
Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
115 Cloning Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Cloning has always been a controversial topic that sparks debates and discussions worldwide. The concept of creating an identical copy of an organism, whether it be a plant, animal, or even a human being, has both fascinated and frightened people for decades. If you have been assigned an essay on cloning and are looking for some inspiration, here are 115 cloning essay topic ideas and examples to help you get started:
- The history and evolution of cloning.
- The ethical implications of cloning.
- The science behind cloning and how it works.
- The benefits and potential applications of cloning in medicine.
- The disadvantages and risks associated with cloning.
- The role of cloning in genetic engineering.
- The cloning of extinct animals: should we bring them back to life?
- The moral dilemma of cloning endangered species.
- The social and psychological impact of human cloning.
- The legal and regulatory challenges of cloning.
- The religious perspectives on cloning.
- The impact of cloning on biodiversity.
- The role of cloning in agriculture and food production.
- The cloning of pets: a luxury or a necessity?
- The cloning of celebrities: the pursuit of immortality?
- The role of cloning in organ transplantation.
- The cloning debate: nature vs. nurture.
- The cloning of body parts: a solution for amputees?
- The cloning of animals for food production: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of endangered plants: preserving biodiversity.
- The cloning of plants for improved crop yield.
- The cloning of athletes: enhancing performance or cheating?
- The cloning of animals for scientific research.
- The potential risks of cloning humans: health and safety concerns.
- The cloning of Neanderthals: ethical considerations.
- The psychological impact on cloned individuals: identity and self-perception.
- The cloning of celebrities: a violation of privacy?
- The cloning of extinct plants: restoring ecosystems.
- The cloning of insects: controlling pests or disrupting ecosystems?
- The cloning of bacteria: implications for antibiotic resistance.
- The cloning of animals for entertainment purposes: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of endangered animals: saving species from extinction.
- The cloning of humans: the quest for immortality.
- The cloning of body parts for transplantation: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of plants for pharmaceutical purposes.
- The potential impact of cloning on global food security.
- The cloning of animals for military purposes: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of humans for organ harvesting: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of animals for cosmetic purposes: vanity or necessity?
- The cloning of animals for companionship: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of animals for scientific testing: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of humans for reproductive purposes: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of animals for zoos and wildlife conservation.
- The cloning of plants for environmental restoration.
- The cloning of animals for therapeutic purposes: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of humans for research purposes: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of animals for military applications: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of humans for genetic enhancement: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of animals for entertainment purposes: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of humans for cosmetic purposes: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of animals for agricultural purposes: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of humans for therapeutic purposes: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of animals for reproductive purposes: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of humans for military applications: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of animals for genetic enhancement: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of humans for entertainment purposes: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of animals for cosmetic purposes: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of humans for agricultural purposes: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of animals for therapeutic purposes: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of humans for reproductive purposes: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of animals for military applications: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of humans for genetic enhancement: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of humans for cosmetic purposes: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of animals for agricultural purposes: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of humans for therapeutic purposes: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of animals for reproductive purposes: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of humans for military applications: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of animals for genetic enhancement: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of humans for entertainment purposes: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of animals for cosmetic purposes: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of humans for agricultural purposes: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of animals for therapeutic purposes: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of humans for reproductive purposes: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of animals for military applications: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of humans for genetic enhancement: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of animals for entertainment purposes: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of humans for cosmetic purposes: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of animals for agricultural purposes: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of humans for therapeutic purposes: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of animals for reproductive purposes: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of humans for military applications: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of animals for genetic enhancement: ethical concerns.
- The cloning of humans for entertainment purposes: ethical considerations.
- The cloning of animals for cosmetic purposes: ethical dilemmas.
- The cloning of humans for agricultural purposes: ethical concerns.
These 115 cloning essay topic ideas and examples should provide you with a solid foundation to start your essay. Remember to choose a topic that interests you the most and conduct thorough research to support your arguments. Good luck!
Want to research companies faster?
Instantly access industry insights
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Leverage powerful AI research capabilities
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2024 Pitchgrade

40+ Cloning Essay Topics: From Sheep to Identity
Today, cloning is not only limited to the realm of science fiction anymore. It’s a real industry and scientific area of research that may significantly change our lives. Perhaps, it’s one of the most controversial investigations in biology. Active debates in the media have led to a widespread belief that cloning may lead to extreme danger. Science fiction books and movies have contributed a lot to this state of affairs as well.
Generally speaking, cloning allows for the reproduction of genetically similar organisms (also known as clean lines). For example, plant cloning is a common process in nature and farming. Usually, the plant is propagated by shoots, cuttings, tendrils, etc. As you can see, nature has cloned organisms for billions of years. So, why can’t we clone other species?
Since the invention of the term “clone” in 1963, genetic engineering has significantly developed. Scientists have learned how to extract genes, develop a polymerase chain reaction method, decode the human genome, and clone a number of mammals. The next step is obvious – human cloning, but it’s connected with various religious, ethical, and technological issues. Should we be afraid of human cloning? Is it possible to clone Hitler or Jesus Christ?
In the list below we want to share with you a list of cloning debate topics connected to animal and human cloning. Enjoy!
Human cloning essay topics
Human cloning has become an extremely popular theme of science fiction, and people have already despaired over the idea of when this technology will step over from the pages and screens to real life. Here we want to share with you some issues and questions related to human cloning.
- Persuade your audience whether human cloning should be allowed.
- Describe the disease-associated gene. How can cloning overcome such a disease? How will it affect diagnosis and treatment?
- Think about whether the potential benefits of human cloning outweigh the ethical side of the creation of artificial life.
- Is it physically safe to clone humans?
- Describe the current findings and future perspectives of human reproductive cloning.
- What are the ethical issues connected to human cloning?
- Discuss the main findings of the Human Genome Project. What are the implications? How would it affect you personally?
- Analyze the issues connected to human cloning in the context of organ transplantation.
- Describe the potential of therapeutic cloning in regenerative medicine. Is it a viable technology?
- Analyze the book “Frankenstein” by Mary Shelley from the perspective of stem cell cloning.
- Analyze the book “Our Posthuman Future” by F. Fukuyama in regards to the advantages and disadvantages of cloning.
- Would you allow the creation of your clone? Why or why not?
- How would human cloning affect us on a global scale?
- Analyze “Never Let Me Go,” a book by Ishiguro, in terms of scientific human cloning.
- Explore reproductive cloning in terms of medical ethics.
- How can human cloning affect our relationships?
- Analyze the reproductive cloning from the perspective of Kant’s theory and Leon Kass’s arguments.
- Approve or disapprove the following statement: “The cloning technology is not perfect; it can lead to the death of the fetus.”
- Analyze cloning from the perspective that it may be used by businessmen to sell organs for transplantation.
- What governmental regulations should be used to control cloning?
- Would it be ethically and morally right to clone dead people?
- Do you think a clone has a soul?
- How is human cloning represented in the media?
- Analyze the situation where the clone is killed by the original from a legislative and ethical side.
- What are the main problems with reproductive cloning? Why haven’t we cloned a human yet?
Interesting cloning debate topics
There are many issues related to cloning that have begun to grow since the 2000s. Today, the number of provocative questions has only increased, and opinions have polarized, dividing people into two opposing camps.
- Describe the positive and negative sides of cloning.
- Is cloning the right path for science? What dangers does it have? Is it worth the money for the research?
- Analyze the characteristics of artificial cloning.
- What is the future of cloning? What are the most prospective researches?
- What are the current methods of using cloning? Describe the latest technologies.
- Describe the positive and negative sides of animal cloning.
- Discuss cloning in the context of bioethics.
- Does cloning relate to responsible citizenship? How?
- Analyze the cloning of bacteria and yeast, and its applications.
- Discuss cloning from a religious perspective. Can we say that cloning is like playing as God?
- Analyze the animal cloning business in South Korea. What insights can it give other countries?
- What are the major ethical dilemmas of genetic cloning?
- Do you think it is bad to clone endangered species? In what situations can cloning be justified?
- Analyze George Bush’s speech on cloning.
- Should scientists be obliged to share both benefits and burdens of cloning research?
- Do you think the US government should invest in cloning?
- Explore the philosophical issues of cloning.
- Analyze the current status of cloning in the US. Is there any governmental law or regulation on cloning in the US? Are there any scientific programs related to cloning?
- Explore the peculiarities of the Dolly sheep cloning.
- Is it ethically right to clone pets?
- Explore the issues connected to cloning animals for food. What cloned animals are already used for food? Should we use cloned animals for food?
- Will cloning limit genetic diversity?
Obviously, cloning has significant potential advantages and several possible negative consequences. As with many scientific advancements of the past, such as airplanes and computers, the only threat is our narrow mindset.
We hope that our list of cloning essay topics will give you some food for thought. If you can’t manage to write an essay by yourself, our writers will eagerly help you! Fill in the order form and enjoy your life!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
What our customers say
Our website uses secure cookies. More details
Get professional help from best writers right from your phone

