Dissertations & projects: Tenses
- Research questions
- The process of reviewing
- Project management
- Literature-based projects

On this page:
“You will use a range of tenses depending on what you are writing about . ” Elizabeth M Fisher, Richard C Thompson, and Daniel Holtom, Enjoy Writing Your Science Thesis Or Dissertation!
Tenses can be tricky to master. Even well respected journals differ in the guidance they give their authors for their use. However, their are some general conventions about what tenses are used in different parts of the report/dissertation. This page gives some advice on standard practice.
What tenses will you use?

There are exceptions however, most notably in the literature review where you will use a mixture of past , present and present perfect tenses (don't worry, that is explained below), when discussing the implications of your findings when the present tense is appropriate and in the recommendations where you are likely to use the future tense.
The tenses used as standard practice in each of these sections of your report are given and explained below.
In your abstract
You have some leeway with tense use in your abstract and guidance does vary which can sometimes be confusing. We recommend the following:
Describing the current situation and reason for your study
Mostly use the present tense, i.e. "This is the current state of affairs and this is why this study is needed."
Occasionally, you may find the need to use something called the present perfect tense when you are describing things that happened in the past but are still relevant. The present perfect tense uses have/has and then the past participle of the verb i.e. Previous research on this topic has focused on...
Describing the aims of your study
Here you have a choice. It is perfectly acceptable to use either the present or past tense, i.e. "This study aims to..." or "This study aimed to..."
Describing your methodology
Use the past tense to describe what you did, i.e. "A qualitative approach was used." "A survey was undertaken to ...". "The blood sample was analysed by..."
Describing your findings
Use the past tense to describe what you found as it is specific to your study, i.e. "The results showed that...", "The analysis indicated that..."
Suggesting the implications of your study
Use the present tense as even though your study took place in the past, your implications remain relevant in the present, i.e. Results revealed x which indicates that..."
Example abstract
An example abstract with reasoning for the tenses chosen can be found at the bottom of this excellent blog post:
Using the Present Tense and Past Tense When Writing an Abstract
In your methodology
The methodology is one of the easiest sections when it comes to tenses as you are explaining to your reader what you did. This is therefore almost exclusively written in the past tense.
Blood specimens were frozen at -80 o C.
A survey was designed using the Jisc Surveys tool.
Participants were purposefully selected.
The following search strategy was used to search the literature:
Very occasionally you may use the present tense if you are justifying a decision you have taken (as the justification is still valid, not just at the time you made the decision). For example:
Purposeful sampling was used to ensure that a range of views were included. This sampling method maximises efficiency and validity as it identifies information-rich cases and ... (Morse & Niehaus, 2009).
In your discussion/conclusion
This will primarily be written in the present tense as you are generally discussing or making conclusions about the relevance of your findings at the present time. So you may write:
The findings of this research suggest that.../are potentially important because.../could open a new avenue for further research...
There will also be times when you use the past tense , especially when referring to part of your own research or previous published research research - but this is usually followed by something in the present tense to indicate the current relevance or the future tense to indicate possible future directions:
Analysis of the survey results found most respondents were not concerned with the processes, just the outcome. This suggests that managers should focus on...
These findings mirrored those of Cheung (2020), who also found that ESL pupils failed to understand some basic yet fundamental instructions. Addressing this will help ensure...
In your introduction
The introduction generally introduces what is in the rest of your document as is therefore describing the present situation and so uses the present tense :
Chapter 3 describes the research methodology.
Depending on your discipline, your introduction may also review the literature so please also see that section below.
In your literature review
The findings of some literature may only be applicable in the specific circumstances that the research was undertaken and so need grounding to that study. Conversely, the findings of other literature may now be accepted as established knowledge. Also, you may consider the findings of older literature to be still relevant and relatively recent literature be already superseded. The tenses you write in will help to indicate a lot of this to the reader. In other words, you will use a mix of tenses in your review depending on what you are implying.
Findings only applicable in the specific circumstances
Use the past tense . For example:
In an early study, Sharkey et al. (1991) found that isoprene emissions were doubled in leaves on sunnier sides of oak and aspen trees.
Using the past tense indicates that you are not implying that isoprene emissions are always doubled on the sunnier side of the trees, just that is what was found in the Sharkey et al. study.
Findings that are still relevant or now established knowledge
Mostly use the present tense , unless the study is not recent and the authors are the subject of the sentence (which you should use very sparingly in a literature review) when you may need to use a mixture of the past and present. For example:
A narrowing of what 'graduateness' represents damages students’ abilities to thrive as they move through what will almost certainly be complex career pathways (Holmes, 2001).
Holmes (2001) argued strongly that a narrowing of what 'graduateness' represents damages students’ abilities to thrive as they move through what will almost certainly be complex career pathways
Both of these imply that you think this is still the case (although it is perhaps more strongly implied in the first example). You may also want to use some academic caution too - such as writing 'may damage' rather than the more definite 'damages'.
Presenting your results
As with your methodology, your results section should be written in the past tense . This indicates that you are accepting that the results are specific to your research. Whilst they may have current implications, that part will not be considered until your discussion/conclusions section(s).
Four main themes were identified from the interview data.
There was a significant change in oxygen levels.
Like with the methodology, you will occasionally switch to present tense to write things like "Table 3.4 shows that ..." but generally, stick to the past tense.
In your recommendations
Not everyone will need to include recommendations and some may have them as part of the conclusions chapter. Recommendations are written in a mixture of the present tense and future tense :
It is recommended that ward layout is adapted, where possible, to provide low-sensory bays for patients with autism. These will still be useable by all patients but...
Useful links
- Verb tenses in scientific manuscripts From International Science Editing
- Which Verb Tenses Should I Use in a Research Paper? Blog from WordVice
- << Previous: Writing style
- Next: Voice >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 1:09 PM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/dissertations
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem

How to Use Tenses within Scientific Writing
Written by: Chloe Collier
One’s tense will vary depending on what one is trying to convey within their paper or section of their paper. For example, the tense may change between the methods section and the discussion section.
Abstract --> Past tense
- The abstract is usually in the past tense due to it showing what has already been studied.
Example: “This study was conducted at the Iyarina Field School, and within the indigenous Waorani community within Yasuni National Park region.”
Introduction --> Present tense
- Example: “ Clidemia heterophylla and Piperaceae musteum are both plants with ant domata, meaning that there is an ant mutualism which protects them from a higher level of herbivory.”
Methods --> Past tense
- In the methods section one would use past tense due to what they have done was in the past.
- It has been debated whether one should use active or passive voice. The scientific journal Nature states that one should use active voice as to convey the concepts more directly.
- Example: “In the geographic areas selected for the study, ten random focal plants were selected as points for the study.”
Results --> Past tense
- Example: “We observed that there was no significant statistical difference in herbivory on Piperaceae between the two locations, Yasuni National Park, Ecuador (01° 10’ 11, 13”S and 77° 10’ 01. 47 NW) and Iyarina Field School, Ecuador (01° 02’ 35.2” S and 77° 43’ 02. 45” W), with the one exception being that there was found to be a statistical significance in the number count within a one-meter radius of Piperaceae musteum (Piperaceae).”
Discussion --> Present tense and past tense
- Example: “Symbiotic ant mutualistic relationships within species will defend their host plant since the plant provides them with food. In the case of Melastomataceae, they have swellings at the base of their petioles that house the ants and aid to protect them from herbivores.”
- One would use past tense to summarize one’s results
- Example: “In the future to further this experiment, we would expand this project and expand our sample size in order to have a more solid base for our findings.”

How To Write A Dissertation Introduction
A Simple Explainer With Examples + Free Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By Dr Eunice Rautenbach (D. Tech) | March 2020
If you’re reading this, you’re probably at the daunting early phases of writing up the introduction chapter of your dissertation or thesis. It can be intimidating, I know.
In this post, we’ll look at the 7 essential ingredients of a strong dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, as well as the essential things you need to keep in mind as you craft each section. We’ll also share some useful tips to help you optimize your approach.
Overview: Writing An Introduction Chapter
- The purpose and function of the intro chapter
- Craft an enticing and engaging opening section
- Provide a background and context to the study
- Clearly define the research problem
- State your research aims, objectives and questions
- Explain the significance of your study
- Identify the limitations of your research
- Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis
A quick sidenote:
You’ll notice that I’ve used the words dissertation and thesis interchangeably. While these terms reflect different levels of research – for example, Masters vs PhD-level research – the introduction chapter generally contains the same 7 essential ingredients regardless of level. So, in this post, dissertation introduction equals thesis introduction.

