experience, opinions, and ideas. Refer to specific ideas or information mentioned in whatever you are responding to. | |
| Take a position on an author’s work and support your position with evidence from the author’s work as well as some research on what others have said about it. | |
| Find a theme or idea that allows you to group together two or more texts that may be different in opinions, ideas, or influences, and explain what organizes them under this theme. (Syntheses can be organized around a thesis or an argument.) | |
| Write a shortened version of something in your own words, focusing only on the main points. Most summaries are written objectively, with no personal opinions from the writer of the summary. There are many different kinds of summaries, depending on the discipline. |
An Introduction to Choosing & Using Sources Copyright © 2015 by Teaching & Learning, Ohio State University Libraries is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

4 Key Points for Effective Assignment Writing

Methodology
By Christina Desouza
Writing an effective assignment is more of an art than a science. It demands critical thinking, thorough research, organized planning, and polished execution. As a professional academic writer with over four years of experience, I've honed these skills and discovered proven strategies for creating standout assignments.
In this article, I will delve into the four key steps of assignment writing, offering detailed advice and actionable tips to help students master this craft.
1. Start With Research
In-depth research is the cornerstone of any high-quality assignment. It allows you to gain a profound understanding of your topic and equip yourself with relevant data, compelling arguments, and unique insights.
Here's how to do it right:
● Diversify Your Sources
Don't limit yourself to the first page of Google results. Make use of academic databases like JSTOR , Google Scholar , PubMed , or your school's online library. These resources house a plethora of scholarly articles, research papers, and academic books that can provide you with valuable information.
● Verify Information
Remember, not all information is created equal. Cross-check facts and data from multiple reliable sources to ensure accuracy. Look for consensus among experts on contentious issues.
● Stay Organized
Keep track of your resources as you go. Tools like Zotero or Mendeley can help you organize your references and generate citations in various formats. This will save you from scrambling to find sources when you're wrapping up your assignment.
1. Prepare Assignment Structure

Creating a well-planned structure for your assignment is akin to drawing a roadmap. It helps you stay on track and ensures that your ideas flow logically. Here's what to consider:
● Develop an Outline
The basic structure of an assignment includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should present the topic and establish the purpose of your assignment. The body should delve into the topic in detail, backed by your research. The conclusion should summarize your findings or arguments without introducing new ideas.
● Use Subheadings
Subheadings make your assignment easier to read and follow. They allow you to break down complex ideas into manageable sections. As a rule of thumb, each paragraph should cover one idea or argument.
● Allocate Word Count
Assignments often come with word limits. Allocate word count for each section of your assignment based on its importance to avoid overwriting or underwriting any part.
1. Start Assignment Writing
Writing your assignment is where your research and planning come to fruition. You now have a robust foundation to build upon, and it's time to craft a compelling narrative.
Here's how to accomplish this:
● Write a Gripping Introduction
Your introduction is the gateway to your assignment. Make it captivating. Start with a hook—a surprising fact, an interesting quote, or a thought-provoking question—to grab your readers' attention. Provide an overview of what your assignment is about and the purpose it serves. A well-crafted introduction sets the tone for the rest of the assignment and motivates your readers to delve deeper into your work.
● Develop a Comprehensive Body
The body of your assignment is where you delve into the details. Develop your arguments, present your data, and discuss your findings. Use clear and concise language. Avoid jargon unless necessary. Each paragraph should cover one idea or argument to maintain readability.
● Craft a Convincing Conclusion
Your conclusion is your final chance to leave an impression on your reader. Summarize your key findings or arguments without introducing new ideas. Reinforce the purpose of your assignment and provide a clear answer to the question or problem you addressed in the introduction. A strong conclusion leaves your readers with a sense of closure and a full understanding of your topic.
● Write Clearly
Use straightforward sentences and avoid jargon. Your goal is to communicate, not to confuse. Tools like Hemingway Editor can help ensure your writing is clear and concise.
● Use Paraphrasingtool.ai
Paraphrasingtool.ai is an AI-powered tool that can enhance your assignment writing. It reformulates your sentences while preserving their meaning. It not only helps you avoid plagiarism but also enhances the readability of your work.
● Cite Your Sources
Citations are a critical part of assignment writing. They acknowledge the work of others you've built upon and demonstrate the depth of your research. Always include in-text citations and a bibliography at the end. This not only maintains academic integrity but also gives your readers resources to delve deeper into the topic if they wish.
1. Review and Proofread The Assignment
Reviewing and proofreading are the final but critical steps in assignment writing. They ensure your assignment is free from errors and that your ideas are coherently presented. Here's how to do it effectively:
● Take a Break
After you finish writing, take a break before you start proofreading. Fresh eyes are more likely to spot mistakes and inconsistencies.
● Read Aloud
Reading your work aloud can help you identify awkward phrasing, run-on sentences, and typos. You're more likely to catch errors when you hear them, as it requires a different type of processing than reading silently.
● Use Proofreading Tools
Digital tools like Grammarly can be your second pair of eyes, helping you spot grammatical errors, typos, and even issues with sentence structure. However, don't rely solely on these tools—make sure to manually review your work as well.
Effective assignment writing is a skill that takes practice to master. It requires meticulous research, organized planning, clear writing, and careful proofreading. The steps and tips outlined in this article are by no means exhaustive, but they provide a solid framework to start from.
Remember, there is always room for improvement. Don't be disheartened by initial challenges. Each assignment is an opportunity to learn, grow, and sharpen your writing skills. So, be persistent, stay curious, and keep refining your craft. With time and practice, you will find yourself writing assignments that are not just excellent, but truly outstanding.


Designing Writing Assignments
Designing Writing Assignments designing-assignments
As you think about creating writing assignments, use these five principles:
- Tie the writing task to specific pedagogical goals.
- Note rhetorical aspects of the task, i.e., audience, purpose, writing situation.
- Make all elements of the task clear.
- Include grading criteria on the assignment sheet.
- Break down the task into manageable steps.
You'll find discussions of these principles in the following sections of this guide.
Writing Should Meet Teaching Goals
Working backwards from goals, guidelines for writing assignments, resource: checksheets, resources: sample assignments.
- Citation Information
To guarantee that writing tasks tie directly to the teaching goals for your class, ask yourself questions such as the following:
- What specific course objectives will the writing assignment meet?
- Will informal or formal writing better meet my teaching goals?
- Will students be writing to learn course material, to master writing conventions in this discipline, or both?
- Does the assignment make sense?
Although it might seem awkward at first, working backwards from what you hope the final papers will look like often produces the best assignment sheets. We recommend jotting down several points that will help you with this step in writing your assignments:
- Why should students write in your class? State your goals for the final product as clearly and concretely as possible.
- Determine what writing products will meet these goals and fit your teaching style/preferences.
- Note specific skills that will contribute to the final product.
- Sequence activities (reading, researching, writing) to build toward the final product.
Successful writing assignments depend on preparation, careful and thorough instructions, and on explicit criteria for evaluation. Although your experience with a given assignment will suggest ways of improving a specific paper in your class, the following guidelines should help you anticipate many potential problems and considerably reduce your grading time.
- Explain the purpose of the writing assignment.
- Make the format of the writing assignment fit the purpose (format: research paper, position paper, brief or abstract, lab report, problem-solving paper, etc.).
II. The assignment
- Provide complete written instructions.
- Provide format models where possible.
- Discuss sample strong, average, and weak papers.
III. Revision of written drafts
Where appropriate, peer group workshops on rough drafts of papers may improve the overall quality of papers. For example, have students critique each others' papers one week before the due date for format, organization, or mechanics. For these workshops, outline specific and limited tasks on a checksheet. These workshops also give you an opportunity to make sure that all the students are progressing satisfactorily on the project.
IV. Evaluation
On a grading sheet, indicate the percentage of the grade devoted to content and the percentage devoted to writing skills (expression, punctuation, spelling, mechanics). The grading sheet should indicate the important content features as well as the writing skills you consider significant.
Visitors to this site are welcome to download and print these guidelines
Checksheet 1: (thanks to Kate Kiefer and Donna Lecourt)
- written out the assignment so that students can take away a copy of the precise task?
- made clear which course goals this writing task helps students meet?
- specified the audience and purpose of the assignment?
- outlined clearly all required sub-parts of the assignment (if any)?
- included my grading criteria on the assignment sheet?
- pointed students toward appropriate prewriting activities or sources of information?
- specified the format of the final paper (including documentation, headings or sections, page layout)?
- given students models or appropriate samples?
- set a schedule that will encourage students to review each other's drafts and revise their papers?
Checksheet 2: (thanks to Jean Wyrick)
- Is the assignment written clearly on the board or on a handout?
- Do the instructions explain the purpose(s) of the assignment?
- Does the assignment fit the purpose?
- Is the assignment stated in precise language that cannot be misunderstood?
- If choices are possible, are these options clearly marked?
- Are there instructions for the appropriate format? (examples: length? typed? cover sheet? type of paper?)
- Are there any special instructions, such as use of a particular citation format or kinds of headings? If so, are these clearly stated?
- Is the due date clearly visible? (Are late assignments accepted? If so, any penalty?)
- Are any potential problems anticipated and explained?
- Are the grading criteria spelled out as specifically as possible? How much does content count? Organization? Writing skills? One grade or separate grades on form and content? Etc.
- Does the grading criteria section specifically indicate which writing skills the teacher considers important as well as the various aspects of content?