Grab our 3 e-books bundle for $27 FREE
- Zoology Topics Topics: 145
- DNA Paper Topics Topics: 113
- Archaeology Topics Topics: 56
- Charles Darwin Research Topics Topics: 51
- Gene Essay Topics Topics: 77
- Space Exploration Paper Topics Topics: 76
- Biology Topics Topics: 101
- Atmosphere Paper Topics Topics: 50
- Genetics Research Topics Topics: 213
- Anatomy Essay Topics Topics: 70
- Extinction Research Topics Topics: 55
- Space Research Topics Topics: 126
- Experiment Research Topics Topics: 146
- Stem Cell Topics Topics: 100
- Action Research Topics Topics: 64
74 Cloning Essay Topics
🏆 best essay topics on cloning, ✍️ cloning essay topics for college, 🎓 most interesting cloning research titles, 🌶️ hot cloning ideas to write about.
- Negative Effects of Human Cloning
- Cloning in Never Let Me Go by Kazuo Ishiguro
- Should Human Cloning Be Allowed?
- DNA Cloning and Sequencing: The Vector pTTQ18
- Cloning Moral and Ethical Issues
- Cloning Discussion: Pros and Cons
- Ethical Issues in Human Cloning: Response
- Human Reproductive Cloning: Benefits and Drawbacks Although the general public opposes reproductive cloning, some argue that its use by different couples would be ethically justified.
- Aspects of Human Embryos Cloning The paper describes and addresses the prompts involved in reproductive cloning, such as the overview of the events, the parties involved, values and motivations.
- Genetic Engineering: Cloning With Pet-28A Embedding genes into plasmid vectors is an integral part of molecular cloning as part of genetic engineering. An example is the cloning of the pectate lyase gene.
- Human Embryo Cloning in the United States Human embryo cloning should not be allowed in the United States because it is an affront to human life and dignity.
- Ethical Issues in Animal Cloning: Acceptable Risk? Engineered animals suffer because of low efficiency thus causing huge amounts of deaths and pregnancy-related predicaments including miscarriage.
- An Experiment in DNA Cloning and Sequencing The aim of this experiment is to clone a fragment of DNA that includes the Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) gene into the vector pTTQ18, which is an expression vector.
- Analysis of Articles by Kevles and Krauthammer on Cloning This article analyzes two articles by Kevles and Krauthammer with very different views on cloning, and points out their strengths and weaknesses.
- Cloning: Issues and Moral Aspects Thesis Cloning is unpredictable and uncertain, so it should be limited to general research only involving any human embryos
- Cloning Influenced by Mobile Cell phones and SIM card cloning cause lots of problems not only to police but also to cell phone companies who suffer financial expenses because of illegal phone system access.
- Genetic Engineering and Cloning Controversy Genetic engineering and cloning are the most controversial issues in modern science. The benefits of cloning are the possibility to treat incurable diseases and increase longevity.
- “Human Cloning” by Rudolf Jaenisch This reading summary essay focuses on the reading “Human Cloning – The Science and Ethics of Nuclear Transplantation” by Rudolf Jaenisch.
- Cloning Research Ethics: Ethical Dispute and Issues Cloning research is one of the most discussed issues in the health care system development. While admitting its benefits, the specialists scrutinize its legal and ethical aspects.
- The Cloning of a DNA Fragment, and a Southern Blot Southern blotting can either be used in the determination of small fragment of a single gene or a large DNA sequence such as part of the genome of an organism.
- Is Cloning “Playing God”? Several types of cloning are practiced among human beings: these are reproductive cloning, therapeutic cloning, and replacement cloning.
- Moral Grounds of the Cloning Cloning is a strategy to reproduce and develop a living organism by retaining all its identical features. This would mean obtaining a Photostat copy of the original one.
- Animal Rights: What of Animal Cloning? Animal cloning is a subject that has attracted substantial controversy, especially after scientists revealed that it is also possible to clone humans.
- Human Cloning: A Socio-Legal and Ethical Appraisal
- Brave New Beef: Animal Cloning and Its Impacts
- Nuclear Reprogramming of Cloned Embryos and Its Implications for Therapeutic Cloning
- Arguing That Cloning Is an Affront to Human Dignity
- Genuine Fakes: Cloning Extinct Species as Science and Spectacle
- Animal Transgenesis and Cloning: Combined Development and Future Perspectives
- Islamic Perspective on Human Cloning and Stem Cell Research
- Cloning: New Breakthroughs Leading to Commercial Opportunities
- Apelin Signaling: A Promising Pathway From Cloning to Pharmacology
- What Religion Has to Say About Cloning
- Reproductive Cloning: Useful Technology or an Unethical Experiment
- The Benefits of Cloning and Where to Draw the Line
- Molecular Cloning of DNA: An Introduction to Techniques and Problems
- Exploring the Many Potential Problems With Cloning Human Beings
- Marshall Barber and the Century of Microinjection: From Cloning of Bacteria to Cloning of Everything
- Nutritional Value of Milk and Meat Products Derived From Cloning
- The Issues Involved in Cloning: Sociology and Bioethics
- Using Therapeutic Cloning to Fight Human Disease: A Conundrum or Reality?
- Cloning Techniques and Applications in Human Health
- National Legislation Concerning Human Reproductive and Therapeutic Cloning
- Therapeutic Cloning Applications for Organ Transplantation
- The Impact of New Cloning Techniques on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases
- Advances in Maize Genomics: The Emergence of Positional Cloning
- Cloning Adult Farm Animals: Possibilities & Problems Associated With Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer
- Potential Uses of Cloning in Breeding Schemes: Dairy Cattle
- Controversial Arguments For and Against the Case of Cloning
- Governing Cloning: United Nations’ Debates and the Institutional Context of Standards
- The US FDA and Animal Cloning: Risk and Regulatory Approach
- Bioprospecting Through Cloning of Whole Natural Product Biosynthetic Gene Clusters
- How Reproductive Cloning Can Save Our Lives in the Future
- Variations and Voids: The Regulation of Human Cloning Around the World
- Cloning From a Gene Database: Bioinformatics
- An Anti-Human Cloning Perspective on Why Genetic Manipulation Should Be Banned
- Criminal Investigation Into Korean Human Cloning
- The Balance Between the Risks and Benefits of Cloning in the Modern World
- Catholic Debate on Stem Cell Research and Embryonic Cloning
- Two Important Issues in Environmental Ethics: Cloning and Genetic Engineering
- Legislative Approaches to Human Cloning in the United States
- Moral and Ethical Issues of Genetic Immortality: To Clone or Not to Clone
- The Impact of Cloning Technology on Biomedical Uses of Livestock
- Views on Cloning: How It Is Wrong to Play God and Create Another Life
- Molecular Cloning as a Powerful Tool for Studying Genes
- Legal Approach to Stem Cell and Cloning Research: A Comparative Analysis of Policies Around the World
- The Cloning of a Self-Replicating RNA Molecule
- Can Artificial Parthenogenesis Sidestep Ethical Pitfalls in Human Therapeutic Cloning?
- Strategies for Cloning and Manipulating Natural and Synthetic Chromosomes
- Cloning the Mammoth: A Complicated Task or Just a Dream?
- Approaches to Cloning Plant Genes Conferring Resistance to Fungal Pathogens
- Global Governance of Human Cloning: The Case of UNESCO
- Reproductive Cloning: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Ethical Issues
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2023, May 18). 74 Cloning Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/cloning-essay-topics/
"74 Cloning Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 18 May 2023, studycorgi.com/ideas/cloning-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2023) '74 Cloning Essay Topics'. 18 May.
1. StudyCorgi . "74 Cloning Essay Topics." May 18, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/cloning-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "74 Cloning Essay Topics." May 18, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/cloning-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2023. "74 Cloning Essay Topics." May 18, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/cloning-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Cloning were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on June 20, 2024 .
- IELTS Scores
- Life Skills Test
- Find a Test Centre
- Alternatives to IELTS
- General Training
- Academic Word List
- Topic Vocabulary
- Collocation
- Phrasal Verbs
- Writing eBooks
- Reading eBook
- All eBooks & Courses
- Sample Essays
- Human Cloning Essay
IELTS Human Cloning Essay
This is a model answer for a human cloning essay.
If you look at the task, the wording is slightly different from the common 'do you agree or disagree' essay.
However, it is essentially asking the same thing.
As people live longer and longer, the idea of cloning human beings in order to provide spare parts is becoming a reality. The idea horrifies most people, yet it is no longer mere science fiction.
To what extent do you agree with such a procedure?
Have you any reservations?
Understanding the Question and Task

You are asked if you agree with human cloning to use their body parts (in other words, what are the benefits), and what reservations (concerns) you have (in other words, what are the disadvantages).
So the best way to answer this human cloning essay is probably to look at both sides of the issue as has been done in the model answer.
As always, you must read the question carefully to make sure you answer it fully and do not go off topic.
You are specifically being asked to discuss the issue of creating human clones to then use their body parts. If you write about other issues to do with human cloning, you may go off topic.
Model Human Cloning Essay
You should spend about 40 minutes on this task.
Write about the following topic:
Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own experience or knowledge.
Write at least 250 words.
Model Answer for Human Cloning Essay
The cloning of animals has been occurring for a number of years now, and this has now opened up the possibility of cloning humans too. Although there are clear benefits to humankind of cloning to provide spare body parts, I believe it raises a number of worrying ethical issues.
Due to breakthroughs in medical science and improved diets, people are living much longer than in the past. This, though, has brought with it problems. As people age, their organs can fail so they need replacing. If humans were cloned, their organs could then be used to replace those of sick people. It is currently the case that there are often not enough organ donors around to fulfil this need, so cloning humans would overcome the issue as there would then be a ready supply.
However, for good reasons, many people view this as a worrying development. Firstly, there are religious arguments against it. It would involve creating other human beings and then eventually killing them in order to use their organs, which it could be argued is murder. This is obviously a sin according to religious texts. Also, dilemmas would arise over what rights these people have, as surely they would be humans just like the rest of us. Furthermore, if we have the ability to clone humans, it has to be questioned where this cloning will end. Is it then acceptable for people to start cloning relatives or family members who have died?
To conclude, I do not agree with this procedure due to the ethical issues and dilemmas it would create. Cloning animals has been a positive development, but this is where it should end.
(276 words)
The essay is well-organized, with a clear introducion which introduces the topic:
- The cloning of animals has been occurring for a number of years now, and this has now opened up the possibility of cloning humans too.
And it has a thesis statement that makes it clear exactly how the human cloning essay will be structured and what the candidate's opinion is:
- Although there are clear benefits to humankind of cloning to provide spare body parts, I believe it raises a number of worrying ethical issues.
The first body paragraph discusses the advantages of cloning humans, and then the second body paragraph looks at the problems associated with this. The change of direction to look at the other side is clearly marked with a transition word ("however") and a topic sentence:
- However, for good reasons, many people view this as a worrying development.
Other transition words are used effectively to guide the reader through the ideas in the human cloning essay: Firstly,.. Also,... Furthermore,...
The candidate demonstrates that they can use a mix of complex structures. For example:
- Due to breakthroughs in medical science and improved diets, people are living much longer than in the past.
- It would involve creating another human and then eventually killing it in order to use its organs, which it could be argued is murder.
- ...if we have the ability to clone humans, it has to be questioned where this cloning will end.
<<< Back
Next >>>
More Agree / Disagree Essays:

Role of Schools Essay: How should schools help children develop?
This role of schools essay for IELTS is an agree disagree type essay where you have to discuss how schools should help children to develop.
IELTS Sample Essay: Is alternative medicine ineffective & dangerous?
IELTS sample essay about alternative and conventional medicine - this shows you how to present a well-balanced argument. When you are asked whether you agree (or disagree), you can look at both sides of the argument if you want.

Extinction of Animals Essay: Should we prevent this from happening?
In this extinction of animals essay for IELTS you have to decide whether you think humans should do what they can to prevent the extinction of animal species.

Ban Smoking in Public Places Essay: Should the government ban it?
Ban smoking in public places essay: The sample answer shows you how you can present the opposing argument first, that is not your opinion, and then present your opinion in the following paragraph.
IELTS Internet Essay: Is the internet damaging social interaction?
Internet Essay for IELTS on the topic of the Internet and social interaction. Included is a model answer. The IELTS test usually focuses on topical issues. You have to discuss if you think that the Internet is damaging social interaction.

Examinations Essay: Formal Examinations or Continual Assessment?
Examinations Essay: This IELTS model essay deals with the issue of whether it is better to have formal examinations to assess student’s performance or continual assessment during term time such as course work and projects.

Scientific Research Essay: Who should be responsible for its funding?
Scientific research essay model answer for Task 2 of the test. For this essay, you need to discuss whether the funding and controlling of scientific research should be the responsibility of the government or private organizations.

Employing Older People Essay: Is the modern workplace suitable?
Employing Older People Essay. Examine model essays for IELTS Task 2 to improve your score. This essay tackles the issue of whether it it better for employers to hire younger staff rather than those who are older.

Sample IELTS Writing: Is spending on the Arts a waste of money?
Sample IELTS Writing: A common topic in IELTS is whether you think it is a good idea for government money to be spent on the arts. i.e. the visual arts, literary and the performing arts, or whether it should be spent elsewhere, usually on other public services.

Essay for IELTS: Are some advertising methods unethical?
This is an agree / disagree type question. Your options are: 1. Agree 100% 2. Disagree 100% 3. Partly agree. In the answer below, the writer agrees 100% with the opinion. There is an analysis of the answer.

Return of Historical Objects and Artefacts Essay
This essay discusses the topic of returning historical objects and artefacts to their country of origin. It's an agree/disagree type IELTS question.

Paying Taxes Essay: Should people keep all the money they earn?
Paying Taxes Essay: Read model essays to help you improve your IELTS Writing Score for Task 2. In this essay you have to decide whether you agree or disagree with the opinion that everyone should be able to keep their money rather than paying money to the government.

IELTS Vegetarianism Essay: Should we all be vegetarian to be healthy?
Vegetarianism Essay for IELTS: In this vegetarianism essay, the candidate disagrees with the statement, and is thus arguing that everyone does not need to be a vegetarian.

Truthfulness in Relationships Essay: How important is it?
This truthfulness in relationships essay for IELTS is an agree / disagree type essay. You need to decide if it's the most important factor.

Dying Languages Essay: Is a world with fewer languages a good thing?
Dying languages essays have appeared in IELTS on several occasions, an issue related to the spread of globalisation. Check out a sample question and model answer.

Multinational Organisations and Culture Essay
Multinational Organisations and Culture Essay: Improve you score for IELTS Essay writing by studying model essays. This Essay is about the extent to which working for a multinational organisation help you to understand other cultures.
Technology Development Essay: Are earlier developments the best?
This technology development essay shows you a complex IELTS essay question that is easily misunderstood. There are tips on how to approach IELTS essay questions

Airline Tax Essay: Would taxing air travel reduce pollution?
Airline Tax Essay for IELTS. Practice an agree and disagree essay on the topic of taxing airlines to reduce low-cost air traffic. You are asked to decide if you agree or disagree with taxing airlines in order to reduce the problems caused.