Start with why.
To craft a high-quality dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, you need to understand exactly what this chapter needs to achieve. In other words, what’s its purpose ? As the name suggests, the introduction chapter needs to introduce the reader to your research so that they understand what you’re trying to figure out, or what problem you’re trying to solve. More specifically, you need to answer four important questions in your introduction chapter.
These questions are:
- What will you be researching? (in other words, your research topic)
- Why is that worthwhile? (in other words, your justification)
- What will the scope of your research be? (in other words, what will you cover and what won’t you cover)
- What will the limitations of your research be? (in other words, what will the potential shortcomings of your research be?)
Simply put, your dissertation’s introduction chapter needs to provide an overview of your planned research , as well as a clear rationale for it. In other words, this chapter has to explain the “what” and the “why” of your research – what’s it all about and why’s that important.
Simple enough, right?
Well, the trick is finding the appropriate depth of information. As the researcher, you’ll be extremely close to your topic and this makes it easy to get caught up in the minor details. While these intricate details might be interesting, you need to write your introduction chapter on more of a “need-to-know” type basis, or it will end up way too lengthy and dense. You need to balance painting a clear picture with keeping things concise. Don’t worry though – you’ll be able to explore all the intricate details in later chapters.

Now that you understand what you need to achieve from your introduction chapter, we can get into the details. While the exact requirements for this chapter can vary from university to university, there are seven core components that most universities will require. We call these the seven essential ingredients .
The 7 Essential Ingredients
- The opening section – where you’ll introduce the reader to your research in high-level terms
- The background to the study – where you’ll explain the context of your project
- The research problem – where you’ll explain the “gap” that exists in the current research
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you’ll clearly state what your research will aim to achieve
- The significance (or justification) – where you’ll explain why your research is worth doing and the value it will provide to the world
- The limitations – where you’ll acknowledge the potential limitations of your project and approach
- The structure – where you’ll briefly outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis to help orient the reader
By incorporating these seven essential ingredients into your introduction chapter, you’ll comprehensively cover both the “ what ” and the “ why ” I mentioned earlier – in other words, you’ll achieve the purpose of the chapter.
Side note – you can also use these 7 ingredients in this order as the structure for your chapter to ensure a smooth, logical flow. This isn’t essential, but, generally speaking, it helps create an engaging narrative that’s easy for your reader to understand. If you’d like, you can also download our free introduction chapter template here.
Alright – let’s look at each of the ingredients now.

#1 – The Opening Section
The very first essential ingredient for your dissertation introduction is, well, an introduction or opening section. Just like every other chapter, your introduction chapter needs to start by providing a brief overview of what you’ll be covering in the chapter.
This section needs to engage the reader with clear, concise language that can be easily understood and digested. If the reader (your marker!) has to struggle through it, they’ll lose interest, which will make it harder for you to earn marks. Just because you’re writing an academic paper doesn’t mean you can ignore the basic principles of engaging writing used by marketers, bloggers, and journalists. At the end of the day, you’re all trying to sell an idea – yours is just a research idea.
So, what goes into this opening section?
Well, while there’s no set formula, it’s a good idea to include the following four foundational sentences in your opening section:
1 – A sentence or two introducing the overall field of your research.
For example:
“Organisational skills development involves identifying current or potential skills gaps within a business and developing programs to resolve these gaps. Management research, including X, Y and Z, has clearly established that organisational skills development is an essential contributor to business growth.”
2 – A sentence introducing your specific research problem.
“However, there are conflicting views and an overall lack of research regarding how best to manage skills development initiatives in highly dynamic environments where subject knowledge is rapidly and continuously evolving – for example, in the website development industry.”
3 – A sentence stating your research aims and objectives.
“This research aims to identify and evaluate skills development approaches and strategies for highly dynamic industries in which subject knowledge is continuously evolving.”.
4 – A sentence outlining the layout of the chapter.
“This chapter will provide an introduction to the study by first discussing the background and context, followed by the research problem, the research aims, objectives and questions, the significance and finally, the limitations.”
As I mentioned, this opening section of your introduction chapter shouldn’t be lengthy . Typically, these four sentences should fit neatly into one or two paragraphs, max. What you’re aiming for here is a clear, concise introduction to your research – not a detailed account.
PS – If some of this terminology sounds unfamiliar, don’t stress – I’ll explain each of the concepts later in this post.
#2 – Background to the study
Now that you’ve provided a high-level overview of your dissertation or thesis, it’s time to go a little deeper and lay a foundation for your research topic. This foundation is what the second ingredient is all about – the background to your study.
So, what is the background section all about?
Well, this section of your introduction chapter should provide a broad overview of the topic area that you’ll be researching, as well as the current contextual factors . This could include, for example, a brief history of the topic, recent developments in the area, key pieces of research in the area and so on. In other words, in this section, you need to provide the relevant background information to give the reader a decent foundational understanding of your research area.
Let’s look at an example to make this a little more concrete.
If we stick with the skills development topic I mentioned earlier, the background to the study section would start by providing an overview of the skills development area and outline the key existing research. Then, it would go on to discuss how the modern-day context has created a new challenge for traditional skills development strategies and approaches. Specifically, that in many industries, technical knowledge is constantly and rapidly evolving, and traditional education providers struggle to keep up with the pace of new technologies.
Importantly, you need to write this section with the assumption that the reader is not an expert in your topic area. So, if there are industry-specific jargon and complex terminology, you should briefly explain that here , so that the reader can understand the rest of your document.
Don’t make assumptions about the reader’s knowledge – in most cases, your markers will not be able to ask you questions if they don’t understand something. So, always err on the safe side and explain anything that’s not common knowledge.

#3 – The research problem
Now that you’ve given your reader an overview of your research area, it’s time to get specific about the research problem that you’ll address in your dissertation or thesis. While the background section would have alluded to a potential research problem (or even multiple research problems), the purpose of this section is to narrow the focus and highlight the specific research problem you’ll focus on.
But, what exactly is a research problem, you ask?
Well, a research problem can be any issue or question for which there isn’t already a well-established and agreed-upon answer in the existing research. In other words, a research problem exists when there’s a need to answer a question (or set of questions), but there’s a gap in the existing literature , or the existing research is conflicting and/or inconsistent.
So, to present your research problem, you need to make it clear what exactly is missing in the current literature and why this is a problem . It’s usually a good idea to structure this discussion into three sections – specifically:
- What’s already well-established in the literature (in other words, the current state of research)
- What’s missing in the literature (in other words, the literature gap)
- Why this is a problem (in other words, why it’s important to fill this gap)
Let’s look at an example of this structure using the skills development topic.
Organisational skills development is critically important for employee satisfaction and company performance (reference). Numerous studies have investigated strategies and approaches to manage skills development programs within organisations (reference).
(this paragraph explains what’s already well-established in the literature)
However, these studies have traditionally focused on relatively slow-paced industries where key skills and knowledge do not change particularly often. This body of theory presents a problem for industries that face a rapidly changing skills landscape – for example, the website development industry – where new platforms, languages and best practices emerge on an extremely frequent basis.
(this paragraph explains what’s missing from the literature)
As a result, the existing research is inadequate for industries in which essential knowledge and skills are constantly and rapidly evolving, as it assumes a slow pace of knowledge development. Industries in such environments, therefore, find themselves ill-equipped in terms of skills development strategies and approaches.
(this paragraph explains why the research gap is problematic)
As you can see in this example, in a few lines, we’ve explained (1) the current state of research, (2) the literature gap and (3) why that gap is problematic. By doing this, the research problem is made crystal clear, which lays the foundation for the next ingredient.
#4 – The research aims, objectives and questions
Now that you’ve clearly identified your research problem, it’s time to identify your research aims and objectives , as well as your research questions . In other words, it’s time to explain what you’re going to do about the research problem.
So, what do you need to do here?
Well, the starting point is to clearly state your research aim (or aims) . The research aim is the main goal or the overarching purpose of your dissertation or thesis. In other words, it’s a high-level statement of what you’re aiming to achieve.
Let’s look at an example, sticking with the skills development topic:
“Given the lack of research regarding organisational skills development in fast-moving industries, this study will aim to identify and evaluate the skills development approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK”.
As you can see in this example, the research aim is clearly outlined, as well as the specific context in which the research will be undertaken (in other words, web development companies in the UK).
Next up is the research objective (or objectives) . While the research aims cover the high-level “what”, the research objectives are a bit more practically oriented, looking at specific things you’ll be doing to achieve those research aims.
Let’s take a look at an example of some research objectives (ROs) to fit the research aim.
- RO1 – To identify common skills development strategies and approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK.
- RO2 – To evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies and approaches.
- RO3 – To compare and contrast these strategies and approaches in terms of their strengths and weaknesses.
As you can see from this example, these objectives describe the actions you’ll take and the specific things you’ll investigate in order to achieve your research aims. They break down the research aims into more specific, actionable objectives.
The final step is to state your research questions . Your research questions bring the aims and objectives another level “down to earth”. These are the specific questions that your dissertation or theses will seek to answer. They’re not fluffy, ambiguous or conceptual – they’re very specific and you’ll need to directly answer them in your conclusions chapter .
The research questions typically relate directly to the research objectives and sometimes can look a bit obvious, but they are still extremely important. Let’s take a look at an example of the research questions (RQs) that would flow from the research objectives I mentioned earlier.
- RQ1 – What skills development strategies and approaches are currently being used by web development companies in the UK?
- RQ2 – How effective are each of these strategies and approaches?
- RQ3 – What are the strengths and weaknesses of each of these strategies and approaches?
As you can see, the research questions mimic the research objectives , but they are presented in question format. These questions will act as the driving force throughout your dissertation or thesis – from the literature review to the methodology and onward – so they’re really important.
A final note about this section – it’s really important to be clear about the scope of your study (more technically, the delimitations ). In other words, what you WILL cover and what you WON’T cover. If your research aims, objectives and questions are too broad, you’ll risk losing focus or investigating a problem that is too big to solve within a single dissertation.
Simply put, you need to establish clear boundaries in your research. You can do this, for example, by limiting it to a specific industry, country or time period. That way, you’ll ringfence your research, which will allow you to investigate your topic deeply and thoroughly – which is what earns marks!
Need a helping hand?
#5 – Significance
Now that you’ve made it clear what you’ll be researching, it’s time to make a strong argument regarding your study’s importance and significance . In other words, now that you’ve covered the what, it’s time to cover the why – enter essential ingredient number 5 – significance.
Of course, by this stage, you’ve already briefly alluded to the importance of your study in your background and research problem sections, but you haven’t explicitly stated how your research findings will benefit the world . So, now’s your chance to clearly state how your study will benefit either industry , academia , or – ideally – both . In other words, you need to explain how your research will make a difference and what implications it will have .
Let’s take a look at an example.
“This study will contribute to the body of knowledge on skills development by incorporating skills development strategies and approaches for industries in which knowledge and skills are rapidly and constantly changing. This will help address the current shortage of research in this area and provide real-world value to organisations operating in such dynamic environments.”
As you can see in this example, the paragraph clearly explains how the research will help fill a gap in the literature and also provide practical real-world value to organisations.
This section doesn’t need to be particularly lengthy, but it does need to be convincing . You need to “sell” the value of your research here so that the reader understands why it’s worth committing an entire dissertation or thesis to it. This section needs to be the salesman of your research. So, spend some time thinking about the ways in which your research will make a unique contribution to the world and how the knowledge you create could benefit both academia and industry – and then “sell it” in this section.