- What part of the course grade is this assignment?
- Does the assignment include use of models (strong, average, weak) or samples outlines?
Sample Full-Semester Assignment from Ag Econ 4XX
Good analytical writing is a rigorous and difficult task. It involves a process of editing and rewriting, and it is common to do a half dozen or more drafts. Because of the difficulty of analytical writing and the need for drafting, we will be completing the assignment in four stages. A draft of each of the sections described below is due when we finish the class unit related to that topic (see due dates on syllabus). I will read the drafts of each section and provide comments; these drafts will not be graded but failure to pass in a complete version of a section will result in a deduction in your final paper grade. Because of the time both you and I are investing in the project, it will constitute one-half of your semester grade.
Content, Concepts and Substance
Papers will focus on the peoples and policies related to population, food, and the environment of your chosen country. As well as exploring each of these subsets, papers need to highlight the interrelations among them. These interrelations should form part of your revision focus for the final draft. Important concepts relevant to the papers will be covered in class; therefore, your research should be focused on the collection of information on your chosen country or region to substantiate your themes. Specifically, the paper needs to address the following questions.
- Population - Developing countries have undergone large changes in population. Explain the dynamic nature of this continuing change in your country or region and the forces underlying the changes. Better papers will go beyond description and analyze the situation at hand. That is, go behind the numbers to explain what is happening in your country with respect to the underlying population dynamics: structure of growth, population momentum, rural/urban migration, age structure of population, unanticipated populations shocks, etc. DUE: WEEK 4.
- Food - What is the nature of food consumption in your country or region? Is the average daily consumption below recommended levels? Is food consumption increasing with economic growth? What is the income elasticity of demand? Use Engel's law to discuss this behavior. Is production able to stay abreast with demand given these trends? What is the nature of agricultural production: traditional agriculture or green revolution technology? Is the trend in food production towards self-sufficiency? If not, can comparative advantage explain this? Does the country import or export food? Is the politico-economic regime supportive of a progressive agricultural sector? DUE: WEEK 8.
- Environment - This is the third issue to be covered in class. It is crucial to show in your paper the environmental impact of agricultural production techniques as well as any direct impacts from population changes. This is especially true in countries that have evolved from traditional agriculture to green revolution techniques in the wake of population pressures. While there are private benefits to increased production, the use of petroleum-based inputs leads to environmental and human health related social costs which are exacerbated by poorly defined property rights. Use the concepts of technological externalities, assimilative capacity, property rights, etc. to explain the nature of this situation in your country or region. What other environmental problems are evident? Discuss the problems and methods for economically measuring environmental degradation. DUE: WEEK 12.
- Final Draft - The final draft of the project should consider the economic situation of agriculture in your specified country or region from the three perspectives outlined above. Key to such an analysis are the interrelationships of the three perspectives. How does each factor contribute to an overall analysis of the successes and problems in agricultural policy and production of your chosen country or region? The paper may conclude with recommendations, but, at the very least, it should provide a clear summary statement about the challenges facing your country or region. DUE: WEEK15.
Landscape Architecture 3XX: Design Critique
Critical yet often overlooked components of the landscape architect's professional skills are the ability to critically evaluate existing designs and the ability to eloquently express him/herself in writing. To develop your skills at these fundamental components, you are to professionally critique a built project with which you are personally and directly familiar. The critique is intended for the "informed public" as might be expected to be read in such features in The New York Times or Columbus Monthly ; therefore, it should be insightful and professionally valid, yet also entertaining and eloquent. It should reflect a sophisticated knowledge of the subject without being burdened with professional jargon.
As in most critiques or reviews, you are attempting not only to identify the project's good and bad features but also to interpret the project's significance and meaning. As such, the critique should have a clear "point of view" or thesis that is then supported by evidence (your description of the place) that persuades the reader that your thesis is valid. Note, however, that your primary goal is not to force the reader to agree with your point of view but rather to present a valid discussion that enriches and broadens the reader's understanding of the project.
To assist in the development of the best possible paper, you are to submit a typed draft by 1:00 pm, Monday, February 10th. The drafts will be reviewed as a set and will then serve as a basis of an in-class writing improvement seminar on Friday, February 14th. The seminar will focus on problems identified in the set of drafts, so individual papers will not have been commented on or marked. You may also submit a typed draft of your paper to the course instructor for review and comment at any time prior to the final submission.
Final papers are due at 2:00 pm, Friday, February 23rd.
Animal/Dairy/Poultry Science 2XX: Comparative Animal Nutrition
Purpose: Students should be able to integrate lecture and laboratory material, relate class material to industry situations, and improve their problem-solving abilities.
Assignment 1: Weekly laboratory reports (50 points)
For the first laboratory, students will be expected to provide depth and breadth of knowledge, creativity, and proper writing format in a one-page, typed, double-spaced report. Thus, conciseness will be stressed. Five points total will be possible for the first draft, another five points possible will be given to a student peer-reviewer of the draft, and five final points will be available for a second draft. This assignment, in its entirety, will be due before the first midterm (class 20). Any major writing flaws will be addressed early so that students can grasp concepts stressed by the instructors without major impact on their grades. Additional objectives are to provide students with skills in critically reviewing papers and to acquaint writers and reviewers of the instructors' expectations for assignments 2 and 3, which are weighted much more heavily.
Students will submit seven one-page handwritten reports from each week's previous laboratory. These reports will cover laboratory classes 2-9; note that one report can be dropped and week 10 has no laboratory. Reports will be graded (5 points each) by the instructors for integration of relevant lecture material or prior experience with the current laboratory.
Assignment 2: Group problem-solving approach to a nutritional problem in the animal industry (50 points)
Students will be divided into groups of four. Several problems will be offered by the instructors, but a group can choose an alternative, approved topic. Students should propose a solution to the problem. Because most real-life problems are solved by groups of employees and (or) consultants, this exercise should provide students an opportunity to practice skills they will need after graduation. Groups will divide the assignment as they see fit. However, 25 points will be based on an individual's separate assignment (1-2 typed pages), and 25 points will be based on the group's total document. Thus, it is assumed that papers will be peer-reviewed. The audience intended will be marketing directors, who will need suitable background, illustrations, etc., to help their salespersons sell more products. This assignment will be started in about the second week of class and will be due by class 28.
Assignment 3: Students will develop a topic of their own choosing (approved by instructors) to be written for two audiences (100 points).
The first assignment (25 points) will be written in "common language," e.g., to farmers or salespersons. High clarity of presentation will be expected. It also will be graded for content to assure that the student has developed the topic adequately. This assignment will be due by class 38.
Concomitant with this assignment will be a first draft of a scientific term paper on the same subject. Ten scientific articles and five typed, double-spaced pages are minimum requirements. Basic knowledge of scientific principles will be incorporated into this term paper written to an audience of alumni of this course working in a nutrition-related field. This draft (25 points) will be due by class 38. It will be reviewed by a peer who will receive up to 25 points for his/her critique. It will be returned to the student and instructor by class 43. The final draft, worth an additional 25 points, will be due before class 50 and will be returned to the student during the final exam period.
Integration Papers - HD 3XX
Two papers will be assigned for the semester, each to be no more than three typewritten pages in length. Each paper will be worth 50 points.
Purpose: The purpose of this assignment is to aid the student in learning skills necessary in forming policy-making decisions and to encourage the student to consider the integral relationship between theory, research, and social policy.
Format: The student may choose any issue of interest that is appropriate to the socialization focus of the course, but the issue must be clearly stated and the student is advised to carefully limit the scope of the issue question.
There are three sections to the paper:
First: One page will summarize two conflicting theoretical approaches to the chosen issue. Summarize only what the selected theories may or would say about the particular question you've posed; do not try to summarize the entire theory. Make clear to a reader in what way the two theories disagree or contrast. Your text should provide you with the basic information to do this section.
Second: On the second page, summarize (abstract) one relevant piece of current research. The research article must be chosen from a professional journal (not a secondary source) written within the last five years. The article should be abstracted and then the student should clearly show how the research relates to the theoretical position(s) stated earlier, in particular, and to the socialization issue chosen in general. Be sure the subjects used, methodology, and assumptions can be reasonably extended to your concern.
Third: On the third page, the student will present a policy guideline (for example, the Colorado courts should be required to include, on the child's behalf, a child development specialist's testimony at all custody hearings) that can be supported by the information gained and presented in the first two pages. My advice is that you picture a specific audience and the final purpose or use of such a policy guideline. For example, perhaps as a child development specialist you have been requested to present an informed opinion to a federal or state committee whose charge is to develop a particular type of human development program or service. Be specific about your hypothetical situation and this will help you write a realistic policy guideline.
Sample papers will be available in the department reading room.
SP3XX Short Essay Grading Criteria
A (90-100): Thesis is clearly presented in first paragraph. Every subsequent paragraph contributes significantly to the development of the thesis. Final paragraph "pulls together" the body of the essay and demonstrates how the essay as a whole has supported the thesis. In terms of both style and content, the essay is a pleasure to read; ideas are brought forth with clarity and follow each other logically and effortlessly. Essay is virtually free of misspellings, sentence fragments, fused sentences, comma splices, semicolon errors, wrong word choices, and paragraphing errors.