Free University Education Essay: Should it be paid for or free?
Free university education Model IELTS essay. Learn how to write high-scoring IELTS essays. The issue of free university education is an essay topic that comes up in the IELTS test. This essay therefore provides you with some of the key arguments about this topic.

Internet vs Newspaper Essay: Which will be the best source of news?
A recent topic to write about in the IELTS exam was an Internet vs Newspaper Essay. The question was: Although more and more people read news on the internet, newspapers will remain the most important source of news. To what extent do you agree or disagree?
Any comments or questions about this page or about IELTS? Post them here. Your email will not be published or shared.
Band 7+ eBooks
"I think these eBooks are FANTASTIC!!! I know that's not academic language, but it's the truth!"
Linda, from Italy, Scored Band 7.5

Bargain eBook Deal! 30% Discount

All 4 Writing eBooks for just $25.86 Find out more >>
IELTS Modules:
Other resources:.
- All Lessons
- Band Score Calculator
- Writing Feedback
- Speaking Feedback
- Teacher Resources
- Free Downloads
- Recent Essay Exam Questions
- Books for IELTS Prep
- Useful Links

Recent Articles
IELTS Essay: Living with Climate Change
Aug 23, 24 02:37 AM
Grammar in IELTS Listening
Aug 22, 24 02:54 PM
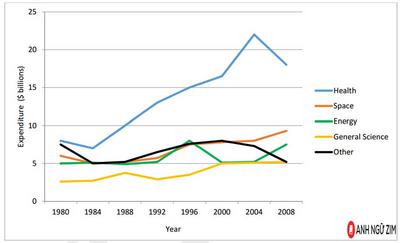
IELTS Line Graph: Governments Expenditure on Research
Jul 23, 24 01:27 PM
Important pages
IELTS Writing IELTS Speaking IELTS Listening IELTS Reading All Lessons Vocabulary Academic Task 1 Academic Task 2 Practice Tests
Connect with us
Before you go...
30% discount - just $25.86 for all 4 writing ebooks.

Copyright © 2022- IELTSbuddy All Rights Reserved
IELTS is a registered trademark of University of Cambridge, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia. This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia.
24/7 writing help on your phone
To install StudyMoose App tap and then “Add to Home Screen”
Cloning - Free Essay Examples and Topic Ideas
There are many different opinions on cloning and whether cloning is ethical or not. Cloning has been banned in multiple countries and American states. Many people have successfully made a clone of mammals, but never a human, and researchers are saying it may not be long until a human is cloned.
- 📘 Free essay examples for your ideas about Cloning
- 🏆 Best Essay Topics on Cloning
- ⚡ Simple & Cloning Easy Topics
- 🎓 Good Research Topics about Cloning
- 📖 Essay guide on Cloning
- ❓ Questions and Answers
Essay examples
Essay topic.
Save to my list
Remove from my list
- Human Cloning: is it Morally Ethical?
- Cloning Animals by Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer
- Cloning: Failures and Risks
- Ethical and Policy Issues of Human Cloning
- The War on Cloning
- Cloning Argumentative Essay
- Against Human Cloning- Argumentative
- Ethical Issues of Human Cloning
- Human Cloning
- The Potential Benefits of Human Cloning
- The Ethical Dilemma of Therapeutic Cloning
- An Inside Look at Equine Cloning
- The advantages and disadvantages of cloning
- Embryonic Stem Cells is Immoral
- The Different Challenges in The Cloning of Baby Jason
- Should Scientists be Allowed to Experiment with Human Cloning
- Cloning: Antibody Cells CD34, CD45, CD73, CD90 and CD105
- The Perfect Copy (Unraveling the Cloning Debate) by Nicholas Agar
- A dystopian novel functions as a median to contrast between
- Cloning in Plants & Animals
- Disadvantages of Human Cloning
- Pros and Cons of Cloning
- The Ethics and Science of Cloning: Where to Draw the Line
- Ideas about Cloning Essay
- Frankenstein and Human Cloning
- The fact of cloning
- Does cloning benefit or endanger society?
- Reasons Why Cloning is Unethical
- Cloning in The Adoration Of Jenna Fox
Cloning Process
“Cloning describes the process used to create an exact genetic replica of another cell, tissue or organism,” according to MedlinePlus. The clone is the copied material, which has the same genetic built as the original. The gene is the basic unit of genetic material.
The genetic instructions inside the living cell are called deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA. Researchers have cloned whole organisms and biological materials. Researchers use different kinds of techniques to make gene copies. The procedure starts with inserting a gene from a certain organism, this is called “foreign DNA” into genetic material or a carrier, called the vector. A vector could be something like a bacteria cell or virus. Once the gene has been inserted, it is placed in laboratory conditions, which causes it to multiply. This results in the gene being copied many times over. There are three different kinds of artificial cloning; gene cloning, reproductive cloning, and therapeutic cloning.
Gene Cloning
Gene cloning, or DNA cloning, is very different from reproductive and therapeutic cloning. Gene cloning produces the copies or sections of DNA. Reproductive cloning creates copies of whole animals or humans. Therapeutic cloning produces embryonic stem cells for experiments targeted towards creating tissues to replace injured or diseased tissues, according to the National Humans Research Genome Research Institute. Reproductive and therapeutic cloning are used for different purposes, but share a lot of techniques. The first mammal was cloned in 1997 which led many people to think it wouldn’t be long until scientist would be able to clone humans. Immediately after, a council on bioethics and an emergency report both published reports claiming that the technology was unsafe and dangerous, and that it should be banned, even for scientific research. There is currently no information on anyone successfully cloning a human embryo, but there have been many claims that a human has been cloned, but no evidence of it.
Cloning Humans
Cloning humans are actually much more difficult than cloning mammals. This is because two proteins called spindle proteins, that are essential to cell division, are located very close to the chromosome in primate eggs. Because of this, the removal of the egg’s nucleus to make room for the donor nucleus, also removes the spindle proteins, interfering with cell division. In other mammals, the two spindle fibers are more spread out and not located as close to the chromosomes. So during removal of the egg’s nucleus, there is no loss of spindle fibers. There are many pros and cons to cloning humans. A pro to cloning humans would be that it could eliminate defective genes. When humans reproduce there is an increase in damage to their DNA lines, which creates defective and mutated genes. These genes could be terminated by cloning healthy human cells.
Usage of Cloning
Another pro is that cloning technology can potentially cure some disorders. This can be done by replacing damaged tissues or organs within the body because the transplanting process could become much simpler. Along with cloning humans, there are also many cons, one major example is that it interferes with nature. Another con of cloning humans is that it could easily decrease the value of human life significantly and cloning humans operates against many religious ethics. A group of animals that have vertebrates, higher animals, consist of billions of cells. Almost all of these cells have a nucleus, which contains genetic information in the form of DNA. The information is the exact same for every cell in the animal. Scientists use the Nuclear Transfer technique to clone animals. Scientists start by removing the nucleus from a cell, this nucleus is called the donor nucleus. Scientists then put the donor nucleus into an egg cell from the species whose nucleus has been destroyed. The egg cell now has a new nucleus and the same genetic makeup as the donor animal. Once the egg has a new nucleus, the cell must be activated to create the embryo. An embryo is a mass of cells that can grow into a fully formed organism, according to World Book Student. To activate the cell, scientists normally give the cell a small electric shock.
Next the DNA of the donor egg must be reprogrammed by the egg. When scientist reprogram the DNA, they are activating part of the DNA not active in the parent cell. This allows the cell to develop into an entire organism instead of just a copy of the donor cell. Scientists do not fully understand how the egg can reprogram such like this, yet programming techniques like these have a very high failure rate. These experiments often result in the death of the cloned embryo and sometimes scientists even place the cloned embryo into the womb of a substitute mother, who carries the clone until birth. Scientist were already cloning amphibians in the 50’s such as frogs and salamanders. The first mammal cloned was in 1996 by a British team led by Ian Wilmut. It was a sheep named Dolly. Since this sheep was cloned, many other countries have used similar techniques to clone mice, cats, and cows. Some cons to cloning animals are that cloning animals have a very low success rate, actually, 95% of cloning attempts end in failure. Cloning attempts also have a high rate of many birth defects or illnesses.
Cloning is also the least reliable way of reproduction and another con is that cloning is very, very expensive. Along with cons, there are a couple pros to cloning animals. One would be that it would help to restore species that are going extinct, which could help certain ecosystems survive longer, but this would majorly affect “the circle of life”. There are many ethnic concerns to cloning animals and humans and for many different reasons. Cloning experiments have given scientists a lot of information on biological processes, that could be used to develop treatments for many diseases.
Scientists have still not perfected a technique used to clone mammals, and still, find it difficult to consistently produce healthy clones. Most cloned embryos do not even make it to birth, and cloned animals have a much higher chance of being born with birth defects than naturally produced animals. Cloning is the process of making an exact copy of someone or something. There are three different kinds of cloning, gene cloning, reproductive cloning, and therapeutic cloning. Cloning a human embryo has been attempted at many time but never successfully. Many pros and cons to both forms of cloning prove that cloning can be taken as ethical or unethical, depending on Geib, Claudia.
- “We’re Getting Closer to Cloning Humans. Here’s What’s Stopping Us.” Futurism, Futurism, 16 Apr. 2018, futurism.com/human-cloning-whats-stopping.
- “Cloning Fact Sheet.” National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), 21 Mar. 2017, www.genome.gov/25020028/cloning-fact-sheet/.
- Seidel, George E., Jr. ‘Cloning.’ World Book Student, World Book, 2018, www.worldbookonline.com/student-new/#/article/home/ar 119610. Accessed 15 Oct. 2018. What Is Cloning, learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/cloning/whatiscloning/.
- Office of the Commissioner. “Consumer Updates – Animal Cloning and Food Safety.” U S Food and Drug Administration Home Page, Office of the Commissioner, www.fda.gov/ForConsumers/ConsumerUpdates/ucm148768.htm.
FAQ about Cloning
👋 Hi! I’m your smart assistant Amy!
Don’t know where to start? Type your requirements and I’ll connect you to an academic expert within 3 minutes.
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Health
Essay Samples on Cloning
Pros and cons of human cloning, why it should never be legalized.
Over the years, technological advancement has made human life easier and has led to ground breaking discoveries. Human cloning is one of the most controversial issues especially in the field of Biology because tampering with human life seems so wrong to many but to others,...
Seeing The Value Of Human Life With Human Cloning
Humans have been known for making lives in its easiest state. Their ability to innovate and explore several things has taken over the world more than what we could imagine. A lot of times, specifically in the field of science and technology, where people have...