#6 – The limitations
Now that you’ve “sold” your research to the reader and hopefully got them excited about what’s coming up in the rest of your dissertation, it’s time to briefly discuss the potential limitations of your research.
But you’re probably thinking, hold up – what limitations? My research is well thought out and carefully designed – why would there be limitations?
Well, no piece of research is perfect . This is especially true for a dissertation or thesis – which typically has a very low or zero budget, tight time constraints and limited researcher experience. Generally, your dissertation will be the first or second formal research project you’ve ever undertaken, so it’s unlikely to win any research awards…
Simply put, your research will invariably have limitations. Don’t stress yourself out though – this is completely acceptable (and expected). Even “professional” research has limitations – as I said, no piece of research is perfect. The key is to recognise the limitations upfront and be completely transparent about them, so that future researchers are aware of them and can improve the study’s design to minimise the limitations and strengthen the findings.
Generally, you’ll want to consider at least the following four common limitations. These are:
- Your scope – for example, perhaps your focus is very narrow and doesn’t consider how certain variables interact with each other.
- Your research methodology – for example, a qualitative methodology could be criticised for being overly subjective, or a quantitative methodology could be criticised for oversimplifying the situation (learn more about methodologies here ).
- Your resources – for example, a lack of time, money, equipment and your own research experience.
- The generalisability of your findings – for example, the findings from the study of a specific industry or country can’t necessarily be generalised to other industries or countries.
Don’t be shy here. There’s no use trying to hide the limitations or weaknesses of your research. In fact, the more critical you can be of your study, the better. The markers want to see that you are aware of the limitations as this demonstrates your understanding of research design – so be brutal.
#7 – The structural outline
Now that you’ve clearly communicated what your research is going to be about, why it’s important and what the limitations of your research will be, the final ingredient is the structural outline.The purpose of this section is simply to provide your reader with a roadmap of what to expect in terms of the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
In this section, you’ll need to provide a brief summary of each chapter’s purpose and contents (including the introduction chapter). A sentence or two explaining what you’ll do in each chapter is generally enough to orient the reader. You don’t want to get too detailed here – it’s purely an outline, not a summary of your research.
Let’s look at an example:
In Chapter One, the context of the study has been introduced. The research objectives and questions have been identified, and the value of such research argued. The limitations of the study have also been discussed.
In Chapter Two, the existing literature will be reviewed and a foundation of theory will be laid out to identify key skills development approaches and strategies within the context of fast-moving industries, especially technology-intensive industries.
In Chapter Three, the methodological choices will be explored. Specifically, the adoption of a qualitative, inductive research approach will be justified, and the broader research design will be discussed, including the limitations thereof.
So, as you can see from the example, this section is simply an outline of the chapter structure, allocating a short paragraph to each chapter. Done correctly, the outline will help your reader understand what to expect and reassure them that you’ll address the multiple facets of the study.
By the way – if you’re unsure of how to structure your dissertation or thesis, be sure to check out our video post which explains dissertation structure .
Keep calm and carry on.
Hopefully you feel a bit more prepared for this challenge of crafting your dissertation or thesis introduction chapter now. Take a deep breath and remember that Rome wasn’t built in a day – conquer one ingredient at a time and you’ll be firmly on the path to success.
Let’s quickly recap – the 7 ingredients are:
- The opening section – where you give a brief, high-level overview of what your research will be about.
- The study background – where you introduce the reader to key theory, concepts and terminology, as well as the context of your study.
- The research problem – where you explain what the problem with the current research is. In other words, the research gap.
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you clearly state what your dissertation will investigate.
- The significance – where you explain what value your research will provide to the world.
- The limitations – where you explain what the potential shortcomings and limitations of your research may be.
- The structural outline – where you provide a high-level overview of the structure of your document
If you bake these ingredients into your dissertation introduction chapter, you’ll be well on your way to building an engaging introduction chapter that lays a rock-solid foundation for the rest of your document.
Remember, while we’ve covered the essential ingredients here, there may be some additional components that your university requires, so be sure to double-check your project brief!

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
44 Comments
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident enough in undertaking my thesis on the survey;The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction
Glad to hear that. Good luck with your thesis!
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident now undertaking my thesis; The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction.
Thanks so much for this article. I found myself struggling and wasting a lot of time in my thesis writing but after reading this article and watching some of your youtube videos, I now have a clear understanding of what is required for a thesis.
Thank you Derek, i find your each post so useful. Keep it up.
Thank you so much Derek ,for shedding the light and making it easier for me to handle the daunting task of academic writing .
Thanks do much Dereck for the comprehensive guide. It will assist me queit a lot in my thesis.
thanks a lot for helping
i LOVE the gifs, such a fun way to engage readers. thanks for the advice, much appreciated
Thanks a lot Derek! It will be really useful to the beginner in research!
You’re welcome
This is a well written, easily comprehensible, simple introduction to the basics of a Research Dissertation../the need to keep the reader in mind while writing the dissertation is an important point that is covered../ I appreciate the efforts of the author../
The instruction given are perfect and clear. I was supposed to take the course , unfortunately in Nepal the service is not avaialble.However, I am much more hopeful that you will provide require documents whatever you have produced so far.
Thank you very much
Thanks so much ❤️😘 I feel am ready to start writing my research methodology
This is genuinely the most effective advice I have ever been given regarding academia. Thank you so much!
This is one of the best write up I have seen in my road to PhD thesis. regards, this write up update my knowledge of research
I was looking for some good blogs related to Education hopefully your article will help. Thanks for sharing.
This is an awesome masterpiece. It is one of the most comprehensive guides to writing a Dissertation/Thesis I have seen and read.
You just saved me from going astray in writing a Dissertation for my undergraduate studies. I could not be more grateful for such a relevant guide like this. Thank you so much.
Thank you so much Derek, this has been extremely helpful!!
I do have one question though, in the limitations part do you refer to the scope as the focus of the research on a specific industry/country/chronological period? I assume that in order to talk about whether or not the research could be generalized, the above would need to be already presented and described in the introduction.
Thank you again!
Phew! You have genuinely rescued me. I was stuck how to go about my thesis. Now l have started. Thank you.
This is the very best guide in anything that has to do with thesis or dissertation writing. The numerous blends of examples and detailed insights make it worth a read and in fact, a treasure that is worthy to be bookmarked.
Thanks a lot for this masterpiece!
Powerful insight. I can now take a step
Thank you very much for these valuable introductions to thesis chapters. I saw all your videos about writing the introduction, discussion, and conclusion chapter. Then, I am wondering if we need to explain our research limitations in all three chapters, introduction, discussion, and conclusion? Isn’t it a bit redundant? If not, could you please explain how can we write in different ways? Thank you.
Excellent!!! Thank you…
Thanks for this informative content. I have a question. The research gap is mentioned in both the introduction and literature section. I would like to know how can I demonstrate the research gap in both sections without repeating the contents?
I’m incredibly grateful for this invaluable content. I’ve been dreading compiling my postgrad thesis but breaking each chapter down into sections has made it so much easier for me to engage with the material without feeling overwhelmed. After relying on your guidance, I’m really happy with how I’ve laid out my introduction.
Thank you for the informative content you provided
Hi Derrick and Team, thank you so much for the comprehensive guide on how to write a dissertation or a thesis introduction section. For some of us first-timers, it is a daunting task. However, the instruction with relevant examples makes it clear and easy to follow through. Much appreciated.
It was so helpful. God Bless you. Thanks very much
I thank you Grad coach for your priceless help. I have two questions I have learned from your video the limitations of the research presented in chapter one. but in another video also presented in chapter five. which chapter limitation should be included? If possible, I need your answer since I am doing my thesis. how can I explain If I am asked what is my motivation for this research?
You explain what moment in life caused you to have a peaked interest in the thesis topic. Personal experiences? Or something that had an impact on your life, or others. Something would have caused your drive of topic. Dig deep inside, the answer is within you!
Thank you guys for the great work you are doing. Honestly, you have made the research to be interesting and simplified. Even a novice will easily grasp the ideas you put forward, Thank you once again.
Excellent piece!
I feel like just settling for a good topic is usually the hardest part.
Thank you so much. My confidence has been completely destroyed during my first year of PhD and you have helped me pull myself together again
Happy to help 🙂
I am so glad I ran into your resources and did not waste time doing the wrong this. Research is now making so much sense now.
Gratitude to Derrick and the team I was looking for a solid article that would aid me in drafting the thesis’ introduction. I felt quite happy when I came across the piece you wrote because it was so well-written and insightful. I wish you success in the future.
thank you so much. God Bless you
Thank you so much Grad Coach for these helpful insights. Now I can get started, with a great deal of confidence.
It’s ‘alluded to’ not ‘eluded to’.
This is great!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Verbs are direct, vigorous communicators. Use a chosen verb tense consistently throughout the same and adjacent paragraphs of a paper to ensure smooth expression.
Use the following verb tenses to report information in APA Style papers.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Literature review (or whenever discussing other researchers’ work) | Past | Martin (2020) addressed |
| Present perfect | Researchers have studied | |
| Method Description of procedure | Past | Participants took a survey |
| Present perfect | Others have used similar approaches | |
| Reporting of your own or other researchers’ results | Past | Results showed Scores decreased Hypotheses were not supported |
| Personal reactions | Past | I felt surprised |
| Present perfect | I have experienced | |
| Present | I believe | |
| Discussion of implications of results or of previous statements | Present | The results indicate The findings mean that |
| Presentation of conclusions, limitations, future directions, and so forth | Present | We conclude Limitations of the study are Future research should explore |
Verb tense is covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 4.12 and the Concise Guide Section 2.12
From the APA Style blog