B (80-89): Thesis is clearly presented in first paragraph. Every subsequent paragraph contributes significantly to the development of the thesis. Final paragraph "pulls together" the body of the essay and demonstrates how the essay as a whole has supported the thesis. In terms of style and content, the essay is still clear and progresses logically, but the essay is somewhat weaker due to awkward word choice, sentence structure, or organization. Essay may have a few (approximately 3) instances of misspellings, sentence fragments, fused sentences, comma splices, semicolon errors, wrong word choices, and paragraphing errors.
C (70-79): There is a thesis, but the reader may have to hunt for it a bit. All the paragraphs contribute to the thesis, but the organization of these paragraphs is less than clear. Final paragraph simply summarizes essay without successfully integrating the ideas presented into a unified support for thesis. In terms of style and content, the reader is able to discern the intent of the essay and the support for the thesis, but some amount of mental gymnastics and "reading between the lines" is necessary; the essay is not easy to read, but it still has said some important things. Essay may have instances (approximately 6) of misspellings, sentence fragments, fused sentences, comma splices, semicolon errors, wrong word choices, and paragraphing errors.
D (60-69): Thesis is not clear. Individual paragraphs may have interesting insights, but the paragraphs do not work together well in support of the thesis. In terms of style and content, the essay is difficult to read and to understand, but the reader can see there was a (less than successful) effort to engage a meaningful subject. Essay may have several instances (approximately 6) of misspellings, sentence fragments, fused sentences, comma splices, semicolon errors, wrong word choices, and paragraphing errors.
Teacher Comments
Patrick Fitzhorn, Mechanical Engineering: My expectations for freshman are relatively high. I'm jaded with the seniors, who keep disappointing me. Often, we don't agree on the grading criteria.
There's three parts to our writing in engineering. The first part, is the assignment itself.
The four types: lab reports, technical papers, design reports, and proposals. The other part is expectations in terms of a growth of writing style at each level in our curriculum and an understanding of that from students so they understand that high school writing is not acceptable as a senior in college. Third, is how we transform our expectations into justifiable grades that have real feedback for the students.
To the freshman, I might give a page to a page and one half to here's how I want the design report. To the seniors it was three pages long. We try to capture how our expectations change from freshman to senior. I bet the structure is almost identical...
We always give them pretty rigorous outlines. Often times, the way students write is to take the outline we give them and students write that chunk. Virtually every writing assignment we give, we provide a writing outline of the writing style we want. These patterns are then used in industry. One organization style works for each of the writing styles. Between faculty, some minute details may change with organization, but there is a standard for writers to follow.
Interviewer: How do students determine purpose
Ken Reardon, Chemical Engineerin: Students usually respond to an assignment. That tells them what the purpose is. . . . I think it's something they infer from the assignment sheet.
Interviewer What types of purposes are there?
Ken Reardon: Persuading is the case with proposals. And informing with progress and the final results. Informing is to just "Here are the results of analysis; here's the answer to the question." It's presenting information. Persuasion is analyzing some information and coming to a conclusion. More of the writing I've seen engineers do is a soft version of persuasion, where they're not trying to sell. "Here's my analysis, here's how I interpreted those results and so here's what I think is worthwhile." Justifying.
Interviewer: Why do students need to be aware of this concept?
Ken Reardon: It helps to tell the reader what they're reading. Without it, readers don't know how to read.
Kiefer, Kate. (1997). Designing Writing Assignments. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/teaching/guide.cfm?guideid=101

Writing Guide: Types of Assignments & Best Practices
- Home & Appointments
- Types of Assignments & Best Practices
- Tables & Figures
- Thesis & Project Guide
The most common types of writing assignments you will encounter at MLTS
- How to approach a writing assignment
- Expository writing & research papers
- Compare & Contrast paper
- Book & Literature Reviews
- Reflective writing
- Online discussion posts
- Thesis/Project
As a graduate student, you will be assigned a variety of types of writing projects. A good rule of thumb in approaching any writing project is to ask yourself: for whom am I writing and why? Or, who is my audience and what do they expect from my writing? Your assignments will almost invariably require you to make one or more arguments. A good argument is well-written, logical, and supported by evidence.
Expository writing involves understanding, explaining, analyzing, and/or evaluating a topic. It includes your standard graduate school essay, book review, or research paper where your instructor requires you to analyze and/or study a topic. In general, your audience for such assignments will be your course instructor. You can think of such writing assignments as your instructor asking you to make an argument. Your instructor wants to gauge your creative thinking skills and how well you understand the course material by seeing how well you can make an argument related to that material. Remember: a good argument is well-written, logical, and supported by evidence.
An expository paper is therefore not about you (at least not directly); it is about the facts you have learned and researched and the argument you have built from those facts. Therefore, unless you are quoting someone, you should avoid using first person pronouns (the words I, me, my, we, us, our ) in your writing. Let your facts and arguments speak for themselves instead of beginning statements with "I think" or "I believe."
A compare & contrast assignment is a type of expository & research paper assignment. It is important to organize your writing around the themes you are comparing & contrasting. If, for example, you are assigned to compare & contrast, say, Augustine's Confessions and The Autobiography of Malcolm X , a common mistake students make is to write the first part of their essay strictly about Augustine's Confessions , and the second part of the essay strictly about The Autobiography of Malcolm X . In a good compare & contrast essay, you instead explore an issue in every paragraph or two, and show how, in this case, both Augustine & Malcolm X share common ground or differ on that issue. Then, move onto another issue and show how both Augustne and Malcolm X covered it.
Unless your instructor directs you otherwise, you should not use first person pronouns ( I, me, my ) in such a paper.
A book review assignment is meant to be an analysis of a book, not a chapter-by-chapter summary of a book. Instead of organizing your paper sequentially (the first paragraph is about chapter 1, the second paragraph is about chapter 2, etc.), organize your paragraphs around the themes of the book that are thread throughout the book. Topics to consider in a book review include (but are not limited to):
- What are the author's arguments, and how successful is she in making those arguments?
- What sort of sources does the author utilize?
- What methodology/methodologies does the author utilize?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the book?
A literature review is similar to a book review assignment in that it is meant to be an analysis of a theme or themes across several books/articles. What have various authors written about your topic? That said, as you will typically have less space to talk about each work (perhaps a paragraph or less for each work as opposed to multiple pages), you might end up moving from one author's findings to another. For a literature review in a thesis, think of a literature review as a mini-essay within your broader thesis with its own mini-introduction, thesis statement, and conclusion.
Unless your instructor directs you otherwise, book reviews and literature reviews should be written like expository & research papers. In particular, you should not use first person pronouns ( I, me, my ). So, instead of writing: "I think this book is a good analysis of ___," write: "This book is a good analysis of ___."
Reflective essays are especially common in theology courses. Reflective writing requires that you explicitly write about yourself and your own views. To put it another way, you typically have two audiences to write for in such an assignment: your instructor and yourself. As such, and unlike a standard expository paper, such essays require you to write about yourself using first person pronouns ( I, me, my) and use statements like “I think” and “I believe.” Otherwise, a reflective essay shares a lot with expository writing. You are still making arguments, and you still need evidence from cited sources! Unless your instructor tells you otherwise, you should still include a good title, introduction paragraph, thesis statement, conclusion, and bibliography.
For online courses, you will likely have to take part in classroom or group discussions online, in which you will be encouraged or even required to respond to your classmates. Such writing assignments often include a reflective element. Discussion posts are almost always shorter than essays and as such may not need long introductions or conclusions. That said, a discussion post is not like a Facebook or social media post! Good discussion posts are long and well-written enough to convey one or more thoughtful, insightful observations; you cannot just "like" someone else's post or only write "Good job!" If you decide to challenge or critique a classmate’s post—and you are certainly encouraged to do so!—you should do so in a respectful and constructive manner. As your main audience for online discussions are your own classmates and, to a lesser extent, your instructor, it is often okay to use relatively more informal language and to refer to yourself using first person pronouns ( I, me, my ). Finally, as with reflective essays, discussion posts still benefit from evidence. Even if a discussion post is relatively less formal than an essay, if you quote, paraphrase, or draw ideas from outside sources, you still must cite them! If the online medium does not allow for footnotes, use parenthetical references for citations (see chapter 19 of Turabian).
Those of you taking preaching courses or earning a DMin degree will have to write and submit your sermons. On one hand, your main audience for such a writing assignment is the congregation to whom you may preach. The language, tone, message, level of detail, etc. of a good sermon will depend on the precise context of your congregation and the message you want to impart. Therefore, unlike an expository essay or a reflective essay, you have a lot more freedom in how you chose to organize your sermon, as well as how formal or not you want the language to be.
On the other hand, in submitting such assignments, you also have a secondary audience: your instructor. As such, you may still need to include citations, even if you would not read them out loud in your sermon. In submitting a sermon as an assignment, you may also need to include some sort of write up or commentary, which your instructor may require to be expository and/or reflective in nature.
Those of you earning an MAR or DMin will finish your coursework by proposing, researching, writing, and defending a thesis or project. A thesis/project should be an original contribution to your field of study. To put it another way, the audience for your thesis/project is not just your advisor, but the broader academic and/or ministerial community. A good thesis/project can go on to become the first draft of a published academic journal article or a chapter or two of a book. Your thesis/project should be largely expository, but it may also include reflective sections.
It is never too early to start thinking about what you want to do for your thesis/project! You can try to make your thesis/project writing process easier by writing your course papers on topics within or adjacent to what you think you want to do for your thesis/project; that said, if you do so, you will need to cite these earlier works in your final thesis. See our citation guide for help with that.