Human Clones In Never Let Me Go By Kazuo Ishiguro
Kazuo Ishiguro is a British writer of Japanese origin. In 2005, he published his novel Never Let Me Go, which exploded the minds of reading and thinking auditory. The novel Never Let Me Go by Kazuo Ishiguro develops in a dystopian world where human clones...
- Never Let Me Go
Some Questions To Kamala Harris
My name is 20985 I am a student who is concerned about cloning. It is my understanding that a bill is being developed to approve both therapeutic and reproductive cloning. Cloning causes suffering to the person or animal being experimented on, this process brings out...
- Kamala Harris
Embryonic Stem Cell Research on Cloning
An acceptable definition of cloning is the act of making an identical copy or in scientific terms is the reproduction of a fragment of DNA places in an organism's so that there is enough to analyze or use in protein production. There are two types...
- Stem Cell Research
Stressed out with your paper?
Consider using writing assistance:
- 100% unique papers
- 3 hrs deadline option
Raelism and Science: Debate about Human Cloning
As far as anyone knows, scientists have yet to clone a human being. For more than 20 years, cloning has been the center of a long, ethical debate between Raelians and scientists. The arguments of the debate range from exposing the views that weight the...
Raising Awareness about Cloning and Its Purpose
If you could end world hunger, or even theoretically exponentially extend your own life or the life of others, would you do it? Even if the way to do it is controversial and has been viewed as unethical? Scientists all over the world have researched...
The Ethics Comprehension of Cloning
On March 11, 1997, a team of scientists in Scotland awed the world by announcing they had successfully cloned a sheep, Dolly. This astonishing accomplishment shifted the question from “is cloning possible” to “how far can we take this technology” (Timmer, 2017). It is just...
- Advantages of Technology
The History Of Cloning & My Attitude To Human Cloning
Human cloning will happen but at a price. Variation will get lower because we are making replicas of the humans. This might sound crazy but I think there's a chance that high power countries using cloning to make armies of soldier like movies. By using...
Determining the Function of Eugenics in Cloning
Cloning is a process that has been debated for decades, and all the arguments are now coming to a head. The thought of cloning has been around since the turn of the century, but was not given much publication until the genre of science fiction...
The Bioethic Concerns Surrounding Human Cloning
In 2002, the first human clone was made. Although the insignificant company was second guessed, their product, baby Eve, was a genuine human clone as proved by the DNA test conducted by Michael Guillen, science editor at ABC News and a former Harvard University mathematician....
Best topics on Cloning
1. Pros and Cons of Human Cloning, Why it Should Never Be Legalized
2. Seeing The Value Of Human Life With Human Cloning
3. Human Clones In Never Let Me Go By Kazuo Ishiguro
4. Some Questions To Kamala Harris
5. Embryonic Stem Cell Research on Cloning
6. Raelism and Science: Debate about Human Cloning
7. Raising Awareness about Cloning and Its Purpose
8. The Ethics Comprehension of Cloning
9. The History Of Cloning & My Attitude To Human Cloning
10. Determining the Function of Eugenics in Cloning
11. The Bioethic Concerns Surrounding Human Cloning
- Mental Illness
- Major Depressive Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Cerebral Palsy
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Cloning — A Controversy Over the Idea of Human Cloning
A Controversy Over The Idea of Human Cloning
- Categories: Cloning
About this sample

Words: 1012 |
Published: Sep 12, 2018
Words: 1012 | Pages: 2 | 6 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Nursing & Health

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 1435 words
2 pages / 729 words
4 pages / 1596 words
8 pages / 3463 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Animal cloning, a scientific technique that involves creating genetically identical copies of animals, has been a subject of fascination, debate, and innovation since its inception. This complex and ethically charged topic has [...]
Human cloning is one of the most revolutionary yet controversial topics in the world of genetic research. To clone, or create an organism with an exact genetic copy as that of an existing organism’s, not only provokes a plethora [...]
The concept or definition of cloning is to asexually produce an exact copy of an organism just by using it’s genetic information. Thus, when referring to human cloning, it is the act of artificially producing a genetically [...]
Understanding any functionally biological product is very important. For this, we need to understand and know the location of that particular gene from where the product from that gene is being transcribed and translated. The [...]
Dealing with a death, both physically and emotionally, is one of our society’s greatest struggles. In our society, the ways in which people physically deal with dead bodies include harvesting the organs for science and [...]
Statistically, prostate cancer is the most common male cancer in the UK. Patients with a prostate cancer diagnosis often have a number of treatment options available to them which include surgery in the form of a radical [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Subscribe to this podcast
Listen&Learn: Cloning

Pre-listening vocabulary
- genetic: relating to genes
- identical: exactly the same
- organism: any individual living thing
- embryo: an unborn, developing organism
- advanced: modern and complex
- ethical: relating to the moral concepts of “right” or “wrong”
Listening activity
Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 1:11 — 1.1MB)
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | More
Gapfill exercise
Comprehension questions, discussion/essay questions.
- The article says that many people have ethical concerns about the consequences of human cloning. What do you think some of those concerns might be?
- Do you think human cloning should be legal? Why or why not?
Cloning is the process of creating a genetically identical copy of an organism. Researchers have been experimenting with cloning since the 1900s, when they attempted to create genetic copies of animal embryos. As technology became more advanced, it became possible to make clones of fully-grown creatures. The first successful cloning of an adult organism was in 1996, when a British research group managed to produce a cloned sheep. The sheep’s name was Dolly, and she lived for six years. Scientists have since managed to clone many other types of animals. In fact, there are now companies that offer expensive pet cloning services. The idea of human cloning has come up in scientific discussions , but many people have ethical concerns about the consequences. Because of this, human cloning is illegal in several countries.
16 comments
Many people have ethical concerns about the consequences of human cloning. They think cloning is against religion and not aligned with how nature works. I beg to differ, though. With proper regulation, we can actually benefit from cloning. As the population grows larger, humans need more food. Cloning technology can create a copy of healthy poultry animals and breed them. With good breeding, we can have better quality livestock.
I want to be a member of this group.
This text is really interesting.
Correction from yesterday writing about this topic.
1.We are not ready to realize such human clones because our mind is not prepared to accept with the advance of science. We require regulating it, and for specific reasons I think, it would be possible for an exact part of the body, respecting human rights.
2.It will be possible in the future, when humans accomplish a big development and they regulate with detail this sort of issues. Then, religion groups will work in this matter for enhancing human quality instead of discussing the existence of God. God will guide us that we get science advances instead of fighting among us for whom will be more powerful around the world. Finally, ethical concerns are the core of discussion, but God will give us the right way to agree in this topic.
1 We are not ready to realize this kind of human clones because of our mind isn’t prepared to accept this advances of the science. we require to regulate it, and for an specific cases might be possible for specific part of de body, respecting human rights.
It will be possible in the future, when human being accomplish a big development and they regulate with detail this sort of issues. Then, religion groups will work in this matter for enhance human quality instead of discuses the existence of God. God will guide us to get science advances instead of fighting among us for whom will be more powerful around the world. Finally, ethical concerns is the core of discussion, but God will give us the right way to reach an agreement in this topic.
it is interesting.
Very intresting article. Thank!
I guess whem you talk about clone human organ it sounds good for me, because that can save human lives, but clone humans it’s against the natural las. Thanks for teaching us.
I think that isn’t a good idea. Those experiments because can be bad in the wrong hands
1, I think it is a process of divine order 2. I Think of course I think that is should not be legal, respect the natural order.
i want to thank you for this information
I want to become a member it can help me a lot for my pronunciation and how to speak proper grammar
it helps you to exercise your Listening skills, particularly in English language. I had fun listening, listening tract is informative. I love it!
I want to be a member of this club
Just test purpose for English learning.
Leave a comment
Email * (not published)
Ethics of Cloning Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Animal cloning became recognized as a commercial venture in 2001, with the intention to improve the quality of herds. It is one of the many ways in the field of genetics that has been used to improve and advance the quality of life. However, serious scrutiny from several advocacy groups considers the venture as a violation against fundamental environment and ethic principles.
‘Dolly’ was a sheep and the first living organism to be cloned, in 1997 in Scotland by Ian Wilmut and colleagues. This invention was associated with scientific and ethical implications hence, raised a lot of interest and concern from the public. The University of Hawaii subsequently came up with a process through which mass cloning could occur, while using mice. In both cases, somatic cell nuclear transfer was used. Scientists coined the term cloning in reference to duplication of biological material.
It is important to understand that, contrary to what the media reports on cloning, with a focus on reproductive cloning, there are a variety of cloning technologies besides the production of genetic twin of an organism. This paper will give insight into the various technologies behind cloning, will help in understanding what animal and human cloning are all about, and subsequently present an exhaustively argued out ethical stand.
The cloning of Dolly was received with great attention, and was seen as a theoretical possibility of human cloning. However, it was a shocking revelation that led to the proposal of various bans on human cloning.
Some scholars have taken up a balanced approach based on the pros and cons of cloning and have argued out that cloning should be regulated rather than banned. This regulation would be based on one’s intention of using the cloning process because, one cannot ignore the fact that cloning is a solution for infertility, as well as, protecting endangered species (Federation of Veterinarians of Europe 4-5).
It is important to understand that cloning is not associated with the production of a clone that has the same size and age as its donor, but rather, it is a form of twinning referred to as ‘delayed twining’. One great misunderstanding associated with a clone as we shall see is that which states that a clone is an exact replica of the donor, while in actual sense, this is not the case.
Various types of Cloning
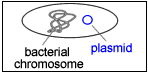
To start with, there is recombinant DNA technology or DNA cloning, gene cloning, or molecular cloning (U.S. Department of Energy Genome Program’s Para 3-4). This refers to the movement of the selected DNA segment from one organism, to a genetic factor characterized by self-replication, such as bacterial plasmid (picture below). Bacterial plasmids often play a great role in the production of multiple and similar copies of a particular gene. This helps in generating enough material for a detailed study.
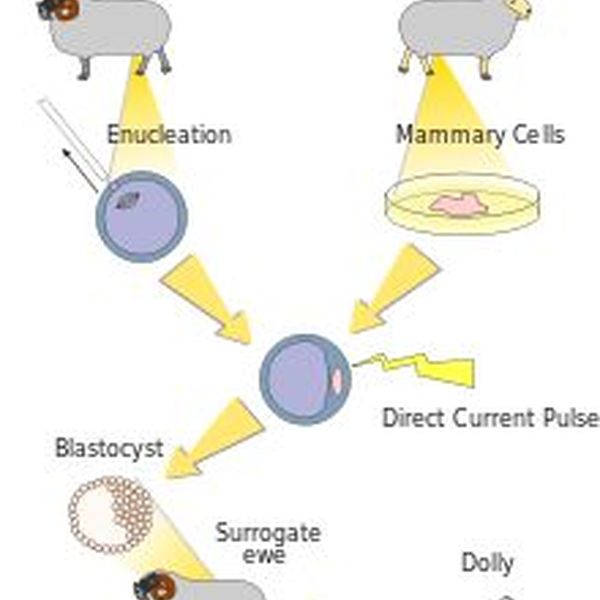
Reproductive cloning, the popular one and which continues to be a contentious topic, is a kind of cloning that involves generating an animal that has got the same nuclear DNA as its host (the donor animal). The process used is referred to as somatic cell nuclear transfer, and it was the method used to create Dolly (U.S. Department of Energy Genome Program’s Para 3-5).
Chemicals and electric current are used to ensure that cell division takes place. The uterus is used as the medium for gestation for a cloned embryo, once it reaches a certain stage. While in uterus, gestation continues until the clone grows and develops into a full-term fetus for birth. The cloning of both humans and animals through reproductive cloning has not been accurate enough and is at the experimentation stage. Until now, there is no one successful human clone that has been created.
There is another kind of cloning known as therapeutic/embryo cloning and this is the type of cloning where human embryos are produced for research purposes. This cloning process is apparently similar to reproduction cloning, but in this case, the embryos are not implanted into a uterus/womb, rather, they are used to produce stem cells that are useful for studying human development and treatment of diseases. Therapeutic cloning involves the use of stem cells, whose purpose is well known in relation to organ/tissue transplant.
Since this paper intends to focus on human and animal cloning, it will therefore talk about reproductive and therapeutic cloning because they both seem to cover the actual purpose of this paper: human and animal cloning.
Animal Cloning
Cloning of animals is a relatively new technology, whose role is to breed elite animals, and replace dead ones. Even though animal cloning was previously exercised, it only managed to catch the public’s attention in 1997. Animal cloning in the US is far more established compared with any other nation hence, the reason why the FDA recommends consumption of products from cloned animals (The Foods Standard Agency 4).
In 2002, Dolly (seen in the picture below) appeared healthy and had given birth to six healthy lambs. It is presumed that it was during the very same year that Dolly radically suffered from lung cancer and arthritis.