Check your tone: Keeping it professional
When writing an APA Style paper, present ideas in a clear and straightforward manner. In this kind of scholarly writing, keep a professional tone.

The “no second-person” myth
Many writers believe the “no second-person” myth, which is that there is an APA Style guideline against using second-person pronouns such as “you” or “your.” On the contrary, you can use second-person pronouns in APA Style writing.
The “no first-person” myth
Whether expressing your own views or actions or the views or actions of yourself and fellow authors, use the pronouns “I” and “we.”

Navigating the not-so-hidden treasures of the APA Style website
This post links directly to APA Style topics of interest that users may not even know exist on the website.

Welcome, singular “they”
This blog post provides insight into how this change came about and provides a forum for questions and feedback.
How to write a PhD in a hundred steps (or more)
A workingmumscholar's journey through her phd and beyond, changing tenses as you write your dissertation.
The PhD student I am supervising sent the first draft of her methodology chapter yesterday with a series of questions and notes for me and the co-supervisor. One of them was about tense: she is writing everything in the present and future tense, but wondered if this was a mistake. It got me thinking (again) about tense in the PhD thesis , and the process of moving from future to past as the project progresses.
I have written here a little about the gap between the logic of discovery and the logic of display or dissemination in writing. As you are working, everything is either ‘I am doing this’ and ‘I will be doing that eventually’. This is pretty much the tense in which you write your proposal – proposals are forward looking. So, as you start you research, you will naturally be thinking now, and on to the next steps, and your writing will most likely reflect this in the tenses you choose. This is the logic of discovery . As you move along, you will make decisions, close some doors, open others , and your argument will unfold and form as you do so.

So what to do now, in the midst of your research and writing – can and should you anticipate being finished and therefore writing everything in the methodology in the past tense, or do you worry about that later? It does seem like more work to write in the voice of discovery while you are still discovering things, and then write again later in the voice of dissemination as you reorganise and display your thinking with the benefit of (some) hindsight. However, I would caution against trying to anticipate too much . A significant part of doing a PhD is the process of doing a piece of research, and learning through missteps, successes and issues like the one discussed here how doing and writing about research feels and looks and sounds. That way, you can go on to do further research, either on your own or with others post-PhD, and you can eventually supervise PhD students yourself.

So my advice, if you are stuck in a similar spot to my PhD student is this: be where you are . Think and write your way through this patch, and write in whatever tense and voice feels most authentic to you at this point. The good news is that there will be time for rewriting, polishing and updating before you submit, and it’s quite a pleasant feeling to go back to this methodology chapter after the findings have been presented and analysed, and find that you can edit, sharpen and focus that section to create a tight, accurate and interesting narrative about the nuts and bolts of your PhD. As you do so, every time you do so, your researcher capacity and voice and ability to add to the conversation through the knowledge you are making grows, and that is what being an academic researcher is about.
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
How To Write Your Dissertation Introduction
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Definition: Dissertation Introduction
- 3 Dissertation Introduction Structure
- 4 Writing a Dissertation Introduction
- 5 Dissertation Introduction Tips
- 6 Dissertation Introduction Example
- 7 In a Nutshell
Definition: Dissertation Introduction
Background information is what needs to appear first when it comes to the dissertation introduction. The structure of the other points doesn’t follow any sequence, and it is entirely up to you. You might consider introducing your main focus by presenting the aims and objectives that explain why your research area is essential, and the overall need for that particular research field. The ‘value’ section is crucial to those who will be judging the merit of your work and needs to be in your dissertation introduction, and this is important because it demonstrates that you have considered how it adds value.
What is a dissertation introduction?
The introduction of your dissertation justifies your dissertation, the thesis, or other research projects. It also explains what you are trying to answer ( research question ) and why it’s essential to do this research. It is important that the aim of the research and what it can offer to the academic community is heavily emphasized.
How do you write an introduction to a dissertation literature review?
The dissertation introduction describes your dissertation topic and provides the right context for reviewing the literature. You should create good reasons, explain the organizational sequence, and also state your scope of the review. The introduction should clearly ouline the main topics that are going to be discussed.
How do you write an introduction to a PhD?
A practical PhD dissertation introduction must establish the research area by situating your research in a broader context. It must also develop and justify your niche by describing why your research is needed. Also, state the significance of your study by explaining how you conducted your research.
Tip: For a full outline of the dissertation structure , take a look at our blog post.
How long should a dissertation introduction be?
The introduction of the dissertation consists of ten percent of the whole paper. If you are writing a dissertation of five thousand words, the introductory section should consist of five hundred words. Refer to your research questions or hypothesis if you’re having trouble writing your dissertation introduction.
What is the purpose of a dissertation introduction?
The primary purpose of writing a dissertation introduction is to introduce the dissertation topic and the primary purpose of your study. You also demonstrate the relevance of your discussion whilst convincing readers of its practical and scientific significance. It’s important that you catch the reader’s attention and this can be done by using persuasive examples from related sources.
How can I start my dissertation introduction?
Some reliable tips for starting your dissertation introduction include the use of a catchy opening sentence that will get the attention of your reader. Don’t mention everything at this point, but only outline your topic and relevant arguments. Additionally, keep your language straightforward and don’t promise anything that cannot be delivered later.
Tip: It can be hard to fight off writer’s block , so head over to our blog article for some tips. However, if you’re still having trouble writing your dissertation introduction, start writing the body of the dissertation and come back to the introduction later!
Dissertation Introduction Structure
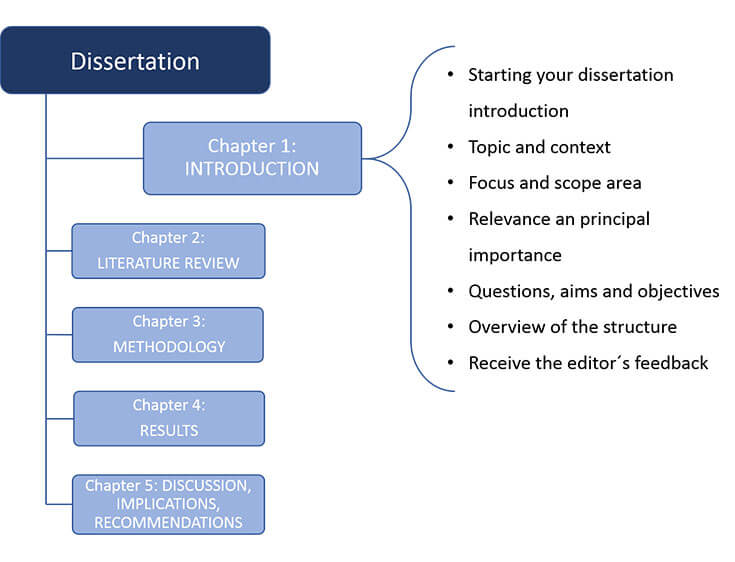
How to structure the introduction of your dissertation:
1. Introduction
Starting your dissertation introduction – this should be the last part to write. You can write a rough draft to help guide you. It’s crucial to draw the reader’s attention with a well-built beginning. Set your research introduction stage with a clear focus and purpose that gives a direction.