For more information on writing a thesis or project, from choosing a topic to submitting it, check out our Thesis & Project Guide .
Tips for Composing Good Academic Prose
- Proofread, proofread, proofread!
- Find evidence to support your thesis statement from good quality sources
- Use quotations as evidence, not filler
- Be careful not to turn long sentences into run-on sentences
- Relatively longer paragraphs are generally better than short ones
- Make sure your paper flows well from one idea to the next
- When possible, avoid using the passive voice
- Be precise and crystal-clear in your statements and arguments
- Use the present tense when paraphrasing an author or setting up a quotation
- Use repetition of words carefully
First and most importantly: Proofread your paper over before you submit it to make sure that it reads well and is without errors! Read your paper over as you are writing it. Check over your work with spell check. Before you submit it, read it over one last time to catch anything you missed. If possible, consider reading the work out loud: you will be more likely to spot problems in your writing than if you read it in your head. If you are able to do so, ask a friend or schedule an appointment with the Writing Center for a review. Another pair of eyes can often spot a mistake or problem that the writer has overlooked.
Find evidence to support your thesis from good quality sources. Your research and writing should be based on the study of reputable primary and secondary sources. Typically, this means books published by academic presses and academic journal articles. Wikipedia, YouTube, random websites, and dictionary entries are generally not considered to be good sources for academic writing, although there are instances when it is acceptable to use and cite them, like if you were researching how topics in Black theology are represented or misrepresented on Wikipedia. If you need help in finding good resources for your paper, consult a librarian.
Quotations are meant to be evidence to support your argument; they are not filler to meet a length requirement. While you must quote and paraphrase sources, you should not quote or paraphrase more than you need. When possible, consider paraphrasing over quoting. Keep in mind that your writing assignments are supposed to showcase your thinking and writing, not the thinking and writing of whoever you are citing.
Be careful not to turn long sentences into run-on sentences. Long sentences are not always bad: when well-written, a long sentence can read better and help convey complex ideas better than a series of short sentences. A run-on sentence, on the other hand, occurs when multiple sentences are inappropriately lumped into a single sentence. Therefore, when reading your paper over, keep an eye out for any sentence that you can break into multiple sentences.
Relatively longer paragraphs are generally better than short ones. If your paragraph is three sentences or less, consider if you can write more about that paragraph's topic or incorporate it into another paragraph. If a paragraph represents one idea, then a longer paragraph typically shows that you have better considered and flushed out that idea. That said, if your paragraph is longer than a page, you could probably shorten it or break it into two paragraphs.
Make sure your paper flows well from one idea to the next. Does your third paragraph make sense following your second paragraph? Do you drop ideas and only pick them up much later? Cut and paste sentences and paragraphs around as necessary.
When possible, avoid using the passive voice. This can be tricky! The passive voice is when you use the verb “to be” next to and in conjunction with another verb to make the object of the sentence into the subject. For example, compare the active sentence: “Kate Turabian wrote the book” to its passive equivalent: “The book was written by Kate Turabian.” Grammatically speaking, in the latter, passive sentence, "The book" is the subject, even though in a real world active sense, it is the object.
Writers consider passive sentences not as good because, like in the above example, they can be wordier than necessary and take the focus off the real subject. There are exceptions in which it is good to use the passive voice. For example, if you were writing an article about Kate Turabian, it would be better to write: “Kate Turabian was born in 1893” instead of “Kate Turabian’s mother gave birth to her in 1893.” The former sentence keeps Kate Turabian, the focus of the paper, as the subject, while the latter sounds a little weird (maybe English speakers are too squeamish, but we typically do not recount someone's birth in that way).
At its worst, the passive voice can obscure the subject and make facts unclear. Consider the sentence: "Jackie Robinson's signing with the Brooklyn Dodgers in 1946 was considered a crucial moment in the Civil Rights movement." With the passive voice, the reader does not know who exactly considered that so? Did all Americans in 1946 think this? Did some specific people come to recognize it later? Compare that sentence to: "Martin Luther King, Jr. considered Jackie Robinson's signing with the Brooklyn Dodgers in 1946 a crucial moment in the Civil Rights movement."
Be precise and crystal-clear in your statements and arguments. Similar to how the passive voice can make facts unclear, overly general language can make for weak arguments. Consider the argument: "Many people now support same-sex marriage." Many people? Which people? "Many" and "people" are very general terms and do not tell us much in this statement; the more specific you can be, the better your argument:
- Despite official church statements, many American Catholics now support same-sex marriage.
- [Specific number]% of Chicagoans now support same-sex marriage.
- Many South African theologians, including [so-and-so] and [so-and so], now support same-sex marriage.
In general, use the present tense when paraphrasing an author or setting up a quotation. While you should use the past tense when writing about events in the past, you should in general use the present tense when discussing a scholar's writing. Scholarship is a ongoing discussion. When you read and discuss an author's work, that author is making an argument right now in the present, even if she is dead. So, do not write:
Carl Jung wrote: "The psyche... Carl Jung said, "The psyche... Carl Jung argued that...
but instead:
Carl Jung writes: "The psyche... Carl Jung says, "The psyche... Carl Jung argues that...
Use repetition of words carefully. When done well, repeating words can sound good and emphasize ideas. When done poorly, repetition sounds monotonous. Avoid, for example, starting too many sentences or paragraphs with the same word, or overutilizing the same verb. If you need help in bringing variety to your word choices, purchase a thesaurus or check out thesaurus.com .
- << Previous: Formatting
- Next: Tables & Figures >>
- Last Updated: Jun 12, 2024 8:52 AM
- URL: https://library.meadville.edu/writing

Meadville Lombard Wiggin Library 180 N. Wabash Ave. Suite 625 Chicago, IL 60601
Library and Archives Phone: 312-546-6488 Library Email : [email protected] Archives Email : [email protected]
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Technology in the Writing Classroom

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Technology affects both the process and product of composition. Students often complete multimodal writing assignments that combine traditional textual elements with pictures, data visualizations, video, sound, animation, etc. Similarly, students' use of many technologies while composing an assignment can impact the final product. This is true even for technologies that aren't directly involved in the writing process in the way that, for instance, word processors are. Mind mapping technologies can help students relate ideas to one another. Graphic design programs can help students organize their ideas visually or let students write for specific audiences and contexts. Audio recording technologies can give students expressive freedom beyond the constraints of written work. Countless more examples abound.
These technologies, however, should not be introduced to the classroom without forethought. One danger inherent to any technology is that an assignment that uses that technology can inadvertently become more about learning to use the technology than about the intended learning outcomes. Thus, making sure students understand what they are being evaluated on (i.e., their work, and not necessarily their skill with the technology), have access tohelp materials, and have time to get familiar with the technology can all mitigate this danger. These strategies tend to hold true no matter the age of the students. While it's typical to assume that younger students have greater facility with technology because they are "digital natives," research suggests that that's usually not the case. Young students still need to learn to use a new technology just like they would learn any other new skill.
When handled with care, technology can be a boon to the writing classroom. Generally, the benefits of technology in gaining new literacies, learning independent problem solving skills, and showing students the wide range of applications of composition in their lives outweigh the risks. In this resource, we suggest some ways that teachers can take advantage of widely available technologies to teach writing outcomes and help students develop multiple digital literacies.
Mindmapping
There are a number of free options for mindmapping and similar exercises online, including MindMup , Bubbl.us , and Lucidchart , but common office programs like PowerPoint can also do the job.
Stages of the writing process:
- Invention/pre-writing
- Peer review
- Visually organizing an essay or argument
- Synthesis (spatially relating different concepts)
- Reverse-outlining an existing draft to understand how the pieces fit together
Affordances:
- Mindmapping digitally allows for easier movement, erasing, and re-doing than with pen and paper
- No constraints of paper size — maps can go wherever students take them
- Can use images, links, etc. from research in the maps
- Can spatially show (and compare/contrast) the relative importance of points, check for balance in developing arguments
Activities:
- Have a peer reviewer reverse-engineer an outline of their peer's paper and let the writer compare their own outline with the reviewer's. The writer and reviewer can discuss differences between the two outlines, evaluate the reviewer's response to what the writer intends to show in the paper, and make a revision plan.
- Have students synthesize multiple sources together using a mind map; first, make a mind map for each source summarizing its points, then connect the nodes to understand how the sources relate to one another, agree, and disagree.
- Have students create an outline of their paper with a mind map. Compare outlines on the board/projector to understand how different arguments can be organized through visual shapes (narrow at the top and broad at the bottom, like a triangle; narrow at beginning and end and wide in the middle, like a diamond; etc), and what each of these shapes can do.
Collaboration
Especially when teaching remotely, collaboration on writing projects is a common part of writing instruction. Leveraging technology effectively to help facilitate collaboration can help students focus on building collaboration skills rather than focusing on getting in touch with each other, and can help teachers more effectively monitor and help with collaboration in the moment. Tools for collaboration can vary depending on what's available, but Google Docs , Slack , and various kinds of video conferencing software (e.g., Zoom ) are common tools.
Stages:
- All stages, but especially:
- peer review/revision
- brainstorming
Purpose:
- Sharing work among students, especially when remote teaching or in case of absences, not finishing work in class, etc.