One of the scientist involved in producing Dolly said that a problem during the cloning process might have led to her development of arthritis in the hip and knee of her left hind leg at such a tender young age. According to the BBC news, most of the cloned animals had died before birth, or had been born with severe deformities.
It is because of these kinds of revelation that concerns over the health of animal clones that appear healthy, yet, may be having underlying genetic abnormalities have come up. In the case of Dolly, contrary to a sheep’s normal lifespan of 10-16 years, Dolly is said to have suffered an unforeseen and premature death. Some research says that Dolly might have been vulnerable to premature ageing (BBC News para 1-10).
Dr, Dai Grove-White of the Faculty of Veterinary science at Liverpool University said that arthritis was not a common ailment in sheep, and neither was it well recognized. According to Professor Ian Wilmut, more research and data on animal cloning is required because the case with Dolly cannot be used to make a conclusive judgment.
Currently, there are few quantitative studies to give a detailed analytical assessment of the health and welfare of cloned animals during their lifetime as productive organisms. Several confounding and causal factors are thought to have interfered with the assessment process for the reported studies. It has been concluded that cloning is an inefficient process, associated with high failure rate with fatal outcomes (BBC News para 1-10).
Farm animals, especially sheep and cattle, are mainly cloned for the purpose of preserving the breeding capacity of genetically elite animals. In addition, this ensures that loss against valuable genetic and characteristic features is insured. It is the males that are normally cloned. Sheep and cattle, followed by goat, rabbits, pigs and horses were among the first mammalian species to be cloned. Their economic importance, as well as, the well-developed assisted reproduction techniques made this possible.
Pig cloning, which entails the use of worthwhile boars, helps in artificial insemination, and in evaluating the genetic quality of the pigs through a detailed analysis of the carcass. In European farms, animal breeders indulge themselves in the business of selecting parents of highest quality for the next generation by choosing from a diverse and distinct European livestock, where the market is highly competitive.
Despite the fact that there is no practical benefit at present associated with cloning at the farm level, breeding companies are using it at the forefront of worldwide research and development (Federation of Veterinarians of Europe 5). Cloning can be expected to be a valuable process with time in as far as, the production of high value breeding lines that are useful in broadening the elite pedigree stock are concerned.
The escalation in value may be agricultural, encompassing increased performance with regard to food conversion and growth rate; ameliorated health and welfare characterized by resistance to infectious disease and lowered incidence of non-infectious diseases such as mastitis; good conformation marked by reduced prevalence and incidence of disease, and aesthetic value (Federation of Veterinarians of Europe 1-8).
Animal cloning is seen as a means of pet replacement, where owners can easily replace their pet animals. The use of animals or cloning however calls for respect for their intrinsic or inherent value to avoid inflicting too much suffering on them. As at the beginning, humans were given the responsibility of ensuring that they care for the animals, and this is what they ought to ensure they abide by, even during cloning (Federation of Veterinarians of Europe 6).
Human Cloning
There are no certain results that show that it is technically feasible to clone humans. The continued low success rates associated with animal cloning regardless of the tremendous effort put forward to alter the procedures suggest this. In addition, the failure to clone primates also proves this. Safety problems are the reason for the current prohibition on cloning. The limited success despite numerous modifications on procedures for each species, and involving many animals, has further led to this prohibition.
This is because, for the cloning process to be successful with humans, it would involve producing hundreds of ova for research, and treating women with hormones that are not risk-free, and this is highly unethical. Even though preliminary animal evidence would prove to be successful, the first attempts at human cloning would be experimental. As an experimental research process, the ethical principles of human research should be looked into, before endorsing the cloning process.
In 2001, a breakthrough in human cloning was realized when the Advanced Cell Technology in Worcester, Massachusetts reported to having successfully cloned human embryos through therapeutic cloning. The report on human cloning was developed six months after the President’s Council on Bioethics discussed, researched and deliberated on it.
Unanimously, the council decreed that reproductive cloning aimed at producing children was not safe, and in accordance with the stipulated ethical principles of human research hence, should be banned by federal law.
On the basis of the ethical principles of respect for human freedom, dignity and equality, five major categories of concern with regard to reproductive cloning were identified. These are (Iltis 72-73)
- Identity and individuality of cloned children
- Perception of cloned children as objects
- Prospects of new eugenics
- Implication on family
- Implication on societal values
In addressing the issue of ethical principles, there is a need to understand the reasons behind cloning. Unfortunately, the media is very good at creating misunderstanding and is the facilitator for the misunderstanding on replica of a clone. Despite the fact that good reasons for cloning may be laid down, human cloning is the height of technologies. Creation of man by another man is an insult to God and for this simple reason alone, human cloning will always be opposed.
The strong opposition towards cloning mainly rests on the notion that cloning is unnatural. Prior to cloning, there were medical and technological interventions revolving around human reproduction that entailed segregation of sexes and sterilization in the period of state eugenics, artificial insemination during the 1940s and 1950s and family planning, in vitro fertilization (IVF) and related assisted reproduction technologies that included pre-implantation genetic diagnosis and surrogacy in the 1980s and 1990s, and contraception, legalized abortion, medicalization of pregnancy and birth in the 1960s and 1970s (Human genetics Alert 5-8).
Compared with cloning which forces the occurrence of an unnatural reproduction event, these earlier interventions in reproduction work with, and offer solutions to sexual reproduction. The unnaturalness of cloning, conflicts with a given set of moral and social meanings thus, is strongly contested against.
The element of ‘naturalness’ is perceived with positivity, while the ‘artificial’ element is considered inferior. As such, cloning, which characterized by artificialness, receives a negative attitude and reception. It is because of this very same the reason that moratoria were articulately outlined. Most of the religious philosophers have stated their opposition against cloning, claiming that it is wrong to interfere with God’s creation.
Ethics in Cloning
Despite the fact that cloning may never become a globally used procedure, it is hypothetically recommended for couples that cannot either produce a sperm, or an ovum, but wish to have a child that is genetically related to either one of them without having to use sperm or ovum donors.
Basing on people’s attitudes, reproduction is thought to continue being sexual, as this is much cheaper, easier and more fun. Very needy couples, those who are desperate for a child, are likely to use this method and proponents of cloning do not see the need of denying such couples this process. This is because, contrary to a majority of people’s beliefs, the cloned child would be a source of joy for such a couple (Human genetics Alert 8).
The National Research Act (Pub. L. 93-348) was endorsed in 1974 as a way of protecting human subjects for use in biomedical and behavioral research.
Various ethical principles were identified by the National Commission for Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research to govern the conduct of biomedical and behavioral research. Since cloning utilizes medical procedures and technology, whose implication requires professional care due to the genetic and psychological conditions that result from such procedures, it is said to fall within the medical umbrella.
The ethics of research as stipulated by the National Research Act should be carefully evaluated, and especially the role of physicians in practice. The Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs is charged with the responsibility of determining whether; physicians should participate in human cloning, as well as the legality of the process (Office of Human Subjects Research para 1-2).
The many embryos created by nuclear transfer fail to undergo a normal development process as seen Dolly’s case where 277 attempts had to be carried out. The highest published success rate of this process has been at around 5%. In a majority of experiments, the success rate is usually less than 1%, and irrespective of the many attempts, dogs or primates have been difficult to clone (Human Genetics Alert 2).
loned embryos will mainly die at the early stages of embryonic development, or spontaneously abort before the full gestation period has been attained. As has been evidently discussed in this paper, despite the fact that a clone is born, most of the clones are abnormal and die almost immediately after birth, due to the various physiological and anatomical problems that vary from one species to another.
The large offspring syndrome is the main problem, where clones are much larger than normal, and are mainly delivered through caesarean section. Successfully cloned animals like Dolly, are apparently healthy and capable of reproducing healthily and normally. Unfortunately, there seems to be some subtle problems that prevail in these successfully cloned animals, and that are caused by disturbed gene expression, which is likely to manifest itself as the animals continue to age (Gicquel 1338-1341; Jaenisch para 2-6).
Scientists claim that reproductive cloning is associated with some benefits. For one, reproductive cloning could be used to create animals with special qualities. In this sense, mass production of drug-producing animals or animals whose genes have been modified could act as avenues through which human diseases could be studied. In addition, repopulation of endangered species, as well as animals with breeding difficulties is achieved through reproductive cloning.
The gaur, a wild ox and an endangered species, gained recognition as the first endangered animal to be generated and this was in 2001. During the same year, a healthy baby mouflon, an endangered sheep species, was successfully created by scientists in Italy (Federation of Veterinarians of Europe 5). It is obvious that reproductive cloning is not without some benefits, but the ethical issues surrounding it are equally significant.
According to a recent survey in America, 64% were against the idea of cloning, and 63% said that they would not consider buying cloned food albeit safe. As indicated above, it is obvious that cloning is associated with so many benefits. However, this does not mean that cloning can be ethically approved.
Cloning is a very serious issue revolving around various aspects in society like religion, which is defined by certain rules and regulations that cover the right to life, and creation. Life is precious and should not be perceived as a property or item that can be easily owned and sold.
This is actually what cloning is about, since it involves objectification and co-modification of animals and humans, thereby treating them as mere machines that can be easily manufactured. Cloning is also considered to exacerbate problems affecting animals (Pew Commission on Industrial Farm Animal Production para 11-15).
Reports made by the media on the advances involved in cloning, imply that cloning is a means of manufacturing “armies of programmed killers, copying academic geniuses or sport stars, and recreating loved ones that are already dead” (Kass 23-60). The highly held perception of human clones is that they are the exact replica of the donor organism. It is unarguably true that human clones are identical is as far as nuclear genes are concerned.
However, when it comes to twinning as is the case with natural monozygotic twins, other confounding factors apart from mere identical genes are involved. A clone is different from its donor in terms of personality and character as a result of environment, and circumstances that define its life. In human cloning, there is no sharing of genomes to produce a hybrid organism and this may be fatal if the donor organism is susceptible to a certain disease as it only means that the clone will suffer from the same.
Cloning therefore should not be considered an alternative to mortality or terminal illness, because terminal illnesses are passed down to the clone. The natural process of procreation as established during creation is enough to establish a balance within the ecosystem (Kass 23-60). The ethical issue in this approach is that the clone is deprived of its autonomy. People think that a clone is the same as the cloned individual and therefore, is linked to giving the donor individual a second chance to life, while in the actual sense, this is not the case.
No one person can be entirely replaced by another once he/she dies, and it is precisely for this very reason that sport stars and academic geniuses cannot be replicated through generation of clones. Despite the fact that cloning is characterized by persistence of certain genotypes and resultant phenotypic traits, it does not bring about replication (National Bioethics Advisory Commission 629-641).
Creation of a genetic twin, whose form of demarcation is an element of somatic cell nuclear transfer cloning is said to be troubling and fascinating. As indicated by Schwartz (195-206), various cultures throughout the world and as dictated by history, have enjoyed the intrigue derived from the phenomenon of identical twins.
The reason for the fascination is quite easy. If a person witnesses the experience with the identical twins, it is evident that it clearly demonstrates how different these twins are, in person, as well as in personality. Observation of identical twins on the other hand makes one intrigued by the resemblance, expecting that the two identical individuals would have the same abilities and personality since according to the human intuition, body and personality are always intertwined (National Bioethics Advisory Commission 629-641).
Reproductive cloning is linked to a scientifically inaccurate and instinctive fear of multitudes of similar bodies, where each body houses personalities that are considered to be somewhat “less unique, less than distinct, and less autonomous than the normal” (Schwartz 195-206).
Identity and Individuality of Cloned Children
Cloning of humans violates the freedom of uniqueness of an individual. An individual, who feels that he/she is a genetic copy of another person, may undergo intense compelling pressure to become like, or distinct from its progenitor (National Bioethics Advisory Commission 629-641).
The risks that are linked to developmental abnormalities in cloned organisms have led to the preclusion of cloning for the time being. Even with homozygous twins, who share the same genes, they are distinct and not identical and therefore, each person has the right to a unique unrepeated genome.
Lack of autonomy is associated with limited life choices resulting from constrain from self, and expectation from others (National Bioethics Advisory Commission 629-641). There is a strong fear that human cloning is associated with a less-than-autonomous child. This is because; creation of cloned soldiers has led to a diminished physical individuality and psychological autonomy.
The misplaced belief of cloning has actually made people to believe they can determine behavior and personality hence are able to produce “armies of co-operative workers, beatific saints, or crazed soldiers” (Kass 3-17). Human cloning is feared to be more or less like an art because the total genetic blueprint of cloned individuals is pre-selected and pre-determined. In this light, human cloning disregards God’s status as the creator and the process of creation is seen, as another man-made activity.
The ideal idea of parenting is that which appreciates both the differences and similarities between the parents and their children. This kind of parenting is associated with care and teaching, which leads to general, as well as serendipitous developments in their children.
When someone seeks a clone, his mentality of a child is misplaced since the parent-clone considers the child-clone as an exact copy of him/herself and will not appreciate the distinctness that comes with it. As opposed to good parenting which is characterized by a strong parent-child relationship, cloning is fundamentally at odds with unconditional “love, acceptance and openness, all of which are characteristics of good parenting” (Kass 23-60).
It is evident that parenting exercises some form of control over off springs through varied means such as contraception, but reproductive cloning on the other hand is seen to have total specific control over not only a child’s development, but his/her genome as well. This makes the reproduction cloning process to be seen as a manufacturing process.
Cloned children are generated based on the donor’s choice and purpose, hence are synonymous to manufactured objects which are produced to serve an intended purpose. On the other hand, procreation gives rise to very unique beings with certain skills that are special to every individual. Despite the fact that cloning may act as a solution to childless parents, the cloned child can never measure up to a child that is as a result of procreation.
Human and animal cloning, are not in accordance with the natural law of creation. Human beings have taken it upon themselves to create, which according to religious ethical decree, is not acceptable. God is, and will always be the sole creator. Critics of cloning believe that cloning is a means of playing God. According to Kass’ argument, genetic novelty and uniqueness that is apparent with sexual reproduction is very crucial.
This is because; a sexually produced child is free from various setbacks revolving around a cloned child such as societal discrimination, and a feeling of being misplaced in the society. The sexually produced child on the other hand demands respect and equality from other people, and is not seen as some objects that should function as expected (Kass 17-26).
Psychosocial Harm
Human cloning is considered to bring about psychosocial harm to individuals in relation to their autonomy. A clone from an individual with known genetic ‘predispositions and conditions’ is perceived to possess the same ‘predispositions and conditions’ (National Bioethics Advisory Commission 629-641). Unfortunately, what people do not realize is that this is a mere hypothesis that cannot be supported by factual evidence. Gilbert Meilaender (Meilaender cited in National Bioethics Advisory Commission 631) commented that:
Our children begin with a kind of genetic independence of us, their parents. They replicate neither their father nor their mother. That is a reminder of the independence that we must eventually grant to them and for which it is our duty to prepare them. To lose even in principle this sense of the child as gift will not be good for children.
Cloning is associated with predicted genetic disposition based on the parent’s genetic predisposition as indicated by the National Bioethics Advisory Commission (630) and this being the case, various questions concerning the autonomy and best interests of the child born are felt unanswered.
A clone-child is able to see what is expected of him/her if raised by the clone parent and as such, experiences great pressure that forces him/her to live up as per expectations. This deprives the clone child of its freedom and uniqueness in becoming what he/she is, since he/she seeks to become what the world perceives him/her to be. In an example of cloning a sports star, the cloned sports star would hope that his/her clone would be a reflection of his/her characteristics (Kass 23-60).
When such a clone-child does not live up to what is expected of him/her as a sports star, he/she is considered a failure, who has not capitalized on his/her genetic gift. Despite the fact that some clone-children feel confident about their inherent abilities, others may experience limitation on their genetic lot. Failure to perform certain tasks binds the clone-child to the abilities of their clone-parents, and this results in interference of the clone-child’s perception of self and subsequently results in escalated external pressures.
Human cloning would therefore lead to destruction of the natural balance that result from natural procreation since it would psychologically diminish the unlimited potential of new human beings, and in turn exacerbate disturbing intentions for having children (National Bioethics Advisory Commission 629-641).
The probability that some of the human clones are created from cells obtained from individuals, whose permission has not been sought, is a great ethical concern.
If such a probability became a reality, the moral foundations of therapeutic relationships based on personal respect, trust and the physician’s fiduciary responsibility to benefit a patient would be violated. According to Opinion 8.08 of the Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs on informed consent, the council has stipulated that a patient should make his/her own decisions regarding the kind of treatment to be used, where procedures for reproduction are part.
When informed consent is not exercised, then it only means that a physician does not respect an individual’s right to privacy and reproductive freedom (Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs Opinion 8.08). It is because of this ethical principle that cloning should not be carried out without first receiving the consent of an individual.
Reproductive cloning is a mere invention, which is at logger-heads with almost all of the ethical principles defining human research. In human cloning, there are two parties involved, the donor, and the clone.
Therefore, it is important that both parties are content with this cloning process, far from the highly held and appreciated natural process of procreation. This being the case, the effect of human cloning on a child should be evaluated. Critics of human cloning are of the view that the legal and social status of cloned children has not been clearly defined.
The disparity between the child’s genetic blueprint and its social identity is a threat to family stability because it is not clear as to whether the cloned child is qualified for reference as a sibling to a child born through the natural way of procreation. The cloned child’s identity is entirely endangered, since he/she is not aware of his/her identity as well. In addition, the society may undermine the clone-child and this would be an additional torture to the psychological status of this cloned child.
Physical Harm
Cloning is associated with potential for physical harm. Despite the fact that there are convincing cases that favor reproductive cloning, the fundamental principle of injunction as defined by medical ethics and political philosophy should be achieved. The Hippocratic canon and the Nuremberg code, 1946-49 indicate this.
However, substantial risks, to the fetus and physical well being of a child that are as a result of reproductive cloning are far much more weighty, compared with the benefits associated with it (National Bioethics Advisory Commission 629-641).
The Dolly reproductive technique became successful in 277 attempts. The use of this technique in humans is marked by hormonal manipulation of the ovum donor, which is a potential risk factor. The outcome on the other hand can be very serious and fatal, resulting in developmental abnormalities and multiple miscarriages. As noted by John Robertson (Robertson 810-813), a Law professor, before NBAC on March 13, 1997:
The first transfer (into a uterus) of a human (embryo) clone will occur before we know whether it will succeed. Some have argued therefore that the first transfers are somehow unethical because they involve experimentation on the resulting child and no one knows what is going to happen, and one is possibly leading to a child who could be disabled and have developmental difficulties.
According to latest research on mammalian cloning, various defects that normally occur during reprogramming of an egg will not be seen until much later in life of the produced animal clone. The incidence of Dolly is one example; she had been suffering from lung cancer and crippling arthritis before her death (Will We Follow the Sheep 69, 70-72). In other cases, the defects are hideous and go unnoticed, resulting in spectacular and unanticipated deaths.
Techniques used for cloning pose as potential hazards to developing individuals. According to the Human Embryo Research Panel of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in 1994 (1-2), the transfer of embryos into a woman’s uterus should be permitted only when, there is guarantee that no harm will be inflicted on the yet to be born child.
Currently, there is no guarantee that this harm does not exist and therefore, the transfer of embryos into women’s uterus in not permitted. A lot of deaths have been witnessed among amphibian, lamb and mouse fetuses, and these show just how this technology does not provide certainty in as far as long-term safety is concerned.
Human and animal cloning is not ethically justifiable because it violates most of the social and ethical considerations that individuals should consider when dealing with animals/people. Cloning does not respect human life, rather, based on the processes and procedures involved; it treats life like an object. In support of Zoloth’s conclusion, reproductive cloning would be abused by people since they would seek to produce a copy of their selves rather than play the crucial role of parenting a stranger to whom life has been given as stipulated by God, the divine creator.
Every living being should be unique in its own special way but apparently, human and animal cloning violates this principle. This is attributed to disregard for diversity and ecosystem survival by this technology. As opposed to the established natural relationship between humans and nature, cloning fosters the split up from evolution, a natural process that is known to ameliorate the survival instincts of living organisms through diversity, and makes them stronger.
Human cloning encourages destructive processes towards the ecosystem by deepening the alienation between two sets of species. An example is the continued destruction of the environment with the assumption that scientists would instigate the perpetuation of cloned trophy species in zoos (Andra para 5-8).
Human cloning treats women as mere biological functions that provide ova and womb. This process destroys the basic relationships that are associated with the natural process of conception and delivery. The definition of parentage will totally change once human cloning becomes a success and as such, the bonds of parenthood will be radically ruptured.
The element of human dignity is destroyed by human cloning. This is attributed to change in treatment and perception of humans from human beings to variables for experiments and test subjects that can be easily created, manufactured and destroyed (Andra, para 2).
As stipulated in the Universal Declaration on Human Genome and Human Rights, human cloning is a violation against these rights. Reproduction of human beings should be a natural sexual process involving two factors (a male, and a female). However, with the invention of human cloning, it has become an asexual means of reproduction involving only one factor. This change is believed to stir up greater debate as it is feared that human cloning would reduce sexual reproduction to a manufacturing process.
Human cloning does not have respect for human life, if it is to be assumed that human life begins at conception. Lawrence Nelson, an adjunct associate professor of philosophy at the Santa Clara University, supports this predisposition by implying that extracorporeal embryos are entitled to respect by the mere fact that they have life. Too many human embryos would be created and destroyed in the search for a successful clone.
In such a case, disregard for human life is unethical as it is considered to endanger human life. However, Nelson suggests ways through which ethics can be applied in such a case. According to Nelson, respect to human embryos can be portrayed by, using the embryos as the last option for research; using the embryos for research if they have not attained the gastrulation stage by the time they are being used in research studies; not regarding the embryos as mere property, and not destroying them to pleasure (Andra para 7).
In addition, the search for a successful clone in turn would not be a guarantee for a successful life since the clone is susceptible to numerous diseases that eventually result in the clone’s death. Implication on the Family
Human cloning is perceived to affect the family. If a wife produces a clone of herself as a daughter, this distorts the relationship between the father and the daughter. The introduction and endorsement of cloning therefore, is seen to interfere with the family unit. One philosopher wrote that cloning proved to be a major violation of the human nature characterized by “embodied, gendered, and engendering beings- and of social relations developed from this natural ground” (Kass 23-60).
Human cloning would give rise to issues revolving around marital eligibility. In addition, courts would face difficulties trying to solve problems related to assisted reproduction. There is one particular example where a “court found a child conceived using assisted reproductive technologies to have no parents despite having eight individuals from which to choose” (In re Marriage of Buzzanca).
Implication on Social Values
If human cloning would be permitted across the globe, this would mean disruption to the interconnected web of “social values, institutions, practices” that offer support for the healthy growth and development of children (National Bioethics Advisory Commission 629-641).
Human cloning would change the attitude of value towards one’s children as it would shift towards the ability of a child to meet parental expectations. Parents would love their children based on this ability, rather than for who they are. Love, loyalty, nurturing, and steadfastness are the values, which define natural parenthood and with a world of cloning, they would be replaced with avarice, vanity, and narcissism (Kass 23-60).
The ability of man to produce/create living things would render him omnipotent, contrary to the highly held religious values that acknowledge God as the only omnipresent being. Human cloning would escalate the issue of scarce resources because, cloning makes use of the limited researchers and clinicians, who would be better positioned in handling more serious social and medical needs.
Treating Individuals as Objects
It is feared that cloned children would be perceived as mere objects. As a mere object, one is not free to reach their full potential as individuals since they are governed by pressures resulting from other people’s desires and expectations. While talking about objectification of human beings, the paper refers to objectification as the tendency to disregard an individual’s desires or well-being. Rather, it is the control over an individual instead of engaging him/her in a mutual and respectful relationship.
Alternatively, human cloning commodifies the resulting clones by treating them as commodities that can be easily bought, sold, or exchanged in a market place. Cloning, as opposed to other practices, such as genetic screening, or gene therapy, is intended to benefit the nucleus donor and not the cloned child. The other factor that makes the cloned child to be regarded as an object is due to its diminished physical uniqueness.
Eugenic Concerns
The use of eugenic was seen as a step towards selective breeding in agriculture. Eugenic programs oversimplify the role of genes in as far determining human traits and characteristics is concerned, yet, there is limited information on the correlation between genes and behavioral characteristics of successful and rewarding human lives.
Furthermore, the minuscule information that is available indicates that an interaction between genes and the environment is essential for the development of successful and rewarding characters, and not merely due to genes as indicated by the eugenic programs. Cows are bred to increase yields, while sheep are bred to produce sheep with softer fleece, but, it would be unethical to breed superior humans.
To start with, such a practice would only reveal, mankind’s lack of respect for human life and God’s role as the creator of the universe. Production of a superior human being as dictated by science fiction is something that is associated with serious consequence. The American public is renowned for its eugenic ideas, which were engineered by scientific and political leaders, but whose menace became a reality during a grotesque fashion in Nazi Germany (National Bioethics Advisory Commission 629-641).
This paper has said it all, and it is obvious that the risks outweigh the benefits. It is because of this great imbalance that we do not support cloning. The main objective benefits associated with cloning are solving infertility issues, and for transplantation. On the other hand, it is evident that it is incommensurate with almost all of the ethical principles.
As human beings charged with the responsibility of taking care of the environment, where animals are part, we should see to it that the animals are not subjected to intended pain. An evaluation of cloning, being among the many laboratory procedures involving animals, has led us to believe that it is ethically and morally wrong to clone animals, considering reproductive cloning, and therapeutic cloning. Dolly, being the first animal to go public in relation to cloning, was also the reason for the stirred up debate about ethics of cloning.
Physical endangerment is among the various health and safety concerns that arose from this debate. It is true that technology improves our standards of living, and quality of life, but it is also worth noting that it should not be at the expense of other creatures, the embryos, which even though undeveloped, should not be subjected to intended pain. The fact that animals cannot speak does not give humans the right to treat them in a cruel manner either.
It is important to understand that technology is something which is readily accepted and embraced, but when it tends to produce something that is entirely different from the usual, it is then that it faces resistance, as is evident in this case of cloning.
It is because of this very reason that cloning has stirred up strong feelings and has become such a contentious debate. We are of the opinion that cloning is associated with serious risks, which not only affect the clone but the donor as well. The case of Dolly, even though is considered inconclusive by some scientists, shows the challenges associated with cloning.
To start with, too much life is wasted in the numerous attempts carried out. This proves just how cloning disrespects human life. Furthermore, the eventual birth of a clone does not guarantee absence of genetic mutation, which can be very fatal in the long-run. The birth mother on the other hand may suffer from miscarriages, and the ovum donor may suffer from ovum donor hormonal manipulation. A cloned individual is not free, because this element has been indirectly deprived from him/her due to expectations from society.
The various issues raised by cloning makes it impossible for this technology to sail through. It is only until when the benefits of cloning will outweigh the risks associated it that it will be appropriate for physicians to participate in human cloning. As at now, it is not safe to reproduce children through human cloning because of the highly risky procedures involved as have been discussed in the paper.
Regardless of resolved techniques and procedures, weighty concerns will continue to linger around the use of this technology on society and the individual due to anticipated negative effects. Despite the need for more research, it is impossible to imagine that ethical principles will continue to be greatly violated, because for accurate results to be finally obtained, life will not be accorded the respect it deserves. In addition, the society perception of a clone may be difficult to change.
As the final word with regard to cloning, it is an extra-ordinary kind of technology that can be considered to be the epitome of man’s intellectualness. However, it is important to realize that it is not right to compete with God for one because; this technology is seen to mimic God.
Worse is the fact that human cloning will transform creation into a manufacturing process, and violate all the principles that are associated with it. The IVF procedure has already played a very essential role in addressing infertility issues. We think that human cloning will destroy many values that have been amongst us since time in memorial. Therefore, it will only be fair if a continued ban on it prevails.
Works Cited
Andra, Picincu. “The Human Cloning Debate.” Ground Report , 2008. Web.
BBC News. “Animal Cloning: What is the future?” BBC , 4 January 2002. Web.
Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs, American Medical Association. “Opinion 8.08: Informed Consent.” Code of Medical Ethics: Current opinions and annotations. Chicago, IL, 1998.
Federation of Veterinarians of Europe. Animal Cloning . Brussels: FVE, 2009.
Gicquel, Christine, et al. “In vitro fertilization may increase the risk of Beckwith- Wiedemann syndrome related to the abnormal imprinting of the KCNQ1OT gene.” American Journal of Human Genetics 72.5 (2003): 1338-1341.
“Human genetics Alert.” Reproductive Cloning: Ethical and Social Issues, January 2004. Web.
Iltis, Ana S. Research Ethics . New York: Routledge, 2006.
In re Marriage of Buzzanca . The appellate court, 1993.
Jaenisch, R. The biology of nuclear cloning and the potential of embryonic stem cells for transplantation therapy . Background paper for the President’s Commission on Bioethics, 2003. Web. January 2011.
Kass Leon R. The Wisdom of Repugnance. In The Ethics of Human Cloning . Washington ,DC : AEI Press, 1998 : 3-59 .
Meilaender, G. Remarks on Human Cloning to the National Bioethics Advisory Commission. Testimony presented to the National Bioethics Advisory Commission, March 13, 1997.
National Bioethics Advisory Commission. “Report on Cloning by the US Bioethics Advisory Commission: Ethical Considerations.” Human Reproduction Update 3.6 (1997): 629-641.
National Institutes of Health, Report of the Human Embryo Research Panel. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, 1994.
Office of Human Subjects Research. The Belmont Report: Ethical Principles and Guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research . The National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research, 18 April 1979. Web.
Pew Commission on Industrial Farm Animal Production. Putting Meat on the Table: Industrial farm animal production in America . A Project of the Pew Charitable Trusts and Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, 2008. Web.
Robertson, J. A Ban on Cloning and Cloning Research is Unjustified . Testimony Presented to the National Bioethics Advisory Commission, March 14, 1997.
Santa Clara University. The Ethics of Human Cloning and Stem Cell Research . Markkula Center for Applied Ethics, 11 January 2002. Web.
Schwartz, H., The Culture of Copy. New York: Zone Books, 1996.
The Foods Standards Agency. Animal Cloning and Implications for the Food Chain: Findings of Research among the General Public . COI, 2008. Web.
U.S. Department of Energy Genome Program’s. Cloning Fact Sheet . Human Genome Program, 11 May 2009. Web. “Will We Follow the Sheep?” Time, 10 March 1997; p. 69, 70-72
- Ethical Issues Facing Social Researchers
- Welfare and Individual Responsibility
- The New Advancements in Cloning and the Ethical Debate Surrounding It
- Cloning Humans as a Controversial Question
- Counterarguments to Human Cloning
- Analysis of News Article Using Act Utilitarianism and Kant’s Categorical Imperative
- Drug Abuse as an Ethical Issue
- Utilitarian Ethics in Philosophy
- Is It Ethical to Abort Based On Genetic Disability?
- Concept of Utilitarianism Theory
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, December 27). Ethics of Cloning. https://ivypanda.com/essays/ethics-of-cloning/
"Ethics of Cloning." IvyPanda , 27 Dec. 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/ethics-of-cloning/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'Ethics of Cloning'. 27 December.
IvyPanda . 2018. "Ethics of Cloning." December 27, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/ethics-of-cloning/.
1. IvyPanda . "Ethics of Cloning." December 27, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/ethics-of-cloning/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Ethics of Cloning." December 27, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/ethics-of-cloning/.
Never Let Me Go
By kazuo ishiguro, never let me go never let me go and the ethics of human cloning.
The science of human cloning is not the primary concern of Never Let Me Go , and Ishiguro takes artistic license with some of the details of how humans are cloned in his novel. Nevertheless, many of his questions about the ethics of human cloning are ones that have been raised and debated in real life.
These ethical questions first came to the popular consciousness in the 1960s and 1970s, when stem-cell research was first beginning to be conceived, and human cloning began to look like a real possibility. The scientists Joshua Lederberg and James D. Watson wrote articles in The American Naturalist and The Atlantic Monthly , respectively, arguing that cloning was dehumanizing and could result in unforeseen ethical problems. Ishiguro's novel could arguably be read as a rejection of the notion that cloning is dehumanizing; indeed, the purpose of Hailsham is to convince the public that the clones are human.
More recently, scientists and the public have made efforts to distinguish between "therapeutic cloning"—that is, the cloning of cells and tissues to help cure diseases––and "reproductive cloning," which would involve creating “whole” individuals. Many countries, including the United Kingdom and the United States, allow therapeutic cloning, although there is continuing debate, especially in the U.S., about whether the federal government should fund it. Ishiguro's novel merges the two; reproductive cloning is pursued for therapeutic purposes.