2. Topic and its context
Topic and context – introduce your problem and give the necessary background information. Aim to show why the question is timely or essential. Mention a relevant news item like an academic debate.
3. Focus and scope area
Focus and scope – after introduction part, narrow down and focus on defining the scope of your research. For instance, what demographics or communities are you researching? What geographical area are you investigating?
4. Relevance and principal importance
Relevance and importance – show how your research will address the problem gap in your identified research area. Cite relevant literature and describe how the new insights will contribute to the importance of your research. Explain how your research will build on existing research to help solve a practical or theoretical problem.
5. Questions, aims and objectives
Questions and objectives – this is where you set up the expectations of the remaining part of your dissertation. You can formulate the research questions depending on your topic, focus, and discipline. Also, state the methods that you used to get the answers to your questions here if your dissertation doesn’t have a methodology chapter. If your research aims at testing hypotheses, formulate them here.
6. Overview summary
Overview of the structure – this part summarizes sections and shows how the introduction of your dissertation contributes to your aims and objectives. Keep this part short by using one or two sentences to describe the contents of each section.
7. Receive the editor´s feedback
Receive the editor’s feedback – some professional editors will proofread and edit your paper based on instructions given, such as the academic style. They will also check grammar, vague sentences, and style consistency and provide a report on your language use, structure, and layout.
Printing Your Thesis With BachelorPrint
- High-quality bindings with customizable embossing
- 3D live preview to check your work before ordering
- Free express delivery
Configure your binding now!
to the print shop
Writing a Dissertation Introduction
In academic writing , there are active steps that a writer can take to attract the reader’s interest. Establish a specific area by showing your target audience that it’s significant and exciting. Introduce and evaluate previous research in the same area. Determine a niche by indicating the gaps in previous studies.

An excellent dissertation introduction allows you to:
- List hypotheses or research questions
- State the nature of your research primary purposes
- Indicate the outline of your academic project
- Announce important research findings
- State the value of previous studies in that field.
Dissertation Introduction Tips
Knowing when to use which tense in your dissertation or thesis is a common problem. A dissertation introduction is a plan of a study not yet conducted, so any reference needs to be in the future tense. Any reference to a study that is already published should be in the past tense. Statements regarding a program, theory, policy, or a concept that is still in effect should be in the present tense. Stay impersonal and make use of a list.
For example, say: firstly, secondly, etc., rather than first, second, etc.
Use ‘a’ when talking about something in general and ‘the’ when talking about something in particular., dissertation introduction example.
How to write a dissertation introduction:
Dissertation printing & binding
You are already done writing your dissertation and need a high quality printing & binding service? Then you are right to choose BachelorPrint! Check out our 24-hour online printing service. For more information click the button below :
Dissertation Printing & Binding
In a Nutshell
- A dissertation introduction is like a road map that tells your audience the direction your research will take.
- The introduction is the summary of the general context and scope of your topic and gives reference to previous literature on the subject.
- It includes the purpose of your research and the reasoning about why it’s relevant to conduct the study.
- It describes the research processes and gives an idea of the study, and also addresses the type of references available.
- It provides a summary of the specific questions and issues to address in the proposal.
Extremely satisfied, excellent deal with delivery in less than 24h. The print...
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Eigentümer dieser Website, |
| Zweck | Speichert die Einstellungen der Besucher, die in der Cookie Box von Borlabs Cookie ausgewählt wurden. |
| Cookie Name | borlabs-cookie |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Bachelorprint |
| Zweck | Erkennt das Herkunftsland und leitet zur entsprechenden Sprachversion um. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | ip-api.com |
| Cookie Name | georedirect |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Playcanvas |
| Zweck | Display our 3D product animations |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | playcanv.as, playcanvas.as, playcanvas.com |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Cookie von Google zur Steuerung der erweiterten Script- und Ereignisbehandlung. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Cookie Name | _ga,_gat,_gid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Facebook-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .facebook.com |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird zum Entsperren von Google Maps-Inhalten verwendet. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Instagram-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .instagram.com |
| Cookie Name | pigeon_state |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Sitzung |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Openstreetmap Foundation, St John’s Innovation Centre, Cowley Road, Cambridge CB4 0WS, United Kingdom |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um OpenStreetMap-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .openstreetmap.org |
| Cookie Name | _osm_location, _osm_session, _osm_totp_token, _osm_welcome, _pk_id., _pk_ref., _pk_ses., qos_token |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1-10 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Twitter International Company, One Cumberland Place, Fenian Street, Dublin 2, D02 AX07, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Twitter-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .twimg.com, .twitter.com |
| Cookie Name | __widgetsettings, local_storage_support_test |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Unbegrenzt |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Vimeo Inc., 555 West 18th Street, New York, New York 10011, USA |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Vimeo-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | player.vimeo.com |
| Cookie Name | vuid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um YouTube-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
Privacy Policy Imprint
[email protected]
- English English Spanish German French Turkish

How Can You Decide on Tense Usage in Your Dissertation?
The corpus research suggests that the most often used tenses in academic writing are the simple present, the simple past, and the present perfect. Then, what comes next is the future tense.

Which tenses are most common in academic writing?
The corpus research suggests that the most often used tenses in academic writing are the simple present tense, the simple past tense, and the present perfect tense. Then, what comes next is the future tense.
Simple present tense: You can use the simple present to define a general truth or a habitual action. This tense demonstrates that what you state is usually true in the past, present, and future.
Example: Water generally boils at 100C.
Simple past : You may employ the simple past tense to call a completed action that occurred at a specific point in the past (e.g., last month, one hour ago, last Sunday). The specific point of time is 2019 in the following example.
Example: The first known COVID outbreak started in Wuhan, Hubei, China, in November 2019.
Present perfect tense: The present perfect indicates an action occurring at a nonspecific time or repeatedly in the past. However, this action has a close connection with the present time. The present perfect tense may introduce background information in a paragraph, reinforcing the main idea mentioned there. Following the first sentence, switching to the simple past is possible.
Example: Many scientists have employed this method.
Example: Many researchers have investigated how a small firm can succeed after its poor start. They gradually learned what is essential in the market.
Future tense: You may use the future tense to describe an action that will occur at a particular point in the future (It is imperative when writing a research, grant, or dissertation proposal).
Example: I will conduct the ANOVA procedure in my study’s statistical part.
APA guidelines concerning verb tenses
In its last published guideline, APA accentuated the consistency and accuracy in tense verb usage (APA 7, Section 4.12 and Table 4.1). It suggests that you must avoid unnecessary shifts in verb tense within a paragraph or adjacent paragraphs. This avoidance helps secure smooth expression and improves readability. It would be best if you used the past tense (e.g., scientists posed ) or the present perfect (e.g., researchers have concluded ) for the literature review . Thus, you must present the procedure description if you discuss past events. Nonetheless, it would help if you resorted to the past tense to describe the results (for example, ANOVA results revealed that the treatment improved food's shelf-life substantially). In discussing the implications of the results and present conclusions, you must use the present tense (i.e., our results suggest that alcohol consumption increases the accident incidence rate).
When you need to explain what an author or scientist stated or did, you must use the past tense.
Milliken (2012) reported, revealed, stated, found that…..…
Nevertheless, you can shift to the present tense if your research findings can be generalized or held in general:
Hunt (2010) revealed that revising a manuscript improves its chance of acceptance.
Kropf (2016) discovered that color is an essential trait of fresh meat.
Which tense should I use referring to my document (thesis, dissertation, research proposal, etc.)
If you wish to preview what is ahead in your text or elaborate on what is happening at that moment in your document, you must use either the present or future tense.
In this research, I will specify …
In this research, I specify …
In the last chapter, I will elaborate on …
In the last chapter, I elaborate on …
You can also refer back to already presented information, such as a synopsis of discussions that have already occurred or conclusions to your chapters or sections. Then, the tense you have to use is the past tense:
Chapter 1 contained the literature review.
In closing, in this section, I posed information on…
Should I use simple past tense or present perfect tense?
British and American English have slightly varying rules for using the present perfect tense. Scientists have also reported that individual preferences may dictate the usage of the simple past or the present perfect tense in American English. Put differently, an American English writer may opt for the simple past on specific occasions, whereas another American English writer may prefer the present perfect without apparent reasons.
However, you must note that the simple past tense denotes a completed action. Therefore, it usually employs signal words or phrases, including "yesterday," "last year," "a week ago," or "in 2020," to designate the specific time in the past when the action occurred.
I went to Greece in 2011 .
He finished the team member performance report last week .
The present perfect concentrates more on the action without accentuating the specific time it occurred. Note that the action has occurred even though the specific time is unavailable.
I have seen this movie three times .
The present perfect also concentrates more on the result of the action.
He has finished reviewing the manuscript.
You should be able to understand the usage of the present perfect with some signal words such as "since," "already," "just," "until now," "(not) yet," "so far," "ever," "lately," or "recently."
I have already finished the book on the Turkish economy.
Researchers have used this term since it was coined.
He has recently defended his Ph.D. dissertation.
If you need us to make your thesis or dissertation, contact us unhesitatingly!
Best Edit & Proof expert editors and proofreaders focus on offering papers with proper tone, content, and style of academic writing, and also provide an upscale editing and proofreading service for you. If you consider our pieces of advice, you will witness a notable increase in the chance for your research manuscript to be accepted by the publishers. We work together as an academic writing style guide by bestowing subject-area editing and proofreading around several categorized writing styles. With the group of our expert editors, you will always find us all set to help you identify the tone and style that your manuscript needs to get a nod from the publishers.
English formatting service
You can also avail of our assistance if you are looking for editors who can format your manuscript, or just check on the particular styles for the formatting task as per the guidelines provided to you, e.g., APA, MLA, or Chicago/Turabian styles. Best Edit & Proof editors and proofreaders provide all sorts of academic writing help, including editing and proofreading services, using our user-friendly website, and a streamlined ordering process.
Get a free quote for editing and proofreading now!
Visit our order page if you want our subject-area editors or language experts to work on your manuscript to improve its tone and style and give it a perfect academic tone and style through proper editing and proofreading. The process of submitting a paper is very easy and quick. Click here to find out how it works.
Our pricing is based on the type of service you avail of here, be it editing or proofreading. We charge on the basis of the word count of your manuscript that you submit for editing and proofreading and the turnaround time it takes to get it done. If you want to get an instant price quote for your project, copy and paste your document or enter your word count into our pricing calculator.