- Responding to feedback in a way that leaves a written record
- Co-writing documents for a group project
- Brainstorming, taking collaborative notes, or creating a wiki in class
- Rather than discussing peer review or feedback verbally in class, students can write feedback down in comments in Google docs or similar word processing software for later review
- Students can assign action items by tagging their classmates ("@Purdue Pete, could you look at this paragraph when you get a chance and let us know what you think?"); teachers and students can see division of labor in who is participating the most on the document
- Students can still participate remotely in the case of illness or other absence
- In class, students can all contribute to a class document at the same time to create a crowdsourced wiki about a topic, share notes, etc.
- Have students doing group projects write a team charter memo collaboratively, laying out expectations for how their team will work together, solve conflict, and help each other get their work done.
- Have students use separate pages in a Google doc to answer discussion questions or take notes during a think-pair-share activity, so all the notes are available to all students afterwards.
- When introducing a new technology, have students create a list of tools or functions in the technology in a collaborative document, and then assign one tool or function to each student to research and create a guide on how to use it. Assemble the guides into a wiki that students can refer to when using this technology on another assignment.
Audio Production
Writing is not a purely textual endeavor: much of the journalism we encounter is in podcast form. This is not the only audio genre whose production is intertwined with the writing process, however. For instance, pop music can teach poetry in a way that engages young students. Similarly, audio dramas that tell stories with sound design are experiencing a resurgence from the days of radio. Assigning an audio composition can be a great way to help students learn multimodal literacies while still teaching organization, structure, and argument. Additionally, because the various genres of audio composition are more commonplace or "real" for students than something explicitly tied to school, like a traditional essay, these genres can give students opportunities to engage with audience and context in new ways. Though many programs can allow students to edit audio, one free, especially easy-to-use platform is Audacity .
- Remediation
- Reflection after writing
- Specific audience and genre characteristics help students learn to analyze a rhetorical situation and adapt appropriately
- Finding and incorporating fair use music, sounds, and effects teach students about fair use, copyright, and attribution practices in public settings outside school
- Working with speech, sound effects, music, timing, and delivery encourages students to develop multimodal literacies that interact with and build on traditional written literacies.
- Have students produce a 3-5 minute podcast remediating a previous project, like a research paper or a literary analysis. Students can write a script, record the script, and include effects, music, and edit their own speech to fit the time constraints and needs of the piece. Students can then write a short reflection detailing how they rethought their original project with a new audience and context to create the podcast, and what design choices they made to achieve those goals.
- Have students record a voiceover for a PowerPoint or other presentation deck to make a presentation remotely; students can write a short reflection describing how they made conscious rhetorical decisions in accompanying their slide deck.
- Have students record an interview with a classmate, family member, teacher, etc., and edit the interview to tell a cohesive story in 5-10 min. Students can write a short reflection describing how they came up with interview questions, how they decided which material to keep and which to trim or delete, and how they set up the story for an interested audience with music and effects.
Visual Production
Much of the writing we encounter in our daily lives is accompanied by or part of a visually designed composition; blog posts include pictures and GIFs, websites focus on usable design, marketing materials grab our attention with photos and data visualizations, and infographics condense pages of text into quickly digestible bites of information. Many free online tools such as Canva and Piktochart give users templates to start with and the power to customize most features. Commonly available office software also has robust visual design capabilities, and students with access to professional-grade products like Adobe Photoshop can develop facility with industry-standard technology.
- All, but especially:
- Working multimodally encourages students to adapt to changing rhetorical contexts and audiences
- Genre conventions for visual compositions help students gain genre awareness while building visual literacy
- Generally, visual production assignments allow students to play with arrangement and meshing textual and visual elements, similar to audio production
- Since some tools have premade templates students can use as starting places, there can be less anxiety about having to start from nothing; by the same token, students learn how to make customization decisions in accordance with their audience and context
- Like audio production, using a mix of elements means students have the opportunity to learn about citation and fair use outside of a school setting
- Have students remediate an essay or other project into an infographic for public consumption (or poster, to hang in classroom for future students, etc). Students can write a short reflection describing how they decided to rework their original project into something new for a new rhetorical situation.
- Have students create a photo essay with captions; students can write a reflection discussing their choices and intentions.
- Have students redesign a book cover, poster, course syllabus, assignment sheet, or other document to be both more visually appealing and more useable; students can write a reflection describing their rhetorical choices.
- The Student Experience
- Financial Aid
- Degree Finder
- Undergraduate Arts & Sciences
- Departments and Programs
- Research, Scholarship & Creativity
- Centers & Institutes
- Geisel School of Medicine
- Guarini School of Graduate & Advanced Studies
- Thayer School of Engineering
- Tuck School of Business
Campus Life
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Athletics & Recreation
- Student Groups & Activities
- Residential Life
Writing Program
- [email protected] Contact & Department Info Mail
- Writing Instruction
- Writing Support
- Past Prize Winners
- Writing 2-3 Teaching Assistantships
- Apply to Tutor
- Writing Requirement & Scheduling
- Differences Among First-Year Writing Courses
- Writing 2-3
- Humanities 1-2
- First-Year Seminars
- Directed Self-Placement
- Writing 2-3 Registration
- Writing 5 Registration
- First-year Seminar Registration
- Registration FAQ
- Teaching Writing in the First Year
- Expectations for Teaching Writing 2-3
- Expectations for Teaching Writing 5
- Expectations for Teaching First-Year Seminar
- Active Learning
Syllabus and Assignment Design
- Teaching Writing as Process
- Integrating Reading and Writing
- Diagnosing and Responding
- Conducting Writing Workshops
- Collaborative Learning
- Teaching Argument
- Teaching Research
- Addressing Grammar
- Useful Links
- Academic Integrity
- Processes & Practices of a Scholarly Community
- Quality of Sources
- The Writing Center
- Multilingual Support
- News & Events
Search form
- Teaching Guidelines
- Gocsik's Twelve-step Research Assignment
Designing your Syllabus: Backward Design
When you design a syllabus for any course, you begin with the outcomes that you intend for your students to achieve, and you work backwards from these to particular readings and writing assignments. This method, formalized, is called the method of backward design. Backward design is a useful method for any professor in that it ensures that all assignments, readings, and activities will connect students with the outcomes that the professor deems essential to the course.
At the first stage of backward design, writing instructors should consider two issues: what they want their students to know/experience in their courses, and what they want them to be able to do, in these courses and afterwards. Put another way, instructors need to think both about their focusing questions and their course outcomes.
You'll note that the first issue—what instructors want their students to know/experience—distinguishes between knowledge and experience. Indeed, this distinction is significant in a writing class, where course content (while important) does not drive the course. The best writing classes consider the students' experiential learning in their course design. To accomplish the aims of experiential learning, it's important to come up with a course question that can bring together the many smaller questions of the course and that can engage students intellectually and experientially. For instance: What is happiness? What are the roots of violence? What is the nature of the self? Technology: friend or foe?
These are the kinds of questions that can focus course readings and class discussions. They are also the kinds of questions that students can engage with outside of the context of the writing classroom. Finally, they are the kinds of questions around which professors can build a course that is intellectually coherent.
Even more important the the course questions, however, are the course outcomes — in other words, what students should be able to do when the course comes to an end. In the first-year writing classes, an instructor's set of outcomes will be informed by the course outcomes (see the outcomes for Writing 2-3 , Writing 5 , or the First-Year Seminar ) . Take some time to review these outcomes, and to consider how every assignment and classroom activity might work to help students achieve them.
Designing Your Assignment
As you design your assignments, you'll want first to determine the outcomes that each assignment will work to accomplish. If your aim is to ensure, for instance, that students learn how to shape good academic questions, you might ask them to compose, share, and then revise their questions. If you want them to develop their research capabilities, have them take these questions to the library databases in order to look for appropriate sources. If you want to ensure that students learn how to work with sources, ask them to compose a summary and synthesis document, in which they nutshell their sources and show how these sources are in conversation with one another. Finally, if you want to ensure that they learn how to compose and revise, assign drafts and give them feedback. Have their peers offer feedback as well. Whatever you decide to assign, use the outcomes to guide you.
Second, you'll want to scaffold your assignments, so that students can build on their capabilities. You'll see in the examples cited in the paragraph above that each assignment builds on the one before. Students work on one step in the process and get feedback on it (from the instructor or their peers) before moving on to the next challenge. By scaffolding, instructors can be sure that students know how to successfully complete the final assignment. Students can also track the evolution and transfer of their skills.
Third, writing instructors frequently comment that Dartmouth's ten-week term is very short. Assignments must therefore be designed to achieve multiple outcomes. Consider the first step of the assignment sequence outlined above: "Ask students to compose, share, and then revise their questions." Several outcomes are achieved here: students are composing, they are collaborating, and they are revising. If you design your assignments to achieve multiple outcomes, you'll be surprised at how much your students can accomplish.
Whatever assignments you design, do understand that simply making an assignment does not ensure that students will acquire the desired skills. For an assignment to succeed it should be transparent and progressive—that is, your students should understand your goals for the assignment, and they should be able to chart their own development in relation to these goals. The better students understand your assignments and your vision for your course, the better they'll be able to meet the course aims.
Spacing Your Assignments
When designing your syllabus, you will want to consider carefully the spacing of your writing assignments. It's important that students are given enough time to write and to revise their papers. Professors who use a writing assistant will also want to be sure that they provide the writing assistant enough time to read and respond to students' papers.