Never Let Me Go Questions and Answers
The Question and Answer section for Never Let Me Go is a great resource to ask questions, find answers, and discuss the novel.
Never let me go - What are your first impressions of Hailsham?
What are your first impressions of Hailsham?
This is only a short answer space. Generally, Hlisham is a pleasant place with nice cabins and everything they need. Unfortunately, there is an emptiness about it both educationally and in terms of...
“I tried to bring it up once myself, in the dorm after lights-out … question
A lot of thetime, how you were regarded at Hailsham, how much you were liked and respected, had to do with how good you were at “creating.”What questions does this section raise?
In Never Let Me Go, the equation goes like this: being creative =...
Never let me go - Based on chapters 1 & 2, what genre would you categorise the novel as? Why?
Never Let Me Go takes place in a dystopian United Kingdom, where disease has been eradicated. This apparent blessing has been accomplished by breeding human clones, who are forced to donate their vital organs when they reach early adulthood. Kathy...
Study Guide for Never Let Me Go
Never Let Me Go study guide contains a biography of Kazuo Ishiguro, literature essays, quiz questions, major themes, characters, and a full summary and analysis.
- About Never Let Me Go
- Never Let Me Go Summary
- Character List
Essays for Never Let Me Go
Never Let Me Go essays are academic essays for citation. These papers were written primarily by students and provide critical analysis of Never Let Me Go by Kazuo Ishiguro.
- Never Let Me Go: The Emotions Triggered by Art and Entertainment
- Self-Repression and Dystopia: The Bumpy Road to Freedom in "Never Let Me Go"
- Kazuo Ishiguro's Never Let Me Go: The Societal Implications
- Never Let Me Go: The Creation of Kathy's Identity
- Never Let Me Go: A Marxist Attack on Science?
Lesson Plan for Never Let Me Go
- About the Author
- Study Objectives
- Common Core Standards
- Introduction to Never Let Me Go
- Relationship to Other Books
- Bringing in Technology
- Notes to the Teacher
- Related Links
- Never Let Me Go Bibliography
Wikipedia Entries for Never Let Me Go
- Introduction