24/7 customer support | Live support
Contact us to get support with academic editing and proofreading. We have a 24/7 active live chat mode to offer you direct support along with qualified editors to refine and furbish your manuscript.

Stay tuned for updated information about editing and proofreading services!
Follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Medium .
For more posts, click here.
This article explains how can you dictate on tense usage in a dissertation or thesis. To give you an opportunity to practice proofreading, we have left a few spelling, punctuation, or grammatical errors in the text. See if you can spot them! If you spot the errors correctly, you will be entitled to a 10% discount.
- Editing & Proofreading
- Citation Styles
- Grammar Rules
- Academic Writing
- Proofreading
- Microsoft Tools
- Academic Publishing
- Dissertation & Thesis
- Researching
- Job & Research Application
Similar Posts
How to Determine Variability in a Dataset
Population vs Sample | Sampling Methods for a Dissertation
7 Issues to Avoid That may Dent the Quality of Thesis Writing
How to Ensure the Quality of Academic Writing in a Thesis and Dissertation?
How to Define Population and Sample in a Dissertation?
How can You Establish Experimental Design in Your Dissertation?
How Can You Write an Abstract for Your Dissertation?
How to Build Research Methods for Your Dissertation
How to Build a Strong Hypothesis for Your Dissertation
How Can You Develop Solid Research Questions for Your Dissertation?
Recent Posts
How to Determine Central Tendency
ANOVA vs MANOVA: Which Method to Use in Dissertations?
How to Specify Study Variables in Research Papers?
They Also Read

A methodology section explains the entire process of data collection and analysis based on logic and philosophy. This section is an unavoidable part of a dissertation or a research paper. Considering errors in the methodology section enervates the entire dissertation. Here, we bring you a general guide on the steps to compose a flawless methodology section for a dissertation.

The first chapter of your thesis or dissertation includes the introduction. You should provide the reader with a solid start. Next is staging your research with an apparent focus, objective, and direction.

For a high-quality research paper, dissertation, or thesis, a helpful research question plays a critical role in designing it. It precisely suggests what you wish to study, presenting your research's apparent emphasis and objective.

Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Therefore, your research methods form the most critical part of your research design. You must make two crucial decisions during your method planning.