Here are some things to consider:
- Give students time to move through the writing process. If you are teaching a first-year course whose purpose is to make students able writers, you will have to give them time to move through the various inventions, composing, and revision processes. One way of making room for these various steps in the writing process is by assigning a paper in three parts: the pre-draft (which could consist of crafting questions, writing a discovery draft, creating an outline, and so on), the first draft, and the revised final draft.
- Give students time to revise. If we want our students to revise their papers substantively, we must give them adequate time. This means that we need to get their papers back on time, particularly the first drafts. Consider whether you'll need two days, four days, or a full week to return an assignment. Also consider whether or not you expect the student to see a writing assistant or to meet with you between drafts.
- Try not to make a reading assignment on the day a major paper is due. Let your students focus their attention fully on their writing. Schedule writing workshops the day that a paper is due instead.
- Long assignments (particularly those that involve research) work better if you break them up into smaller assignments. Ask students to bring in an annotated bibliography, a working thesis, an outline, etc. Scheduling these shorter assignments ensures that students remain engaged in the writing process. It also prevents them from writing the paper at the last minute.
- Consider what's best for you. Many students and instructors like Monday due dates: students get the weekend to work on their papers, and professors keep their weekends free. Other instructors prefer for papers to come in on Thursday or Friday, so that they can use the weekends to respond. Think of your own rhythms as you plan.
Crafting Your Assignments
Professors often wonder, when creating writing assignments, how detailed the assignments should be. Some professors don't use prompts, requiring students to come up with the topics and questions themselves. Others create detailed writing assignments, arguing that this allows students to save energy for writing their papers (as opposed to generating topics and questions). Still others craft writing prompts that offer students ideas for writing but that leave plenty of room for students to come up with ideas of their own. We'll consider the options of prompting and not prompting here.
The Open Writing Assignment
Professors who don't use writing prompts believe that an important part of scholarship is learning to raise questions that will yield a good academic argument. Instead of creating a writing prompt, these professors craft an assignment process that supports students as they work through the various challenges of scholarly inquiry. In a sense, these professors are asking students to craft their own prompts, and to write the paper that will answer the questions that they outline there. The obvious pedagogical advantage of the open assignment is that it allows students to learn to develop topics on their own. In the open assignment, students are not only permitted to pursue intellectual questions that are of interest to them, they also gain some experience in framing a topic that is neither too narrow nor too broad.
If you elect not to use prompts, you should intend to devote class and conference time to assisting students in this process. For instance, you might ask students to come up with three good academic questions about the course's reading materials. Students can post these questions on the Canvas discussion board. You can then workshop these questions, using class time to talk about which questions will (or won't) yield a good academic argument, and why. You should also comment thoroughly on the questions submitted, raising further questions for the student to consider. You might also invite students to comment on one another's questions on the Canvas site. Students can then revise their questions and resubmit them for another round of feedback before they write.
Some professors find it useful to offer students models of good academic questions. Other professors give explicit instruction regarding what the paper shouldn't do and leave it to the students to determine what they want to do within these parameters. All professors ask students to submit their prompts in advance of drafting so that they can determine, before the students proceed too far, whether or not these topics are appropriate and promising.
Whatever you decide, do note that a prompt-less writing assignment needs a good infrastructure in order to succeed. Indeed, Karen Gocsik's research assignment for Writing 2-3 has twelve steps, indicating the many moments of support and feedback that first-year students require as they work through the process of writing a research paper Your assignment need not have twelve steps to be effective; it may have four steps, for instance, or five. Craft your assignment steps according to the aims of your assignment.
Crafting a Good Prompt
Writing a good prompt for a writing assignment is a difficult task. Too often, professors write prompts for writing assignments knowing exactly what sorts of essays they want their students to produce, only to get papers that miss the mark. How can you produce writing assignments that clearly convey the tasks and questions you want your students to undertake?
Before writing your prompts, you will want to consider a few matters.
- Consider what you want the assignment to require the students to do, in relation to the course outcomes. What outcomes are most important at this point in your course? How can the assignment move students closer to achieving these outcomes?
- Consider what you want the assignment to do, in terms of the larger questions of your course. What questions, in particular, do you want your students to consider? Are these questions related closely or peripherally to topics you've been discussing in class?
- Consider what kinds of thinking you want students to do. Do you want your students to define, illustrate, compare, analyze, or evaluate? You will want to come up with prompts that clearly direct students as to the kind of thinking they will have to do.
- Consider your students' writing processes. Are you focusing on teaching students to place their arguments within a larger conversation or context? If so, your prompt should address the importance of context and suggest things that you want students to consider as they write. Are you hoping to get your students to understand the mechanics of the paragraph? Your prompt might ask students to write paragraphs that summarize, then analyze, then synthesize, so that they can see how different tasks require different paragraph development.
- If the paper involves research, consider outlining your research requirements in a way that educates students about the research process. You may want to require students to use a variety of sources, or to use certain sources that you've either put on reserve or listed in the course syllabus. Understand that students may need help with finding sources, evaluating them, and incorporating them successfully into their arguments. Craft your prompt accordingly.
Once you've determined the outcomes for your writing assignment, you're ready to craft the prompt. Here are some things to consider:
- Break the assignment down into specific tasks. If, for example, you want students to compare the effectiveness of two political movements, you might first ask students to define the goals of each movement; then to consider the history of each movement; then to discuss how the history of the movement affected the creation of its goals; and finally, to consider how history influenced the movement's ultimate success (or failure).
- Break the assignment down into specific questions. For example, if you want students to discuss the formal elements of a particular painting, you might, as Art Historian Joy Kenseth does, ask the students: What is the focus of the painting? How does the artist treat such things as light and shadow, line, space, and composition? How does this treatment communicate the painting's ideas? If you don't want students to answer all of the questions you put to them, but want them simply to consider these questions before writing their responses, make that clear.
- Provide context. A writing prompt that asks students to discuss whether or not the films of Leni Riefenstahl are propagandistic does not point students to the interesting controversy surrounding Riefenstahl's work. Nor does it indicate whether they should limit themselves to discussing the formal elements of Riefenstahl's films, or whether they should include biographical detail. The more contextual information you give your students, the more precise their responses will be.
- Craft each sentence carefully. You will want to be sure that there is no room for misunderstanding the assignment. If you ask students to analyze how a myth informed paintings and sculptors during the first century of the Renaissance, do you want students to examine the works themselves or the artists that produced them? Sometimes a slip in word choice or the careless placement of a modifier can leave students confused as to what, precisely, you are asking them to do.
- Be clear about what you don't want. If you don't want students to discuss Virginia Woolf's personal experiences as they relate to A Room of One's Own , then be sure to instruct them not to include biographical references. In addition, explaining why such information should be excluded will help students to understand better the questions and the desired response.
- Be clear about the paper requirements. Have you indicated the paper's due date? How many pages you require? How many sources you require? What special criteria (if any) you will use when grading this paper? If your requirements are rigid, say so. If you're flexible, let the students know. This may be the aspect of the prompt that students are most anxious about, so offer as much detail as you think is necessary.
- Try to write (or at least to outline) the assignment yourself. If you have trouble outlining a paper based on this prompt, your students will, too. You will want to think about ways of revising the assignment to make it clearer and more manageable.
- Discuss the assignment with the class. When you distribute the assignment to the class, take time to go over it. Ask for their questions. Make notes as to where their understanding of the assignment differs from yours so that you can improve the prompt the next time you use it.
Six ways to prepare writing assignments in the age of AI

By completing this form, you agree to Turnitin's Privacy Policy . Turnitin uses the information you provide to contact you with relevant information. You may unsubscribe from these communications at any time.
Every day, new articles are published about AI and while once ChatGPT was the main focal point, new models are continuing to develop and become a part of everyone's online interactions. Every day, educators are faced with challenges relating to these tools as search engines and social media are attempting to harness AI’s power. Preparing our classrooms to combat academic integrity issues such as student collusion, a “copy-paste,” text spinners, or contract cheating have expanded. Questions about the veracity of online searches powered by AI are now a factor that must also be considered. Every day . We’re in deep now as educators have started to understand the threat, the responsibility, and the promise of AI. Our Turnitin Teaching and Learning team - all former and current educators - is there too, and one thing we’ve learned is that AI isn’t going away… and that’s okay.
More practitioners are beginning to realize that there could be some benefits to AI in education when implemented with intention. It is a balance, though, as not every use of AI tools will support teaching and learning. For example: What if AI is used to replace actual student thinking? What if it’s used to complete an entire assignment? That type of usage is the threat we as educators (yes, I am still teaching!) are working tirelessly to avoid. But WHAT IF there are things we can do to protect our writing assignments against student misuse for classrooms today?
Let’s pull a tool from a therapist toolkit–instead of reacting to AI after it was potentially misused by a student, we can proactively respond by putting some guardrails in place.
We recently shared guidelines that focused on eleven strategies for approaching AI-generated text in your classroom . Today, we’re going to expand on six specific tactics for educators:
1. Update academic integrity policy to inform instruction and assessment practices
2. Communicate new policy and assignment guidelines with students.
3. Review and revise writing assignments and associated scoring tools (rubrics, etc.).
4. Employ the writing process; live in a formative space.
5. Direct students to use writing platforms where multiple drafts can be saved for review.
6. Institute opportunities for students to discuss their work.
Notice that these six strategies focus on careful planning and approaching AI proactively. While time is a luxury educators do not have, these tactics may save time later responding to potential AI misuse cases. Let’s dig into the tactics:
How and to what extent is the use of a generative AI tool acceptable within academic environments? Changes to classroom practice rely on answering this question and updating academic integrity policies accordingly. Now is the time to research, discuss, and decide how institutions will respond to the rapidly evolving technology of AI. Our guide for updating academic integrity policies in the age of AI walks through steps for getting started. We share ideas such as establishing a common lexicon like an AI vocabulary glossary and determining ethical use of AI.