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions
Early cloning experiments
- Reproductive cloning
- Therapeutic cloning
- Ethical controversy

What is cloning?
Why is cloning controversial.
- Where was science invented?
- When did science begin?

Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- National Geographic - Cloning
- Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy - Cloning
- Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy - Cloning
- National Human Genome Research Institute - Cloning Fact Sheet
- National Center for Biotechnology Information - Cloning: Definitions And Applications
- CellPress - Robert Koch: The Grandfather of Cloning?
- Academia - Dolly and the history of cloning
- Live Science - How does cloning work?
- Biology LibreTexts - Cloning
- BCcampus Open Publishing - Plasmids and Cloning Basics
- WebMD - The Facts and Fiction of Cloning
- cloning - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- cloning - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents

Cloning is the process of generating a genetically identical copy of a cell or an organism. Cloning happens all the time in nature. In biomedical research, cloning is broadly defined to mean the duplication of any kind of biological material for scientific study, such as a piece of DNA or an individual cell.
Why is cloning important?
Therapeutic cloning enables the cultivation of stem cells that are genetically identical to a patient. This approach, by avoiding risk of rejection by the immune system, has the potential to benefit many patients, including those affected by Alzheimer disease, diabetes, and spinal cord injury.
The cloning of humans remains universally condemned, primarily for the associated psychological, social, and physiological risks. There are also concerns that cloning promotes eugenics , the idea that humanity could be improved through the selection of individuals possessing desired traits. There also exists controversy over the ethics of therapeutic and research cloning, which makes use of embryos that are otherwise discarded.

cloning , the process of generating a genetically identical copy of a cell or an organism. Cloning happens often in nature—for example, when a cell replicates itself asexually without any genetic alteration or recombination . Prokaryotic organisms (organisms lacking a cell nucleus ) such as bacteria create genetically identical duplicates of themselves using binary fission or budding . In eukaryotic organisms (organisms possessing a cell nucleus) such as humans, all the cells that undergo mitosis , such as skin cells and cells lining the gastrointestinal tract , are clones ; the only exceptions are gametes ( eggs and sperm ), which undergo meiosis and genetic recombination.