Formal writing can cover everything from academic essays to a thesis or dissertation; a few fundamental rules are valid in all types of academic writing. A student can find writing in different formats boring or unbearable. With the following tips, you will start finding academic writing almost enjoyable and utterly rewarding.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Verb Tenses in Academic Writing | Rules, Differences & Examples
Verb Tenses in Academic Writing | Rules, Differences & Examples
Published on 20 October 2022 by Shane Bryson . Revised on 11 September 2023.
Tense communicates an event’s location in time. The different tenses are identified by their associated verb forms. There are three main verb tenses: past , present , and future .
In English, each of these tenses can take four main aspects: simple , perfect , continuous (also known as progressive ), and perfect continuous . The perfect aspect is formed using the verb to have , while the continuous aspect is formed using the verb to be .
In academic writing , the most commonly used tenses are the present simple , the past simple , and the present perfect .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Tenses and their functions, when to use the present simple, when to use the past simple, when to use the present perfect, when to use other tenses.
The table below gives an overview of some of the basic functions of tenses and aspects. Tenses locate an event in time, while aspects communicate durations and relationships between events that happen at different times.
| Tense | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| used for facts, , and truths that are not affected by the passage of time | She of papers for her classes. | |
| used for events completed in the past | She the papers for all of her classes last month. | |
| used for events to be completed in the future | She papers for her classes next semester. | |
| used to describe events that began in the past and are expected to continue, or to emphasise the relevance of past events to the present moment | She papers for most of her classes, but she still has some papers left to write. | |
| used to describe events that happened prior to other events in the past | She several papers for her classes before she switched universities. | |
| used to describe events that will be completed between now and a specific point in the future | She many papers for her classes by the end of the semester. | |
| used to describe currently ongoing (usually temporary) actions | She a paper for her class. | |
| used to describe ongoing past events, often in relation to the occurrence of another event | She a paper for her class when her pencil broke. | |
| used to describe future events that are expected to continue over a period of time | She a lot of papers for her classes next year. | |
| used to describe events that started in the past and continue into the present or were recently completed, emphasising their relevance to the present moment | She a paper all night, and now she needs to get some sleep. | |
| used to describe events that began, continued, and ended in the past, emphasising their relevance to a past moment | She a paper all night, and she needed to get some sleep. | |
| used to describe events that will continue up until a point in the future, emphasising their expected duration | She this paper for three months when she hands it in. |
It can be difficult to pick the right verb tenses and use them consistently. If you struggle with verb tenses in your thesis or dissertation , you could consider using a thesis proofreading service .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
The present simple is the most commonly used tense in academic writing, so if in doubt, this should be your default choice of tense. There are two main situations where you always need to use the present tense.
Describing facts, generalisations, and explanations
Facts that are always true do not need to be located in a specific time, so they are stated in the present simple. You might state these types of facts when giving background information in your introduction .
- The Eiffel tower is in Paris.
- Light travels faster than sound.
Similarly, theories and generalisations based on facts are expressed in the present simple.
- Average income differs by race and gender.
- Older people express less concern about the environment than younger people.
Explanations of terms, theories, and ideas should also be written in the present simple.
- Photosynthesis refers to the process by which plants convert sunlight into chemical energy.
- According to Piketty (2013), inequality grows over time in capitalist economies.
Describing the content of a text
Things that happen within the space of a text should be treated similarly to facts and generalisations.
This applies to fictional narratives in books, films, plays, etc. Use the present simple to describe the events or actions that are your main focus; other tenses can be used to mark different times within the text itself.
- In the first novel, Harry learns he is a wizard and travels to Hogwarts for the first time, finally escaping the constraints of the family that raised him.
The events in the first part of the sentence are the writer’s main focus, so they are described in the present tense. The second part uses the past tense to add extra information about something that happened prior to those events within the book.
When discussing and analyzing nonfiction, similarly, use the present simple to describe what the author does within the pages of the text ( argues , explains , demonstrates , etc).
- In The History of Sexuality , Foucault asserts that sexual identity is a modern invention.
- Paglia (1993) critiques Foucault’s theory.
This rule also applies when you are describing what you do in your own text. When summarising the research in your abstract , describing your objectives, or giving an overview of the dissertation structure in your introduction, the present simple is the best choice of tense.
- This research aims to synthesise the two theories.
- Chapter 3 explains the methodology and discusses ethical issues.
- The paper concludes with recommendations for further research.
The past simple should be used to describe completed actions and events, including steps in the research process and historical background information.
Reporting research steps
Whether you are referring to your own research or someone else’s, use the past simple to report specific steps in the research process that have been completed.
- Olden (2017) recruited 17 participants for the study.
- We transcribed and coded the interviews before analyzing the results.
The past simple is also the most appropriate choice for reporting the results of your research.
- All of the focus group participants agreed that the new version was an improvement.
- We found a positive correlation between the variables, but it was not as strong as we hypothesised .
Describing historical events
Background information about events that took place in the past should also be described in the past simple tense.
- James Joyce pioneered the modernist use of stream of consciousness.
- Donald Trump’s election in 2016 contradicted the predictions of commentators.
The present perfect is used mainly to describe past research that took place over an unspecified time period. You can also use it to create a connection between the findings of past research and your own work.
Summarising previous work
When summarising a whole body of research or describing the history of an ongoing debate, use the present perfect.
- Many researchers have investigated the effects of poverty on health.
- Studies have shown a link between cancer and red meat consumption.
- Identity politics has been a topic of heated debate since the 1960s.
- The problem of free will has vexed philosophers for centuries.
Similarly, when mentioning research that took place over an unspecified time period in the past (as opposed to a specific step or outcome of that research), use the present perfect instead of the past tense.
- Green et al. have conducted extensive research on the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction.
Emphasising the present relevance of previous work
When describing the outcomes of past research with verbs like fi nd , discover or demonstrate , you can use either the past simple or the present perfect.
The present perfect is a good choice to emphasise the continuing relevance of a piece of research and its consequences for your own work. It implies that the current research will build on, follow from, or respond to what previous researchers have done.
- Smith (2015) has found that younger drivers are involved in more traffic accidents than older drivers, but more research is required to make effective policy recommendations.
- As Monbiot (2013) has shown , ecological change is closely linked to social and political processes.
Note, however, that the facts and generalisations that emerge from past research are reported in the present simple.
While the above are the most commonly used tenses in academic writing, there are many cases where you’ll use other tenses to make distinctions between times.
Future simple
The future simple is used for making predictions or stating intentions. You can use it in a research proposal to describe what you intend to do.
It is also sometimes used for making predictions and stating hypotheses . Take care, though, to avoid making statements about the future that imply a high level of certainty. It’s often a better choice to use other verbs like expect , predict, and assume to make more cautious statements.
- There will be a strong positive correlation.
- We expect to find a strong positive correlation.
- H1 predicts a strong positive correlation.
Similarly, when discussing the future implications of your research, rather than making statements with will, try to use other verbs or modal verbs that imply possibility ( can , could , may , might ).
- These findings will influence future approaches to the topic.
- These findings could influence future approaches to the topic.
Present, past, and future continuous
The continuous aspect is not commonly used in academic writing. It tends to convey an informal tone, and in most cases, the present simple or present perfect is a better choice.
- Some scholars are suggesting that mainstream economic paradigms are no longer adequate.
- Some scholars suggest that mainstream economic paradigms are no longer adequate.
- Some scholars have suggested that mainstream economic paradigms are no longer adequate.
However, in certain types of academic writing, such as literary and historical studies, the continuous aspect might be used in narrative descriptions or accounts of past events. It is often useful for positioning events in relation to one another.
- While Harry is traveling to Hogwarts for the first time, he meets many of the characters who will become central to the narrative.
- The country was still recovering from the recession when Donald Trump was elected.
Past perfect
Similarly, the past perfect is not commonly used, except in disciplines that require making fine distinctions between different points in the past or different points in a narrative’s plot.
Sources for this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
Bryson, S. (2023, September 11). Verb Tenses in Academic Writing | Rules, Differences & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/english-language/verb-tenses/
Aarts, B. (2011). Oxford modern English grammar . Oxford University Press.
Butterfield, J. (Ed.). (2015). Fowler’s dictionary of modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Garner, B. A. (2016). Garner’s modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Is this article helpful?
Shane Bryson
Shane finished his master's degree in English literature in 2013 and has been working as a writing tutor and editor since 2009. He began proofreading and editing essays with Scribbr in early summer, 2014.
Other students also liked
Subject-verb agreement | examples, rules & use, english mistakes commonly made in a dissertation | examples.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Tense in summary chapter of a thesis
I am currently writing a cumulative dissertation which is based on several published papers. I am supposed to shortly (one page) summarize each of the papers. These summaries come before the actual papers in the thesis.
Now for me the question about the correct tense in these summaries comes up. For example I have the following sentences
The results reveals that in all weeks the methods led to reduced costs of 10 %. On average, method B needed 14:06 minutes.
Would you rather use the past tense or the present tense in these examples. Here it is said that I should only use the past to refer to something that has been mentioned before. Basically the results and simulations have not been mentioned before. But at the same time the linked page says that I should use the past tense for summaries and to refer to specific simulation runs (which is obviously the case in my examples).
I tend to use present because I have used the present tense for the whole thesis.
What would you advise me to do?
- writing-style
- This is probably better suited to the English Language and Usage stack exchange. – astronat supports the strike Commented Mar 27, 2020 at 14:23
- 2 @astronat I dunno, I followed for some time ELU SE, but honestly it didn't impress me when it comes to academic writing. See also this meta answer of mine . – Massimo Ortolano Commented Mar 27, 2020 at 14:56
- 1 @astronat: I concur with Massimo Ortolano. The use of tenses as described in the question is primarily an academic convention and thus it is certainly on-topic here. It will likely even get better answers. – Wrzlprmft ♦ Commented Mar 28, 2020 at 9:21
4 Answers 4
It's not really about if you have mentioned the work before (don't get confused by the instructions), but that the work itself was done before. So stick with the past tense for the situation here.
In general*, the past tense is safer than present or future. Probably 95%+ of the time you should be in past tense when writing a technical report. And if debating, past or present (either might work), you are usually better off going with the past. Only do the present or future if you know what you are doing as a writer and have a strong reason to change the tense.
- Thanks for your comment guest. To be totally honest, I was told many many times that the basic tense fro scientific papers is the present tense. Most of my writings are in the present tense. I just do not know what to do in this special case. Normally in a summary chapter I also use the past tense as I have already explained everything. But in my special case it is differnt. The summary is about content in papers that have not yet been metioned. So I am really totally confused at the moment. – PeterBe Commented Mar 27, 2020 at 18:58
Your university may have specific guidelines for this, which compel you to make a specific choice. In the absence of those, I would say that this is a matter of personal style. So you can choose whichever style fits you best.
I personally find it most pleasant to write any piece of work, whether it is a single conference paper or a cumulative dissertation, as if the content all appears as a monolithic whole right here right now. Hence, I write everything in present tense, active voice. Others, however, strongly feel that academic writing is more appropriately served by writing dispassionately about it, and that implies writing in passive voice.
I'd say that there is no single correct answer here, which leads to the pleasant conclusion that you cannot really do wrong. I would write your sentence in present tense, since this suits my overall writing style. You should choose the solution that fits your writing style. More important than which tense you choose, is that you apply your choice consistently.
- Thanks Wetenschaap for your answer. I also tend to use the present tense. However, I use passive voice throughout the whole thesis. In conference papers I also use active voice but for the dissertation this is not possible, because I should not use "I" or "we" – PeterBe Commented Mar 29, 2020 at 9:48
Actually using present tense could be dangerous, depending on the situation. Your data was probably gathered in the past. Your conclusions are based on that data. If the study is statistical, based on samples, then there is the measurable possibility that it reached the wrong conclusion.
If the way you write seems to imply, even indirectly , a prediction for the future you could be on dangerous ground. It isn't a question of writing style, but of honest presentation of what you did and what was (past) concluded.
The examples you give certainly seem to imply that past tense is preferable here. You are describing a study that was carried out in the (perhaps recent) past.
- Thanks for the answers. No I have two answers with different opinions. I guess I have to make a decision and there is no wrong or right here. – PeterBe Commented Mar 27, 2020 at 16:38
- 1 Actually, the question isn't an opinion poll. Evaluate the reasoning behind the answers. – Buffy Commented Mar 27, 2020 at 16:58
You should consider all of:
- Present tense : "The results reveal that XYZ", "This method reduces costs by 10%". Use this one when being more abstract, dispassionate, theoretical. You're "committing" less on concrete facts with this tense (but not much less).
- Present perfect tense : "The results have revealed that XYZ", "This method has reduced costs by 10%". The period or duration you're alluding to with this one can be the course of your own research, the period of time in which your research was conducted (as experienced by others, e.g. in the field rather than in academia), or even to recent years up to the present, independently of the time you've done research.
- Past tense : "The results revealed that XYZ", "This method reduced costs by 10%". With this tense, you're alluding to specific events and processes which have concluded already in the past and are known - or will be known by reading the thesis. This is more of a commitment to things having actually happened, and having had impact.
- Future tense or sorta-future infinitive with qualification : "We expect the results to reveal how that XYZ", "This method will, in all likelihood, reduce costs by 10%". With this tense, you're discussing ongoing processes which have not concluded, but of whose conclusion you are certain or almost certain.
- Present Progressive : "The results are now revealing how that XYZ", "This method is reducing costs, by an expected 10%". With this tense, you're strong alluding to very meaningful ongoing processes in the field which are the application of your research. Actually, it's rather similar in rhetorical effect to the future-tense option, except that you're committing that progress is occurring at the very moment you're writing your text.
Don't expect all of the text to use the same tense. Try to choose an overall narrative tense (Present or Present Perfect would be my preference), and choose other tenses in specific sentences or paragraphs in which they're relevant (not too many IMHO).
Also, as others suggest, your university or department may have guidelines on this matter.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged thesis writing-style ..
- Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- How to remove files which confirm to a certain number pattern
- Central alignment of text node in a rectangle in Tikz drawing
- How many people could we get off of the planet in a month?
- Which BASIC dialect first featured a single-character comment introducer?
- What type of directions are fruitful to innovate in quantum hardware?
- What other goals could a space project with the primary goal of experience building with heavy lift rockets perform?
- Calling get_GeodesicArea from ogr2ogr
- Should I be able to see light from a IR Led with my own eyes?
- Would it take less thrust overall to put an object into higher orbit?
- The meaning of “manage” in this context
- How to find intersecting linear equations between two lists?
- Effect of sample size on BIC
- How is Nationality Principle applied in practice?
- Has any spacecraft ever been severely damaged by a micrometeorite?
- dired: How to disable moving the cursor horizontally?
- Population impacts on temperature
- Travel to UK with temporary passport as EU citizen
- What did Scott Lang mean by "living as a tenant of the state"?
- The McDonald's Option
- Consistency strength of HoTT
- In TNG: the Pegasus, why is Geordi in the first meeting with the Admiral?
- Is there a way to swap my longbow from being a ranger for a shortbow?
- bash script quoting frustration
- If you get pulled for secondary inspection at immigration, missing flight, will the airline rebook you?
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process . It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to your field.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review, research methods, avenues for future research, etc.)
In the final product, you can also provide a chapter outline for your readers. This is a short paragraph at the end of your introduction to inform readers about the organizational structure of your thesis or dissertation. This chapter outline is also known as a reading guide or summary outline.
Table of contents
How to outline your thesis or dissertation, dissertation and thesis outline templates, chapter outline example, sample sentences for your chapter outline, sample verbs for variation in your chapter outline, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis and dissertation outlines.
While there are some inter-institutional differences, many outlines proceed in a fairly similar fashion.
- Working Title
- “Elevator pitch” of your work (often written last).
- Introduce your area of study, sharing details about your research question, problem statement , and hypotheses . Situate your research within an existing paradigm or conceptual or theoretical framework .
- Subdivide as you see fit into main topics and sub-topics.
- Describe your research methods (e.g., your scope , population , and data collection ).
- Present your research findings and share about your data analysis methods.
- Answer the research question in a concise way.
- Interpret your findings, discuss potential limitations of your own research and speculate about future implications or related opportunities.
For a more detailed overview of chapters and other elements, be sure to check out our article on the structure of a dissertation or download our template .
To help you get started, we’ve created a full thesis or dissertation template in Word or Google Docs format. It’s easy adapt it to your own requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template