While making institutional changes first is ideal, it may not happen fast enough. Most educators are feeling like they’re already playing catch-up and need tools to respond to AI advances right now. For those educators, we recommend answering the questions for their own classroom even as they work with colleagues and leaders for institutional change. Let’s be agile and develop best practices for AI in our classrooms.
Determining acceptable use of AI will inform changes to instruction and assessment. But what does acceptable use look like? That may vary vastly for each institution, department, classroom, and even assignment, but let’s look at some specific examples. As I suggested earlier, there can be positive benefits for AI in education. Perhaps an educator decides that it’s acceptable for students to use AI writing tools during prewriting (see #3 below) to brainstorm ideas or gain other points of view on a topic. Or maybe the educator decides to allow students to submit a draft to AI to get formative feedback on their work. If educators decide to go down this path, they must choose the right AI tool and personally test it to put parameters in place.
2. Communicate new policy and assignment guidelines with students
Introduce updated policies to students and talk to them about AI. The policy should be easily accessible to all stakeholders, particularly students. Consider asking students to lead activities to paraphrase policies and present to peers. One valuable exercise that Turnitin advocates have suggested is a classic “This… Not That” activity with scenarios that students can sort/label based on their understanding of the policy. Simply create a list of a few scenarios and have students sort which are acceptable and which are not. The activity itself is fantastic, but what is even more powerful is the discussion around why some uses are acceptable and others are not.
3. Review and revise writing assignments and associated scoring tools (rubrics, etc.)
Developing best practices for crafting writing assignments that are resistant to student misuse of AI is imperative. As we’ve all likely read in the media, AI is proficient at some things, but not so proficient at others. If we, as educators, familiarize ourselves with the “answers” from an AI tool, then in theory, we should be able to modify our writing prompts to work around the technology. While this strategy isn’t foolproof, it will certainly help place some of those guardrails.
Let’s take an element that some generative AI writing tools struggle with today. In their current iteration, AI writing tools have been found to list sources that don’t actually exist. When prompted, the tool might provide references, but the sources may be fictitious. Therefore, adding a requirement for students to use verifiable sources with a reference list would help combat this issue. Beyond sources and citations, there’s additional criteria educators can consider when revisiting their assignments. Our team of veteran educators created an AI misuse rubric to help with just that. This rubric proposes four traits: student voice, critical thinking/reasoning, sources and citations, and personalization.
Consider comparing tried and true writing prompts against the rubric. Start by identifying which traits are relevant to an assignment and then assess how the prompt stacks up. Use the weaker areas to consider how it might be modified to better safeguard assignments against AI misuse. The closer a prompt gets to Advanced/Proficient, the less vulnerable to AI misuse it will be.
As a final step, educators should also update their scoring guides or rubrics to reflect new demands of the prompt. Early in my teaching career, a mentor of mine used to say, “Measure what matters most.” As we shift assignment/assessment design, our evaluation tools must be aligned. If scoring guides and rubrics heavily emphasize aspects of writing at which AI tools are skilled, the potential for misuse increases.
4. Employ the writing process; live in the formative space.
The writing process isn’t for novice writers only. Educators everywhere keep hearing how the existence of AI is going to force us to revisit our teaching practices . For those who might have stepped away from implementing the writing process, start there. The writing process isn’t for novice writers only, in part because preparing writing assignments so they include steps like prewriting and drafting will bring visibility to students’ work before a final submission. Leverage that process and require students to submit a draft, leave feedback on their work, and have them make revisions based on the feedback. Creating a writing culture with what feels like open dialogue between student and educator makes it much less likely for students to misuse AI. Additionally, research has proven that specific types of feedback have a quantifiably positive impact on student growth. A portfolio approach is one more way to improve visibility into not only the student’s work, but also their process, all of which adds up to protection against AI misconduct.
5. Direct students to use writing platforms where multiple drafts can be saved for review
Take the writing process a step further by teaching students how to maintain a record of their work. Visibility is more important now than ever as students may find their work challenged. Consider instructing students to write in a single web document, such as Microsoft Word or Google Docs, as a form of verification so that if questions about the document’s originality surface, there will be recorded documentation to clarify the origins of a student’s work.
6. Institute opportunities for students to discuss their work
Will students use ChatGPT if they must discuss their work with a teacher or classmate? Maybe, but the probability certainly decreases. While requiring discussion may not eliminate the risk, it does provide another guardrail. Plan for assignments to include peer reviews, writing conferences, or reflection assignments live or in video format, creating another layer of visibility and open dialogue. Additionally, if they know they’ll need to share their work, students are often more invested. Not to mention, research shows that having students share their work boosts confidence and motivation toward the task ( Simonsmeier et al., 2020 ).
While not exhaustive, these six strategies can at least serve as a place to begin, and by combining them they have an even greater impact. If educators are unsure where to start exactly, our AI misuse checklist lists these principles (and more!) to help guide them down the path of preparing writing assignments in the age of AI.
Further resources
- Updating your academic integrity policy in the age of AI
- AI misuse checklist
- AI misuse rubric
- AI vocabulary glossary
- Source credibility pack to help evaluate both traditional and AI sources
Why Should You Use Writing Assignments in Your Teaching?
Brad hughes, director, writing across the curriculum, university of wisconsin-madison.
Why should you use writing assignments in your teaching? That’s an important question. Even though this is a Writing Across the Curriculum website, designed to encourage faculty to incorporate writing into their teaching, let’s be honest—there are many reasons why you might not want to assign writing in your courses. And many of those reasons have to do with limits on your time. Designing writing assignments and responding to student writing take valuable time—lots of time if you do them carefully. The larger the enrollment is in your classes, the more time responding to student papers takes. You have lots of important course content to cover, so you have limited time for building in a sequence of writing assignments and some instruction around those assignments. . . .
You also need to remember that writing assignments take substantial time for your students to do well. And not all of your students are well prepared to succeed with the writing you assign. This list could go on; the challenges can be formidable.
Yet countless faculty—in every discipline across the university—make writing an integral part of their teaching and reap benefits from doing so. Why? Here are some of the many reasons writing is an especially effective means for students to learn.
- Writing deepens thinking and increases students’ engagement with course material.
- Well-designed writing assignments prompt students to think more deeply about what they’re learning. Writing a book review, for example, forces students to read more thoroughly and critically. As an old saying goes, “How do I know what I think until I hear what I say or see what I’ve written?”
- In fact, research done by Richard Light at Harvard confirms that “students relate writing to intensity of courses. The relationship between the amount of writing for a course and students’ level of engagement—whether engagement is measured by time spent on the course, or the intellectual challenge it presents, or students’ self-reported level of interest in it—is stronger than any relationship we found between student engagement and any other course characteristic” ( The Harvard Assessment Seminars , Second Report, 1992, 25).
- Research done by the Association of American Colleges and Universities demonstrates that writing-intensive courses are a high-impact practice in undergraduate education (George D. Kuh, High-Impact Educational Practices: What They Are, Who Has Access to Them, and Why They Matter , 2008).
- Research done by Michele Eodice, Anne Ellen Geller, and Neal Lerner ( The Meaningful Writing Project , 2017) demonstrates that certain writing projects can be especially meaningful parts of undergraduate education.
- Writing can improve our relationship with our students. When students write papers, we get to know them and their thinking better; they’re more likely to talk with us after class, or come to our office hours to share a draft or seek advice.
- Writing gives us a window into our students’ thinking and learning. Through our students’ writing, we can take pleasure in discovering that students see things in course readings or discussion we didn’t see; students make connections we ourselves hadn’t made. And through our students’ writing, we also discover what confuses our students. Admittedly, we’re not always eager to discover the gaps in our students’ knowledge or understanding, but it’s our job to expand that knowledge and improve students’ thinking.
- Writing assignments can improve our classroom discussions. By helping students keep up with readings, regular writing assignments can prepare students to participate in discussion.
- Writing assignments provide us with an opportunity to teach students to organize ideas, develop points logically, make explicit connections, elaborate ideas, argue points, and situate an argument in the context of previous research-all skills valued in higher education.
- Students remember what they write about-because writing slows thinking down and requires careful, sustained analysis of a subject. No matter how many years it’s been, most of us can remember some paper we wrote as undergraduates, the writing of which deepened our knowledge of a particular subject.
- Students and professors remember what they’ve written, in part, because writing individualizes learning. When a student becomes really engaged with a writing assignment, she has to make countless choices particular to her paper: how to focus the topic, what to read, what to make the central argument, how to organize ideas, how to marshal evidence, which general points to make, how to develop and support general ideas with particulars, how to introduce the topic, what to include and what to omit, which style and tone to adopt. . . .
- Finally, though it’s much more than this, writing is a skill—a skill that atrophies when it isn’t practiced regularly. Because learning to write well is difficult and because it requires sustained and repeated practice, we need to ensure our undergraduates write regularly, throughout the curriculum, in all majors. It’s the responsibility of all of us to ensure that students learn to think and write clearly and deeply.