In biomedical research, cloning is broadly defined to mean the duplication of any kind of biological material for scientific study, such as a piece of DNA or an individual cell. For example, segments of DNA are replicated exponentially by a process known as polymerase chain reaction , or PCR, a technique that is used widely in basic biological research. The type of cloning that is the focus of much ethical controversy involves the generation of cloned embryos , particularly those of humans, which are genetically identical to the organisms from which they are derived, and the subsequent use of these embryos for research, therapeutic, or reproductive purposes.
Reproductive cloning was originally carried out by artificial “twinning,” or embryo splitting, which was first performed on a salamander embryo in the early 1900s by German embryologist Hans Spemann . Later, Spemann, who was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine (1935) for his research on embryonic development, theorized about another cloning procedure known as nuclear transfer . This procedure was performed in 1952 by American scientists Robert W. Briggs and Thomas J. King, who used DNA from embryonic cells of the frog Rana pipiens to generate cloned tadpoles . In 1958 British biologist John Bertrand Gurdon successfully carried out nuclear transfer using DNA from adult intestinal cells of African clawed frogs ( Xenopus laevis ). Gurdon was awarded a share of the 2012 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for this breakthrough.

Advancements in the field of molecular biology led to the development of techniques that allowed scientists to manipulate cells and to detect chemical markers that signal changes within cells. With the advent of recombinant DNA technology in the 1970s, it became possible for scientists to create transgenic clones—clones with genomes containing pieces of DNA from other organisms. Beginning in the 1980s mammals such as sheep were cloned from early and partially differentiated embryonic cells. In 1996 British developmental biologist Ian Wilmut generated a cloned sheep, named Dolly , by means of nuclear transfer involving an enucleated embryo and a differentiated cell nucleus. This technique, which was later refined and became known as somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), represented an extraordinary advance in the science of cloning, because it resulted in the creation of a genetically identical clone of an already grown sheep. It also indicated that it was possible for the DNA in differentiated somatic (body) cells to revert to an undifferentiated embryonic stage, thereby reestablishing pluripotency —the potential of an embryonic cell to grow into any one of the numerous different types of mature body cells that make up a complete organism. The realization that the DNA of somatic cells could be reprogrammed to a pluripotent state significantly impacted research into therapeutic cloning and the development of stem cell therapies.

Soon after the generation of Dolly, a number of other animals were cloned by SCNT, including pigs , goats , rats , mice , dogs , horses , and mules . Despite those successes, the birth of a viable SCNT primate clone would not come to fruition until 2018, and scientists used other cloning processes in the meantime. In 2001 a team of scientists cloned a rhesus monkey through a process called embryonic cell nuclear transfer , which is similar to SCNT except that it uses DNA from an undifferentiated embryo. In 2007 macaque monkey embryos were cloned by SCNT, but those clones lived only to the blastocyst stage of embryonic development. It was more than 10 years later, after improvements to SCNT had been made, that scientists announced the live birth of two clones of the crab-eating macaque ( Macaca fascicularis ), the first primate clones using the SCNT process. (SCNT has been carried out with very limited success in humans, in part because of problems with human egg cells resulting from the mother’s age and environmental factors.)
Cloning Process Essays
Chain of custody, popular essay topics.
- American Dream
- Artificial Intelligence
- Black Lives Matter
- Bullying Essay
- Career Goals Essay
- Causes of the Civil War
- Child Abusing
- Civil Rights Movement
- Community Service
- Cultural Identity
- Cyber Bullying
- Death Penalty
- Depression Essay
- Domestic Violence
- Freedom of Speech
- Global Warming
- Gun Control
- Human Trafficking
- I Believe Essay
- Immigration
- Importance of Education
- Israel and Palestine Conflict
- Leadership Essay
- Legalizing Marijuanas
- Mental Health
- National Honor Society
- Police Brutality
- Pollution Essay
- Racism Essay
- Romeo and Juliet
- Same Sex Marriages
- Social Media
- The Great Gatsby
- The Yellow Wallpaper
- Time Management
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Violent Video Games
- What Makes You Unique
- Why I Want to Be a Nurse
- Send us an e-mail
UPSC Main Paper 1 2024: Important essay topics, previous year’s question paper and more

UPSC Mains 2024 Essay paper: Exam pattern
| | |
| Number of questions | Candidates need to attempt two questions, one from Section A and the other from Section B. |
| Total marks | 250 |
| Marks carried by each question | 125 |
| Duration | 3 hours |
| Type of question | Subjective |
UPSC Mains 2023 question paper for Essay
Upsc mains essay paper: important topics.
- Justice and mercy balance precariously on the edge of circumstances.
- The quest for knowledge is an ever-expanding journey toward the boundaries of understanding.
- True greatness in life is found not in never stumbling, but in the resilience to rise each time we fall.
- Clarity and comprehension emerge beyond the fog of doubt.
- A nation’s strength is reflected in the safety and empowerment of its women.
- Poverty extends beyond financial deprivation, encompassing the denial of opportunities and choices.
- Progress should not compromise democracy and individual freedoms.
- The mind holds the power to transform its own reality, creating heaven or hell within.
- Compassion, empathy, and forgiveness are noble qualities that enhance the human experience.
- In the face of change, some erect barriers while others harness the power of the winds to propel forward.
- The greatest punishment for avoiding leadership is to be ruled by someone less capable.
- The strongest minds often belong to those who speak the least.
- Some rules are more respected when broken than when followed.
- The strong do what they must, and the weak accept what they must.
- True glory lies not in never falling, but in rising each time we do.
- Power doesn’t corrupt; rather, people corrupt power.
Tips to prepare for UPSC Mains Essay paper

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The cloning of animals for cosmetic purposes: ethical concerns. The cloning of humans for agricultural purposes: ethical considerations. The cloning of animals for therapeutic purposes: ethical dilemmas. These 115 cloning essay topic ideas and examples should provide you with a solid foundation to start your essay.
There are a number of ways in which the human cloning is beneficial to mankind the examples include: Better Understanding of Genetic Diseases. Cloning of Organisms and Its Approaches. Artificial embryo twining is the traditional way of cloning and can be said to be the lowest technology in the art of cloning.
40+ Cloning Essay Topics: From Sheep to Identity. Today, cloning is not only limited to the realm of science fiction anymore. It's a real industry and scientific area of research that may significantly change our lives. Perhaps, it's one of the most controversial investigations in biology. Active debates in the media have led to a ...
This reading summary essay focuses on the reading "Human Cloning - The Science and Ethics of Nuclear Transplantation" by Rudolf Jaenisch. Cloning research is one of the most discussed issues in the health care system development. While admitting its benefits, the specialists scrutinize its legal and ethical aspects.
This is a model answer for a human cloning essay. If you look at the task, the wording is slightly different from the common 'do you agree or disagree' essay. However, it is essentially asking the same thing. As people live longer and longer, the idea of cloning human beings in order to provide spare parts is becoming a reality.
132 Genetic Engineering Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. 8 min. Welcome to our list of genetic engineering essay topics! Here, you will find everything from trending research titles to the most interesting genetic engineering topics for presentation. Get inspired with our writing ideas and bonus samples!
Cloning, the process of creating genetically identical organisms, has long been a subject of both fascination and controversy. It raises fundamental ethical, scientific, and societal questions. In this essay, we will delve into the various aspects of cloning, examining both its potential benefits and the concerns it raises.
The Adult DNA cloning is the process that entails removing the DNA from the embryo and replacing it with another one from an adult animal. The method is employed to give an exact duplicate of an existing animal. The process has been successfully carried out on sheep and goats, but not tried on human beings.
Cloning is the process of making a genetically identical organism through the use of a DNA sample. There are three different types of artificial cloning: gene cloning, reproductive cloning and therapeutic cloning. Dolly, the sheep, was the first mammal to have been successfully cloned from an adult cell. There is a specific procedure that has ...
Some Questions To Kamala Harris. My name is 20985 I am a student who is concerned about cloning. It is my understanding that a bill is being developed to approve both therapeutic and reproductive cloning. Cloning causes suffering to the person or animal being experimented on, this process brings out...
(Wikipedia, 2018) The second approach for cloning a human includes taking cells from an existing individual and cloning them, thusly making different people that are identical to that specific individual. (Wikipedia, 2018) With these two techniques nearly available, two critical questions arise. Can we do this, and would it be a good idea for ...
Pages: 2 Words: 813. Cloning. In 1997, when the world first heard about Dolly the sheep, the first mammal to be cloned from an adult, the possibility of cloning a human moved from science fiction into the realm of reality. Now Congress is taking up the question of whether human cloning should be allowed.
The Ethical Implications. of Human Cloning. Michael J. Sandel. IN THIS ESSAY, I WILL CONSIDER the ethics of reproductive and therapeutic cloning. But I want also to advance a more general claim: that the cloning issue,and related debates about genetic engineering,will change the way philos-ophers think about their subject.Much of the debate ...
Cloning is a controversial topic because new areas of science often raise questions about safety. Early experiment performed on animals showed potential dangers. For example, cloned cows developed faulty immune systems. In some studies, cloned animals seemed to grow old faster and die younger than normal members of the species.
Cloning Essays. A Deontological Examination of Moral Principles and Ethical Dilemmas in Biotechnology and Cloning. ... Biotechnology and cloning raise profound questions about the ethical treatment of life, autonomy, and the potential consequences of scientific innovation (Shafique 5). While we grapple with this ethical implication, one ...
Discussion/essay questions. The article says that many people have ethical concerns about the consequences of human cloning. What do you think some of those concerns might be? ... Transcript. Cloning is the process of creating a genetically identical copy of an organism. Researchers have been experimenting with cloning since the 1900s, when ...
Brooks and Jayson L. Lusk (2011) Animal cloning is a process in which scientists can copy the genetic or inherited traits of an animal. 1. Clones are like identical twins only born at different times. Similar to in vitro fertilization, cloned animals begin in a laboratory, but then are born to surrogate mothers.
On the basis of the ethical principles of respect for human freedom, dignity and equality, five major categories of concern with regard to reproductive cloning were identified. These are (Iltis 72-73) Identity and individuality of cloned children. Perception of cloned children as objects.
Nevertheless, many of his questions about the ethics of human cloning are ones that have been raised and debated in real life. These ethical questions first came to the popular consciousness in the 1960s and 1970s, when stem-cell research was first beginning to be conceived, and human cloning began to look like a real possibility.
The Cloning of Human Beings. Cloning is the creation of an exact biological twin generated from the DNA of a donor. In effect, a person creates an exact copy, with the exact genetic sequence, from their own DNA. hile the cloning of human beings has been the realm of science fiction, the creation of sheep clones has pushed the idea of human ...
cloning, the process of generating a genetically identical copy of a cell or an organism. Cloning happens often in nature—for example, when a cell replicates itself asexually without any genetic alteration or recombination. Prokaryotic organisms (organisms lacking a cell nucleus) such as bacteria create genetically identical duplicates of ...
Topic 3. Nuclear energy is better than solar or wind energy. Topic 4. Mobile Phones and hand-held electronic games are noisy and disruptive and should be banned in public places. Topic 5. Less government money should be spent on defence and more money should be spent on protecting the environment. Topic 6.
Chain of Custody. Maintaining a clear and thorough chain of custody records is an essential part of the forensic examination process to prove the validity of digital evidence. Chain of custody refers to comprehensively documenting everyone who handled the evidence, what was done with it, and when, from initial acquisition through analysis and ...
The essay writing paper evaluates a candidate's ability to critically analyze topics, construct logical arguments, and present thoughts clearly and effectively.