It can be easy to fall into a pattern of overusing the same words or sentence constructions, which can make your work monotonous and repetitive for your readers. Consider utilizing some of the alternative constructions presented below.
Example 1: Passive construction
The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise.
Example 2: IS-AV construction
You can also present your information using the “IS-AV” (inanimate subject with an active verb ) construction.
A chapter is an inanimate object, so it is not capable of taking an action itself (e.g., presenting or discussing). However, the meaning of the sentence is still easily understandable, so the IS-AV construction can be a good way to add variety to your text.
Example 3: The “I” construction
Another option is to use the “I” construction, which is often recommended by style manuals (e.g., APA Style and Chicago style ). However, depending on your field of study, this construction is not always considered professional or academic. Ask your supervisor if you’re not sure.
Example 4: Mix-and-match
To truly make the most of these options, consider mixing and matching the passive voice , IS-AV construction , and “I” construction .This can help the flow of your argument and improve the readability of your text.
As you draft the chapter outline, you may also find yourself frequently repeating the same words, such as “discuss,” “present,” “prove,” or “show.” Consider branching out to add richness and nuance to your writing. Here are some examples of synonyms you can use.
| Address | Describe | Imply | Refute |
| Argue | Determine | Indicate | Report |
| Claim | Emphasize | Mention | Reveal |
| Clarify | Examine | Point out | Speculate |
| Compare | Explain | Posit | Summarize |
| Concern | Formulate | Present | Target |
| Counter | Focus on | Propose | Treat |
| Define | Give | Provide insight into | Underpin |
| Demonstrate | Highlight | Recommend | Use |
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
The title page of your thesis or dissertation goes first, before all other content or lists that you may choose to include.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, November 21). Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved August 21, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/dissertation-thesis-outline/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation table of contents in word | instructions & examples, figure and table lists | word instructions, template & examples, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

IMAGES
COMMENTS
What tenses will you use? The majority of your dissertation or research report will be written in the past tense.This is because you are reporting on what you researched, how you did it and what you found.Even if you choose to write up your research as you are doing it, the final report will still read as if it is written after the everything is completed.
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
18. The answer to this question varies across disciplines. Your dissertation presumably falls within some academic discipline. Look at other papers in the same discipline, and see what tenses they use. For example, unlike your suggestion, in math papers the abstract is usually present tense.
Tense communicates an event's place in time. Academic writing commonly uses the present simple, the past simple and the present perfect. ... When summarizing the research in your abstract, describing your objectives, or giving an overview of the dissertation structure in your introduction, the present simple is the best choice of tense.
One's tense will vary depending on what one is trying to convey within their paper or section of their paper. For example, the tense may change between the methods section and the discussion section. The abstract is usually in the past tense due to it showing what has already been studied. Example ...
Craft an enticing and engaging opening section. Provide a background and context to the study. Clearly define the research problem. State your research aims, objectives and questions. Explain the significance of your study. Identify the limitations of your research. Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
Introduction: The introduction often includes several verb tenses, each providing a different context for the statement that is accompanies. First, when stating a fact that is widely accepted, the present tense is appropriate. Examples of such a statement include "DNA is composed of four nucleotides" or
Tense tendencies in academic texts. Published on September 30, 2014 by Shane Bryson . Revised on August 9, 2024. Different sections of academic papers ( theses, dissertations and essays) tend to use different tenses. The following is a breakdown of these tendencies by section. Please note that while it is useful to keep these tendencies in mind ...
Verb Tense. Verbs are direct, vigorous communicators. Use a chosen verb tense consistently throughout the same and adjacent paragraphs of a paper to ensure smooth expression. Use the following verb tenses to report information in APA Style papers. Paper section.
The fundamental question of how to write a thesis introduction that leaves the reader curious and excited to find out more and keep on reading is one of the. ... 6 - Choose the right verb tense: use the present tense to state your topic, reserve the past tense for a description of the background and context. 7 - Avoid including a lot of ...
Writing About Your Research: Verb Tense The following guidelines may help you figure out when to use past and present tense. USE PAST TENSE . . . To describe your methodology and report your results. At the time you write your report, thesis, dissertation or article, you have completed your study, so should use past tense in your methodology
As you are working, everything is either 'I am doing this' and 'I will be doing that eventually'. This is pretty much the tense in which you write your proposal - proposals are forward looking. So, as you start you research, you will naturally be thinking now, and on to the next steps, and your writing will most likely reflect this in ...
Dissertation Introduction Tips. Knowing when to use which tense in your dissertation or thesis is a common problem. A dissertation introduction is a plan of a study not yet conducted, so any reference needs to be in the future tense. Any reference to a study that is already published should be in the past tense.
The corpus research suggests that the most often used tenses in academic writing are the simple present tense, the simple past tense, and the present perfect tense. Then, what comes next is the future tense. Simple present tense: You can use the simple present to define a general truth or a habitual action. This tense demonstrates that what you ...
Tense communicates an event's place in time. Academic writing commonly uses the present simple, the past simple and the present perfect. ... When summarising the research in your abstract, describing your objectives, or giving an overview of the dissertation structure in your introduction, the present simple is the best choice of tense.
1. I am writing an undergraduate dissertation. I am not quite sure what tenses should I use when introducing a chapter and summarizing it. Should I refer to that chapter in present, future or past tenses. E.g. Intro: This chapter provides information about the research methods used in the project. Before conducting a series of experiments to ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Probably 95%+ of the time you should be in past tense when writing a technical report. And if debating, past or present (either might work), you are usually better off going with the past. Only do the present or future if you know what you are doing as a writer and have a strong reason to change the tense. *Caveat.
The document discusses key aspects of writing a dissertation introduction, including tense usage. It states that the introduction requires careful consideration in selecting the appropriate tense to effectively frame the research objectives. Maintaining consistency in tense is essential for clarity. While navigating tense usage can be daunting, seeking guidance can help overcome these ...
When starting your thesis or dissertation process, one of the first requirements is a research proposal or a prospectus. It describes what or who you want to examine, delving into why, when, where, and how you will do so, stemming from your research question and a relevant topic. The proposal or prospectus stage is crucial for the development ...
The document discusses the challenges of writing a dissertation introduction and provides a solution. It states that crafting a compelling dissertation introduction requires an understanding of the research topic and literature review. Many students find the introduction overwhelming due to its complexity, appropriate tense usage, and maintaining a consistent style. The solution is to order ...
This is a short paragraph at the end of your introduction to inform readers about the organizational structure of your thesis or dissertation. This chapter outline is also known as a reading guide or summary outline. Tip You can find a thesis and dissertation outline template below, as well as a chapter outline example, and example sentences ...