Teaching with Digital Assignments
- Types of Digital Assignments
- Classroom Considerations
- Digital Pedagogy
- Assignments by Format
- Tools and Technologies
- Digital Storytelling This link opens in a new window
- Open Educational Resources (OERs) This link opens in a new window
Writing for Digital Assignments
- Digital Projects Toolkit This link opens in a new window
- Digital Assignment Consultation
Additional Reading
Digital Pedagogy Librarian

Digital assignments often have rigorous writing requirements, but can differ from the skills and styles used in composing traditional academic and research papers. Some examples include:
- Multimodal writing, combining text with images, video, and audio
- Script writing for audio and video projects
- Public writing and the writing of content intended for general audiences
- Descriptive and alternative text
- Transcriptions and translations
While the end product of digital assignments may have a smaller word count than essays and final projects, the writing process may be as (or more) intensive and ask students to engage with knowledge in new ways. This page includes resources related to web writing, public writing, and digital writing that may be useful to educators and students engaged in a variety of assignment formats.
- Digital Writing in the College Classroom A brief article defining digital writing and discussing impacts on curricular and information literacy in higher ed.
- Writing for Digital Media Open access textbook focused on writing and digital media. Includes practical strategies and best practices for different forms of digital content.
Public Writing
- Audience Awareness A brief guide to identifying and writing for an audience.
- Writing for a General Audience A brief guide to making academic and research content accessible to a general audience.
- Public Writing A guide from University of Washington with practices and resources about writing for public audiences on the web and in other mediums.
Script Writing
- Create a Script for Your Digital Project A guide to writing a script for digital stories and other types of audio and video projects.
- Creating a Great Podcast Script: 3 Methods Top Podcasters Use An article describing different approaches to writing scripts for podcasts.
- The Journey from Print to Radio Storytelling A guide from NPR with tips for creating effective scripts for audio storytelling projects.
Writing for the Web
- Web Style Guide A user-focused style guide for web content. Chapters 10 - 11 focus on writing and use of images and video in web contexts.
- Writing Clearly and Simply for the Web Guidelines for organizing and writing text content for general audiences on the web.
Accessibility
Descriptive and alternative text are additional forms of writing needed for accessibility in digital stories. Non-text content, including audio, images, data visualizations, figures, and other visual information, should include text that describes what is being communicated. Accessibility considerations can improve your script writing, text-based content in web stories, and selection of multimedia content.
- Writing Helpful Alt Text A simple guide to writing descriptive text for visual information.
- Image Description Guidelines Guidelines and tips for describing all types of images, including diagrams, maps, equations, tables, and more.
- WebAIM: Alternative Text Guide to writing and applying alternative text to many kinds of images.
- DCMP Description Key Guidelines and best practices for describing educational video.
- ABS Guidelines for Verbal Description Guide to descriptions for works of art.
- Writing Accessible StoryMap Content A guide from ArcGIS explaining how to format and edit content for accessibility.
- << Previous: Digital Learning Outcomes
- Next: University Resources >>
- Last Updated: Aug 1, 2024 5:47 PM
- URL: https://libguides.udayton.edu/digital_assignments

- Academic Success
Understanding Writing Assignments
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This guide will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects.
Basic Beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well:
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment Formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think About
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the Assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that he or she will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor.
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information Words - Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation Words - Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply —use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation Words - Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose
As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove her point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, he or she still has to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and she already knows everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present.
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience?
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly.
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality she or he expects.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal.
Technical Details About the Assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks That Don’t Work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material. Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than once course may constitute an academic integrity violation. Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question. Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
Developed and shared by The Writing Center , University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
- Class Attendance
- Semester-At-A-Glance Calendar
- Semester Action Plan
- Using Calendars and Planners
- Studying 101
Watch Asking for Help Video
Ask for Help - We Want You to Succeed
View All Student Tips
815-753-6636 [email protected]
Connect with us

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Common Writing Assignments. These OWL resources will help you understand and complete specific types of writing assignments, such as annotated bibliographies, book reports, and research papers. This section also includes resources on writing academic proposals for conference presentations, journal articles, and books.
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing. Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
Designing Effective Writing Assignments. One of the best ways for students to determine what they know, think, and believe about a given subject is to write about it. To support students in their writing, it is important to provide them with a meaningful writing task, one that has an authentic purpose, clear guidelines, and engages students in ...
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
Academic writing is a formal style of writing used in universities and scholarly publications. You'll encounter it in journal articles and books on academic topics, and you'll be expected to write your essays, research papers, and dissertation in academic style. Academic writing follows the same writing process as other types of texts, but ...
Introduction. Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Developing critical thinking and writing skills are also necessary to demonstrate your ability to understand and apply information about your topic. It is not uncommon to be unsure about the processes of writing ...
Harvard College Writing Center 2 Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt When you receive a paper assignment, your first step should be to read the assignment prompt carefully to make sure you understand what you are being asked to do. Sometimes your assignment will be open-ended ("write a paper about anything in the course that interests you").
Table of contents. Step 1: Prewriting. Step 2: Planning and outlining. Step 3: Writing a first draft. Step 4: Redrafting and revising. Step 5: Editing and proofreading. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the writing process.
1. Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information.
Courses and assignments should be planned with this in mind. Three principles are paramount: 1. Name what you want and imagine students doing it. However free students are to range and explore in a paper, the general kind of paper you're inviting has common components, operations, and criteria of success, and you should make these explicit ...
Writing in college is usually a response to class materials—an assigned reading, a discussion in class, an experiment in a lab. Generally speaking, these writing tasks can be divided into three broad categories: summary assignments, defined-topic assignments, and undefined-topic assignments.
It is based on research as well as the student's own ideas. Depending on the topic, the student may need to use either primary or secondary sources or a combination of both. 3. Literature Reviews. These writing assignments require students to survey existing scholarship on a specific topic and construct an overview of current knowledge.
Instructors can often help students write more effective papers by giving students written instructions about that assignment. Explicit descriptions of assignments on the syllabus or on an "assignment sheet" tend to produce the best results. These instructions might make explicit the process or steps necessary to complete the assignment.
If you take the steps to retain, plan, and understand the meaning behind your writing assignment, you will increase your confidence and success as a writer. Focusing on key words and phrases will provide clues on what actions to take while planning the structure and content of your essay.
For each kind of assignment, you'll find sample timelines and sequences, along with out-of-the-box activities and generalizable advice on teaching with writing ("tips" and "pitfalls to avoid"). The advice and examples in this section are meant to be flexible enough to adapt to a wide range of real-life teaching scenarios and ...
With regular writing practice and targeted feedback, over time they will become more authoritative participants and contributors in your field. Designing successful writing assignments involves some or all of the following six strategies: Explicitly State Assignment Goals. Tie Assignment Goals to Course Goals.
As you think about making up writing assignments, use these five principles: Tie the writing task to specific pedagogical goals, particularly those articulated in the overall course goals. Note rhetorical aspects of the task, i.e., audience, purpose, writing situation. Break down the task into manageable steps. Make all elements of the task clear.
Effective writing assignments, aligned with core learning goals, can help students build on their prior knowledge, apply key concepts introduced in lectures, labs, readings, and discussions, and anticipate future learning. While it is important to make the why behind the assignment clear to students, it's also important to consider the when of the assignment.
Critical Analysis: Write about the argument or reasoning of an author's work. Evaluate. Literary Analysis: Write about your interpretation of the meaning or significance of literary work (novel, play, poem, short story). In the visual arts, we use the term "critique," for writing that does this about films, paintings, etc.
The basic structure of an assignment includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should present the topic and establish the purpose of your assignment. The body should delve into the topic in detail, backed by your research. The conclusion should summarize your findings or arguments without introducing new ideas.
Designing Writing Assignments designing-assignments. As you think about creating writing assignments, use these five principles: Tie the writing task to specific pedagogical goals. Note rhetorical aspects of the task, i.e., audience, purpose, writing situation. Make all elements of the task clear. Include grading criteria on the assignment ...
A compare & contrast assignment is a type of expository & research paper assignment. It is important to organize your writing around the themes you are comparing & contrasting. If, for example, you are assigned to compare & contrast, say, Augustine's Confessions and The Autobiography of Malcolm X, a common mistake students make is to write the first part of their essay strictly about Augustine ...
Technology in the Writing Classroom. Technology affects both the process and product of composition. Students often complete multimodal writing assignments that combine traditional textual elements with pictures, data visualizations, video, sound, animation, etc. Similarly, students' use of many technologies while composing an assignment can ...
The Open Writing Assignment. Professors who don't use writing prompts believe that an important part of scholarship is learning to raise questions that will yield a good academic argument. Instead of creating a writing prompt, these professors craft an assignment process that supports students as they work through the various challenges of ...
Communicate new policy and assignment guidelines with students. 3. Review and revise writing assignments and associated scoring tools (rubrics, etc.). 4. Employ the writing process; live in a formative space. 5. Direct students to use writing platforms where multiple drafts can be saved for review. 6.
Writing deepens thinking and increases students' engagement with course material. Well-designed writing assignments prompt students to think more deeply about what they're learning. Writing a book review, for example, forces students to read more thoroughly and critically.
Public writing and the writing of content intended for general audiences ; Descriptive and alternative text; Transcriptions and translations; While the end product of digital assignments may have a smaller word count than essays and final projects, the writing process may be as (or more) intensive and ask students to engage with knowledge in ...
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This guide will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful ...